a202f5afe060682ab2ef74cc06e487bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Information Systems Project Management MIT-M Chiangmai University Project organization Project Leader , Project manager , Project team Project Selection and Approval ครงท 2 วนท 7 กมภาพนธ 2559
Information Systems Project Management MIT-M Chiangmai University Project organization Project Leader , Project manager , Project team Project Selection and Approval ครงท 2 วนท 7 กมภาพนธ 2559
 วนนไปวดมาหร อยง ไปวดกอนมทก ข ใหพระนำตอนมช วตอย ทำงานหนกตอนม เวลากอนสอบ วนนกบอกไมมเวลาไป ไปวดตอนมทกข ใหพระนำตอนไมมชว ขอพระชวยตอนหมดเ
วนนไปวดมาหร อยง ไปวดกอนมทก ข ใหพระนำตอนมช วตอย ทำงานหนกตอนม เวลากอนสอบ วนนกบอกไมมเวลาไป ไปวดตอนมทกข ใหพระนำตอนไมมชว ขอพระชวยตอนหมดเ

 Quotes…. . • If you always blame others for your mistakes, you will never improve. • To get a project off the ground, tell a colleague it was their idea. They will put their heart and soul into making it successful.
Quotes…. . • If you always blame others for your mistakes, you will never improve. • To get a project off the ground, tell a colleague it was their idea. They will put their heart and soul into making it successful.
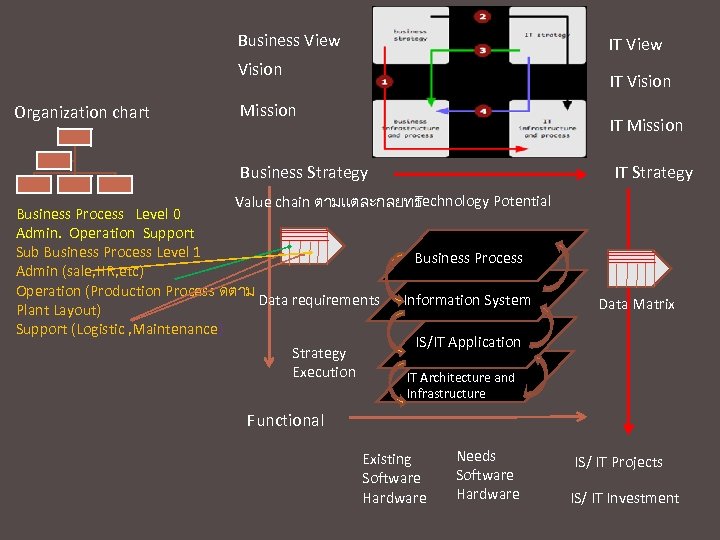 Business View IT View Vision Organization chart IT Vision Mission IT Strategy Business Strategy Technology Potential Value chain ตามแตละกลยทธ Business Process Level 0 Admin. Operation Support Sub Business Process Level 1 Business Process Admin (sale, HR, etc) Operation (Production Process ดตาม Data requirements Information System Plant Layout) Support (Logistic , Maintenance) IS/IT Application Strategy Execution IT Architecture and Data Matrix Infrastructure Functional Existing Software Hardware Needs Software Hardware IS/ IT Projects IS/ IT Investment
Business View IT View Vision Organization chart IT Vision Mission IT Strategy Business Strategy Technology Potential Value chain ตามแตละกลยทธ Business Process Level 0 Admin. Operation Support Sub Business Process Level 1 Business Process Admin (sale, HR, etc) Operation (Production Process ดตาม Data requirements Information System Plant Layout) Support (Logistic , Maintenance) IS/IT Application Strategy Execution IT Architecture and Data Matrix Infrastructure Functional Existing Software Hardware Needs Software Hardware IS/ IT Projects IS/ IT Investment
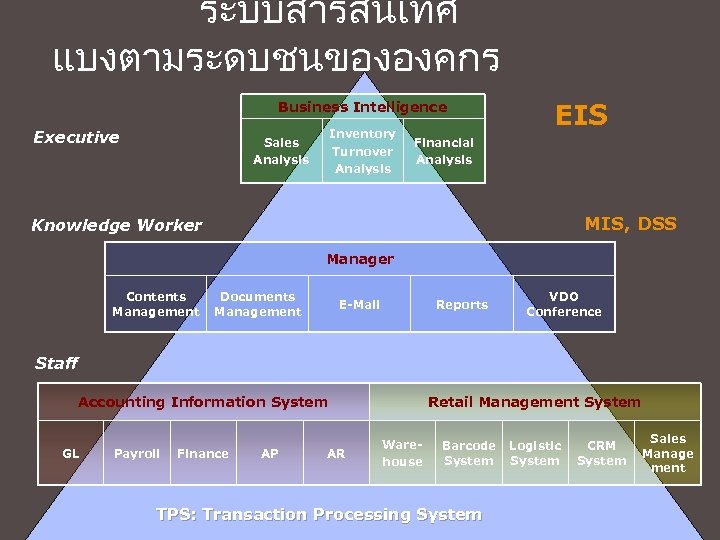 ระบบสารสนเทศ แบงตามระดบชนขององคกร Business Intelligence Executive Inventory Turnover Analysis Sales Analysis EIS Financial Analysis MIS, DSS Knowledge Worker Manager Contents Management Documents Management E-Mail Reports VDO Conference Staff Accounting Information System GL Payroll Finance AP AR Retail Management System Warehouse Barcode System TPS: Transaction Processing System Logistic System CRM System Sales Manage ment
ระบบสารสนเทศ แบงตามระดบชนขององคกร Business Intelligence Executive Inventory Turnover Analysis Sales Analysis EIS Financial Analysis MIS, DSS Knowledge Worker Manager Contents Management Documents Management E-Mail Reports VDO Conference Staff Accounting Information System GL Payroll Finance AP AR Retail Management System Warehouse Barcode System TPS: Transaction Processing System Logistic System CRM System Sales Manage ment
