ea7dfb1e4fe388309be209b8ea8fb739.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT LECTURE 7: RISK MANAGEMENT IDENTIFYING AND You got to be careful if you don’t know where you’re going, ASSESSING RISK not get there. – Yogi Berra because you might
INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT LECTURE 7: RISK MANAGEMENT IDENTIFYING AND You got to be careful if you don’t know where you’re going, ASSESSING RISK not get there. – Yogi Berra because you might
 Discretionary Access Control (DAC) Security Model n The owner of an object controls who and what may access it. n Access is at the owner’s discretion. n Most personal computer operating systems are designed based on the DAC model
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) Security Model n The owner of an object controls who and what may access it. n Access is at the owner’s discretion. n Most personal computer operating systems are designed based on the DAC model
 Mandatory Access Control (MAC) Security Model • Data classification scheme/model – Data owners classify the information assets – Reviews periodically • Security clearance structure – Subjects labeled by level of security clearance (privilege) – Objects labeled by level of classification/sensitivity
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) Security Model • Data classification scheme/model – Data owners classify the information assets – Reviews periodically • Security clearance structure – Subjects labeled by level of security clearance (privilege) – Objects labeled by level of classification/sensitivity
 Role-based Access Control (RBAC) Security Model n Nondiscretionary Controls n An improvement over the mandatory access control (MAC) security model • • Role-based controls Task-based controls n Users are given roles with this role determining access
Role-based Access Control (RBAC) Security Model n Nondiscretionary Controls n An improvement over the mandatory access control (MAC) security model • • Role-based controls Task-based controls n Users are given roles with this role determining access
 Introduction • Information security departments are created primarily to manage IT risk • In any well-developed risk management program, two formal processes are at work – – Risk identification and assessment Risk control
Introduction • Information security departments are created primarily to manage IT risk • In any well-developed risk management program, two formal processes are at work – – Risk identification and assessment Risk control
