f8ebc20124aa476ad84508b8edd2835c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Information Retrieval Adapted from Lectures by Berthier Ribeiro-Neto (Brazil), Prabhakar Raghavan (Yahoo and Stanford) and Christopher Manning (Stanford) Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 1
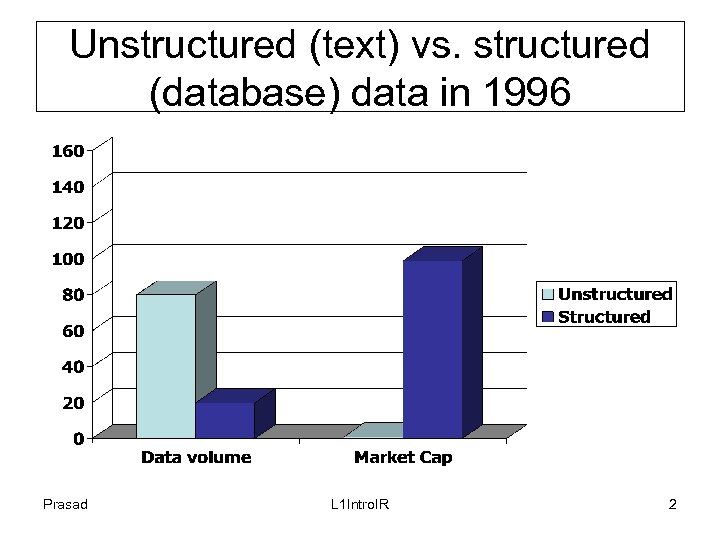
Unstructured (text) vs. structured (database) data in 1996 Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 2
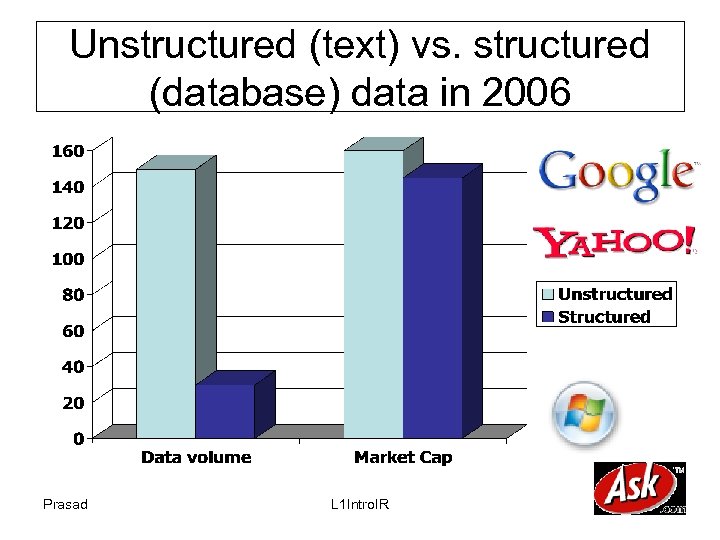
Unstructured (text) vs. structured (database) data in 2006 Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 3
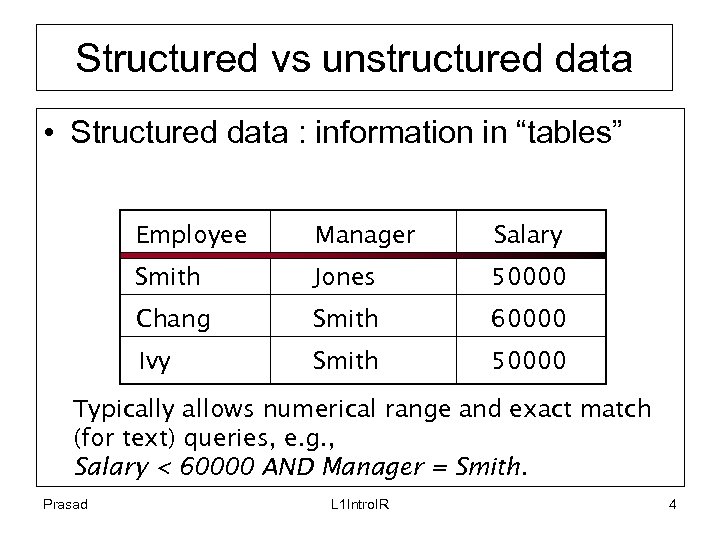
Structured vs unstructured data • Structured data : information in “tables” Employee Manager Salary Smith Jones 50000 Chang Smith 60000 Ivy Smith 50000 Typically allows numerical range and exact match (for text) queries, e. g. , Salary < 60000 AND Manager = Smith. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 4

Unstructured data • Typically refers to free text • Allows q. Keyword-based queries including operators q. More sophisticated “concept” queries, e. g. , • find all web pages dealing with drug abuse Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 5
Semi-structured data • In fact almost no data is “unstructured” q. E. g. , this slide has distinctly identified zones such as the Title and Bullets • Facilitates “semi-structured” search such as q. Title contains data AND Bullets contain search … to say nothing of linguistic structure Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 6
What is IR? • Representation • Keywords/Phrases, Structure/Fonts, Counts, etc • Organization and Storage • Inverted File Index, Compressed, etc • Hardware Architecture and Memory Hierarchy • Access to information items • Interface : Spell-checker to tree-structured display • Visualization : Labeled Clusters, Timelines, Spring graphs, etc. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 7
