0f103e88e2cf7fe994d648fadd743d6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56

 Information Revolution
Information Revolution

 Tariff of 1816 - imports Second Bank of the U. S. Private, profit-making corporation paper money had real value Internal improvements at federal expense- National Roads and Canals John C. Calhoun “Let us conquer space”
Tariff of 1816 - imports Second Bank of the U. S. Private, profit-making corporation paper money had real value Internal improvements at federal expense- National Roads and Canals John C. Calhoun “Let us conquer space”
 Economy Leader ______ Role of Government
Economy Leader ______ Role of Government

 Essential Question: Champion of the “Common Man”? OR “King” Andrew?
Essential Question: Champion of the “Common Man”? OR “King” Andrew?

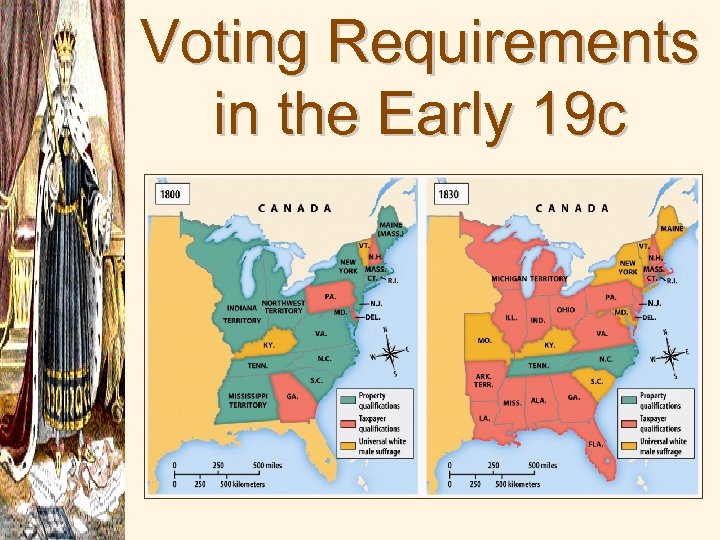 Voting Requirements in the Early 19 c
Voting Requirements in the Early 19 c
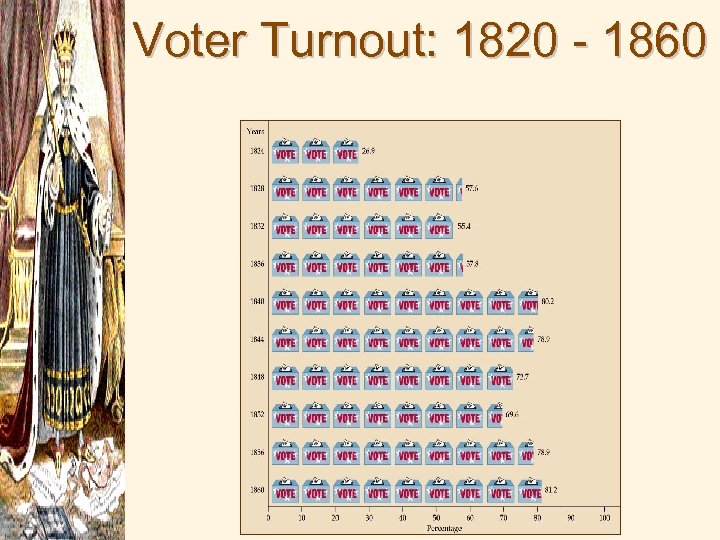 Voter Turnout: 1820 - 1860
Voter Turnout: 1820 - 1860
 Why Increased democratization?
Why Increased democratization?

