d809ffc5f68c993945a82fefa96dfcdd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 108
 Information Technology A. Graham Peace
Information Technology A. Graham Peace
 Purpose n n n n What is the role of IT/MIS in the organization? What do IT people really do? How does technology work? What is e. Business? How is it changing business? How does it impact you? What should we be doing?
Purpose n n n n What is the role of IT/MIS in the organization? What do IT people really do? How does technology work? What is e. Business? How is it changing business? How does it impact you? What should we be doing?
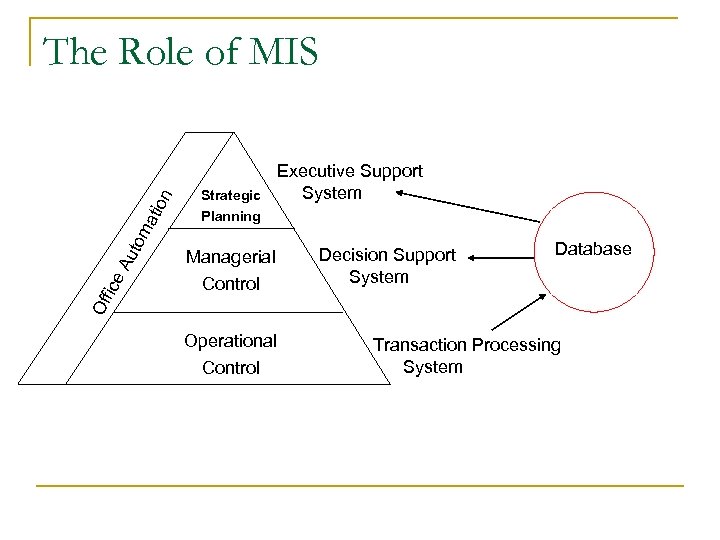 Strategic Executive Support System Planning Managerial Control Decision Support System Database Of fice Au tom ati on The Role of MIS Operational Control Transaction Processing System
Strategic Executive Support System Planning Managerial Control Decision Support System Database Of fice Au tom ati on The Role of MIS Operational Control Transaction Processing System
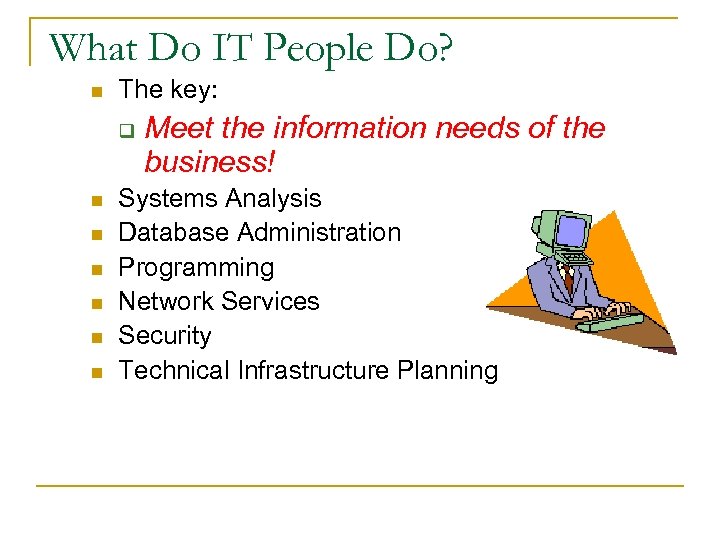 What Do IT People Do? n The key: q n n n Meet the information needs of the business! Systems Analysis Database Administration Programming Network Services Security Technical Infrastructure Planning
What Do IT People Do? n The key: q n n n Meet the information needs of the business! Systems Analysis Database Administration Programming Network Services Security Technical Infrastructure Planning
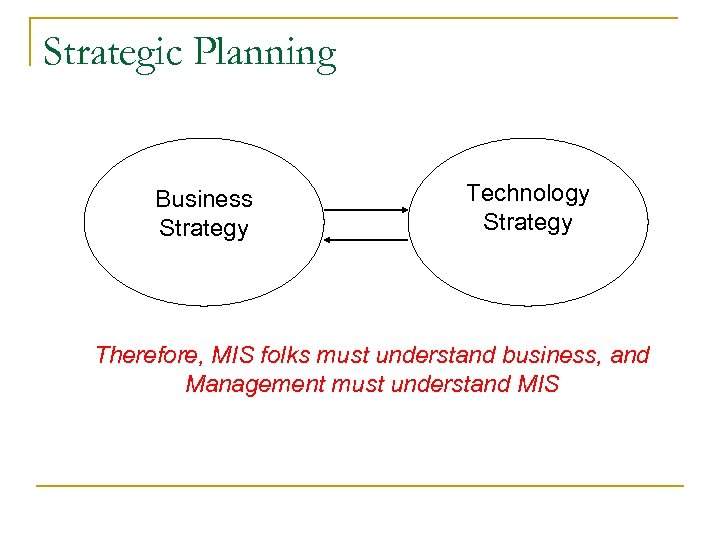 Strategic Planning Business Strategy Technology Strategy Therefore, MIS folks must understand business, and Management must understand MIS
Strategic Planning Business Strategy Technology Strategy Therefore, MIS folks must understand business, and Management must understand MIS
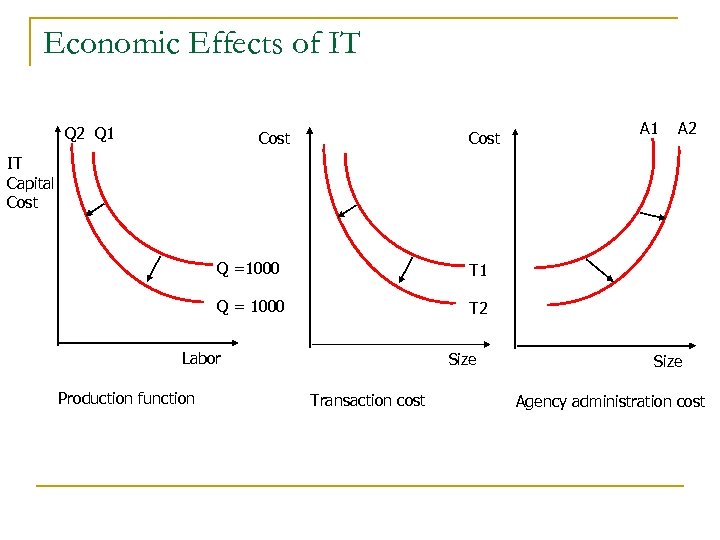 Economic Effects of IT Q 2 Q 1 Cost A 1 A 2 IT Capital Cost Q =1000 T 1 Q = 1000 T 2 Labor Production function Size Transaction cost Size Agency administration cost
