cb3cd4716d522b98cfc973288cefd983.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Information Risk Management Overview Nena Young, CRP, CBCP Texas Department of Information Resources email: nena. young@dir. state. tx. us Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Principles for All Sub-Programs Risk Assessment and Solutions Overview Centered Management Implementation of Controls, including policies Awareness Monitor and Evaluation of Effectiveness Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Bonus Overview In-depth Assessment of risks Comprehensive picture of business and technical processes Identify opportunities for process enhancements and/or re-engineering Rapid, precise, smooth recovery “Insurance Policy” for staying in business. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Program Components: 1. Risk Analysis & Risk Assessment 2. Information Security Program 3. Business Continuity Program Risk Texas Department of Information Resources Security BCP
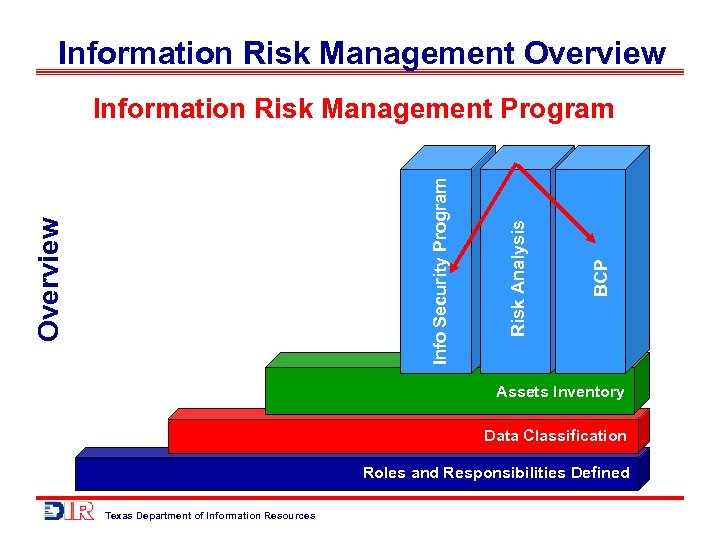
Information Risk Management Overview BCP Risk Analysis Overview Info Security Program Information Risk Management Program Roles and Responsibilities Defined Assets Inventory Data Classification Roles and Responsibilities Defined Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Risk Analysis 1. Risk Analysis & Risk Assessment Risk Analysis - The process of identifying and documenting vulnerabilities and applicable threats to assets. Risk Assessment - Projecting losses, assigning levels of risk, and recommending appropriate measures to protect assets. Risk Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Foundation of all risk management programs Risk Analysis Snapshot in time. Discover compliance with existing policies. Basis for selecting cost-efficient, most appropriate protection measures for assets. Equilibrium- asset loss to countermeasures Provide information on likelihood of threat occurrence and asset impact. Federal government and most states mandate. Ensure reasonable steps are taken to prevent loss of assets. Texas Department of Information Resources