 The “Common Man’s” Presidential Candidate
The “Common Man’s” Presidential Candidate
![Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA]](https://present5.com/presentation/0f103e88e2cf7fe994d648fadd743d6e/image-15.jpg) Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA]
Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA]
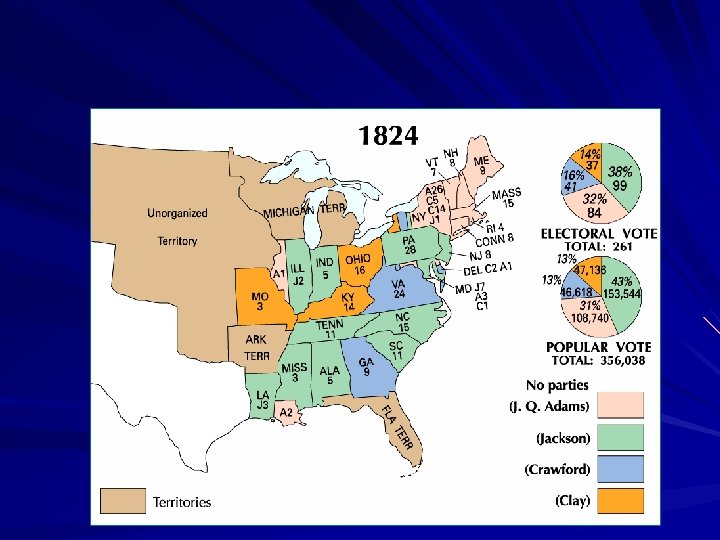
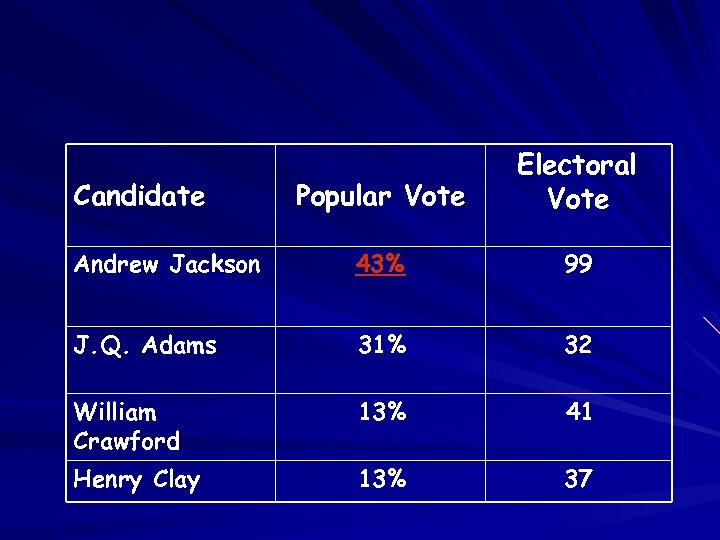 Popular Vote Electoral Vote Andrew Jackson 43% 99 J. Q. Adams 31% 32 William Crawford 13% 41 Henry Clay 13% 37 Candidate
Popular Vote Electoral Vote Andrew Jackson 43% 99 J. Q. Adams 31% 32 William Crawford 13% 41 Henry Clay 13% 37 Candidate
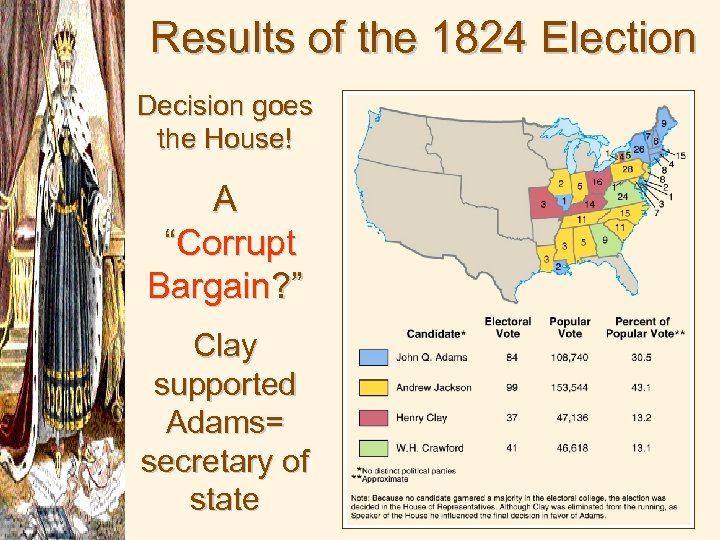 Results of the 1824 Election Decision goes the House! A “Corrupt Bargain? ” Clay supported Adams= secretary of state
Results of the 1824 Election Decision goes the House! A “Corrupt Bargain? ” Clay supported Adams= secretary of state
 Supported American System Authored Monroe Doctrine Neg. Adams-Onis Treaty Fixed 49 parallel $ for internal improvements Continued to define President’s Constitutional role
Supported American System Authored Monroe Doctrine Neg. Adams-Onis Treaty Fixed 49 parallel $ for internal improvements Continued to define President’s Constitutional role

