210e90fd10081d90cc53a1834d159f54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group 10 Cheetah 2 Features Presented By: Sanjit Chakraborty / Jeff Laube Date: Jan 22, 2009 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group 10 Cheetah 2 Features Presented By: Sanjit Chakraborty / Jeff Laube Date: Jan 22, 2009 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
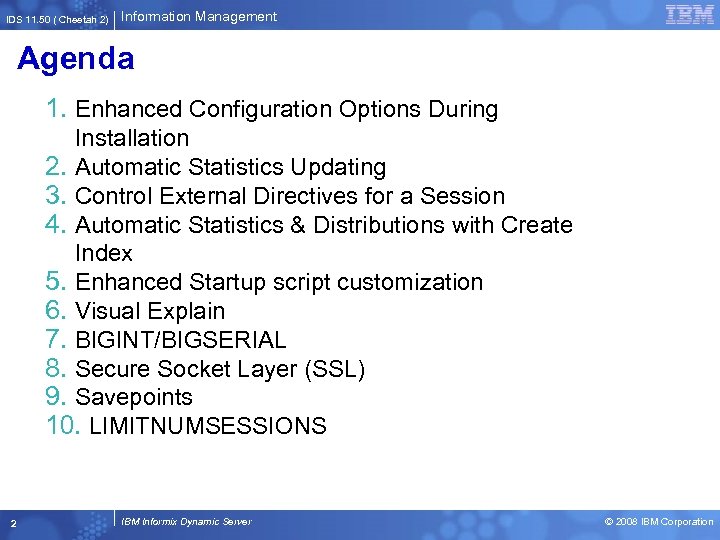 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Agenda 1. Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation 2. Automatic Statistics Updating 3. Control External Directives for a Session 4. Automatic Statistics & Distributions with Create Index 5. Enhanced Startup script customization 6. Visual Explain 7. BIGINT/BIGSERIAL 8. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) 9. Savepoints 10. LIMITNUMSESSIONS 2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Agenda 1. Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation 2. Automatic Statistics Updating 3. Control External Directives for a Session 4. Automatic Statistics & Distributions with Create Index 5. Enhanced Startup script customization 6. Visual Explain 7. BIGINT/BIGSERIAL 8. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) 9. Savepoints 10. LIMITNUMSESSIONS 2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 1: Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 1: Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
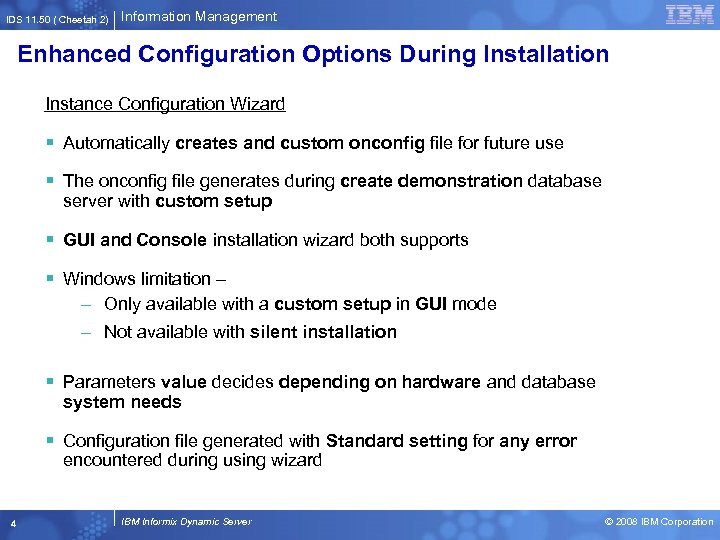 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard § Automatically creates and custom onconfig file for future use § The onconfig file generates during create demonstration database server with custom setup § GUI and Console installation wizard both supports § Windows limitation – – Only available with a custom setup in GUI mode – Not available with silent installation § Parameters value decides depending on hardware and database system needs § Configuration file generated with Standard setting for any error encountered during using wizard 4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard § Automatically creates and custom onconfig file for future use § The onconfig file generates during create demonstration database server with custom setup § GUI and Console installation wizard both supports § Windows limitation – – Only available with a custom setup in GUI mode – Not available with silent installation § Parameters value decides depending on hardware and database system needs § Configuration file generated with Standard setting for any error encountered during using wizard 4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
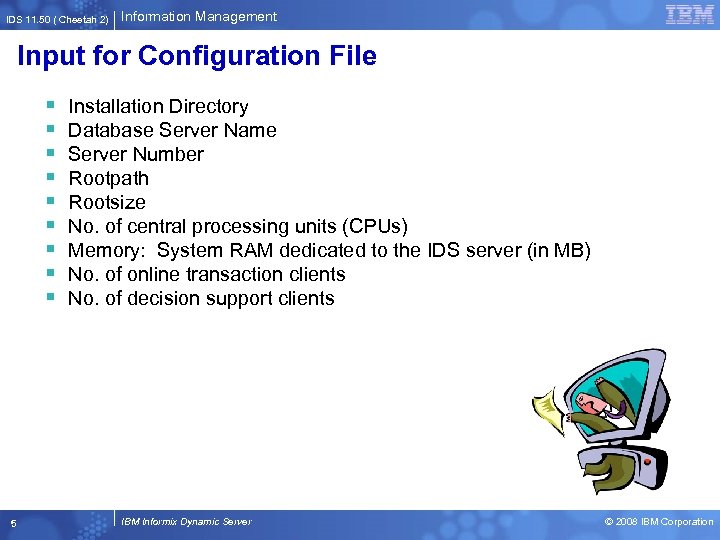 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Input for Configuration File § § § § § 5 Installation Directory Database Server Name Server Number Rootpath Rootsize No. of central processing units (CPUs) Memory: System RAM dedicated to the IDS server (in MB) No. of online transaction clients No. of decision support clients IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Input for Configuration File § § § § § 5 Installation Directory Database Server Name Server Number Rootpath Rootsize No. of central processing units (CPUs) Memory: System RAM dedicated to the IDS server (in MB) No. of online transaction clients No. of decision support clients IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
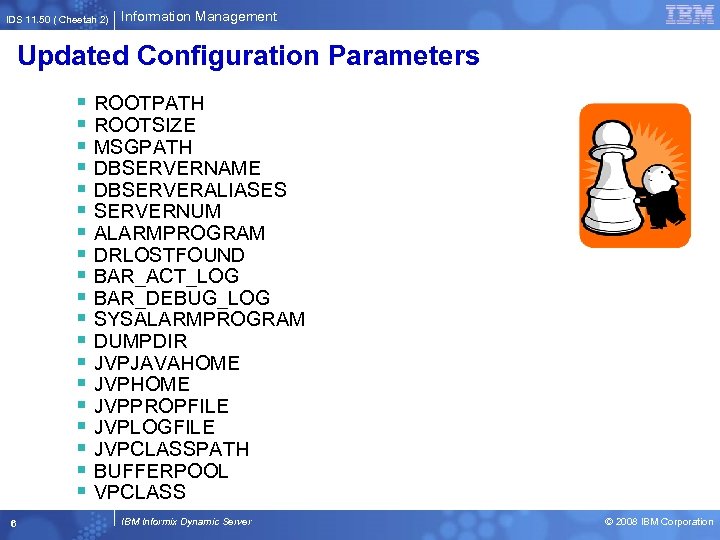 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Updated Configuration Parameters § § § § § 6 ROOTPATH ROOTSIZE MSGPATH DBSERVERNAME DBSERVERALIASES SERVERNUM ALARMPROGRAM DRLOSTFOUND BAR_ACT_LOG BAR_DEBUG_LOG SYSALARMPROGRAM DUMPDIR JVPJAVAHOME JVPPROPFILE JVPLOGFILE JVPCLASSPATH BUFFERPOOL VPCLASS IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Updated Configuration Parameters § § § § § 6 ROOTPATH ROOTSIZE MSGPATH DBSERVERNAME DBSERVERALIASES SERVERNUM ALARMPROGRAM DRLOSTFOUND BAR_ACT_LOG BAR_DEBUG_LOG SYSALARMPROGRAM DUMPDIR JVPJAVAHOME JVPPROPFILE JVPLOGFILE JVPCLASSPATH BUFFERPOOL VPCLASS IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Files Generated § Customized Onconfig file –
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Files Generated § Customized Onconfig file –
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard UNIX install (either Typical or Custom) Do you want to create an IDS demonstration database server instance? [X] 1 - Yes [ ] 2 - No Demonstration Database Instance Configuration [ ] 1 - Use my own configuration file. [ ] 2 - Use the default configuration file. [X] 3 - Customize the default configuration file to suit your needs and hardware. Specify your server configuration parameters (Server Number should be in the range of 0 to 255). Server Name [demo_on] ids 1150 Server Number [0] 50 ROOTPATH [/usr 2/products/11. 50. UC 2/demo/server/online_root] /chunks/1152/chunk 1 ROOTSIZE (MB) [760] 204800 Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] Configuration Setup Modify any values if you want to customize database server configuration settings. Processors to use [1] 1 Memory to use (MB) [512] 128 Online Transaction Clients (applications that frequently update databases with multiuser input) [1] 1000 Decision Support Clients (applications for querying databases to gather reporting information) [1] 25 8 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard UNIX install (either Typical or Custom) Do you want to create an IDS demonstration database server instance? [X] 1 - Yes [ ] 2 - No Demonstration Database Instance Configuration [ ] 1 - Use my own configuration file. [ ] 2 - Use the default configuration file. [X] 3 - Customize the default configuration file to suit your needs and hardware. Specify your server configuration parameters (Server Number should be in the range of 0 to 255). Server Name [demo_on] ids 1150 Server Number [0] 50 ROOTPATH [/usr 2/products/11. 50. UC 2/demo/server/online_root] /chunks/1152/chunk 1 ROOTSIZE (MB) [760] 204800 Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] Configuration Setup Modify any values if you want to customize database server configuration settings. Processors to use [1] 1 Memory to use (MB) [512] 128 Online Transaction Clients (applications that frequently update databases with multiuser input) [1] 1000 Decision Support Clients (applications for querying databases to gather reporting information) [1] 25 8 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard Installation log after configuration parameters set: Installing IBM Informix Dynamic Server Version 11. 50. Please wait. . . Creating demonstration database server instance. . . - Creating demonstration database server onconfig file at /usr 2/products/11. 50. UC 2/etc/onconfig. ids 1150 Creating demonstration database server instance. . . - Demonstration database server instance initialized successfully. Please read the information below. The IBM Informix Dynamic Server demonstration database server has been created. Check the log file to determine if it was successfully initialized: /usr 2/products/11. 50. UC 2/demo/server/online. log. (Note: the above log is the verbose output to screen, it is not logged to a physical file) 9 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard Installation log after configuration parameters set: Installing IBM Informix Dynamic Server Version 11. 50. Please wait. . . Creating demonstration database server instance. . . - Creating demonstration database server onconfig file at /usr 2/products/11. 50. UC 2/etc/onconfig. ids 1150 Creating demonstration database server instance. . . - Demonstration database server instance initialized successfully. Please read the information below. The IBM Informix Dynamic Server demonstration database server has been created. Check the log file to determine if it was successfully initialized: /usr 2/products/11. 50. UC 2/demo/server/online. log. (Note: the above log is the verbose output to screen, it is not logged to a physical file) 9 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard Windows install 10 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard Windows install 10 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard 11 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard 11 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
