d6f6deb1763e2a18d10697670ba88e3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 Information Extraction Jordi Turmo TALP Research Centre Dep. Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya turmo@lsi. upc. edu http: //www. lsi. upc. edu/~turmo Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Information Extraction Jordi Turmo TALP Research Centre Dep. Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya turmo@lsi. upc. edu http: //www. lsi. upc. edu/~turmo Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Definition • Goal: Localization and extraction, in a specific format, of the relevant information included in a collection of documents • Input requirements: scenario of extraction and document collection • Output requirements: output format Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Definition • Goal: Localization and extraction, in a specific format, of the relevant information included in a collection of documents • Input requirements: scenario of extraction and document collection • Output requirements: output format Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Typology • Different points of view: − conceptual coverage: restricted-domain IE vs. opendomain IE − language coverage: monoligual IE vs. multilingual IE − media coverage: written text IE, speech IE, image IE, multimedia IE − document type: IE from free text, from semistructured documents, from structured documents (including Web pages in HTML and XML) − task: TE, TR, ST, others Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Typology • Different points of view: − conceptual coverage: restricted-domain IE vs. opendomain IE − language coverage: monoligual IE vs. multilingual IE − media coverage: written text IE, speech IE, image IE, multimedia IE − document type: IE from free text, from semistructured documents, from structured documents (including Web pages in HTML and XML) − task: TE, TR, ST, others Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Typology • Different points of view: − conceptual converage: restricted-domain IE vs. open -domain IE − language coverage: monoligual IE vs. multilingual IE − media coverage: written text IE, speech IE, image IE, multimedia IE − document type: IE from free text, from semistructured documents, from structured documents (including Web pages in HTML and XML) − task: TE, TR, ST, others Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Typology • Different points of view: − conceptual converage: restricted-domain IE vs. open -domain IE − language coverage: monoligual IE vs. multilingual IE − media coverage: written text IE, speech IE, image IE, multimedia IE − document type: IE from free text, from semistructured documents, from structured documents (including Web pages in HTML and XML) − task: TE, TR, ST, others Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 1: Structured documents • Web pages • A list of members of an organization per document • English • Scenario of Extraction Name, degree, school and affiliation of the member Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 1: Structured documents • Web pages • A list of members of an organization per document • English • Scenario of Extraction Name, degree, school and affiliation of the member Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
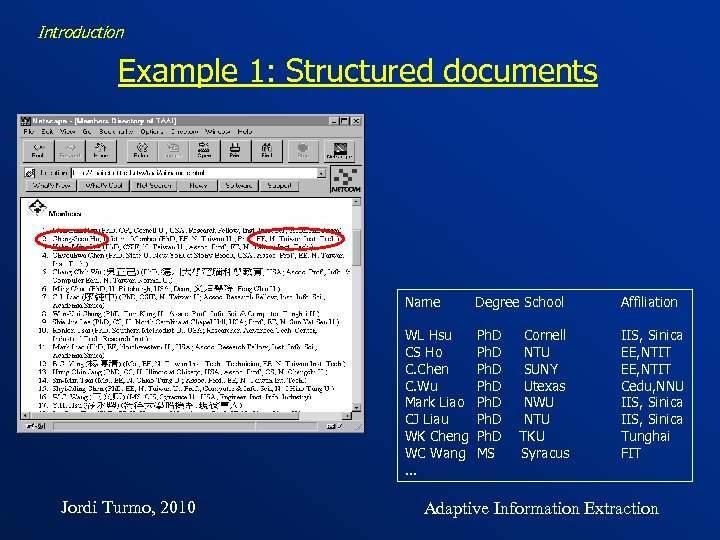 Introduction Example 1: Structured documents Name Affiliation WL Hsu CS Ho C. Chen C. Wu Mark Liao CJ Liau WK Cheng WC Wang. . . Jordi Turmo, 2010 Degree School Ph. D Ph. D MS IIS, Sinica EE, NTIT Cedu, NNU IIS, Sinica Tunghai FIT Cornell NTU SUNY Utexas NWU NTU TKU Syracus Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 1: Structured documents Name Affiliation WL Hsu CS Ho C. Chen C. Wu Mark Liao CJ Liau WK Cheng WC Wang. . . Jordi Turmo, 2010 Degree School Ph. D Ph. D MS IIS, Sinica EE, NTIT Cedu, NNU IIS, Sinica Tunghai FIT Cornell NTU SUNY Utexas NWU NTU TKU Syracus Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 2: Semi-structured documents • 485 seminar announcements • A description of one seminar per document • English • Scenario of Extraction Speaker, location, start time and end time of the seminar Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 2: Semi-structured documents • 485 seminar announcements • A description of one seminar per document • English • Scenario of Extraction Speaker, location, start time and end time of the seminar Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 2: Semi-structured documents Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 2: Semi-structured documents Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 3: Free text • 318 Wall Street Journal articles • A description of an incident per document • English • Scenario of Extraction Type of incident, perpetrator, target, date, location, effects and instrument Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 3: Free text • 318 Wall Street Journal articles • A description of an incident per document • English • Scenario of Extraction Type of incident, perpetrator, target, date, location, effects and instrument Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 3: Free text A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador leaving a large part of the city without energy, but no casualties have been reported. According to unofficial sources, the bomb -allegedly detonated by urban guerrilla commandos- blew up a power tower in the northwestern part of San Salvador at 0650. Incident type: bombing date: March 19 Location: El Salvador: San Salvador (city) Perpetrator: urban guerrilla commandos Physical target: power tower Human target: Effect on physical target: destroyed Effect on human target: no injury or death Instrument: bomb Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 3: Free text A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador leaving a large part of the city without energy, but no casualties have been reported. According to unofficial sources, the bomb -allegedly detonated by urban guerrilla commandos- blew up a power tower in the northwestern part of San Salvador at 0650. Incident type: bombing date: March 19 Location: El Salvador: San Salvador (city) Perpetrator: urban guerrilla commandos Physical target: power tower Human target: Effect on physical target: destroyed Effect on human target: no injury or death Instrument: bomb Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 4: Free text • 78 documents • A description of mushroom per document • Spanish • Scenario of Extraction colors of parts of mushrooms and the circumstances in which they occur Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 4: Free text • 78 documents • A description of mushroom per document • Spanish • Scenario of Extraction colors of parts of mushrooms and the circumstances in which they occur Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 4: Free text Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 4: Free text Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
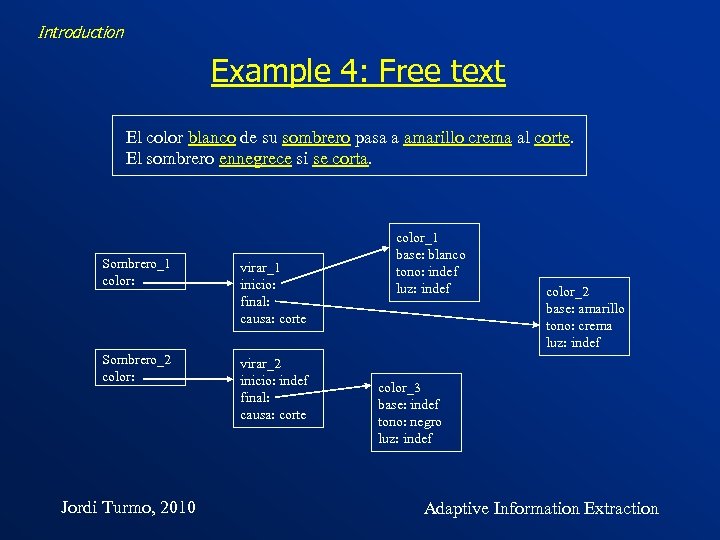 Introduction Example 4: Free text El color blanco de su sombrero pasa a amarillo crema al corte. El sombrero ennegrece si se corta. Sombrero_1 color: virar_1 inicio: final: causa: corte Sombrero_2 color: virar_2 inicio: indef final: causa: corte Jordi Turmo, 2010 color_1 base: blanco tono: indef luz: indef color_2 base: amarillo tono: crema luz: indef color_3 base: indef tono: negro luz: indef Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 4: Free text El color blanco de su sombrero pasa a amarillo crema al corte. El sombrero ennegrece si se corta. Sombrero_1 color: virar_1 inicio: final: causa: corte Sombrero_2 color: virar_2 inicio: indef final: causa: corte Jordi Turmo, 2010 color_1 base: blanco tono: indef luz: indef color_2 base: amarillo tono: crema luz: indef color_3 base: indef tono: negro luz: indef Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 5: Combination • 78 documents • A description of mushroom per document • Spanish • Scenario of Extraction Names of the mushroom in different languages, ethimology colors of parts of mushrooms and the circumstances in which they occur Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 5: Combination • 78 documents • A description of mushroom per document • Spanish • Scenario of Extraction Names of the mushroom in different languages, ethimology colors of parts of mushrooms and the circumstances in which they occur Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Example 5: Combination Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Example 5: Combination Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Applications • • IE from the Web Building of news DBs Information Integration Support for QA and Summarization … Limitation when P<80% Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Applications • • IE from the Web Building of news DBs Information Integration Support for QA and Summarization … Limitation when P<80% Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction References • • D. E. Appelt, D. J. Israel, 1999 E. Hovy, 1999 R. J. Mooney, C. Cardie, 1999 Muslea, 1999 J. Cowie, Y. Wilks, 2000 M. T. Pazienza, 2003 Turmo et al. 2005 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction References • • D. E. Appelt, D. J. Israel, 1999 E. Hovy, 1999 R. J. Mooney, C. Cardie, 1999 Muslea, 1999 J. Cowie, Y. Wilks, 