6e180032175e2e6b1d40f24e6fc1032e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Infrastructure Attack Vectors and Mitigation Benno Overeinder NLnet Labs http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/

What Is Internet Infrastructure? • What makes the network of networks eventually the Internet – IP (v 4/v 6): protocol to exchange data between endpoints – DNS: resolving human readable names to IP addresses – routing: inter-domain routing between networks, making IP addresses globally reachable • Thus presentation not about end-points – nothing about trojans, botnets, viruses, etc – it is about the network between the end-points http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

The Nature of Attacks on the Internet Infrastructure • DNS spoofing – redirect to websites that are “evil twins” – stealing personal information or money • DDo. S amplification reflection attacks – knock-out competitor: business or in gaming – blackmailing: receive money to stop DDo. S • Route hijacks – knock-out competitor or inspecting traffic – intention (malicious or mistake) difficult to assess http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

DNS SPOOFING AND DNSSEC http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
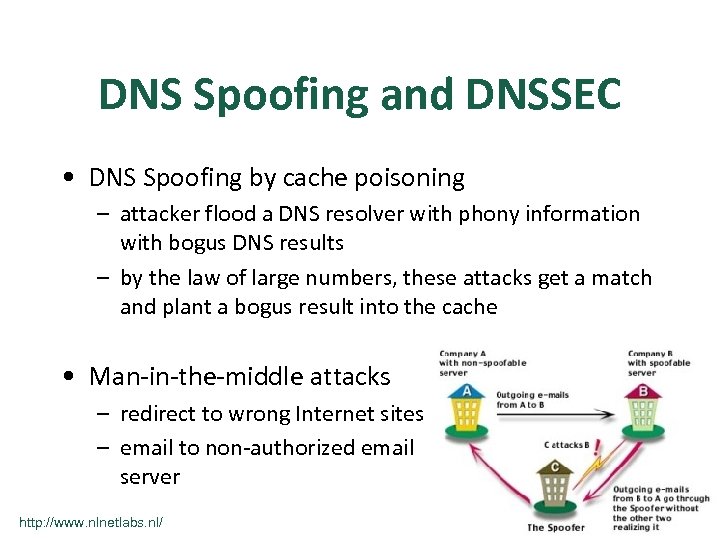
DNS Spoofing and DNSSEC • DNS Spoofing by cache poisoning – attacker flood a DNS resolver with phony information with bogus DNS results – by the law of large numbers, these attacks get a match and plant a bogus result into the cache • Man-in-the-middle attacks – redirect to wrong Internet sites – email to non-authorized email server http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

the on e What is DNSSEC? slid ev ers ion • Digital signatures are added to responses by authoritative servers for a zone • Validating resolver can use signature to verify that response is not tampered with • Trust anchor is the key used to sign the DNS root • Signature validation creates a chain of overlapping signatures from trust anchor to signature of response credits Geoff Huston http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
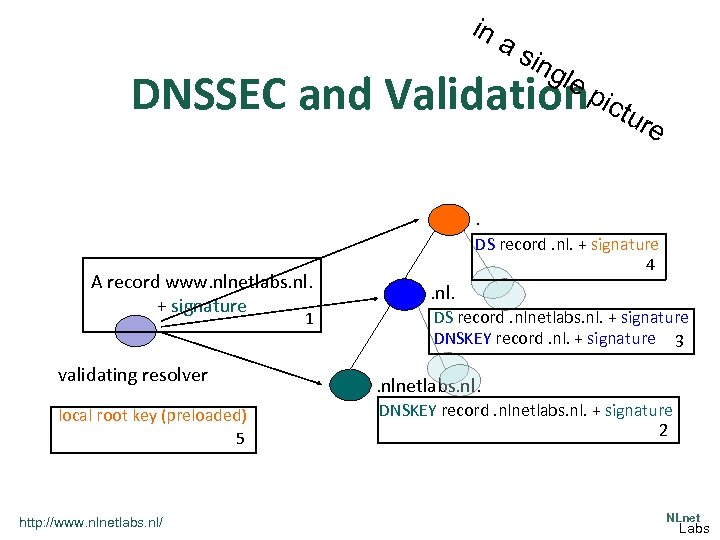
in as ing le DNSSEC and Validationpictur e . A record www. nlnetlabs. nl. + signature 1 validating resolver local root key (preloaded) 5 http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ DS record. nl. + signature 4 . nl. DS record. nlnetlabs. nl. + signature DNSKEY record. nl. + signature 3 . nlnetlabs. nl. DNSKEY record. nlnetlabs. nl. + signature 2 NLnet Labs