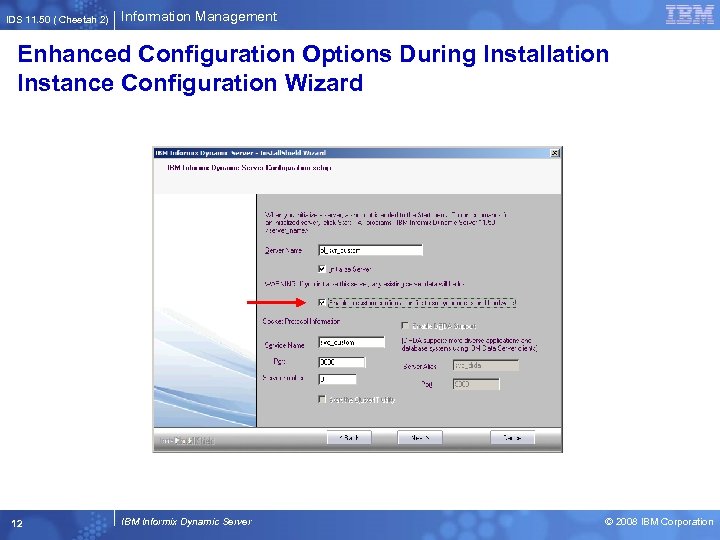 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard . 12 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard . 12 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard . 13 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation Instance Configuration Wizard . 13 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 2: Automatic Statistics Updating (AUS) IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 2: Automatic Statistics Updating (AUS) IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Why Auto Update Statistics (AUS)? § Users must update statistics and distributions manually to help optimizer make correct decisions to run query efficiently – Many of us do not realize this and encounter poor performance § When to run Update Statistics? § What statistics and distributions need to be updated? – Not easy to understand – Change periodically – Differ for each system § AUS provides ability to automate the maintenance of optimizer statistics 15 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Why Auto Update Statistics (AUS)? § Users must update statistics and distributions manually to help optimizer make correct decisions to run query efficiently – Many of us do not realize this and encounter poor performance § When to run Update Statistics? § What statistics and distributions need to be updated? – Not easy to understand – Change periodically – Differ for each system § AUS provides ability to automate the maintenance of optimizer statistics 15 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management AUS Implementation § A set of procedures which will be invoked by the database scheduler to automate update statistics – Installed as part of the server – Users can write SQL statements to manipulate the AUS configuration § Open Admin Tool (OAT) graphical interface allows easier control of the different AUS policies – Open source download available from iiug. org and IBM websites – Display AUS information in easy to read format – Simple point and click interface 16 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management AUS Implementation § A set of procedures which will be invoked by the database scheduler to automate update statistics – Installed as part of the server – Users can write SQL statements to manipulate the AUS configuration § Open Admin Tool (OAT) graphical interface allows easier control of the different AUS policies – Open source download available from iiug. org and IBM websites – Display AUS information in easy to read format – Simple point and click interface 16 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management AUS Implementation - Database Tasks § Tasks in ph_task table § Auto Update Statistics Evaluation – Analyzes all the tables in all logged databases – Locates tables which require new or updated optimizer statistics – Builds the update statistics commands – Inserts the commands into the table aus_cmd_list § Auto Update Statistics Refresh – Executes the update statistics commands from aus_cmd_list table in a priority order within a specified time – After the command completes, it is moved to the aus_cmd_comp table 17 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management AUS Implementation - Database Tasks § Tasks in ph_task table § Auto Update Statistics Evaluation – Analyzes all the tables in all logged databases – Locates tables which require new or updated optimizer statistics – Builds the update statistics commands – Inserts the commands into the table aus_cmd_list § Auto Update Statistics Refresh – Executes the update statistics commands from aus_cmd_list table in a priority order within a specified time – After the command completes, it is moved to the aus_cmd_comp table 17 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
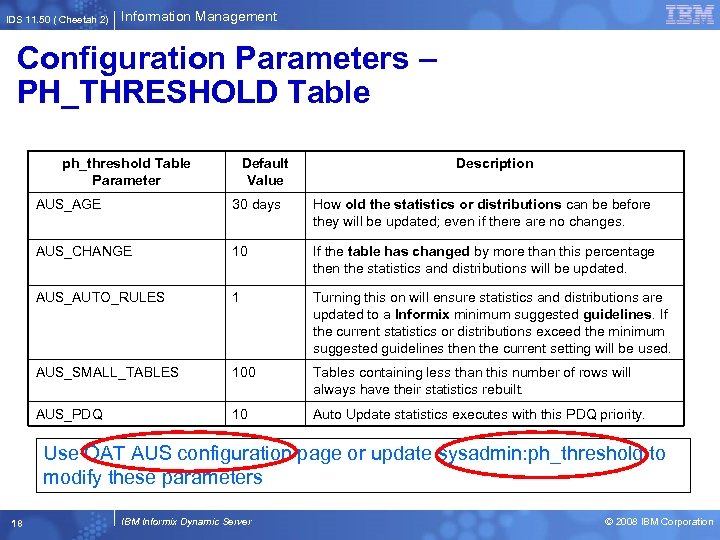 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Configuration Parameters – PH_THRESHOLD Table ph_threshold Table Parameter Default Value Description AUS_AGE 30 days How old the statistics or distributions can be before they will be updated; even if there are no changes. AUS_CHANGE 10 If the table has changed by more than this percentage then the statistics and distributions will be updated. AUS_AUTO_RULES 1 Turning this on will ensure statistics and distributions are updated to a Informix minimum suggested guidelines. If the current statistics or distributions exceed the minimum suggested guidelines then the current setting will be used. AUS_SMALL_TABLES 100 Tables containing less than this number of rows will always have their statistics rebuilt. AUS_PDQ 10 Auto Update statistics executes with this PDQ priority. Use OAT AUS configuration page or update sysadmin: ph_threshold to modify these parameters 18 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Configuration Parameters – PH_THRESHOLD Table ph_threshold Table Parameter Default Value Description AUS_AGE 30 days How old the statistics or distributions can be before they will be updated; even if there are no changes. AUS_CHANGE 10 If the table has changed by more than this percentage then the statistics and distributions will be updated. AUS_AUTO_RULES 1 Turning this on will ensure statistics and distributions are updated to a Informix minimum suggested guidelines. If the current statistics or distributions exceed the minimum suggested guidelines then the current setting will be used. AUS_SMALL_TABLES 100 Tables containing less than this number of rows will always have their statistics rebuilt. AUS_PDQ 10 Auto Update statistics executes with this PDQ priority. Use OAT AUS configuration page or update sysadmin: ph_threshold to modify these parameters 18 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Scheduling Information § Since AUS is a resource intensive operation, a specific run window can be defined. The run window definition includes start time, the end time and the days of the week to run the job. § Can be configured from the Open Admin tool. § Implemented by setting the start and end times of the AUS refresh (Auto Update Statistics Refresh) task in ph_task table in sysadmin. § Default runtime window is 1: 00 AM – 5: 00 AM daily. . 19 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Scheduling Information § Since AUS is a resource intensive operation, a specific run window can be defined. The run window definition includes start time, the end time and the days of the week to run the job. § Can be configured from the Open Admin tool. § Implemented by setting the start and end times of the AUS refresh (Auto Update Statistics Refresh) task in ph_task table in sysadmin. § Default runtime window is 1: 00 AM – 5: 00 AM daily. . 