 Risk Management “The process of determining the maximum acceptable level of overall risk to and from a proposed activity, then using risk assessment techniques to determine the initial level of risk and, if this is excessive, developing a strategy to ameliorate appropriate individual risks until the overall level of risk is reduced to an acceptable level. ”
Risk Management “The process of determining the maximum acceptable level of overall risk to and from a proposed activity, then using risk assessment techniques to determine the initial level of risk and, if this is excessive, developing a strategy to ameliorate appropriate individual risks until the overall level of risk is reduced to an acceptable level. ”
 Knowing Yourself & The Enemy • Identifying, examining and understanding the information and how it is processed, stored, and transmitted • Identifying, examining, and understanding the threats facing the organization’s information assets
Knowing Yourself & The Enemy • Identifying, examining and understanding the information and how it is processed, stored, and transmitted • Identifying, examining, and understanding the threats facing the organization’s information assets
 Communities of Interest: All Play a role • Information Security • Information Technology • Management and Users
Communities of Interest: All Play a role • Information Security • Information Technology • Management and Users
 Risk Terminology • • • Asset & Asset valuation Threat Vulnerability Exposure Risk
Risk Terminology • • • Asset & Asset valuation Threat Vulnerability Exposure Risk
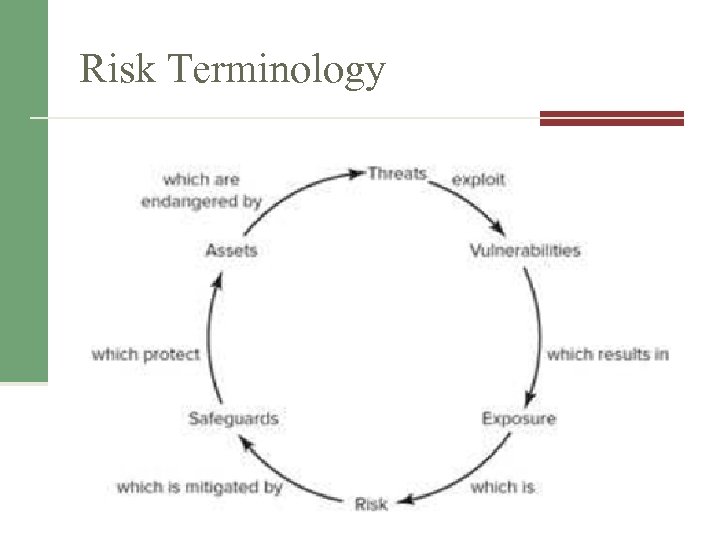 Risk Terminology
Risk Terminology
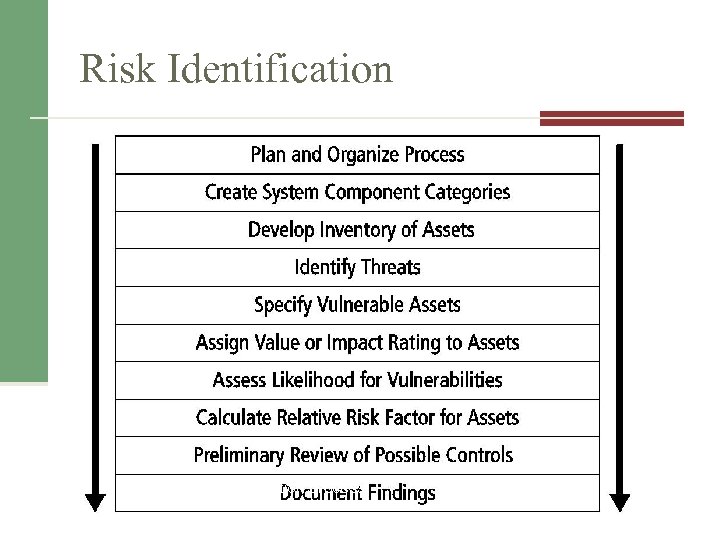 Risk Identification Figure 8 -1 Risk identification process Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Risk Identification Figure 8 -1 Risk identification process Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
 Asset Identification Identify organization’s information assets n Inventory: software/hardware, and networking elements n n More easily tracked (automated inventory system) People, procedures, data and info n May take more time / ongoing
Asset Identification Identify organization’s information assets n Inventory: software/hardware, and networking elements n n More easily tracked (automated inventory system) People, procedures, data and info n May take more time / ongoing
 Creating an Inventory of Information Assets • Determine which attributes of each information asset should be tracked • Potential asset attributes – Name, IP address – MAC address, asset type – Physical location, logical location – Controlling entity