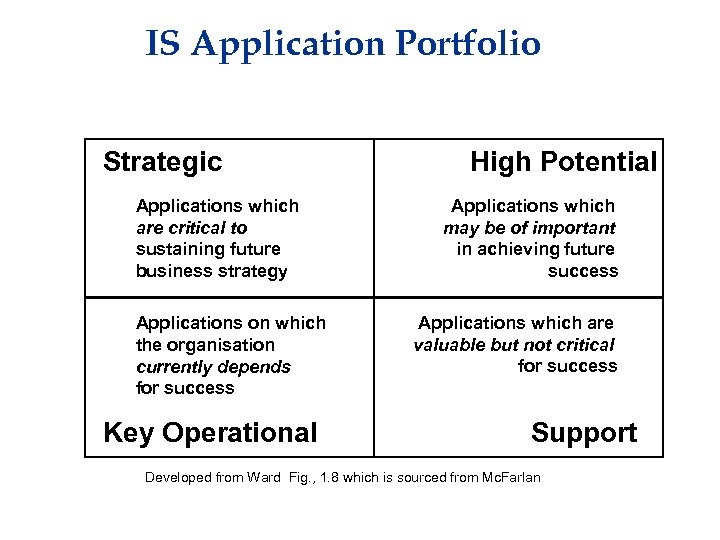 IS Application Portfolio Strategic Applications which are critical to sustaining future business strategy Applications on which the organisation currently depends for success Key Operational High Potential Applications which may be of important in achieving future success Applications which are valuable but not critical for success Support Developed from Ward Fig. , 1. 8 which is sourced from Mc. Farlan
IS Application Portfolio Strategic Applications which are critical to sustaining future business strategy Applications on which the organisation currently depends for success Key Operational High Potential Applications which may be of important in achieving future success Applications which are valuable but not critical for success Support Developed from Ward Fig. , 1. 8 which is sourced from Mc. Farlan
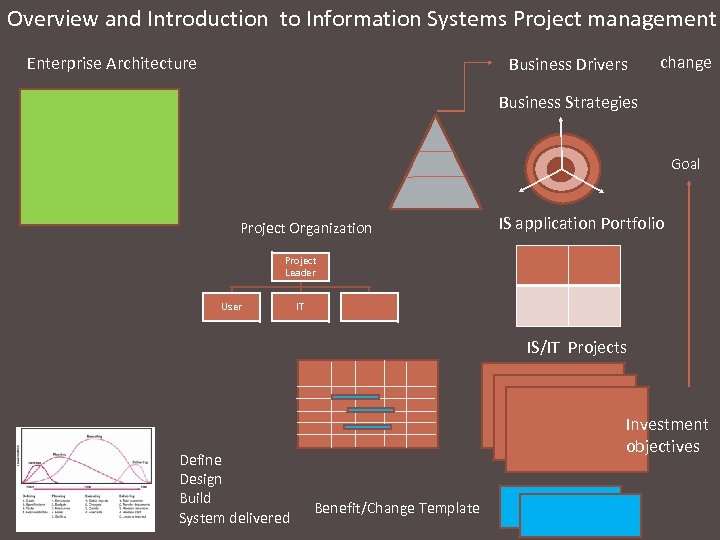 Overview and Introduction to Information Systems Project management Enterprise Architecture Business Drivers change Business Strategies Goal Project Organization IS application Portfolio Project Leader User IT IS/IT Projects Define Design Build System delivered Investment objectives Benefit/Change Template
Overview and Introduction to Information Systems Project management Enterprise Architecture Business Drivers change Business Strategies Goal Project Organization IS application Portfolio Project Leader User IT IS/IT Projects Define Design Build System delivered Investment objectives Benefit/Change Template
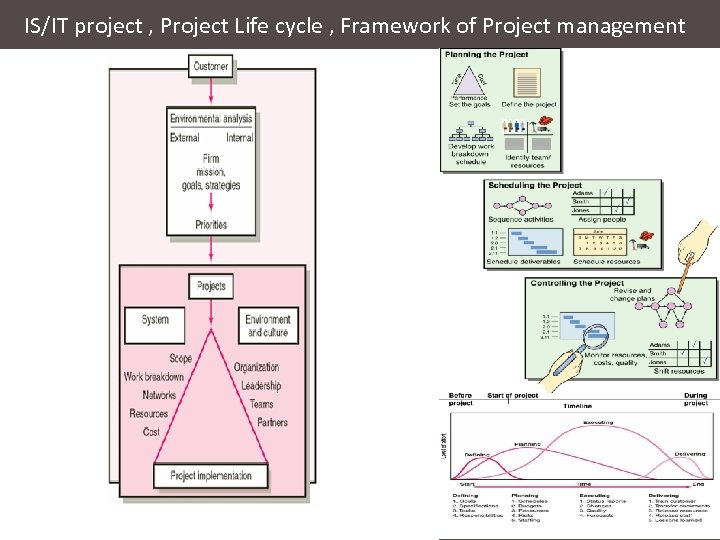 IS/IT project , Project Life cycle , Framework of Project management
IS/IT project , Project Life cycle , Framework of Project management
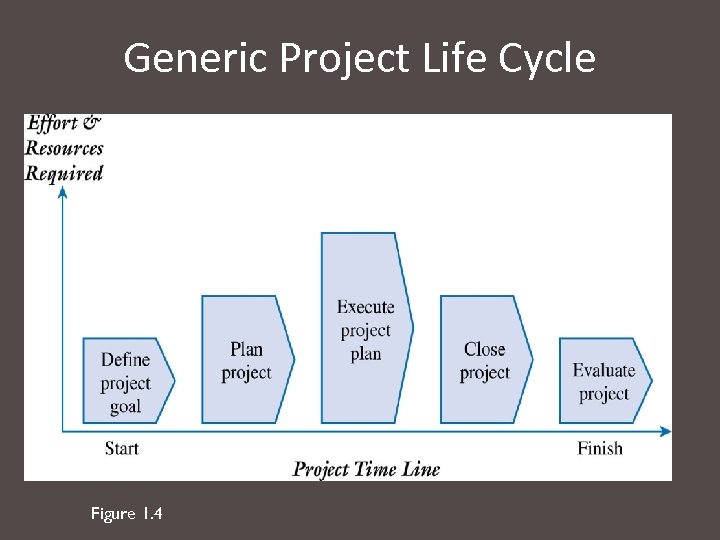 Generic Project Life Cycle Figure 1. 4
Generic Project Life Cycle Figure 1. 4
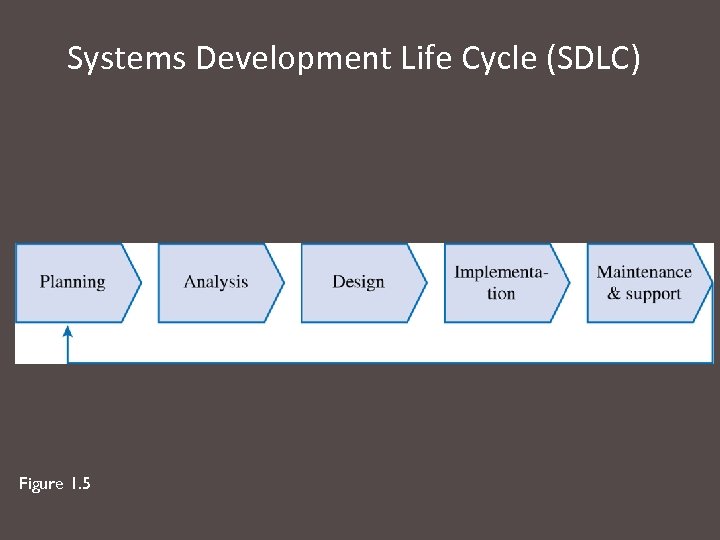 Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Figure 1. 5
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Figure 1. 5
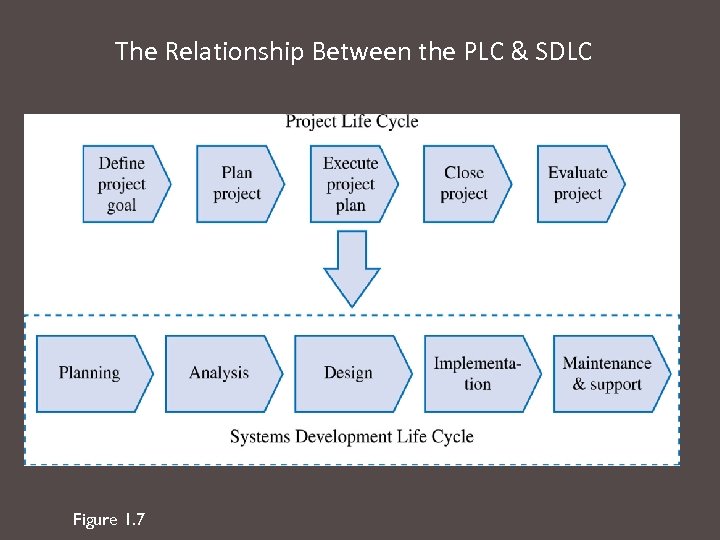 The Relationship Between the PLC & SDLC Figure 1. 7
The Relationship Between the PLC & SDLC Figure 1. 7
 หวขอวนน 1. อ. เดชนะ มาคยเรอง การบรหารโครงการอยางไรใหสำเรจดวยทมโ ครงการ นกศกษาฟงจบแลวใหสรปเนอหาสงเปนก ลม และนำไปเปนแนวทางประยกตใชในกลมตวเ อง 2. สงรายชอกลมและเสนอหวขอโครงการในรป ของ Power point 3. มาวเคราะหและอภปรายโครงการทเสนอ 1. Project Idea
หวขอวนน 1. อ. เดชนะ มาคยเรอง การบรหารโครงการอยางไรใหสำเรจดวยทมโ ครงการ นกศกษาฟงจบแลวใหสรปเนอหาสงเปนก ลม และนำไปเปนแนวทางประยกตใชในกลมตวเ อง 2. สงรายชอกลมและเสนอหวขอโครงการในรป ของ Power point 3. มาวเคราะหและอภปรายโครงการทเสนอ 1. Project Idea
 หวขอวนน 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Project Ideas Project Screening Project Selection and Approval Project Organization Project Leader Project Manager Project Team