2000 M. T. Pazienza, 2003 Turmo et al. 2005 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Introduction Recent events • IJCAI 2001 Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2001) • ECML 03/PKDD Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2003) • AAAI 04 Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2004) • EACL 06 Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2006) • COLING-ACL 06 Workshop on Information Extraction Beyond the Document • ACE conferences Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Introduction Recent events • IJCAI 2001 Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2001) • ECML 03/PKDD Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2003) • AAAI 04 Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2004) • EACL 06 Workshop on Adaptive Text Extraction and Mining (ATEM-2006) • COLING-ACL 06 Workshop on Information Extraction Beyond the Document • ACE conferences Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
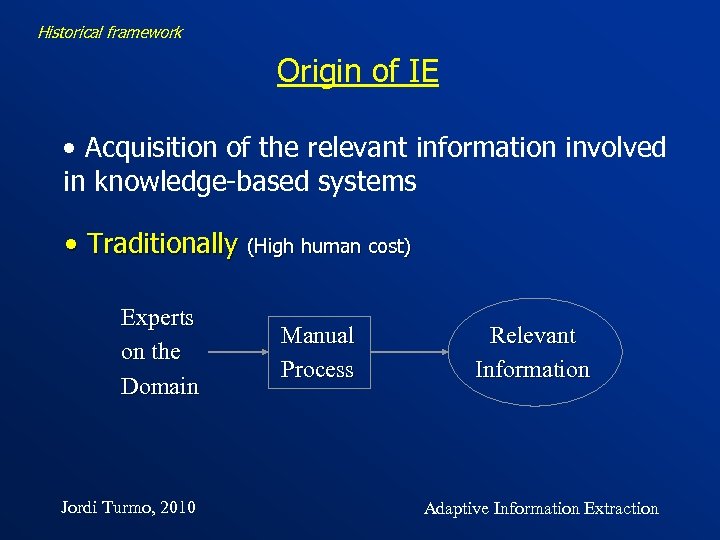 Historical framework Origin of IE • Acquisition of the relevant information involved in knowledge-based systems • Traditionally (High human cost) Experts on the Domain Jordi Turmo, 2010 Manual Process Relevant Information Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework Origin of IE • Acquisition of the relevant information involved in knowledge-based systems • Traditionally (High human cost) Experts on the Domain Jordi Turmo, 2010 Manual Process Relevant Information Adaptive Information Extraction
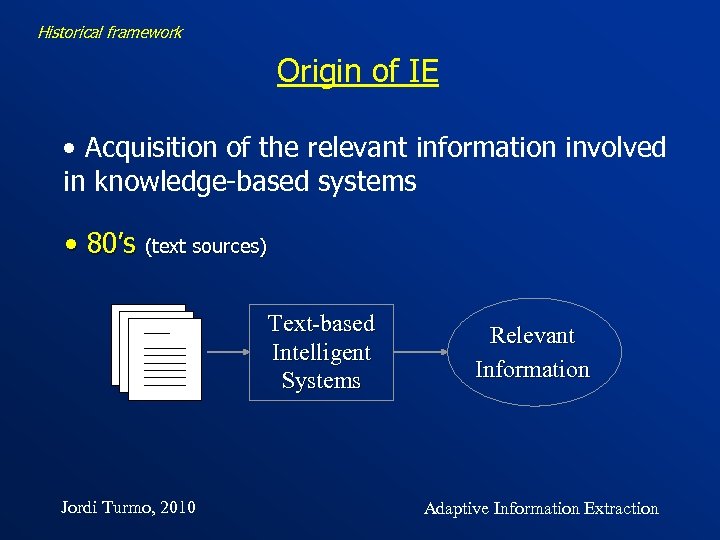 Historical framework Origin of IE • Acquisition of the relevant information involved in knowledge-based systems • 80’s (text sources) Text-based Intelligent Systems Jordi Turmo, 2010 Relevant Information Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework Origin of IE • Acquisition of the relevant information involved in knowledge-based systems • 80’s (text sources) Text-based Intelligent Systems Jordi Turmo, 2010 Relevant Information Adaptive Information Extraction
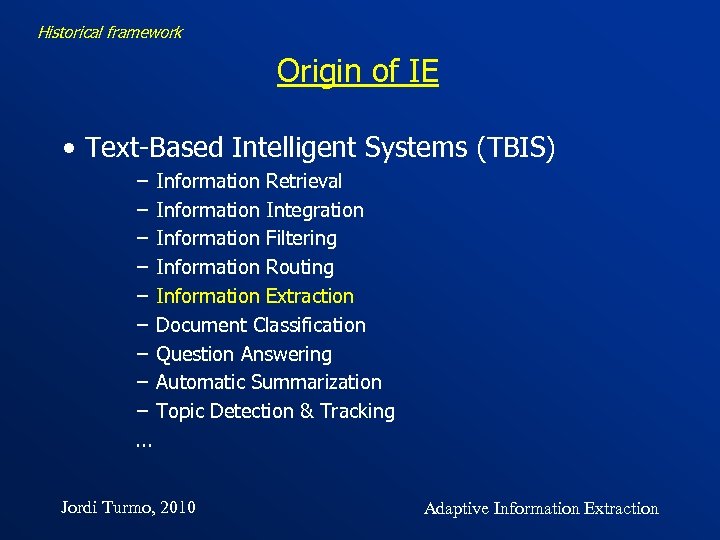 Historical framework Origin of IE • Text-Based Intelligent Systems (TBIS) − Information Retrieval − Information Integration − Information Filtering − Information Routing − Information Extraction − Document Classification − Question Answering − Automatic Summarization − Topic Detection & Tracking. . . Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework Origin of IE • Text-Based Intelligent Systems (TBIS) − Information Retrieval − Information Integration − Information Filtering − Information Routing − Information Extraction − Document Classification − Question Answering − Automatic Summarization − Topic Detection & Tracking. . . Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Historical framework Relevant Historical Programs • Precedents: LSP (Sager, 81), FRUMP (De. Jong, 82), JASPER (Hayes, 86) • in USA − (1987 -1991): MUC [US Navy] − TIPSTER (1991 -1998): MUC [DARPA] − TIDES (1999 -): ACE [NIST] • in Europe − LRE (1993 -1996): TREE, AVENTINUS, FACILE, ECRAN, SPARKLE − PASCAL excellence network (2003 -) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework Relevant Historical Programs • Precedents: LSP (Sager, 81), FRUMP (De. Jong, 82), JASPER (Hayes, 86) • in USA − (1987 -1991): MUC [US Navy] − TIPSTER (1991 -1998): MUC [DARPA] − TIDES (1999 -): ACE [NIST] • in Europe − LRE (1993 -1996): TREE, AVENTINUS, FACILE, ECRAN, SPARKLE − PASCAL excellence network (2003 -) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
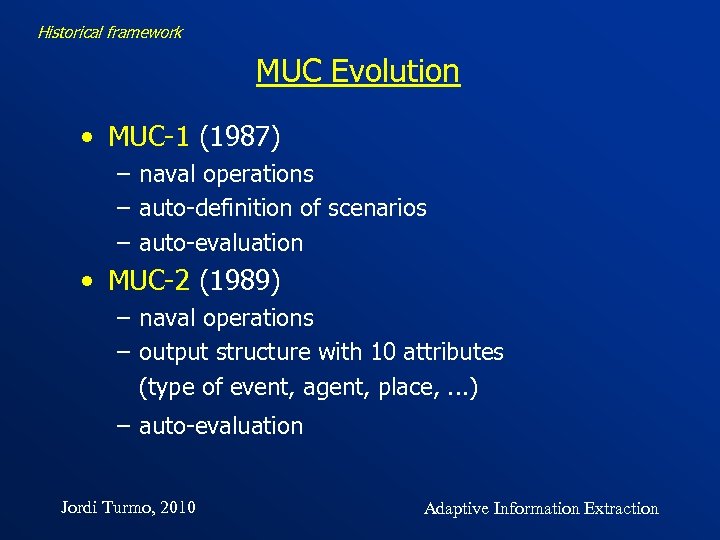 Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-1 (1987) – naval operations – auto-definition of scenarios – auto-evaluation • MUC-2 (1989) – naval operations – output structure with 10 attributes (type of event, agent, place, . . . ) – auto-evaluation Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-1 (1987) – naval operations – auto-definition of scenarios – auto-evaluation • MUC-2 (1989) – naval operations – output structure with 10 attributes (type of event, agent, place, . . . ) – auto-evaluation Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