DNSSEC Deployment • Open source authoritative DNS name servers supporting DNSSEC – e. g. , NSD, BIND 9, and Knot • Open source DNSSEC validating resolvers – e. g. , Unbound, BIND 9 • Google Public DNS – DNSSEC validation – 8. 8 and 8. 8. 4. 4 – 2001: 4860: : 8888 and 2001: 4860: : 8844 http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

DNSSEC and Community RIPE IETF • DNS Working Group at RIPE meetings • DNSOP Working Group at IETF meetings • DNS Working Group mailing list dns-wg@ripe. net • DNSOP Working Group mailing list dnsop@ietf. org • DNSSEC training course http: //www. ripe. net/lirservices/training/courses • RFC on operational practiceshttp: //tools. ietf. or g/html/rfc 6781 http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Other References to DNSSEC • ISOC Deploy 360 – http: //www. internetsociety. org/deploy 360/dnssec/ – information on basics, deployment, training, etc. • DNSSEC Deployment Initiative – https: //www. dnssec-deployment. org – mailing list dnssec-deployment@dnssecdeployment. org • Open. DNSSEC – open-source turn-key solution for DNSSEC – www. opendnssec. org http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

AMPLIFICATION ATTACKS AND SOURCE ADDRESS FILTERING http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
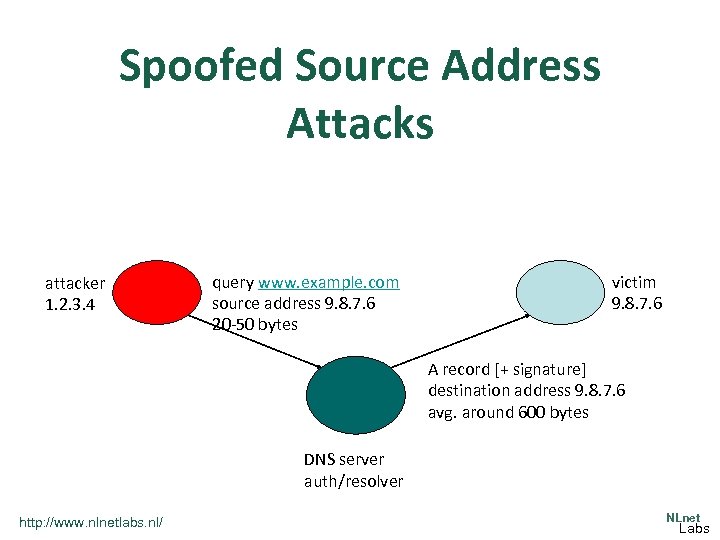
Spoofed Source Address Attacks attacker 1. 2. 3. 4 query www. example. com source address 9. 8. 7. 6 20 -50 bytes victim 9. 8. 7. 6 A record [+ signature] destination address 9. 8. 7. 6 avg. around 600 bytes DNS server auth/resolver http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
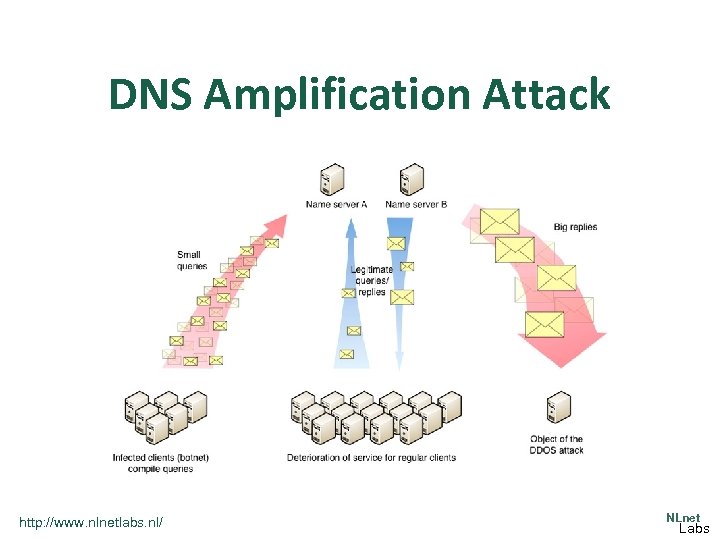
DNS Amplification Attack http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Recent DDo. S Attacks with Spoofed Traffic • The new normal: 200 -400 Gbps DDo. S Attacks • March 2013: 300 Gbps DDo. S attack – victim Spamhaus – DNS amplication attack – [offender arrested by Spanish police and handed over to Dutch police] • Februari 2014: 400 Gbps DDo. S attack – victim customers of Cloud. Flare – NTP amplification http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Mitigation to Amplification Attacks • DNS amplification attacks – response rate limiting (RRL) – RRL available in NSD, BIND 9, and Knot • NTP – secure NTP template from Team Cymru http: //www. teamcymru. org/Reading. Room/Templates/securentp-template. html http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