หวขอวนน 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Project Ideas Project Screening Project Selection and Approval Project Organization Project Leader Project Manager Project Team
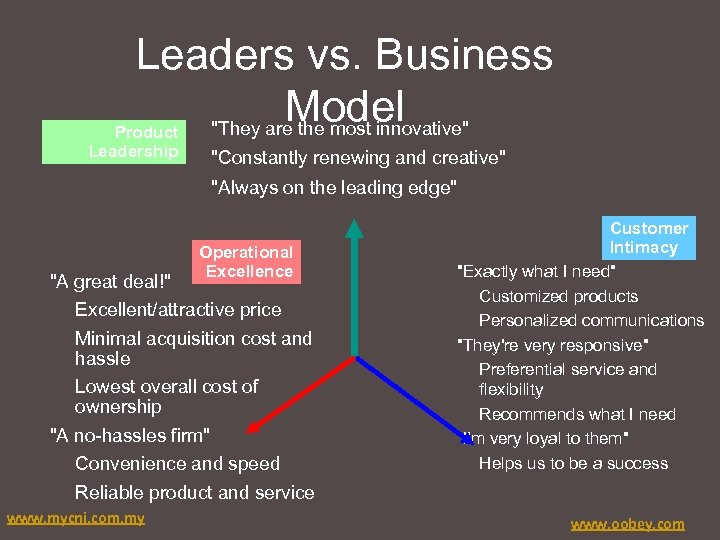 Leaders vs. Business Model "They are the most innovative" Product Leadership "Constantly renewing and creative" "Always on the leading edge" "A great deal!" Operational Excellence Excellent/attractive price Minimal acquisition cost and hassle Lowest overall cost of ownership "A no-hassles firm" Convenience and speed Customer Intimacy "Exactly what I need" Customized products Personalized communications "They're very responsive" Preferential service and flexibility Recommends what I need "I'm very loyal to them" Helps us to be a success Reliable product and service www. mycni. com. my www. oobey. com
Leaders vs. Business Model "They are the most innovative" Product Leadership "Constantly renewing and creative" "Always on the leading edge" "A great deal!" Operational Excellence Excellent/attractive price Minimal acquisition cost and hassle Lowest overall cost of ownership "A no-hassles firm" Convenience and speed Customer Intimacy "Exactly what I need" Customized products Personalized communications "They're very responsive" Preferential service and flexibility Recommends what I need "I'm very loyal to them" Helps us to be a success Reliable product and service www. mycni. com. my www. oobey. com
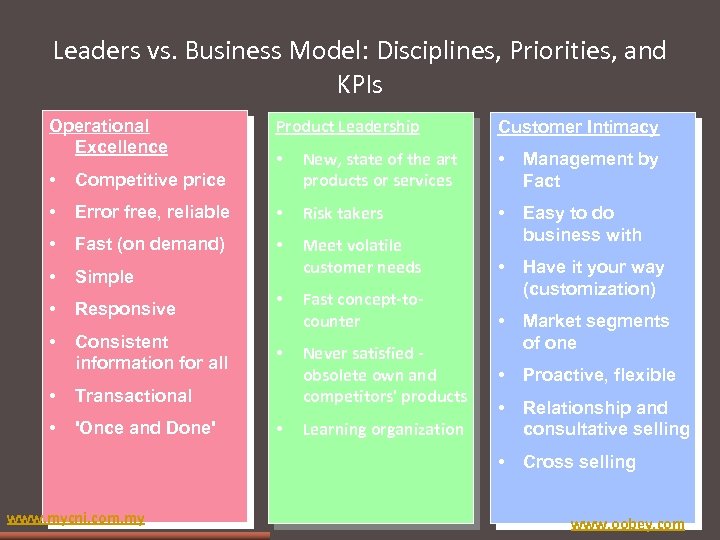 Leaders vs. Business Model: Disciplines, Priorities, and KPIs Operational Excellence Product Leadership Customer Intimacy • New, state of the art products or services • Management by Fact • Competitive price • Error free, reliable • Risk takers • • Fast (on demand) • • Simple Meet volatile customer needs Easy to do business with • • Responsive • • Consistent information for all Fast concept-to- counter Have it your way (customization) Market segments of one • Proactive, flexible • Relationship and consultative selling • Cross selling • 'Once and Done' • Transactional • • www. mycni. com. my • Never satisfied - obsolete own and competitors' products Learning organization www. oobey. com
Leaders vs. Business Model: Disciplines, Priorities, and KPIs Operational Excellence Product Leadership Customer Intimacy • New, state of the art products or services • Management by Fact • Competitive price • Error free, reliable • Risk takers • • Fast (on demand) • • Simple Meet volatile customer needs Easy to do business with • • Responsive • • Consistent information for all Fast concept-to- counter Have it your way (customization) Market segments of one • Proactive, flexible • Relationship and consultative selling • Cross selling • 'Once and Done' • Transactional • • www. mycni. com. my • Never satisfied - obsolete own and competitors' products Learning organization www. oobey. com
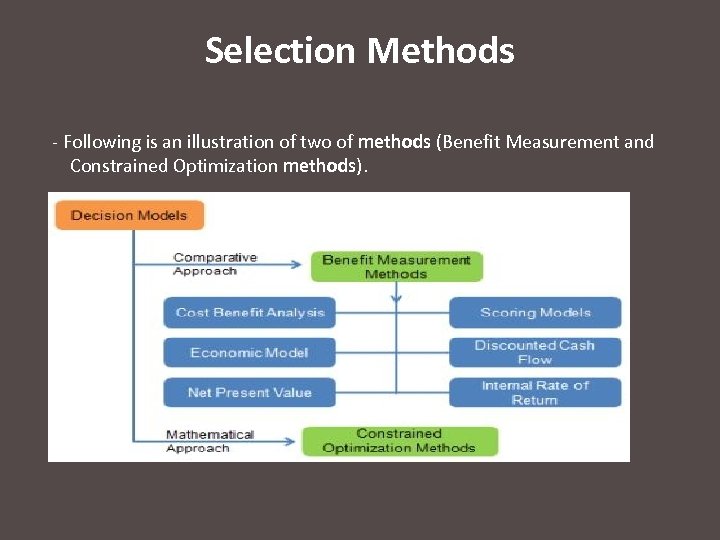 Selection Methods - Following is an illustration of two of methods (Benefit Measurement and Constrained Optimization methods).
