b71ca1a682d170b2fbac22a65af796fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Infrastructure Action Plan: March 22, 2004 An Update Presentation to the Advisors of the Executive Directors
Infrastructure Action Plan: March 22, 2004 An Update Presentation to the Advisors of the Executive Directors
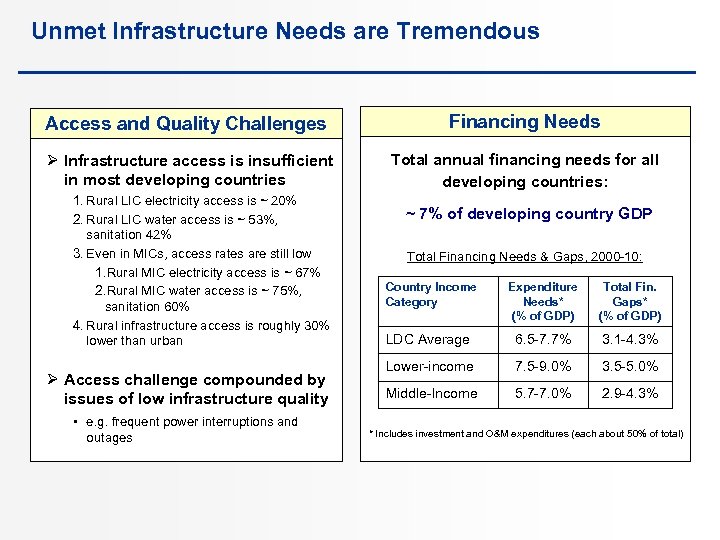 Unmet Infrastructure Needs are Tremendous Access and Quality Challenges Ø Infrastructure access is insufficient in most developing countries 1. Rural LIC electricity access is ~ 20% 2. Rural LIC water access is ~ 53%, sanitation 42% 3. Even in MICs, access rates are still low 1. Rural MIC electricity access is ~ 67% 2. Rural MIC water access is ~ 75%, sanitation 60% 4. Rural infrastructure access is roughly 30% lower than urban Ø Access challenge compounded by issues of low infrastructure quality • e. g. frequent power interruptions and outages Financing Needs Total annual financing needs for all developing countries: ~ 7% of developing country GDP Total Financing Needs & Gaps, 2000 -10: Country Income Category Expenditure Total Fin. Needs* Gaps* (% of GDP) LDC Average 6. 5 -7. 7% 3. 1 -4. 3% Lower-income 7. 5 -9. 0% 3. 5 -5. 0% Middle-Income 5. 7 -7. 0% 2. 9 -4. 3% * Includes investment and O&M expenditures (each about 50% of total)
Unmet Infrastructure Needs are Tremendous Access and Quality Challenges Ø Infrastructure access is insufficient in most developing countries 1. Rural LIC electricity access is ~ 20% 2. Rural LIC water access is ~ 53%, sanitation 42% 3. Even in MICs, access rates are still low 1. Rural MIC electricity access is ~ 67% 2. Rural MIC water access is ~ 75%, sanitation 60% 4. Rural infrastructure access is roughly 30% lower than urban Ø Access challenge compounded by issues of low infrastructure quality • e. g. frequent power interruptions and outages Financing Needs Total annual financing needs for all developing countries: ~ 7% of developing country GDP Total Financing Needs & Gaps, 2000 -10: Country Income Category Expenditure Total Fin. Needs* Gaps* (% of GDP) LDC Average 6. 5 -7. 7% 3. 1 -4. 3% Lower-income 7. 5 -9. 0% 3. 5 -5. 0% Middle-Income 5. 7 -7. 0% 2. 9 -4. 3% * Includes investment and O&M expenditures (each about 50% of total)
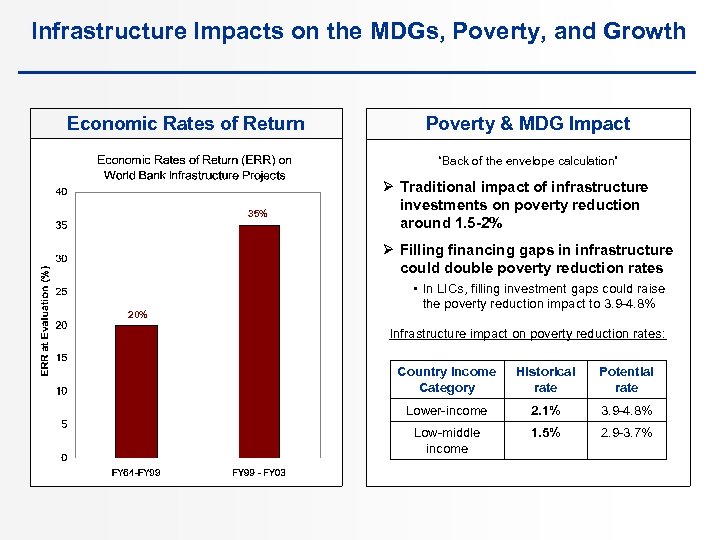 Infrastructure Impacts on the MDGs, Poverty, and Growth Economic Rates of Return Poverty & MDG Impact “Back of the envelope calculation” 35% Ø Traditional impact of infrastructure investments on poverty reduction around 1. 5 -2% Ø Filling financing gaps in infrastructure could double poverty reduction rates 20% • In LICs, filling investment gaps could raise the poverty reduction impact to 3. 9 -4. 8% Infrastructure impact on poverty reduction rates: Country Income Category Historical rate Potential rate Lower-income 2. 1% 3. 9 -4. 8% Low-middle income 1. 5% 2. 9 -3. 7%