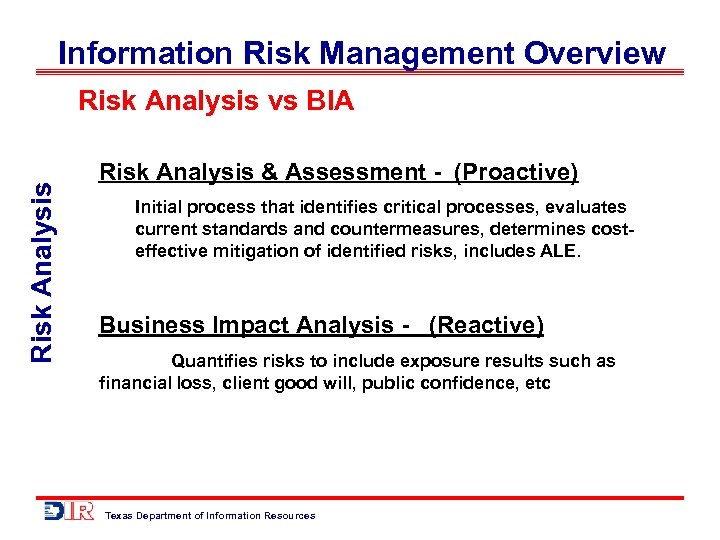
Information Risk Management Overview Risk Analysis vs BIA Risk Analysis & Assessment - (Proactive) Initial process that identifies critical processes, evaluates current standards and countermeasures, determines costeffective mitigation of identified risks, includes ALE. Business Impact Analysis - (Reactive) Quantifies risks to include exposure results such as financial loss, client good will, public confidence, etc Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Jargon Risk Analysis Assets - Anything with value and is worth protecting or preserving. Threats - Events or actions which always exists and can generate undesirable impacts or loss of assets. Can be either human or environmental. Vulnerabilities - The “windows of opportunity” which allow threats to materialize. The exposures. Conditions of weakness. Countermeasures - (Safeguards, Controls) - Devices, processes, actions, procedures that can reduce vulnerabilities. Preventive, Detective, Corrective. Risk - Potential for a threat to exploit a vulnerability. A threat + a vulnerability = a RISK. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Risk Analysis The Basics Assets identified. Threats identified. Vulnerabilities identified. Asset Losses identified. Protective measures identified and proposed. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Quantitative vs Qualitative Risk Analysis Theoretically. . . Quantitative Qualitative Objective Numeric Values Asset Value Descriptive, Immeasurable Values Impact Characteristics Frequency of Threats No Quantifiable Data Countermeasure Cost. Effectiveness No ALE Use of Complex Calculations (confidence factors, probabilities, SLE, ALE, ) Texas Department of Information Resources Yes/No; Low/Medium/High; Vital/Critical/Important; good/bad Rankings based on judgement

