bcb47562f3a23bb5fedea6d6a2ad4e1c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Information Technology: Propelling Economic Growth By U Thein Oo Patron, Myanmar Computer Federation Chairman, Myanmar ICT Development Cooperation Chairman, Steering Committee for Yangon & Mandalay Computer Universities (Co. E)

MESSAGE 1 • It is widely accepted (also in Myanmar) that ICT is at the centre of an economic and social transformation. • Advances in ICTs have dramatically changed the World economy over the last few decades. • The fact that ICT can propelled economic development is proven. • The intrinsic value of ICT lies not in its ease for communications and information but rather as an enabler for growth and development. ICT is considered as a powerful tool for economic growth and poverty eradication.
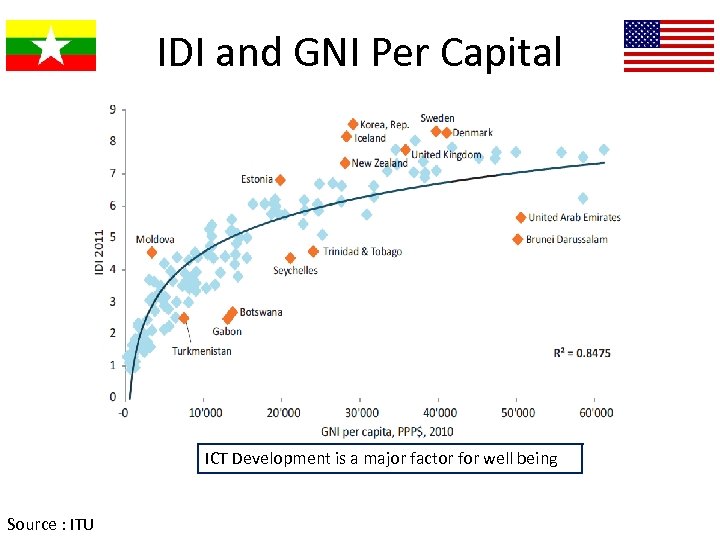
IDI and GNI Per Capital ICT Development is a major factor for well being Source : ITU
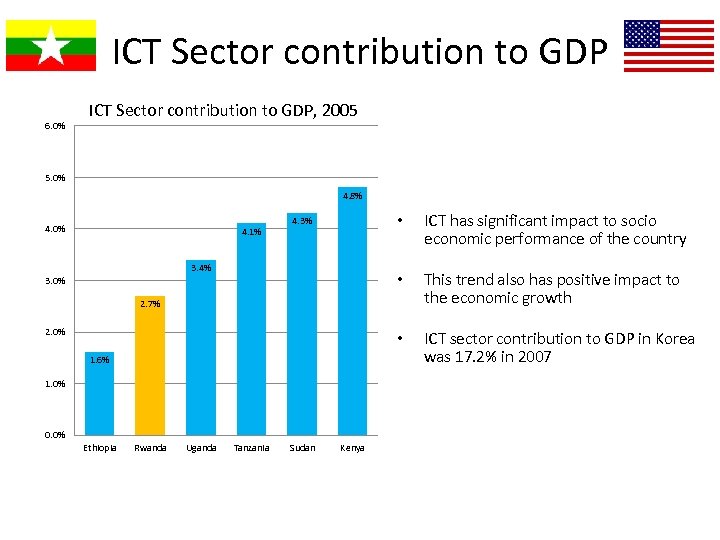
ICT Sector contribution to GDP 6. 0% ICT Sector contribution to GDP, 2005 5. 0% 4. 8% 4. 3% 3. 4% 3. 0% ICT has significant impact to socio economic performance of the country • 4. 1% • This trend also has positive impact to the economic growth • 4. 0% ICT sector contribution to GDP in Korea was 17. 2% in 2007 2. 7% 2. 0% 1. 6% 1. 0% 0. 0% Ethiopia Rwanda Uganda Tanzania Sudan Kenya

MESSAGE 2 • Myanmar had plan but no implementation • Myanmar leaders, business communities and even general public recognize that ICT is a key enabler for socioeconomic development. • There are efforts in preparing ICT development plans. – 2001 -2005 Master plan – 2006 -2010 Master plan and Action plan – 2011 -2015 Follow up plan • But there is still not much concrete implementation efforts for ICT development.