Selection Methods - Following is an illustration of two of methods (Benefit Measurement and Constrained Optimization methods).
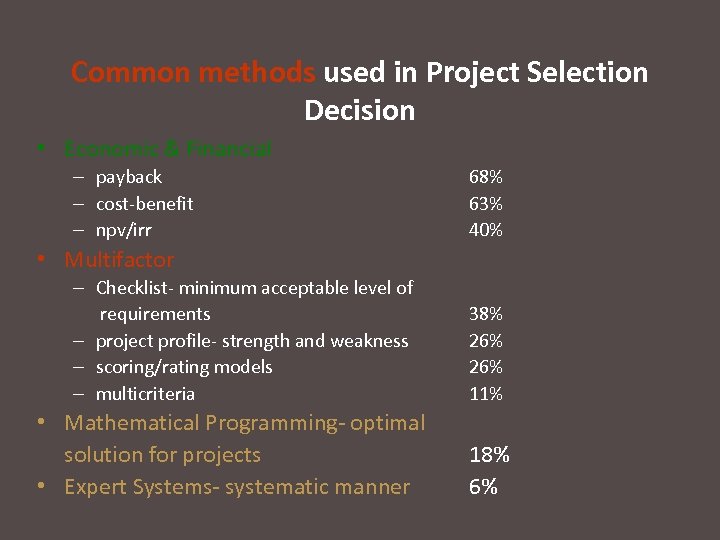 Common methods used in Project Selection Decision • Economic & Financial – payback – cost-benefit – npv/irr 68% 63% 40% • Multifactor – Checklist- minimum acceptable level of requirements – project profile- strength and weakness – scoring/rating models – multicriteria • Mathematical Programming- optimal solution for projects • Expert Systems- systematic manner 38% 26% 11% 18% 6%
Common methods used in Project Selection Decision • Economic & Financial – payback – cost-benefit – npv/irr 68% 63% 40% • Multifactor – Checklist- minimum acceptable level of requirements – project profile- strength and weakness – scoring/rating models – multicriteria • Mathematical Programming- optimal solution for projects • Expert Systems- systematic manner 38% 26% 11% 18% 6%
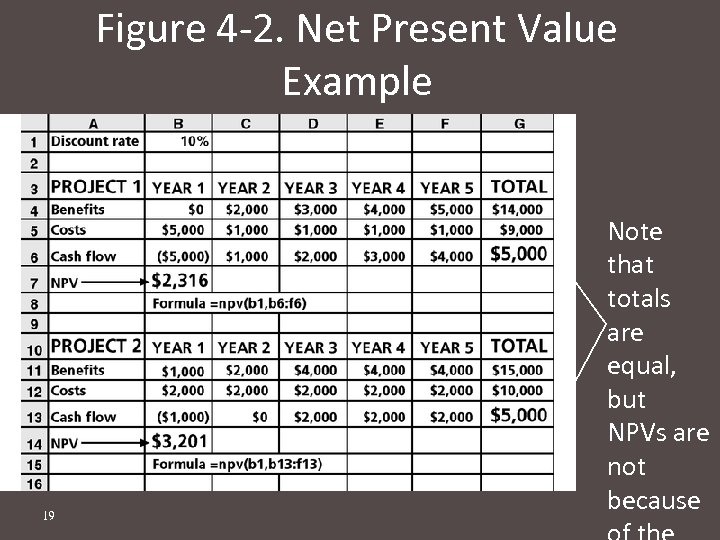 Figure 4 -2. Net Present Value Example 19 Note that totals are equal, but NPVs are not because
Figure 4 -2. Net Present Value Example 19 Note that totals are equal, but NPVs are not because
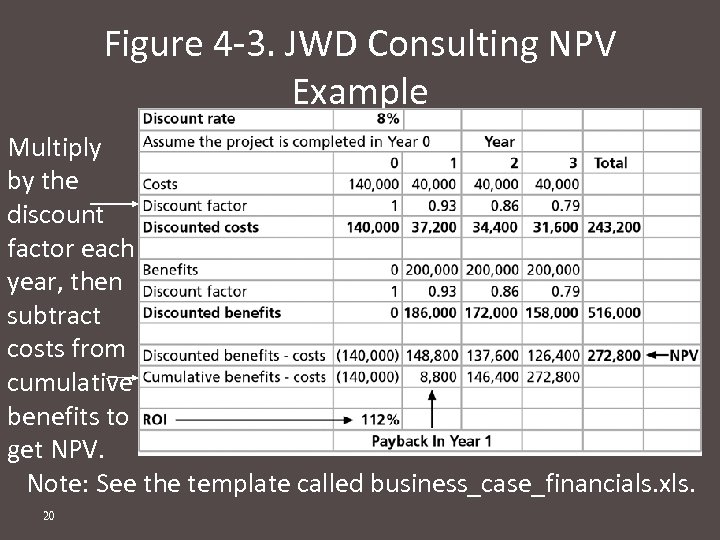 Figure 4 -3. JWD Consulting NPV Example Multiply by the discount factor each year, then subtract costs from cumulative benefits to get NPV. Note: See the template called business_case_financials. xls. 20
Figure 4 -3. JWD Consulting NPV Example Multiply by the discount factor each year, then subtract costs from cumulative benefits to get NPV. Note: See the template called business_case_financials. xls. 20
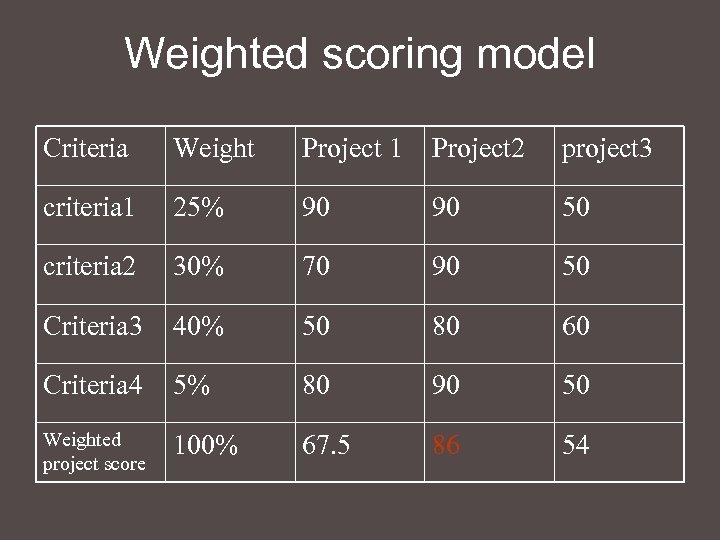 Weighted scoring model Criteria Weight Project 1 Project 2 project 3 criteria 1 25% 90 90 50 criteria 2 30% 70 90 50 Criteria 3 40% 50 80 60 Criteria 4 5% 80 90 50 Weighted project score 100% 67. 5 86 54
Weighted scoring model Criteria Weight Project 1 Project 2 project 3 criteria 1 25% 90 90 50 criteria 2 30% 70 90 50 Criteria 3 40% 50 80 60 Criteria 4 5% 80 90 50 Weighted project score 100% 67. 5 86 54
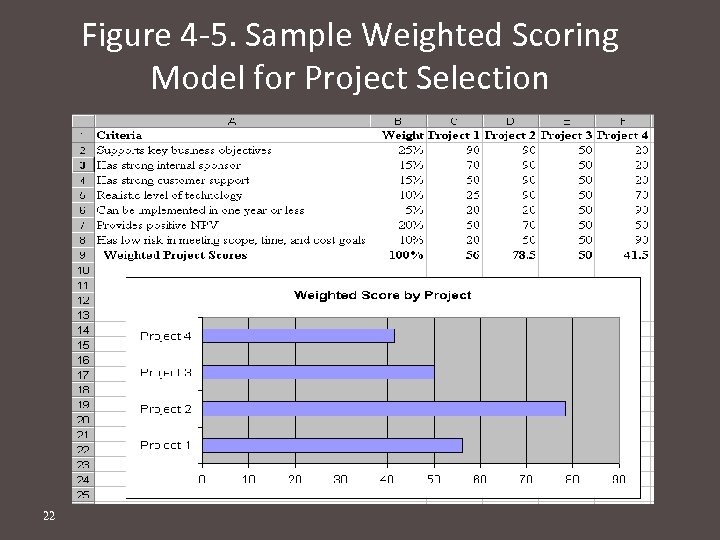 Figure 4 -5. Sample Weighted Scoring Model for Project Selection 22
Figure 4 -5. Sample Weighted Scoring Model for Project Selection 22
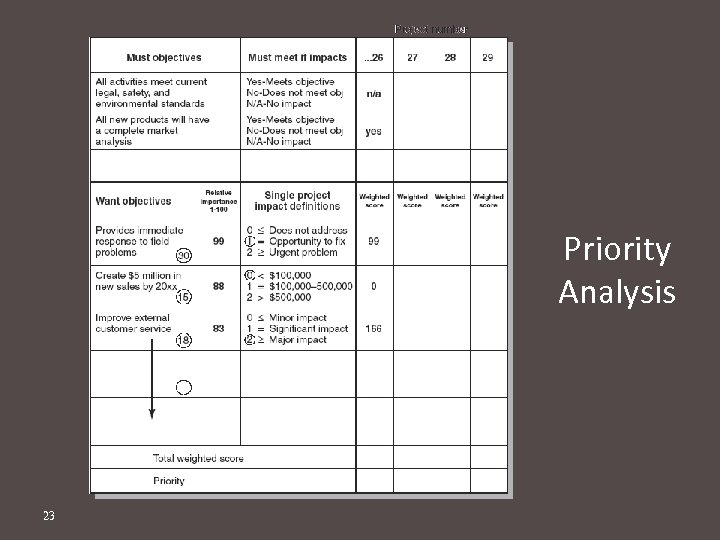 Priority Analysis 23
Priority Analysis 23
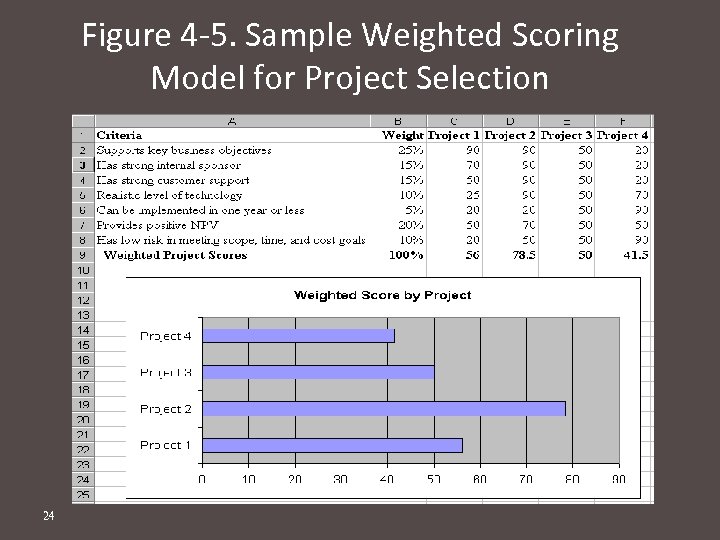 Figure 4 -5. Sample Weighted Scoring Model for Project Selection 24
Figure 4 -5. Sample Weighted Scoring Model for Project Selection 24
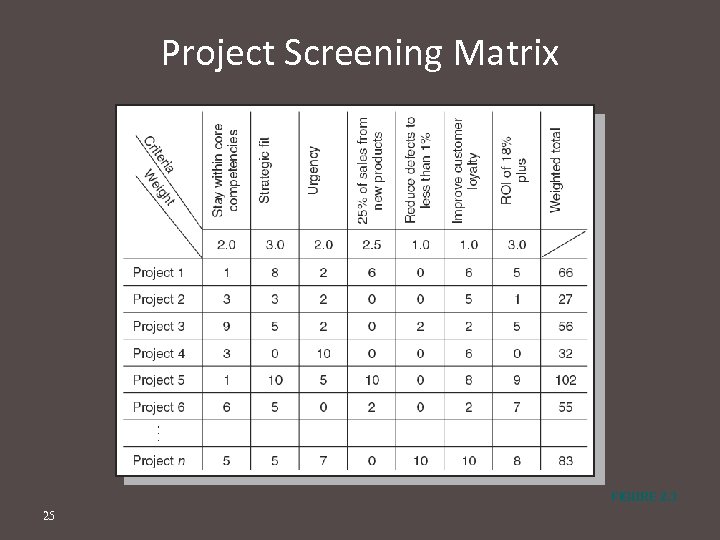 Project Screening Matrix FIGURE 2. 3 25
Project Screening Matrix FIGURE 2. 3 25