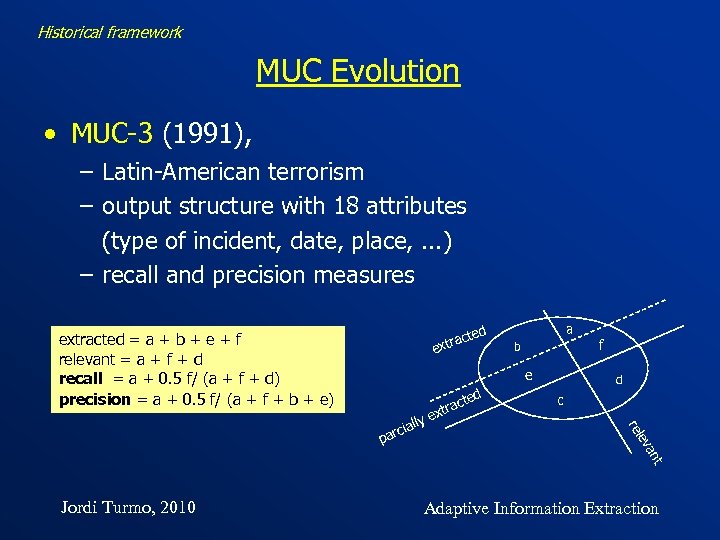 Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-3 (1991), – Latin-American terrorism – output structure with 18 attributes (type of incident, date, place, . . . ) – recall and precision measures cted xtra e extracted = a + b + e + f relevant = a + f + d recall = a + 0. 5 f/ (a + f + d) precision = a + 0. 5 f/ (a + f + b + e) a b e d c ev rel lly rcia pa ex ed act tr f t an Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-3 (1991), – Latin-American terrorism – output structure with 18 attributes (type of incident, date, place, . . . ) – recall and precision measures cted xtra e extracted = a + b + e + f relevant = a + f + d recall = a + 0. 5 f/ (a + f + d) precision = a + 0. 5 f/ (a + f + b + e) a b e d c ev rel lly rcia pa ex ed act tr f t an Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-4 (1992), – Latin-American terrorism – 24 attributes – F-score (harmonic average) • MUC-5 (1993), – Financial news, microelectronics – English, Japanese Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-4 (1992), – Latin-American terrorism – 24 attributes – F-score (harmonic average) • MUC-5 (1993), – Financial news, microelectronics – English, Japanese Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
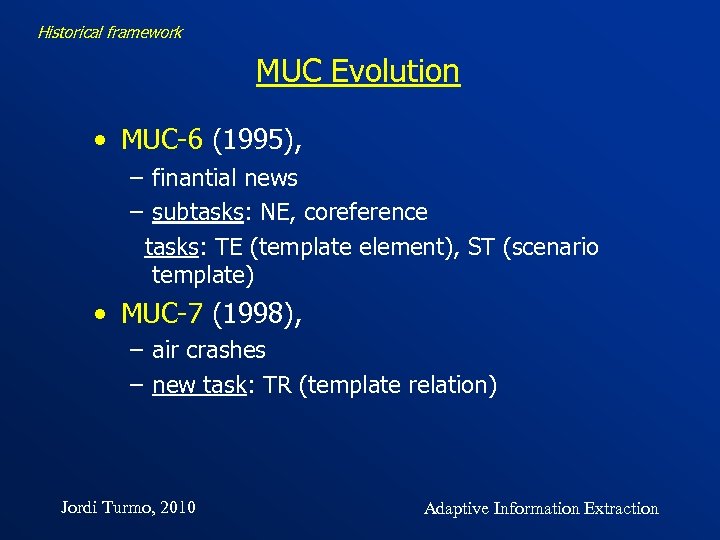 Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-6 (1995), – finantial news – subtasks: NE, coreference tasks: TE (template element), ST (scenario template) • MUC-7 (1998), – air crashes – new task: TR (template relation) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-6 (1995), – finantial news – subtasks: NE, coreference tasks: TE (template element), ST (scenario template) • MUC-7 (1998), – air crashes – new task: TR (template relation) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
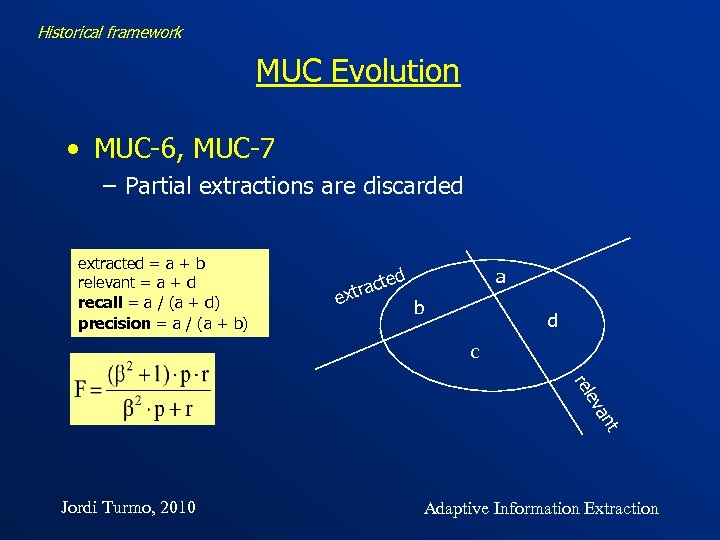 Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-6, MUC-7 – Partial extractions are discarded extracted = a + b relevant = a + d recall = a / (a + d) precision = a / (a + b) d acte extr a b d c t an ev rel Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Historical framework MUC Evolution • MUC-6, MUC-7 – Partial extractions are discarded extracted = a + b relevant = a + d recall = a / (a + d) precision = a / (a + b) d acte extr a b d c t an ev rel Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
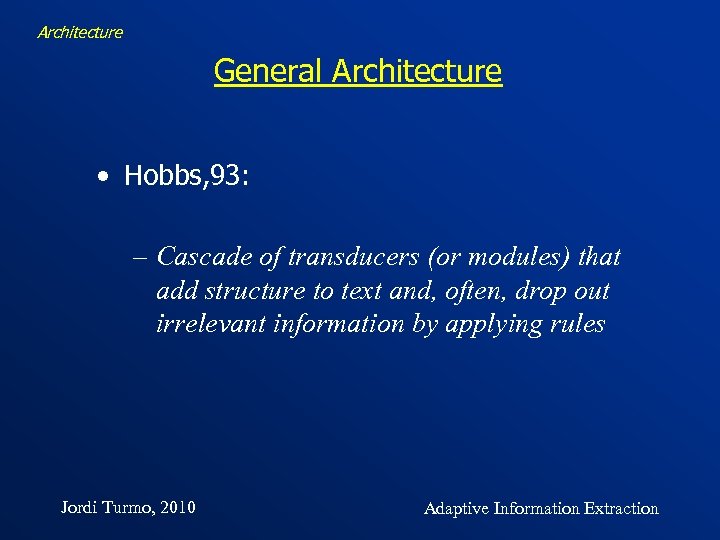 Architecture General Architecture • Hobbs, 93: – Cascade of transducers (or modules) that add structure to text and, often, drop out irrelevant information by applying rules Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture General Architecture • Hobbs, 93: – Cascade of transducers (or modules) that add structure to text and, often, drop out irrelevant information by applying rules Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
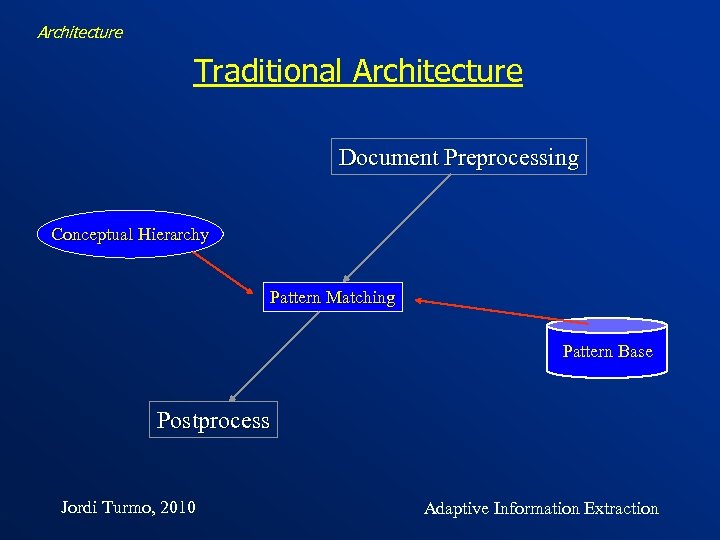 Architecture Traditional Architecture Document Preprocessing Conceptual Hierarchy Pattern Matching Pattern Base Postprocess Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Traditional Architecture Document Preprocessing Conceptual Hierarchy Pattern Matching Pattern Base Postprocess Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
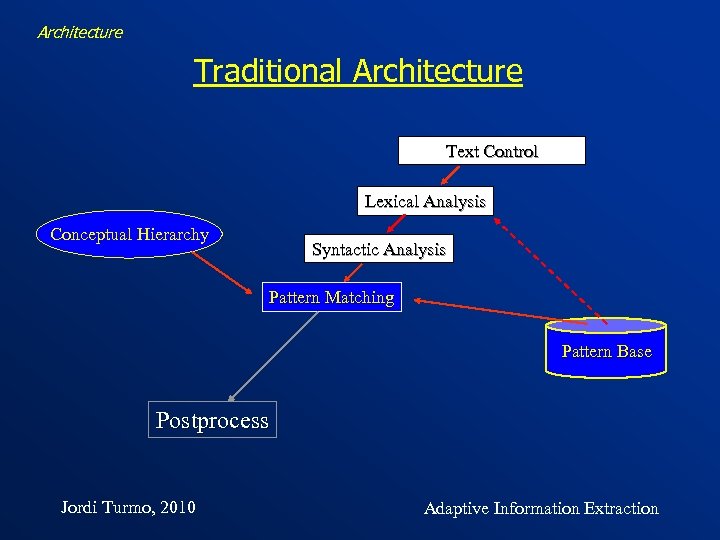 Architecture Traditional Architecture Text Control Lexical Analysis Conceptual Hierarchy Syntactic Analysis Pattern Matching Pattern Base Postprocess Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Traditional Architecture Text Control Lexical Analysis Conceptual Hierarchy Syntactic Analysis Pattern Matching Pattern Base Postprocess Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
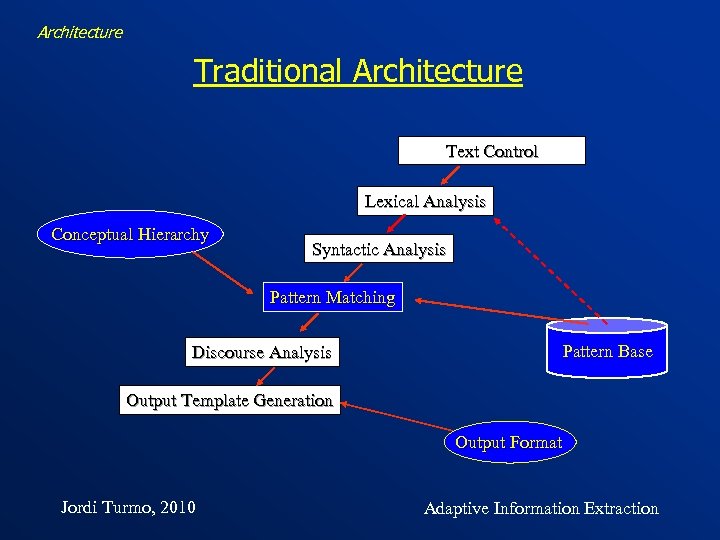 Architecture Traditional Architecture Text Control Lexical Analysis Conceptual Hierarchy Syntactic Analysis Pattern Matching Pattern Base Discourse Analysis Output Template Generation Output Format Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Traditional Architecture Text Control Lexical Analysis Conceptual Hierarchy Syntactic Analysis Pattern Matching Pattern Base Discourse Analysis Output Template Generation Output Format Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Text control • • • Filtering relevant documents Guessing the language of the documents Splitting documents into textual zones Filtering relevant zones Splitting text into appropriate units (eg. sentences) • Filtering relevant units • Tokenizing units Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Text control • • • Filtering relevant documents Guessing the language of the documents Splitting documents into textual zones Filtering relevant zones Splitting text into appropriate units (eg. sentences) • Filtering relevant units • Tokenizing units Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Text control • Example Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Text control • Example Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Text control • Example
Architecture Text control • Example