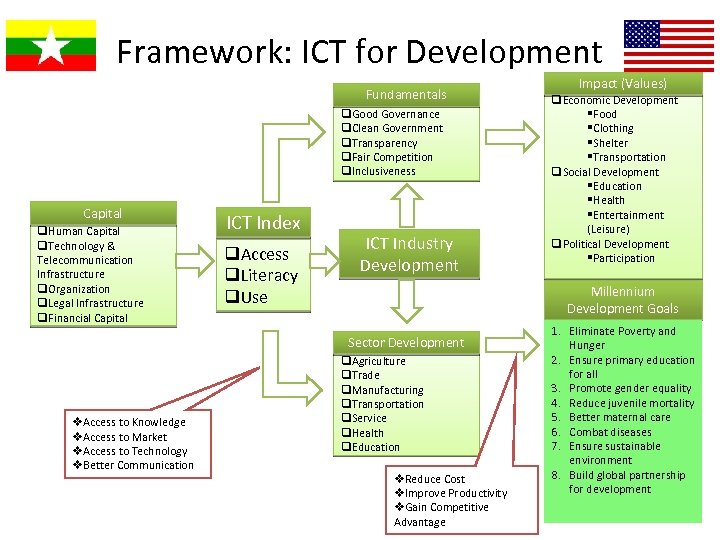
Framework: ICT for Development Fundamentals q. Good Governance q. Clean Government q. Transparency q. Fair Competition q. Inclusiveness Capital q. Human Capital q. Technology & Telecommunication Infrastructure q. Organization q. Legal Infrastructure q. Financial Capital ICT Index q. Access q. Literacy q. Use ICT Industry Development Millennium Development Goals Sector Development v. Access to Knowledge v. Access to Market v. Access to Technology v. Better Communication Impact (Values) q. Economic Development §Food §Clothing §Shelter §Transportation q. Social Development §Education §Health §Entertainment (Leisure) q. Political Development §Participation q. Agriculture q. Trade q. Manufacturing q. Transportation q. Service q. Health q. Education v. Reduce Cost v. Improve Productivity v. Gain Competitive Advantage 1. Eliminate Poverty and Hunger 2. Ensure primary education for all 3. Promote gender equality 4. Reduce juvenile mortality 5. Better maternal care 6. Combat diseases 7. Ensure sustainable environment 8. Build global partnership for development
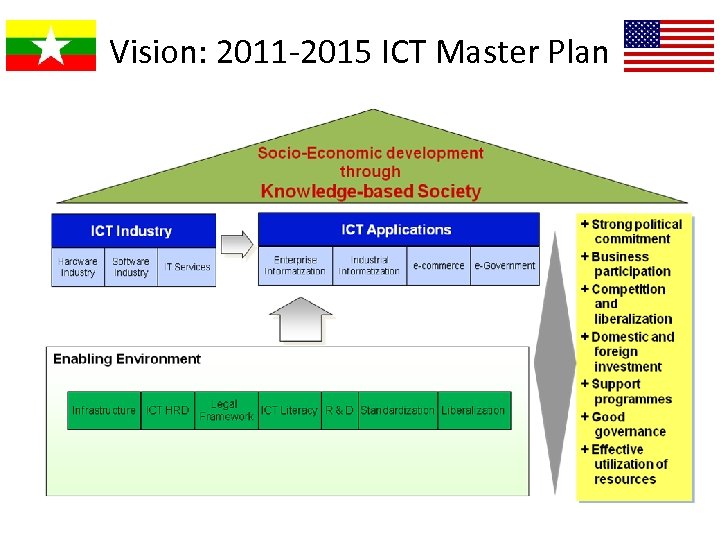
Vision: 2011 -2015 ICT Master Plan
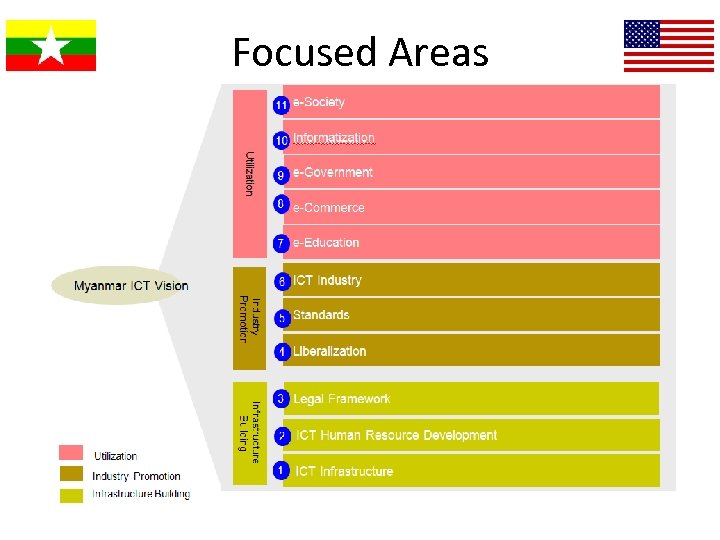
Focused Areas
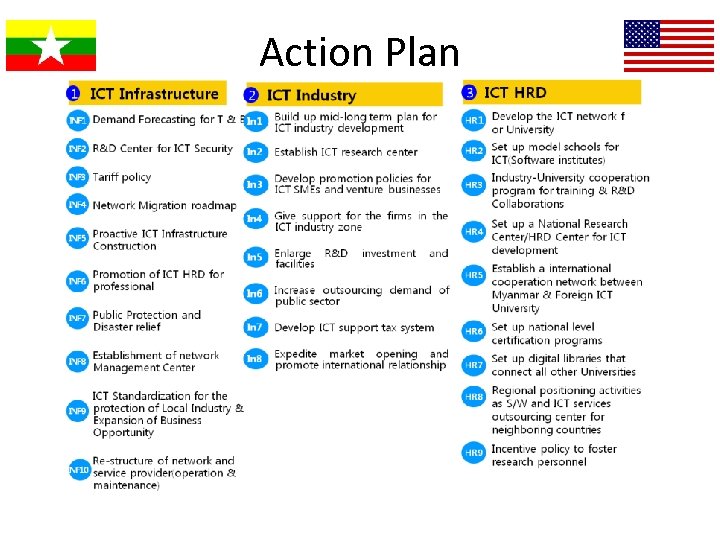