19 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 3: Automatic Statistics & distributions With Create Index IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 3: Automatic Statistics & distributions With Create Index IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Indexes and Statistics/Distributions § Common Mistake – Create an index and see no improvement in select performance § Without statistics or distributions the index will not be considered by the optimizer § We need to run UPDATE STATISTICS LOW at a minimum for newly created indexes to be considered for query access plans. Why can’t this be done automatically when new indexes are created? 21 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Indexes and Statistics/Distributions § Common Mistake – Create an index and see no improvement in select performance § Without statistics or distributions the index will not be considered by the optimizer § We need to run UPDATE STATISTICS LOW at a minimum for newly created indexes to be considered for query access plans. Why can’t this be done automatically when new indexes are created? 21 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
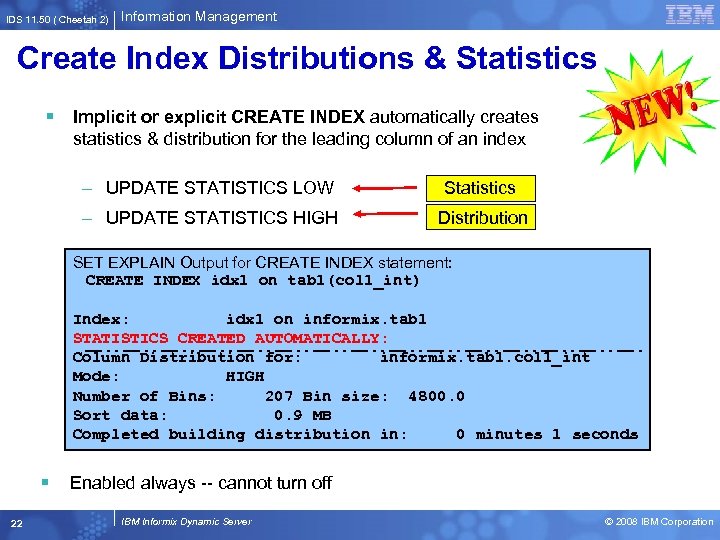 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Create Index Distributions & Statistics § Implicit or explicit CREATE INDEX automatically creates statistics & distribution for the leading column of an index – UPDATE STATISTICS LOW Statistics – UPDATE STATISTICS HIGH Distribution SET EXPLAIN Output for CREATE INDEX statement: CREATE INDEX idx 1 on tab 1(col 1_int) Index: idx 1 on informix. tab 1 STATISTICS CREATED AUTOMATICALLY: Column Distribution for: informix. tab 1. col 1_int Mode: HIGH Number of Bins: 207 Bin size: 4800. 0 Sort data: 0. 9 MB Completed building distribution in: 0 minutes 1 seconds § Enabled always -- cannot turn off 22 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Create Index Distributions & Statistics § Implicit or explicit CREATE INDEX automatically creates statistics & distribution for the leading column of an index – UPDATE STATISTICS LOW Statistics – UPDATE STATISTICS HIGH Distribution SET EXPLAIN Output for CREATE INDEX statement: CREATE INDEX idx 1 on tab 1(col 1_int) Index: idx 1 on informix. tab 1 STATISTICS CREATED AUTOMATICALLY: Column Distribution for: informix. tab 1. col 1_int Mode: HIGH Number of Bins: 207 Bin size: 4800. 0 Sort data: 0. 9 MB Completed building distribution in: 0 minutes 1 seconds § Enabled always -- cannot turn off 22 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
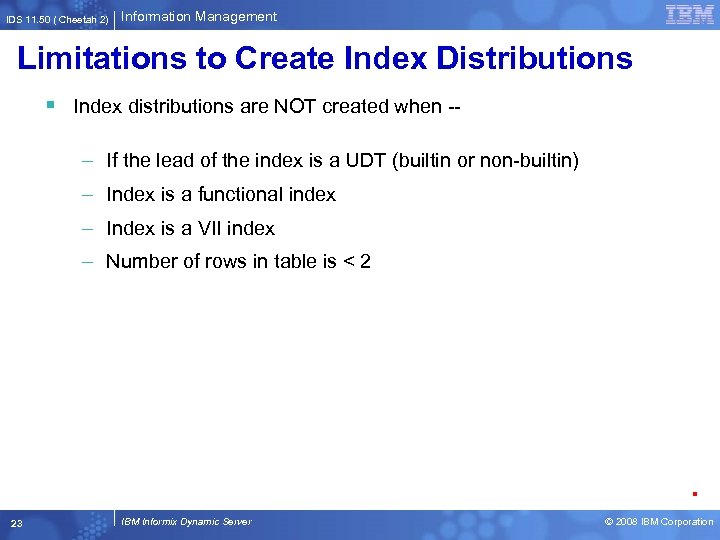 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Limitations to Create Index Distributions § Index distributions are NOT created when -– If the lead of the index is a UDT (builtin or non-builtin) – Index is a functional index – Index is a VII index – Number of rows in table is < 2 . 23 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Limitations to Create Index Distributions § Index distributions are NOT created when -– If the lead of the index is a UDT (builtin or non-builtin) – Index is a functional index – Index is a VII index – Number of rows in table is < 2 . 23 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 4: Control External Directives for a Session IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 4: Control External Directives for a Session IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
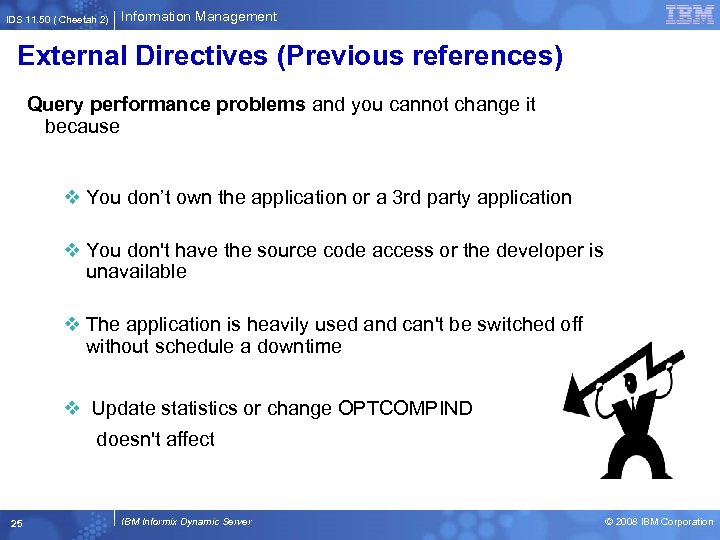 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management External Directives (Previous references) Query performance problems and you cannot change it because v You don’t own the application or a 3 rd party application v You don't have the source code access or the developer is unavailable v The application is heavily used and can't be switched off without schedule a downtime v Update statistics or change OPTCOMPIND doesn't affect 25 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management External Directives (Previous references) Query performance problems and you cannot change it because v You don’t own the application or a 3 rd party application v You don't have the source code access or the developer is unavailable v The application is heavily used and can't be switched off without schedule a downtime v Update statistics or change OPTCOMPIND doesn't affect 25 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management External Directives (Previous references) § External optimizer directives are useful when it is not feasible rewrite a query for a short-term solution to a problem § Enabling external directives Environment Variable: IFX_EXTDIRECTIVES Configuration parameter: EXT_DIRECTIVES § SQL Syntax: SAVE EXTERNAL DIRECTIVES
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management External Directives (Previous references) § External optimizer directives are useful when it is not feasible rewrite a query for a short-term solution to a problem § Enabling external directives Environment Variable: IFX_EXTDIRECTIVES Configuration parameter: EXT_DIRECTIVES § SQL Syntax: SAVE EXTERNAL DIRECTIVES
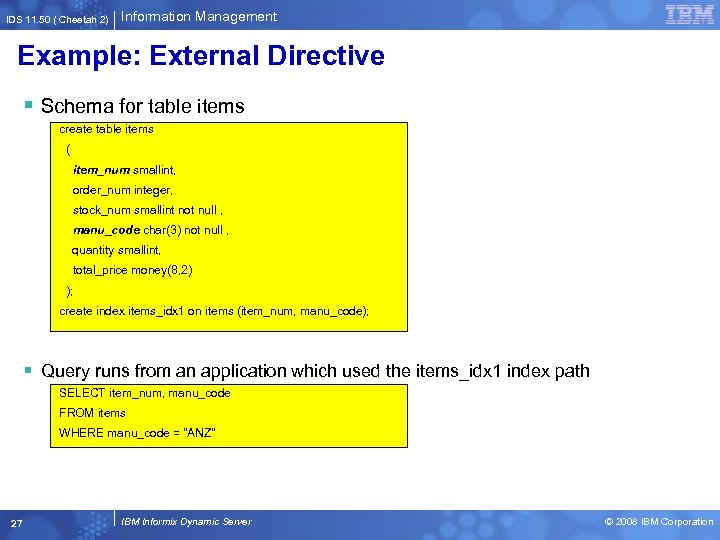 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Example: External Directive § Schema for table items create table items ( item_num smallint, order_num integer, stock_num smallint not null , manu_code char(3) not null , quantity smallint, total_price money(8, 2) ); create index items_idx 1 on items (item_num, manu_code); § Query runs from an application which used the items_idx 1 index path SELECT item_num, manu_code FROM items WHERE manu_code = "ANZ" 27 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Example: External Directive § Schema for table items create table items ( item_num smallint, order_num integer, stock_num smallint not null , manu_code char(3) not null , quantity smallint, total_price money(8, 2) ); create index items_idx 1 on items (item_num, manu_code); § Query runs from an application which used the items_idx 1 index path SELECT item_num, manu_code FROM items WHERE manu_code = "ANZ" 27 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
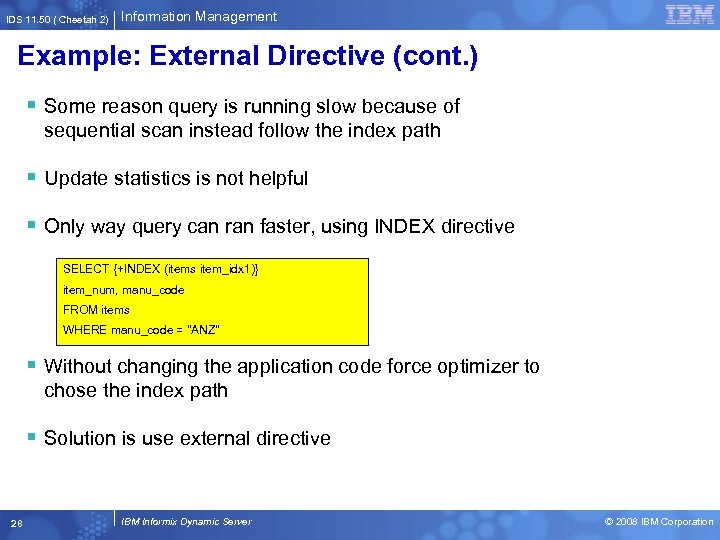 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Example: External Directive (cont. ) § Some reason query is running slow because of sequential scan instead follow the index path § Update statistics is not helpful § Only way query can ran faster, using INDEX directive SELECT {+INDEX (items item_idx 1)} item_num, manu_code FROM items WHERE manu_code = "ANZ" § Without changing the application code force optimizer to chose the index path § Solution is use external directive 28 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Example: External Directive (cont. ) § Some reason query is running slow because of sequential scan instead follow the index path § Update statistics is not helpful § Only way query can ran faster, using INDEX directive SELECT {+INDEX (items item_idx 1)} item_num, manu_code FROM items WHERE manu_code = "ANZ" § Without changing the application code force optimizer to chose the index path § Solution is use external directive 28 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Example: External Directive (cont. ) § Save and Active the query as external directive SAVE EXTERNAL DIRECTIVES --+INDEX(items item_idx 1) ACTIVE FOR SELECT item_num, manu_code FROM items WHERE manu_code = "ANZ" § If external directive enabled, query should follow the index path Environment Variable: IFX_EXTDIRECTIVES Configuration parameter: EXT_DIRECTIVES 29 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Example: External Directive (cont. ) § Save and Active the query as external directive SAVE EXTERNAL DIRECTIVES --+INDEX(items item_idx 1) ACTIVE FOR SELECT item_num, manu_code FROM items WHERE manu_code = "ANZ" § If external directive enabled, query should follow the index path Environment Variable: IFX_EXTDIRECTIVES Configuration parameter: EXT_DIRECTIVES 29 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
