724dbaeb3543503fe5f2fa06ef0f9375.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Information Processes & Technology HSC Seminar Singleton High School 28 th May 2010 Tony Skimmings Computer Co-ordinator/Network Administrator IPT Teacher Dungog High School
Information Processes & Technology HSC Seminar Singleton High School 28 th May 2010 Tony Skimmings Computer Co-ordinator/Network Administrator IPT Teacher Dungog High School
 ? ? ?
? ? ?
 Seminar Outline Introduction Course Format HSC Exam Format Core Topic 1 – Project Management Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Exam Preparation / Resources
Seminar Outline Introduction Course Format HSC Exam Format Core Topic 1 – Project Management Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Exam Preparation / Resources
 IPT Course Format Core Topics Project Management (20%) Information Systems and Databases (20%) Communication Systems (20%) Option Strands (40%) TWO of the following options: Transaction Processing Systems Decision Support Systems Automated Manufacturing Systems Multimedia Systems
IPT Course Format Core Topics Project Management (20%) Information Systems and Databases (20%) Communication Systems (20%) Option Strands (40%) TWO of the following options: Transaction Processing Systems Decision Support Systems Automated Manufacturing Systems Multimedia Systems
 Changes to IPT syllabus The IPT syllabus has changed. 2009 was the first year that content from the new syllabus will be examined.
Changes to IPT syllabus The IPT syllabus has changed. 2009 was the first year that content from the new syllabus will be examined.
 The HSC Exam
The HSC Exam
 Exam Format
Exam Format
 Exam Trends Look at past HSC exam papers for trends. Try and identify topics which are regularly examined. Eg SQL from Core topic 2 has been examined in every HSC except 2007 Eg Note the trend towards Web 2. 0 technologies in the most recent exams
Exam Trends Look at past HSC exam papers for trends. Try and identify topics which are regularly examined. Eg SQL from Core topic 2 has been examined in every HSC except 2007 Eg Note the trend towards Web 2. 0 technologies in the most recent exams
 Core Topic 1 – Project Management System Development Cycle Understanding the problem Planning Designing Implementing Testing, Evaluating maintaining
Core Topic 1 – Project Management System Development Cycle Understanding the problem Planning Designing Implementing Testing, Evaluating maintaining
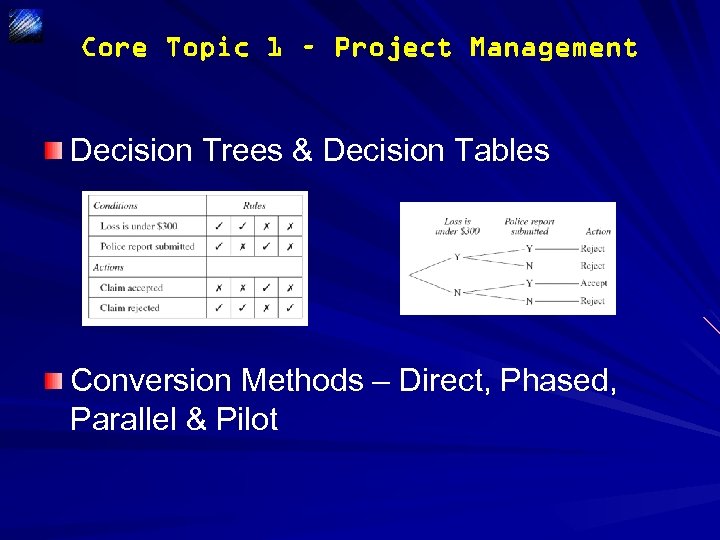 Core Topic 1 – Project Management Decision Trees & Decision Tables Conversion Methods – Direct, Phased, Parallel & Pilot
Core Topic 1 – Project Management Decision Trees & Decision Tables Conversion Methods – Direct, Phased, Parallel & Pilot
 Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2003
Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2003
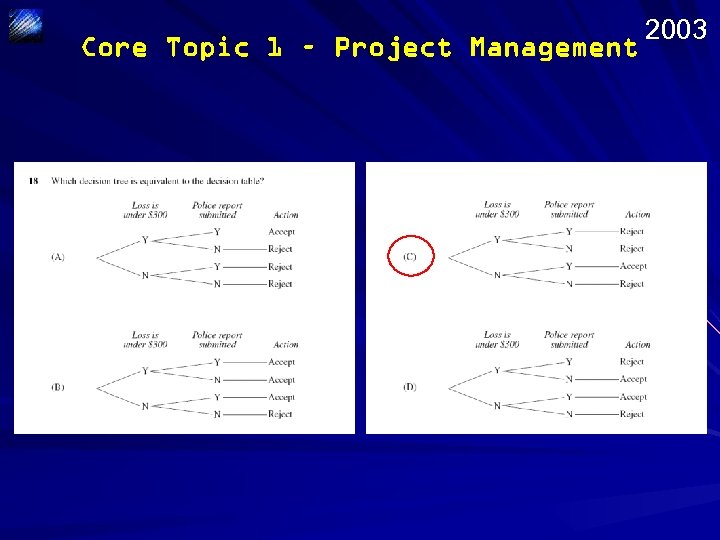 Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2003
Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2003
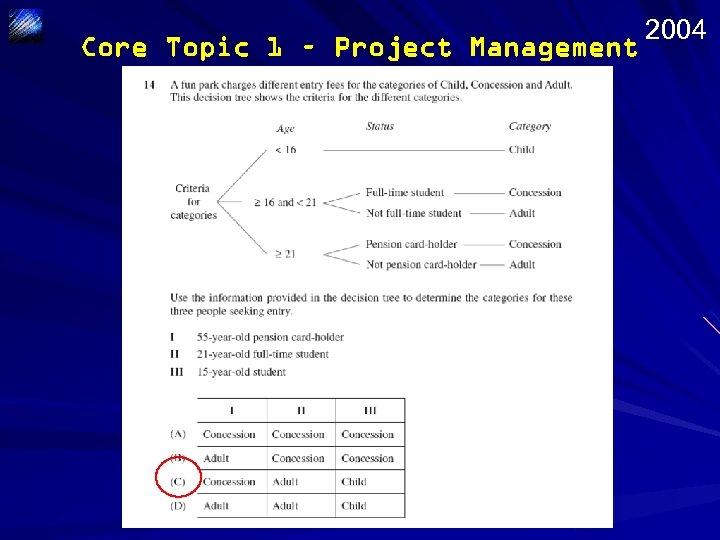 Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2004
Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2004
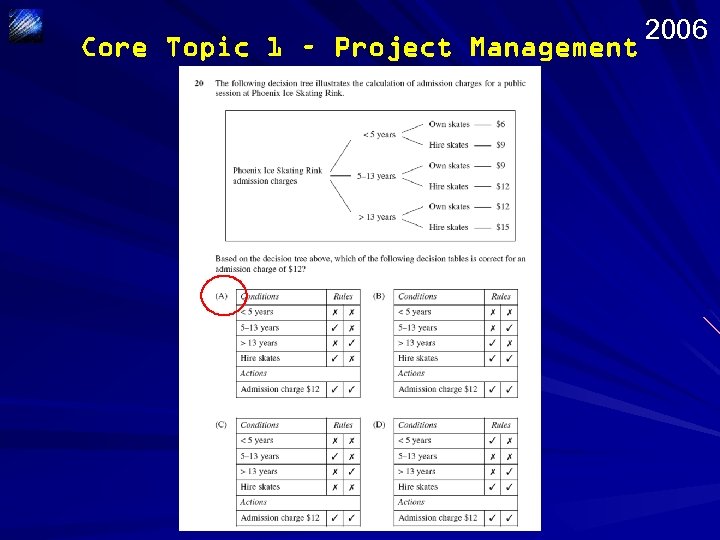 Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2006
Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2006
 Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2003
Core Topic 1 – Project Management 2003
 Core Topic 1 – Project Management Sample answer There are four main methods of implementation. Parallel conversion requires that both the previous manual system and this new one run concurrently until the developer and client are satisfied that the new system is performing as expected. This would normally require two sets of resources which in itself is a disadvantage, but for this company the approach would not be feasible as it would mean that customers would receive two orders – one from the business they rang, and the other as a result of the order being processed by head office and sent to the nearest branch for delivery. Pilot implementation means that the complete system is installed in one isolated area of the business to see if it works well. When the developer and client are satisfied, it can be installed across the whole company. For Gourmet Bytes, this would mean that one or two businesses could convert to the new system, with head office handling the orders for both of these branches, and all other businesses remaining with the previous manual system. This would be a good approach, as employees and management still working with the previous system could watch the new system in operation, and be trained at one of the computerised branches prior to the full implementation of the new system. The only disadvantage would be due to the fact that only two branches are computerised, meaning that a customer order could be relayed to a branch that is not necessarily close to the customer’s location.
Core Topic 1 – Project Management Sample answer There are four main methods of implementation. Parallel conversion requires that both the previous manual system and this new one run concurrently until the developer and client are satisfied that the new system is performing as expected. This would normally require two sets of resources which in itself is a disadvantage, but for this company the approach would not be feasible as it would mean that customers would receive two orders – one from the business they rang, and the other as a result of the order being processed by head office and sent to the nearest branch for delivery. Pilot implementation means that the complete system is installed in one isolated area of the business to see if it works well. When the developer and client are satisfied, it can be installed across the whole company. For Gourmet Bytes, this would mean that one or two businesses could convert to the new system, with head office handling the orders for both of these branches, and all other businesses remaining with the previous manual system. This would be a good approach, as employees and management still working with the previous system could watch the new system in operation, and be trained at one of the computerised branches prior to the full implementation of the new system. The only disadvantage would be due to the fact that only two branches are computerised, meaning that a customer order could be relayed to a branch that is not necessarily close to the customer’s location.