Action Plan
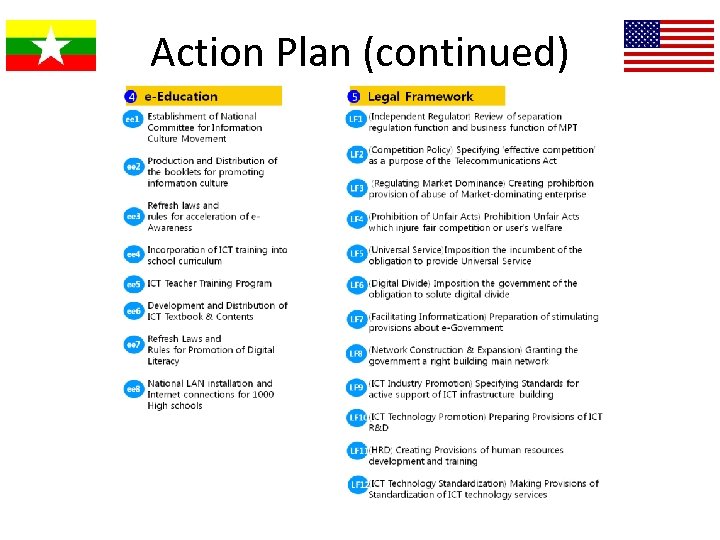
Action Plan (continued)

MESSAGE 3 • Just developing and talking about vision, mission and reform and not putting concrete efforts leave Myanmar at the bottom of IDI ranking and consequently economic development.
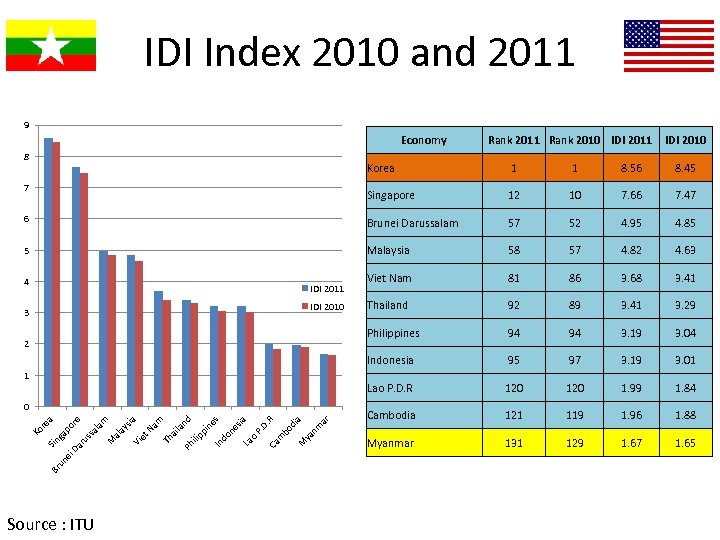
IDI Index 2010 and 2011 9 Economy 8 Rank 2011 Rank 2010 IDI 2011 IDI 2010 Korea 1 1 8. 56 8. 45 Singapore 12 10 7. 66 7. 47 6 Brunei Darussalam 57 52 4. 95 4. 85 5 Malaysia 58 57 4. 82 4. 63 Viet Nam 81 86 3. 68 3. 41 Thailand 92 89 3. 41 3. 29 Philippines 94 94 3. 19 3. 04 Indonesia 95 97 3. 19 3. 01 Lao P. D. R 120 1. 99 1. 84 Cambodia 121 119 1. 96 1. 88 Myanmar 131 129 1. 67 1. 65 7 4 IDI 2011 IDI 2010 3 2 1 ar nm ya M bo d ia R m Ca La o P. D. sia s ne do In ilip pi ne nd ila Ph m Th a Na sia Vi et ay al am Source : ITU M al re ru ss po Br un ei Da Sin ga Ko r ea 0
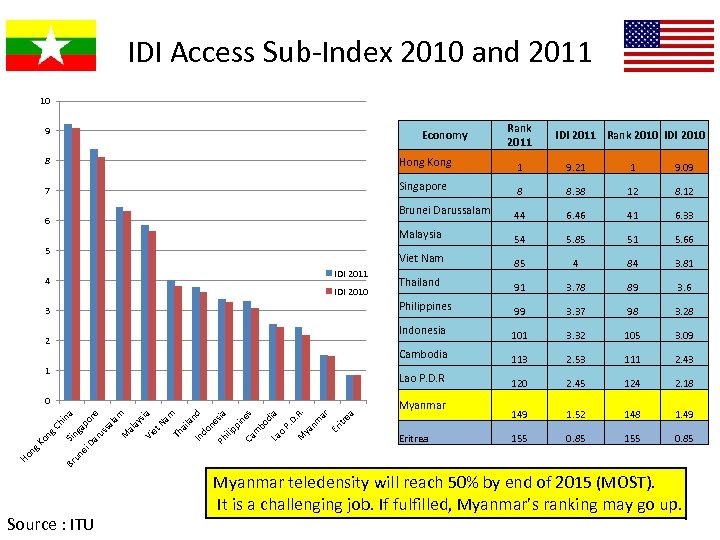
IDI Access Sub-Index 2010 and 2011 10 9 Economy Rank 2011 IDI 2011 Rank 2010 IDI 2010 8 Hong Kong 1 9. 21 1 9. 09 7 Singapore 8 8. 38 12 8. 12 Brunei Darussalam 44 6. 46 41 6. 33 Malaysia 54 5. 85 51 5. 66 Viet Nam 85 4 84 3. 81 Thailand 91 3. 78 89 3. 6 Philippines 99 3. 37 98 3. 28 Indonesia 101 3. 32 105 3. 09 Cambodia 113 2. 53 111 2. 