Information Risk Management Overview Risk Analysis In the Real World. . . Risk Analysis Involves Both Quantifiable measurements. Judgements based on experience and knowledge. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Ten Steps Organize and Define the Scope Risk Analysis Identify and Value the Assets Identify Applicable Threats Identify and Describe Vulnerabilities Establish Pairings (relationships) Determine the Impact of Threat Occurrence Measure Existing Countermeasures Determine Residual Risks Recommend Additional Countermeasures Prepare a Risk Analysis Report Texas Department of Information Resources
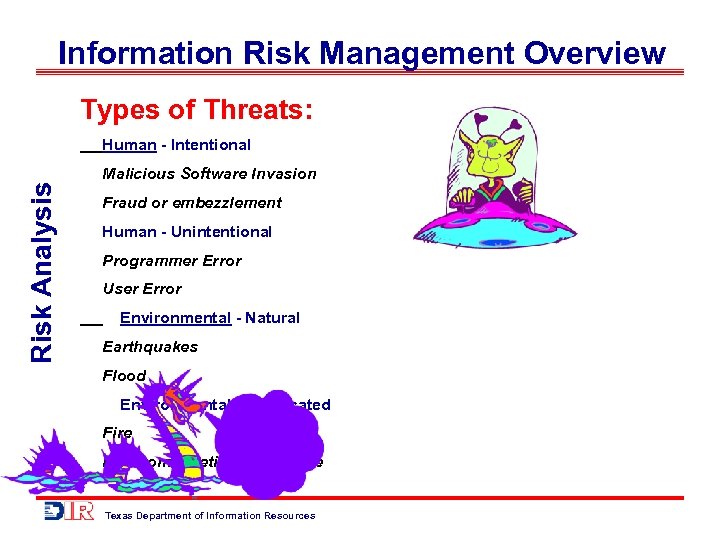
Information Risk Management Overview Types of Threats: Risk Analysis Human - Intentional Malicious Software Invasion Fraud or embezzlement Human - Unintentional Programmer Error User Error Environmental - Natural Earthquakes Flood Environmental - Fabricated Fire Electromagnetic interference Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Risk Analysis Impact of Threat Occurrence Impact (Loss) Categories. Disclosure - Classification or sensitivity of information. Who has access Modification - A realized threat causes unauthorized changes in an asset. Destruction - Threat activity causes damage to an asset, making it unusable. Denial of Service - A realized threat causes a loss of availability. Texas Department of Information Resources
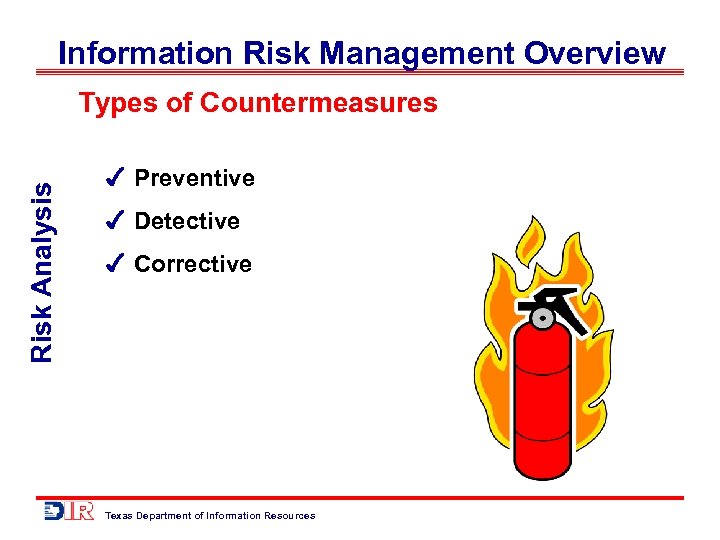
Information Risk Management Overview Risk Analysis Types of Countermeasures Preventive Detective Corrective Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Threats Assets ur es Vulnerabilities ea s m un te r Impacts Co Risk Analysis Residual Risks are accepted, mitigated, transferred. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Knowledge Base Needed Risk Analysis Analysts Need to: Know current and historical internal environment. Know current and historical external environment. Understand dependencies and vulnerabilities. Understand threat profiles. Understand countermeasure choices and related costs. Be able to apply cost-benefit analysis to risks and countermeasures Texas Department of Information Resources
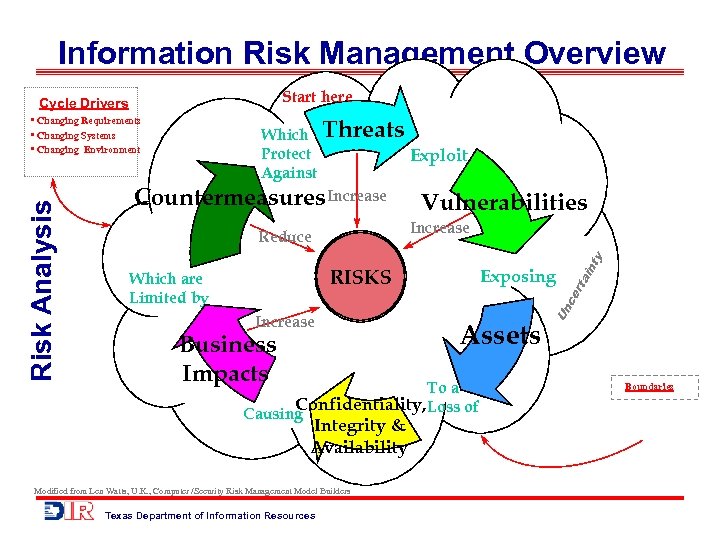