 Core Topic 1 – Project Management Phased implementation requires that the system be installed in phases, where the next stage of the system is installed only when the previous stage has been well implemented. This approach has the advantage that is a particular stage fails it is possible to fall back to the previous stage without abandoning the whole system. In addition, employees are exposed to learning new parts of the system in small stages only. The approach requires that individual stages can be clearly identified – in the case of Gourmet Bytes it is difficult to see how the previous system could remain in use while stages of the new centralised system are introduced. This is because the two systems are fundamentally different in terms of resources used and the method of processing, and it would be difficult to integrate the two system. Direct cutover is the implementation of the new system over a very short time period, such as overnight or over a weekend. It can be traumatic for users if the system is not fully tested and it fails, or if the employees have not been well trained in its use. If, however, the system has been well tested, the employees feel confident in its use and it has been designed to be human centred and is well documented, then it should be a relatively smooth implementation to convert from the old manual system to the new computerised system over this short time period. The advantage of doing this is that the system benefits would be immediately realised to Gourmet Bytes, and customers should benefit greatly from the improved service they now can be offered. This therefore would probably be the best method of implementation to be used by Gourmet Bytes.
Core Topic 1 – Project Management Phased implementation requires that the system be installed in phases, where the next stage of the system is installed only when the previous stage has been well implemented. This approach has the advantage that is a particular stage fails it is possible to fall back to the previous stage without abandoning the whole system. In addition, employees are exposed to learning new parts of the system in small stages only. The approach requires that individual stages can be clearly identified – in the case of Gourmet Bytes it is difficult to see how the previous system could remain in use while stages of the new centralised system are introduced. This is because the two systems are fundamentally different in terms of resources used and the method of processing, and it would be difficult to integrate the two system. Direct cutover is the implementation of the new system over a very short time period, such as overnight or over a weekend. It can be traumatic for users if the system is not fully tested and it fails, or if the employees have not been well trained in its use. If, however, the system has been well tested, the employees feel confident in its use and it has been designed to be human centred and is well documented, then it should be a relatively smooth implementation to convert from the old manual system to the new computerised system over this short time period. The advantage of doing this is that the system benefits would be immediately realised to Gourmet Bytes, and customers should benefit greatly from the improved service they now can be offered. This therefore would probably be the best method of implementation to be used by Gourmet Bytes.
 Core Topic 1 – Project Management Criteria Marks 5 • A response that shows sound understanding of conversion methods. Answer should include adequate description of four conversion methods, an appropriate recommendation and relevant justification of the recommendation 3– 4 • A response that shows clear understanding of at least two conversion methods. A better response should include a recommendation and some relevant justification of the recommendation 1– 2 • A response that shows limited understanding of conversion method(s). At least one conversion method is named and/or briefly described and/or a recommendation proposed and/or justified. Simply naming conversion method(s) will attract a maximum of 1 mark Most candidates displayed a good understanding of the four conversion methods. Better responses included an appropriate recommendation and justification suitable for the described scenario. Poorer responses often confused conversion methods and were not able to provide an appropriate recommendation.
Core Topic 1 – Project Management Criteria Marks 5 • A response that shows sound understanding of conversion methods. Answer should include adequate description of four conversion methods, an appropriate recommendation and relevant justification of the recommendation 3– 4 • A response that shows clear understanding of at least two conversion methods. A better response should include a recommendation and some relevant justification of the recommendation 1– 2 • A response that shows limited understanding of conversion method(s). At least one conversion method is named and/or briefly described and/or a recommendation proposed and/or justified. Simply naming conversion method(s) will attract a maximum of 1 mark Most candidates displayed a good understanding of the four conversion methods. Better responses included an appropriate recommendation and justification suitable for the described scenario. Poorer responses often confused conversion methods and were not able to provide an appropriate recommendation.