 Architecture Lexical analysis • Identifying morpho-syntactic categories and semantic categories of words ØGeneral lexicon • Recognizing terminology words Ø Specific dictionaries • Recognizing time expressions, quantities, abbreviations, … • Extending abbreviations Ø Lists of abbrev. + expansion Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Lexical analysis • Identifying morpho-syntactic categories and semantic categories of words ØGeneral lexicon • Recognizing terminology words Ø Specific dictionaries • Recognizing time expressions, quantities, abbreviations, … • Extending abbreviations Ø Lists of abbrev. + expansion Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
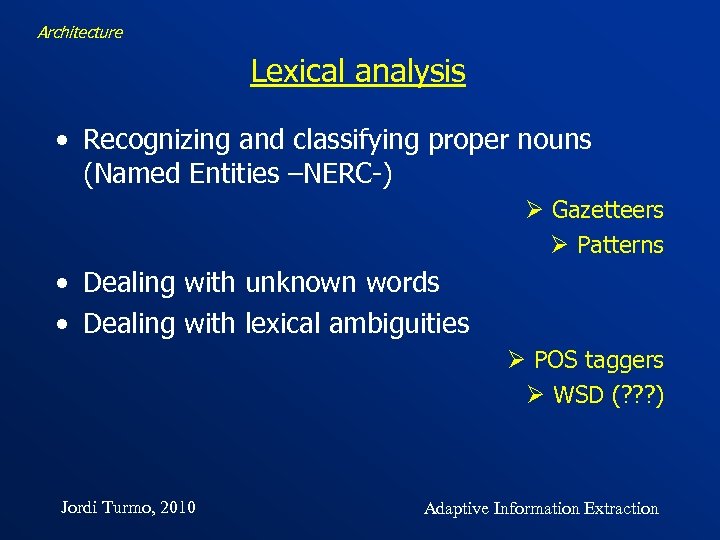 Architecture Lexical analysis • Recognizing and classifying proper nouns (Named Entities –NERC-) Ø Gazetteers Ø Patterns • Dealing with unknown words • Dealing with lexical ambiguities Ø POS taggers Ø WSD (? ? ? ) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Lexical analysis • Recognizing and classifying proper nouns (Named Entities –NERC-) Ø Gazetteers Ø Patterns • Dealing with unknown words • Dealing with lexical ambiguities Ø POS taggers Ø WSD (? ? ? ) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
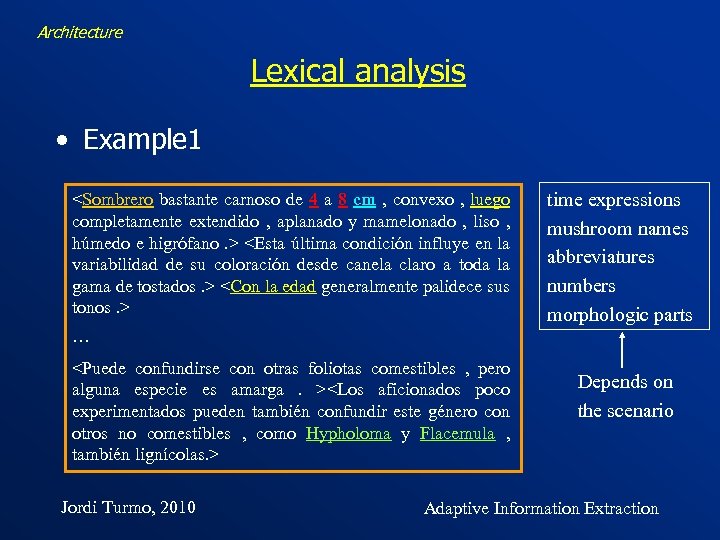 Architecture Lexical analysis • Example 1
Architecture Lexical analysis • Example 1
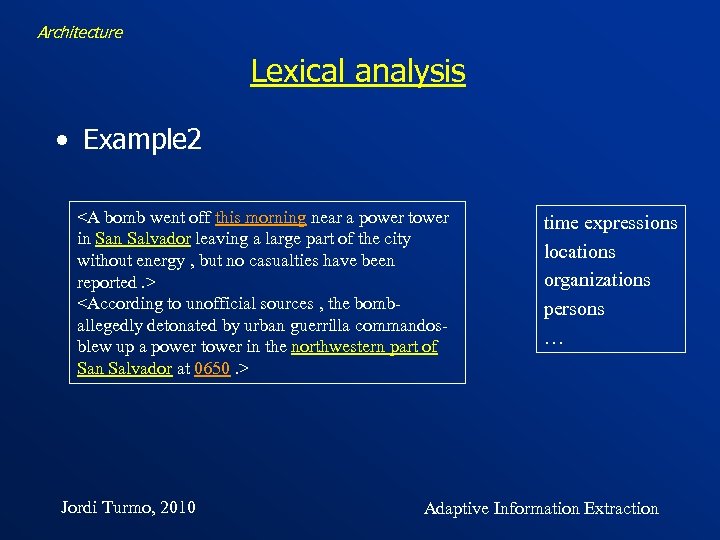 Architecture Lexical analysis • Example 2
Architecture Lexical analysis • Example 2
 Architecture Syntactic analysis • Full parsing (Lolita, La. SIE-II) – – inefficient, sizes of the grammars missing robustness (off vocabulary) treebank grammars cascaded grammars • Solves some problems related to the tuning and incompleteness Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Syntactic analysis • Full parsing (Lolita, La. SIE-II) – – inefficient, sizes of the grammars missing robustness (off vocabulary) treebank grammars cascaded grammars • Solves some problems related to the tuning and incompleteness Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Syntactic analysis • Partial parsing −the most commonly used −chunks or phrasal trees (noun phrases, verbal phrases, prep phrases, adj phrases, adv phrases) −absence of global dependences Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Syntactic analysis • Partial parsing −the most commonly used −chunks or phrasal trees (noun phrases, verbal phrases, prep phrases, adj phrases, adv phrases) −absence of global dependences Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Semantic interpretation • Compositive semantics − full parsing + λ-expressions −La. SIE, La. SIE-II −Entries with λ-expressions in the Lexicons − partial parsing + gramatical relations [Vilain, 99] − output = logical forms Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Semantic interpretation • Compositive semantics − full parsing + λ-expressions −La. SIE, La. SIE-II −Entries with λ-expressions in the Lexicons − partial parsing + gramatical relations [Vilain, 99] − output = logical forms Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
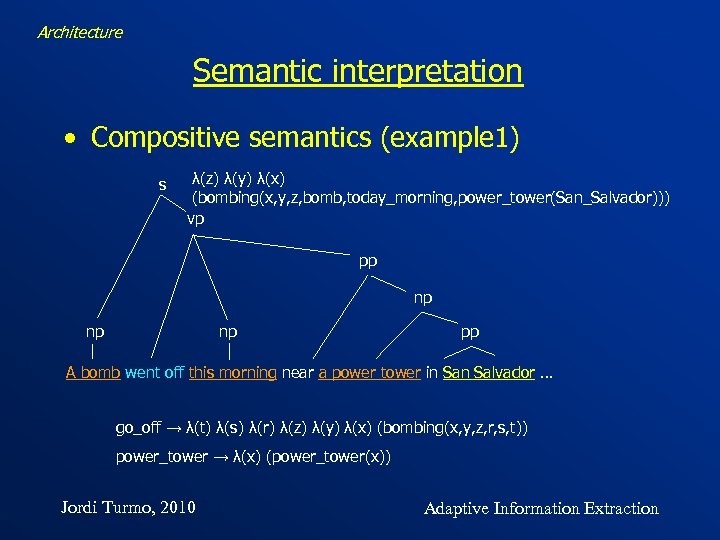 Architecture Semantic interpretation • Compositive semantics (example 1) s λ(z) λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, z, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) vp pp np np np pp A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador … go_off → λ(t) λ(s) λ(r) λ(z) λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, z, r, s, t)) power_tower → λ(x) (power_tower(x)) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Semantic interpretation • Compositive semantics (example 1) s λ(z) λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, z, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) vp pp np np np pp A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador … go_off → λ(t) λ(s) λ(r) λ(z) λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, z, r, s, t)) power_tower → λ(x) (power_tower(x)) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
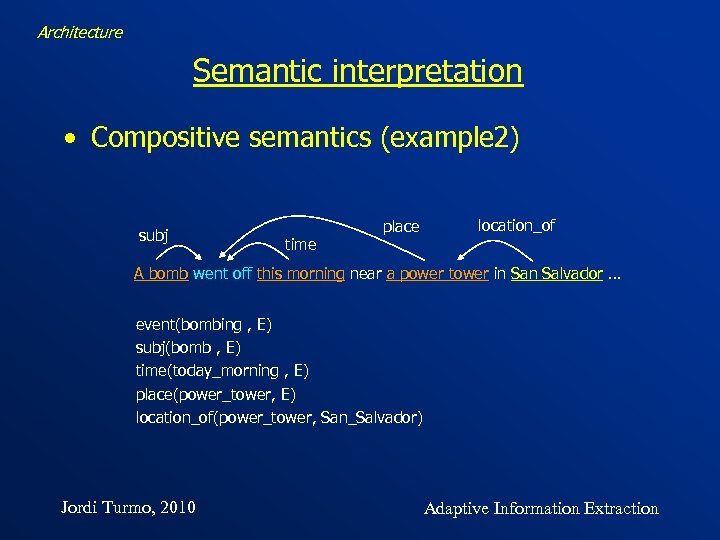 Architecture Semantic interpretation • Compositive semantics (example 2) subj time place location_of A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador … event(bombing , E) subj(bomb , E) time(today_morning , E) place(power_tower, E) location_of(power_tower, San_Salvador) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Semantic interpretation • Compositive semantics (example 2) subj time place location_of A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador … event(bombing , E) subj(bomb , E) time(today_morning , E) place(power_tower, E) location_of(power_tower, San_Salvador) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Semantic interpretation • Pattern matching −after partial parsing + svo dependences −the most extended −patterns can be implemented in different ways −scenario driven approach (TE, TR, ST, …) −Output = partial templates Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Semantic interpretation • Pattern matching −after partial parsing + svo dependences −the most extended −patterns can be implemented in different ways −scenario driven approach (TE, TR, ST, …) −Output = partial templates Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
