00c9cf6513b61e7d27940bff33f3c996.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 93
 Information Systems Software: Software, Systems and Applications Software Term: 2009/2010 Week 5 Management Information Systems
Information Systems Software: Software, Systems and Applications Software Term: 2009/2010 Week 5 Management Information Systems
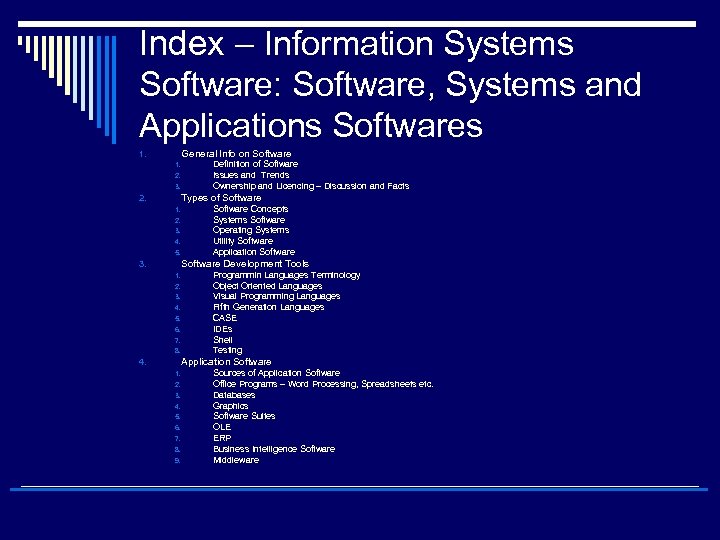 Index – Information Systems Software: Software, Systems and Applications Softwares General Info on Software 1. 1. 2. 3. Definition of Software Issues and Trends Ownership and Licencing – Discussion and Facts Types of Software 2. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Software Concepts Systems Software Operating Systems Utility Software Application Software Development Tools 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Programmin Languages Terminology Object Oriented Languages Visual Programming Languages Fifth Generation Languages CASE IDEs Shell Testing Application Software 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Sources of Application Software Office Programs – Word Processing, Spreadsheets etc. Databases Graphics Software Suites OLE ERP Business Intelligence Software Middleware
Index – Information Systems Software: Software, Systems and Applications Softwares General Info on Software 1. 1. 2. 3. Definition of Software Issues and Trends Ownership and Licencing – Discussion and Facts Types of Software 2. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Software Concepts Systems Software Operating Systems Utility Software Application Software Development Tools 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Programmin Languages Terminology Object Oriented Languages Visual Programming Languages Fifth Generation Languages CASE IDEs Shell Testing Application Software 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Sources of Application Software Office Programs – Word Processing, Spreadsheets etc. Databases Graphics Software Suites OLE ERP Business Intelligence Software Middleware
 What is ‘Software’? n n n No computer can work without software! A series of detailed statements/instructions that control the operation of a computer system. Software exists as programs or a set of programs that are developed by computer programmers. Programs carry out special tasks, they are formed by command lines. In order to execute or have its instructions performed by the computer, a program must be stored in the computer’s primary storage along with the required data. p “Stored program” p Once a program finishes executing, the computer hardware can bu used for another task by loading a new program into primary storage.
What is ‘Software’? n n n No computer can work without software! A series of detailed statements/instructions that control the operation of a computer system. Software exists as programs or a set of programs that are developed by computer programmers. Programs carry out special tasks, they are formed by command lines. In order to execute or have its instructions performed by the computer, a program must be stored in the computer’s primary storage along with the required data. p “Stored program” p Once a program finishes executing, the computer hardware can bu used for another task by loading a new program into primary storage.
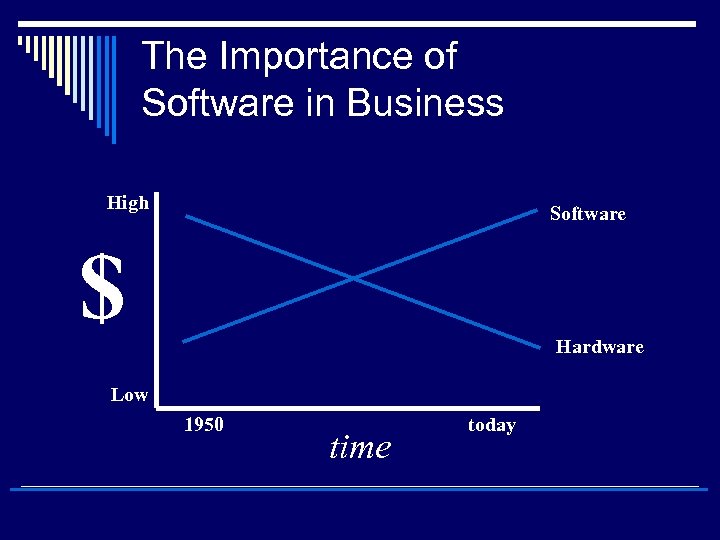 The Importance of Software in Business High Software $ Hardware Low 1950 time today
The Importance of Software in Business High Software $ Hardware Low 1950 time today
 Spheres of Influence o Personal n Softwares that serve the needs of an individual user o Workgroup n Two or more people who work together to achieve a common goal o Enterprise n Softwares that support the firm in its interaction with its environment.
Spheres of Influence o Personal n Softwares that serve the needs of an individual user o Workgroup n Two or more people who work together to achieve a common goal o Enterprise n Softwares that support the firm in its interaction with its environment.
 Commercial Terms of Software o Software licensing Protection by software vendors to prevent unauthorized use n Question: Should software have licences? n Article Reading on Stallman’s Free Software Movement o Software upgrades n A revised version of software that usually includes fixes of known problems, plus enhancements to existing capabilities o Global software support n Software that is distributed around the globe may require unique support mechanisms due to local political and economic conditions n
Commercial Terms of Software o Software licensing Protection by software vendors to prevent unauthorized use n Question: Should software have licences? n Article Reading on Stallman’s Free Software Movement o Software upgrades n A revised version of software that usually includes fixes of known problems, plus enhancements to existing capabilities o Global software support n Software that is distributed around the globe may require unique support mechanisms due to local political and economic conditions n
 Ownership o Freeware: n Copyrighted software given away for free by the author. Although it is available for free, the author retains the copyright, which means that you cannot do anything with it that is not expressly allowed by the author. Usually, the author allows people to use the software, but not sell it. o Shareware: n n Software distributed on the basis of an honor system. Most shareware is delivered free of charge, but the author usually requests that you pay a small fee if you like the program and use it regularly. By sending the small fee, you become registered with the producer so that you can receive service assistance and updates. You can copy shareware and pass it along to friends and colleagues, but they too are expected to pay a fee if they use the product. Shareware is inexpensive because it is usually produced by a single programmer and is offered directly to customers. Thus, there are practically no packaging or advertising expenses. Note that shareware differs from public-domain software in that shareware is copyrighted. This means that you cannot sell a shareware product as your own. o Public-domain software: n Refers to any program that is not copyrighted. Public-domain software is free and can be used without restrictions. The term public-domain software is often used incorrectly to include freeware, free software that is nevertheless copyrighted.
Ownership o Freeware: n Copyrighted software given away for free by the author. Although it is available for free, the author retains the copyright, which means that you cannot do anything with it that is not expressly allowed by the author. Usually, the author allows people to use the software, but not sell it. o Shareware: n n Software distributed on the basis of an honor system. Most shareware is delivered free of charge, but the author usually requests that you pay a small fee if you like the program and use it regularly. By sending the small fee, you become registered with the producer so that you can receive service assistance and updates. You can copy shareware and pass it along to friends and colleagues, but they too are expected to pay a fee if they use the product. Shareware is inexpensive because it is usually produced by a single programmer and is offered directly to customers. Thus, there are practically no packaging or advertising expenses. Note that shareware differs from public-domain software in that shareware is copyrighted. This means that you cannot sell a shareware product as your own. o Public-domain software: n Refers to any program that is not copyrighted. Public-domain software is free and can be used without restrictions. The term public-domain software is often used incorrectly to include freeware, free software that is nevertheless copyrighted.
 Open Source Software o o o o Open source software produced by a community of several hundred thousand programmers around the world. According to the leading open soırce professional community, Open. Source. org, open source software is free and can be modified by users. Works derived from the original code must also be free, and the software can be redistributed by the user without additional licensing. OSS is by definition not restricted to any specific operating system or hardware technology, although most open source software is currently based on a Linux or Unix operating system. OSS is based on the premise that it is superior to commercially produced proprietary software. Because thousands of programmers working for no pay can read, perfect, distribute, and modify the source code much faster, an with reliable results, than small teams of programmers working for a single software company. The open source movement has been evolving for more than 30 years and has demostrated after many years of effort that it can produce commercially acceptable, high quality software. Thousands of OSS are available from websites including Linux OS, Apache HTTP Server, Mozilla Firefox web browser, Open. Office desktop suite. Read Open Source Initiative…
Open Source Software o o o o Open source software produced by a community of several hundred thousand programmers around the world. According to the leading open soırce professional community, Open. Source. org, open source software is free and can be modified by users. Works derived from the original code must also be free, and the software can be redistributed by the user without additional licensing. OSS is by definition not restricted to any specific operating system or hardware technology, although most open source software is currently based on a Linux or Unix operating system. OSS is based on the premise that it is superior to commercially produced proprietary software. Because thousands of programmers working for no pay can read, perfect, distribute, and modify the source code much faster, an with reliable results, than small teams of programmers working for a single software company. The open source movement has been evolving for more than 30 years and has demostrated after many years of effort that it can produce commercially acceptable, high quality software. Thousands of OSS are available from websites including Linux OS, Apache HTTP Server, Mozilla Firefox web browser, Open. Office desktop suite. Read Open Source Initiative…
 Linux and Open Source Software o Linux is the most famous OSS. Linux is related to UNIX. o Created by the Finnish Programmer Linus Torvalds and first posted o o o o to Internet in August 1991. Linux applications are embedded in cell phones, smartphones, netbooks, and other handheld devices. Linux is available in free versions downloadable from the internet or in low cost commercial versions that include tools and support from vendors such as Red Hat. Linux is currently a small but rapidly growing presence on the desktop, especially as an operating system for netbooks. Has a major role in back office running LAN(local area networks), Web servers, high-performance computings. (20% of server operating system) More than 24 countries in Asia, Europe and Latin America have adopted open source software and Linux. Have implications for corporate software platforms: cost reduction, reliability, integration. Major hardware and software vendors like IBM, HP, Dell, Oracle, SAP now offer Linux compatible versions of their products.