Economic Effects of IT Q 2 Q 1 Cost A 1 A 2 IT Capital Cost Q =1000 T 1 Q = 1000 T 2 Labor Production function Size Transaction cost Size Agency administration cost
 e. Business: Trends and Definitions “In the short run, all change is overestimated, but in the long run, the effects of change are always underestimated. ” (Arthur C. Clarke)
e. Business: Trends and Definitions “In the short run, all change is overestimated, but in the long run, the effects of change are always underestimated. ” (Arthur C. Clarke)
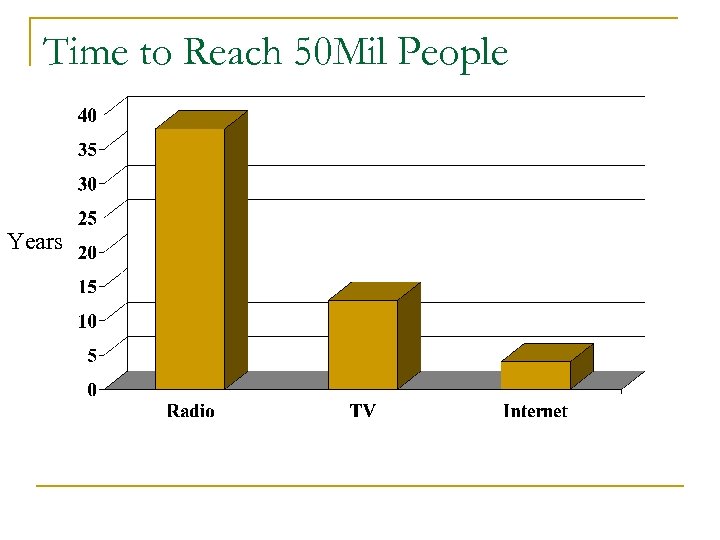 Time to Reach 50 Mil People Years
Time to Reach 50 Mil People Years
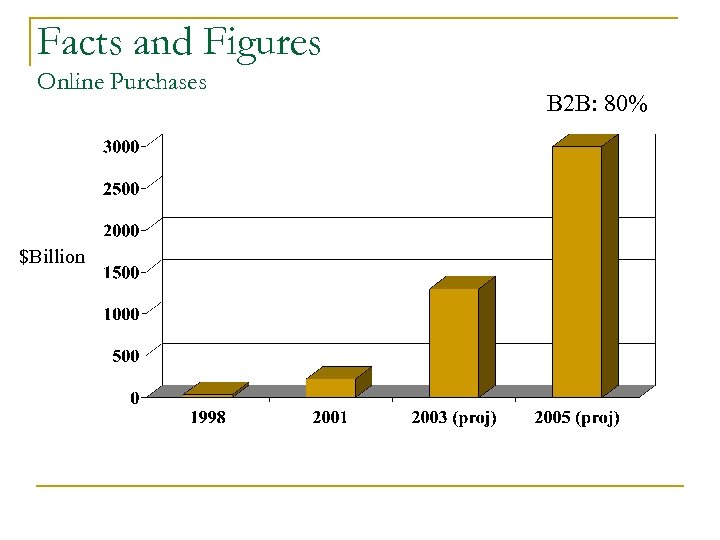 Facts and Figures Online Purchases $Billion B 2 B: 80%
Facts and Figures Online Purchases $Billion B 2 B: 80%
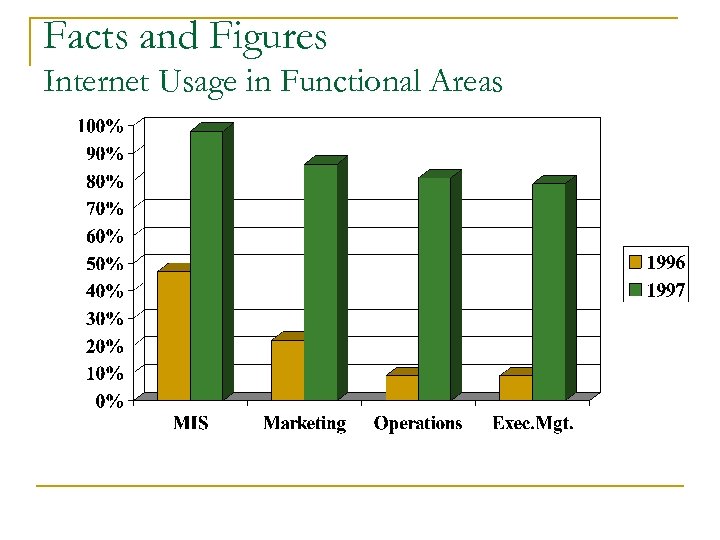 Facts and Figures Internet Usage in Functional Areas
Facts and Figures Internet Usage in Functional Areas
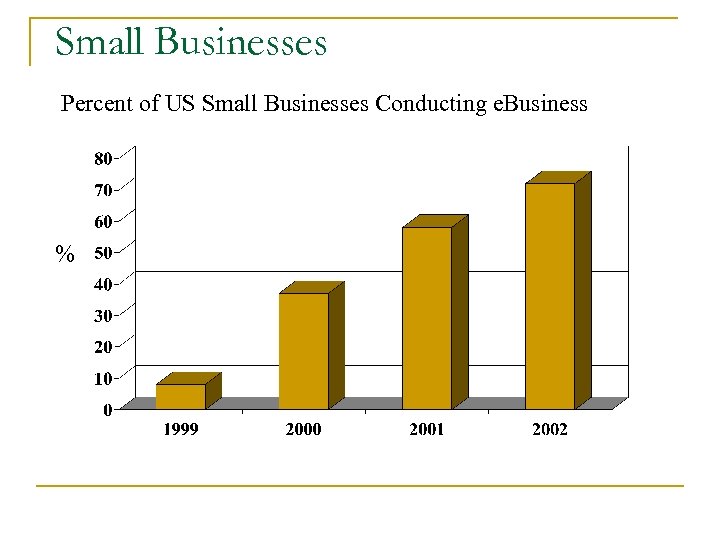 Small Businesses Percent of US Small Businesses Conducting e. Business %
Small Businesses Percent of US Small Businesses Conducting e. Business %
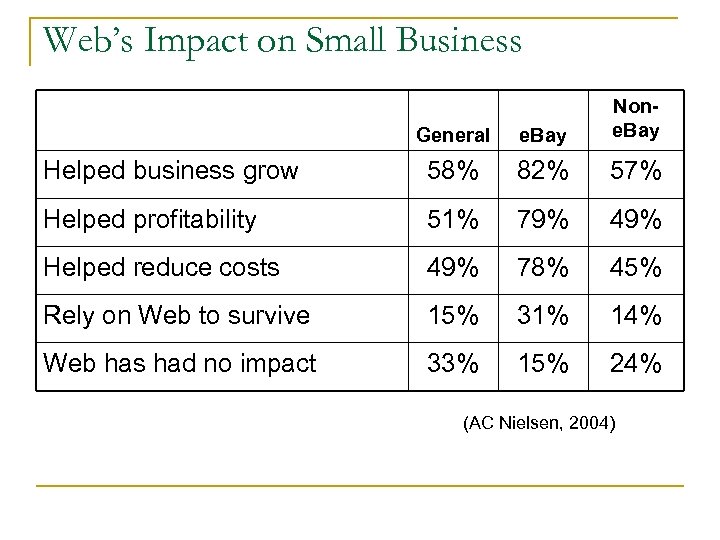 Web’s Impact on Small Business General e. Bay None. Bay Helped business grow 58% 82% 57% Helped profitability 51% 79% 49% Helped reduce costs 49% 78% 45% Rely on Web to survive 15% 31% 14% Web has had no impact 33% 15% 24% (AC Nielsen, 2004)
Web’s Impact on Small Business General e. Bay None. Bay Helped business grow 58% 82% 57% Helped profitability 51% 79% 49% Helped reduce costs 49% 78% 45% Rely on Web to survive 15% 31% 14% Web has had no impact 33% 15% 24% (AC Nielsen, 2004)
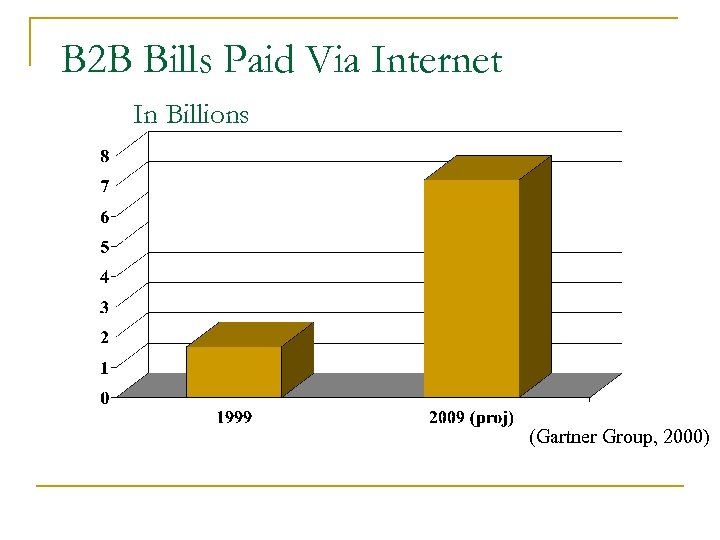 B 2 B Bills Paid Via Internet In Billions (Gartner Group, 2000)
B 2 B Bills Paid Via Internet In Billions (Gartner Group, 2000)
 Facts and Figures n n n Global online population: 800 M Web pages in existence: 9 Billion European net access by 12/2004: 250 M European’s Banking By Net: 50 M US Consumer Spending on Online Content in 2002: $1. 3 Billion