Ultimate Focus of IR • Satisfying user information need q Emphasis is on retrieval of information (not data) • User information need q. Printer reviews q. Book prices and availability q. Words in which all vowels appear q. Anagram/Permutations of art • Predicting which documents are relevant, and then linearly ranking them. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 8
DIKW Hierarchy • Data: Symbolic units q. E. g. , Records of customer. q. E. g. , Bytes from sensors. • Information : Data with an interpretation (Who? , What? , When? , Where? ). q. E. g. , Records of current/new customer grouped by their ages. q. E. g. , Variation in temperature readings. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 9
DIKW Hierarchy • Knowledge : Information organized with theoretical concepts or abstract ideas (How? ) q. E. g. , How many customer have cancelled the accounts in current fiscal year? q. E. g. , Analysis of temperature variation over the years and their causes. • Wisdom : Understanding of fundamental principles + Human Judgement q. E. g. , What strategies can be employed to retain customers in the face of cheaper alternatives? q. E. g. , Global warming issues and the future of Earth. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 10
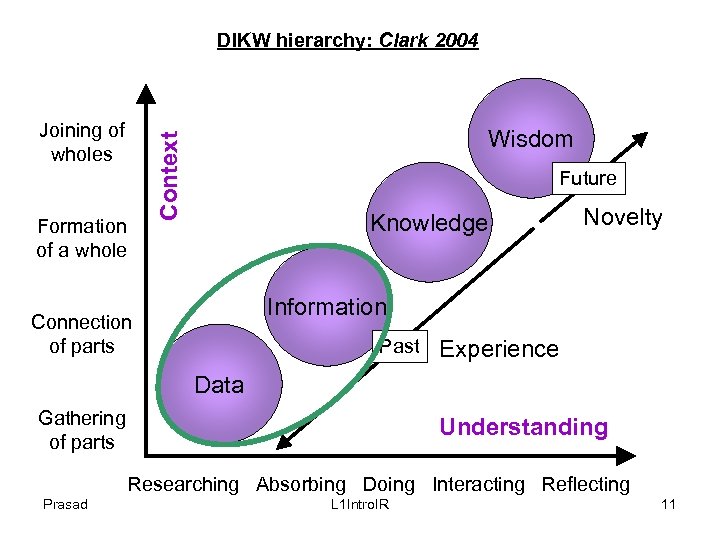
DIKW hierarchy: Clark 2004 Formation of a whole Wisdom Context Joining of wholes Future Knowledge Novelty Information Connection of parts Past Experience Data Gathering of parts Understanding Researching Absorbing Doing Interacting Reflecting Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 11