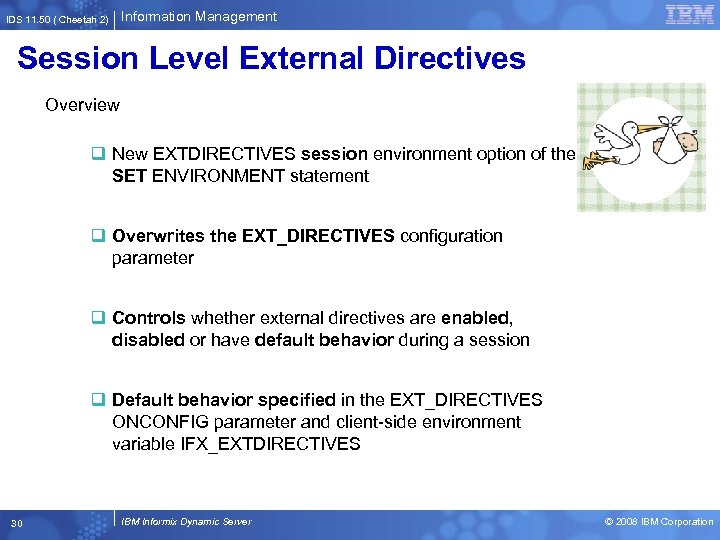 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Session Level External Directives Overview q New EXTDIRECTIVES session environment option of the SET ENVIRONMENT statement q Overwrites the EXT_DIRECTIVES configuration parameter q Controls whether external directives are enabled, disabled or have default behavior during a session q Default behavior specified in the EXT_DIRECTIVES ONCONFIG parameter and client-side environment variable IFX_EXTDIRECTIVES 30 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Session Level External Directives Overview q New EXTDIRECTIVES session environment option of the SET ENVIRONMENT statement q Overwrites the EXT_DIRECTIVES configuration parameter q Controls whether external directives are enabled, disabled or have default behavior during a session q Default behavior specified in the EXT_DIRECTIVES ONCONFIG parameter and client-side environment variable IFX_EXTDIRECTIVES 30 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Control External Directives for a Session q Syntax SET ENVIRONMENT EXTDIRECTIVES ‘[DEFAULT | off | on]’; or SET ENVIRONMENT EXTDIRECTIVES ‘[DEFAULT | 0 | 1]’; q Example * Disable external directives within a session SET ENVIRONMENT EXTDIRECTIVES ‘off’; . 31 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Control External Directives for a Session q Syntax SET ENVIRONMENT EXTDIRECTIVES ‘[DEFAULT | off | on]’; or SET ENVIRONMENT EXTDIRECTIVES ‘[DEFAULT | 0 | 1]’; q Example * Disable external directives within a session SET ENVIRONMENT EXTDIRECTIVES ‘off’; . 31 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 5: Enhanced Startup script customization IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 5: Enhanced Startup script customization IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
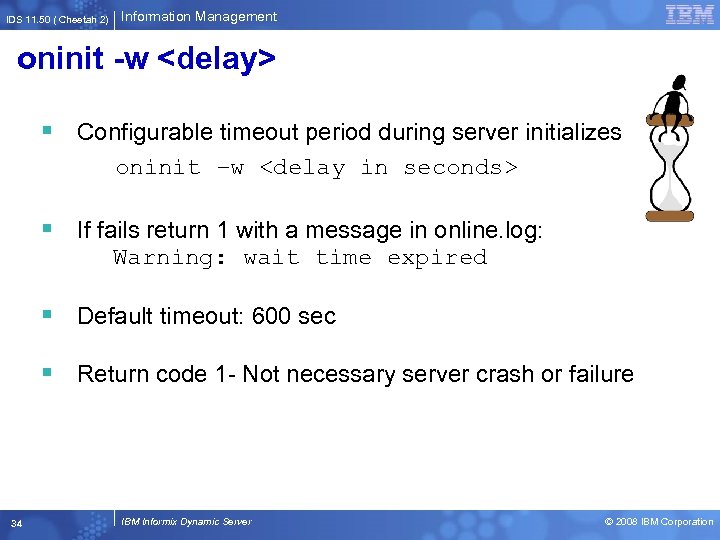
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management New oninit option: -w § Use to customize startup scripts and automate startup for the oninit utility. § The -w option forces the server to wait until it successfully initializes before returning a shell prompt. § The -w option provides a return code so that you can check if the IDS started without incident return 0 when success return 1 when initialization fails or configurable timeout achieved § In case of failure online. log updated appropriately 33 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management New oninit option: -w § Use to customize startup scripts and automate startup for the oninit utility. § The -w option forces the server to wait until it successfully initializes before returning a shell prompt. § The -w option provides a return code so that you can check if the IDS started without incident return 0 when success return 1 when initialization fails or configurable timeout achieved § In case of failure online. log updated appropriately 33 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management oninit -w
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management oninit -w
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Notes § In a high-availability environment, you can only use the oninit -w command on primary servers; it is not valid on secondary servers § Returns success when sysmaster, sysutils, sysuser and sysadmin are successfully created . 35 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Notes § In a high-availability environment, you can only use the oninit -w command on primary servers; it is not valid on secondary servers § Returns success when sysmaster, sysutils, sysuser and sysadmin are successfully created . 35 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 6: Visual Explain IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 6: Visual Explain IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § A new user defined function (C-UDR) EXPLAIN_SQL was implemented in IDS 11. 50. § The new UDR EXPLAIN_SQL can be used to obtain a query explain output in XML format. § IBM Data Studio can interpret the XML formatted explain file and show the query plan graphically to the user. 37 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § A new user defined function (C-UDR) EXPLAIN_SQL was implemented in IDS 11. 50. § The new UDR EXPLAIN_SQL can be used to obtain a query explain output in XML format. § IBM Data Studio can interpret the XML formatted explain file and show the query plan graphically to the user. 37 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § EXPLAIN_SQL UDR is mainly implemented to allow common tooling such as the new IBM Data Studio to be able to get XML explain output through the function and show users the graphical query plans. § If user wants to obtain the XML explain output and use their own graphic tool to see the query plan, the UDR should be ran by JDBC or JCC program. 38 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § EXPLAIN_SQL UDR is mainly implemented to allow common tooling such as the new IBM Data Studio to be able to get XML explain output through the function and show users the graphical query plans. § If user wants to obtain the XML explain output and use their own graphic tool to see the query plan, the UDR should be ran by JDBC or JCC program. 38 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
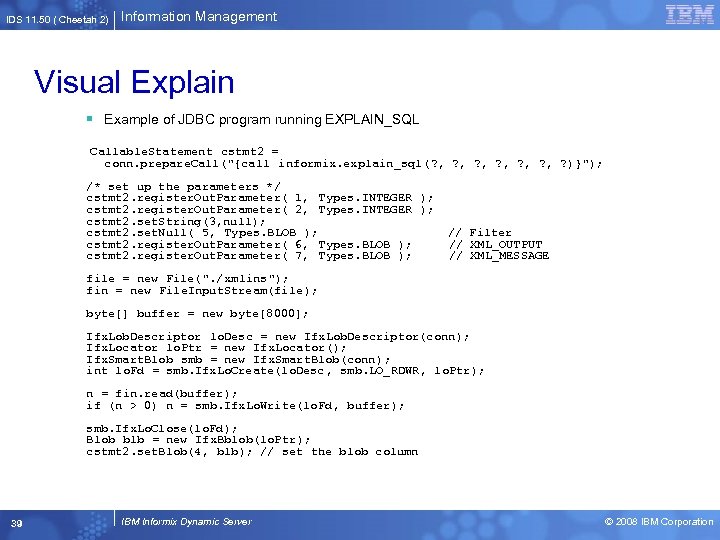 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Example of JDBC program running EXPLAIN_SQL Callable. Statement cstmt 2 = conn. prepare. Call("{call informix. explain_sql(? , ? , ? , ? )}"); /* set up the parameters */ cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 1, Types. INTEGER ); cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 2, Types. INTEGER ); cstmt 2. set. String(3, null); cstmt 2. set. Null( 5, Types. BLOB ); cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 6, Types. BLOB ); cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 7, Types. BLOB ); // Filter // XML_OUTPUT // XML_MESSAGE file = new File(". /xmlins"); fin = new File. Input. Stream(file); byte[] buffer = new byte[8000]; Ifx. Lob. Descriptor lo. Desc = new Ifx. Lob. Descriptor(conn); Ifx. Locator lo. Ptr = new Ifx. Locator(); Ifx. Smart. Blob smb = new Ifx. Smart. Blob(conn); int lo. Fd = smb. Ifx. Lo. Create(lo. Desc, smb. LO_RDWR, lo. Ptr); n = fin. read(buffer); if (n > 0) n = smb. Ifx. Lo. Write(lo. Fd, buffer); smb. Ifx. Lo. Close(lo. Fd); Blob blb = new Ifx. Bblob(lo. Ptr); cstmt 2. set. Blob(4, blb); // set the blob column 39 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Example of JDBC program running EXPLAIN_SQL Callable. Statement cstmt 2 = conn. prepare. Call("{call informix. explain_sql(? , ? , ? , ? )}"); /* set up the parameters */ cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 1, Types. INTEGER ); cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 2, Types. INTEGER ); cstmt 2. set. String(3, null); cstmt 2. set. Null( 5, Types. BLOB ); cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 6, Types. BLOB ); cstmt 2. register. Out. Parameter( 