Creating an Inventory of Information Assets • Determine which attributes of each information asset should be tracked • Potential asset attributes – Name, IP address – MAC address, asset type – Physical location, logical location – Controlling entity
 Creating an Inventory of Information Assets (cont’d. ) • Identifying people, procedures and data assets • Sample attributes – People - Position name/number/ID – Procedures – Description/Intended purpose – Data – Classification & Owner/creator/manager
Creating an Inventory of Information Assets (cont’d. ) • Identifying people, procedures and data assets • Sample attributes – People - Position name/number/ID – Procedures – Description/Intended purpose – Data – Classification & Owner/creator/manager
 Asset: Classifying and Categorizing • Determine whether the asset categories are meaningful • Inventory should also reflect each asset’s sensitivity and security priority • Classification categories must be comprehensive and mutually exclusive • Not one schema for all assets
Asset: Classifying and Categorizing • Determine whether the asset categories are meaningful • Inventory should also reflect each asset’s sensitivity and security priority • Classification categories must be comprehensive and mutually exclusive • Not one schema for all assets
 Asset Valuation • Assign a relative value: – As each information asset is identified, categorized, and classified Goal: assign value to encompass both tangible and intangible costs
Asset Valuation • Assign a relative value: – As each information asset is identified, categorized, and classified Goal: assign value to encompass both tangible and intangible costs
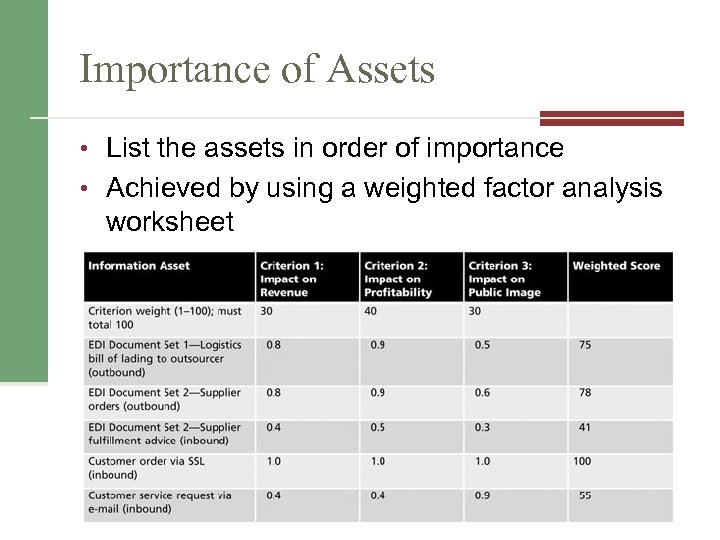 Importance of Assets • List the assets in order of importance • Achieved by using a weighted factor analysis worksheet
Importance of Assets • List the assets in order of importance • Achieved by using a weighted factor analysis worksheet
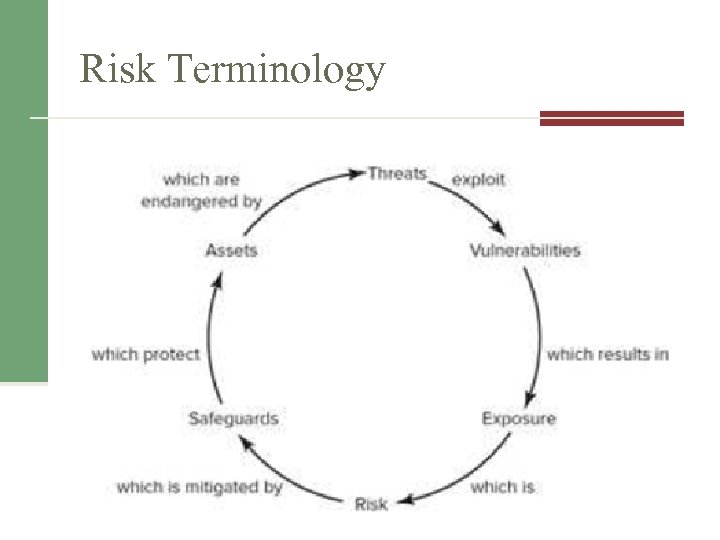 Risk Terminology
Risk Terminology
 Threat Identification • Any organization typically faces a wide variety of threats
Threat Identification • Any organization typically faces a wide variety of threats
 Threat Assessment • Each threat presents a unique challenge to information security • Each must be further examined to determine its potential to affect the targeted information asset
Threat Assessment • Each threat presents a unique challenge to information security • Each must be further examined to determine its potential to affect the targeted information asset