Infrastructure Impacts on the MDGs, Poverty, and Growth Economic Rates of Return Poverty & MDG Impact “Back of the envelope calculation” 35% Ø Traditional impact of infrastructure investments on poverty reduction around 1. 5 -2% Ø Filling financing gaps in infrastructure could double poverty reduction rates 20% • In LICs, filling investment gaps could raise the poverty reduction impact to 3. 9 -4. 8% Infrastructure impact on poverty reduction rates: Country Income Category Historical rate Potential rate Lower-income 2. 1% 3. 9 -4. 8% Low-middle income 1. 5% 2. 9 -3. 7%
 Significant Progress on Implementing the Infrastructure Action Plan § Action Plan introduced to revitalize the Bank Group’s infrastructure business – July 2003 § The Board’s and Senior Management’s consistent communication on the importance of infrastructure enabled the successful implementation of the Action Plan § Regional management teams have also swiftly responded to increased client demand for infrastructure Ø e. g. South Asia regional strategy Ø e. g. some key new CASs (Indonesia)
Significant Progress on Implementing the Infrastructure Action Plan § Action Plan introduced to revitalize the Bank Group’s infrastructure business – July 2003 § The Board’s and Senior Management’s consistent communication on the importance of infrastructure enabled the successful implementation of the Action Plan § Regional management teams have also swiftly responded to increased client demand for infrastructure Ø e. g. South Asia regional strategy Ø e. g. some key new CASs (Indonesia)
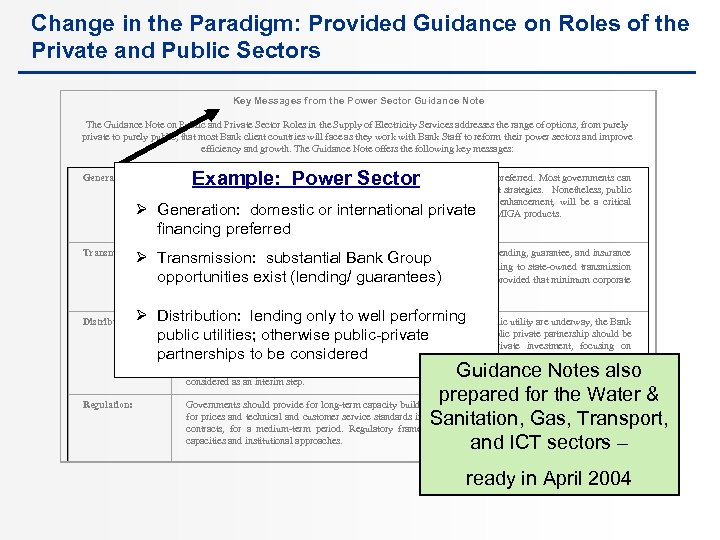 Change in the Paradigm: Provided Guidance on Roles of the Private and Public Sectors Key Messages from the Power Sector Guidance Note The Guidance Note on Public and Private Sector Roles in the Supply of Electricity Services addresses the range of options, from purely private to purely public, that most Bank client countries will face as they work with Bank Staff to reform their power sectors and improve efficiency and growth. The Guidance Note offers the following key messages: Example: Power Sector Generation: Private financing, whether from local, regional or international investors, is preferred. Most governments can create a substantial role for private generators within their sector development strategies. Nonetheless, public support, in the form of IDA/IBRD guarantees and other forms of credit