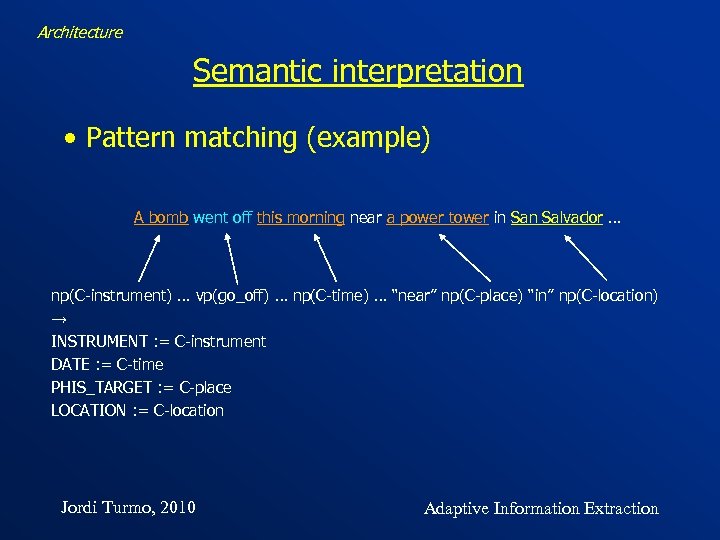 Architecture Semantic interpretation • Pattern matching (example) A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador … np(C-instrument) … vp(go_off) … np(C-time) … “near” np(C-place) “in” np(C-location) → INSTRUMENT : = C-instrument DATE : = C-time PHIS_TARGET : = C-place LOCATION : = C-location Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Semantic interpretation • Pattern matching (example) A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador … np(C-instrument) … vp(go_off) … np(C-time) … “near” np(C-place) “in” np(C-location) → INSTRUMENT : = C-instrument DATE : = C-time PHIS_TARGET : = C-place LOCATION : = C-location Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
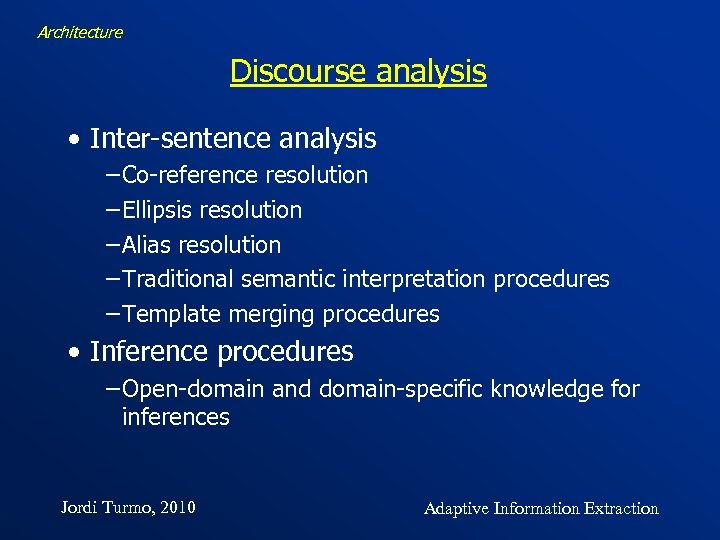 Architecture Discourse analysis • Inter-sentence analysis −Co-reference resolution −Ellipsis resolution −Alias resolution −Traditional semantic interpretation procedures −Template merging procedures • Inference procedures −Open-domain and domain-specific knowledge for inferences Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Discourse analysis • Inter-sentence analysis −Co-reference resolution −Ellipsis resolution −Alias resolution −Traditional semantic interpretation procedures −Template merging procedures • Inference procedures −Open-domain and domain-specific knowledge for inferences Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
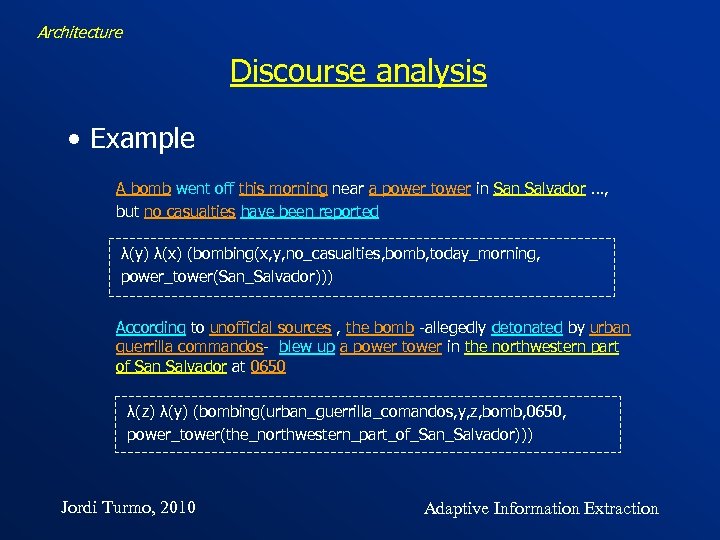 Architecture Discourse analysis • Example A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador …, but no casualties have been reported λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) According to unofficial sources , the bomb -allegedly detonated by urban guerrilla commandos- blew up a power tower in the northwestern part of San Salvador at 0650 λ(z) λ(y) (bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, y, z, bomb, 0650, power_tower(the_northwestern_part_of_San_Salvador))) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Discourse analysis • Example A bomb went off this morning near a power tower in Salvador …, but no casualties have been reported λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) According to unofficial sources , the bomb -allegedly detonated by urban guerrilla commandos- blew up a power tower in the northwestern part of San Salvador at 0650 λ(z) λ(y) (bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, y, z, bomb, 0650, power_tower(the_northwestern_part_of_San_Salvador))) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
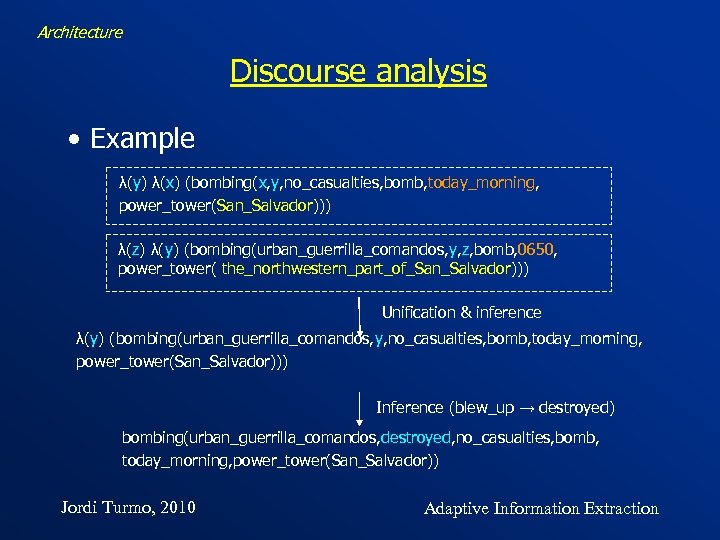 Architecture Discourse analysis • Example λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) λ(z) λ(y) (bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, y, z, bomb, 0650, power_tower( the_northwestern_part_of_San_Salvador))) Unification & inference λ(y) (bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, y, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) Inference (blew_up → destroyed) bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, destroyed, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador)) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Discourse analysis • Example λ(y) λ(x) (bombing(x, y, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) λ(z) λ(y) (bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, y, z, bomb, 0650, power_tower( the_northwestern_part_of_San_Salvador))) Unification & inference λ(y) (bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, y, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador))) Inference (blew_up → destroyed) bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, destroyed, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador)) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Architecture Output template generation • Mapping of the extracted pieces into the desired output format • Specific inferences: − Normalization to predefined values of slots − Mandatory slots − Extracted information that implies different slot values Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Output template generation • Mapping of the extracted pieces into the desired output format • Specific inferences: − Normalization to predefined values of slots − Mandatory slots − Extracted information that implies different slot values Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