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Database basics Databases contain 4 main components – Tables, Forms, Queries and Reports There are two main types of databases: Flat File – 1 Table Relational – Multiple Tables linked together with keys Relational Databases are defined with a schema
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Database basics Databases contain 4 main components – Tables, Forms, Queries and Reports There are two main types of databases: Flat File – 1 Table Relational – Multiple Tables linked together with keys Relational Databases are defined with a schema
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Entity (Table)- An entity is a specific “thing” or “topic” about data that is collected and stored, eg. Entities on Students in school DB Attribute (Field)- An attribute is the defined property of an entity. Attributes are the same as in a flat file database, eg. Student Surname Relationship - A relationship is the way in which entities (tables) are related to one another. eg Student table linked to Subjects table Tuple (Record) – A piece of information in a table. Eg. A Entity students details Tuple Attribute
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Entity (Table)- An entity is a specific “thing” or “topic” about data that is collected and stored, eg. Entities on Students in school DB Attribute (Field)- An attribute is the defined property of an entity. Attributes are the same as in a flat file database, eg. Student Surname Relationship - A relationship is the way in which entities (tables) are related to one another. eg Student table linked to Subjects table Tuple (Record) – A piece of information in a table. Eg. A Entity students details Tuple Attribute
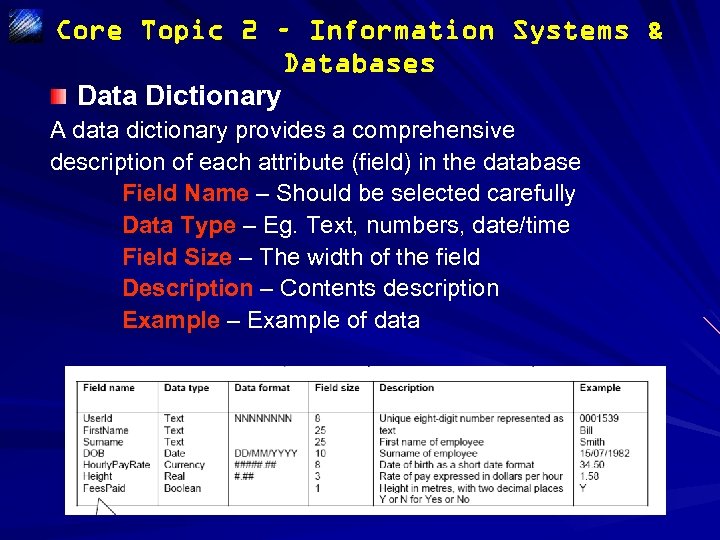 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Data Dictionary A data dictionary provides a comprehensive description of each attribute (field) in the database Field Name – Should be selected carefully Data Type – Eg. Text, numbers, date/time Field Size – The width of the field Description – Contents description Example – Example of data
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases Data Dictionary A data dictionary provides a comprehensive description of each attribute (field) in the database Field Name – Should be selected carefully Data Type – Eg. Text, numbers, date/time Field Size – The width of the field Description – Contents description Example – Example of data
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases SQL Structured Query Language (SQL) is the code which represents queries. SQL queries are designed to search a database for specific data. SELECT (Fields is to be displayed) FROM (Tables to be used) WHERE (Search criteria) ORDER BY (Sequence in which the results are displayed);
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases SQL Structured Query Language (SQL) is the code which represents queries. SQL queries are designed to search a database for specific data. SELECT (Fields is to be displayed) FROM (Tables to be used) WHERE (Search criteria) ORDER BY (Sequence in which the results are displayed);
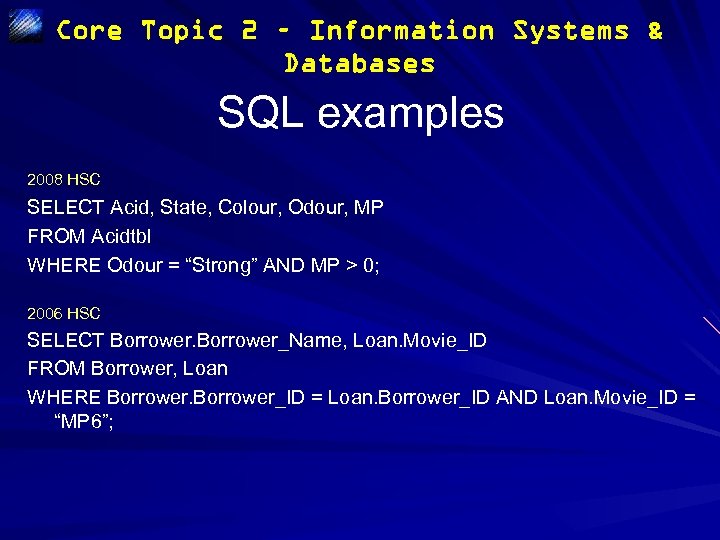 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases SQL examples 2008 HSC SELECT Acid, State, Colour, Odour, MP FROM Acidtbl WHERE Odour = “Strong” AND MP > 0; 2006 HSC SELECT Borrower_Name, Loan. Movie_ID FROM Borrower, Loan WHERE Borrower_ID = Loan. Borrower_ID AND Loan. Movie_ID = “MP 6”;
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases SQL examples 2008 HSC SELECT Acid, State, Colour, Odour, MP FROM Acidtbl WHERE Odour = “Strong” AND MP > 0; 2006 HSC SELECT Borrower_Name, Loan. Movie_ID FROM Borrower, Loan WHERE Borrower_ID = Loan. Borrower_ID AND Loan. Movie_ID = “MP 6”;
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2005
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2005
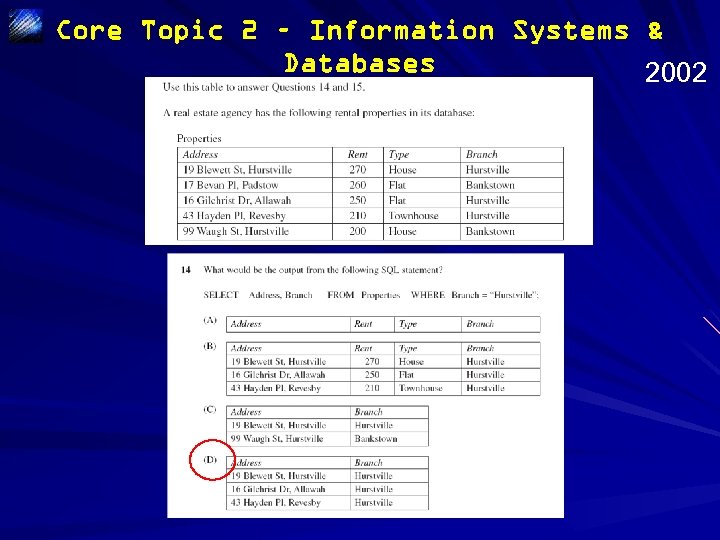 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002