Information Risk Management Overview Start here Cycle Drivers Which Threats Protect Exploit Against Countermeasures Increase Vulnerabilities Increase Business Impacts Exposing Assets To a Confidentiality, Loss of Causing Integrity & Availability Modified from Len Watts, U. K. , Computer /Security Risk Management Model Builders Texas Department of Information Resources ce rta RISKS Which are Limited by int y Reduce Un Risk Analysis • Changing Requirements • Changing Systems • Changing Environment Boundaries

Information Risk Management Overview 2. Information Security Program Protection of an organization’s information assets. Purpose - The preservation of the confidentiality, integrity, and availability” (CIA) of information. Can add utility and authenticity. Security Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Purpose: A Secure Enterprise Protection of Assets Security Protection of Goodwill Integrity of Applications and Data Due Diligence Protection of Employees, Shareholders, Partners, Clients Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Eight Steps Security 1. Management Sponsorship and Support 2. Organize and Define the Scope 3. Risk Analysis 4. Policies and Procedures 5. Controls 6. Security Breach Reporting and Investigation 7. Awareness Training 8. Monitor and Test Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview The Bad Guys Competitors Security Employees (58 - 80%) Foreign Governments Political Activists Professional Spies Reprinted from Cohen & Assc Presentation Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Why Do They Attack? Fun/Challenge Coercion Security Testing Vengeance Military Advantage Mental Instability Economic Advantage Religious/Political Beliefs Evidence Self-Defense Money Texas Department of Information Resources
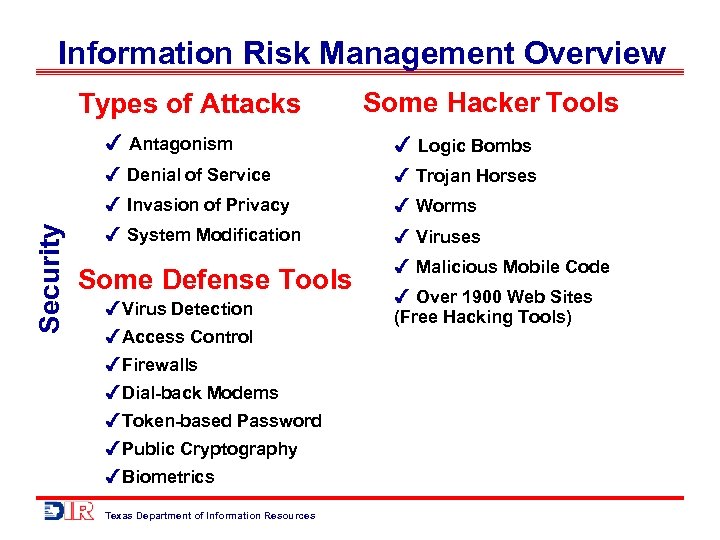
Information Risk Management Overview Types of Attacks Some Hacker Tools Logic Bombs Denial of Service Trojan Horses Invasion of Privacy Security Antagonism Worms System Modification Viruses Some Defense Tools Virus Detection Access Control Firewalls Dial-back Modems Token-based Password Public Cryptography Biometrics Texas Department of Information Resources Malicious Mobile Code Over 1900 Web Sites (Free Hacking Tools)

