27d150bebba031a809320d4a19415eb9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Information Technology and Systems © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Information Technology and Systems © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Information System • A collection of related components that interact to perform a task in order to accomplish a goal. • The integration of several elements of a business process to effect a specific outcome • A process that refines raw facts into meaningful information • Provides opportunities to improve internal operations, create competitive advantage in the marketplace, improve patient care delivery, enhance research, and provide better service © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Information System • A collection of related components that interact to perform a task in order to accomplish a goal. • The integration of several elements of a business process to effect a specific outcome • A process that refines raw facts into meaningful information • Provides opportunities to improve internal operations, create competitive advantage in the marketplace, improve patient care delivery, enhance research, and provide better service © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
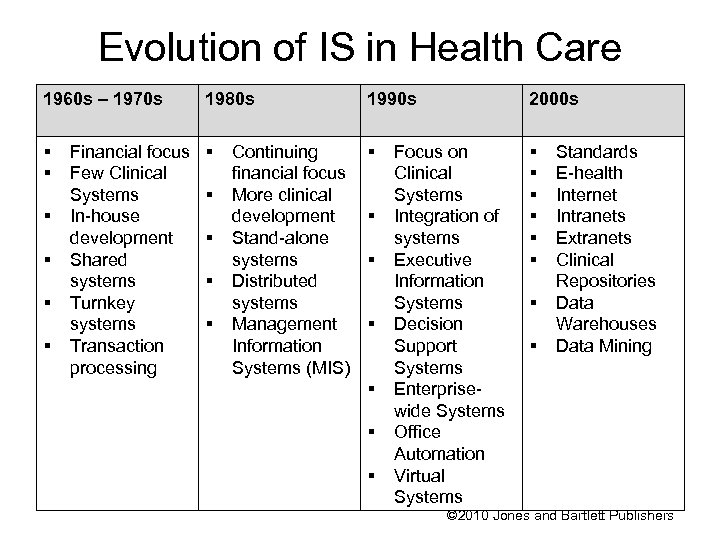 Evolution of IS in Health Care 1960 s – 1970 s 1980 s 1990 s 2000 s Financial focus Few Clinical Systems In-house development Shared systems Turnkey systems Transaction processing Continuing financial focus More clinical development Stand-alone systems Distributed systems Management Information Systems (MIS) Focus on Clinical Systems Integration of systems Executive Information Systems Decision Support Systems Enterprisewide Systems Office Automation Virtual Systems Standards E-health Internet Intranets Extranets Clinical Repositories Data Warehouses Data Mining © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Evolution of IS in Health Care 1960 s – 1970 s 1980 s 1990 s 2000 s Financial focus Few Clinical Systems In-house development Shared systems Turnkey systems Transaction processing Continuing financial focus More clinical development Stand-alone systems Distributed systems Management Information Systems (MIS) Focus on Clinical Systems Integration of systems Executive Information Systems Decision Support Systems Enterprisewide Systems Office Automation Virtual Systems Standards E-health Internet Intranets Extranets Clinical Repositories Data Warehouses Data Mining © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
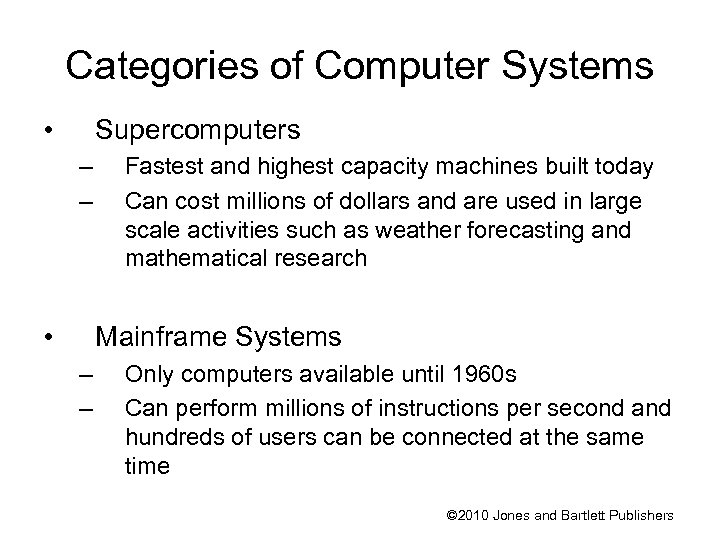 Categories of Computer Systems • Supercomputers – – • Fastest and highest capacity machines built today Can cost millions of dollars and are used in large scale activities such as weather forecasting and mathematical research Mainframe Systems – – Only computers available until 1960 s Can perform millions of instructions per second and hundreds of users can be connected at the same time © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Categories of Computer Systems • Supercomputers – – • Fastest and highest capacity machines built today Can cost millions of dollars and are used in large scale activities such as weather forecasting and mathematical research Mainframe Systems – – Only computers available until 1960 s Can perform millions of instructions per second and hundreds of users can be connected at the same time © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
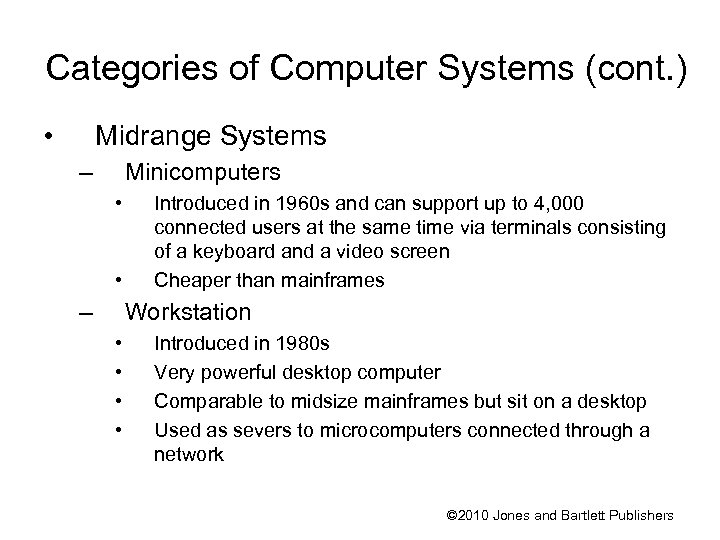 Categories of Computer Systems (cont. ) • Midrange Systems – Minicomputers • • – Introduced in 1960 s and can support up to 4, 000 connected users at the same time via terminals consisting of a keyboard and a video screen Cheaper than mainframes Workstation • • Introduced in 1980 s Very powerful desktop computer Comparable to midsize mainframes but sit on a desktop Used as severs to microcomputers connected through a network © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Categories of Computer Systems (cont. ) • Midrange Systems – Minicomputers • • – Introduced in 1960 s and can support up to 4, 000 connected users at the same time via terminals consisting of a keyboard and a video screen Cheaper than mainframes Workstation • • Introduced in 1980 s Very powerful desktop computer Comparable to midsize mainframes but sit on a desktop Used as severs to microcomputers connected through a network © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