Linux and Open Source Software o Linux is the most famous OSS. Linux is related to UNIX. o Created by the Finnish Programmer Linus Torvalds and first posted o o o o to Internet in August 1991. Linux applications are embedded in cell phones, smartphones, netbooks, and other handheld devices. Linux is available in free versions downloadable from the internet or in low cost commercial versions that include tools and support from vendors such as Red Hat. Linux is currently a small but rapidly growing presence on the desktop, especially as an operating system for netbooks. Has a major role in back office running LAN(local area networks), Web servers, high-performance computings. (20% of server operating system) More than 24 countries in Asia, Europe and Latin America have adopted open source software and Linux. Have implications for corporate software platforms: cost reduction, reliability, integration. Major hardware and software vendors like IBM, HP, Dell, Oracle, SAP now offer Linux compatible versions of their products.
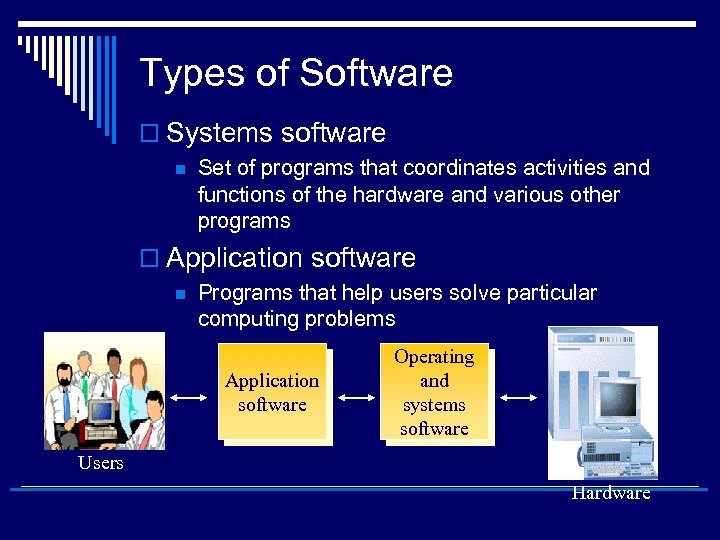 Types of Software o Systems software n Set of programs that coordinates activities and functions of the hardware and various other programs o Application software n Programs that help users solve particular computing problems Application software Operating and systems software Users Hardware
Types of Software o Systems software n Set of programs that coordinates activities and functions of the hardware and various other programs o Application software n Programs that help users solve particular computing problems Application software Operating and systems software Users Hardware
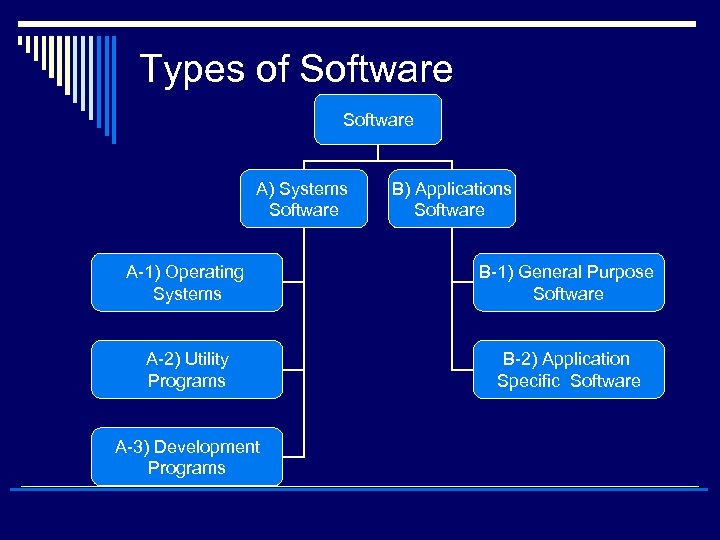 Types of Software A) Systems Software B) Applications Software A-1) Operating Systems B-1) General Purpose Software A-2) Utility Programs B-2) Application Specific Software A-3) Development Programs
Types of Software A) Systems Software B) Applications Software A-1) Operating Systems B-1) General Purpose Software A-2) Utility Programs B-2) Application Specific Software A-3) Development Programs
 A) Systems Software o An interface or buffer between application software and o o o hardware Controls the computer hardware and acts as an interface with applications programs Manages and controls the operation of the computer as it performs tasks on behalf of the user Manager of computer resources lke Central Processing Unit (CPU), printers, terminals, telecom links, and other peripheral equipments. İntermediary between the software used by end users and the computer itself. System software provides the platform on which applications sofware runs.
A) Systems Software o An interface or buffer between application software and o o o hardware Controls the computer hardware and acts as an interface with applications programs Manages and controls the operation of the computer as it performs tasks on behalf of the user Manager of computer resources lke Central Processing Unit (CPU), printers, terminals, telecom links, and other peripheral equipments. İntermediary between the software used by end users and the computer itself. System software provides the platform on which applications sofware runs.
 A-1) Operating System Functions n n n n Perform common computer hardware functions Provide a user interface Provide a degree of hardware independence Manage system memory Manage processing tasks Provide networking capability Control access to system resources Manage files
A-1) Operating System Functions n n n n Perform common computer hardware functions Provide a user interface Provide a degree of hardware independence Manage system memory Manage processing tasks Provide networking capability Control access to system resources Manage files
 A-1) Commercial operating systems o Windows ( o Unix o Linux o Solaris 10 o OS/2 o Many others, more than 80 o TCO is important
A-1) Commercial operating systems o Windows ( o Unix o Linux o Solaris 10 o OS/2 o Many others, more than 80 o TCO is important
 A-1) Commercial operating systems o Windows (At the client level, 95% of PCs and 45% of handheld devices use MS Windows OS) n Windows comprises 70% of the server operating market. Windows Server 2008 is capable of providing enterprise-wide operating system and network services. o Unix o Linux n n o o Unix or Linux servers are 30%. Unix and Linux are scalable, reliable, less expensice than mainframe operating systems. They can also run on different processors. (IBM, HP, Sun) Solaris 10 OS/2 Many others, more than 80 TCO is important
A-1) Commercial operating systems o Windows (At the client level, 95% of PCs and 45% of handheld devices use MS Windows OS) n Windows comprises 70% of the server operating market. Windows Server 2008 is capable of providing enterprise-wide operating system and network services. o Unix o Linux n n o o Unix or Linux servers are 30%. Unix and Linux are scalable, reliable, less expensice than mainframe operating systems. They can also run on different processors. (IBM, HP, Sun) Solaris 10 OS/2 Many others, more than 80 TCO is important
 A-1) Network Operating System o Provide the majority of facilities required to support workgroup computing; n n n Centralized storage space can be created for the excusive use of workgroup members Security features can be used to restrict access the data by those outside of workgroup The network group can be given network privileges that allow individual members access that are not normally available to others.
A-1) Network Operating System o Provide the majority of facilities required to support workgroup computing; n n n Centralized storage space can be created for the excusive use of workgroup members Security features can be used to restrict access the data by those outside of workgroup The network group can be given network privileges that allow individual members access that are not normally available to others.
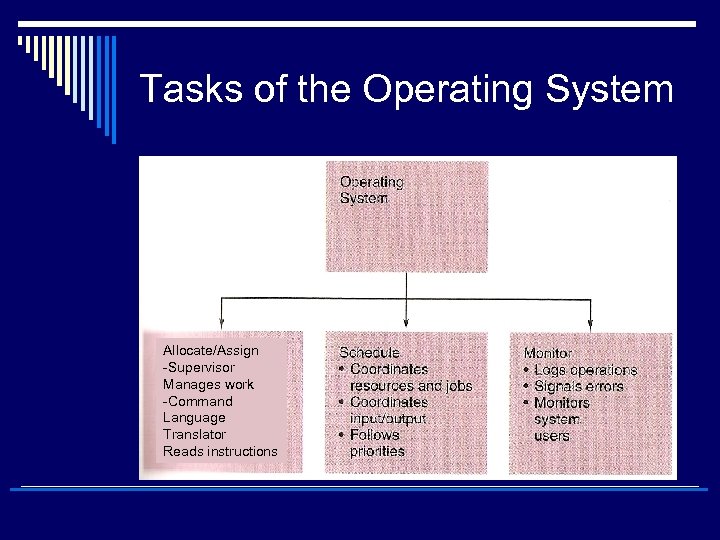 Tasks of the Operating System Allocate/Assign -Supervisor Manages work -Command Language Translator Reads instructions
Tasks of the Operating System Allocate/Assign -Supervisor Manages work -Command Language Translator Reads instructions
 A-2) Utility Programs o Programs used to merge and sort sets of data, keep track of computer jobs being run, compress files of data before they are stored or transmitted over a network, and perform other important tasks o Also monitor system performance and provide security controls o In network manage the data traffic.
A-2) Utility Programs o Programs used to merge and sort sets of data, keep track of computer jobs being run, compress files of data before they are stored or transmitted over a network, and perform other important tasks o Also monitor system performance and provide security controls o In network manage the data traffic.