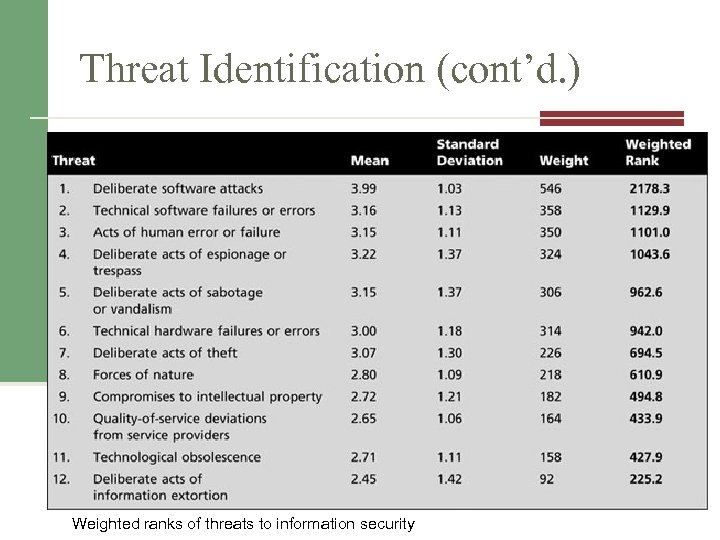 Threat Identification (cont’d. ) Weighted ranks of threats to information security Source: Adapted from M. E. Whitman. Enemy at the gates: Threats to information security. Communications of the ACM, August 2003. Reprinted with permission
Threat Identification (cont’d. ) Weighted ranks of threats to information security Source: Adapted from M. E. Whitman. Enemy at the gates: Threats to information security. Communications of the ACM, August 2003. Reprinted with permission
 Vulnerability Assessment • Vulnerability Assessment – Review every information asset for each threat – Leads to the creation of a list of vulnerabilities that remain potential risks to the organization • Vulnerabilities are specific avenues that threat agents can exploit to attack an information asset
Vulnerability Assessment • Vulnerability Assessment – Review every information asset for each threat – Leads to the creation of a list of vulnerabilities that remain potential risks to the organization • Vulnerabilities are specific avenues that threat agents can exploit to attack an information asset
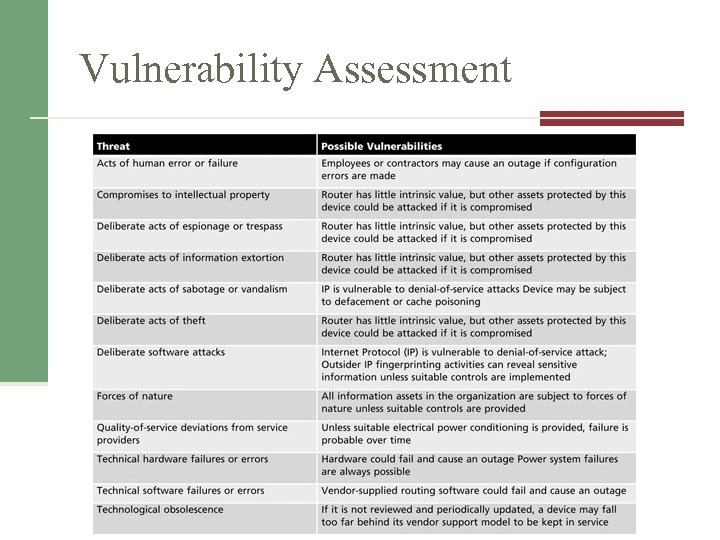 Vulnerability Assessment Table 8 -4 Vulnerability assessmentofof a DMZ router ed. Management Information Security, 3 rd Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Vulnerability Assessment Table 8 -4 Vulnerability assessmentofof a DMZ router ed. Management Information Security, 3 rd Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
 The TVA Worksheet • At the end of the risk identification process, a list of assets and their vulnerabilities has been developed • List serves as the starting point for the next step in the risk management process - risk assessment • Another list prioritizes threats facing the organization based on the weighted table discussed earlier
The TVA Worksheet • At the end of the risk identification process, a list of assets and their vulnerabilities has been developed • List serves as the starting point for the next step in the risk management process - risk assessment • Another list prioritizes threats facing the organization based on the weighted table discussed earlier
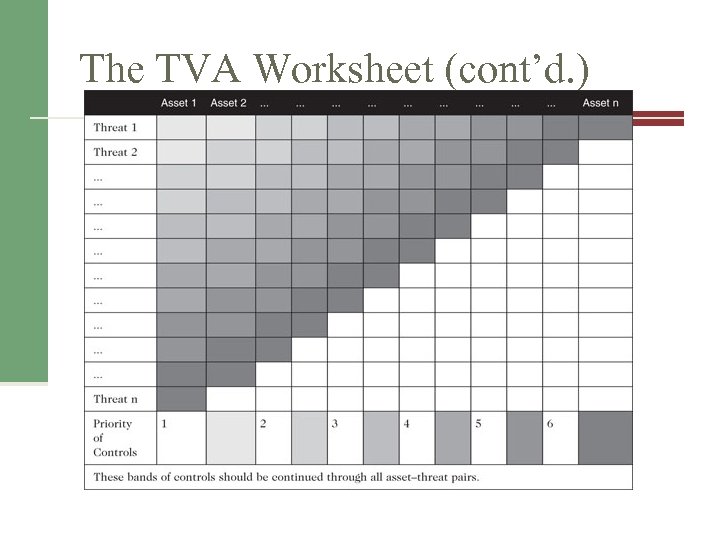 The TVA Worksheet (cont’d. ) Table 8 -5 Sample TVA spreadsheet Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
The TVA Worksheet (cont’d. ) Table 8 -5 Sample TVA spreadsheet Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
 Introduction to Risk Assessment • The goal is to create a method to evaluate the relative risk of each listed vulnerability Figure 8 -3 Risk identification estimate factors Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Introduction to Risk Assessment • The goal is to create a method to evaluate the relative risk of each listed vulnerability Figure 8 -3 Risk identification estimate factors Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