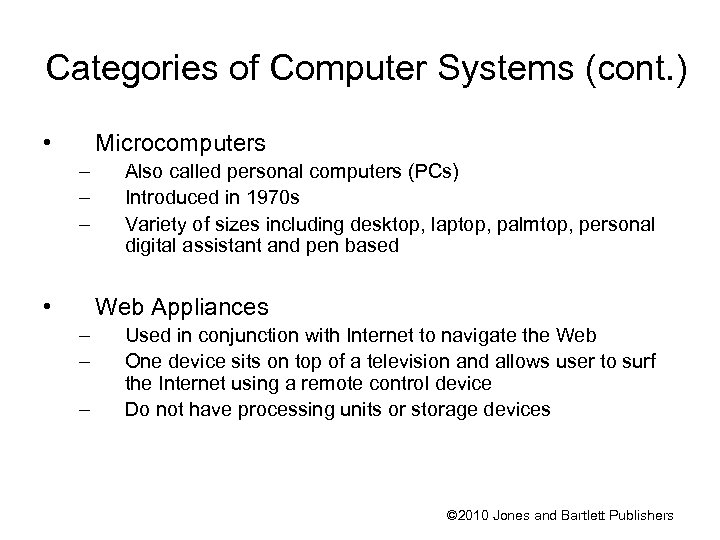 Categories of Computer Systems (cont. ) • Microcomputers – – – • Also called personal computers (PCs) Introduced in 1970 s Variety of sizes including desktop, laptop, palmtop, personal digital assistant and pen based Web Appliances – – – Used in conjunction with Internet to navigate the Web One device sits on top of a television and allows user to surf the Internet using a remote control device Do not have processing units or storage devices © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Categories of Computer Systems (cont. ) • Microcomputers – – – • Also called personal computers (PCs) Introduced in 1970 s Variety of sizes including desktop, laptop, palmtop, personal digital assistant and pen based Web Appliances – – – Used in conjunction with Internet to navigate the Web One device sits on top of a television and allows user to surf the Internet using a remote control device Do not have processing units or storage devices © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 5 Programming Languages • Machine language – • • – – – – Binary representation of 0, 1 Assembly language – High level languages Replaced 0, 1 • Very high level languages – • BASIC COBOL FORTRAN PASCAL MUMPS JAVA HTML XML Structured Query Language (SQL) Natural languages – Artificial Intelligence © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
5 Programming Languages • Machine language – • • – – – – Binary representation of 0, 1 Assembly language – High level languages Replaced 0, 1 • Very high level languages – • BASIC COBOL FORTRAN PASCAL MUMPS JAVA HTML XML Structured Query Language (SQL) Natural languages – Artificial Intelligence © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 System versus Application Software • System software – Set of instructions that direct actual computer operation functions – Acts as a conductor for all the hardware components and application software • • • Operation system Utility programs Language Translator • Application software – Set of instructions used to accomplish various types of business process • • Productivity Specialty software Education and Reference Entertainment © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
System versus Application Software • System software – Set of instructions that direct actual computer operation functions – Acts as a conductor for all the hardware components and application software • • • Operation system Utility programs Language Translator • Application software – Set of instructions used to accomplish various types of business process • • Productivity Specialty software Education and Reference Entertainment © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
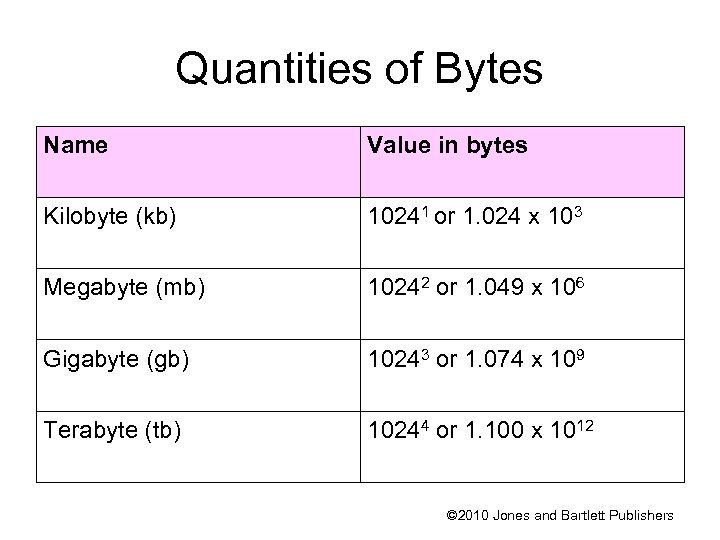 Quantities of Bytes Name Value in bytes Kilobyte (kb) 10241 or 1. 024 x 103 Megabyte (mb) 10242 or 1. 049 x 106 Gigabyte (gb) 10243 or 1. 074 x 109 Terabyte (tb) 10244 or 1. 100 x 1012 © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Quantities of Bytes Name Value in bytes Kilobyte (kb) 10241 or 1. 024 x 103 Megabyte (mb) 10242 or 1. 049 x 106 Gigabyte (gb) 10243 or 1. 074 x 109 Terabyte (tb) 10244 or 1. 100 x 1012 © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 5 Types of Information Systems • Transaction processing system (TPS) – – – Collects and stores data about transactions Manages the different kinds of transactions that occur in a healthcare facility Example: • • Patient Management information system (MIS) – – Supported by transaction processing systems Provides routine information to managers for decision making © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
5 Types of Information Systems • Transaction processing system (TPS) – – – Collects and stores data about transactions Manages the different kinds of transactions that occur in a healthcare facility Example: • • Patient Management information system (MIS) – – Supported by transaction processing systems Provides routine information to managers for decision making © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 5 Types of Information Systems (cont. ) • Executive information system (EIS) – – • Interactive system that allow top managers to answer “what if” queries and project trends Several databases are attached to type of system including external and internal operations and special management Expert system (ES) – – • Generates advice or suggest a decision A knowledge system built from a set of rules applied to specific problems Decision support system (DSS) – – An interactive system that helps managers solve problems and make decisions Example: • Clinical DSS that alerts physician when lab results are outside normal range © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