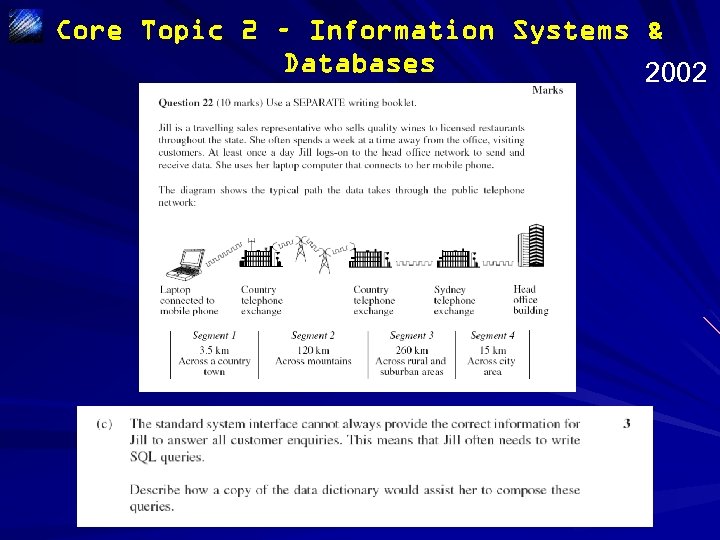 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002 Sample Answer An SQL query requires the field names to be correctly spelt and their data types to be known. The data types will affect whether a value used in a search criterion includes the use of quotes (for a text value) or no quotes (for a numeric value). eg a typical query that Jill would need to construct could be: SELECT price, description FROM wine_lists WHERE price < 35 AND type = “shiraz” OR colour_code = “ 2” Jill would need to know that the attribute colour_code uses an underscore (and not a full stop for example), and that type and colour_code attributes are both text, requiring quotes around the comparison value, whilst price is numeric.
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002 Sample Answer An SQL query requires the field names to be correctly spelt and their data types to be known. The data types will affect whether a value used in a search criterion includes the use of quotes (for a text value) or no quotes (for a numeric value). eg a typical query that Jill would need to construct could be: SELECT price, description FROM wine_lists WHERE price < 35 AND type = “shiraz” OR colour_code = “ 2” Jill would need to know that the attribute colour_code uses an underscore (and not a full stop for example), and that type and colour_code attributes are both text, requiring quotes around the comparison value, whilst price is numeric.
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002 Criteria/Marks 3 • Demonstrates a clear understanding of data dictionaries by describing how a data dictionary would assist Jill in this situation 2 • Demonstrates an understanding of data dictionaries and how they are used to compose queries, links the use of a data dictionary to the scenario 1 • Demonstrates some knowledge of a data dictionary by identifying its main features. Does not relate these features to the scenario. Candidates generally were able to identify characteristics of a data dictionary but were unable to describe how a copy of the data dictionary would help compose SQL queries. Responses were often general in their description of data dictionaries without again linking it to the scenario. Some candidates constructed SQL queries to help support their responses. It was pleasing to see that many candidates were able to correctly use SQL but this was not an important feature of the response required.
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2002 Criteria/Marks 3 • Demonstrates a clear understanding of data dictionaries by describing how a data dictionary would assist Jill in this situation 2 • Demonstrates an understanding of data dictionaries and how they are used to compose queries, links the use of a data dictionary to the scenario 1 • Demonstrates some knowledge of a data dictionary by identifying its main features. Does not relate these features to the scenario. Candidates generally were able to identify characteristics of a data dictionary but were unable to describe how a copy of the data dictionary would help compose SQL queries. Responses were often general in their description of data dictionaries without again linking it to the scenario. Some candidates constructed SQL queries to help support their responses. It was pleasing to see that many candidates were able to correctly use SQL but this was not an important feature of the response required.
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2003
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2003
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2003 Sample Answer SELECT First_name, Last_name, Home_phone FROM FRIENDS WHERE State=“NSW” ORDER BY Last_name Ascending; Criteria/Marks 3 • A correct SQL query that contains the required fields, table name, selection criteria and sort order as outlined in the question. Correct SQL keywords must be used (Full marks may be awarded to a solution with minor syntax errors) 1– 2 • An incomplete query that displays some understanding of SQL. At a minimum students must undertake some selection of fields • The aim of this part was to construct an SQL query. The majority of candidates showed an understanding of SQL. The better responses demonstrated a good understanding of the keywords and relevant data required for each. Poor responses only showed a selection of the required fields and in some instances the criteria required, while others could only show the keywords of SELECT, FROM, WHERE, ORDER BY, without being able to apply this syntax to the given data.