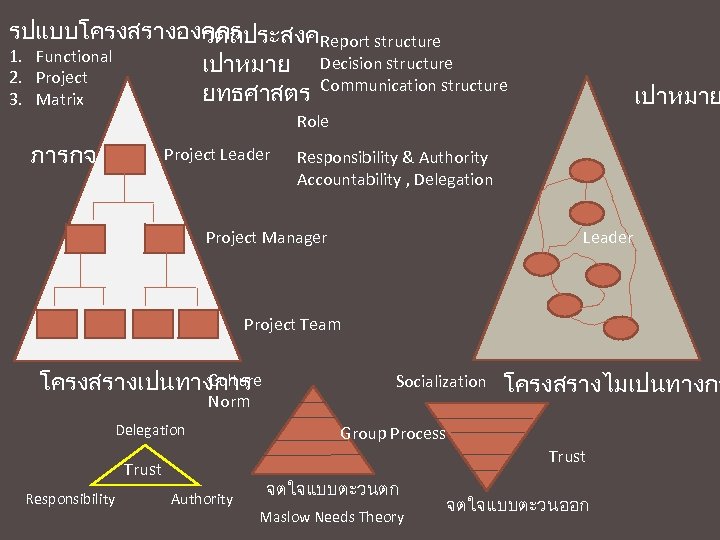 รปแบบโครงสรางองคกร วตถประสงคReport structure 1. Functional เปาหมาย Decision structure 2. Project ยทธศาสตร Communication structure 3. Matrix เปาหมาย Role ภารกจ Project Leader Responsibility & Authority Accountability , Delegation Project Manager Leader Project Team Culture โครงสรางเปนทางการ Norm Delegation โครงสรางไมเปนทางกา Group Process Trust Responsibility Socialization Authority จตใจแบบตะวนตก Maslow Needs Theory จตใจแบบตะวนออก
รปแบบโครงสรางองคกร วตถประสงคReport structure 1. Functional เปาหมาย Decision structure 2. Project ยทธศาสตร Communication structure 3. Matrix เปาหมาย Role ภารกจ Project Leader Responsibility & Authority Accountability , Delegation Project Manager Leader Project Team Culture โครงสรางเปนทางการ Norm Delegation โครงสรางไมเปนทางกา Group Process Trust Responsibility Socialization Authority จตใจแบบตะวนตก Maslow Needs Theory จตใจแบบตะวนออก
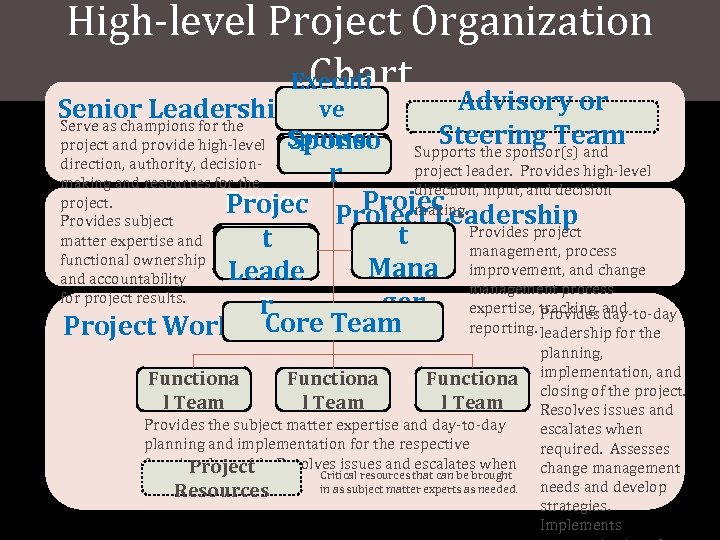 High-level Project Organization Chart Executi Advisory or Senior Leadership ve Serve as champions for the Steering Team Sponso Supports the sponsor(s) and project and provide high-level Sponsor direction, authority, decisionproject leader. Provides high-level r making and resources for the direction, input, and decision project. Project Leadership making. Provides subject Provides project t t matter expertise and management, process functional ownership Mana improvement, and change Leade and accountability management process for project results. ger r expertise, tracking, and Provides day-to-day Core Team reporting. leadership for the Project Work Teams Functiona l Team Provides the subject matter expertise and day-to-day planning and implementation for the respective functional area(s). Resolves issues and escalates when Project Critical resources that can be brought required. in as subject matter experts as needed. Resources planning, implementation, and closing of the project. Resolves issues and escalates when required. Assesses change management needs and develop strategies. Implements
High-level Project Organization Chart Executi Advisory or Senior Leadership ve Serve as champions for the Steering Team Sponso Supports the sponsor(s) and project and provide high-level Sponsor direction, authority, decisionproject leader. Provides high-level r making and resources for the direction, input, and decision project. Project Leadership making. Provides subject Provides project t t matter expertise and management, process functional ownership Mana improvement, and change Leade and accountability management process for project results. ger r expertise, tracking, and Provides day-to-day Core Team reporting. leadership for the Project Work Teams Functiona l Team Provides the subject matter expertise and day-to-day planning and implementation for the respective functional area(s). Resolves issues and escalates when Project Critical resources that can be brought required. in as subject matter experts as needed. Resources planning, implementation, and closing of the project. Resolves issues and escalates when required. Assesses change management needs and develop strategies. Implements
