55ae42a34297860b3f3523d58de58946.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Informations System Security Comprehensive Model NSTISSI 4011 COEN 250 Fall 2007 T. Schwarz, S. J.
Informations System Security Comprehensive Model NSTISSI 4011 COEN 250 Fall 2007 T. Schwarz, S. J.
 Information System Security n Main Goals: CIA ¨ Confidentiality ¨ Integrity ¨ Availability
Information System Security n Main Goals: CIA ¨ Confidentiality ¨ Integrity ¨ Availability
 Information System Security n Confidentiality ¨ Security Policy: Set of rules that determines whether a given subject can gain access to a specific object ¨ Confidentiality: Assurance that access controls are enforced
Information System Security n Confidentiality ¨ Security Policy: Set of rules that determines whether a given subject can gain access to a specific object ¨ Confidentiality: Assurance that access controls are enforced
 Information System Security n Integrity ¨ Quality of information that identifies how closely the data represent reality
Information System Security n Integrity ¨ Quality of information that identifies how closely the data represent reality
 Information System Security n Availability ¨ Information is provided to authorized users when it is requested
Information System Security n Availability ¨ Information is provided to authorized users when it is requested
 Information System Security n Information States ¨ Transmission ¨ Storage ¨ Processing
Information System Security n Information States ¨ Transmission ¨ Storage ¨ Processing
 Information System Security n Security Measures ¨ Technology ¨ Policy and Practice Policy: Formulation of Security Posture n Practice: Procedures followed to enhance security posture. n ¨ Education, Training, Awareness
Information System Security n Security Measures ¨ Technology ¨ Policy and Practice Policy: Formulation of Security Posture n Practice: Procedures followed to enhance security posture. n ¨ Education, Training, Awareness
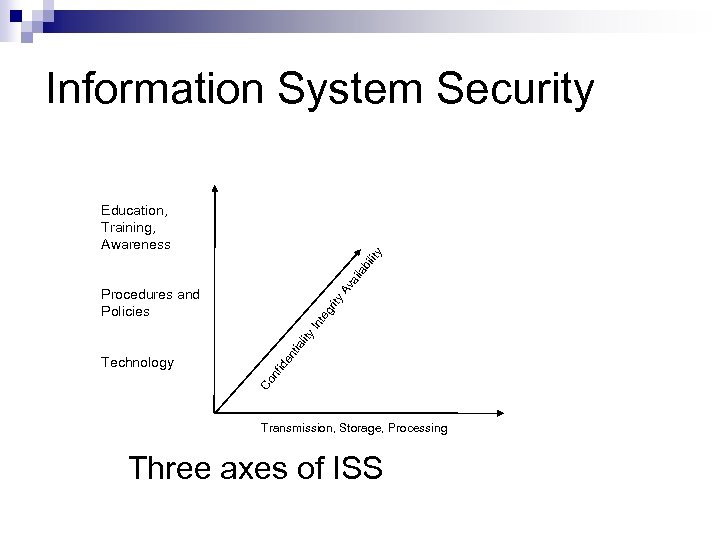 Information System Security Av ai la bi lity Education, Training, Awareness Co nf Technology id en t ia lity In te gr ity Procedures and Policies Transmission, Storage, Processing Three axes of ISS
Information System Security Av ai la bi lity Education, Training, Awareness Co nf Technology id en t ia lity In te gr ity Procedures and Policies Transmission, Storage, Processing Three axes of ISS
 NTISSI 4011 Training Standards n Awareness ¨ Creates sensitivity to threats and vulnerabilities of national security information systems ¨ Recognition of the need to protect data, information, and the means of processing ¨ Building working knowledge of principles and practices of INFOSEC n Performance Level ¨ Skill or ability to design, execute, or evaluate agency INFOSEC security procedures and practices
NTISSI 4011 Training Standards n Awareness ¨ Creates sensitivity to threats and vulnerabilities of national security information systems ¨ Recognition of the need to protect data, information, and the means of processing ¨ Building working knowledge of principles and practices of INFOSEC n Performance Level ¨ Skill or ability to design, execute, or evaluate agency INFOSEC security procedures and practices
 Elements of Computer Security n n n n Computer security should support the mission of the organization Computer security is an integral element of sound management Computer security should be cost effective Computer security responsibilities and accountability should be made explicit System owners have computer security responsibilities outside their own organizations Computer security requires a comprehensive and integrated approach Computer security should be periodically reassessed Computer security is constrained by societal factors. NIST 800 -12