7, Types. BLOB ); // Filter // XML_OUTPUT // XML_MESSAGE file = new File(". /xmlins"); fin = new File. Input. Stream(file); byte[] buffer = new byte[8000]; Ifx. Lob. Descriptor lo. Desc = new Ifx. Lob. Descriptor(conn); Ifx. Locator lo. Ptr = new Ifx. Locator(); Ifx. Smart. Blob smb = new Ifx. Smart. Blob(conn); int lo. Fd = smb. Ifx. Lo. Create(lo. Desc, smb. LO_RDWR, lo. Ptr); n = fin. read(buffer); if (n > 0) n = smb. Ifx. Lo. Write(lo. Fd, buffer); smb. Ifx. Lo. Close(lo. Fd); Blob blb = new Ifx. Bblob(lo. Ptr); cstmt 2. set. Blob(4, blb); // set the blob column 39 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Example of JDBC program running EXPLAIN_SQL … continued Result. Set rs = cstmt 2. execute. Query(); int outmajver = cstmt 2. get. Int(1); int outminver = cstmt 2. get. Int(2); /* read the xml explain output if there is any */ while (rs. next()) { byte[] buf = new byte[80000]; b = (Ifx. Bblob) rs. get. Blob(1); if (b != null { Ifx. Locator loptr = b. get. Locator(); Ifx. Smart. Blob smbl = new Ifx. Smart. Blob(conn); int lofd = smbl. Ifx. Lo. Open(loptr, smbl. LO_RDONLY); outfile = new File(". /out. xml"); fout = new File. Output. Stream(outfile ); int size = smbl. Ifx. Lo. Read(lofd, fout, 80000); smbl. Ifx. Lo. Close(lofd); smbl. Ifx. Lo. Release(loptr); } } 40 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Example of JDBC program running EXPLAIN_SQL … continued Result. Set rs = cstmt 2. execute. Query(); int outmajver = cstmt 2. get. Int(1); int outminver = cstmt 2. get. Int(2); /* read the xml explain output if there is any */ while (rs. next()) { byte[] buf = new byte[80000]; b = (Ifx. Bblob) rs. get. Blob(1); if (b != null { Ifx. Locator loptr = b. get. Locator(); Ifx. Smart. Blob smbl = new Ifx. Smart. Blob(conn); int lofd = smbl. Ifx. Lo. Open(loptr, smbl. LO_RDONLY); outfile = new File(". /out. xml"); fout = new File. Output. Stream(outfile ); int size = smbl. Ifx. Lo. Read(lofd, fout, 80000); smbl. Ifx. Lo. Close(lofd); smbl. Ifx. Lo. Release(loptr); } } 40 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Example of JDBC program running EXPLAIN_SQL … continued /* get blob out parameters */ outmsg_b = (Ifx. Bblob)cstmt 2. get. Blob(7); if (outmsg_b == null) System. out. println("outmsg_b is null"); else { Ifx. Locator xml_msg_loptr = outmsg_b. get. Locator(); Ifx. Smart. Blob xml_msg_smbl = new Ifx. Smart. Blob(conn); int msg_out_lofd = xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Open(xml_msg_loptr , xml_msg_smbl. LO_RDONLY); msg_outfile = new File(". /xml_msg. xml"); msg_out_fout = new File. Output. Stream(msg_outfile ); int xml_msg_size = xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Read(msg_out_lofd , msg_out_fout, 80000); xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Close(msg_out_lofd ); xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Release(xml_msg_loptr ); } 41 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Example of JDBC program running EXPLAIN_SQL … continued /* get blob out parameters */ outmsg_b = (Ifx. Bblob)cstmt 2. get. Blob(7); if (outmsg_b == null) System. out. println("outmsg_b is null"); else { Ifx. Locator xml_msg_loptr = outmsg_b. get. Locator(); Ifx. Smart. Blob xml_msg_smbl = new Ifx. Smart. Blob(conn); int msg_out_lofd = xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Open(xml_msg_loptr , xml_msg_smbl. LO_RDONLY); msg_outfile = new File(". /xml_msg. xml"); msg_out_fout = new File. Output. Stream(msg_outfile ); int xml_msg_size = xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Read(msg_out_lofd , msg_out_fout, 80000); xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Close(msg_out_lofd ); xml_msg_smbl. Ifx. Lo. Release(xml_msg_loptr ); } 41 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Sample XML explain output
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Sample XML explain output
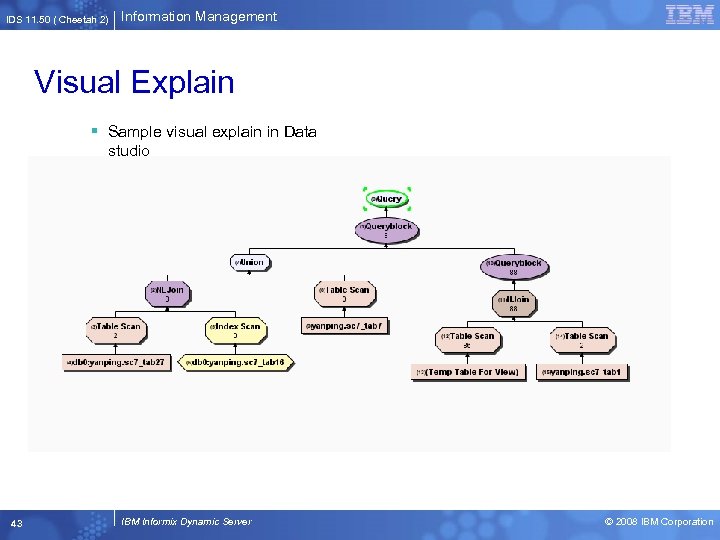 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Sample visual explain in Data studio 43 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Visual Explain § Sample visual explain in Data studio 43 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 7: BIGINT / BIGSERIAL IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 7: BIGINT / BIGSERIAL IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Overview: § New ANSI standard SQL data types BIGINT and BIGSERIAL were introduced in IDS. § Aims to provide a better performance alternative to INT 8 and SERIAL 8 data types. However, IDS will continue its support of INT 8 and SERIAL 8 data types in existing customer applications. 45 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Overview: § New ANSI standard SQL data types BIGINT and BIGSERIAL were introduced in IDS. § Aims to provide a better performance alternative to INT 8 and SERIAL 8 data types. However, IDS will continue its support of INT 8 and SERIAL 8 data types in existing customer applications. 45 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § INT 8 and SERIAL 8 data types which are internally implemented as a 10 -byte structure, ifx_int 8_t. INT 8 and SERIAL 8 take up to 10 byte of storage in IDS. § This feature will implement BIGINT and BIGSERIAL data types using native 8 -byte integers. It will take 8 -byte to store these data types. § Like INT 8, BIGINT will store numbers range from 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 to 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 [(2^63 -1) to 2^63 -1]. § The number – 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 808 is a reserved for a NULL value and cannot be used. 46 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § INT 8 and SERIAL 8 data types which are internally implemented as a 10 -byte structure, ifx_int 8_t. INT 8 and SERIAL 8 take up to 10 byte of storage in IDS. § This feature will implement BIGINT and BIGSERIAL data types using native 8 -byte integers. It will take 8 -byte to store these data types. § Like INT 8, BIGINT will store numbers range from 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 to 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 [(2^63 -1) to 2^63 -1]. § The number – 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 808 is a reserved for a NULL value and cannot be used. 46 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § Like SERIAL 8, BIGSERIAL will store numbers range from 1 to 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 [or 1 to 2^63 -1]. § Compare to INT 8, BIGINT requires less storage space and more important, should offer better performance in general because all arithmetic operations will be done using the native 8 -byte integer instead of dealing with the 10 -byte ifx_int 8_t structure. § BIGINT and BIGSERIAL will be reserved keywords. § A table can have only one SERIAL column, and either one SERIAL 8 column or one BIGSERIAL column. 47 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § Like SERIAL 8, BIGSERIAL will store numbers range from 1 to 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 [or 1 to 2^63 -1]. § Compare to INT 8, BIGINT requires less storage space and more important, should offer better performance in general because all arithmetic operations will be done using the native 8 -byte integer instead of dealing with the 10 -byte ifx_int 8_t structure. § BIGINT and BIGSERIAL will be reserved keywords. § A table can have only one SERIAL column, and either one SERIAL 8 column or one BIGSERIAL column. 