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2003 Sample Answer SELECT First_name, Last_name, Home_phone FROM FRIENDS WHERE State=“NSW” ORDER BY Last_name Ascending; Criteria/Marks 3 • A correct SQL query that contains the required fields, table name, selection criteria and sort order as outlined in the question. Correct SQL keywords must be used (Full marks may be awarded to a solution with minor syntax errors) 1– 2 • An incomplete query that displays some understanding of SQL. At a minimum students must undertake some selection of fields • The aim of this part was to construct an SQL query. The majority of candidates showed an understanding of SQL. The better responses demonstrated a good understanding of the keywords and relevant data required for each. Poor responses only showed a selection of the required fields and in some instances the criteria required, while others could only show the keywords of SELECT, FROM, WHERE, ORDER BY, without being able to apply this syntax to the given data.
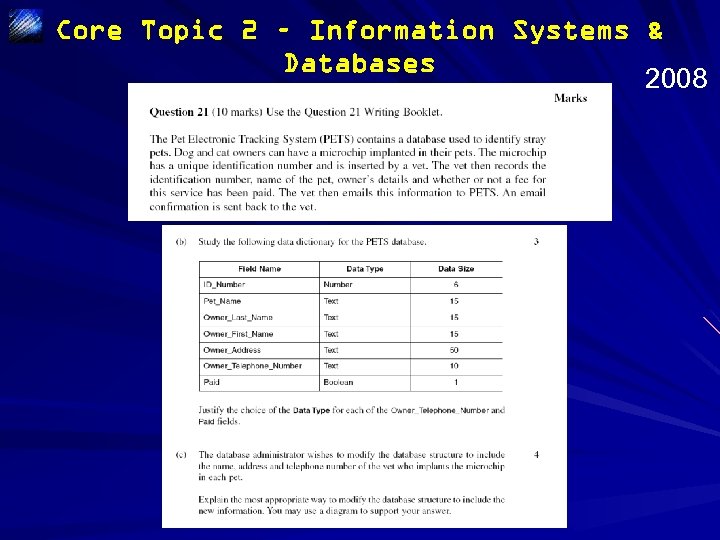 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2008
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2008
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2008 Sample Answer With reference to the Owner_Telephone_Number field, the text data type is appropriate because it allows numbers with leading zeros to be stored without being lost. If this field was set to numerical data type the leading zero would be lost. The text data type also allows for entry of other characters such as brackets around area codes or spaces. Since no calculations are done on telephone numbers, text is also appropriate. For the Paid field the Boolean data type is appropriate. It allows for greater data integrity. If it were set to something like text people could enter Yes or Y or True or T. When you search on this field it would not give you all the information, ie Boolean data type improves data integrity. It also saves space in the database.
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 2008 Sample Answer With reference to the Owner_Telephone_Number field, the text data type is appropriate because it allows numbers with leading zeros to be stored without being lost. If this field was set to numerical data type the leading zero would be lost. The text data type also allows for entry of other characters such as brackets around area codes or spaces. Since no calculations are done on telephone numbers, text is also appropriate. For the Paid field the Boolean data type is appropriate. It allows for greater data integrity. If it were set to something like text people could enter Yes or Y or True or T. When you search on this field it would not give you all the information, ie Boolean data type improves data integrity. It also saves space in the database.
 Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 3 Provides a clear justification for the use of each data type with reference to the characteristics of each data type 2 Provides clear characteristics and justification for the use of one of the data types AND limited characteristics and justification for the other OR Identifies a characteristic of both data types 1 Identifies a characteristic of one of the data types Better responses justified the choice of data type for the Owner_Telephone_Number (text) and Paid (Boolean) fields by providing characteristics as well as a justification for their inclusion. Mid-range responses provided characteristics of the data types only. In weaker responses, candidates attempted to resolve an incorrectly identified error in the data dictionary, stating that number and currency were a better choice of data type, or they restated parts of the question.
Core Topic 2 – Information Systems & Databases 3 Provides a clear justification for the use of each data type with reference to the characteristics of each data type 2 Provides clear characteristics and justification for the use of one of the data types AND limited characteristics and justification for the other OR Identifies a characteristic of both data types 1 Identifies a characteristic of one of the data types Better responses justified the choice of data type for the Owner_Telephone_Number (text) and Paid (Boolean) fields by providing characteristics as well as a justification for their inclusion. Mid-range responses provided characteristics of the data types only. In weaker responses, candidates attempted to resolve an incorrectly identified error in the data dictionary, stating that number and currency were a better choice of data type, or they restated parts of the question.