43 Lao P. D. R 120 2. 45 124 2. 18 149 1. 52 148 1. 49 155 0. 85 6 5 IDI 2011 4 IDI 2010 3 2 1 0 Eritrea Br Ho ng Ko ng Ch i Sin na un ga ei po Da re ru ss al am M al ay sia Vi et Na m Th ai la nd In do ne sia Ph ilip pi ne Ca s m bo di a La o P. D. R M ya. nm ar Er itr ea Myanmar Source : ITU Myanmar teledensity will reach 50% by end of 2015 (MOST). It is a challenging job. If fulfilled, Myanmar’s ranking may go up.
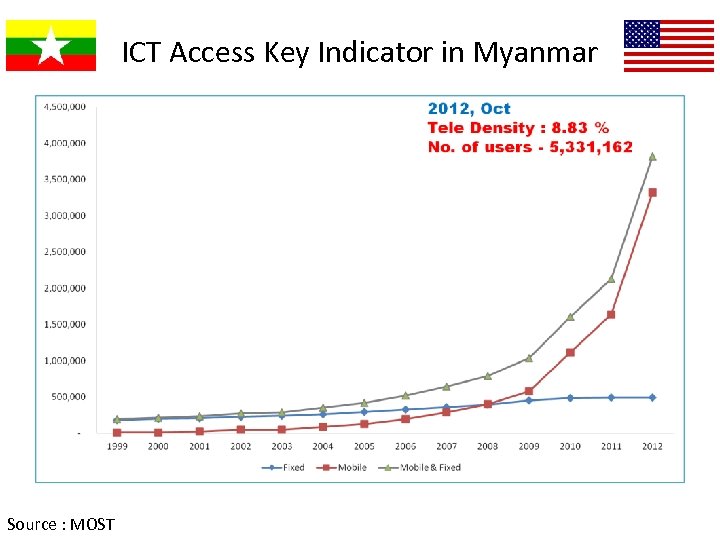
ICT Access Key Indicator in Myanmar Source : MOST
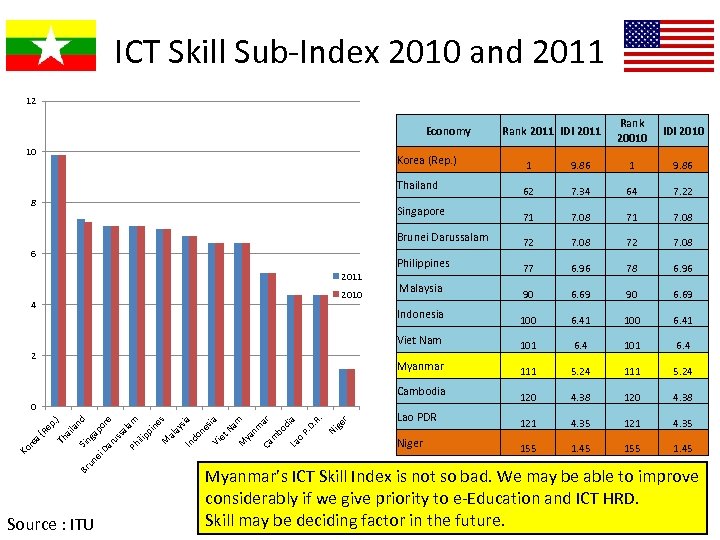
ICT Skill Sub-Index 2010 and 2011 12 Economy 10 Rank 2011 IDI 2011 Rank 20010 IDI 2010 Korea (Rep. ) ila Sin nd Br un ga ei po Da re ru ss al Ph am ilip pi ne s M al ay sia In do ne sia Vi et Na m M ya nm ar Ca m bo di a La o P. D. R. Ni ge r p. ) Th a Re a( re Ko 71 7. 08 72 7. 08 77 6. 96 78 6. 96 Malaysia 90 6. 69 100 6. 41 101 6. 4 111 5. 24 Cambodia Source : ITU 7. 22 Myanmar 0 64 Viet Nam 2 7. 34 Indonesia 4 62 Philippines 2010 9. 86 Brunei Darussalam 2011 1 Singapore 6 9. 86 Thailand 8 1 120 4. 38 Lao PDR 121 4. 35 Niger 155 1. 45 Myanmar’s ICT Skill Index is not so bad. We may be able to improve considerably if we give priority to e-Education and ICT HRD. Skill may be deciding factor in the future.