 Systems Software Concepts o User interface p A function of the operating system and other softwares that allows individuals to access and command the computer o Command-based user interface p A particular user interface that requires text commands be given to the computer to perform basic activities p E. g. , unix, DOS o Graphical user interface (GUI) p A UI that uses pictures (icons) and menus displayed on the screen to send commands to the computer system
Systems Software Concepts o User interface p A function of the operating system and other softwares that allows individuals to access and command the computer o Command-based user interface p A particular user interface that requires text commands be given to the computer to perform basic activities p E. g. , unix, DOS o Graphical user interface (GUI) p A UI that uses pictures (icons) and menus displayed on the screen to send commands to the computer system
 Systems Software Concepts o Hardware independence n Operating system (OS) provides hardware independence for application software n Application software interfaces with the operating system which interfaces with the hardware n When the hardware is changed, the operating system is changed so that the application software is not required to be changed
Systems Software Concepts o Hardware independence n Operating system (OS) provides hardware independence for application software n Application software interfaces with the operating system which interfaces with the hardware n When the hardware is changed, the operating system is changed so that the application software is not required to be changed
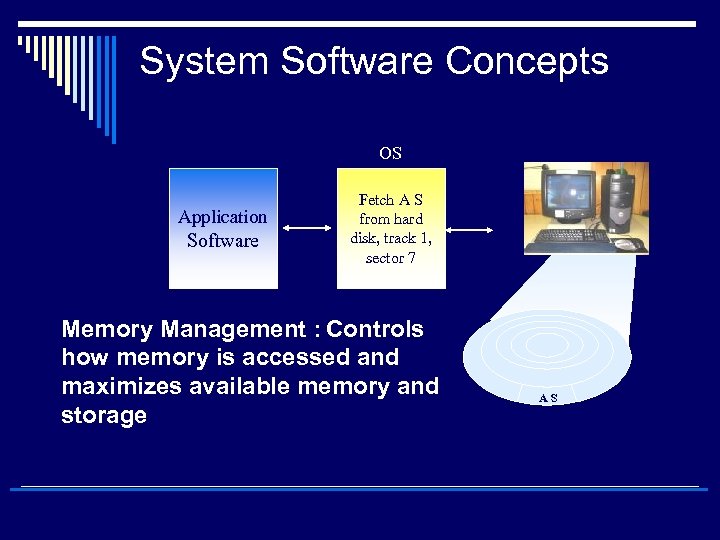 System Software Concepts OS Application Software Fetch A S from hard disk, track 1, sector 7 Memory Management : Controls how memory is accessed and maximizes available memory and storage AS
System Software Concepts OS Application Software Fetch A S from hard disk, track 1, sector 7 Memory Management : Controls how memory is accessed and maximizes available memory and storage AS
 System Software Concepts o Virtual memory n n n n n Memory that allocates space in secondary storage to supplement the immediate, functional memory capacity of RAM An imaginary memory area supported by some operating systems (for example, Windows but not DOS) in conjunction with the hardware. You can think of virtual memory as an alternate set of memory addresses. Programs use these virtual addresses rather than real addresses to store instructions and data. When the program is actually executed, the virtual addresses are converted into real memory addresses. The purpose of virtual memory is to enlarge the address space, the set of addresses a program can utilize. When the page is needed, the operating system copies it from disk to main memory, translating the virtual addresses into real addresses. For example, virtual memory might contain twice as many addresses as main memory. A program using all of virtual memory, therefore, would not be able to fit in main memory all at once. Nevertheless, the computer could execute such a program by copying into main memory those portions of the program needed at any given point during execution. To facilitate copying virtual memory into real memory, the operating system divides virtual memory into pages, each of which contains a fixed number of addresses. Each page is stored on a disk until it is needed The process of translating virtual addresses into real addresses is called mapping. The copying of virtual pages from disk to main memory is known as paging or swapping. o Paging n A function of virtual memory allowing the computer to store currently needed pages in RAM while the rest of the pages wait in secondary storage
System Software Concepts o Virtual memory n n n n n Memory that allocates space in secondary storage to supplement the immediate, functional memory capacity of RAM An imaginary memory area supported by some operating systems (for example, Windows but not DOS) in conjunction with the hardware. You can think of virtual memory as an alternate set of memory addresses. Programs use these virtual addresses rather than real addresses to store instructions and data. When the program is actually executed, the virtual addresses are converted into real memory addresses. The purpose of virtual memory is to enlarge the address space, the set of addresses a program can utilize. When the page is needed, the operating system copies it from disk to main memory, translating the virtual addresses into real addresses. For example, virtual memory might contain twice as many addresses as main memory. A program using all of virtual memory, therefore, would not be able to fit in main memory all at once. Nevertheless, the computer could execute such a program by copying into main memory those portions of the program needed at any given point during execution. To facilitate copying virtual memory into real memory, the operating system divides virtual memory into pages, each of which contains a fixed number of addresses. Each page is stored on a disk until it is needed The process of translating virtual addresses into real addresses is called mapping. The copying of virtual pages from disk to main memory is known as paging or swapping. o Paging n A function of virtual memory allowing the computer to store currently needed pages in RAM while the rest of the pages wait in secondary storage
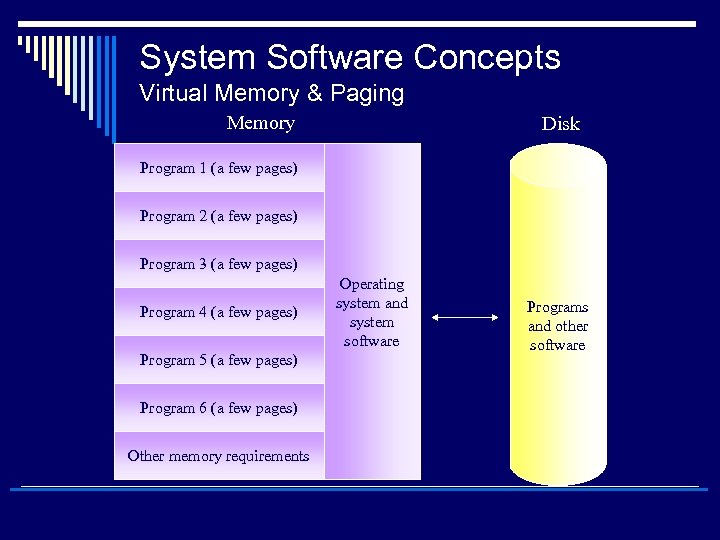 System Software Concepts Virtual Memory & Paging Memory Disk Program 1 (a few pages) Program 2 (a few pages) Program 3 (a few pages) Program 4 (a few pages) Program 5 (a few pages) Program 6 (a few pages) Other memory requirements Operating system and system software Programs and other software
System Software Concepts Virtual Memory & Paging Memory Disk Program 1 (a few pages) Program 2 (a few pages) Program 3 (a few pages) Program 4 (a few pages) Program 5 (a few pages) Program 6 (a few pages) Other memory requirements Operating system and system software Programs and other software
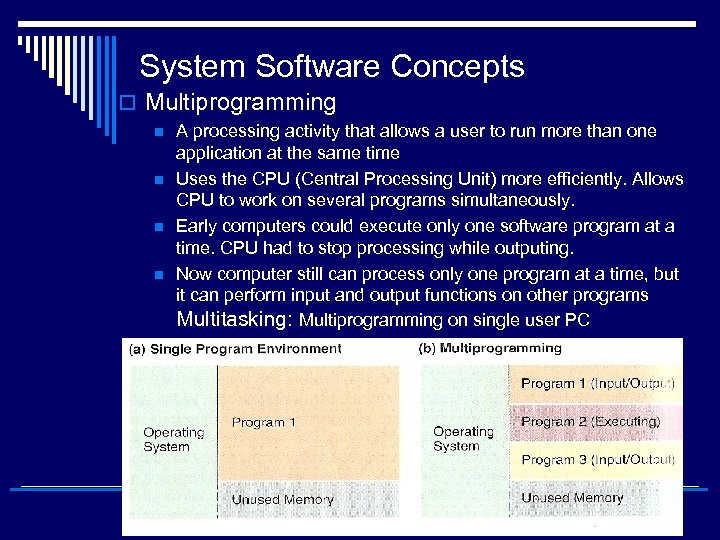 System Software Concepts o Multiprogramming n n A processing activity that allows a user to run more than one application at the same time Uses the CPU (Central Processing Unit) more efficiently. Allows CPU to work on several programs simultaneously. Early computers could execute only one software program at a time. CPU had to stop processing while outputing. Now computer still can process only one program at a time, but it can perform input and output functions on other programs Multitasking: Multiprogramming on single user PC
System Software Concepts o Multiprogramming n n A processing activity that allows a user to run more than one application at the same time Uses the CPU (Central Processing Unit) more efficiently. Allows CPU to work on several programs simultaneously. Early computers could execute only one software program at a time. CPU had to stop processing while outputing. Now computer still can process only one program at a time, but it can perform input and output functions on other programs Multitasking: Multiprogramming on single user PC
 System Software Concepts o Multithreading n A processing activity that is basically multitasking within a single application o Time-sharing n A processing activity that allows more than one person to use a computer system at the same time
System Software Concepts o Multithreading n A processing activity that is basically multitasking within a single application o Time-sharing n A processing activity that allows more than one person to use a computer system at the same time
 System Software Concepts o Network capability n Aids in connecting the computer to a network o Access to system resources n Provides security for unauthorized access o File management n Ensures that files in secondary storage are available when needed, and they are protected against unauthorized usage
System Software Concepts o Network capability n Aids in connecting the computer to a network o Access to system resources n Provides security for unauthorized access o File management n Ensures that files in secondary storage are available when needed, and they are protected against unauthorized usage
 A-3) Development Tools/ Programs o Allows users to develop their own software in order to carry out processing tasks using programming languages.
A-3) Development Tools/ Programs o Allows users to develop their own software in order to carry out processing tasks using programming languages.