Elements of Computer Security n n n n Computer security should support the mission of the organization Computer security is an integral element of sound management Computer security should be cost effective Computer security responsibilities and accountability should be made explicit System owners have computer security responsibilities outside their own organizations Computer security requires a comprehensive and integrated approach Computer security should be periodically reassessed Computer security is constrained by societal factors. NIST 800 -12
 Common Threats n Errors and Omissions ¨ ¨ n Fraud and Theft ¨ ¨ n n n Insiders / outsiders Computer as tools / targets Employee sabotage Loss of physical / infrastructure support Malicious hacking Espionage ¨ n Users Entry clerks System operators Software engineers Industrial / foreign government Malicious codes Privacy
Common Threats n Errors and Omissions ¨ ¨ n Fraud and Theft ¨ ¨ n n n Insiders / outsiders Computer as tools / targets Employee sabotage Loss of physical / infrastructure support Malicious hacking Espionage ¨ n Users Entry clerks System operators Software engineers Industrial / foreign government Malicious codes Privacy
 Management Controls n Computer Security Policy ¨ Definition of term n “Documentation of computer security decisions. ” n But term encompasses wide range of meanings. ¨ Three basic types n Program policy ¨ n Issue specific policies ¨ n creates an organization’s computer security program address specific issues such as use of crypto, private use of equipment, software installation, etc. System specific policies ¨ focuses on a single system
Management Controls n Computer Security Policy ¨ Definition of term n “Documentation of computer security decisions. ” n But term encompasses wide range of meanings. ¨ Three basic types n Program policy ¨ n Issue specific policies ¨ n creates an organization’s computer security program address specific issues such as use of crypto, private use of equipment, software installation, etc. System specific policies ¨ focuses on a single system
 Management Controls n Tools to implement policy ¨ Standards n specify uniform use of specific technologies ¨ e. g. organization-wide identification badges ¨ Guidelines n assists users, systems personnel, etc in effectively securing a system ¨ Procedures n normally assist in complying with applicable security policies, standards, and guidelines
Management Controls n Tools to implement policy ¨ Standards n specify uniform use of specific technologies ¨ e. g. organization-wide identification badges ¨ Guidelines n assists users, systems personnel, etc in effectively securing a system ¨ Procedures n normally assist in complying with applicable security policies, standards, and guidelines
 Management Controls n Program Policy Head of organization issues program policy to establish the org. ’s computer security program. ¨ Basic Components ¨ n n n Purpose Scope Responsibility ¨ ¨ n assigned to a newly created or existing office establishes roles of officials and offices in the org. Compliance ¨ ¨ General compliance, e. g. specifying an oversight office Use of specific penalties and disciplinary actions § A policy usually only creates the structure
Management Controls n Program Policy Head of organization issues program policy to establish the org. ’s computer security program. ¨ Basic Components ¨ n n n Purpose Scope Responsibility ¨ ¨ n assigned to a newly created or existing office establishes roles of officials and offices in the org. Compliance ¨ ¨ General compliance, e. g. specifying an oversight office Use of specific penalties and disciplinary actions § A policy usually only creates the structure