5 Types of Information Systems (cont. ) • Executive information system (EIS) – – • Interactive system that allow top managers to answer “what if” queries and project trends Several databases are attached to type of system including external and internal operations and special management Expert system (ES) – – • Generates advice or suggest a decision A knowledge system built from a set of rules applied to specific problems Decision support system (DSS) – – An interactive system that helps managers solve problems and make decisions Example: • Clinical DSS that alerts physician when lab results are outside normal range © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 6 Components of an HIS • Patient Scheduling, Admission, Discharge, Transfer system • Business and financial systems • Communication and networking applications • Departmental systems such as radiology and pharmacy • Documentation systems used to collect, store and retrieve patient data • Reminder and advice functions © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
6 Components of an HIS • Patient Scheduling, Admission, Discharge, Transfer system • Business and financial systems • Communication and networking applications • Departmental systems such as radiology and pharmacy • Documentation systems used to collect, store and retrieve patient data • Reminder and advice functions © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Strategic Information System Planning • • Process of identifying and assigning priorities to the various upgrades and changes that might be made in an organization’s information system Ensures all changes contribute to the achievement of the organization’s strategic goals and objectives • Establishes enterprise wide priorities for information systems • Serves as a guide to make decisions of resource allocations • Sets stage for system development life cycle • Lead by the Chief Information Officer © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Strategic Information System Planning • • Process of identifying and assigning priorities to the various upgrades and changes that might be made in an organization’s information system Ensures all changes contribute to the achievement of the organization’s strategic goals and objectives • Establishes enterprise wide priorities for information systems • Serves as a guide to make decisions of resource allocations • Sets stage for system development life cycle • Lead by the Chief Information Officer © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) • System analysis – Identify business issue or problem that needs to be solved – Feasibility of the system is assessed and the scope of project defined – Assess information needs of users and define the functional requirements of system – Provides a system that meets user and or department needs and that also supports the strategic objectives of the organization © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) • System analysis – Identify business issue or problem that needs to be solved – Feasibility of the system is assessed and the scope of project defined – Assess information needs of users and define the functional requirements of system – Provides a system that meets user and or department needs and that also supports the strategic objectives of the organization © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 SDLC (cont. ) • System design – – Specify details of new system (logical and physical design) Decide how system will be designed or selected Built in-house Turnkey © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
SDLC (cont. ) • System design – – Specify details of new system (logical and physical design) Decide how system will be designed or selected Built in-house Turnkey © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 SDLC (cont. ) • System Implementation – – – – • Select project manager Make system operational Test system Train users Prepare site Install hardware and software Manage organization change and system impact System evaluation – Evaluate system against pre-developed criteria © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
SDLC (cont. ) • System Implementation – – – – • Select project manager Make system operational Test system Train users Prepare site Install hardware and software Manage organization change and system impact System evaluation – Evaluate system against pre-developed criteria © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Nolan’s 6 Stage Theory • Initiation - initiates automation • Expansion - growth of automation • Control - manage information technology growth • Integration - integrates systems through policies and procedures • Data Administration - databases developed and information is critical • Maturity - growth of application is the focus on strategic importance of organization © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Nolan’s 6 Stage Theory • Initiation - initiates automation • Expansion - growth of automation • Control - manage information technology growth • Integration - integrates systems through policies and procedures • Data Administration - databases developed