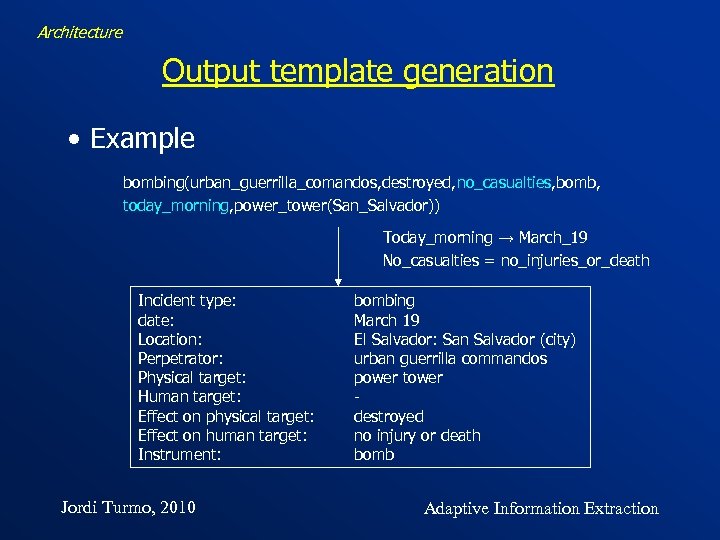 Architecture Output template generation • Example bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, destroyed, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador)) Today_morning → March_19 No_casualties = no_injuries_or_death Incident type: date: Location: Perpetrator: Physical target: Human target: Effect on physical target: Effect on human target: Instrument: Jordi Turmo, 2010 bombing March 19 El Salvador: San Salvador (city) urban guerrilla commandos power tower destroyed no injury or death bomb Adaptive Information Extraction
Architecture Output template generation • Example bombing(urban_guerrilla_comandos, destroyed, no_casualties, bomb, today_morning, power_tower(San_Salvador)) Today_morning → March_19 No_casualties = no_injuries_or_death Incident type: date: Location: Perpetrator: Physical target: Human target: Effect on physical target: Effect on human target: Instrument: Jordi Turmo, 2010 bombing March 19 El Salvador: San Salvador (city) urban guerrilla commandos power tower destroyed no injury or death bomb Adaptive Information Extraction
 Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
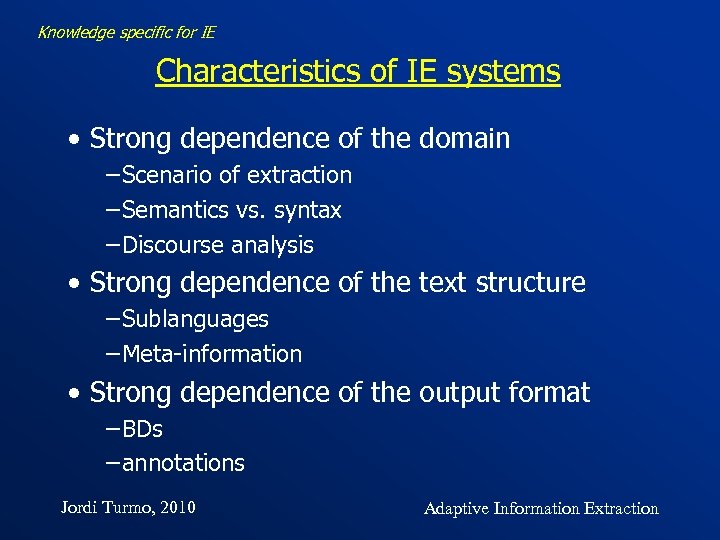 Knowledge specific for IE Characteristics of IE systems • Strong dependence of the domain −Scenario of extraction −Semantics vs. syntax −Discourse analysis • Strong dependence of the text structure −Sublanguages −Meta-information • Strong dependence of the output format −BDs −annotations Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Characteristics of IE systems • Strong dependence of the domain −Scenario of extraction −Semantics vs. syntax −Discourse analysis • Strong dependence of the text structure −Sublanguages −Meta-information • Strong dependence of the output format −BDs −annotations Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Knowledge specific for IE Characteristics of IE systems • Importance of the portability and tuning • Importance of the Knowledge Engineering −Modularity −Basic tasks and specific tasks −Use of weak and local knowledge • Importance of the NL resources −MDRs, ontologies, general lexicons, specific dictionaries, … Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Characteristics of IE systems • Importance of the portability and tuning • Importance of the Knowledge Engineering −Modularity −Basic tasks and specific tasks −Use of weak and local knowledge • Importance of the NL resources −MDRs, ontologies, general lexicons, specific dictionaries, … Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Knowledge specific for IE Knowledge resources • Knowledge more or less stable − general lexicon − general grammar − basic NL processors: segmenters, taggers, parsers, … • Domain dependent knowledge − Domain specific vocabularies, terminology − gazetteers and patterns for NERC − IE patterns Knowledge specifically used for IE Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Knowledge resources • Knowledge more or less stable − general lexicon − general grammar − basic NL processors: segmenters, taggers, parsers, … • Domain dependent knowledge − Domain specific vocabularies, terminology − gazetteers and patterns for NERC − IE patterns Knowledge specifically used for IE Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
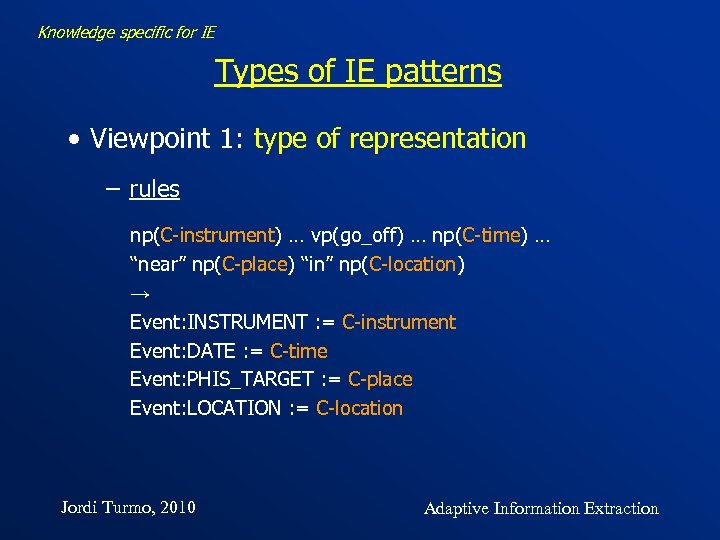 Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 1: type of representation − rules np(C-instrument) … vp(go_off) … np(C-time) … “near” np(C-place) “in” np(C-location) → Event: INSTRUMENT : = C-instrument Event: DATE : = C-time Event: PHIS_TARGET : = C-place Event: LOCATION : = C-location Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 1: type of representation − rules np(C-instrument) … vp(go_off) … np(C-time) … “near” np(C-place) “in” np(C-location) → Event: INSTRUMENT : = C-instrument Event: DATE : = C-time Event: PHIS_TARGET : = C-place Event: LOCATION : = C-location Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
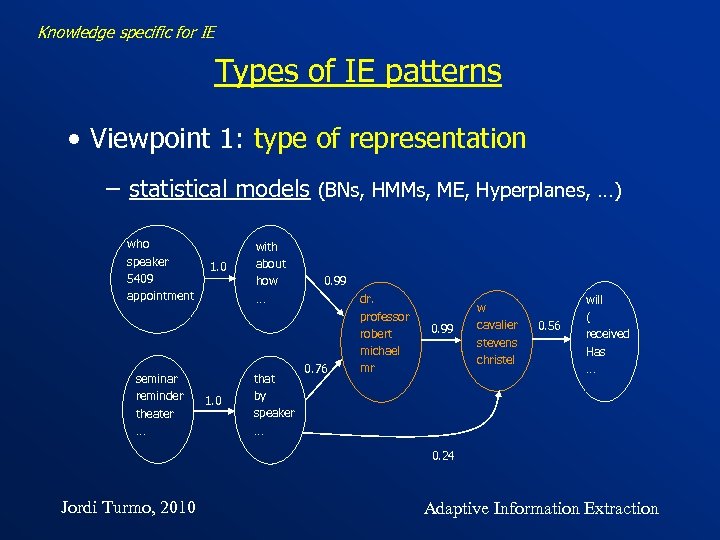 Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 1: type of representation − statistical models (BNs, HMMs, ME, Hyperplanes, …) who speaker 5409 appointment seminar reminder theater … 1. 0 with about how … that by speaker … 0. 99 0. 76 dr. professor robert michael mr 0. 99 w cavalier stevens christel 0. 56 will ( received Has … 0. 24 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 1: type of representation − statistical models (BNs, HMMs, ME, Hyperplanes, …) who speaker 5409 appointment seminar reminder theater … 1. 0 with about how … that by speaker … 0. 99 0. 76 dr. professor robert michael mr 0. 99 w cavalier stevens christel 0. 56 will ( received Has … 0. 24 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