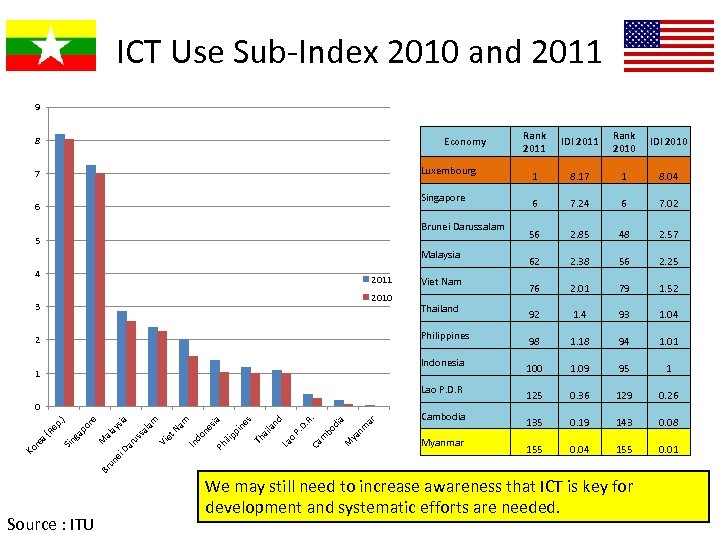
ICT Use Sub-Index 2010 and 2011 9 8 Economy Luxembourg 7 Singapore 6 Brunei Darussalam 5 Malaysia 4 2011 2010 3 Viet Nam Thailand Philippines 2 Indonesia 1 Lao P. D. R ar nm ya M bo d ia R. m D. Ca P. nd La o ila s Th a pi ne sia ilip Ph do ne m et am Na In Da ei Cambodia Myanmar IDI 2011 Rank 2010 IDI 2010 1 8. 17 1 8. 04 6 7. 24 6 7. 02 56 2. 85 48 2. 57 62 2. 38 56 2. 25 76 2. 01 79 1. 52 92 1. 4 93 1. 04 98 1. 18 94 1. 01 100 1. 09 95 1 125 0. 36 129 0. 26 135 0. 19 143 0. 08 155 0. 04 155 0. 01 Br un Vi al sia ay al M ru ss re po Sin ga Ko re a( Re p. ) 0 Rank 2011 Source : ITU We may still need to increase awareness that ICT is key for development and systematic efforts are needed.