and information is critical • Maturity - growth of application is the focus on strategic importance of organization © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Classification of Information Systems Administrative • Admission, Discharge, Transfers (ADT) • Human Resources • Materials management • Facilities management Financial • Budgeting • Billing • Payments Clinical • CPR • Results Reporting • Patient care management • Order Entry • Point of care documentation • Nursing Services • Laboratory • Pharmacy • Clinical decision support • Research, QI, Peer Review Outpatient • Appointment Scheduling • • Patient billing Electronic insurance payment Automatic payment posting Patient collection and mail-merge Medical record data capture and retrieval Prescription writing Report generation Research, QI, Peer Review Research • • Data mart Data mining © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Classification of Information Systems Administrative • Admission, Discharge, Transfers (ADT) • Human Resources • Materials management • Facilities management Financial • Budgeting • Billing • Payments Clinical • CPR • Results Reporting • Patient care management • Order Entry • Point of care documentation • Nursing Services • Laboratory • Pharmacy • Clinical decision support • Research, QI, Peer Review Outpatient • Appointment Scheduling • • Patient billing Electronic insurance payment Automatic payment posting Patient collection and mail-merge Medical record data capture and retrieval Prescription writing Report generation Research, QI, Peer Review Research • • Data mart Data mining © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 5 Major Database Models • Relational – Data stored in predefined tables that contain rows and columns similar to a spreadsheet • Hierarchical – Supports treelike structure that consist of parent (root) and child segments; many-tomay relationships difficult to represent – Each parent has a child or more; each child has only one parent – User queries database; search seeks answer from parent to child • Network – Similar to hierarchical except that a child can have more than one parent – Parent referred to as owner; child as member – Supports many-to-many relationship • Object-oriented – Stores objects of data – Can model relational data or data types such as graphics, movies and audio • Object-relational – Combines best of relational and object-oriented – Uses both traditional data types (currency, integers and strings) and advanced data types (graphics, movies and audio) © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
5 Major Database Models • Relational – Data stored in predefined tables that contain rows and columns similar to a spreadsheet • Hierarchical – Supports treelike structure that consist of parent (root) and child segments; many-tomay relationships difficult to represent – Each parent has a child or more; each child has only one parent – User queries database; search seeks answer from parent to child • Network – Similar to hierarchical except that a child can have more than one parent – Parent referred to as owner; child as member – Supports many-to-many relationship • Object-oriented – Stores objects of data – Can model relational data or data types such as graphics, movies and audio • Object-relational – Combines best of relational and object-oriented – Uses both traditional data types (currency, integers and strings) and advanced data types (graphics, movies and audio) © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Data Warehouses • Provide organizations the ability to access data from multiple databases and to combine the results into a single question and reporting interface • Integrate organization wide data into a single repository from which managers can pose ad hoc queries, run reports and perform a variety of analyses • Sets up large stores of data for strategic decision support analysis • Analytical databases designed to support strategic and tactical decision making • Selected data are extracted from multiple sources in the organization’s information system • • Subject oriented, integrated, time variant and nonvolatile collection of data in support of management’s decision making process Organization uses historical data and integrate them with a variety of analytical techniques to help solve problems • In order for the value of the data warehouse to be realized, techniques such as data mining must be applied © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Data Warehouses • Provide organizations the ability to access data from multiple databases and to combine the results into a single question and reporting interface • Integrate organization wide data into a single repository from which managers can pose ad hoc queries, run reports and perform