Facts and Figures n n n Global online population: 800 M Web pages in existence: 9 Billion European net access by 12/2004: 250 M European’s Banking By Net: 50 M US Consumer Spending on Online Content in 2002: $1. 3 Billion
 (Global Reach, 2004)
(Global Reach, 2004)
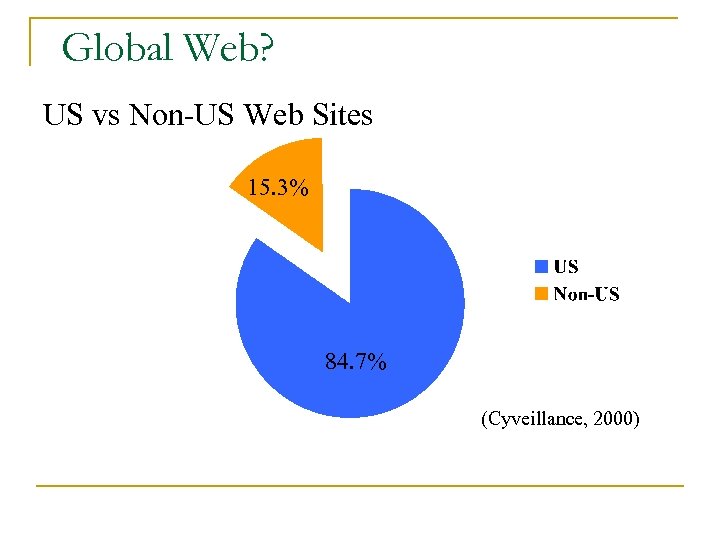 Global Web? US vs Non-US Web Sites 15. 3% 84. 7% (Cyveillance, 2000)
Global Web? US vs Non-US Web Sites 15. 3% 84. 7% (Cyveillance, 2000)
 (An Atlas of Cyberspace, 2004)
(An Atlas of Cyberspace, 2004)
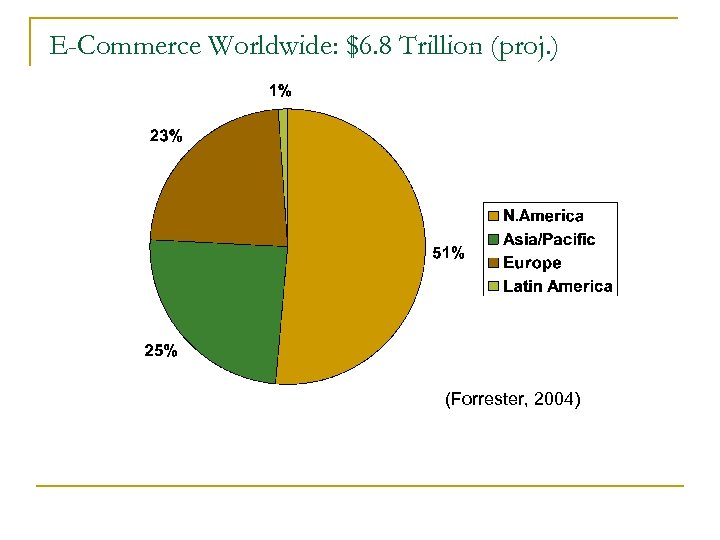 E-Commerce Worldwide: $6. 8 Trillion (proj. ) (Forrester, 2004)
E-Commerce Worldwide: $6. 8 Trillion (proj. ) (Forrester, 2004)
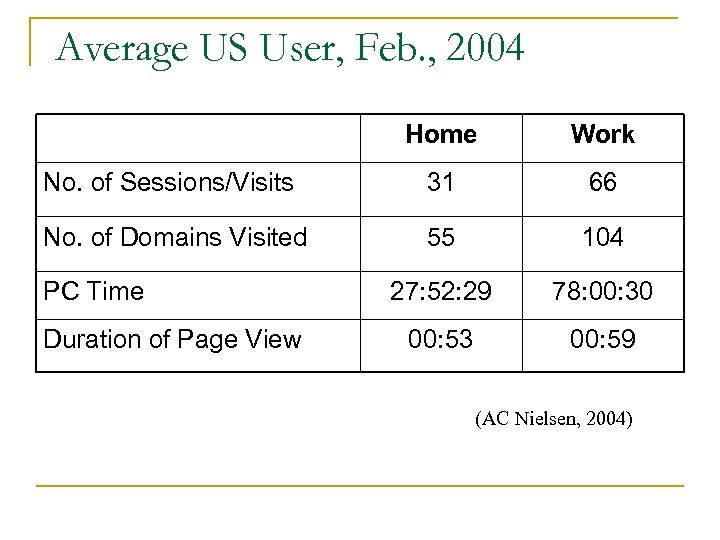 Average US User, Feb. , 2004 Home Work No. of Sessions/Visits 31 66 No. of Domains Visited 55 104 27: 52: 29 78: 00: 30 00: 53 00: 59 PC Time Duration of Page View (AC Nielsen, 2004)
Average US User, Feb. , 2004 Home Work No. of Sessions/Visits 31 66 No. of Domains Visited 55 104 27: 52: 29 78: 00: 30 00: 53 00: 59 PC Time Duration of Page View (AC Nielsen, 2004)
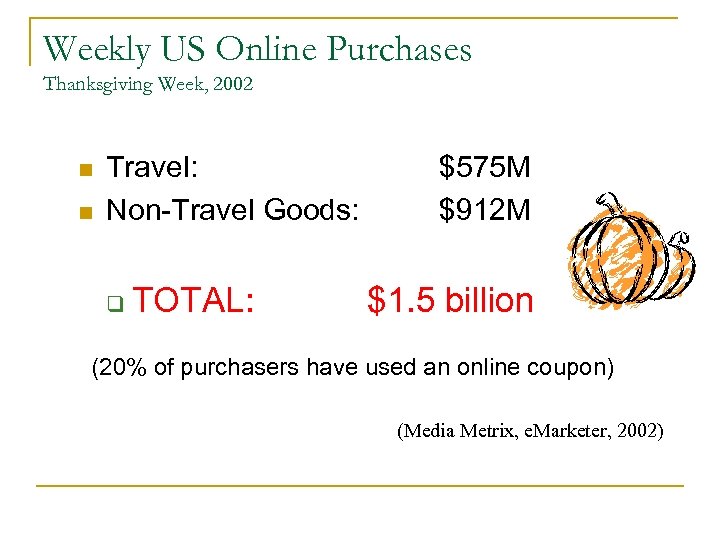 Weekly US Online Purchases Thanksgiving Week, 2002 n n Travel: Non-Travel Goods: q TOTAL: $575 M $912 M $1. 5 billion (20% of purchasers have used an online coupon) (Media Metrix, e. Marketer, 2002)
Weekly US Online Purchases Thanksgiving Week, 2002 n n Travel: Non-Travel Goods: q TOTAL: $575 M $912 M $1. 5 billion (20% of purchasers have used an online coupon) (Media Metrix, e. Marketer, 2002)
 History: Old vs New n Pet Supplies: q Old: Petsmart up 152% q New: Pets. com liquidated n Software: q Old: E. Boutique up 100% q New: Egghead. com Chapter 11 n Food: q Old: Albertson’s up 31% q New: Webvan Chapter 11
History: Old vs New n Pet Supplies: q Old: Petsmart up 152% q New: Pets. com liquidated n Software: q Old: E. Boutique up 100% q New: Egghead. com Chapter 11 n Food: q Old: Albertson’s up 31% q New: Webvan Chapter 11