 Programming Languages: Terminology (1) o Programming Language: Coding schemes used to write both systems and application software o Language translator n Systems software that converts a programmer’s source code into its equivalent in machine language o Source code n High-level program code written by the programmer o Object code n Another name for machine language code
Programming Languages: Terminology (1) o Programming Language: Coding schemes used to write both systems and application software o Language translator n Systems software that converts a programmer’s source code into its equivalent in machine language o Source code n High-level program code written by the programmer o Object code n Another name for machine language code
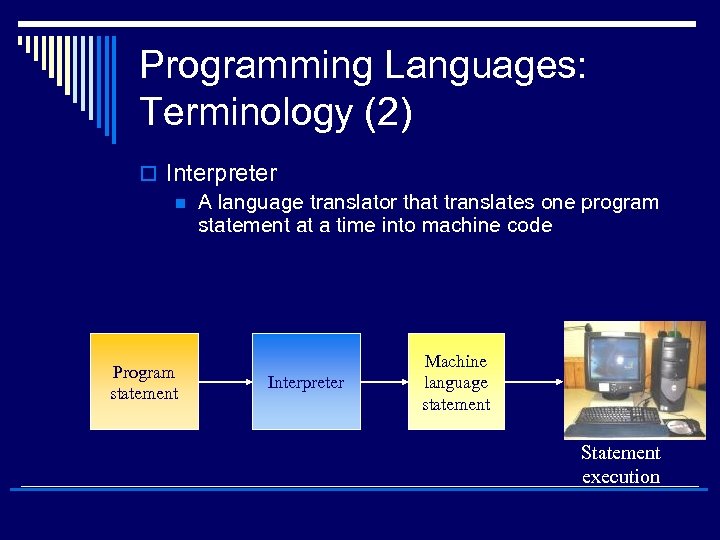 Programming Languages: Terminology (2) o Interpreter n A language translator that translates one program statement at a time into machine code Program statement Interpreter Machine language statement Statement execution
Programming Languages: Terminology (2) o Interpreter n A language translator that translates one program statement at a time into machine code Program statement Interpreter Machine language statement Statement execution
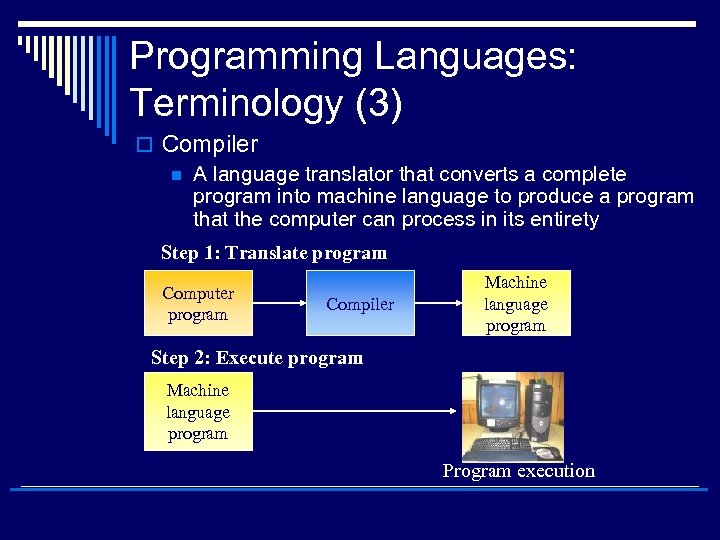 Programming Languages: Terminology (3) o Compiler n A language translator that converts a complete program into machine language to produce a program that the computer can process in its entirety Step 1: Translate program Computer program Compiler Machine language program Step 2: Execute program Machine language program Program execution
Programming Languages: Terminology (3) o Compiler n A language translator that converts a complete program into machine language to produce a program that the computer can process in its entirety Step 1: Translate program Computer program Compiler Machine language program Step 2: Execute program Machine language program Program execution
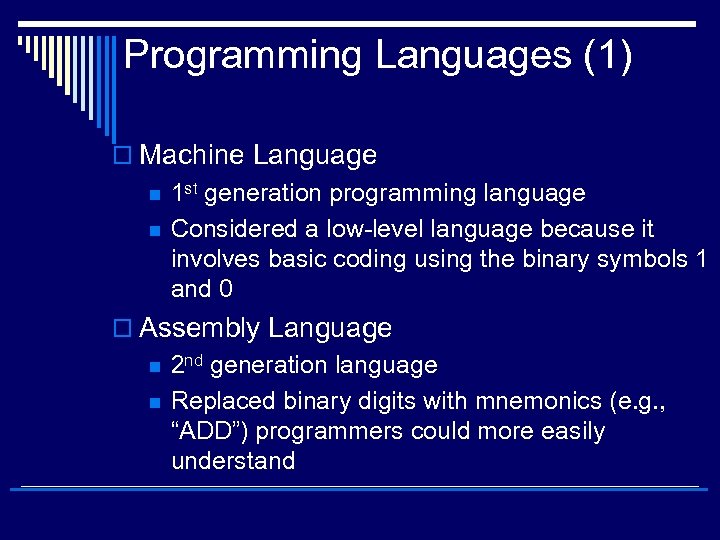 Programming Languages (1) o Machine Language n n 1 st generation programming language Considered a low-level language because it involves basic coding using the binary symbols 1 and 0 o Assembly Language n n 2 nd generation language Replaced binary digits with mnemonics (e. g. , “ADD”) programmers could more easily understand
Programming Languages (1) o Machine Language n n 1 st generation programming language Considered a low-level language because it involves basic coding using the binary symbols 1 and 0 o Assembly Language n n 2 nd generation language Replaced binary digits with mnemonics (e. g. , “ADD”) programmers could more easily understand
 Programming Languages (2) o Third Generation Languages Continued trend to more symbolic code (e. g. COBOL, JAVA…) o Fourth Generation Languages (4 GLs) n Languages that are less procedural and even more English-like than thirdgeneration languages (e. g. FOCUS) n
Programming Languages (2) o Third Generation Languages Continued trend to more symbolic code (e. g. COBOL, JAVA…) o Fourth Generation Languages (4 GLs) n Languages that are less procedural and even more English-like than thirdgeneration languages (e. g. FOCUS) n
 Programming Languages (3) o Query languages n n Used to ask the computer questions in English-like sentences Also known as database languages o Structured query language (SQL) n A standardized language often used to perform database queries and manipulations
Programming Languages (3) o Query languages n n Used to ask the computer questions in English-like sentences Also known as database languages o Structured query language (SQL) n A standardized language often used to perform database queries and manipulations
 Objects An object combines data structures with any functions needed to manipulate the data it holds. Ex: an object called “Employee” might be created to store details of staff. As a data structure it contains name, adress, age, wage… Benefit: 1. changes can be made on the object without altering any other part of the system 2. new objects can be created quickly and easily from existing ones 3. objects can be copied into new systems with little difficulty.
Objects An object combines data structures with any functions needed to manipulate the data it holds. Ex: an object called “Employee” might be created to store details of staff. As a data structure it contains name, adress, age, wage… Benefit: 1. changes can be made on the object without altering any other part of the system 2. new objects can be created quickly and easily from existing ones 3. objects can be copied into new systems with little difficulty.
 Object Oriented Languages (1) o Languages that allow interaction of programming objects, including data elements and the actions that will be performed on them.
Object Oriented Languages (1) o Languages that allow interaction of programming objects, including data elements and the actions that will be performed on them.
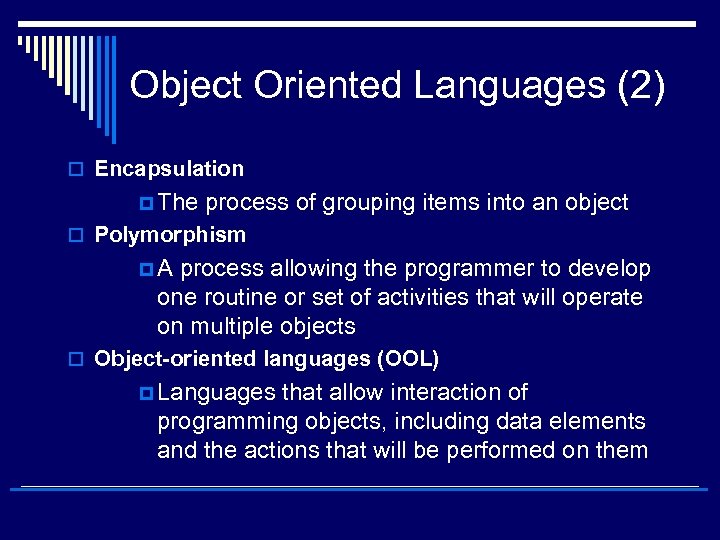 Object Oriented Languages (2) o Encapsulation p The process of grouping items into an object o Polymorphism p. A process allowing the programmer to develop one routine or set of activities that will operate on multiple objects o Object-oriented languages (OOL) p Languages that allow interaction of programming objects, including data elements and the actions that will be performed on them
Object Oriented Languages (2) o Encapsulation p The process of grouping items into an object o Polymorphism p. A process allowing the programmer to develop one routine or set of activities that will operate on multiple objects o Object-oriented languages (OOL) p Languages that allow interaction of programming objects, including data elements and the actions that will be performed on them
 Object Oriented Languages (3) o Inheritance p Property used to describe objects in a group of objects taking on characteristics of other objects in the same group or class of objects o Reusable code p The instruction code within an object that can be reused in different programs for a variety of applications o Examples p Smalltalk, C++, Java
Object Oriented Languages (3) o Inheritance p Property used to describe objects in a group of objects taking on characteristics of other objects in the same group or class of objects o Reusable code p The instruction code within an object that can be reused in different programs for a variety of applications o Examples p Smalltalk, C++, Java
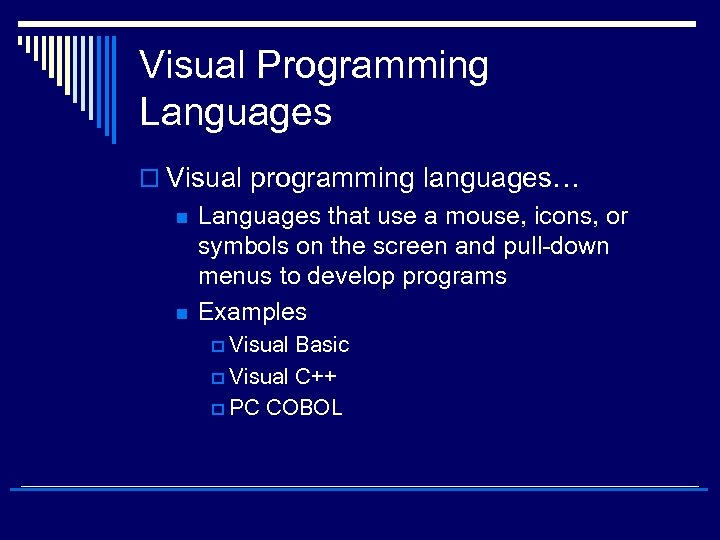 Visual Programming Languages o Visual programming languages… n n Languages that use a mouse, icons, or symbols on the screen and pull-down menus to develop programs Examples p Visual Basic p Visual C++ p PC COBOL
Visual Programming Languages o Visual programming languages… n n Languages that use a mouse, icons, or symbols on the screen and pull-down menus to develop programs Examples p Visual Basic p Visual C++ p PC COBOL
 Fifth-Generation Languages o 5 th generation languages… n n Combines rule-based code generation, component management, visual programming techniques, and reuse management Knowledge-based management p An approach to the development of computer programs in which you do not tell a computer how to do a job, but what you want it to do
Fifth-Generation Languages o 5 th generation languages… n n Combines rule-based code generation, component management, visual programming techniques, and reuse management Knowledge-based management p An approach to the development of computer programs in which you do not tell a computer how to do a job, but what you want it to do
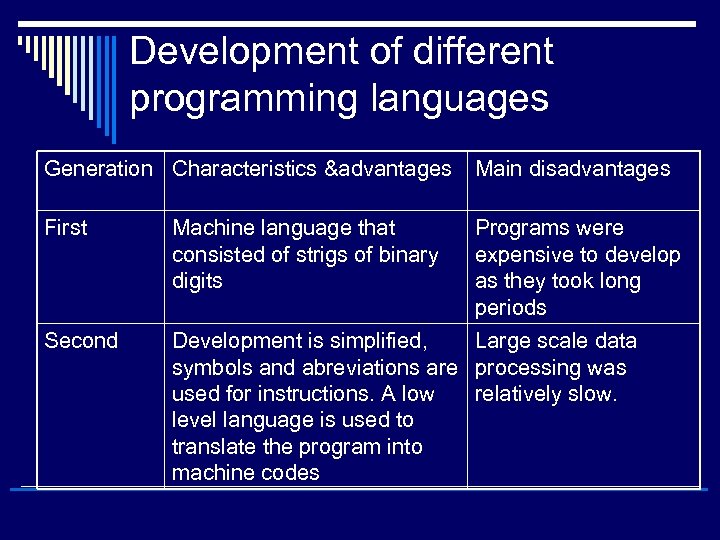 Development of different programming languages Generation Characteristics &advantages Main disadvantages First Machine language that consisted of strigs of binary digits Programs were expensive to develop as they took long periods Second Development is simplified, Large scale data symbols and abreviations are processing was used for instructions. A low relatively slow. level language is used to translate the program into machine codes
Development of different programming languages Generation Characteristics &advantages Main disadvantages First Machine language that consisted of strigs of binary digits Programs were expensive to develop as they took long periods Second Development is simplified, Large scale data symbols and abreviations are processing was used for instructions. A low relatively slow. level language is used to translate the program into machine codes
 Development of different programming languages Generation Characteristics & advantages Main disadvantages Third Commands are made up of english like of statements Resulting applications were sometimes slow and inefficient Fourth Greater ease of use, even non Some programming technical users develop their own knowledge is still necessary applications Fifth Programming system accept a spoken question from a user then generate program intended to produce the required info Artificial intelligence techniques are still not sufficiently developed to make it a practical reality
Development of different programming languages Generation Characteristics & advantages Main disadvantages Third Commands are made up of english like of statements Resulting applications were sometimes slow and inefficient Fourth Greater ease of use, even non Some programming technical users develop their own knowledge is still necessary applications Fifth Programming system accept a spoken question from a user then generate program intended to produce the required info Artificial intelligence techniques are still not sufficiently developed to make it a practical reality
 CASE (Computer Aided Software Engineering) Tools o CASE is the use of computer based support in the software development process o This definition includes all kinds of computer based support for any of the managerial, admnistrative or technical aspects of any part of a software project. o Ex: document production, version control of source code, debugging, design method support…
CASE (Computer Aided Software Engineering) Tools o CASE is the use of computer based support in the software development process o This definition includes all kinds of computer based support for any of the managerial, admnistrative or technical aspects of any part of a software project. o Ex: document production, version control of source code, debugging, design method support…
 IDE’s: Integrated development environments o Combine the features of many tools, into one complete package o They are simpler and easier to do simple tasks, such as searching for content only in files in the project. o They are often used for development of enterprise level applications.