47 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § BIGINT and BIGSERIAL uses native 8 -byte data type of the OS. On 32 -bit platforms it is ‘long’. Under certain compiler options the ‘long’ is not supported. During compilations of customer application if they detect error they can remove the Compiler option that causes not define ‘long’. The alternative to this compile with –DNOBIGINT, by doing this customer may not be able to use this feature fully in their applications. § The new SQL data types will be classified as Exact Numeric Types under Built-in Data Types and will be applicable to all DDL/DML statements wherever built-in data types are currently used. 48 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § BIGINT and BIGSERIAL uses native 8 -byte data type of the OS. On 32 -bit platforms it is ‘long’. Under certain compiler options the ‘long’ is not supported. During compilations of customer application if they detect error they can remove the Compiler option that causes not define ‘long’. The alternative to this compile with –DNOBIGINT, by doing this customer may not be able to use this feature fully in their applications. § The new SQL data types will be classified as Exact Numeric Types under Built-in Data Types and will be applicable to all DDL/DML statements wherever built-in data types are currently used. 48 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § The BIGINT and BIGSERIAL SQL data types is supported in the following products – IDS and its Utilities – ESQL/C – ODBC – JDBC – Common Clients and derivatives 49 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Description § The BIGINT and BIGSERIAL SQL data types is supported in the following products – IDS and its Utilities – ESQL/C – ODBC – JDBC – Common Clients and derivatives 49 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
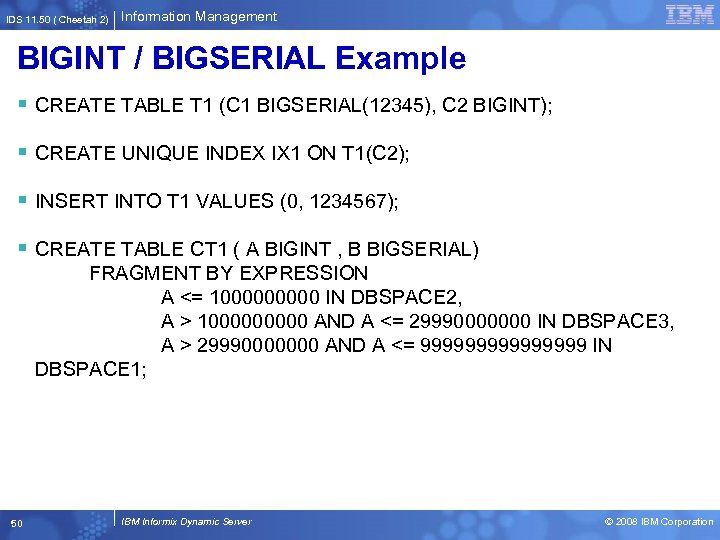 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Example § CREATE TABLE T 1 (C 1 BIGSERIAL(12345), C 2 BIGINT); § CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IX 1 ON T 1(C 2); § INSERT INTO T 1 VALUES (0, 1234567); § CREATE TABLE CT 1 ( A BIGINT , B BIGSERIAL) FRAGMENT BY EXPRESSION A <= 100000 IN DBSPACE 2, A > 100000 AND A <= 29990000000 IN DBSPACE 3, A > 29990000000 AND A <= 99999999 IN DBSPACE 1; 50 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management BIGINT / BIGSERIAL Example § CREATE TABLE T 1 (C 1 BIGSERIAL(12345), C 2 BIGINT); § CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IX 1 ON T 1(C 2); § INSERT INTO T 1 VALUES (0, 1234567); § CREATE TABLE CT 1 ( A BIGINT , B BIGSERIAL) FRAGMENT BY EXPRESSION A <= 100000 IN DBSPACE 2, A > 100000 AND A <= 29990000000 IN DBSPACE 3, A > 29990000000 AND A <= 99999999 IN DBSPACE 1; 50 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 8: Secure Socket Layer (SSL) IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 8: Secure Socket Layer (SSL) IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Secure Socket Layer § Communication protocol that provides privacy and integrity for data communication over the network § Uses encryption to provide end-to-end secure connection § At present, IDS supports encrypted communication only with SQLI clients (using Encryption Communication Support Module) § With SSL, encrypted communication will be possible with DRDA clients too 52 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Secure Socket Layer § Communication protocol that provides privacy and integrity for data communication over the network § Uses encryption to provide end-to-end secure connection § At present, IDS supports encrypted communication only with SQLI clients (using Encryption Communication Support Module) § With SSL, encrypted communication will be possible with DRDA clients too 52 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Digital Certificates, Certificate Authority (CA) and Keystores § Digital Certificates are electronic ID cards issued by trusted parties know as Certificate Authority (e. g. Veri. Sign) § SSL feature in IDS uses digital certificates to exchange keys for encryption and server authentication § Digital certificates are stored in key database (also known as keystore) § IBM’s Global Security Kit bundled with IDS server and client provides an i. Keyman utility that can be used to create keystores and manage digital certificates 53 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Digital Certificates, Certificate Authority (CA) and Keystores § Digital Certificates are electronic ID cards issued by trusted parties know as Certificate Authority (e. g. Veri. Sign) § SSL feature in IDS uses digital certificates to exchange keys for encryption and server authentication § Digital certificates are stored in key database (also known as keystore) § IBM’s Global Security Kit bundled with IDS server and client provides an i. Keyman utility that can be used to create keystores and manage digital certificates 53 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Digital Certificates cont… § Both client and server must have keystore for housing digital certificates § Server side keystore will store digital certificate issued (or signed) by Certificate Authority such as Veri. Sign § Client side keystore will store digital certificate of Certificate Authority (also called root certificate) that issued the server digital certificate 54 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Digital Certificates cont… § Both client and server must have keystore for housing digital certificates § Server side keystore will store digital certificate issued (or signed) by Certificate Authority such as Veri. Sign § Client side keystore will store digital certificate of Certificate Authority (also called root certificate) that issued the server digital certificate 54 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
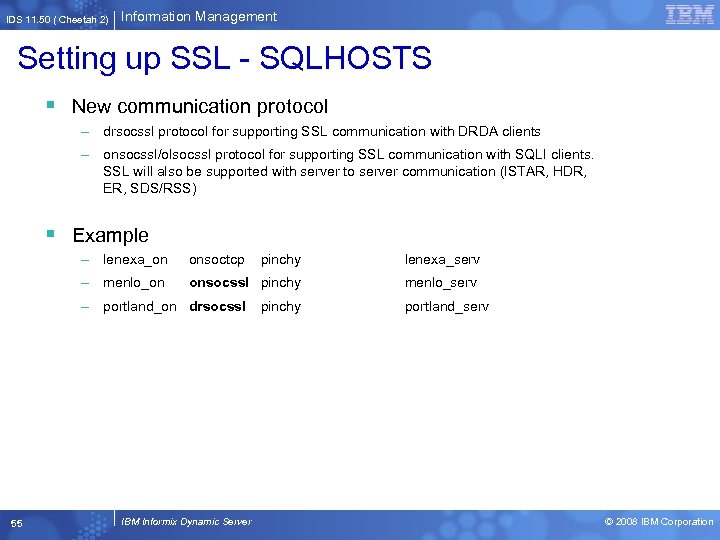 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL - SQLHOSTS § New communication protocol – drsocssl protocol for supporting SSL communication with DRDA clients – onsocssl/olsocssl protocol for supporting SSL communication with SQLI clients. SSL will also be supported with server to server communication (ISTAR, HDR, ER, SDS/RSS) § Example – lenexa_on onsoctcp pinchy lenexa_serv – menlo_on onsocssl pinchy menlo_serv – portland_on drsocssl pinchy 55 IBM Informix Dynamic Server portland_serv © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL - SQLHOSTS § New communication protocol – drsocssl protocol for supporting SSL communication with DRDA clients – onsocssl/olsocssl protocol for supporting SSL communication with SQLI clients. SSL will also be supported with server to server communication (ISTAR, HDR, ER, SDS/RSS) § Example – lenexa_on onsoctcp pinchy lenexa_serv – menlo_on onsocssl pinchy menlo_serv – portland_on drsocssl pinchy 55 IBM Informix Dynamic Server portland_serv © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL - ONCONFIG § New parameters – SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL – Specifies label of server digital certificate in keystore. If not configured, the server will use the default label in keystore for SSL communication e. g. SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL ids_label § Changes to existing parameters – NETTYPE – Describes connection parameters such as number of poll threads, max connections and class of virtual process for poll threads for connection protocols NETTYPE protocol, poll threads, connections, VP class Specify the protocol as iiippp where: iii=[ipc|soc|tli] ppp=[shm|str|tcp|spx|imc|ssl] e. g. NETTYPE socssl, 3, 50, NET 56 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL - ONCONFIG § New parameters – SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL – Specifies label of server digital certificate in keystore. If not configured, the server will use the default label in keystore for SSL communication e. g. SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL ids_label § Changes to existing parameters – NETTYPE – Describes connection parameters such as number of poll threads, max connections and class of virtual process for poll threads for connection protocols NETTYPE protocol, poll threads, connections, VP class Specify the protocol as iiippp where: iii=[ipc|soc|tli] ppp=[shm|str|tcp|spx|imc|ssl] e. g. NETTYPE socssl, 3, 50, NET 56 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL - ONCONFIG § All SSL encryption/decryption operations are performed on encrypt VP. Encrypt VPs can be configured via VPCLASS parameter e. g. VPCLASS encrypt, num=5 § SSL and non-SSL connection protocols can be configured for a single instance using server aliases e. g. DBSERVERNAME DBSERVERALIASES menlo_on lenexa_on, portland_on where menlo_on is onsocssl, lenexa_on is onsoctcp and portland_on is drsocssl connection protocol 57 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL - ONCONFIG § All SSL encryption/decryption operations are performed on encrypt VP. Encrypt VPs can be configured via VPCLASS parameter e. g. VPCLASS encrypt, num=5 § SSL and non-SSL connection protocols can be configured for a single instance using server aliases e. g. DBSERVERNAME DBSERVERALIASES menlo_on lenexa_on, portland_on where menlo_on is onsocssl, lenexa_on is onsoctcp and portland_on is drsocssl connection protocol 57 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § IBM’s Global Security Kit (GSKit) will be installed as part of IDS and CSDK installations § GSKit contains i. Keyman utility that can be used to create keystores and manage digital certificates needed for SSL communication § More information on i. Keyman is available at: http: //w 303. ibm. com/software/sales/saletool. nsf/resources/GSKITi. Key man/$file/GSK 7 c_SSL_Ikm_Guide. pdf 58 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § IBM’s Global Security Kit (GSKit) will be installed as part of IDS and CSDK installations § GSKit contains i. Keyman utility that can be used to create keystores and manage digital certificates needed for SSL communication § More information on i. Keyman is available at: http: //w 303. ibm. com/software/sales/saletool. nsf/resources/GSKITi. Key man/$file/GSK 7 c_SSL_Ikm_Guide. pdf 58 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § The keystore for server is password protected. Password is stored encrypted in stash file (also created by i. Keyman utility) § One keystore per server instance. It stores server’s digital certificate and root CA certificates of other servers its connecting to (as in ISTAR, HDR, ER, SDS/RSS) § Location and name of server keystore and its password stash file is predefined: $INFORMIXDIR/ssl/
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § The keystore for server is password protected. Password is stored encrypted in stash file (also created by i. Keyman utility) § One keystore per server instance. It stores server’s digital certificate and root CA certificates of other servers its connecting to (as in ISTAR, HDR, ER, SDS/RSS) § Location and name of server keystore and its password stash file is predefined: $INFORMIXDIR/ssl/
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § Password is optional for client keystore. § Client keystores root CA certificates of all servers the client is connecting to. SQLI and DRDA clients can share same keystore § Location and name of client keystore and its password stash file can be configured via new configuration file: – $INFORMIXDIR/etc/conssl. cfg New client configuration parameters: – SSL_KEYSTORE_FILE – Specifies fully qualified filename of client keystore – SSL_KEYSTORE_STH – Specifies fully qualified filename of client stash file If conssl. cfg does not exist or if any of above parameters are not configured, the keystore and stash file will default to: $INFORMIXDIR/etc/client. kdb and $INFORMIXDIR/etc/client. sth 60 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § Password is optional for client keystore. § Client keystores root CA certificates of all servers the client is connecting to. SQLI and DRDA clients can share same keystore § Location and name of client keystore and its password stash file can be configured via new configuration file: – $INFORMIXDIR/etc/conssl. cfg New client configuration parameters: – SSL_KEYSTORE_FILE – Specifies fully qualified filename of client keystore – SSL_KEYSTORE_STH – Specifies fully qualified filename of client stash file If conssl. cfg does not exist or if any of above parameters are not configured, the keystore and stash file will default to: $INFORMIXDIR/etc/client. kdb and $INFORMIXDIR/etc/client. sth 60 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § Prerequisites for i. Keyman utility – IBM JDK/JRE 1. 3. 1, 1. 4. 1 or higher with JCE PKS Security packages § Environment for i. Keyman utility – export JAVA_HOME=
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates § Prerequisites for i. Keyman utility – IBM JDK/JRE 1. 3. 1, 1. 4. 1 or higher with JCE PKS Security packages § Environment for i. Keyman utility – export JAVA_HOME=
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates Sample commands for creating keystore and self-signed test certificates* using i. Keyman command line utility: § Server Keystore – – gsk 7 cmd -keydb -create -db menlo_on. kdb -pw snoopy -type cms -stash – gsk 7 cmd -cert -extract -db menlo_on. kdb -format ascii -label ids_label -pw snoopy -target ids_label. cert gsk 7 cmd -cert -create -db menlo_on. kdb -pw snoopy -label ids_label -dn "CN=menlo. ibm. com, O=ibm, C=US" -size 1024 -default_cert yes where DBSERVERNAME is menlo_on SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL is ids_label § Client Keystore – – gsk 7 cmd -keydb -create -db client. kdb -pw snoopy -type cms -stash gsk 7 cmd -cert -add -db client. kdb -pw snoopy -label ids_label -file ids_label. cert -format ascii *In production systems, digital certificates will be requested from Certificate Authority. Refer to i. Keyman User Guide for more information on this. 62 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Setting up SSL – Keystores and Digital certificates Sample commands for creating keystore and self-signed test certificates* using i. Keyman command line utility: § Server Keystore – – gsk 7 cmd -keydb -create -db menlo_on. kdb -pw snoopy -type cms -stash – gsk 7 cmd -cert -extract -db menlo_on. kdb -format ascii -label ids_label -pw snoopy -target ids_label. cert gsk 7 cmd -cert -create -db menlo_on. kdb -pw snoopy -label ids_label -dn "CN=menlo. ibm. com, O=ibm, C=US" -size 1024 -default_cert yes where DBSERVERNAME is menlo_on SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL is ids_label § Client Keystore – – gsk 7 cmd -keydb -create -db client. kdb -pw snoopy -type cms -stash gsk 7 cmd -cert -add -db client. kdb -pw snoopy -label ids_label -file ids_label. cert -format ascii *In production systems, digital certificates will be requested from Certificate Authority. Refer to i. Keyman User Guide for more information on this. 62 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Recap of SSL setup § sqlhosts