… or BCP 38 and Filter Spoofed Traffic • BCP 38 (and related BCP 84) • Filter your customers – strict filter traffic from your customers – strict unicast reverse path forwarding (u. RPF) – don’t be part of the problem • Filter your transit – difficult to strict filter your transit – feasible or loose u. RPF – feasible not well supported by hardware vendors http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Address Spoofing and Community RIPE IETF and others • RIPE meetings in plenary and working groups • BCP 38 and BCP 84 • RIPE document 431 and 432 – http: //www. ripe. net/ripe/docs /ripe-431 – http: //www. ripe. net/ripe/docs /ripe-432 • IETF SAVI WG • Open Resolver Project openresolverproject. org • Open NTP Project openntpproject. org • RIPE training course http: //www. ripe. net/lirservices/training/courses http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

ROUTE HIJACKS AND RPKI http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Recent News on Internet Routing Security • April 2, 2014: “Indonesia Hijacks the World” – Indosat leaked over 320, 000 routes (out of 500, 000) of the global routing table multiple times over a two-hour period – claimed that it “owned” many of the world’s networks – few hundred were widely accepted • 0. 2% low impact (5 -25% of routes) • 0. 06% medium impact (25 -50% of routes) • 0. 03% high impact (more than 50% of routes) – for details see http: //www. renesys. com/2014/04/indonesia-hijacksworld/ http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
Less Recent News on Internet Routing Security • April 8, 2010: “China Hijacks 15% of the Internet” – 50, 000 of 340, 000 IP address blocks makes 15% – for roughly 15 minutes • Hijacking 15% of the routes, does not imply 15% of Internet traffic • More realistic guesses – order of 1% to 2% traffic actually diverted • much less in Europe and US – order of 0. 015% based on 80 ATLAS ISP observations • but still an estimation http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Even Less Recent News on Internet Routing Security • February 2008: Pakistan’s attempt to block You. Tube access within their country takes down You. Tube globally – mistakenly the You. Tube block was also sent to a network outside of Pakistan, and propagated • August 2008: Kapela & Pilosov showed effective man-in-the-middle attack – already known to the community, but never tested in real http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Old News on Internet Routing Security • January 2006: Con-Edison hijacks a chunk of the Internet • December 24, 2004: TTNet in Turkey hijacks the Internet (aka Christmas Turkey hijack) • May 2004: Malaysian ISP blocks Yahoo Santa Clara data center • May 2003: Northrop Grumman hit by spammers • April 1997: The "AS 7007 incident”, maybe the earliest notable example? http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
Today’s Routing Infrastructure is Insecure • The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the sole inter-domain routing protocol used • BGP is based on informal trust models – routing by rumor – business agreements between networks • Routing auditing is a low value activity – and not always done with sufficient thoroughness http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
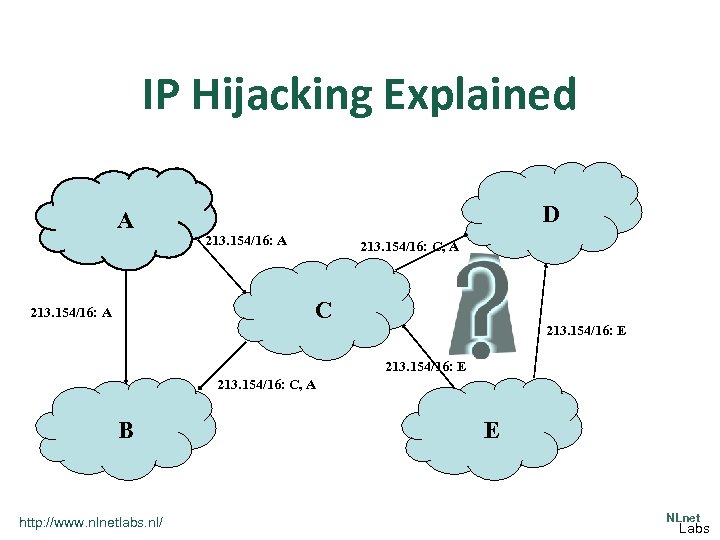
IP Hijacking Explained A D 213. 154/16: A 213. 154/16: C, A C 213. 154/16: A 213. 154/16: E 213. 154/16: C, A B http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ E NLnet Labs