enhancement, will be a critical component of many private financings in the generation, along with IFC and MIGA products. Ø Generation: domestic or international private financing preferred Transmission: Depending on country policy and sector circumstances, there are substantial lending, guarantee, and insurance Ø Transmission: the Bank, IFC, and MIGA. The Bank could commit lending to state-owned transmission substantial Bank Group opportunities for opportunities exist (lending/ guarantees) companies, as a key component of an overall sector development program, provided that minimum corporate governance standards are met. Ø Distribution: lending only to well performing Where public provision is working, or improvements in performance in a public utility are underway, the Bank can consider providing financial support. Where it is not, some form of public private partnership should be public utilities; otherwise public-private considered, such as concession and OBA projects that can attract private investment, focusing on partnerships in service considered expansion. If private investment still cannot be attracted, then improvements to be quality and service Distribution: Guidance Notes also prepared for the Water & Governments should provide for long-term capacity building but should fix, to the extent possible, provisions for prices and technical and customer service standards in the key regulatory instruments, such as licenses or Sanitation, Gas, Transport, contracts, for a medium-term period. Regulatory frameworks should be designed bearing in mind local capacities and institutional approaches. and ICT sectors – management contracts/leases, accompanied by public investment in part financed by the Bank, can be considered as an interim step. Regulation: ready in April 2004
Change in the Paradigm: Provided Guidance on Roles of the Private and Public Sectors Key Messages from the Power Sector Guidance Note The Guidance Note on Public and Private Sector Roles in the Supply of Electricity Services addresses the range of options, from purely private to purely public, that most Bank client countries will face as they work with Bank Staff to reform their power sectors and improve efficiency and growth. The Guidance Note offers the following key messages: Example: Power Sector Generation: Private financing, whether from local, regional or international investors, is preferred. Most governments can create a substantial role for private generators within their sector development strategies. Nonetheless, public support, in the form of IDA/IBRD guarantees and other forms of credit enhancement, will be