IDE’s: Integrated development environments o Combine the features of many tools, into one complete package o They are simpler and easier to do simple tasks, such as searching for content only in files in the project. o They are often used for development of enterprise level applications.
 Shell o Special tools used for development of expert and knowledge based systems
Shell o Special tools used for development of expert and knowledge based systems
 Tests o Validation: whether the program achieves intented purpose? o Verification: whether the program contains no error
Tests o Validation: whether the program achieves intented purpose? o Verification: whether the program contains no error
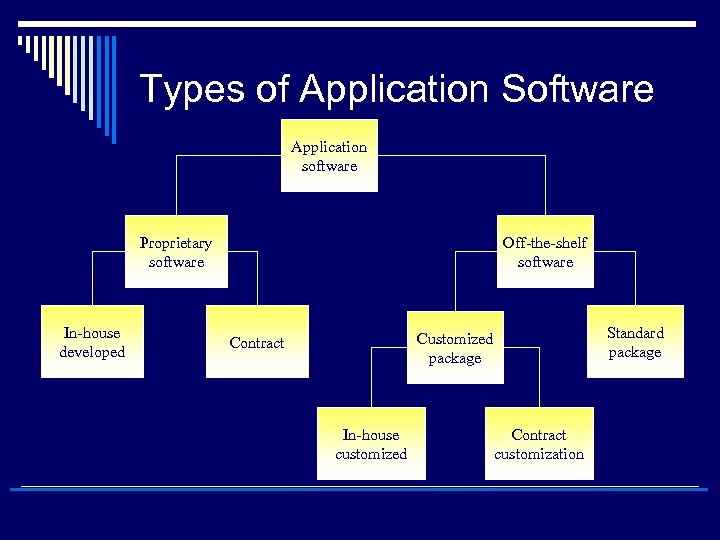
 Types of Application Software o Proprietary: Designed to solve a unique and specific problem n n In-house: Development of application software using the company’s resources Contract: Developed for a particular company o Off-the-shelf: An existing software program that can be used without considerable changes expected n n Customized package: Blend of external and internal software development p In-house customized p Contract customization Standard Package
Types of Application Software o Proprietary: Designed to solve a unique and specific problem n n In-house: Development of application software using the company’s resources Contract: Developed for a particular company o Off-the-shelf: An existing software program that can be used without considerable changes expected n n Customized package: Blend of external and internal software development p In-house customized p Contract customization Standard Package
 Types of Application Software Application software Proprietary software In-house developed Off-the-shelf software Standard package Customized package Contract In-house customized Contract customization
Types of Application Software Application software Proprietary software In-house developed Off-the-shelf software Standard package Customized package Contract In-house customized Contract customization
 B-1) General-purpose applications o Document production o Graphics (drawing, photo editing, diagramming) o Spreadsheets (for processing numerical info) o Databases (for storage and retrieval of info) o Multimedia o Software for using the Internet: Online Services o Management application of the productivity software: Software Suites
B-1) General-purpose applications o Document production o Graphics (drawing, photo editing, diagramming) o Spreadsheets (for processing numerical info) o Databases (for storage and retrieval of info) o Multimedia o Software for using the Internet: Online Services o Management application of the productivity software: Software Suites
 Document Production - Word Processing Provides assistance in formulating, formatting, and printing documents such as letters, memos, and papers. 49 26
Document Production - Word Processing Provides assistance in formulating, formatting, and printing documents such as letters, memos, and papers. 49 26
 Graphics Program Helps make a presentation; develops brochures, illustrations, etc. Usually called Presentation Graphics 50
Graphics Program Helps make a presentation; develops brochures, illustrations, etc. Usually called Presentation Graphics 50
 Spreadsheet Provides a wide range of built-in functions for statistical, financial, logical, database, graphics, and data and time calculations. 51 27
Spreadsheet Provides a wide range of built-in functions for statistical, financial, logical, database, graphics, and data and time calculations. 51 27
 Spreadsheets are used for o Financial applications o Modelling and simulation n Modelling: Creating a numerical representation of an existing situation or set of circumstances n What if? Analysis: describes the ability see the predicted effect of a change made to a numerical model o Statistical analysis n Goal seeking: describes a way of automatically changing the values in a formula until a desired result is achieved
Spreadsheets are used for o Financial applications o Modelling and simulation n Modelling: Creating a numerical representation of an existing situation or set of circumstances n What if? Analysis: describes the ability see the predicted effect of a change made to a numerical model o Statistical analysis n Goal seeking: describes a way of automatically changing the values in a formula until a desired result is achieved
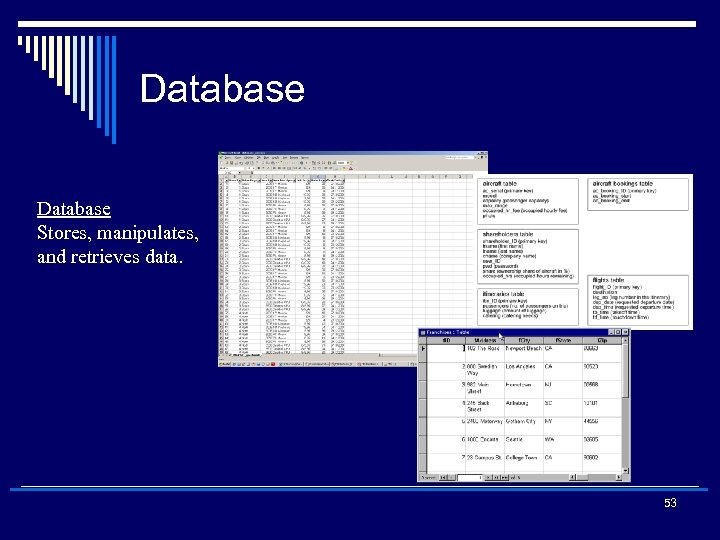 Database Stores, manipulates, and retrieves data. 53 28
Database Stores, manipulates, and retrieves data. 53 28
 On-Line Services Provide access to various information resources. (Figure 4. 12) 54 30
On-Line Services Provide access to various information resources. (Figure 4. 12) 54 30
 Software Suite Collection of personal productivity software such as word processor, spreadsheet, and database. 55 31
Software Suite Collection of personal productivity software such as word processor, spreadsheet, and database. 55 31
 Software Concepts – OLEObject Linking and Embedding o A compound document standard developed by Microsoft Corporation. o Support for OLE is built into the Windows and Macintosh operating systems. A competing compound document standard developed jointly by IBM, Apple Computer, and other computer firms is called Open. Doc. o A software feature that allows you to copy text from one document to another or embed graphics from one program into another program or document (you can create objects with one (Server) application and then link or embed them in a second (Client) application). Embedded objects retain their original format and links to the application that created them. o Server Application n The application that supplies objects you place into other applications o Client application n The application that accepts objects from other applications
Software Concepts – OLEObject Linking and Embedding o A compound document standard developed by Microsoft Corporation. o Support for OLE is built into the Windows and Macintosh operating systems. A competing compound document standard developed jointly by IBM, Apple Computer, and other computer firms is called Open. Doc. o A software feature that allows you to copy text from one document to another or embed graphics from one program into another program or document (you can create objects with one (Server) application and then link or embed them in a second (Client) application). Embedded objects retain their original format and links to the application that created them. o Server Application n The application that supplies objects you place into other applications o Client application n The application that accepts objects from other applications
 OLE Concepts o Copy n Copy data from one application and place it in another o Link n Changes made to the server object to automatically appear in all linked client objects o Embed n An object to become part of the client document
OLE Concepts o Copy n Copy data from one application and place it in another o Link n Changes made to the server object to automatically appear in all linked client objects o Embed n An object to become part of the client document
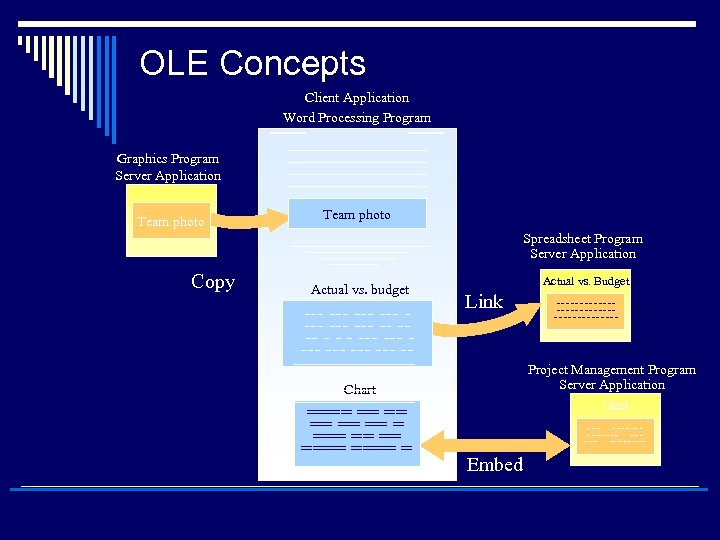 OLE Concepts Client Application Word Processing Program Graphics Program Server Application Team photo Spreadsheet Program Server Application Copy Actual vs. budget --- --- -- - - - --- --- --- -- Actual vs. Budget Link Project Management Program Server Application Chart ==== == == ==== = ------------------- Chart -------- Embed
OLE Concepts Client Application Word Processing Program Graphics Program Server Application Team photo Spreadsheet Program Server Application Copy Actual vs. budget --- --- -- - - - --- --- --- -- Actual vs. Budget Link Project Management Program Server Application Chart ==== == == ==== = ------------------- Chart -------- Embed