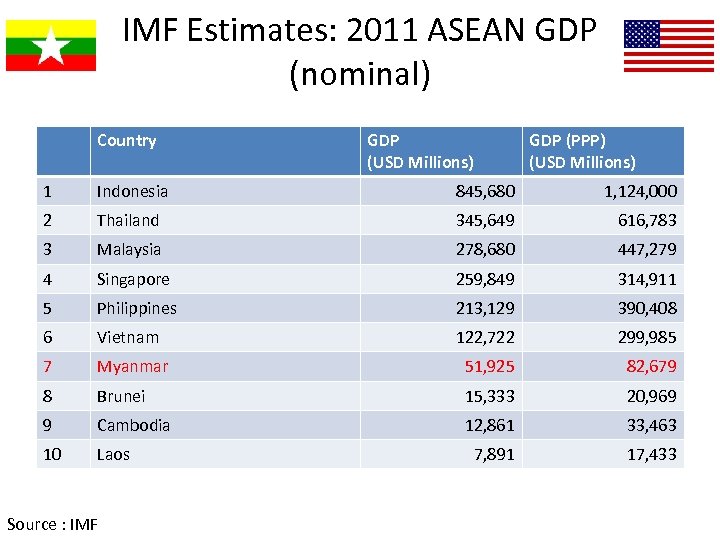
IMF Estimates: 2011 ASEAN GDP (nominal) Country GDP (USD Millions) GDP (PPP) (USD Millions) 1 Indonesia 845, 680 1, 124, 000 2 Thailand 345, 649 616, 783 3 Malaysia 278, 680 447, 279 4 Singapore 259, 849 314, 911 5 Philippines 213, 129 390, 408 6 Vietnam 122, 722 299, 985 7 Myanmar 51, 925 82, 679 8 Brunei 15, 333 20, 969 9 Cambodia 12, 861 33, 463 10 Laos 7, 891 17, 433 Source : IMF
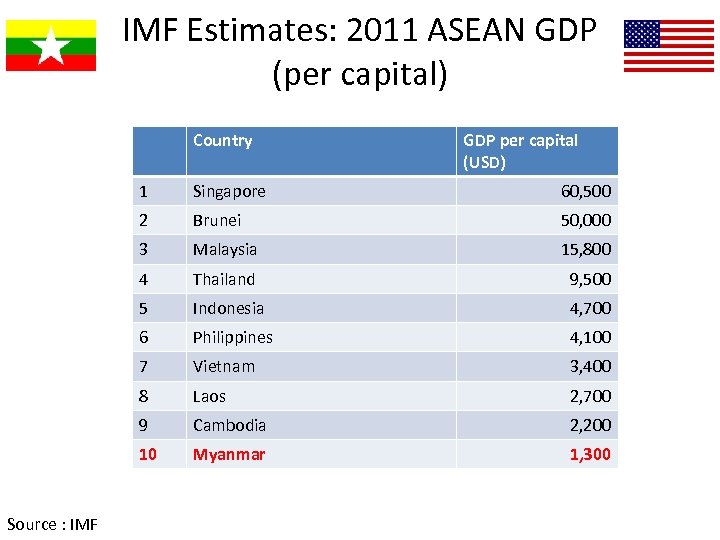
IMF Estimates: 2011 ASEAN GDP (per capital) Country GDP per capital (USD) 1 60, 500 2 Brunei 50, 000 3 Malaysia 15, 800 4 Thailand 9, 500 5 Indonesia 4, 700 6 Philippines 4, 100 7 Vietnam 3, 400 8 Laos 2, 700 9 Cambodia 2, 200 10 Source : IMF Singapore Myanmar 1, 300

MESSAGE 4 • Myanmar is really changing • ICT Developmentin Myanmar is at the early stage • There are many opportunities for cooperation with countries like United States
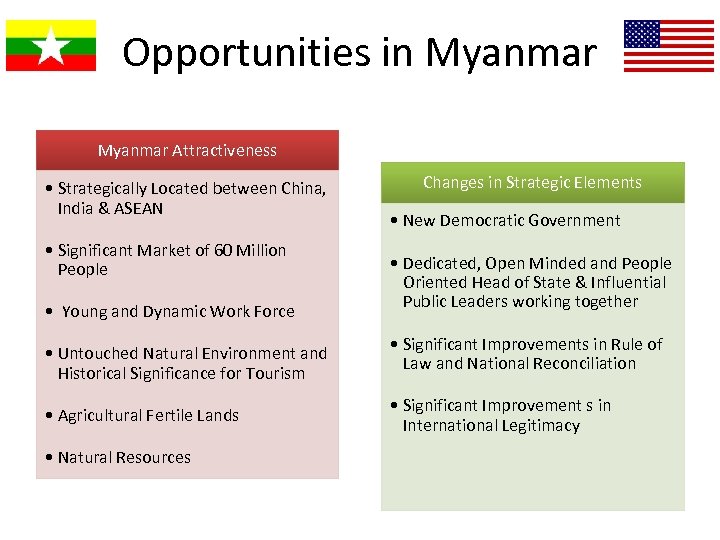
Opportunities in Myanmar Attractiveness • Strategically Located between China, India & ASEAN • Significant Market of 60 Million People • Young and Dynamic Work Force • Untouched Natural Environment and Historical Significance for Tourism • Agricultural Fertile Lands • Natural Resources Changes in Strategic Elements • New Democratic Government • Dedicated, Open Minded and People Oriented Head of State & Influential Public Leaders working together • Significant Improvements in Rule of Law and National Reconciliation • Significant Improvement s in International Legitimacy
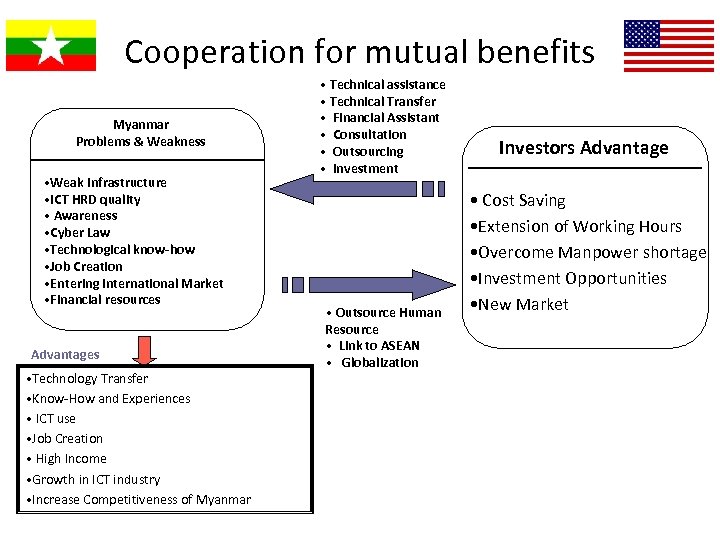