You see things; and you say "Why? " But I dream things that never were; and I say "Why not? " George Bernard Shaw Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 12
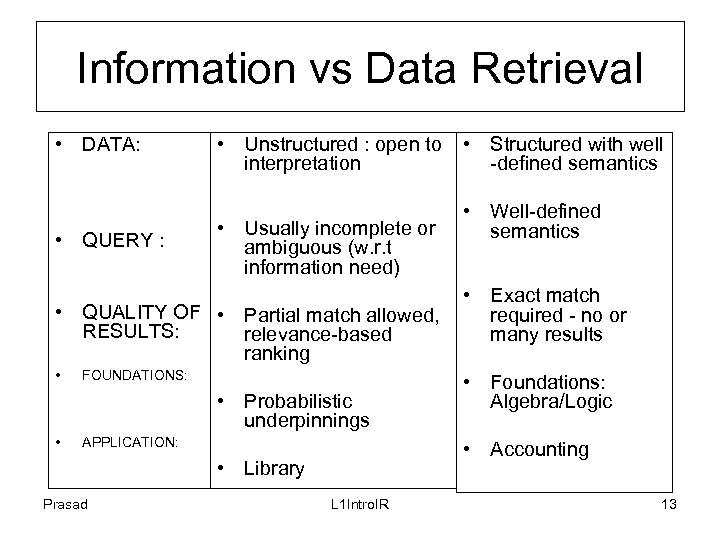
Information vs Data Retrieval • DATA: • QUERY : • Unstructured : open to interpretation • Usually incomplete or ambiguous (w. r. t information need) • QUALITY OF • Partial match allowed, RESULTS: relevance-based ranking • FOUNDATIONS: • Probabilistic underpinnings • APPLICATION: • Well-defined semantics • Exact match required - no or many results • Foundations: Algebra/Logic • Accounting • Library Prasad • Structured with well -defined semantics L 1 Intro. IR 13
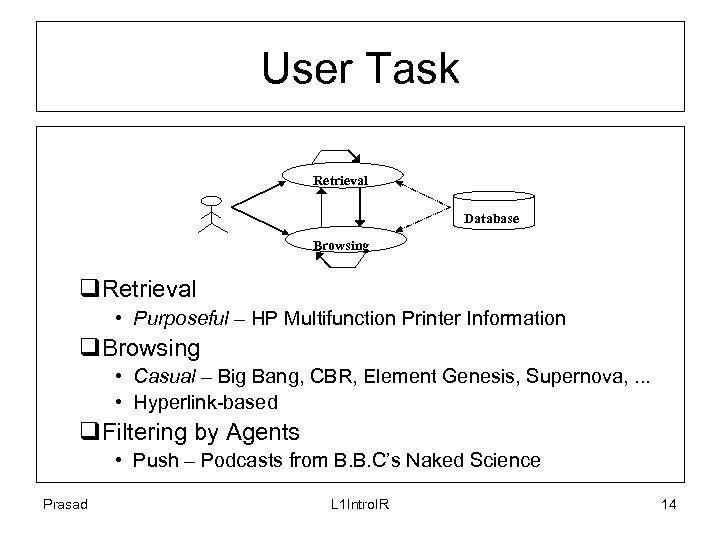
User Task Retrieval Database Browsing q. Retrieval • Purposeful – HP Multifunction Printer Information q. Browsing • Casual – Big Bang, CBR, Element Genesis, Supernova, . . . • Hyperlink-based q. Filtering by Agents • Push – Podcasts from B. B. C’s Naked Science Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 14
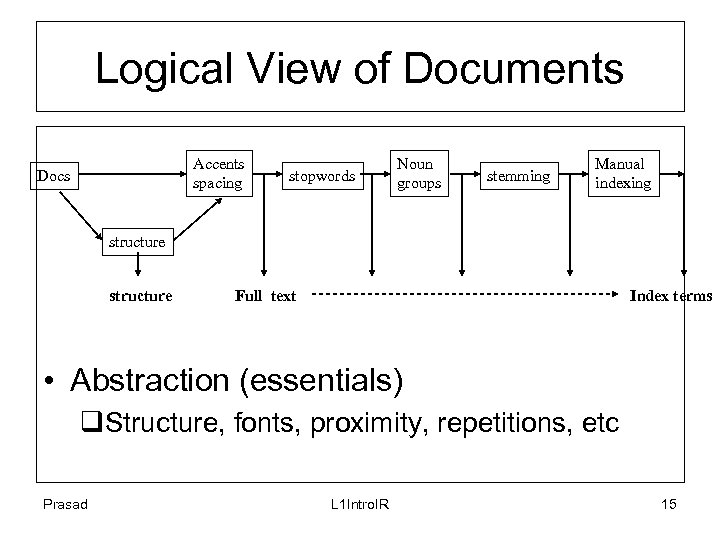
Logical View of Documents Accents spacing Docs stopwords Noun groups stemming Manual indexing structure Full text Index terms • Abstraction (essentials) q. Structure, fonts, proximity, repetitions, etc Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 15
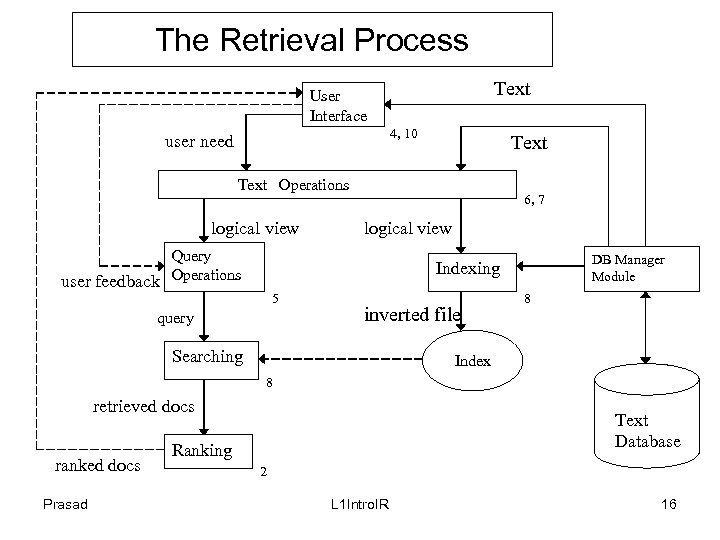
The Retrieval Process Text User Interface 4, 10 user need Text Operations logical view Query user feedback Operations 6, 7 logical view DB Manager Module Indexing 5 query inverted file Searching 8 Index 8 retrieved docs ranked docs Prasad Text Database Ranking 2 L 1 Intro. IR 16