Information Risk Management Overview Security Internet Older than… “Pong” Digital Watches IBM PC Disco Micro. Soft Current Concept of “Hackers” +12 M Hosts, 120 M Users (70 M-USA), 12% Growth a Month 1 Billion users by 2005, 66% abroad New Web Site every 4 seconds Electronic Commerce - Single Sites Over 100, 000 Requests a Day + 80% Web Sites - Mobile Code Enabled +90% EC Applications use Mobile Code -50% Major Organizations w/Internet Use Firewall Texas Department of Information Resources
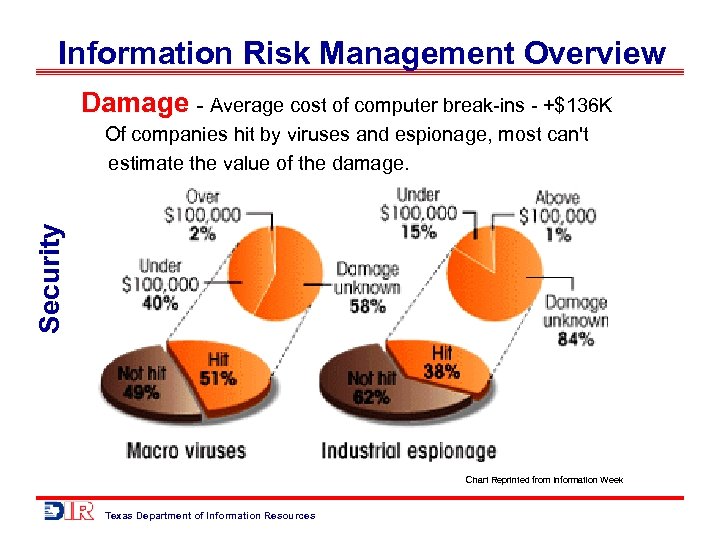
Information Risk Management Overview Damage - Average cost of computer break-ins - +$136 K Security Of companies hit by viruses and espionage, most can't estimate the value of the damage. Chart Reprinted from Information Week Texas Department of Information Resources
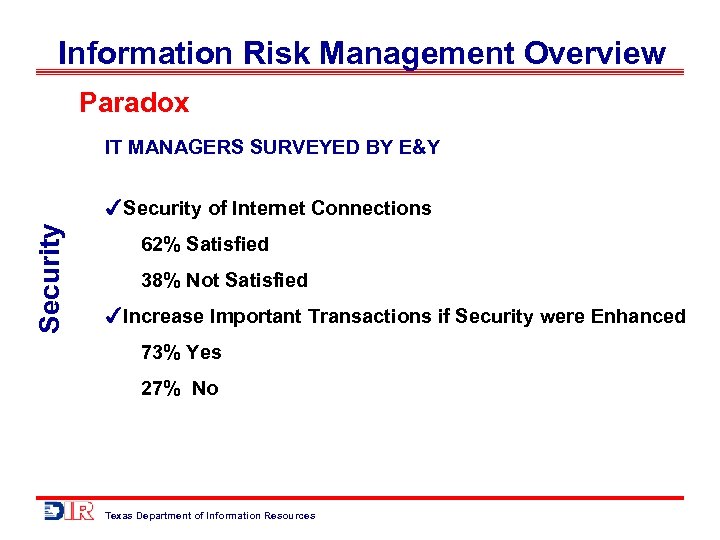
Information Risk Management Overview Paradox IT MANAGERS SURVEYED BY E&Y Security of Internet Connections 62% Satisfied 38% Not Satisfied Increase Important Transactions if Security were Enhanced 73% Yes 27% No Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Increasing Need for Security Most Fortune 500 Companies Penetrated by Cybercriminals 17% of Intrusion Victims Report to Authorities Security FBI Estimate - $10 B a year in Electronic Crimes Increasing Scams +100, 000 Investors Victim to Phony Web Sites High-tech revolutionary devices Partnership with Micro. Soft Initial Public Offering with the SEC Tens of Thousands Probing Attacks against Pentagon annually Origin of Attacks Camouflaged through other Countries DISA Vulnerability Testing Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Some Road Blocks to Security Lack of Sufficient Budget Security Lack of Resources - Management Support, Staff Lack of Awareness Lack of Tools Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Security Knowledge Base Needed (CISSP) Access control Telecommunications and network security BCP Security management practices – policies, standards, control