 Management Controls n Issue-specific Policy ¨ Applies to a specific issue such as n n n ¨ Internet Access E-mail Privacy Use of unofficial software Basic Components n Issue statement ¨ n n n Define issue with any relevant terms, distinctions, conditions Statement of org. ’s position on issue Applicability Roles and responsibilities Compliance Points of contact and supplementary information
Management Controls n Issue-specific Policy ¨ Applies to a specific issue such as n n n ¨ Internet Access E-mail Privacy Use of unofficial software Basic Components n Issue statement ¨ n n n Define issue with any relevant terms, distinctions, conditions Statement of org. ’s position on issue Applicability Roles and responsibilities Compliance Points of contact and supplementary information
 Management Controls n System Specific Policies ¨ Components n Security objectives ¨ ¨ n Operational security rules ¨ n concrete well defined Rules for operating a system: Who can do what to which specific classes and records of data, under what conditions Often accompanied by implementing procedures and guidelines
Management Controls n System Specific Policies ¨ Components n Security objectives ¨ ¨ n Operational security rules ¨ n concrete well defined Rules for operating a system: Who can do what to which specific classes and records of data, under what conditions Often accompanied by implementing procedures and guidelines
 Management Controls n System specific policy implementations ¨ Technology plays not the sole role in enforcing system-specific policies Technology: limits printing of confidential information to a specific printer n Non-technology: access to printer output is guarded n
Management Controls n System specific policy implementations ¨ Technology plays not the sole role in enforcing system-specific policies Technology: limits printing of confidential information to a specific printer n Non-technology: access to printer output is guarded n
 Management Controls Computer Security Program Management n OMB Circular A-130 establishes requirement for federal agencies to establish computer security programs n Federal agencies are complex: ¨ Management occurs at different levels, at least n n Centralized level System level
Management Controls Computer Security Program Management n OMB Circular A-130 establishes requirement for federal agencies to establish computer security programs n Federal agencies are complex: ¨ Management occurs at different levels, at least n n Centralized level System level
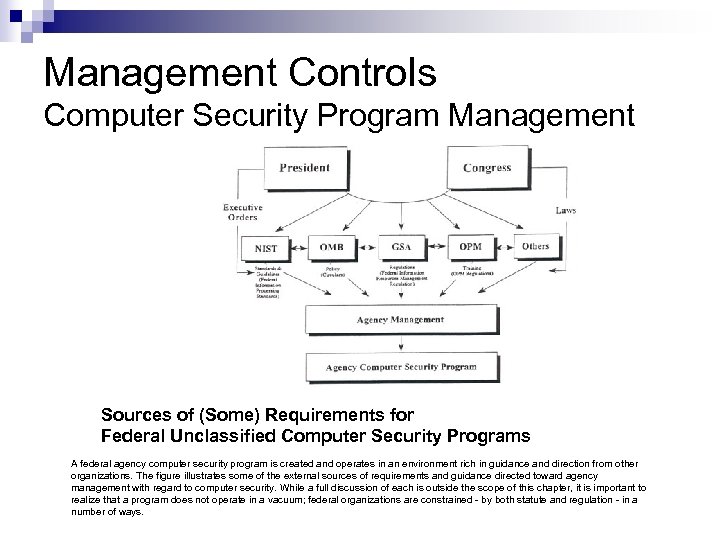 Management Controls Computer Security Program Management Sources of (Some) Requirements for Federal Unclassified Computer Security Programs A federal agency computer security program is created and operates in an environment rich in guidance and direction from other organizations. The figure illustrates some of the external sources of requirements and guidance directed toward agency management with regard to computer security. While a full discussion of each is outside the scope of this chapter, it is important to realize that a program does not operate in a vacuum; federal organizations are constrained - by both statute and regulation - in a number of ways.
Management Controls Computer Security Program Management Sources of (Some) Requirements for Federal Unclassified Computer Security Programs A federal agency computer security program is created and operates in an environment rich in guidance and direction from other organizations. The figure illustrates some of the external sources of requirements and guidance directed toward agency management with regard to computer security. While a full discussion of each is outside the scope of this chapter, it is important to realize that a program does not operate in a vacuum; federal organizations are constrained - by both statute and regulation - in a number of ways.