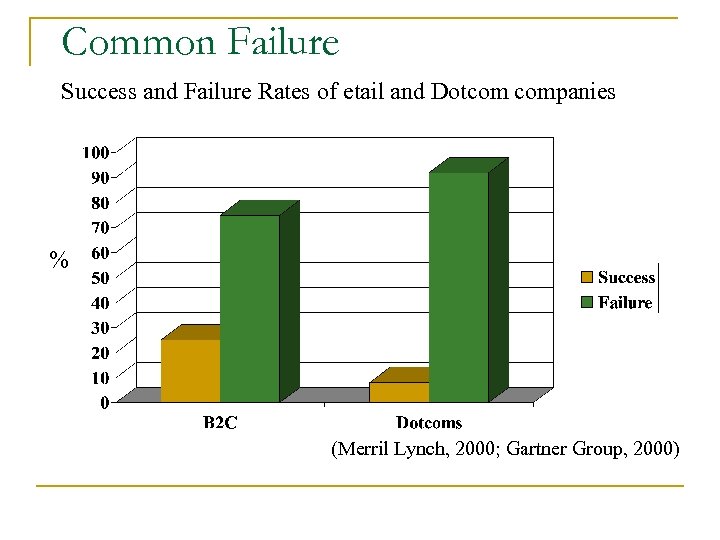 Common Failure Success and Failure Rates of etail and Dotcom companies % (Merril Lynch, 2000; Gartner Group, 2000)
Common Failure Success and Failure Rates of etail and Dotcom companies % (Merril Lynch, 2000; Gartner Group, 2000)
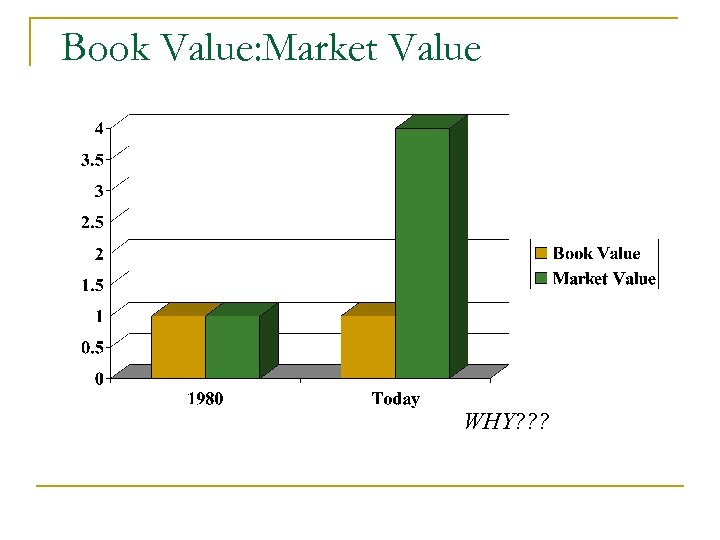 Book Value: Market Value WHY? ? ?
Book Value: Market Value WHY? ? ?
 "Within five years time, all companies will be Internet companies, or they won't be companies at all. ” (Grove, 1999)
"Within five years time, all companies will be Internet companies, or they won't be companies at all. ” (Grove, 1999)
 Definitions Internet n Intranet n Extranet n World Wide Web n Packet-Switching n
Definitions Internet n Intranet n Extranet n World Wide Web n Packet-Switching n
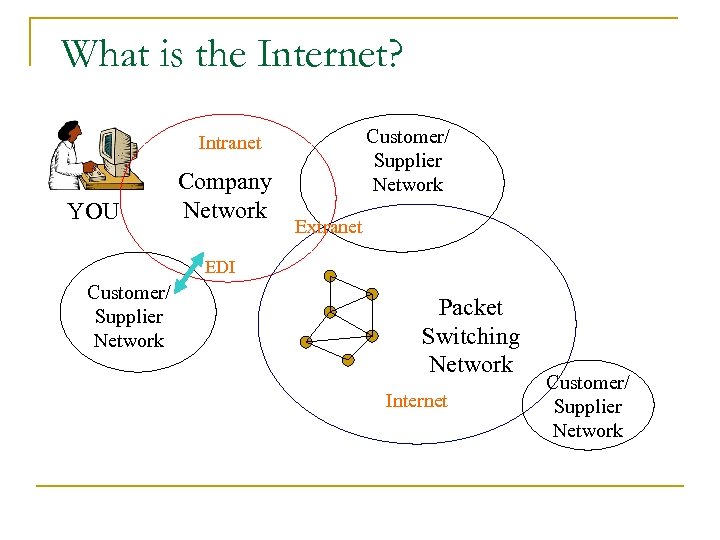 What is the Internet? Customer/ Supplier Network Intranet YOU Company Network Extranet EDI Customer/ Supplier Network Packet Switching Network Internet Customer/ Supplier Network
What is the Internet? Customer/ Supplier Network Intranet YOU Company Network Extranet EDI Customer/ Supplier Network Packet Switching Network Internet Customer/ Supplier Network
 e. Business Myths n n n Everyone is Doing It! It’s Easy! It’s Cheap! It’s Lucrative! The Internet Levels the Playing Field Intermediaries Go Away
e. Business Myths n n n Everyone is Doing It! It’s Easy! It’s Cheap! It’s Lucrative! The Internet Levels the Playing Field Intermediaries Go Away
 e. Business Myths n n n Mass Marketing is Over It’s the Domain of Computers Product Commoditization is Key It’s a Fad (the NASDAQ collapse proves it!) It’s ordering on the Web (B 2 C) One World, One Web
e. Business Myths n n n Mass Marketing is Over It’s the Domain of Computers Product Commoditization is Key It’s a Fad (the NASDAQ collapse proves it!) It’s ordering on the Web (B 2 C) One World, One Web
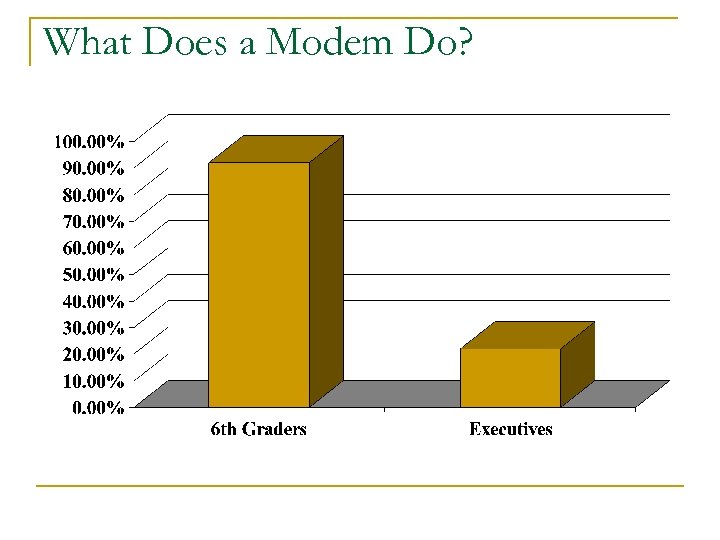 What Does a Modem Do?
What Does a Modem Do?