 B-2) Application-specific software o Programs that are intented to serve a specific purpose or carry out a clearly defined information processing task eg. Payroll processing, ERP…
B-2) Application-specific software o Programs that are intented to serve a specific purpose or carry out a clearly defined information processing task eg. Payroll processing, ERP…
 Productivity software o Describes a category of computer software that aims to support users in performing a variety of common tasks
Productivity software o Describes a category of computer software that aims to support users in performing a variety of common tasks
 Workgroup Application Software o Groupware n Software that helps groups of people work together more efficiently and effectively o Collaborative computing software n Software that helps teams of people work together toward a common goal
Workgroup Application Software o Groupware n Software that helps groups of people work together more efficiently and effectively o Collaborative computing software n Software that helps teams of people work together toward a common goal
 Enterprise Application Software o Enterprise application software… n n Software that benefits the entire organization Examples Accounts receivable Sales ordering Accounts payable Order entry Cash-flow analysis Check processing Manufacturing control Receiving General Ledger Retail Operations
Enterprise Application Software o Enterprise application software… n n Software that benefits the entire organization Examples Accounts receivable Sales ordering Accounts payable Order entry Cash-flow analysis Check processing Manufacturing control Receiving General Ledger Retail Operations
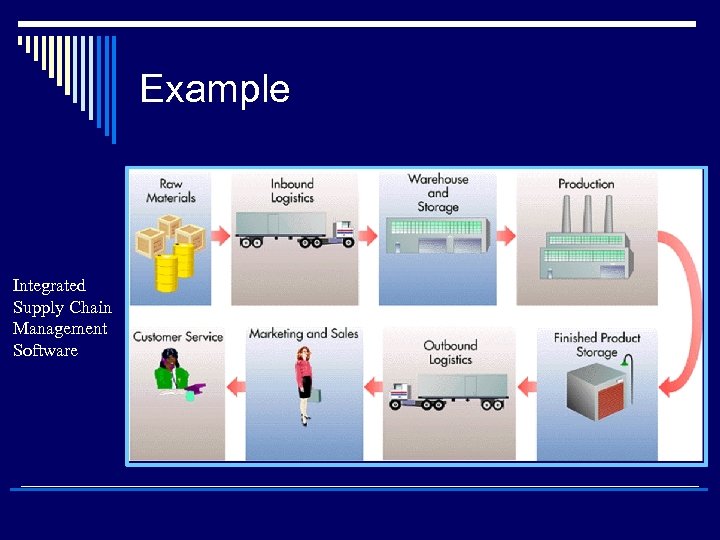 Example Integrated Supply Chain Management Software
Example Integrated Supply Chain Management Software
 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) o US firms spent about 250 billion USD in 2008 on software for enterprise applications. o A set of integrated programs that manage a company’s vital business operations for an entire multi-site, global organization o Short for enterprise resource planning, a business management system that integrates all facets of the business, including planning, manufacturing, sales, and marketing. As the ERP methodology has become more popular, software applications have emerged to help business managers implement ERP. o Vendor examples SAP 1 st Oracle (2 nd acquired People. Soft) Axapta by MS QAD JD Edwards Ross Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) o US firms spent about 250 billion USD in 2008 on software for enterprise applications. o A set of integrated programs that manage a company’s vital business operations for an entire multi-site, global organization o Short for enterprise resource planning, a business management system that integrates all facets of the business, including planning, manufacturing, sales, and marketing. As the ERP methodology has become more popular, software applications have emerged to help business managers implement ERP. o Vendor examples SAP 1 st Oracle (2 nd acquired People. Soft) Axapta by MS QAD JD Edwards Ross Systems
 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) o US firms spent about 250 billion USD in 2008 on software for enterprise applications. o Vendor examples: SAP 1 st, Oracle (2 nd acquired People. Soft), Axapta by MS, SSA, QAD, JD Edwards, Ross Systems o Since most large firms already use ERP and have developed long term contacts with vendors, Microsoft is heading for lower levels of the market. o ERP Vendors Market in 2005 (ref. Gartner. Quest) Vendor share(%) SAP Oracle Applications The Sage Group Microsoft Dynamics SSA Global Technologies Revenue (million $) Market 1949 1374 1121 916 464 30. 332 21. 383 17. 444 14. 255 7. 22
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) o US firms spent about 250 billion USD in 2008 on software for enterprise applications. o Vendor examples: SAP 1 st, Oracle (2 nd acquired People. Soft), Axapta by MS, SSA, QAD, JD Edwards, Ross Systems o Since most large firms already use ERP and have developed long term contacts with vendors, Microsoft is heading for lower levels of the market. o ERP Vendors Market in 2005 (ref. Gartner. Quest) Vendor share(%) SAP Oracle Applications The Sage Group Microsoft Dynamics SSA Global Technologies Revenue (million $) Market 1949 1374 1121 916 464 30. 332 21. 383 17. 444 14. 255 7. 22
 Middlewares o Special type of softwares which aim to integrate various application softwares o They are also known as enterprise application integration. o Used for achieving firmwide integration by linking the firm’s existing application systems. n Major Vendor BEA was acquired by Oracle.
Middlewares o Special type of softwares which aim to integrate various application softwares o They are also known as enterprise application integration. o Used for achieving firmwide integration by linking the firm’s existing application systems. n Major Vendor BEA was acquired by Oracle.
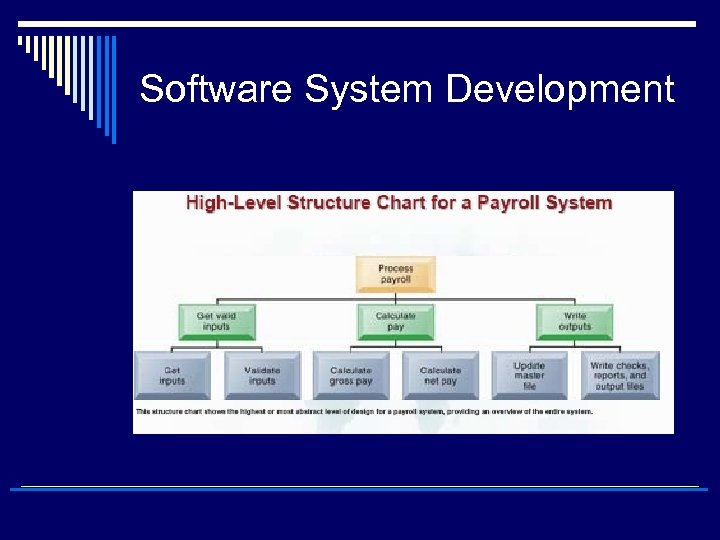 Software System Development
Software System Development
 Software System Development Structured Methodologies • Structured refers to the fact that techniques are step by step, with each step building on the previous one. • Data flow diagram: Primary tool for structured analysis that graphically illustrates a system’s component processes and the flow of data between them. • Process specifications: Specifications that describe the logic of the processes occurring within the lowest levels of a data flow diagram. • Structure chart: System documentation showing each level of design, the relationship among the levels, and the overall place in the design structure; can document one program, one system, or part of one program.
Software System Development Structured Methodologies • Structured refers to the fact that techniques are step by step, with each step building on the previous one. • Data flow diagram: Primary tool for structured analysis that graphically illustrates a system’s component processes and the flow of data between them. • Process specifications: Specifications that describe the logic of the processes occurring within the lowest levels of a data flow diagram. • Structure chart: System documentation showing each level of design, the relationship among the levels, and the overall place in the design structure; can document one program, one system, or part of one program.
 Systems Development o The activities that go into producing an information system solution to an organizational problem or opportunity are calles SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT. o Systems development is a STRUCTURED PROBLEM SOLVING with DISTINCT activities like: n n n n Systems Analysis Systems Design Programming Testing Conversion Production Maintenance
Systems Development o The activities that go into producing an information system solution to an organizational problem or opportunity are calles SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT. o Systems development is a STRUCTURED PROBLEM SOLVING with DISTINCT activities like: n n n n Systems Analysis Systems Design Programming Testing Conversion Production Maintenance
 Software System Development o Activities here take place in SEQUENTIAL ORDER. o But, some of these activities may be repeated or take place simultaneously, depending on the approach to system building.
Software System Development o Activities here take place in SEQUENTIAL ORDER. o But, some of these activities may be repeated or take place simultaneously, depending on the approach to system building.