a critical component of many private financings in the generation, along with IFC and MIGA products. Ø Generation: domestic or international private financing preferred Transmission: Depending on country policy and sector circumstances, there are substantial lending, guarantee, and insurance Ø Transmission: the Bank, IFC, and MIGA. The Bank could commit lending to state-owned transmission substantial Bank Group opportunities for opportunities exist (lending/ guarantees) companies, as a key component of an overall sector development program, provided that minimum corporate governance standards are met. Ø Distribution: lending only to well performing Where public provision is working, or improvements in performance in a public utility are underway, the Bank can consider providing financial support. Where it is not, some form of public private partnership should be public utilities; otherwise public-private considered, such as concession and OBA projects that can attract private investment, focusing on partnerships in service considered expansion. If private investment still cannot be attracted, then improvements to be quality and service Distribution: Guidance Notes also prepared for the Water & Governments should provide for long-term capacity building but should fix, to the extent possible, provisions for prices and technical and customer service standards in the key regulatory instruments, such as licenses or Sanitation, Gas, Transport, contracts, for a medium-term period. Regulatory frameworks should be designed bearing in mind local capacities and institutional approaches. and ICT sectors – management contracts/leases, accompanied by public investment in part financed by the Bank, can be considered as an interim step. Regulation: ready in April 2004
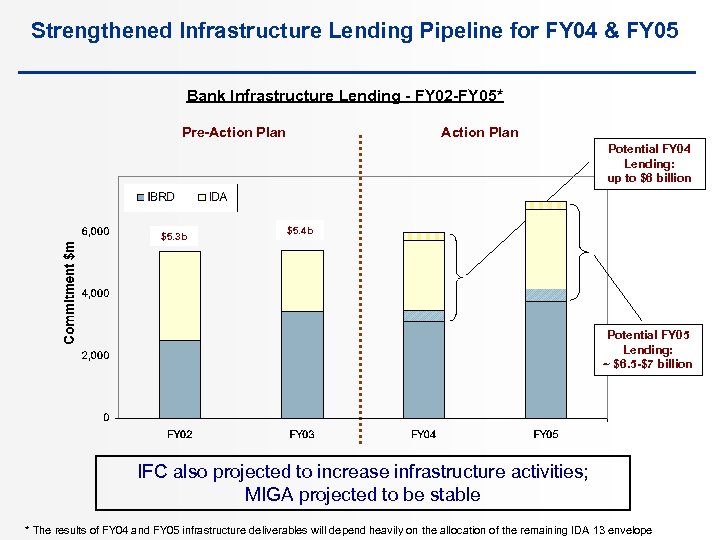 Strengthened Infrastructure Lending Pipeline for FY 04 & FY 05 Bank Infrastructure Lending - FY 02 -FY 05* Pre-Action Plan Potential FY 04 Lending: up to $6 billion $5. 3 b $5. 4 b Potential FY 05 Lending: ~ $6. 5 -$7 billion IFC also projected to increase infrastructure activities; MIGA projected to be stable * The results of FY 04 and FY 05 infrastructure deliverables will depend heavily on the allocation of the remaining IDA 13 envelope
Strengthened Infrastructure Lending Pipeline for FY 04 & FY 05 Bank Infrastructure Lending - FY 02 -FY 05* Pre-Action Plan Potential FY 04 Lending: up to $6 billion $5. 3 b $5. 4 b Potential FY 05 Lending: ~ $6. 5 -$7 billion IFC also projected to increase infrastructure activities; MIGA projected to be stable * The results of FY 04 and FY 05 infrastructure deliverables will depend heavily on the allocation of the remaining IDA 13 envelope