 End of Era of Good Feelings
End of Era of Good Feelings

 Rachel Jackson Final Divorce Decree
Rachel Jackson Final Divorce Decree
 Jackson in Mourning for His Wife
Jackson in Mourning for His Wife
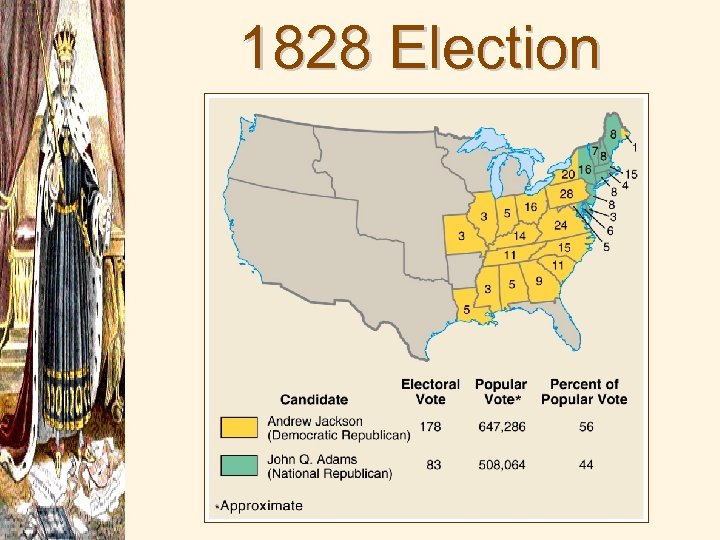 1828 Election Results
1828 Election Results
 The New “Jackson Coalition” 3 The Planter Elite in the South 3 People on the Frontier 3 State Politicians – spoils 3 Immigrants in the cities. system
The New “Jackson Coalition” 3 The Planter Elite in the South 3 People on the Frontier 3 State Politicians – spoils 3 Immigrants in the cities. system
 Jackson’s Faith in the “Common Man” 3 3 3 Intense distrust of Eastern “establishment, ” monopolies, & special privilege. His heart & soul was with the “plain folk. ” Belief that the common man was capable of uncommon achievements.
Jackson’s Faith in the “Common Man” 3 3 3 Intense distrust of Eastern “establishment, ” monopolies, & special privilege. His heart & soul was with the “plain folk. ” Belief that the common man was capable of uncommon achievements.
 The Reign of “King Mob”
The Reign of “King Mob”
 Andrew Jackson as President
Andrew Jackson as President
 Jackson v. Calhoun
Jackson v. Calhoun
 The “Peggy Eaton Affair”
The “Peggy Eaton Affair”


![The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC] Calhoun’s disciple The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC] Calhoun’s disciple](https://present5.com/presentation/0f103e88e2cf7fe994d648fadd743d6e/image-34.jpg) The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC] Calhoun’s disciple
The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC] Calhoun’s disciple
 1830 Webster : Liberty and Union, now and forever, one and inseparable. Illegal, unconstitutional, treasonous Jackson : Our Federal Union—it must be preserved. Calhoun : The Union, next to our liberty, most dear.
1830 Webster : Liberty and Union, now and forever, one and inseparable. Illegal, unconstitutional, treasonous Jackson : Our Federal Union—it must be preserved. Calhoun : The Union, next to our liberty, most dear.

 1832 Tariff Conflict 3 1828 -->ariff of Abomination Tariff T Exposition and Protest 3 1832 --> new tariff 3 South Carolina’s reaction? 3 Jackson’s response ? 3 Clay’s “Compromise” Tariff?
1832 Tariff Conflict 3 1828 -->ariff of Abomination Tariff T Exposition and Protest 3 1832 --> new tariff 3 South Carolina’s reaction? 3 Jackson’s response ? 3 Clay’s “Compromise” Tariff?