 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Network Hardware Devices Hubs and Switches Routers Modems Bridges and Gateways Network Interface Cards (NIC) mobile phones Cables wireless access points Bluetooth devices
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Network Hardware Devices Hubs and Switches Routers Modems Bridges and Gateways Network Interface Cards (NIC) mobile phones Cables wireless access points Bluetooth devices
 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Packet switching demo
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Packet switching demo
 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems The Postal analogy Data packets = Postcards Computer/Device = Houses Router = Post Office Switch = Postman Hub = Junk Mail deliverer
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems The Postal analogy Data packets = Postcards Computer/Device = Houses Router = Post Office Switch = Postman Hub = Junk Mail deliverer
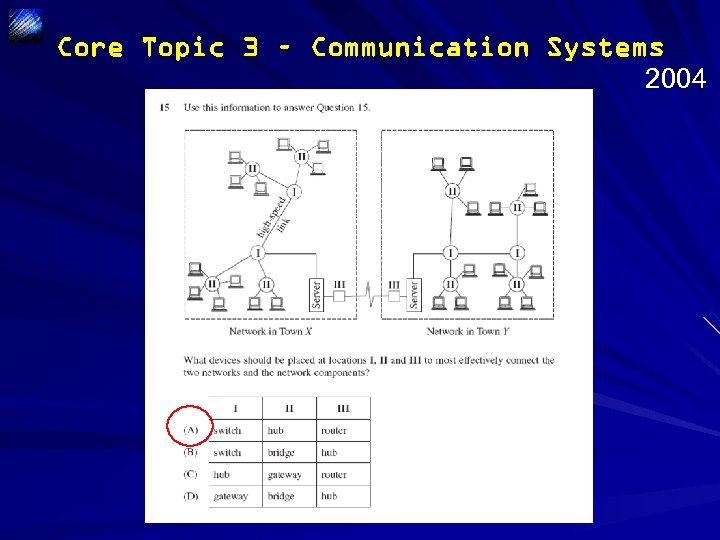 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems 2004
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems 2004
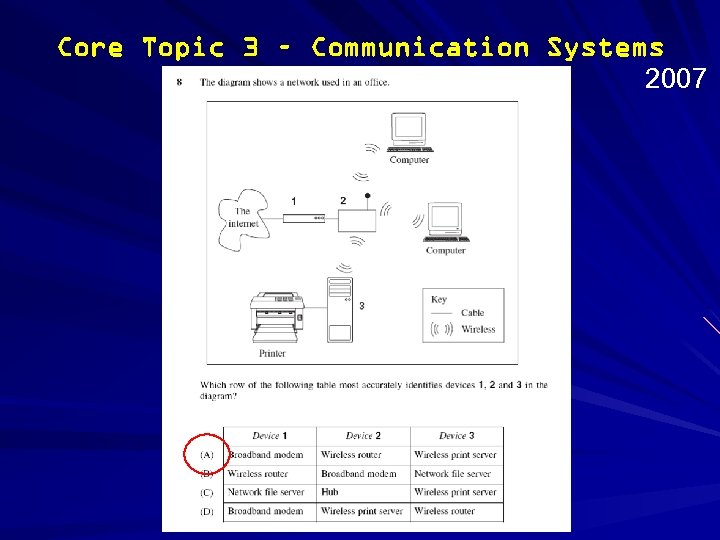 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems 2007
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems 2007
 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems 2002
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems 2002
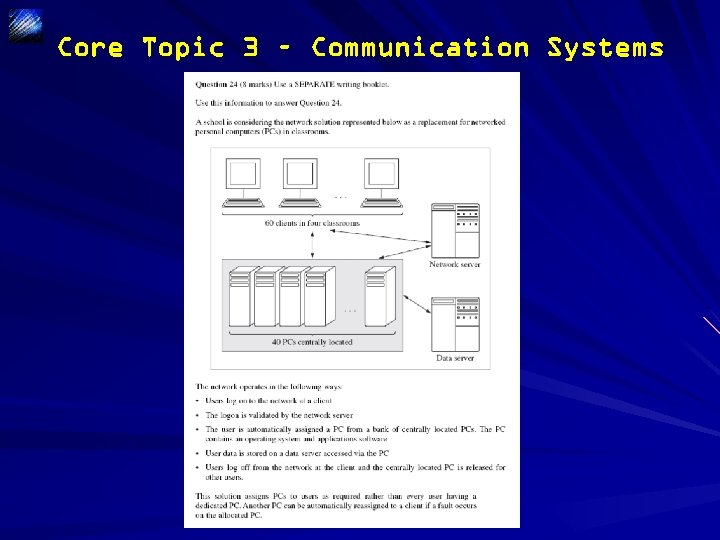 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems
 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Sample Answer The network that the school is considering uses “client – server” network architecture. The 40 centrally located PCs are the clients which are controlled by the network server. The data server provides storage for user files. The terminals in the classrooms simply provide a connection to the centrally located PCs. They do not actually carry out any processing of data. When a user logs on at the terminal an IP address is assigned to the centrally located PC and the user’s credentials are authenticated. When a user logs off at the terminal the session will be closed. All of these processes are carried out by the network server. When a user accesses application software (eg. A word processing package) the processing is being carried out on the centrally located PCs with the data being sent to the terminal in the classroom.