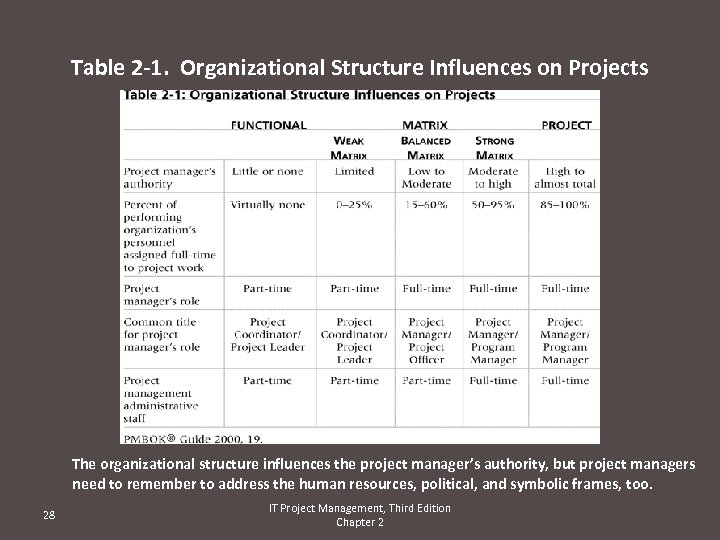 Table 2 -1. Organizational Structure Influences on Projects The organizational structure influences the project manager’s authority, but project managers need to remember to address the human resources, political, and symbolic frames, too. 28 IT Project Management, Third Edition Chapter 2
Table 2 -1. Organizational Structure Influences on Projects The organizational structure influences the project manager’s authority, but project managers need to remember to address the human resources, political, and symbolic frames, too. 28 IT Project Management, Third Edition Chapter 2
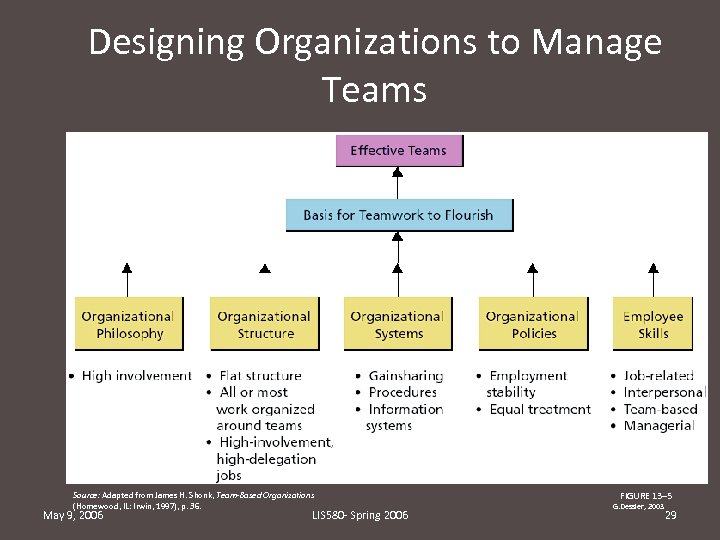 Designing Organizations to Manage Teams Source: Adapted from James H. Shonk, Team-Based Organizations (Homewood, IL: Irwin, 1997), p. 36. May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 FIGURE 13– 5 G. Dessler, 2003 29
Designing Organizations to Manage Teams Source: Adapted from James H. Shonk, Team-Based Organizations (Homewood, IL: Irwin, 1997), p. 36. May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 FIGURE 13– 5 G. Dessler, 2003 29
 Managing & Leading “Managers are people who do things right and leaders are people who do the right thing. ” – Bennis and Nanus, 1985 “Most U. S. corporations today are over-managed and under led. ” – Kotter, Harvard Business Review 2001 l l l Enforcing Standards Resolving Issues Budgeting Planning Reviewing Status l l l Coaching Providing Vision Motivating Aligning Stakeholders Demonstrating Standards and Providing Structure
Managing & Leading “Managers are people who do things right and leaders are people who do the right thing. ” – Bennis and Nanus, 1985 “Most U. S. corporations today are over-managed and under led. ” – Kotter, Harvard Business Review 2001 l l l Enforcing Standards Resolving Issues Budgeting Planning Reviewing Status l l l Coaching Providing Vision Motivating Aligning Stakeholders Demonstrating Standards and Providing Structure

 Table 2 -4. Most Significant Characteristics of Effective and Ineffective Project Managers Effective Project Managers Ineffective Project Manag Lead by example Are visionaries Are technically competent Are decisive Are good communicators Are good motivators Stand up to upper management when necessary • Support team members • Encourage new ideas • • 32 • • • Set bad examples Are not self-assured Lack technical expertise Are poor communicators Are poor motivators IT Project Management, Third Edition Chapter 2
Table 2 -4. Most Significant Characteristics of Effective and Ineffective Project Managers Effective Project Managers Ineffective Project Manag Lead by example Are visionaries Are technically competent Are decisive Are good communicators Are good motivators Stand up to upper management when necessary • Support team members • Encourage new ideas • • 32 • • • Set bad examples Are not self-assured Lack technical expertise Are poor communicators Are poor motivators IT Project Management, Third Edition Chapter 2