Cooperation for mutual benefits Myanmar Problems & Weakness • Weak Infrastructure • ICT HRD quality • Awareness • Cyber Law • Technological know-how • Job Creation • Entering international Market • Financial resources Advantages • Technology Transfer • Know-How and Experiences • ICT use • Job Creation • High Income • Growth in ICT industry • Increase Competitiveness of Myanmar • Technical assistance • Technical Transfer • Financial Assistant • Consultation • Outsourcing • Investment • Outsource Human Resource • Link to ASEAN • Globalization Investors Advantage • Cost Saving • Extension of Working Hours • Overcome Manpower shortage • Investment Opportunities • New Market
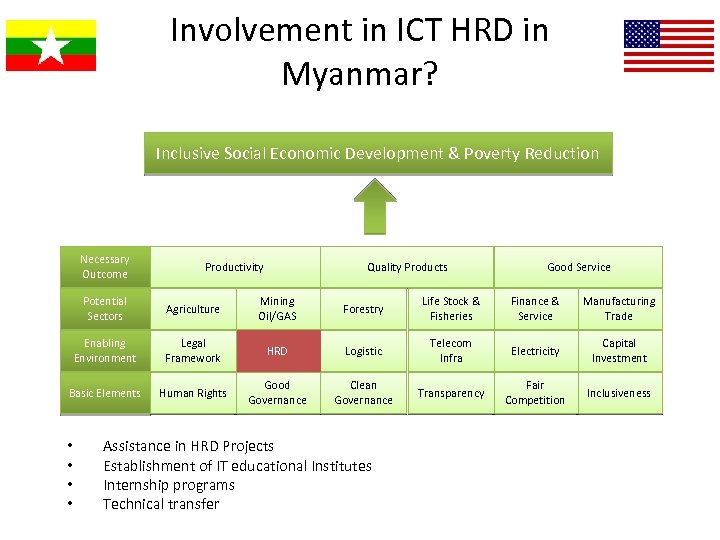
Involvement in ICT HRD in Myanmar? Inclusive Social Economic Development & Poverty Reduction Necessary Outcome Productivity Quality Products Good Service Potential Sectors Agriculture Mining Oil/GAS Forestry Life Stock & Fisheries Finance & Service Manufacturing Trade Enabling Environment Legal Framework HRD Logistic Telecom Infra Electricity Capital Investment Basic Elements Human Rights Good Governance Clean Governance Transparency Fair Competition Inclusiveness • • Assistance in HRD Projects Establishment of IT educational Institutes Internship programs Technical transfer
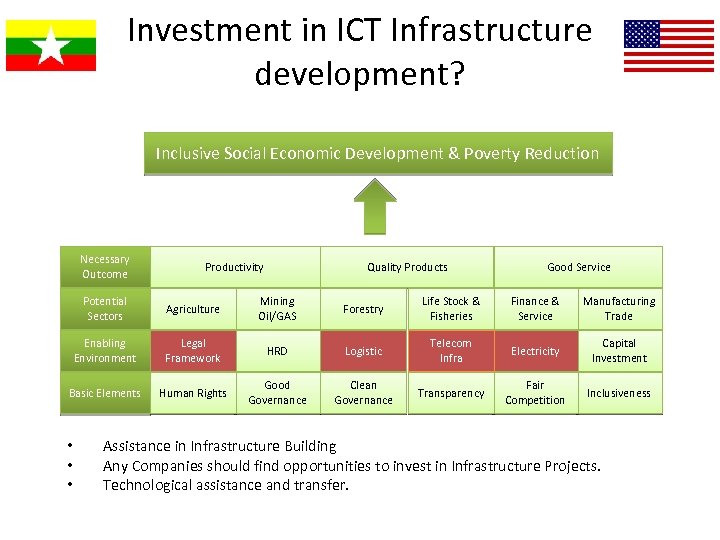
Investment in ICT Infrastructure development? Inclusive Social Economic Development & Poverty Reduction Necessary Outcome Productivity Quality Products Good Service Potential Sectors Agriculture Mining Oil/GAS Forestry Life Stock & Fisheries Finance & Service Manufacturing Trade Enabling Environment Legal Framework HRD Logistic Telecom Infra Electricity Capital Investment Basic Elements Human Rights Good Governance Clean Governance Transparency Fair Competition Inclusiveness • • • Assistance in Infrastructure Building Any Companies should find opportunities to invest in Infrastructure Projects. Technological assistance and transfer.