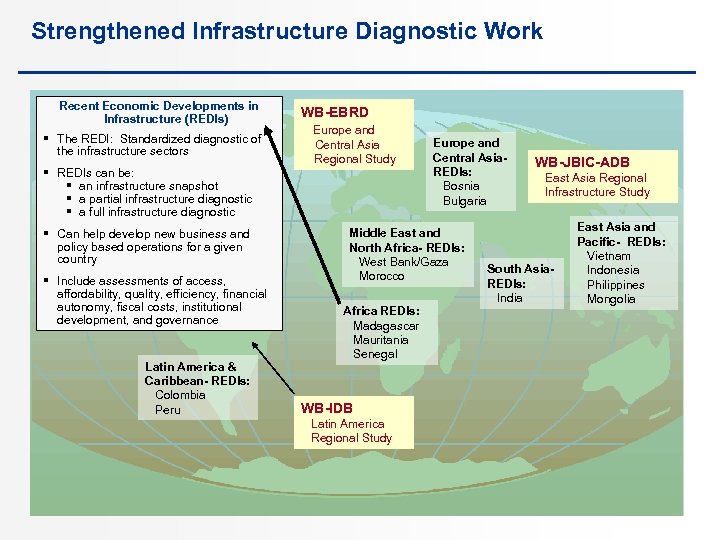 Strengthened Infrastructure Diagnostic Work Recent Economic Developments in Infrastructure (REDIs) § The REDI: Standardized diagnostic of the infrastructure sectors WB-EBRD Europe and Central Asia Regional Study § REDIs can be: § an infrastructure snapshot § a partial infrastructure diagnostic § a full infrastructure diagnostic § Can help develop new business and policy based operations for a given country § Include assessments of access, affordability, quality, efficiency, financial autonomy, fiscal costs, institutional development, and governance Latin America & Caribbean- REDIs: Colombia Peru Europe and Central Asia- REDIs: Bosnia Bulgaria Middle East and North Africa- REDIs: West Bank/Gaza Morocco Africa REDIs: Madagascar Mauritania Senegal WB-IDB Latin America Regional Study WB-JBIC-ADB East Asia Regional Infrastructure Study South Asia- REDIs: India East Asia and Pacific- REDIs: Vietnam Indonesia Philippines Mongolia
Strengthened Infrastructure Diagnostic Work Recent Economic Developments in Infrastructure (REDIs) § The REDI: Standardized diagnostic of the infrastructure sectors WB-EBRD Europe and Central Asia Regional Study § REDIs can be: § an infrastructure snapshot § a partial infrastructure diagnostic § a full infrastructure diagnostic § Can help develop new business and policy based operations for a given country § Include assessments of access, affordability, quality, efficiency, financial autonomy, fiscal costs, institutional development, and governance Latin America & Caribbean- REDIs: Colombia Peru Europe and Central Asia- REDIs: Bosnia Bulgaria Middle East and North Africa- REDIs: West Bank/Gaza Morocco Africa REDIs: Madagascar Mauritania Senegal WB-IDB Latin America Regional Study WB-JBIC-ADB East Asia Regional Infrastructure Study South Asia- REDIs: India East Asia and Pacific- REDIs: Vietnam Indonesia Philippines Mongolia
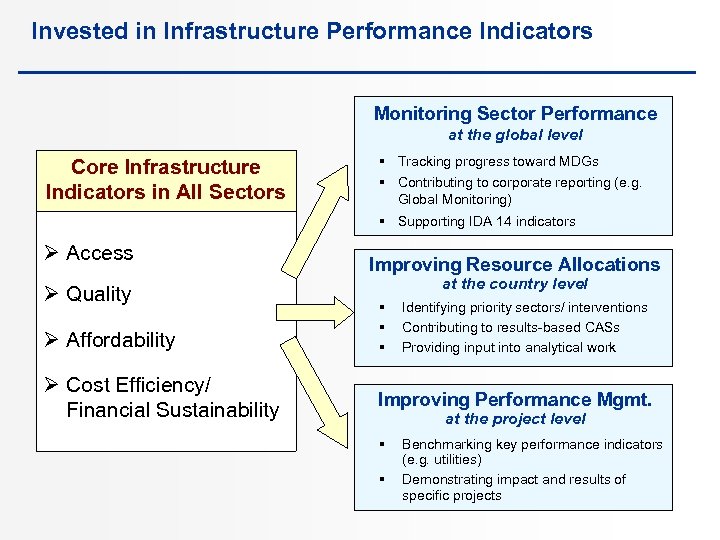 Invested in Infrastructure Performance Indicators Monitoring Sector Performance at the global level Core Infrastructure Indicators in All Sectors § Tracking progress toward MDGs § Contributing to corporate reporting (e. g. Global Monitoring) § Supporting IDA 14 indicators Ø Access Ø Quality Ø Affordability Ø Cost Efficiency/ Financial Sustainability Improving Resource Allocations at the country level § § § Identifying priority sectors/ interventions Contributing to results-based CASs Providing input into analytical work Improving Performance Mgmt. at the project level § § Benchmarking key performance indicators (e. g. utilities) Demonstrating impact and results of specific projects