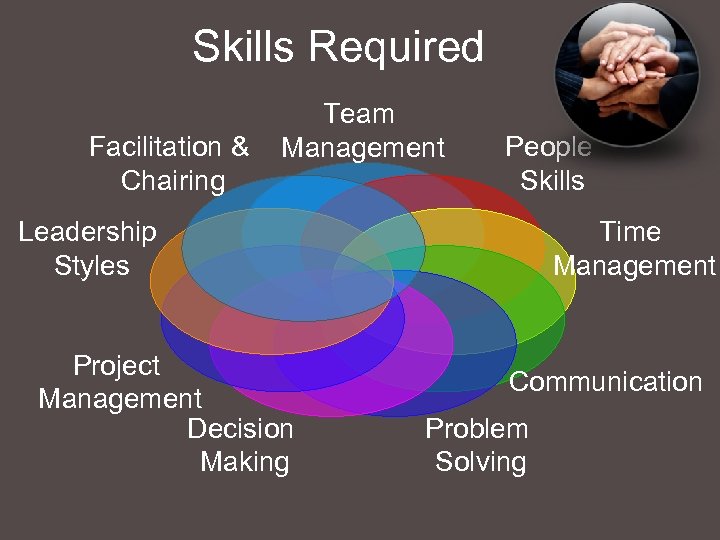 Skills Required Facilitation & Chairing Team Management People Skills Leadership Styles Project Management Decision Making Time Management Communication Problem Solving
Skills Required Facilitation & Chairing Team Management People Skills Leadership Styles Project Management Decision Making Time Management Communication Problem Solving
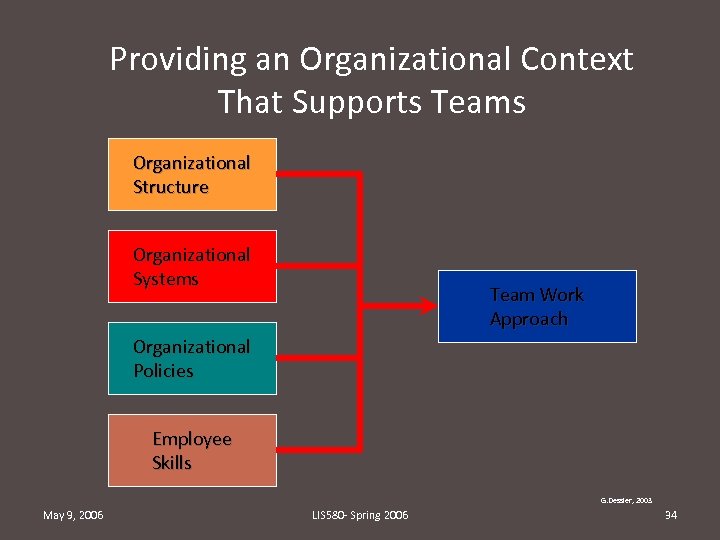 Providing an Organizational Context That Supports Teams Organizational Structure Organizational Systems Team Work Approach Organizational Policies Employee Skills G. Dessler, 2003 May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 34
Providing an Organizational Context That Supports Teams Organizational Structure Organizational Systems Team Work Approach Organizational Policies Employee Skills G. Dessler, 2003 May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 34
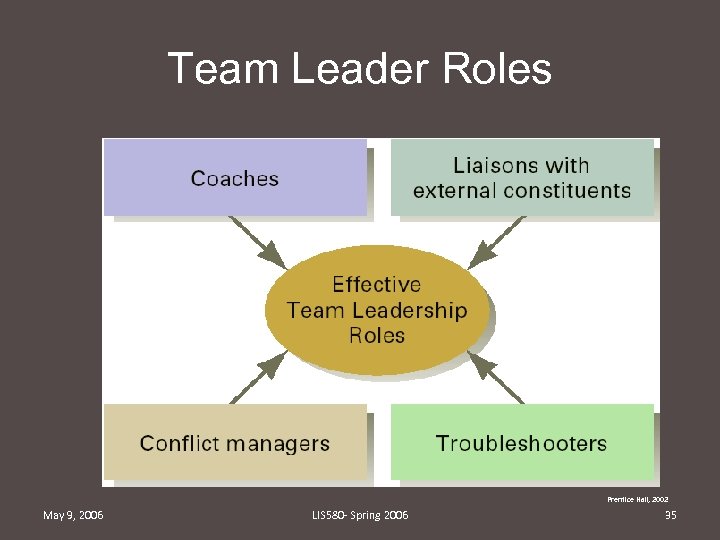 Team Leader Roles Prentice Hall, 2002 May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 35
Team Leader Roles Prentice Hall, 2002 May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 35
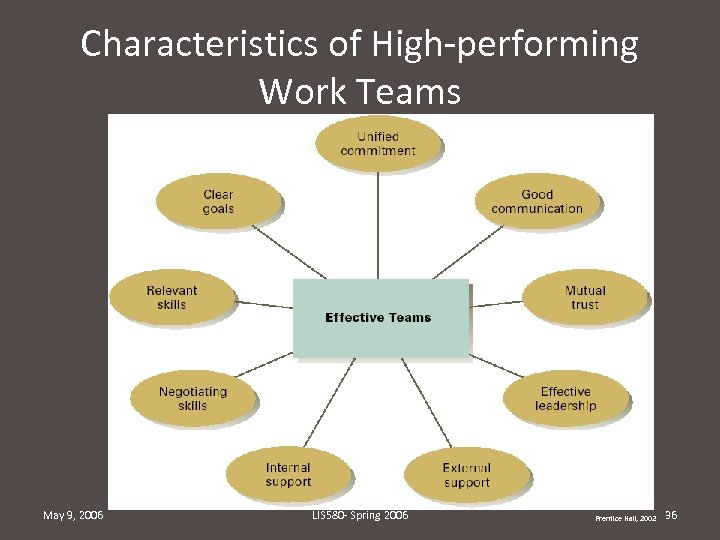 Characteristics of High-performing Work Teams May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 Prentice Hall, 2002 36
Characteristics of High-performing Work Teams May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 Prentice Hall, 2002 36
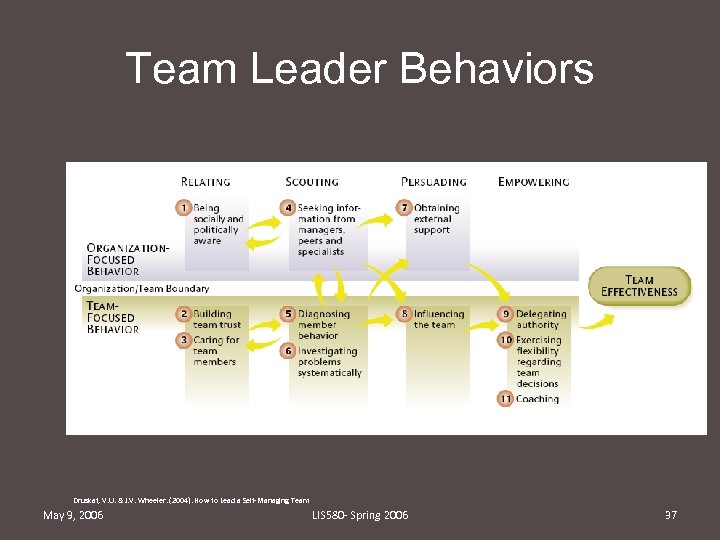 Team Leader Behaviors Druskat, V. U. & J. V. Wheeler. (2004). How to Lead a Self-Managing Team May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 37
Team Leader Behaviors Druskat, V. U. & J. V. Wheeler. (2004). How to Lead a Self-Managing Team May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 37
 Effective Project Teams v. Clear Sense of Mission v. Productive Interdependency v. Cohesiveness v. Trust v. Enthusiasm v. Results Orientation 6 -38
Effective Project Teams v. Clear Sense of Mission v. Productive Interdependency v. Cohesiveness v. Trust v. Enthusiasm v. Results Orientation 6 -38
 Reasons Why Teams Fail • Poorly developed or unclear goals • Poorly defined project team roles & • • • interdependencies Lack of project team motivation Poor communication Poor leadership Turnover among project team members Dysfunctional behavior 6 -39
Reasons Why Teams Fail • Poorly developed or unclear goals • Poorly defined project team roles & • • • interdependencies Lack of project team motivation Poor communication Poor leadership Turnover among project team members Dysfunctional behavior 6 -39