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems Sample Answer The network that the school is considering uses “client – server” network architecture. The 40 centrally located PCs are the clients which are controlled by the network server. The data server provides storage for user files. The terminals in the classrooms simply provide a connection to the centrally located PCs. They do not actually carry out any processing of data. When a user logs on at the terminal an IP address is assigned to the centrally located PC and the user’s credentials are authenticated. When a user logs off at the terminal the session will be closed. All of these processes are carried out by the network server. When a user accesses application software (eg. A word processing package) the processing is being carried out on the centrally located PCs with the data being sent to the terminal in the classroom.
 Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems • 2– 3 Response clearly indicates the relationship between the client and server(s) in terms of processing when a user logs on and accesses an application package. Better responses will do this for both log on and application package access • 1 Response describes where some processing takes place OR • Response describes what processing takes place Candidates needed to clearly show that they understood the nature of processing in a client/server network. Better responses clearly stated that processing was away from the client in the classroom, with usernames and passwords being validated in the server. Some responses identified the server as the processor of the login details, but a generic statement of ‘accessing the application software from the centrally located PCs’ indicated that they were unsure of where the processing was occurring, as required by the question. Responses needed to indicate where the processing occurred. Better responses also indicated unambiguously that the application software was running on the centrally located PCs, with the clients in the classroom only acting as an interface to the user. Weaker responses simply rewrote the information from the stimulus material, which did not clearly display the candidate’s knowledge.
Core Topic 3 – Communication Systems • 2– 3 Response clearly indicates the relationship between the client and server(s) in terms of processing when a user logs on and accesses an application package. Better responses will do this for both log on and application package access • 1 Response describes where some processing takes place OR • Response describes what processing takes place Candidates needed to clearly show that they understood the nature of processing in a client/server network. Better responses clearly stated that processing was away from the client in the classroom, with usernames and passwords being validated in the server. Some responses identified the server as the processor of the login details, but a generic statement of ‘accessing the application software from the centrally located PCs’ indicated that they were unsure of where the processing was occurring, as required by the question. Responses needed to indicate where the processing occurred. Better responses also indicated unambiguously that the application software was running on the centrally located PCs, with the clients in the classroom only acting as an interface to the user. Weaker responses simply rewrote the information from the stimulus material, which did not clearly display the candidate’s knowledge.
 Exam Preparation / Tips / Resources “Failing to prepare is preparing to fail” The exam is based on the entire HSC course. It is very important to understand that you must be able to apply your knowledge to a variety of scenarios where you must recognise that the question involves communication systems or database information systems. Your answers must relate to the question, the scenario given and show that you can apply the facts you have learnt to the given situations. As well as the content for the course it is essential to understand the glossary of key words used in all of the HSC examinations. Words from identify to critically analyse will assist you in determining the depth that is required in your answer. The glossary of key words is available online. Relate practical experiences, projects and assessments from class to questions.
Exam Preparation / Tips / Resources “Failing to prepare is preparing to fail” The exam is based on the entire HSC course. It is very important to understand that you must be able to apply your knowledge to a variety of scenarios where you must recognise that the question involves communication systems or database information systems. Your answers must relate to the question, the scenario given and show that you can apply the facts you have learnt to the given situations. As well as the content for the course it is essential to understand the glossary of key words used in all of the HSC examinations. Words from identify to critically analyse will assist you in determining the depth that is required in your answer. The glossary of key words is available online. Relate practical experiences, projects and assessments from class to questions.
 Exam Preparation / Tips / Resources Use your knowledge the network at your school, your library or perhaps where you have a part-time job. Look around you, investigate information systems, ask questions. What is the purpose of the system? Inquire about the information technology used such as hardware and software, identify the data and the participants and the environment of the system. In the examination: Read the question carefully Underline the important aspects of the given scenario Identify what the key words, such as compare and contrast, are asking you to do Relate your answer to the case study, scenario or real-life problem that is in the question Use diagrams where possible and relevant.
Exam Preparation / Tips / Resources Use your knowledge the network at your school, your library or perhaps where you have a part-time job. Look around you, investigate information systems, ask questions. What is the purpose of the system? Inquire about the information technology used such as hardware and software, identify the data and the participants and the environment of the system. In the examination: Read the question carefully Underline the important aspects of the given scenario Identify what the key words, such as compare and contrast, are asking you to do Relate your answer to the case study, scenario or real-life problem that is in the question Use diagrams where possible and relevant.
 Exam Preparation / Tips / Resources Board of Studies – for Past HSCs, Exam Notes, Multiple Choice questions, Standards Packages. HSC Online Internet resources – SMH study guides, howstuffworks, webopedia etc **** Most importantly your Teacher and classmates.
Exam Preparation / Tips / Resources Board of Studies – for Past HSCs, Exam Notes, Multiple Choice questions, Standards Packages. HSC Online Internet resources – SMH study guides, howstuffworks, webopedia etc **** Most importantly your Teacher and classmates.