a variety of analyses • Sets up large stores of data for strategic decision support analysis • Analytical databases designed to support strategic and tactical decision making • Selected data are extracted from multiple sources in the organization’s information system • • Subject oriented, integrated, time variant and nonvolatile collection of data in support of management’s decision making process Organization uses historical data and integrate them with a variety of analytical techniques to help solve problems • In order for the value of the data warehouse to be realized, techniques such as data mining must be applied © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Data Marts • Subset of a data warehouse that supports the requirements of a particular department or business function • Focuses on the data needs for a specific department or business function as opposed to warehouse that stores data for the entire organization • Tailored to meet needs of department • Amount of historical data and level or granularity (detail) can be specific to needs of department © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Data Marts • Subset of a data warehouse that supports the requirements of a particular department or business function • Focuses on the data needs for a specific department or business function as opposed to warehouse that stores data for the entire organization • Tailored to meet needs of department • Amount of historical data and level or granularity (detail) can be specific to needs of department © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Data Mining • Encourages a broad view of all data for a set of patients to explore relationships among the data that might not be readily apparent during the initial hypothesis • The extraction of data from large databases to uncover previously unknown information to help managers make decisions • Helps to uncover previously unknown and hidden information trends • Identifies patterns and relationships among variables that were previously unrecognized using predictive modeling, database segmentation, link analysis and deviation detection • In order to perform data mining, a data warehouse is needed © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Data Mining • Encourages a broad view of all data for a set of patients to explore relationships among the data that might not be readily apparent during the initial hypothesis • The extraction of data from large databases to uncover previously unknown information to help managers make decisions • Helps to uncover previously unknown and hidden information trends • Identifies patterns and relationships among variables that were previously unrecognized using predictive modeling, database segmentation, link analysis and deviation detection • In order to perform data mining, a data warehouse is needed © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 HIM Security and Protection • Employ a security program • Employees should only have access to information on a need to know basis • Equipment and information should be secure from threats and unauthorized access • Hardware should be secured from extreme temperatures, power outages, and other environmental threats and installed according to manufacturer instructions • Software system should be in place for SDLC © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
HIM Security and Protection • Employ a security program • Employees should only have access to information on a need to know basis • Equipment and information should be secure from threats and unauthorized access • Hardware should be secured from extreme temperatures, power outages, and other environmental threats and installed according to manufacturer instructions • Software system should be in place for SDLC © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 HIM Security and Protection (cont. ) • Access to specific applications should be limited • System should automatically log all transactions through audit trails • Firewalls system to prevent access to a private network from the outside or limit access to the outside from within • Encrypt data • Ensure Internet security • Authenticate communication (aging passwords) © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