 Systems Analysis o The analysis of the problem to be solved with an information system. n n Defining the problem Identifying the causes Specifying the solution (several alternative solutions) Identifying the information requirements to be met. o Create a road map of existing organisation and system n n Identify the primary owners and users of data Identify the existing hardware and software. o Detail the problems of existing system n n n Examine documents, work papers, procedures Observe system operations Interview key users of the systems o Identify the problem areas and objectives of the solution n n Building a new IS Improving an existing IS
Systems Analysis o The analysis of the problem to be solved with an information system. n n Defining the problem Identifying the causes Specifying the solution (several alternative solutions) Identifying the information requirements to be met. o Create a road map of existing organisation and system n n Identify the primary owners and users of data Identify the existing hardware and software. o Detail the problems of existing system n n n Examine documents, work papers, procedures Observe system operations Interview key users of the systems o Identify the problem areas and objectives of the solution n n Building a new IS Improving an existing IS
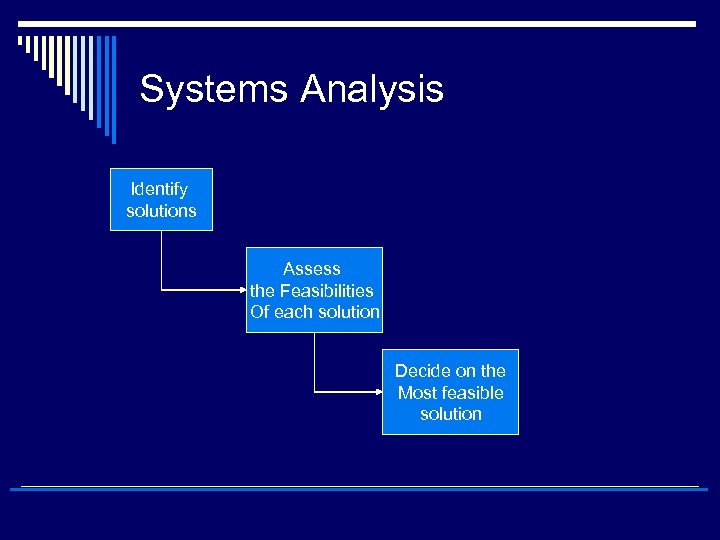 Systems Analysis Identify solutions Assess the Feasibilities Of each solution Decide on the Most feasible solution
Systems Analysis Identify solutions Assess the Feasibilities Of each solution Decide on the Most feasible solution
 Systems Analysis o Systems analysis include a FEASIBILITY STUDY Is the solution feasible? n Is the solution achievable? (Financial, technical, organisational standpoints) n o Feasibility study n n Is the proposed system a good investment? Is the technology needed for the system available? Can the technology needed be handled by the firms’ IT professionals? Can the organisation handle the changes brought by the system? o Written systems proposal report describing the costs and benefits, pros and cons of alternatives. n Management assessment
Systems Analysis o Systems analysis include a FEASIBILITY STUDY Is the solution feasible? n Is the solution achievable? (Financial, technical, organisational standpoints) n o Feasibility study n n Is the proposed system a good investment? Is the technology needed for the system available? Can the technology needed be handled by the firms’ IT professionals? Can the organisation handle the changes brought by the system? o Written systems proposal report describing the costs and benefits, pros and cons of alternatives. n Management assessment
 Systems Analysis Establishing Information Requirements o Hardest task – what a system should do to meet information requirements o Who needs n n What information? Where? When? How? o Carefully define the objectives of the system o Develop a detailed description of functions that the system should perform n Faulty requirements analysis is a leading cause of systems failure and high costs p p Either be discarded because of poor performance Or undergo major modifications o Alternative approaches for requirements analysis
Systems Analysis Establishing Information Requirements o Hardest task – what a system should do to meet information requirements o Who needs n n What information? Where? When? How? o Carefully define the objectives of the system o Develop a detailed description of functions that the system should perform n Faulty requirements analysis is a leading cause of systems failure and high costs p p Either be discarded because of poor performance Or undergo major modifications o Alternative approaches for requirements analysis
 Software System Development Term Project Scope
Software System Development Term Project Scope
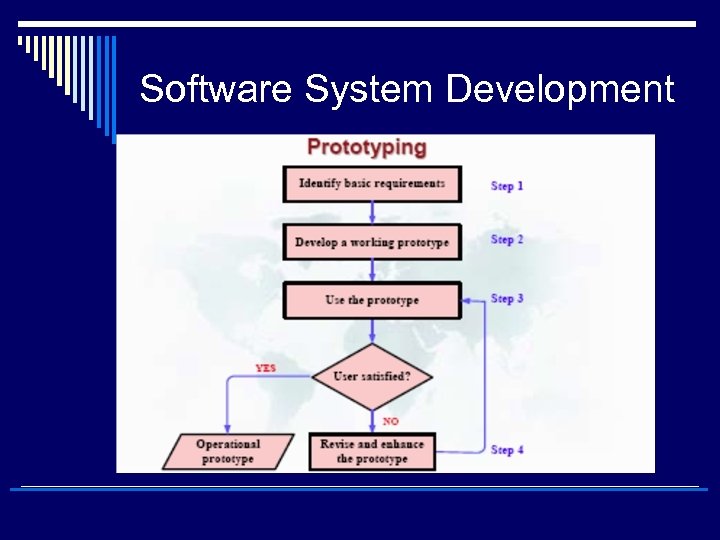 Software System Development
Software System Development
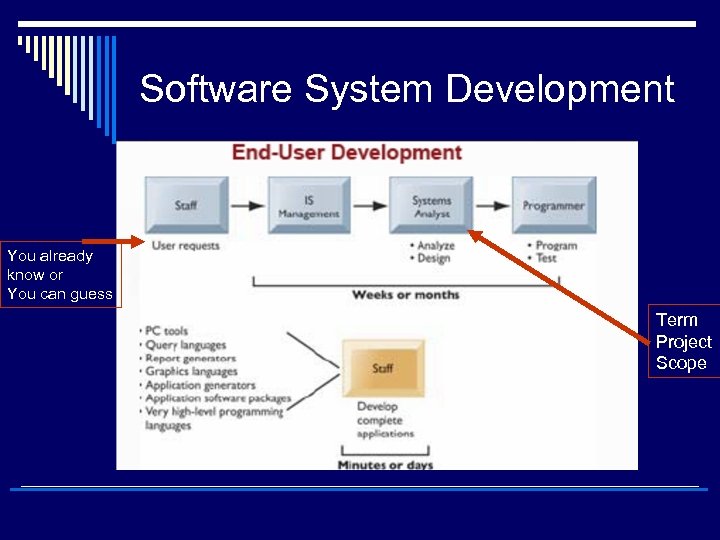 Software System Development You already know or You can guess Term Project Scope
Software System Development You already know or You can guess Term Project Scope
 Systems Design o Shows how the system will fulfill the objective of systems analysis o Systems design is the OVERALL PLAN or MODEL FOR THE SYSTEM n n n Like Blue print of a building Consists of all specifications that give the system its FORM and STRUCTURE Carefully define the objectives of the system o Detail the system specifications that will deliver the functions identified during the systems analysis n Specs should adress all components of the system solution p p p Managerial Organisational Technological o Alternative approaches for requirements analysis
Systems Design o Shows how the system will fulfill the objective of systems analysis o Systems design is the OVERALL PLAN or MODEL FOR THE SYSTEM n n n Like Blue print of a building Consists of all specifications that give the system its FORM and STRUCTURE Carefully define the objectives of the system o Detail the system specifications that will deliver the functions identified during the systems analysis n Specs should adress all components of the system solution p p p Managerial Organisational Technological o Alternative approaches for requirements analysis
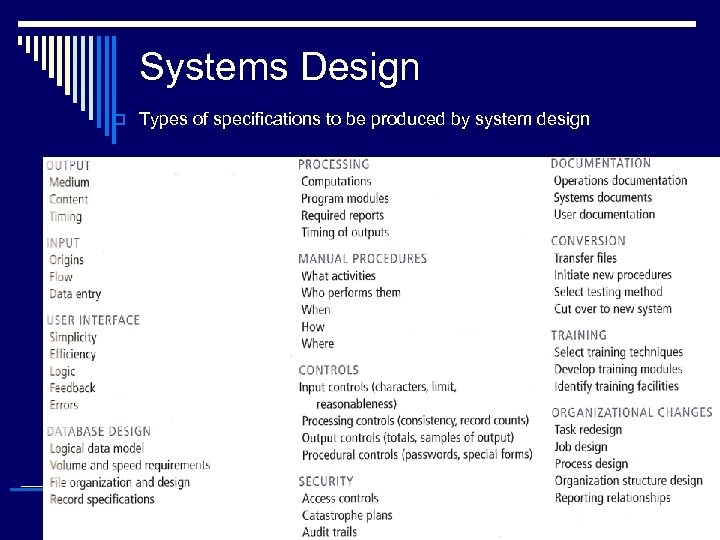 Systems Design o Types of specifications to be produced by system design
Systems Design o Types of specifications to be produced by system design
 Systems Design o Shows how the system will fulfill the objective of systems analysis o Systems design is the OVERALL PLAN or MODEL FOR THE SYSTEM n n n Like Blue print of a building – like houses and buildings IS may have many possible designs Consists of all specifications that give the system its FORM and STRUCTURE Carefully define the objectives of the system o Detail the system specifications that will deliver the functions identified during the systems analysis n Specs should adress all components of the system solution p p p Managerial Organisational Technological o Each design represents a unique blend of all components o Superior design is the “easy and efficient” design that n n fulfills USER REQUIREMENTS Within a specific set of CONSTRAINTS (technical, organisational, financial, time)