of risk control of Risk information classification security awareness organizational architecture policy development risk management Security architecture and models Law, investigation, and ethics Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Knowledge Base Needed (CISSP) (con’t) Application and system development security Security Cryptography Computer operations security Physical security threats and facility requirements personnel physical access control microcomputer physical security “. . . information protection is not a simple matter, and it cannot be addressed from a single perspective. It is a pervasive problem that must be pursued in a holistic manner in order to provide its benefits. ” Texas Department of Information Resources
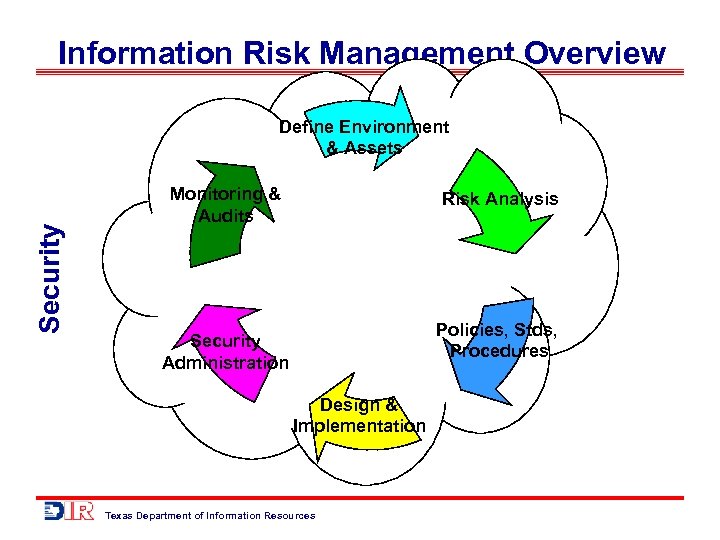
Information Risk Management Overview Security Define Environment & Assets Monitoring & Audits Risk Analysis Policies, Stds, Procedures Security Administration Design & Implementation Texas Department of Information Resources
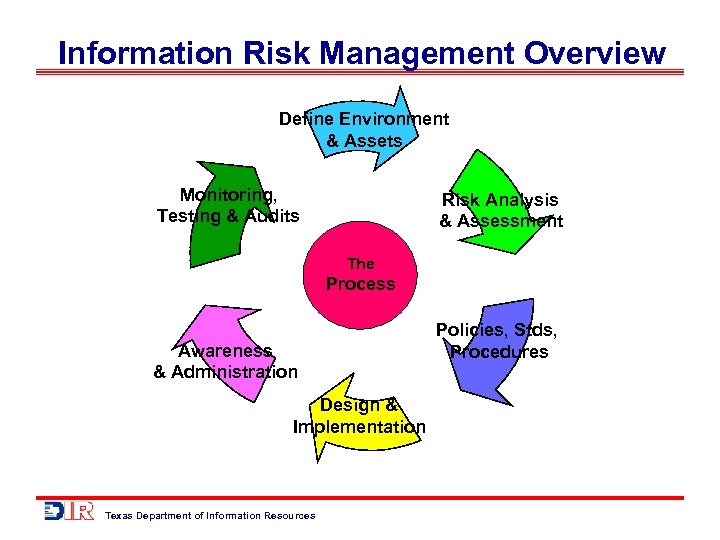
Information Risk Management Overview Define Environment & Assets Monitoring, Testing & Audits Risk Analysis & Assessment The Process Awareness & Administration Design & Implementation Texas Department of Information Resources Policies, Stds, Procedures

Information Risk Management Overview 3. Business Continuity Program BCP - Spells out what, who, how, and when for a quick and smooth restoration of critical operations after a catastrophic disruptive event, minimizes losses, and eventually returns to business as normal. BCP Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview A Rose by Any Other Name. . . Business Resumption Plan BCP Disaster Recovery Plan Crisis Management Plan Contingency Plan Business Continuity Plan Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Goals BCP Identify weaknesses and implement a disaster prevention program Minimize the duration of a serious disruption to business operations Facilitate effective co-ordination of recovery tasks; and reduce the complexity of the recovery effort Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Sources of Interruptions are Numerous Natural Tornadoes, Floods, Fires. . . BCP Human Terrorist’s Attacks. . . Most Frequent (Less Sensational) Equipment Failure, Theft, Employee Sabotage. . . Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview BCP Twelve Steps 1. Pre-planning (Senior Mgmt Commitment/Support, Policies) 2. Risk Analysis 3. Business Impact Analysis 4. Identify Resources and Requirements Needed 5. Emergency Response 6. Coordination with Public Authorities 7. Public Relations and Crisis Communications 8. Strategic Alternatives 9. Plan Development/Implementation 10. Testing/Exercises 11. Awareness 12. Maintenance Texas Department of Information Resources
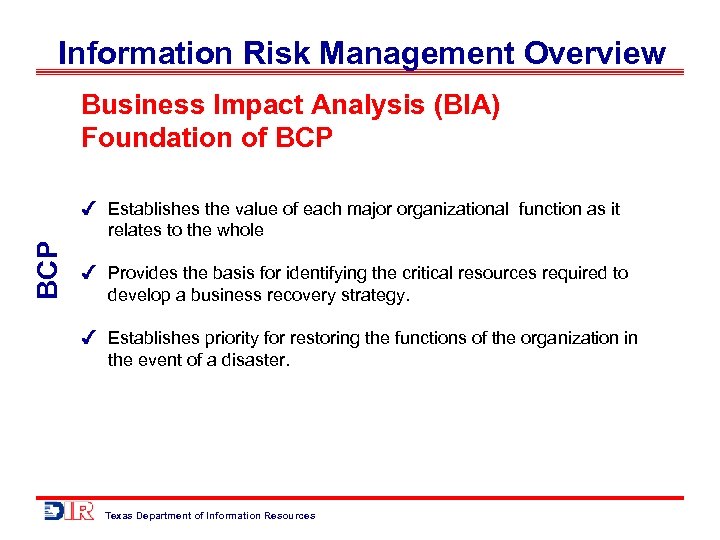
Information Risk Management Overview Business Impact Analysis (BIA) Foundation of BCP Establishes the value of each major organizational function as it relates to the whole Provides the basis for identifying the critical resources required to develop a business recovery strategy. Establishes priority for restoring the functions of the organization in the event of a disaster. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Impacts Revenue BCP Legal - fines, penalties Goodwill, Client & Stockholder Confidence Note: Losses May not be Dollars. Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Six Steps to BIA 1. Identify the Critical Business Functions BCP 2. Prioritize These Functions 3. Identify Dependencies and Resources Needed 4. Identify Points of Failure for Each Function 5. Estimate Probable Impact of Loss for Each Point of Failure 6. Determine if a Contingency Plan is Required Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview BCP Failing to Test Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Staying Current BCP Conduct BIA on planned periodic time or after major change Make sure a plan is included for each critical function that has a critical impact on mission accomplishment Continue to test and evaluate plans at least once a year Keep personnel responsibilities up to date