HIM Security and Protection (cont. ) • Access to specific applications should be limited • System should automatically log all transactions through audit trails • Firewalls system to prevent access to a private network from the outside or limit access to the outside from within • Encrypt data • Ensure Internet security • Authenticate communication (aging passwords) © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Intranets versus Extranets • Intranet – – – Special form of a LAN Networking capability within one organization that uses Internet technologies, software which uses HTML and web browser software to accomplish computer communications within the organization Servers are located inside a firewall or security barrier and can be accessible only to authenticated users on a specific network • Extranets – Similar to intranet – Provides network connectivity between suppliers to allow direct connection to each other’s network © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Intranets versus Extranets • Intranet – – – Special form of a LAN Networking capability within one organization that uses Internet technologies, software which uses HTML and web browser software to accomplish computer communications within the organization Servers are located inside a firewall or security barrier and can be accessible only to authenticated users on a specific network • Extranets – Similar to intranet – Provides network connectivity between suppliers to allow direct connection to each other’s network © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Internet Network Protocols • Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol – Web servers that support an SSL session have an address that begins with “https” instead of “http” • IP (internet protocol) Telephony – Allows real time calls to be initiated through the Internet instead of public telephone system © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Internet Network Protocols • Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol – Web servers that support an SSL session have an address that begins with “https” instead of “http” • IP (internet protocol) Telephony – Allows real time calls to be initiated through the Internet instead of public telephone system © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Electronic Health Record (EHR) • Any information relating to the past, present or future physical, mental health or condition of an individual. Resides in electronic systems used to capture, transmit, receive, store, retrieve, link and manipulate multimedia data for the primary purpose of providing health care and health related services • Form of computer based health record in which information is stored by whole files instead of by an individual data elements © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Electronic Health Record (EHR) • Any information relating to the past, present or future physical, mental health or condition of an individual. Resides in electronic systems used to capture, transmit, receive, store, retrieve, link and manipulate multimedia data for the primary purpose of providing health care and health related services • Form of computer based health record in which information is stored by whole files instead of by an individual data elements © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Capabilities of EHR • Positively impact workflow operations • Improve administrative process • Include uniform core data elements and standardized coding • Use common data dictionary • Perform searches • 24 hour access with rapid retrieval • Links to other information systems • Real time alerts and possible remedies © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Capabilities of EHR • Positively impact workflow operations • Improve administrative process • Include uniform core data elements and standardized coding • Use common data dictionary • Perform searches • 24 hour access with rapid retrieval • Links to other information systems • Real time alerts and possible remedies © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Role of HIM Professional • Information broker – Intermediary between a client and an information product or group of services • Advocate for effective system development or selection by assuming prominent role in the system development life cycle • Custodian of patient health information regardless of media on which it is maintained © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Role of HIM Professional • Information broker – Intermediary between a client and an information product or group of services • Advocate for effective system development or selection by assuming prominent role in the system development life cycle • Custodian of patient health information regardless of media on which it is maintained © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Role of HIM Professional (cont. ) • Establish policies, procedures, systems and safeguards to ensure patient health information is documented, maintained and disclosed in accordance with all health information laws, regulations and standards • Ensure the functionality of Electronic Health Record systems with respect to the practice of Health Information Management and its support of other business functions of the organization • Information