Invested in Infrastructure Performance Indicators Monitoring Sector Performance at the global level Core Infrastructure Indicators in All Sectors § Tracking progress toward MDGs § Contributing to corporate reporting (e. g. Global Monitoring) § Supporting IDA 14 indicators Ø Access Ø Quality Ø Affordability Ø Cost Efficiency/ Financial Sustainability Improving Resource Allocations at the country level § § § Identifying priority sectors/ interventions Contributing to results-based CASs Providing input into analytical work Improving Performance Mgmt. at the project level § § Benchmarking key performance indicators (e. g. utilities) Demonstrating impact and results of specific projects
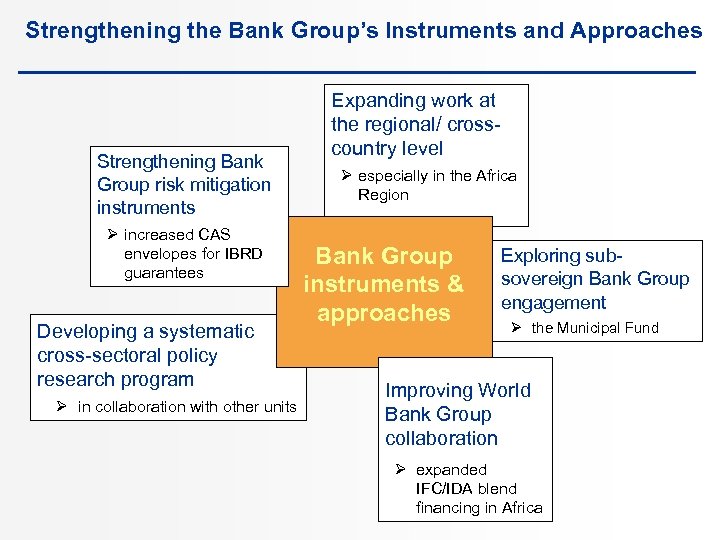 Strengthening the Bank Group’s Instruments and Approaches Strengthening Bank Group risk mitigation instruments Ø increased CAS envelopes for IBRD guarantees Developing a systematic cross-sectoral policy research program Ø in collaboration with other units Expanding work at the regional/ crosscountry level Ø especially in the Africa Region Bank Group instruments & approaches Exploring subsovereign Bank Group engagement Ø the Municipal Fund Improving World Bank Group collaboration Ø expanded IFC/IDA blend financing in Africa
Strengthening the Bank Group’s Instruments and Approaches Strengthening Bank Group risk mitigation instruments Ø increased CAS envelopes for IBRD guarantees Developing a systematic cross-sectoral policy research program Ø in collaboration with other units Expanding work at the regional/ crosscountry level Ø especially in the Africa Region Bank Group instruments & approaches Exploring subsovereign Bank Group engagement Ø the Municipal Fund Improving World Bank Group collaboration Ø expanded IFC/IDA blend financing in Africa
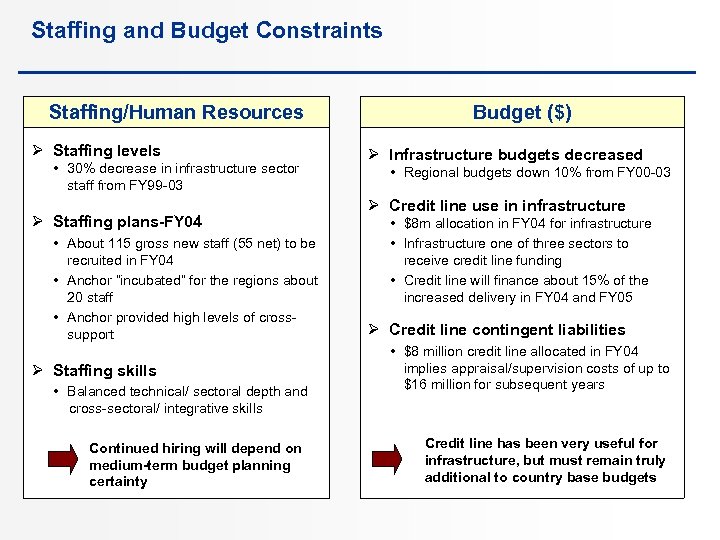 Staffing and Budget Constraints Staffing/Human Resources Ø Staffing levels • 30% decrease in infrastructure sector staff from FY 99 -03 Ø Staffing plans-FY 04 • About 115 gross new staff (55 net) to be recruited in FY 04 • Anchor “incubated” for the regions about 20 staff • Anchor provided high levels of crosssupport Ø Staffing skills • Balanced technical/ sectoral depth and cross-sectoral/ integrative skills Continued hiring will depend on medium-term budget planning certainty Budget ($) Ø Infrastructure budgets decreased • Regional budgets down 10% from FY 00 -03 Ø Credit line use in infrastructure • $8 m allocation in FY 04 for infrastructure • Infrastructure one of three sectors to receive credit line funding • Credit line will finance about 15% of the increased delivery in FY 04 and FY 05 Ø Credit line contingent liabilities • $8 million credit line allocated in FY 04 implies appraisal/supervision costs of up to $16 million for subsequent years Credit line has been very useful for infrastructure, but must remain truly additional to country base budgets