 Likelihood • The overall rating of the probability that a specific vulnerability will be exploited • Using the information documented during the risk identification process, you can assign weighted scores based on the value of each information asset
Likelihood • The overall rating of the probability that a specific vulnerability will be exploited • Using the information documented during the risk identification process, you can assign weighted scores based on the value of each information asset
 Percentage of Risk Mitigated by Current Controls • If a vulnerability is fully managed by an existing control, it can be set aside • If it is partially controlled, estimate what percentage of the vulnerability has been controlled
Percentage of Risk Mitigated by Current Controls • If a vulnerability is fully managed by an existing control, it can be set aside • If it is partially controlled, estimate what percentage of the vulnerability has been controlled
 Uncertainty • It is not possible to know everything about every vulnerability • The degree to which a current control can reduce risk is also subject to estimation error • Uncertainty is an estimate made by the manager using judgment and experience
Uncertainty • It is not possible to know everything about every vulnerability • The degree to which a current control can reduce risk is also subject to estimation error • Uncertainty is an estimate made by the manager using judgment and experience
 Risk Determination – Example 1 Asset A has a value of 50 and has one vulnerability, which has a likelihood of 1. 0 with no current controls. Your assumptions and data are 90% accurate Risk: [Asset Value(AV) x Likelihood(L)] – Controls(AV*L) + Uncertainty (AV*L) Risk = [50 x 1. 0] – 0. 0(50*1. 0) + 0. 1(50*1. 0) = 55
Risk Determination – Example 1 Asset A has a value of 50 and has one vulnerability, which has a likelihood of 1. 0 with no current controls. Your assumptions and data are 90% accurate Risk: [Asset Value(AV) x Likelihood(L)] – Controls(AV*L) + Uncertainty (AV*L) Risk = [50 x 1. 0] – 0. 0(50*1. 0) + 0. 1(50*1. 0) = 55
 Risk Determination – Example 2 Asset B has a value of 100 and has two vulnerabilities: n vulnerability #1 has a likelihood of 0. 5 with a current contro that addresses 50% of its risk n vulnerability # 2 has a likelihood of 0. 1 with no current cont Your assumptions and data are 80% accurate Risk: [Asset Value(AV) x Likelihood(L)] – Controls(AV*L) + Uncertainty (AV*L) Risk 1 = [100 x 0. 5] – 0. 5(100*0. 5) + 0. 2(100*0. 5) = 35 Risk 2 = [100 x 0. 1] – 0. 0(100*0. 1) + 0. 2(100*0. 1) = 12