retrieval, analysis and policy development © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Role of HIM Professional (cont. ) • Establish policies, procedures, systems and safeguards to ensure patient health information is documented, maintained and disclosed in accordance with all health information laws, regulations and standards • Ensure the functionality of Electronic Health Record systems with respect to the practice of Health Information Management and its support of other business functions of the organization • Information retrieval, analysis and policy development © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Role of HIM Professional (cont. ) • Under the information engineering domain – Strategic planning • – Data modeling • – Analyzing the processes of an organization usually on a departmental basis Data administration • – Development of a detailed logical database design Process modeling • – Identification of goals and the critical success factors of the enterprise Administrative rather than technical functions associated with data and database management Interface design • • Content or layout of screens and reports May use CASE tools such as screen painters, report generators or prototyping software © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Role of HIM Professional (cont. ) • Under the information engineering domain – Strategic planning • – Data modeling • – Analyzing the processes of an organization usually on a departmental basis Data administration • – Development of a detailed logical database design Process modeling • – Identification of goals and the critical success factors of the enterprise Administrative rather than technical functions associated with data and database management Interface design • • Content or layout of screens and reports May use CASE tools such as screen painters, report generators or prototyping software © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 Chief Information Officer (CIO) • Senior level executive manager of IRM • Responsibilities – – – Lead strategic information system planning process Help leadership team use information systems in support of strategic planning and management Oversee the organizations Information Resources Management (IRM) functions © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
Chief Information Officer (CIO) • Senior level executive manager of IRM • Responsibilities – – – Lead strategic information system planning process Help leadership team use information systems in support of strategic planning and management Oversee the organizations Information Resources Management (IRM) functions © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 E-commerce • Allows consumers to learn • Provides – Physician referral services about medicines they are – Listing of health care taking, buy medicines, learn classes and seminars about diseases, disease – Information on clinical trials prevention and other – Uses Internet to create activities • The marketing, buying, selling and support of products and services over the Internet, intranets, and extranets • Involves electronic data interchange (EDI) and electronic funds transfer (EFT) payment systems bulletin boards, electronic surveys, newsletters, and email information on diagnoses and treatment of diseases – External links to federal agencies and other organizations that provide health care – Builds strategic alliance with customers, suppliers, consultants and competitors © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
E-commerce • Allows consumers to learn • Provides – Physician referral services about medicines they are – Listing of health care taking, buy medicines, learn classes and seminars about diseases, disease – Information on clinical trials prevention and other – Uses Internet to create activities • The marketing, buying, selling and support of products and services over the Internet, intranets, and extranets • Involves electronic data interchange (EDI) and electronic funds transfer (EFT) payment systems bulletin boards, electronic surveys, newsletters, and email information on diagnoses and treatment of diseases – External links to federal agencies and other organizations that provide health care – Builds strategic alliance with customers, suppliers, consultants and competitors © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
 E-Health • Companies provide a range of services – – – Storing personal health data Reference information on a variety of health issues Manage health care superstores © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers
E-Health • Companies provide a range of services – – – Storing personal health data Reference information on a variety of health issues Manage health care superstores © 2010 Jones and Bartlett Publishers