 The National Bank Debate Nicholas Biddle President Jackson
The National Bank Debate Nicholas Biddle President Jackson
 Jackson’s Use of Federal Power VETO 1832
Jackson’s Use of Federal Power VETO 1832
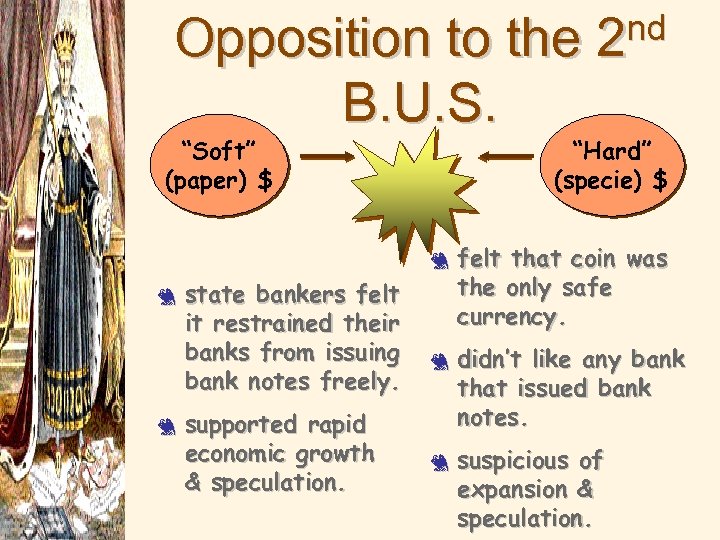 Opposition to the B. U. S. “Soft” (paper) $ “Hard” (specie) $ 3 3 3 state bankers felt it restrained their banks from issuing bank notes freely. supported rapid economic growth & speculation. nd 2 3 3 felt that coin was the only safe currency. didn’t like any bank that issued bank notes. suspicious of expansion & speculation.
Opposition to the B. U. S. “Soft” (paper) $ “Hard” (specie) $ 3 3 3 state bankers felt it restrained their banks from issuing bank notes freely. supported rapid economic growth & speculation. nd 2 3 3 felt that coin was the only safe currency. didn’t like any bank that issued bank notes. suspicious of expansion & speculation.
 The “Monster” Is Destroyed!
The “Monster” Is Destroyed!
 The Downfall of “Mother Bank”
The Downfall of “Mother Bank”