 Nine e. Business Rules 1. 2. 3. Technology is now a driver of business strategy Controlling information flows is more powerful than controlling product flows Inability to overthrow outdated business designs leads to failure
Nine e. Business Rules 1. 2. 3. Technology is now a driver of business strategy Controlling information flows is more powerful than controlling product flows Inability to overthrow outdated business designs leads to failure
 Nine e. Business Rules 4. 5. 6. New business designs must create flexibility e. Business enables organizations to listen to customers Use technology to innovate and enhance the product experience
Nine e. Business Rules 4. 5. 6. New business designs must create flexibility e. Business enables organizations to listen to customers Use technology to innovate and enhance the product experience
 Nine e. Business Rules 7. 8. 9. Reconfigurable ebusiness communities will be used to meet customer needs Strong leadership is imperative! Long-Term Success is a thing of the past (adapted from Kalakota and Robinson, 1999)
Nine e. Business Rules 7. 8. 9. Reconfigurable ebusiness communities will be used to meet customer needs Strong leadership is imperative! Long-Term Success is a thing of the past (adapted from Kalakota and Robinson, 1999)
 e. Business Trends Increased Speed of Service n Self-Service n Integrated Solutions n Sales and Service Convergence n Ease of Use n
e. Business Trends Increased Speed of Service n Self-Service n Integrated Solutions n Sales and Service Convergence n Ease of Use n
 e. Business Trends n Flexible Fulfillment n Effective Outsourcing n Process Visibility
e. Business Trends n Flexible Fulfillment n Effective Outsourcing n Process Visibility
 e. Business Trends n Integration, Integration!
e. Business Trends n Integration, Integration!
 Trend Commonalities Efficiency n Effectiveness n Relationship Management n Integration n Opportunities for Creativity! n
Trend Commonalities Efficiency n Effectiveness n Relationship Management n Integration n Opportunities for Creativity! n
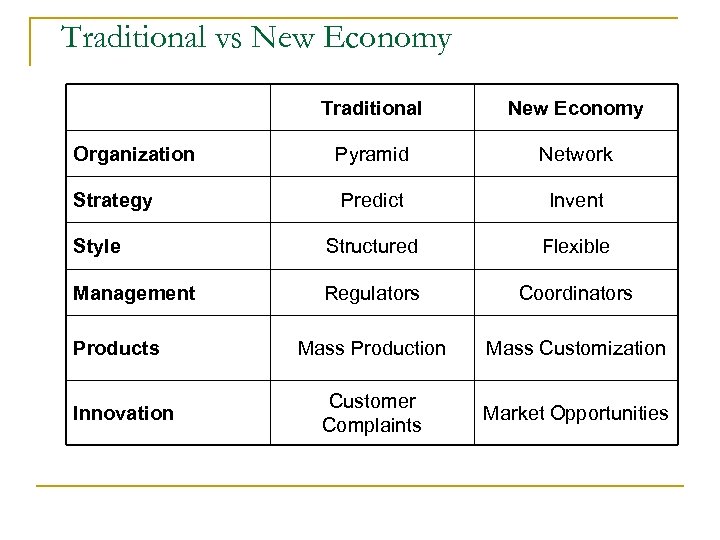 Traditional vs New Economy Traditional New Economy Organization Pyramid Network Strategy Predict Invent Style Structured Flexible Management Regulators Coordinators Mass Production Mass Customization Customer Complaints Market Opportunities Products Innovation
Traditional vs New Economy Traditional New Economy Organization Pyramid Network Strategy Predict Invent Style Structured Flexible Management Regulators Coordinators Mass Production Mass Customization Customer Complaints Market Opportunities Products Innovation
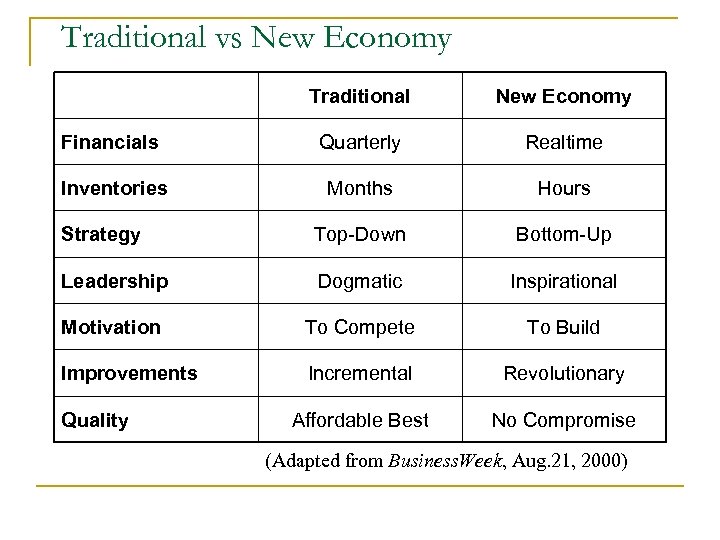 Traditional vs New Economy Traditional New Economy Financials Quarterly Realtime Inventories Months Hours Strategy Top-Down Bottom-Up Leadership Dogmatic Inspirational Motivation To Compete To Build Improvements Incremental Revolutionary Affordable Best No Compromise Quality (Adapted from Business. Week, Aug. 21, 2000)
Traditional vs New Economy Traditional New Economy Financials Quarterly Realtime Inventories Months Hours Strategy Top-Down Bottom-Up Leadership Dogmatic Inspirational Motivation To Compete To Build Improvements Incremental Revolutionary Affordable Best No Compromise Quality (Adapted from Business. Week, Aug. 21, 2000)
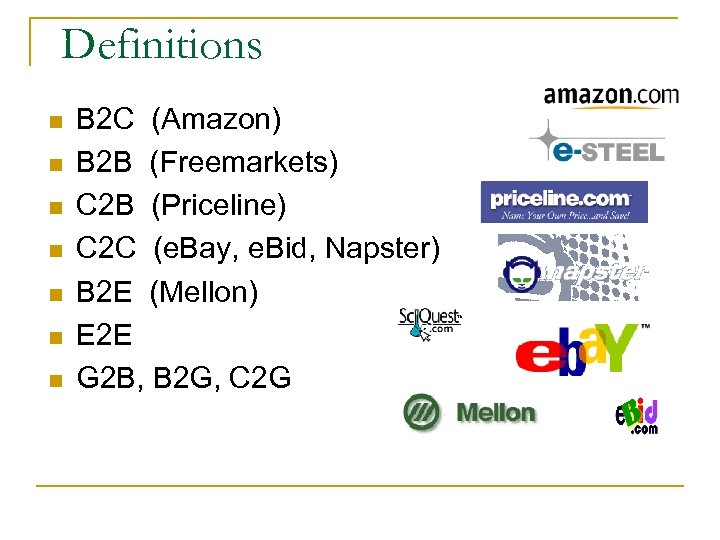 Definitions n n n n B 2 C (Amazon) B 2 B (Freemarkets) C 2 B (Priceline) C 2 C (e. Bay, e. Bid, Napster) B 2 E (Mellon) E 2 E G 2 B, B 2 G, C 2 G
Definitions n n n n B 2 C (Amazon) B 2 B (Freemarkets) C 2 B (Priceline) C 2 C (e. Bay, e. Bid, Napster) B 2 E (Mellon) E 2 E G 2 B, B 2 G, C 2 G
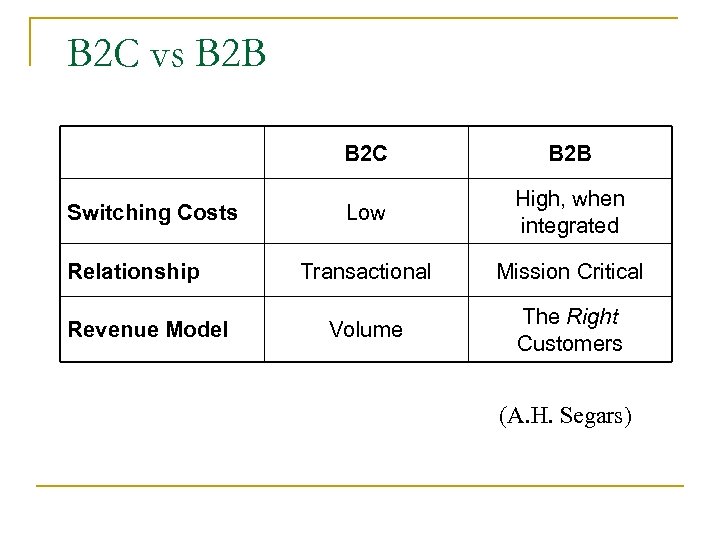 B 2 C vs B 2 B B 2 C Switching Costs Relationship Revenue Model B 2 B Low High, when integrated Transactional Mission Critical Volume The Right Customers (A. H. Segars)
B 2 C vs B 2 B B 2 C Switching Costs Relationship Revenue Model B 2 B Low High, when integrated Transactional Mission Critical Volume The Right Customers (A. H. Segars)
 Agility & Flexibility n Flexibility q n Planned responsiveness to anticipated contingencies Agility q The ability to change maneuver states, the time dependence of maneuverability
Agility & Flexibility n Flexibility q n Planned responsiveness to anticipated contingencies Agility q The ability to change maneuver states, the time dependence of maneuverability
 See a penny……
See a penny……
 OODA Observe n Orient n Decide n Act n
OODA Observe n Orient n Decide n Act n
 What Really Is e. Business? ?