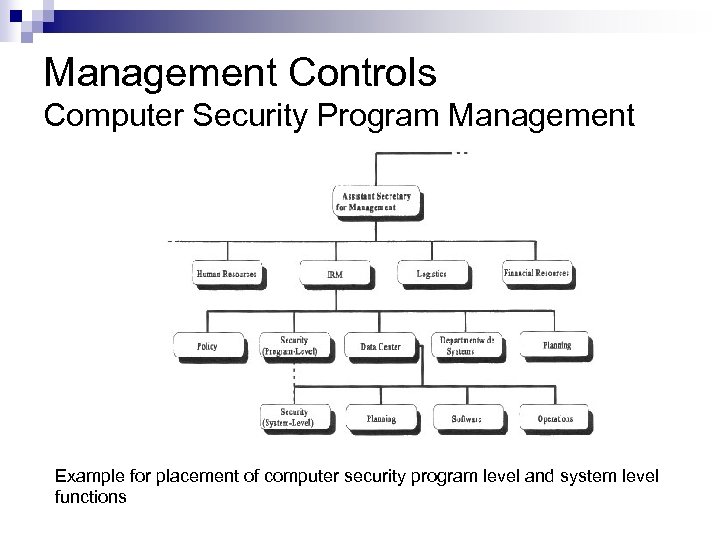 Management Controls Computer Security Program Management Example for placement of computer security program level and system level functions
Management Controls Computer Security Program Management Example for placement of computer security program level and system level functions
 Management Controls Computer Security Risk Management Basic assumption: Computers can never be fully secured n Risk Assessment n ¨ Process of analyzing and interpreting risk ¨ 3 basic activities Determining assessment scope and methodology n Collecting and analyzing data n Interpreting risk analysis results n
Management Controls Computer Security Risk Management Basic assumption: Computers can never be fully secured n Risk Assessment n ¨ Process of analyzing and interpreting risk ¨ 3 basic activities Determining assessment scope and methodology n Collecting and analyzing data n Interpreting risk analysis results n
 Management Controls Computer Security Risk Management n Components of Risk Assessment ¨ Asset Valuation ¨ Consequence Assessment ¨ Threat Identification ¨ Vulnerabilities ¨ Safeguards ¨ Likelihood
Management Controls Computer Security Risk Management n Components of Risk Assessment ¨ Asset Valuation ¨ Consequence Assessment ¨ Threat Identification ¨ Vulnerabilities ¨ Safeguards ¨ Likelihood
 Management Controls Assurance n Assurance Degree of confidence that the security measures work as intended to protect system and information ¨ Not a measurement ¨ n Accreditation Management official’s formal acceptance of adequacy of a system’s security ¨ Components ¨ n Technical features ¨ n Operational practices ¨ n Is the system operated according to stated procedures? Overall security ¨ n Do they operate as intended? Are there threats that are not addressed? Remaining risks ¨ Acceptability?
Management Controls Assurance n Assurance Degree of confidence that the security measures work as intended to protect system and information ¨ Not a measurement ¨ n Accreditation Management official’s formal acceptance of adequacy of a system’s security ¨ Components ¨ n Technical features ¨ n Operational practices ¨ n Is the system operated according to stated procedures? Overall security ¨ n Do they operate as intended? Are there threats that are not addressed? Remaining risks ¨ Acceptability?