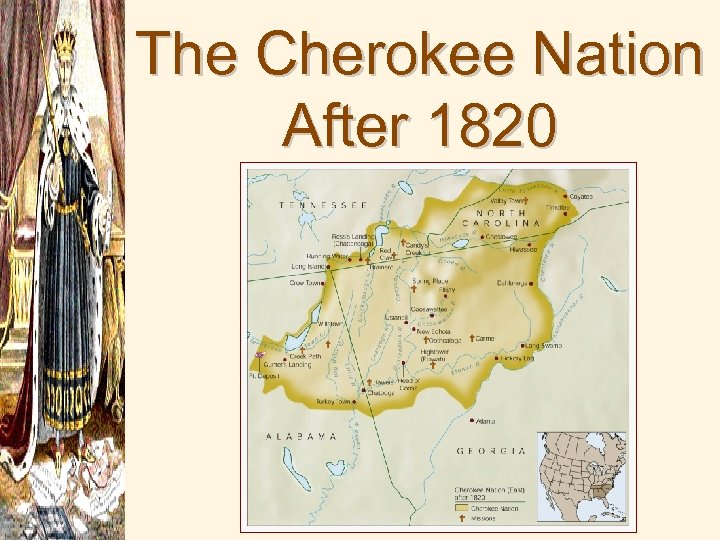 The Cherokee Nation After 1820
The Cherokee Nation After 1820
 Civilized Nation? ? ?
Civilized Nation? ? ?
 Indian Removal 3 Jackson’s Goal? 3 Did Jackson have the Constitutional right to remove and displace the Native Americans? 3 Factor in the following cases: 3 Johnson v. M’Intosh 3 Cherokee Nation v. Georgia 3 Worcester 3 Jackson’s v. Georgia Quote: John Marshall has made his decision, now let him enforce it!
Indian Removal 3 Jackson’s Goal? 3 Did Jackson have the Constitutional right to remove and displace the Native Americans? 3 Factor in the following cases: 3 Johnson v. M’Intosh 3 Cherokee Nation v. Georgia 3 Worcester 3 Jackson’s v. Georgia Quote: John Marshall has made his decision, now let him enforce it!
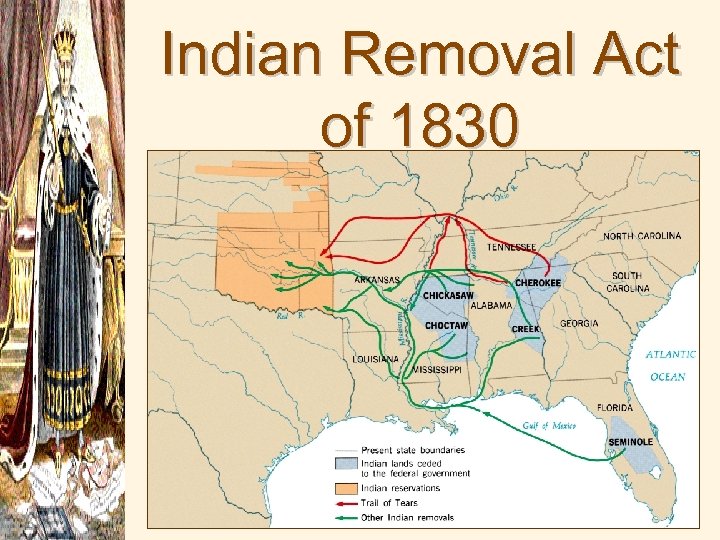 Indian Removal Act of 1830
Indian Removal Act of 1830
 Trail of Tears (1838 -1839)
Trail of Tears (1838 -1839)
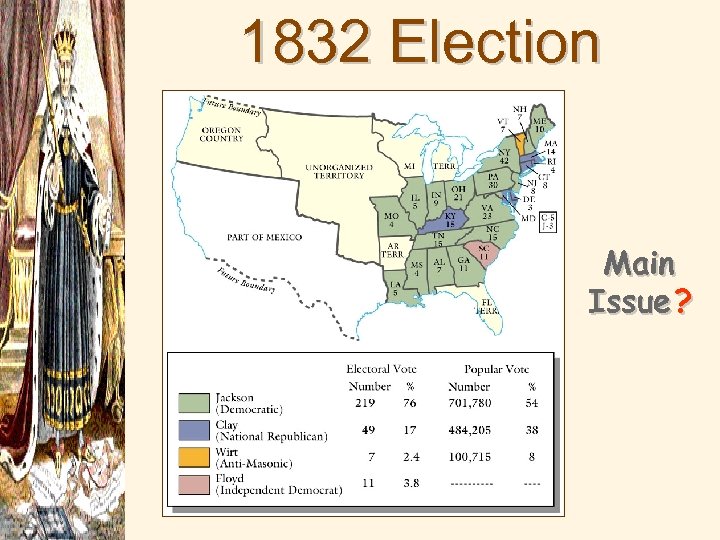 1832 Election Results Main Issue ?