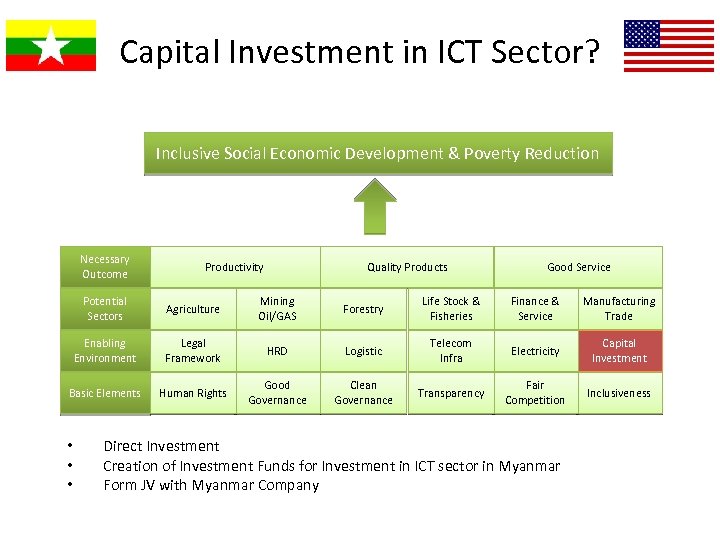
Capital Investment in ICT Sector? Inclusive Social Economic Development & Poverty Reduction Necessary Outcome Productivity Quality Products Good Service Potential Sectors Agriculture Mining Oil/GAS Forestry Life Stock & Fisheries Finance & Service Manufacturing Trade Enabling Environment Legal Framework HRD Logistic Telecom Infra Electricity Capital Investment Basic Elements Human Rights Good Governance Clean Governance Transparency Fair Competition Inclusiveness • • • Direct Investment Creation of Investment Funds for Investment in ICT sector in Myanmar Form JV with Myanmar Company
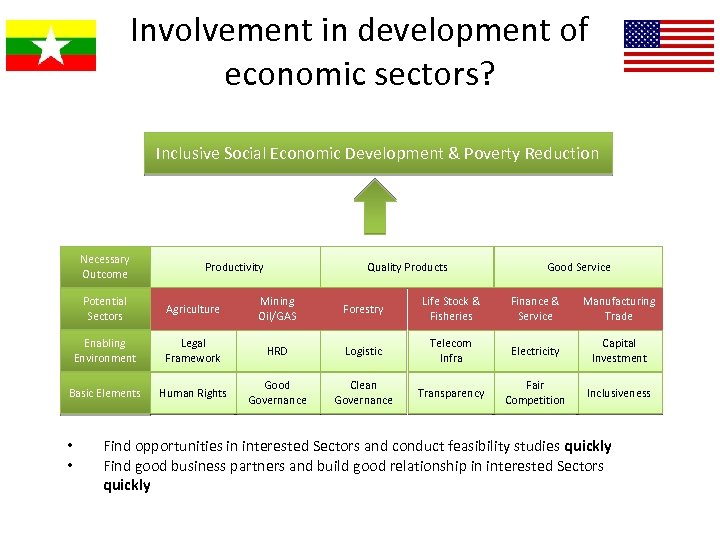
Involvement in development of economic sectors? Inclusive Social Economic Development & Poverty Reduction Necessary Outcome Productivity Quality Products Good Service Potential Sectors Agriculture Mining Oil/GAS Forestry Life Stock & Fisheries Finance & Service Manufacturing Trade Enabling Environment Legal Framework HRD Logistic Telecom Infra Electricity Capital Investment Basic Elements Human Rights Good Governance Clean Governance Transparency Fair Competition Inclusiveness • • Find opportunities in interested Sectors and conduct feasibility studies quickly Find good business partners and build good relationship in interested Sectors quickly

Conclusion • We need to recognize that ICT 4 D is a program aimed at bridging the digital -divide and bolstering economic development by ensuring equal access to up-to-date Information and Communication Technologies. • Myanmar is really changing and reversal is impossible • Development in Myanmar presents enormous Investment Opportunities in IT Sector. However, Investment will only be fruitful only with assistance and technology transfer contributing to capacity building. • Government commitment and involvement in ICT 4 D is very important at the initial stage where private sector cooperation is insufficient. There must be cooperation and coordination between the two governments. • Helping Myanmar in development will be mutually beneficial to America. We can become political, social and economic partners.

Thank You!
bcb47562f3a23bb5fedea6d6a2ad4e1c.ppt