Risk Determination – Example 2 Asset B has a value of 100 and has two vulnerabilities: n vulnerability #1 has a likelihood of 0. 5 with a current contro that addresses 50% of its risk n vulnerability # 2 has a likelihood of 0. 1 with no current cont Your assumptions and data are 80% accurate Risk: [Asset Value(AV) x Likelihood(L)] – Controls(AV*L) + Uncertainty (AV*L) Risk 1 = [100 x 0. 5] – 0. 5(100*0. 5) + 0. 2(100*0. 5) = 35 Risk 2 = [100 x 0. 1] – 0. 0(100*0. 1) + 0. 2(100*0. 1) = 12
 Qualitative Risk Analysis • • Evaluate opinions, feelings, ideas Scenarios Brainstorming Delphi technique Storyboarding Focus groups Surveys, questionnaires, checklists One-on-one meetings, interviews
Qualitative Risk Analysis • • Evaluate opinions, feelings, ideas Scenarios Brainstorming Delphi technique Storyboarding Focus groups Surveys, questionnaires, checklists One-on-one meetings, interviews
 Qualitative Risk Assessment n For a given scope of assets, identify: n Vulnerabilities n Threat probability (Low / medium / high) n Impact (Low / medium / high) n Countermeasures
Qualitative Risk Assessment n For a given scope of assets, identify: n Vulnerabilities n Threat probability (Low / medium / high) n Impact (Low / medium / high) n Countermeasures
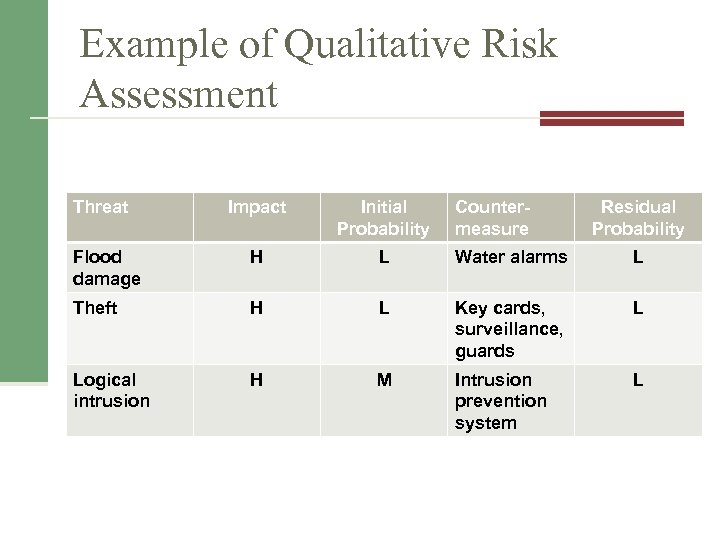 Example of Qualitative Risk Assessment Threat Impact Initial Probability Countermeasure Residual Probability Flood damage H L Water alarms L Theft H L Key cards, surveillance, guards L Logical intrusion H M Intrusion prevention system L
Example of Qualitative Risk Assessment Threat Impact Initial Probability Countermeasure Residual Probability Flood damage H L Water alarms L Theft H L Key cards, surveillance, guards L Logical intrusion H M Intrusion prevention system L
 Quantitative Risk Assessment n Extension of a qualitative risk assessment. Metrics for each risk are: Asset value: replacement cost and/or income derived through the use of an asset n Exposure Factor (EF): portion of asset's value lost through a threat (also called impact) n Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) = Asset ($) x EF (%) n
Quantitative Risk Assessment n Extension of a qualitative risk assessment. Metrics for each risk are: Asset value: replacement cost and/or income derived through the use of an asset n Exposure Factor (EF): portion of asset's value lost through a threat (also called impact) n Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) = Asset ($) x EF (%) n