1832 Election Results Main Issue ?
 Jackson and Taney
Jackson and Taney
 The Specie Circular (1836) 3 “wildcat banks. ” 3 buy future federal land only with gold or silver. 3 Jackson’s goal?
The Specie Circular (1836) 3 “wildcat banks. ” 3 buy future federal land only with gold or silver. 3 Jackson’s goal?
 Results of the Specie Circular $ Banknotes loose their value. $ Land sales plummeted. $ Credit not available. $ Businesses began to fail. $ Unemployment rose. The Panic of 1837!
Results of the Specie Circular $ Banknotes loose their value. $ Land sales plummeted. $ Credit not available. $ Businesses began to fail. $ Unemployment rose. The Panic of 1837!
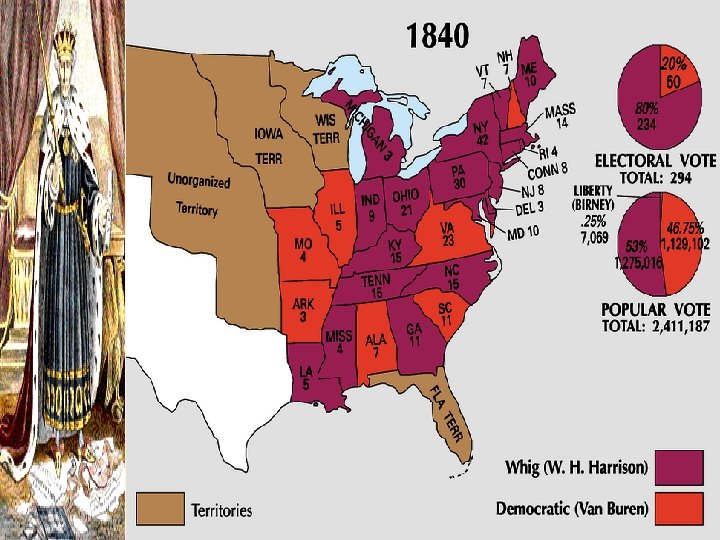
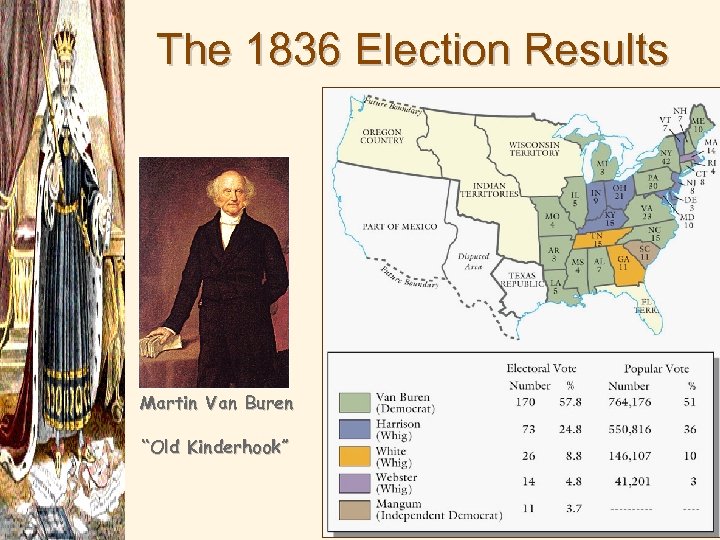 The 1836 Election Results Martin Van Buren “Old Kinderhook”
The 1836 Election Results Martin Van Buren “Old Kinderhook”
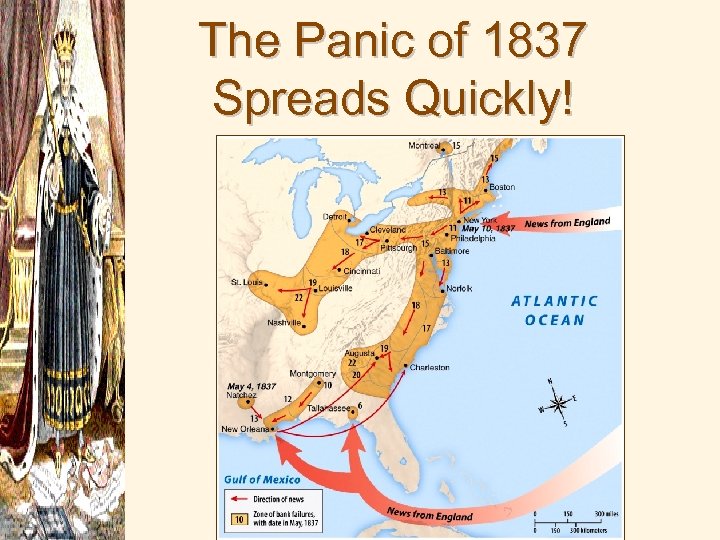 The Panic of 1837 Spreads Quickly!
The Panic of 1837 Spreads Quickly!