Staffing and Budget Constraints Staffing/Human Resources Ø Staffing levels • 30% decrease in infrastructure sector staff from FY 99 -03 Ø Staffing plans-FY 04 • About 115 gross new staff (55 net) to be recruited in FY 04 • Anchor “incubated” for the regions about 20 staff • Anchor provided high levels of crosssupport Ø Staffing skills • Balanced technical/ sectoral depth and cross-sectoral/ integrative skills Continued hiring will depend on medium-term budget planning certainty Budget ($) Ø Infrastructure budgets decreased • Regional budgets down 10% from FY 00 -03 Ø Credit line use in infrastructure • $8 m allocation in FY 04 for infrastructure • Infrastructure one of three sectors to receive credit line funding • Credit line will finance about 15% of the increased delivery in FY 04 and FY 05 Ø Credit line contingent liabilities • $8 million credit line allocated in FY 04 implies appraisal/supervision costs of up to $16 million for subsequent years Credit line has been very useful for infrastructure, but must remain truly additional to country base budgets
 Key Challenges Going Forward Revitalizing the Bank Group’s infrastructure business is a medium-term challenge Ensuring better Bank Group collaboration on infrastructure Addressing fiscal constraints to public investments Ensuring infrastructure retains its high quality ratings - currently the highest of any network Improving Bank Group services in Middle-Income Countries Engaging the public on infrastructure’s impact on poverty reduction
Key Challenges Going Forward Revitalizing the Bank Group’s infrastructure business is a medium-term challenge Ensuring better Bank Group collaboration on infrastructure Addressing fiscal constraints to public investments Ensuring infrastructure retains its high quality ratings - currently the highest of any network Improving Bank Group services in Middle-Income Countries Engaging the public on infrastructure’s impact on poverty reduction
 Infrastructure Action Plan Website For more information on the Infrastructure Action Plan, please visit our website: http: //fpd-int. worldbank. org/plan. nsf
Infrastructure Action Plan Website For more information on the Infrastructure Action Plan, please visit our website: http: //fpd-int. worldbank. org/plan. nsf