What Really Is e. Business? ?
 e. Business vs e. Commerce n e. Commerce: "Buying and selling over digital media“ n e. Business: "e-Business is the complex fusion of business processes, enterprise applications, and organizational structure necessary to create a high-performance business model. " (Kalakota and Robinson, 1999)
e. Business vs e. Commerce n e. Commerce: "Buying and selling over digital media“ n e. Business: "e-Business is the complex fusion of business processes, enterprise applications, and organizational structure necessary to create a high-performance business model. " (Kalakota and Robinson, 1999)
 The Dimensions of E-Commerce Source: Choi et al. (1997), p. 18.
The Dimensions of E-Commerce Source: Choi et al. (1997), p. 18.
 e. Business Opportunities n Supply Chain Efficiency q q q Decreased Overhead Reduced Transaction Costs Market Efficiencies Increased Inventory Turns New Markets Increased Revenues
e. Business Opportunities n Supply Chain Efficiency q q q Decreased Overhead Reduced Transaction Costs Market Efficiencies Increased Inventory Turns New Markets Increased Revenues
 e. Business Opportunities n Better Customer Experiences q q q Community Customization Personalization Entertainment Access
e. Business Opportunities n Better Customer Experiences q q q Community Customization Personalization Entertainment Access
 e. Business Opportunities n Efficient Markets q q Perfect Information Economic Efficiency Elimination of Boundaries Reduced Transaction Costs
e. Business Opportunities n Efficient Markets q q Perfect Information Economic Efficiency Elimination of Boundaries Reduced Transaction Costs
 e. Business Is: n Supply Chain Integration ERP Suppliers Extranet Internet EDI The Organization Customers
e. Business Is: n Supply Chain Integration ERP Suppliers Extranet Internet EDI The Organization Customers
 Model of Internet Consumer Satisfaction Third Party Seal of Approval Vendor Reputation Legal Support Trust in Web Shopping Customer Service Pricing Attractiveness Web Site Store Front Security Privacy Transaction Safety Authentication Integrity System Reliability Customer Satisfaction Speed of Operation Repeat Web Purchase (Brand Loyalty) Ease of Use Content, Quality Format Reliability Non-repudiation Timeliness Completeness
Model of Internet Consumer Satisfaction Third Party Seal of Approval Vendor Reputation Legal Support Trust in Web Shopping Customer Service Pricing Attractiveness Web Site Store Front Security Privacy Transaction Safety Authentication Integrity System Reliability Customer Satisfaction Speed of Operation Repeat Web Purchase (Brand Loyalty) Ease of Use Content, Quality Format Reliability Non-repudiation Timeliness Completeness
 CRM Integrated Sales, Marketing and Service n Consistent, Dependable and Convenient Interactions n 360 Degree Customer View n
CRM Integrated Sales, Marketing and Service n Consistent, Dependable and Convenient Interactions n 360 Degree Customer View n
 CRM Integration Customer Content n Customer Contact Info n End-To-End Business Processes n Interenterprise Customer Care n Systems n
CRM Integration Customer Content n Customer Contact Info n End-To-End Business Processes n Interenterprise Customer Care n Systems n
 CRM Core Competencies Cross-Selling, Up-Selling n Direct Marketing & Fulfillment n Customer Service & Support n Field Service Operations n Retention Management n
CRM Core Competencies Cross-Selling, Up-Selling n Direct Marketing & Fulfillment n Customer Service & Support n Field Service Operations n Retention Management n
 Delivering Customer Service in Cyberspace n n n Traditional: do the work for the customer E-commerce delivered: gives tools to the customer to do the work for him/herself (log: tracking, troubleshooting, FAQ) with: q Improved communication q Automated process q Speedier resolution of problems E-service—online help for online transactions q Foundation of service—responsible and effective order fulfillment q Customer-centered services—order tracing, configuration, customization, security/trust q Value-added services--dynamic brokering, online auctions, online training and education
Delivering Customer Service in Cyberspace n n n Traditional: do the work for the customer E-commerce delivered: gives tools to the customer to do the work for him/herself (log: tracking, troubleshooting, FAQ) with: q Improved communication q Automated process q Speedier resolution of problems E-service—online help for online transactions q Foundation of service—responsible and effective order fulfillment q Customer-centered services—order tracing, configuration, customization, security/trust q Value-added services--dynamic brokering, online auctions, online training and education
 Product Life Cycle and Customer Service n n n Requirements: assisting the customer to determine needs Acquisition: helping the customer to acquire a product or service Ownership: supporting the customer on an ongoing basis Retirement: helping the client to dispose of a service or product Service must be provided in all of them
Product Life Cycle and Customer Service n n n Requirements: assisting the customer to determine needs Acquisition: helping the customer to acquire a product or service Ownership: supporting the customer on an ongoing basis Retirement: helping the client to dispose of a service or product Service must be provided in all of them
 CRM n n n CRM in action—customer-focused e-commerce Make it easy for customers to do business online Business processes redesigned from customer’s point of view Design a comprehensive, evolving e-commerce architecture Foster customer loyalty by: q Personalized service q Streamline business processes q Own customer’s total experience
CRM n n n CRM in action—customer-focused e-commerce Make it easy for customers to do business online Business processes redesigned from customer’s point of view Design a comprehensive, evolving e-commerce architecture Foster customer loyalty by: q Personalized service q Streamline business processes q Own customer’s total experience
 Customer Service Functions n n n Provide search and comparison capabilities Provide free products and services Provide specialized information and services Allow customers to order customized products and services Enable customers to track accounts or order status
Customer Service Functions n n n Provide search and comparison capabilities Provide free products and services Provide specialized information and services Allow customers to order customized products and services Enable customers to track accounts or order status
 Customer Service Tools n n n Personalized Web pages q Used to record purchases and preference q Direct customized information to customers efficiently FAQs q Customers find answers quickly q Not customized, no personalized feeling and no contribution to relationship marketing Tracking tools q Customers track their orders saving time and money for all q Example: Fed. Ex’s package tracking
Customer Service Tools n n n Personalized Web pages q Used to record purchases and preference q Direct customized information to customers efficiently FAQs q Customers find answers quickly q Not customized, no personalized feeling and no contribution to relationship marketing Tracking tools q Customers track their orders saving time and money for all q Example: Fed. Ex’s package tracking
 Other Customer Support Tools n n Chat rooms—discuss issues with company experts and with other customers E-mail and automated response q q q n Disseminate general information Send specific product information Conduct correspondence regarding any topic (mostly inquiries from customers) Help desks and call centers q q A comprehensive customer service entity E-commerce vendors take care of customer service issues communicated through various contact channels n n Web channels (automated e-mail reply) Web knowledge bases (portal-like self service) Call center agents or field service personnel Troubleshooting tools—assist customers in solving their own problems