for client and server – onsocssl/drsocssl § onconfig for server – SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL – NETTYPE for socssl – VPCLASS for encrypt VP § conssl. cfg for client – SSL_KEYSTORE_FILE – SSL_KEYSTORE_STH § keystores and digital certificates for client and server § Initialize server and all communication between client and server or between servers on onsocssl/drsocssl port will be encrypted using SSL protocol 63 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Recap of SSL setup § sqlhosts for client and server – onsocssl/drsocssl § onconfig for server – SSL_KEYSTORE_LABEL – NETTYPE for socssl – VPCLASS for encrypt VP § conssl. cfg for client – SSL_KEYSTORE_FILE – SSL_KEYSTORE_STH § keystores and digital certificates for client and server § Initialize server and all communication between client and server or between servers on onsocssl/drsocssl port will be encrypted using SSL protocol 63 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 9: Savepoints IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 9: Savepoints IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint Description § New SQL statements and options offer a mechanism to undo portions of an SQL transaction § A user can arbitrarily mark points within one SQL transaction, called a savepoint § If an error occurs during execution, it can rollback the database changes made between the time the savepoint was started and the time the savepoint rollback request is issued. 65 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint Description § New SQL statements and options offer a mechanism to undo portions of an SQL transaction § A user can arbitrarily mark points within one SQL transaction, called a savepoint § If an error occurs during execution, it can rollback the database changes made between the time the savepoint was started and the time the savepoint rollback request is issued. 65 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint: new SQL § Establish a savepoint
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint: new SQL § Establish a savepoint
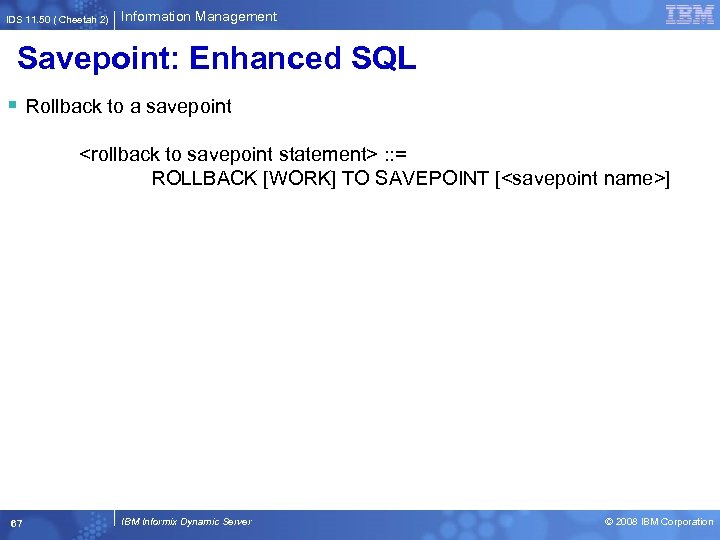 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint: Enhanced SQL § Rollback to a savepoint
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint: Enhanced SQL § Rollback to a savepoint
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint Example SAVEPOINT order_two; order: UPDATE goods_one SET count = count – order_quantity; UPDATE goods_two SET count = count – order_quantity; # if any of the above two statements fail, rollback to savepoint order_two ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT order_two; order_quantity -=20; goto order; #if both update statements succeed, erase the savepoint order_two RELEASE SAVEPOINT order_two; 68 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoint Example SAVEPOINT order_two; order: UPDATE goods_one SET count = count – order_quantity; UPDATE goods_two SET count = count – order_quantity; # if any of the above two statements fail, rollback to savepoint order_two ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT order_two; order_quantity -=20; goto order; #if both update statements succeed, erase the savepoint order_two RELEASE SAVEPOINT order_two; 68 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
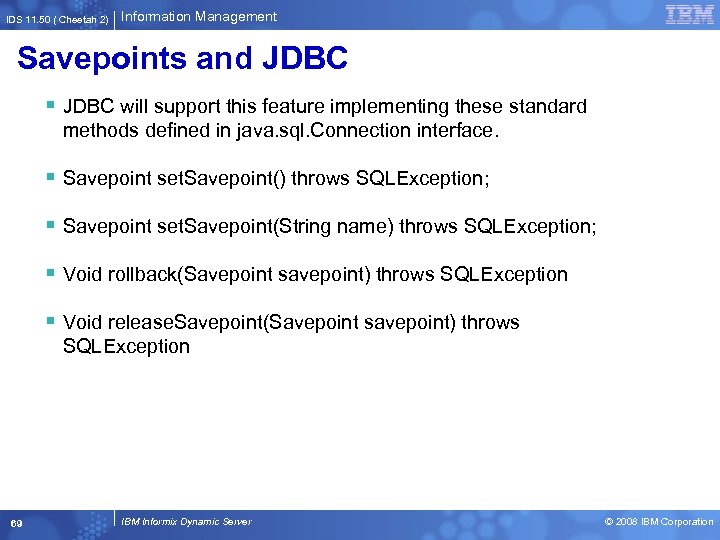 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoints and JDBC § JDBC will support this feature implementing these standard methods defined in java. sql. Connection interface. § Savepoint set. Savepoint() throws SQLException; § Savepoint set. Savepoint(String name) throws SQLException; § Void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException § Void release. Savepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException 69 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management Savepoints and JDBC § JDBC will support this feature implementing these standard methods defined in java. sql. Connection interface. § Savepoint set. Savepoint() throws SQLException; § Savepoint set. Savepoint(String name) throws SQLException; § Void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException § Void release. Savepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException 69 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 10: LIMITNUMSESSIONS IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management KC Informix Users Group Feature 10: LIMITNUMSESSIONS IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management LIMITNUMSESSIONS § New ONCONFIG parameter: LIMITNUMSESSIONS max#sessions, print_warning max#sessions = 0 to 2097152. The default is 0. print_warning = 0 (off) or 1 (on). The default is 0. § Defines the max number of sessions that you want connected to IDS. § Warning messages will be reported to the online. log as the max value is approached if print_warning is on. 71 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management LIMITNUMSESSIONS § New ONCONFIG parameter: LIMITNUMSESSIONS max#sessions, print_warning max#sessions = 0 to 2097152. The default is 0. print_warning = 0 (off) or 1 (on). The default is 0. § Defines the max number of sessions that you want connected to IDS. § Warning messages will be reported to the online. log as the max value is approached if print_warning is on. 71 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management LIMITNUMSESSIONS Example § ONCONFIG setting: LIMITNUMSESSIONS 100, 1 § Because print_warning is on, an online. log message reports that the max number of sessions, 100, is being approached as the number of user sessions closes in on this limit § If user session 101 attempts to connect to the server, the error -25571 is reported to client and a message in the online. log reports that the maximum number of sessions has been reached and no new sessions can connect until the current number of connections falls below this limit 72 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management LIMITNUMSESSIONS Example § ONCONFIG setting: LIMITNUMSESSIONS 100, 1 § Because print_warning is on, an online. log message reports that the max number of sessions, 100, is being approached as the number of user sessions closes in on this limit § If user session 101 attempts to connect to the server, the error -25571 is reported to client and a message in the online. log reports that the maximum number of sessions has been reached and no new sessions can connect until the current number of connections falls below this limit 72 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management LIMITNUMSESSIONS Additional Information § LIMITNUMSESSIONS is not intended to provide a means for enforcing user license agreements. § LIMITNUMSESSIONS will not affect informix or DBSA users. 73 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) Information Management LIMITNUMSESSIONS Additional Information § LIMITNUMSESSIONS is not intended to provide a means for enforcing user license agreements. § LIMITNUMSESSIONS will not affect informix or DBSA users. 73 IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) 74 Information Management IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) 74 Information Management IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
 IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) 75 Information Management IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation
IDS 11. 50 ( Cheetah 2) 75 Information Management IBM Informix Dynamic Server © 2008 IBM Corporation