Systems Design o Shows how the system will fulfill the objective of systems analysis o Systems design is the OVERALL PLAN or MODEL FOR THE SYSTEM n n n Like Blue print of a building – like houses and buildings IS may have many possible designs Consists of all specifications that give the system its FORM and STRUCTURE Carefully define the objectives of the system o Detail the system specifications that will deliver the functions identified during the systems analysis n Specs should adress all components of the system solution p p p Managerial Organisational Technological o Each design represents a unique blend of all components o Superior design is the “easy and efficient” design that n n fulfills USER REQUIREMENTS Within a specific set of CONSTRAINTS (technical, organisational, financial, time)
 Systems Design – Role of End Users o User information requirements drive the entire system-building effort o Users must have sufficient control over the design process to ensure the system reflects their priorities and information needs n Not the biases of technical staff o Working on design increases users’ understanding and acceptance of the system o Insufficient user involvement in the design effort is a major cause of system failure n USer participation in alternative system development methods
Systems Design – Role of End Users o User information requirements drive the entire system-building effort o Users must have sufficient control over the design process to ensure the system reflects their priorities and information needs n Not the biases of technical staff o Working on design increases users’ understanding and acceptance of the system o Insufficient user involvement in the design effort is a major cause of system failure n USer participation in alternative system development methods
 Completing the systems development process o Remaining steps in systems development process translate the solution specs established in systems analysis and design into a fully operational information system n n n Programming Testing Conversion Production Maintenance
Completing the systems development process o Remaining steps in systems development process translate the solution specs established in systems analysis and design into a fully operational information system n n n Programming Testing Conversion Production Maintenance
 Systems Programming o System specs are translated into software program code. May be ; n n Outsourced Purchase of the software package from a vendor Purchase of software services from ASP (Application Service Provider) Developed in-house
Systems Programming o System specs are translated into software program code. May be ; n n Outsourced Purchase of the software package from a vendor Purchase of software services from ASP (Application Service Provider) Developed in-house
 Testing o Exhaustive and thorough testing to ascertaion whether the system produces the right results n Will the system produce the desired results under known conditions? o Do not underrate the time needed for testing in project plan o Test data must be carefully prepared o Results must be reviewed o Corrections must be made n Maybe a part of the system will be redesigned
Testing o Exhaustive and thorough testing to ascertaion whether the system produces the right results n Will the system produce the desired results under known conditions? o Do not underrate the time needed for testing in project plan o Test data must be carefully prepared o Results must be reviewed o Corrections must be made n Maybe a part of the system will be redesigned
 Testing Steps o 1. Unit Testing (Program testing) n Testing each program separately in the system p p o 2. Systems Testing n n n Testing the functioning to the IS as a whole. Try to determine whether the discrete modules function together as planned Try to determine discrepencies that exist between the way system works and the way it was conceived p p p o to locate errors in the programs To focus on finding all the ways to make a program fail (Not to quarantee that programs are error free- it is impossible) Find the problem, than correct it Performance time Capacity for file storage Handling peak loads REcovery and start capabilities Manual procedures 3. Acceptance Testing n n Final certification of the system – ready to be used in production Acceptance tests are evaluated by users and reviewed by management- all parties should be satisfied
Testing Steps o 1. Unit Testing (Program testing) n Testing each program separately in the system p p o 2. Systems Testing n n n Testing the functioning to the IS as a whole. Try to determine whether the discrete modules function together as planned Try to determine discrepencies that exist between the way system works and the way it was conceived p p p o to locate errors in the programs To focus on finding all the ways to make a program fail (Not to quarantee that programs are error free- it is impossible) Find the problem, than correct it Performance time Capacity for file storage Handling peak loads REcovery and start capabilities Manual procedures 3. Acceptance Testing n n Final certification of the system – ready to be used in production Acceptance tests are evaluated by users and reviewed by management- all parties should be satisfied
 Testing Steps o Work with users to devise a systematic test plan o Test plan includes all preperations of all testing types
Testing Steps o Work with users to devise a systematic test plan o Test plan includes all preperations of all testing types
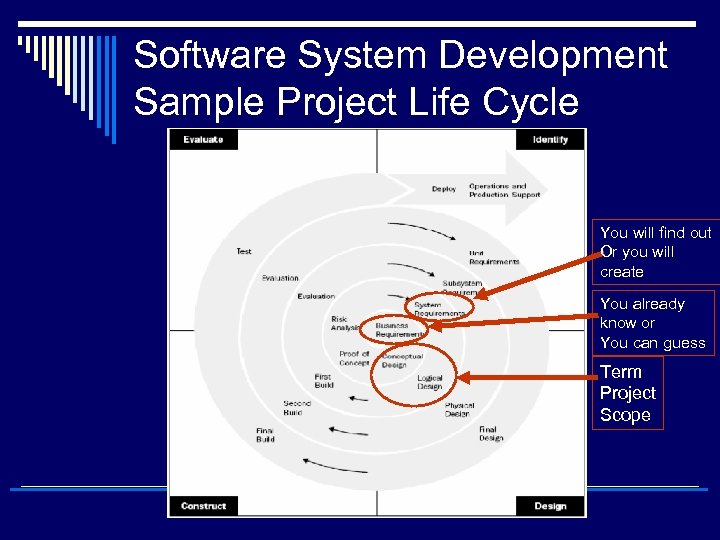 Software System Development Sample Project Life Cycle You will find out Or you will create You already know or You can guess Term Project Scope
Software System Development Sample Project Life Cycle You will find out Or you will create You already know or You can guess Term Project Scope
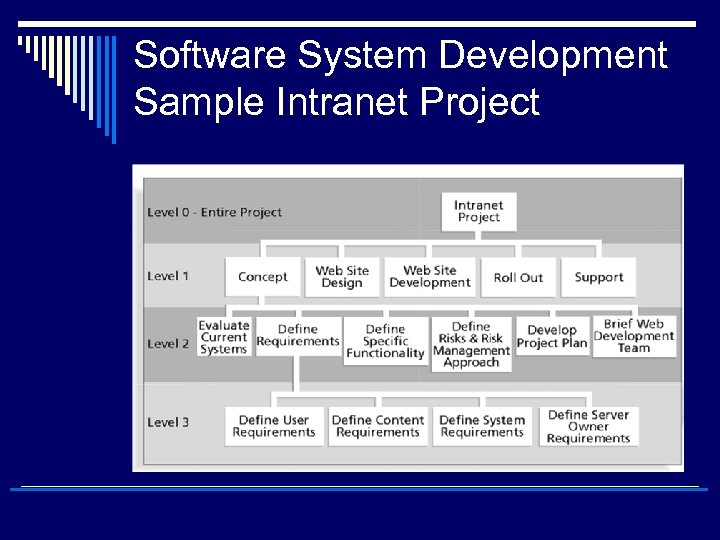 Software System Development Sample Intranet Project
Software System Development Sample Intranet Project
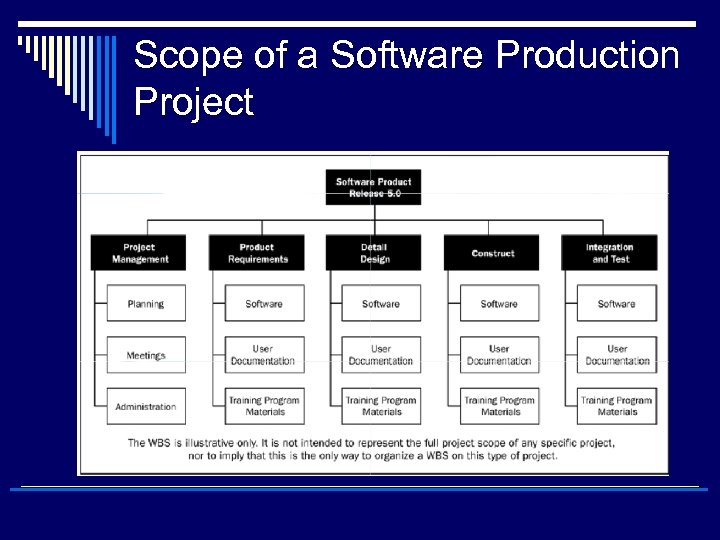 Scope of a Software Production Project
Scope of a Software Production Project
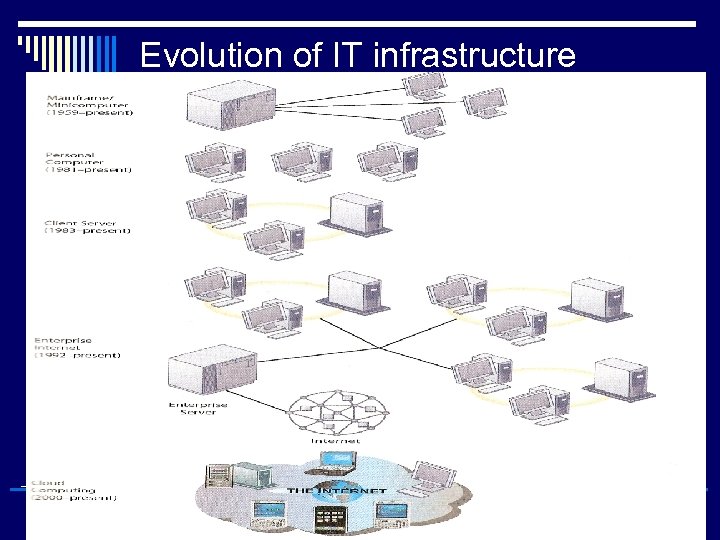 Evolution of IT infrastructure
Evolution of IT infrastructure
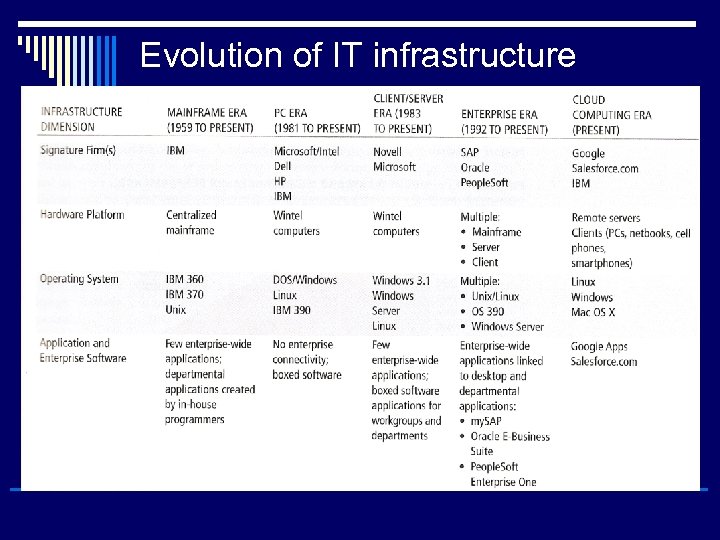 Evolution of IT infrastructure
Evolution of IT infrastructure
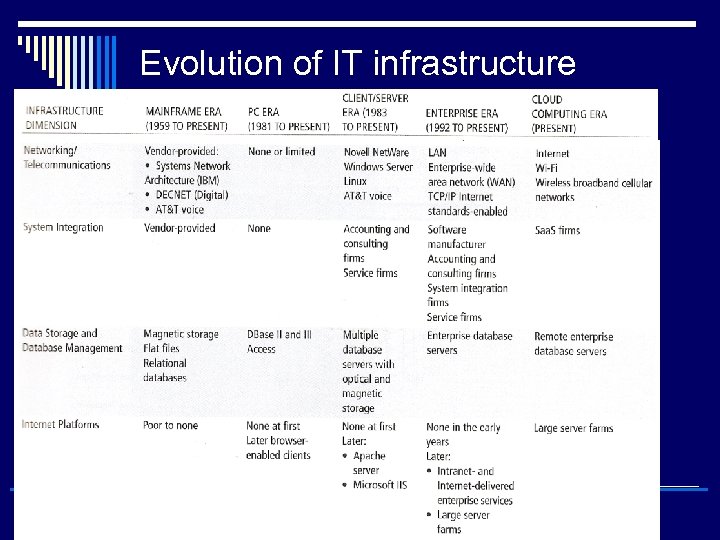 Evolution of IT infrastructure
Evolution of IT infrastructure