Other Customer Support Tools n n Chat rooms—discuss issues with company experts and with other customers E-mail and automated response q q q n Disseminate general information Send specific product information Conduct correspondence regarding any topic (mostly inquiries from customers) Help desks and call centers q q A comprehensive customer service entity E-commerce vendors take care of customer service issues communicated through various contact channels n n Web channels (automated e-mail reply) Web knowledge bases (portal-like self service) Call center agents or field service personnel Troubleshooting tools—assist customers in solving their own problems
 Justifying Customer Service and CRM Programs n Two problems— q q n Most of the benefits are intangible Substantial benefits reaped only from loyal customers, after several years Need for metrics—standards to determine appropriate level of customer support q q q Response and download times Up-to-date site and availability of relevant content Others
Justifying Customer Service and CRM Programs n Two problems— q q n Most of the benefits are intangible Substantial benefits reaped only from loyal customers, after several years Need for metrics—standards to determine appropriate level of customer support q q q Response and download times Up-to-date site and availability of relevant content Others
 CRM Business Drivers Survey of 509 companies % Respondents (AMR Research, 2002)
CRM Business Drivers Survey of 509 companies % Respondents (AMR Research, 2002)
 Web Pages n “Stickiness” n Design n Technical Aspects n Local vs Global
Web Pages n “Stickiness” n Design n Technical Aspects n Local vs Global
 ERP Unifies the “back-office” functions n Finance, HR, Marketing, Sales, Logistics, Manufacturing, etc. n Creates Information Efficiency n Baan, SAP, JD Edwards, Oracle n
ERP Unifies the “back-office” functions n Finance, HR, Marketing, Sales, Logistics, Manufacturing, etc. n Creates Information Efficiency n Baan, SAP, JD Edwards, Oracle n
 Current State of SCM n n Majority of companies do not see SCM as strategic SCM software is usually modular q n <25% of users use more than one module 12% gather data from more than 5% of their customers and suppliers q Collaboration is a buzzword
Current State of SCM n n Majority of companies do not see SCM as strategic SCM software is usually modular q n <25% of users use more than one module 12% gather data from more than 5% of their customers and suppliers q Collaboration is a buzzword
 Security n Quick response to emergencies q Disruption in supply chain n n Customers Suppliers Internal e. Terrorism Information is a key!
Security n Quick response to emergencies q Disruption in supply chain n n Customers Suppliers Internal e. Terrorism Information is a key!
 Visibility n n Identification of materials as they move through the system Visibility of suppliers’ production processes Visibility through to the customer Identification of where the information is!
Visibility n n Identification of materials as they move through the system Visibility of suppliers’ production processes Visibility through to the customer Identification of where the information is!
 SC Software n SCM software q q n Help to plan efficient supply chains Does not necessarily improve visibility SC Event Management software q q q Specifically designed to improve visibility Do not replace traditional SCM software e. g. Celarix, Manugistics, Optum, Saltare
SC Software n SCM software q q n Help to plan efficient supply chains Does not necessarily improve visibility SC Event Management software q q q Specifically designed to improve visibility Do not replace traditional SCM software e. g. Celarix, Manugistics, Optum, Saltare
 Agility n n Ability to restructure Supply Chain quickly Difficult with multiple systems q n Especially after mergers and acquisitions Difficult with ASPs and outsourcing
Agility n n Ability to restructure Supply Chain quickly Difficult with multiple systems q n Especially after mergers and acquisitions Difficult with ASPs and outsourcing
 e. Procurement EDI n Intermediaries n Markets n Electronic Payment n
e. Procurement EDI n Intermediaries n Markets n Electronic Payment n
 Markets Supplier Side n Buyer Side n Intermediary n
Markets Supplier Side n Buyer Side n Intermediary n
 Why Do Firms Use B 2 B Markets to Buy Indirect Materials? n n n Improve Process Efficiency Reduce Product Costs Improve Information Reduce Rogue Purchasing Streamline Supply Chain Improve Service 71% 59% 51% 37% 16% 14% (Forrester Research, 2000)
Why Do Firms Use B 2 B Markets to Buy Indirect Materials? n n n Improve Process Efficiency Reduce Product Costs Improve Information Reduce Rogue Purchasing Streamline Supply Chain Improve Service 71% 59% 51% 37% 16% 14% (Forrester Research, 2000)
 The Value Chain n Disintermediation q n Breaking Apart Reintermediation q Putting back together
The Value Chain n Disintermediation q n Breaking Apart Reintermediation q Putting back together
 Opportunities Communicate Collaborate Coordinate EDI Inter-Ent. Email Elect. Mkts Alliances Communities Channel Int. SC Integration e. Business Enterprise Integration Corp. Email Scheduling KM Communities Order Mgt. Purchasing Work Group Dept. Email Scheduling Teams e. Discussion Sales Auto. Internal Ops. Inter. Enterprise Coalitions
Opportunities Communicate Collaborate Coordinate EDI Inter-Ent. Email Elect. Mkts Alliances Communities Channel Int. SC Integration e. Business Enterprise Integration Corp. Email Scheduling KM Communities Order Mgt. Purchasing Work Group Dept. Email Scheduling Teams e. Discussion Sales Auto. Internal Ops. Inter. Enterprise Coalitions
 Book Value: Market Value WHY? ? ?
Book Value: Market Value WHY? ? ?
 Leadership Traits n Passion q n Speed q n Stay ahead of the curve Humility q n Make the dream clear You must be willing to explain yourself Discovery q The future path must be defined (Citrin & Neff, 2000)
Leadership Traits n Passion q n Speed q n Stay ahead of the curve Humility q n Make the dream clear You must be willing to explain yourself Discovery q The future path must be defined (Citrin & Neff, 2000)
 Leadership Capabilities n n n Lead By Example Develop Solid Business Strategies Build Great Management Teams Inspire Employees Flexibility and Proactive Management Reward Performance (Citrin & Neff, 2000)
Leadership Capabilities n n n Lead By Example Develop Solid Business Strategies Build Great Management Teams Inspire Employees Flexibility and Proactive Management Reward Performance (Citrin & Neff, 2000)
 New Leadership Capabilities n n n Obsessive Focus on Customers Build Cross-Functional Organizations Manage with a Business Model (not a Strategic Plan) Promote the Business Model Foster Risk-Takers in the Company Work Extremely Hard (Citrin & Neff, 2000)
New Leadership Capabilities n n n Obsessive Focus on Customers Build Cross-Functional Organizations Manage with a Business Model (not a Strategic Plan) Promote the Business Model Foster Risk-Takers in the Company Work Extremely Hard (Citrin & Neff, 2000)
 Mastering Value n n Design Your Business Model Master The Risks Manage Your Asset Portfolio Measure and Report
Mastering Value n n Design Your Business Model Master The Risks Manage Your Asset Portfolio Measure and Report
 Moving to e. Business Knowledge Building n Capability Evaluation n e. Business Design n
Moving to e. Business Knowledge Building n Capability Evaluation n e. Business Design n
 The e. Business Panorama Business Value Convergence Industry Transformation Value-Chain Integration Channel Enhancement Leverage of e. Business (Deise et al, 2000)
The e. Business Panorama Business Value Convergence Industry Transformation Value-Chain Integration Channel Enhancement Leverage of e. Business (Deise et al, 2000)
 Guidelines for Transformation Create a Sense of Urgency n Create a Vision n Communicate the Vision n Empower People to Act n Form a Guiding Coalition n Institutionalize New Processes n
Guidelines for Transformation Create a Sense of Urgency n Create a Vision n Communicate the Vision n Empower People to Act n Form a Guiding Coalition n Institutionalize New Processes n
 Strategy – The Vision n n n Where Should We Be in Five Years? What Will Be Our Business Model? How Will Our Processes Support This? What Skills and People Will We Need? How Will We Be Organized? What Will Be Our Infostructure? (Shaw, 2000)
Strategy – The Vision n n n Where Should We Be in Five Years? What Will Be Our Business Model? How Will Our Processes Support This? What Skills and People Will We Need? How Will We Be Organized? What Will Be Our Infostructure? (Shaw, 2000)
 Change Management!