 Why Teams Fail: The Leadership, Focus, and Capability Pyramid Source: Adapted from Steven Rayner, “Team Traps: What They Are, How to Avoid Them. ” National Productivity Review. Summer 1996, p. 107. Reprinted by permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc. FIGURE 13– 3 May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 G. Dessler, 2003 40
Why Teams Fail: The Leadership, Focus, and Capability Pyramid Source: Adapted from Steven Rayner, “Team Traps: What They Are, How to Avoid Them. ” National Productivity Review. Summer 1996, p. 107. Reprinted by permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc. FIGURE 13– 3 May 9, 2006 LIS 580 - Spring 2006 G. Dessler, 2003 40
 Stages in Group Development 1. Forming – members become acquainted 2. Storming – conflict begins 3. Norming – members reach agreement 4. Performing – members work together 5. Adjourning – group disbands Punctuated Equilibrium is a different model 6 -41
Stages in Group Development 1. Forming – members become acquainted 2. Storming – conflict begins 3. Norming – members reach agreement 4. Performing – members work together 5. Adjourning – group disbands Punctuated Equilibrium is a different model 6 -41
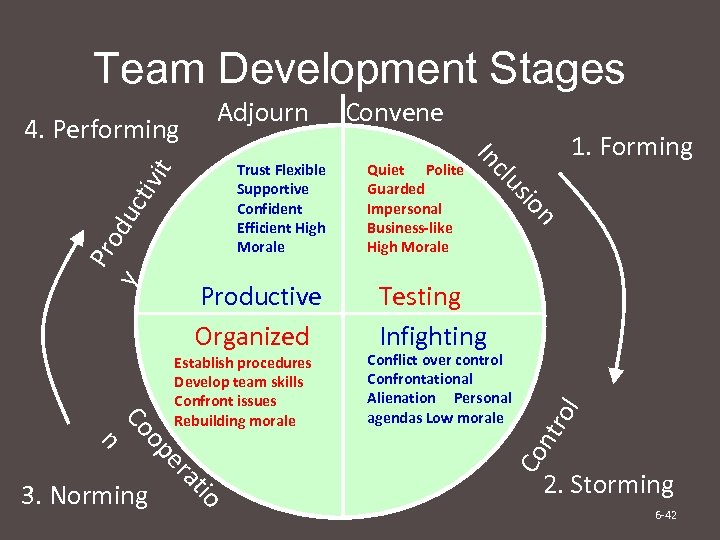 Team Development Stages Testing Infighting Conflict over control Confrontational Alienation Personal agendas Low morale ol vit cti du y Pro io at er 3. Norming n n op Co Establish procedures Develop team skills Confront issues Rebuilding morale sio clu Productive Organized Quiet Polite Guarded Impersonal Business-like High Morale In Trust Flexible Supportive Confident Efficient High Morale 1. Forming ntr 4. Performing Convene Co Adjourn 2. Storming 6 -42
Team Development Stages Testing Infighting Conflict over control Confrontational Alienation Personal agendas Low morale ol vit cti du y Pro io at er 3. Norming n n op Co Establish procedures Develop team skills Confront issues Rebuilding morale sio clu Productive Organized Quiet Polite Guarded Impersonal Business-like High Morale In Trust Flexible Supportive Confident Efficient High Morale 1. Forming ntr 4. Performing Convene Co Adjourn 2. Storming 6 -42
 หวขอเรยนและมอบหมายงานคร งตอไป 1. งานคนควาเดยว Project Planning , Project charter , Project Estimation 2. งานกลม ไปวางแผนโครงการแลวนำมาเขยนเปนข อเสนอโครงการตามหลกการตามทคนมา Project Proposal (Logic chart) , Project Charter , Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) เตรยมมานำเสนอในรปของ Power point 2. เรมไปทำ Project Estimation
หวขอเรยนและมอบหมายงานคร งตอไป 1. งานคนควาเดยว Project Planning , Project charter , Project Estimation 2. งานกลม ไปวางแผนโครงการแลวนำมาเขยนเปนข อเสนอโครงการตามหลกการตามทคนมา Project Proposal (Logic chart) , Project Charter , Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) เตรยมมานำเสนอในรปของ Power point 2. เรมไปทำ Project Estimation