and test for readiness Involve key personnel in operational planning Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Knowledge Base Needed (CRP, CBCP) Project initiation and management Risk evaluation and control BCP BIA Developing business continuity strategies Emergency response and operations Developing and implementing business continuity plans Awareness and training programs Maintaining and exercising business continuity plans Public relations and crisis communications Coordination with public authorities Texas Department of Information Resources
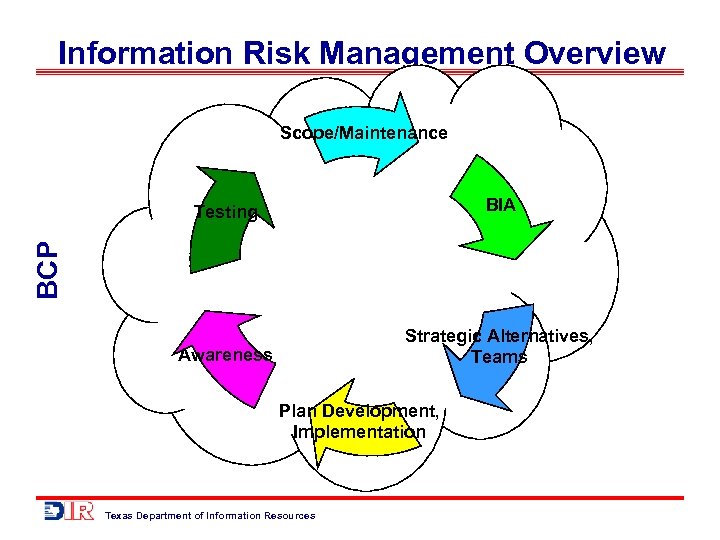
Information Risk Management Overview Scope/Maintenance BIA Awareness Strategic Alternatives, Teams BCP Testing Plan Development, Implementation Texas Department of Information Resources
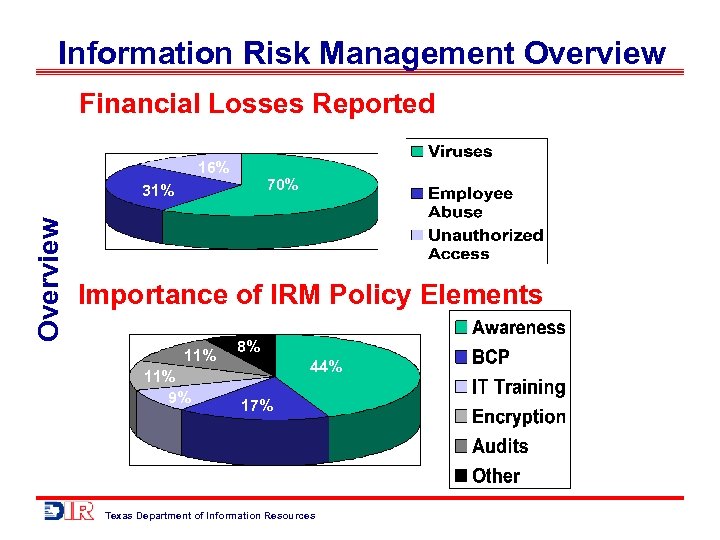
Information Risk Management Overview Financial Losses Reported 16% 70% Overview 31% Importance of IRM Policy Elements 11% 9% 8% 44% 17% Texas Department of Information Resources
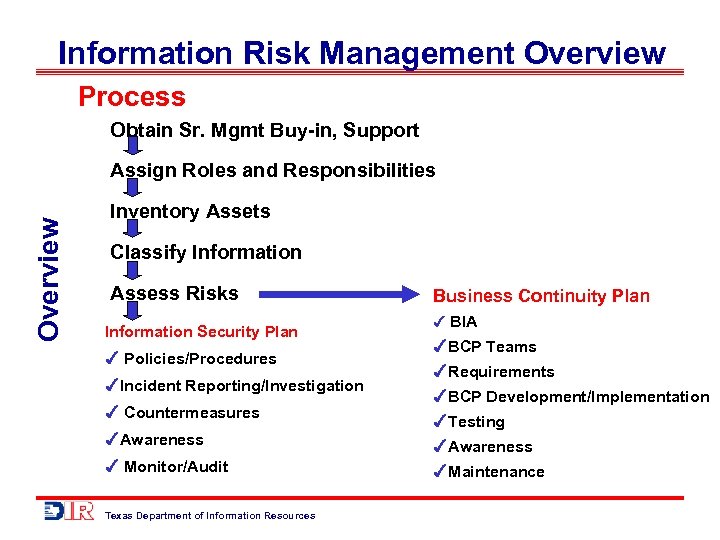
Information Risk Management Overview Process Obtain Sr. Mgmt Buy-in, Support Overview Assign Roles and Responsibilities Inventory Assets Classify Information Assess Risks Information Security Plan Policies/Procedures Incident Reporting/Investigation Countermeasures Business Continuity Plan BIA BCP Teams Requirements BCP Development/Implementation Testing Awareness Monitor/Audit Maintenance Texas Department of Information Resources

Information Risk Management Overview Last Words “Risk is a part of every activity and can never be eliminated, nor can all the risks ever be known. Risk in itself is not bad; risk is often essential to progress. But we must learn to balance the possible negative consequences of risk [to assets] against the potential benefits of its associated opportunity. ” “Risk Management in Practice, ” SEI Technical Review Go ahead and take risks… just be sure that everything will turn out. . Disasters are inevitable. . Survival isn't. . Texas Department of Information Resources
cb3cd4716d522b98cfc973288cefd983.ppt