 Operational Controls Personnel / User Issues n Two principles ¨ Separation of duties ¨ Least privilege n Staffing ¨ Job definition ¨ Sensitivity determination ¨ Filling position n Screening applicants n Selecting individual ¨ Training and Awareness Creation
Operational Controls Personnel / User Issues n Two principles ¨ Separation of duties ¨ Least privilege n Staffing ¨ Job definition ¨ Sensitivity determination ¨ Filling position n Screening applicants n Selecting individual ¨ Training and Awareness Creation
 Operational Controls Personnel / User Issues n User Administration ¨ User account management n Identification n Authentication n Access Verification ¨ Auditing n Verify periodically legitimacy of current accounts and access authorizations ¨ Modification / Removal of Access n n Contractor Access Management Public Access Considerations
Operational Controls Personnel / User Issues n User Administration ¨ User account management n Identification n Authentication n Access Verification ¨ Auditing n Verify periodically legitimacy of current accounts and access authorizations ¨ Modification / Removal of Access n n Contractor Access Management Public Access Considerations
 Operational Controls Contingency & Disaster Preparation n Contingency planning in six steps ¨ Identification of mission-critical functions ¨ Identification of resources that support critical functions ¨ Anticipation of potential contingencies / disasters ¨ Selecting contingency planning strategies ¨ Implementing contingency strategies ¨ Testing and revisiting strategies
Operational Controls Contingency & Disaster Preparation n Contingency planning in six steps ¨ Identification of mission-critical functions ¨ Identification of resources that support critical functions ¨ Anticipation of potential contingencies / disasters ¨ Selecting contingency planning strategies ¨ Implementing contingency strategies ¨ Testing and revisiting strategies
 Operational Controls Incident Response n Incident Response: Actions taken to deal with an incident. Detection Countermeasures Incident Response: Containment & Repair
Operational Controls Incident Response n Incident Response: Actions taken to deal with an incident. Detection Countermeasures Incident Response: Containment & Repair
 Operational Controls Incident Response n Establishment of Successful Incident Handling Capability ¨ Components n n n ¨ Understanding of constituency Education of constituency Centralized communication Expertise in requisite technology Links to other groups assisting in incident handling, as needed Technical support n n n Nationwide / worldwide reporting facility for incidents Rapid communications Secure communications for incidents involving national security
Operational Controls Incident Response n Establishment of Successful Incident Handling Capability ¨ Components n n n ¨ Understanding of constituency Education of constituency Centralized communication Expertise in requisite technology Links to other groups assisting in incident handling, as needed Technical support n n n Nationwide / worldwide reporting facility for incidents Rapid communications Secure communications for incidents involving national security
 Operational Controls Awareness, Training, & Education n n Basic premise: people are fallible Two main benefits ¨ Improvement n n Buy-in Knowledge and skills ¨ Increased n of employment behavior ability to hold employees accountable Dissemination and enforcement of policies presupposes awareness
Operational Controls Awareness, Training, & Education n n Basic premise: people are fallible Two main benefits ¨ Improvement n n Buy-in Knowledge and skills ¨ Increased n of employment behavior ability to hold employees accountable Dissemination and enforcement of policies presupposes awareness
 Operational Controls Awareness, Training, & Education n Awareness ¨ “What” ¨ Information n Training ¨ “How” ¨ Knowledge n Education ¨ “Why” ¨ Insight
Operational Controls Awareness, Training, & Education n Awareness ¨ “What” ¨ Information n Training ¨ “How” ¨ Knowledge n Education ¨ “Why” ¨ Insight
 Operational Controls Security Considerations in Computer Support and Operations ¨ Everything n User support – Help desk ¨ Needs related n n done to run a computer system to recognize which problems are security Example: Failed login can result from logout caused by hacker running a password guessing attack Software support ¨ Control of software used on a system ¨ Software can only be modified with proper authorization
Operational Controls Security Considerations in Computer Support and Operations ¨ Everything n User support – Help desk ¨ Needs related n n done to run a computer system to recognize which problems are security Example: Failed login can result from logout caused by hacker running a password guessing attack Software support ¨ Control of software used on a system ¨ Software can only be modified with proper authorization