Change Management!
 Application Service Providers n n n Use the Web Deliver and Manage Applications Multiple Customers ERP, CRM, SCM, groupware, etc. Cost Savings: 50% (Gartner Group) Outsourcing!
Application Service Providers n n n Use the Web Deliver and Manage Applications Multiple Customers ERP, CRM, SCM, groupware, etc. Cost Savings: 50% (Gartner Group) Outsourcing!
 ASP Growth (projected) (Cahners In-Stat)
ASP Growth (projected) (Cahners In-Stat)
 ASPs n Benefits to the ASP vendor q Companies generate revenues from sources other than connectivity and transport n n Lucrative Web site hosting Web design consulting Hosted applications with access charges Benefits to the leasing companies q Saves time and various expenses in the initial development stage (i. e. , labor costs) q Reduces software maintenance, upgrading applications, and training time q Reduces time-too-market q Enhances ability to adapt to changing market conditions
ASPs n Benefits to the ASP vendor q Companies generate revenues from sources other than connectivity and transport n n Lucrative Web site hosting Web design consulting Hosted applications with access charges Benefits to the leasing companies q Saves time and various expenses in the initial development stage (i. e. , labor costs) q Reduces software maintenance, upgrading applications, and training time q Reduces time-too-market q Enhances ability to adapt to changing market conditions
 Security Consulting Expenditures (in billions) $14. 8 B $6. 2 B
Security Consulting Expenditures (in billions) $14. 8 B $6. 2 B
 Reported Security Incidents (CERT, 2004)
Reported Security Incidents (CERT, 2004)
 Ethical Issues n Privacy q q n Intellectual Property Rights q q n Databases Cookies Copyright Infringement Software/Music Piracy Digital Divide (Accessibility)
Ethical Issues n Privacy q q n Intellectual Property Rights q q n Databases Cookies Copyright Infringement Software/Music Piracy Digital Divide (Accessibility)
 Privacy n Sites Tracking Visitors: 97% n Sites Informing Visitors of Tracking: 62% n Sites Allowing Third Party Tracking: 57%
Privacy n Sites Tracking Visitors: 97% n Sites Informing Visitors of Tracking: 62% n Sites Allowing Third Party Tracking: 57%
 Privacy Survey: Is online security a major concern? % (Wright, 2000)
Privacy Survey: Is online security a major concern? % (Wright, 2000)
 The Digital Divide Percentage of US Households with Internet Access (US Dept of Commerce, 2000)
The Digital Divide Percentage of US Households with Internet Access (US Dept of Commerce, 2000)
 But…. Online Hours per Month Hunters who attend tractor pulls and earn less than $30, 000 Surfers who earn over $136, 000 and live in the suburbs
But…. Online Hours per Month Hunters who attend tractor pulls and earn less than $30, 000 Surfers who earn over $136, 000 and live in the suburbs
 Legal Issues Taxes n e. Signatures (10/1) n Biometrics n e. Contract Law n q n UCITA International q Tariffs, Regulations, Jurisdiction
Legal Issues Taxes n e. Signatures (10/1) n Biometrics n e. Contract Law n q n UCITA International q Tariffs, Regulations, Jurisdiction
 Successes
Successes
 Failures
Failures
 Who Knows? ? ?
Who Knows? ? ?
 The Future n Wireless q n n n PDAs XML Positioning Systems Digital Convergence (HDTV!) Digital Ink/Literature Open Source?
The Future n Wireless q n n n PDAs XML Positioning Systems Digital Convergence (HDTV!) Digital Ink/Literature Open Source?
 Wireless Users (in Millions) Europe USA Japan Africa
Wireless Users (in Millions) Europe USA Japan Africa
 Mobile Telephones Per 100 inhabitants (ITU, 2003)
Mobile Telephones Per 100 inhabitants (ITU, 2003)
 Worldwide Wireless Web Users (in Millions) (The Industry Standard, 2000)
Worldwide Wireless Web Users (in Millions) (The Industry Standard, 2000)
 2 nd Generation Wireless n CDMA q q q n GSM q q n Developed by Qualcomm Used by Sprint and Verizon in US Used by IDO and DDI in Japan Developed by European consortium Globally dominant (but not in US) TDMA q q AT&T, Bell. South, Southwestern Bell Used in US but not globally compatible
2 nd Generation Wireless n CDMA q q q n GSM q q n Developed by Qualcomm Used by Sprint and Verizon in US Used by IDO and DDI in Japan Developed by European consortium Globally dominant (but not in US) TDMA q q AT&T, Bell. South, Southwestern Bell Used in US but not globally compatible
 Intermediate Technologies n CDMA q n GSM q n Upgrading to faster interim service (64 kbps) EDGE q q q Built on GSM and TDMA by AT&T Meets 3 G standards May not fully implemented by all TDMA operators
Intermediate Technologies n CDMA q n GSM q n Upgrading to faster interim service (64 kbps) EDGE q q q Built on GSM and TDMA by AT&T Meets 3 G standards May not fully implemented by all TDMA operators
 3 G Wireless n n ITU has established performance requirements W-CDMA q Europe’s GSM 3 G technology cdma 2000 q 3 G technology for US 2 G CDMA operators AT&T q Expects many GSM operators to adopt EDGE q Could create global compatibility for TDMA/EDGE users
3 G Wireless n n ITU has established performance requirements W-CDMA q Europe’s GSM 3 G technology cdma 2000 q 3 G technology for US 2 G CDMA operators AT&T q Expects many GSM operators to adopt EDGE q Could create global compatibility for TDMA/EDGE users
 Short-Range Wireless n Bluetooth q q q n Cable replacement technology File sharing Shorter range (10 m) 802. 11 (Wi-Fi) q q Wireless LAN Faster Greater range (100 m) Moxi
Short-Range Wireless n Bluetooth q q q n Cable replacement technology File sharing Shorter range (10 m) 802. 11 (Wi-Fi) q q Wireless LAN Faster Greater range (100 m) Moxi
 Farther Out n Biometrics q n n Biotechnology 3 D Virtual Reality Chat Rooms q n n n Iris Scanning, Fingerprint Nanobot Reality (50 years out) Voice Synthesis Speech Recognition Robotics Translation RF
Farther Out n Biometrics q n n Biotechnology 3 D Virtual Reality Chat Rooms q n n n Iris Scanning, Fingerprint Nanobot Reality (50 years out) Voice Synthesis Speech Recognition Robotics Translation RF
 Farther Out (cont. ) n Artificial Intelligence q Machines will equal the capacity of the human brain in 2020 “Before the next century is over, human beings will no longer be the most intelligent entity on this planet. ” (Kurzweil, 1999)
Farther Out (cont. ) n Artificial Intelligence q Machines will equal the capacity of the human brain in 2020 “Before the next century is over, human beings will no longer be the most intelligent entity on this planet. ” (Kurzweil, 1999)