 Quantitative Risk Assessment n Metrics (cont. ) n Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) n n Probability of loss in a year, % Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE) = SLE x ARO
Quantitative Risk Assessment n Metrics (cont. ) n Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) n n Probability of loss in a year, % Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE) = SLE x ARO
 Example of Quantitative Risk Assesment n Theft of a laptop computer, with the data encrypted n Asset value: $4, 000 Exposure factor ? 100% SLE, ARO, ALE ? n SLE = 4000 * 100% = 4, 000 n ARO = 10% chance of theft / year n ALE = 10% * 4000 = 400
Example of Quantitative Risk Assesment n Theft of a laptop computer, with the data encrypted n Asset value: $4, 000 Exposure factor ? 100% SLE, ARO, ALE ? n SLE = 4000 * 100% = 4, 000 n ARO = 10% chance of theft / year n ALE = 10% * 4000 = 400
 Example of Quantitative Risk Assesment n Dropping a laptop computer and breaking the screen n Asset value: $4, 000 Exposure factor ? 50% SLE, ARO, ALE ? n SLE = $4, 000 x 50% = $2, 000 n ARO = 25% chance of damaging / year n ALE = 25% x $2, 000 = $500
Example of Quantitative Risk Assesment n Dropping a laptop computer and breaking the screen n Asset value: $4, 000 Exposure factor ? 50% SLE, ARO, ALE ? n SLE = $4, 000 x 50% = $2, 000 n ARO = 25% chance of damaging / year n ALE = 25% x $2, 000 = $500
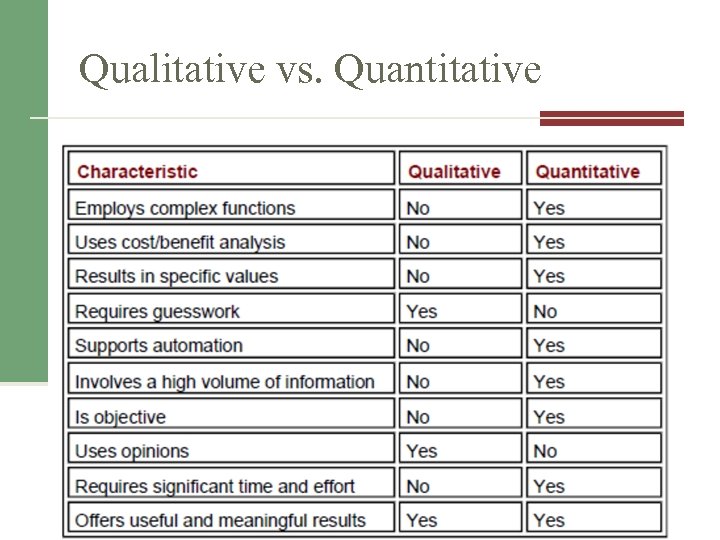 Qualitative vs. Quantitative
Qualitative vs. Quantitative
 Documenting the Results of Risk Assessment • Goals of the risk management process – To identify information assets and their vulnerabilities – To rank them according to the need for protection • In preparing this list, a wealth of factual information about the assets and the threats they face is collected • The final summarized document is the ranked vulnerability risk worksheet
Documenting the Results of Risk Assessment • Goals of the risk management process – To identify information assets and their vulnerabilities – To rank them according to the need for protection • In preparing this list, a wealth of factual information about the assets and the threats they face is collected • The final summarized document is the ranked vulnerability risk worksheet
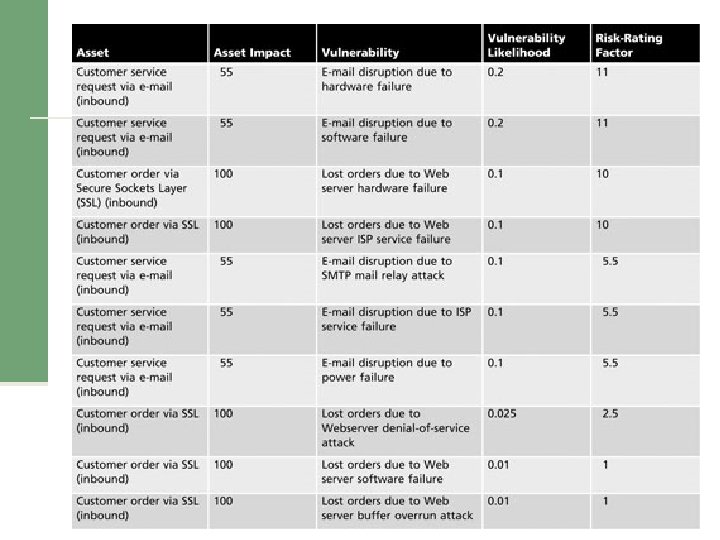 Table 8 -9 Ranked vulnerability risk worksheet Management of Information Security, 3 rd ed. Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning
Table 8 -9 Ranked vulnerability risk worksheet Management of Information Security, 3 rd ed. Source: Course Technology/Cengage Learning