 Operational Controls Security Considerations in Computer Support and Operations n Configuration Management ¨ Goal: to ensure that changes to the system do not unintentionally or unknowingly diminish security n Backups ¨ critical n for contingency planning Media control ¨ Provide physical and environmental protection and accountability for removable media n n Documentation Maintenance
Operational Controls Security Considerations in Computer Support and Operations n Configuration Management ¨ Goal: to ensure that changes to the system do not unintentionally or unknowingly diminish security n Backups ¨ critical n for contingency planning Media control ¨ Provide physical and environmental protection and accountability for removable media n n Documentation Maintenance
 Operational Controls Physical and Environmental Security n Protect computer systems from ¨ Interruptions in providing computer services ¨ Physical damage ¨ Unauthorized access of information n Example: Tempest program ¨ Loss of control over system ¨ Physical theft n Mobile and portable systems present new range of issues
Operational Controls Physical and Environmental Security n Protect computer systems from ¨ Interruptions in providing computer services ¨ Physical damage ¨ Unauthorized access of information n Example: Tempest program ¨ Loss of control over system ¨ Physical theft n Mobile and portable systems present new range of issues
 Technical Controls Identification and Authentication n Identification: ¨ n Authentication ¨ n Means by which a user provides a claimed identity to the system Means of establishing the validity of the claim Identification and Authentication based on ¨ What you know. n ¨ What you have. n ¨ Physical key, smart card. What you are. n ¨ E. g. password, pass-phrase, (secret key, private key). Biometrics. Where you are. n E. g. trusted machine, access to room, …
Technical Controls Identification and Authentication n Identification: ¨ n Authentication ¨ n Means by which a user provides a claimed identity to the system Means of establishing the validity of the claim Identification and Authentication based on ¨ What you know. n ¨ What you have. n ¨ Physical key, smart card. What you are. n ¨ E. g. password, pass-phrase, (secret key, private key). Biometrics. Where you are. n E. g. trusted machine, access to room, …
 Technical Controls Logical Access Control n Access ¨ Ability n to do something with a computing resource Access control ¨ Means by which this ability is explicitly enabled or restricted n Not to be confused with ¨ Authorization n Permission to use computer resource ¨ Authentication n Proof of identity
Technical Controls Logical Access Control n Access ¨ Ability n to do something with a computing resource Access control ¨ Means by which this ability is explicitly enabled or restricted n Not to be confused with ¨ Authorization n Permission to use computer resource ¨ Authentication n Proof of identity
 Technical Controls Logical Access Control n Access Criteria typically based on Identity ¨ Roles ¨ Location ¨ Time ¨ n ¨ Personnel files only accessible during normal business hours Transactions n n Phone inquiry answered by computer Computer authenticates inquirer If too complicated, requires human clerk to answer Computer grants clerk permission to access inquirer’s record for the duration of the transaction
Technical Controls Logical Access Control n Access Criteria typically based on Identity ¨ Roles ¨ Location ¨ Time ¨ n ¨ Personnel files only accessible during normal business hours Transactions n n Phone inquiry answered by computer Computer authenticates inquirer If too complicated, requires human clerk to answer Computer grants clerk permission to access inquirer’s record for the duration of the transaction
 Technical Controls Audit Trails n Audit Trail ¨ Series n of records of computer events Auditing ¨ Review and analysis of management, operational, and technical controls n Establishing audit trails helps to establish ¨ Individual accountability ¨ Reconstruction of events ¨ Intrusion detection ¨ Problem analysis
Technical Controls Audit Trails n Audit Trail ¨ Series n of records of computer events Auditing ¨ Review and analysis of management, operational, and technical controls n Establishing audit trails helps to establish ¨ Individual accountability ¨ Reconstruction of events ¨ Intrusion detection ¨ Problem analysis
 Technical Controls Cryptography Tool to establish C, I, & A n Relies on technology and key management n
Technical Controls Cryptography Tool to establish C, I, & A n Relies on technology and key management n