IR Basics • Models and retrievaluation • Query languages and operations • Improve inferring query context – (query expansion, relevance feedback) • Text operations • Improve gleaning of document semantics – (stemming keywords) • Efficient Access: Index and Search q. Visualization, Multimedia, Applications, … Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 17

Clustering and classification • Given a set of docs, group them into clusters based on their contents. • Given a set of topics, plus a new doc D, decide which topic(s) D belongs to. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 18

The web and its challenges • Unusual and diverse documents • Unusual and diverse users, queries, information needs • Beyond terms, exploit ideas from social networks qlink analysis, clickstreams. . . • How do search engines work? And how can we make them better? Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 19

More sophisticated semistructured search • Title is about Object Oriented Programming AND Author something like stro*rup qwhere * is the wild-card operator • Issues: qhow do you process “about”? qhow do you rank results? • The focus of XML search. Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 20

More sophisticated information retrieval • Cross-language information retrieval • Question answering • Summarization • Text mining • … Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 21
Future Progress: Factors/Trends • Large, uncontrolled publishing media q. Quality issues • Cheap, fast and wide access q. Ease of use (query formulation) • Variety and flexibility q. Navigational and Visualization aids q. Directory-based (Table of contents) vs Keywordsbased (Inverted File Index) • Index terms (automatic/human-created) vs Full-text • Privacy, Security, Copyright Prasad L 1 Intro. IR 22
f8ebc20124aa476ad84508b8edd2835c.ppt