Typical Threats • Derivation of traffic (man-in-the-middle) – third party inspection, denial of service, subversion • Dropping traffic – denial of service, compound attacks • Adding false addresses – support for compound attacks • Isolating/removing routers from the network http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
Current Methods to Secure Routing Infrastructure • Filtering, filtering, … – IP prefix filtering – AS path filtering – max prefix filtering • Monitoring IP prefix / AS path – detect changes in route origin announcement – services provided by e. g. RIPE NCC, open source projects, and commercial partners • However, there is no trusted and authoritative data repository http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
Secure Inter-Domain Routing • Focus of the IETF Secure Inter-Domain Routing (SIDR) working group • Create trusted and authoritative resource data infrastructure – IP addresses and AS networks • Improve on IP prefix filtering and AS path filtering – who holds the “right-of-usage” of a resource http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs

Resource PKI: First Step to Improve Security • Regional Internet Registries (RIPE, APNIC, etc. ) issue resource certificates – proof of ownership of resources (IP addresses) – … and recursively repeated by NIR/LIR/… • owner of IP addresses publishes signed route origin attestations – private key signed ROA states right of use of addresses by a network (the route origin) • ISPs can validate BGP routing announcements – validate ownership of route origin by checking signature in ROA with public key in resource certificate http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
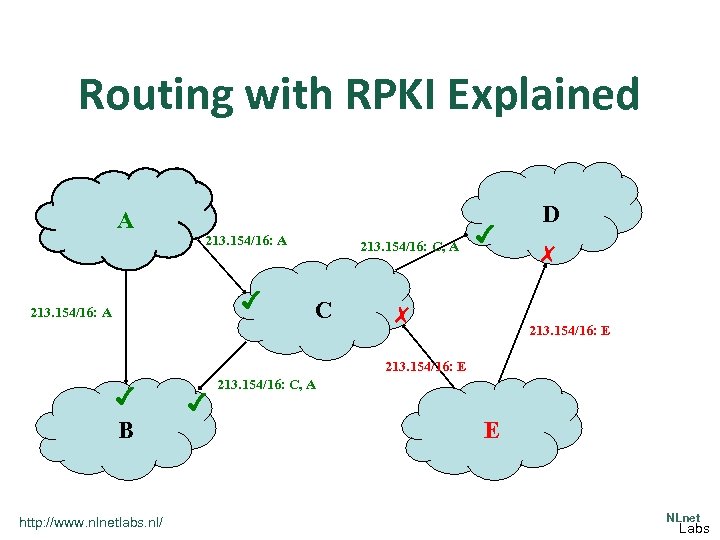
Routing with RPKI Explained A 213. 154/16: A ✔ 213. 154/16: A 213. 154/16: C, A C ✔ ✗ D ✗ 213. 154/16: E ✔ B http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ ✔ 213. 154/16: C, A E NLnet Labs
Routing Security and Community RIPE • Enable RPKI in RIPE LIR portal for your resources • RPKI origin validation in Cisco, Juniper, Alcatel. Lucent, … and open source software Quagga and BIRD • RIPE meetings in plenary and Routing WG routingwg@ripe. net http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ IETF and others • IETF SIDR WG for RPKI and BGPSEC protocol standardization • IETF GROW WG on operational problems • ISOC Deploy 360 Programme http: //www. internetsociety. org/deploy 360/securingbgp/tools/ NLnet Labs

Summary • Internet a dangerous place? – yes/no, not different from the real world • We have a shared responsibility in securing our infrastructure (the Internet is you!) – deploy DNSSEC – BCP 38 and BCP 84 – route filtering and RPKI • Excellent training courses by RIPE NCC • Contact me or staff of RIPE NCC for questions http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ NLnet Labs
6e180032175e2e6b1d40f24e6fc1032e.ppt