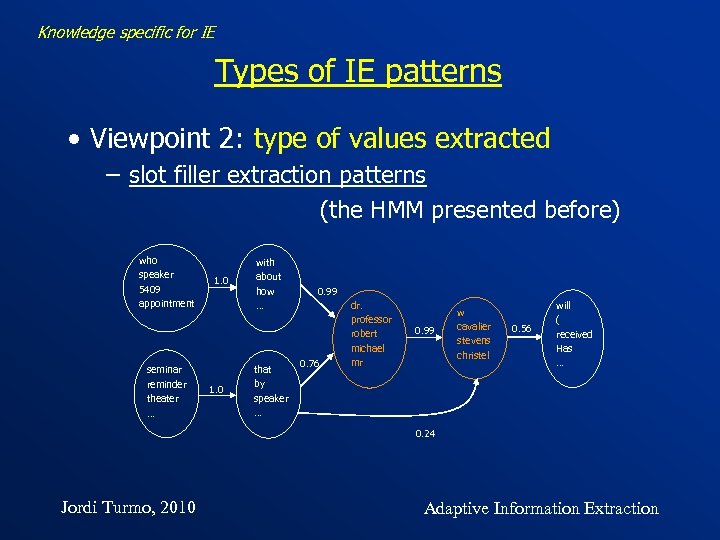 Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 2: type of values extracted − slot filler extraction patterns (the HMM presented before) who speaker 5409 appointment seminar reminder theater … 1. 0 with about how … that by speaker … 0. 99 0. 76 dr. professor robert michael mr 0. 99 w cavalier stevens christel 0. 56 will ( received Has … 0. 24 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 2: type of values extracted − slot filler extraction patterns (the HMM presented before) who speaker 5409 appointment seminar reminder theater … 1. 0 with about how … that by speaker … 0. 99 0. 76 dr. professor robert michael mr 0. 99 w cavalier stevens christel 0. 56 will ( received Has … 0. 24 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
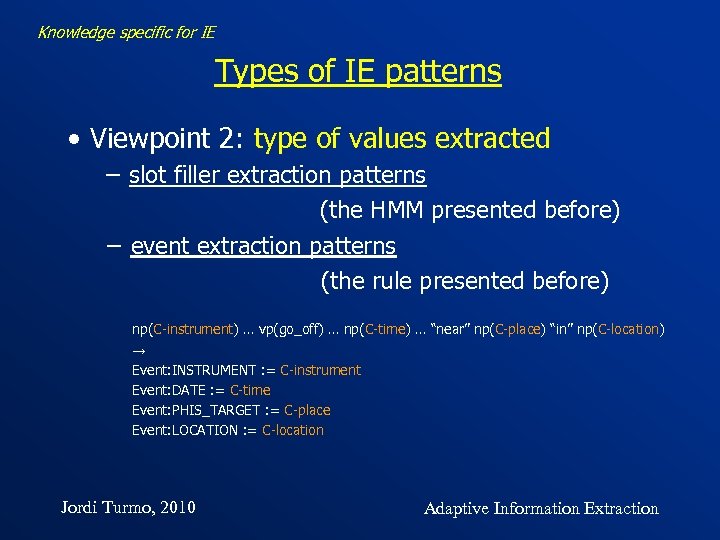 Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 2: type of values extracted − slot filler extraction patterns (the HMM presented before) − event extraction patterns (the rule presented before) np(C-instrument) … vp(go_off) … np(C-time) … “near” np(C-place) “in” np(C-location) → Event: INSTRUMENT : = C-instrument Event: DATE : = C-time Event: PHIS_TARGET : = C-place Event: LOCATION : = C-location Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 2: type of values extracted − slot filler extraction patterns (the HMM presented before) − event extraction patterns (the rule presented before) np(C-instrument) … vp(go_off) … np(C-time) … “near” np(C-place) “in” np(C-location) → Event: INSTRUMENT : = C-instrument Event: DATE : = C-time Event: PHIS_TARGET : = C-place Event: LOCATION : = C-location Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
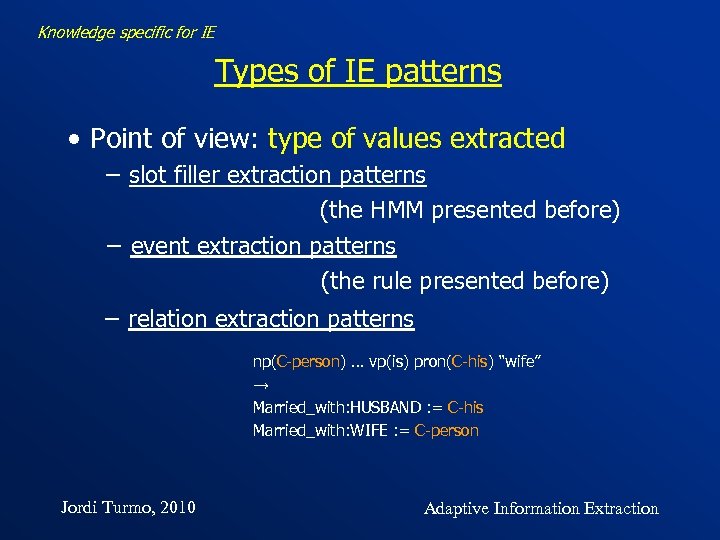 Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Point of view: type of values extracted − slot filler extraction patterns (the HMM presented before) − event extraction patterns (the rule presented before) − relation extraction patterns np(C-person) … vp(is) pron(C-his) “wife” → Married_with: HUSBAND : = C-his Married_with: WIFE : = C-person Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Point of view: type of values extracted − slot filler extraction patterns (the HMM presented before) − event extraction patterns (the rule presented before) − relation extraction patterns np(C-person) … vp(is) pron(C-his) “wife” → Married_with: HUSBAND : = C-his Married_with: WIFE : = C-person Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 3: number of slot fillers extracted − single-slot IE patterns (the HMM presented before) − multi-slot IE patterns (both rules presented before) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Knowledge specific for IE Types of IE patterns • Viewpoint 3: number of slot fillers extracted − single-slot IE patterns (the HMM presented before) − multi-slot IE patterns (both rules presented before) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
 Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Summary • Information Extraction Systems • Introduction • Historical framework • Architecture • Knowledge specific for IE • Examples • Evaluation • Multilinguality • Adaptability Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
![Examples of IE systems Methodologies [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER Examples of IE systems Methodologies [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER](https://present5.com/presentation/d6f6deb1763e2a18d10697670ba88e3e/image-66.jpg) Examples of IE systems Methodologies [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER HASTEN PROTEUS ALEMBIC PIE TURBIO PLUM IE 2 LOUELLA SIFT Reference Gaizauskas et al, 1995 Humphreys et al, 1998 Garigliano et al, 1998 Lehnert et al, 1991 Hobbs et al, 1993 Fisher et al, 1995 Krupka, 1995 Grishman, 1995 Aberdeen et al, 1993 Lin, 1995 Turmo, 2002 Weischedel et al, 1995 Aone et al, 1998 Childs et al, 1995 Miller et al, 1998 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Parsing Semantics Discourse indepth understanding template merging Chunking Pattern matching Gramm relations interp Partial Parsing semantic interpretation procedures pattern matching Pattern matching template merging - sintactico-semantic parsing Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems Methodologies [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER HASTEN PROTEUS ALEMBIC PIE TURBIO PLUM IE 2 LOUELLA SIFT Reference Gaizauskas et al, 1995 Humphreys et al, 1998 Garigliano et al, 1998 Lehnert et al, 1991 Hobbs et al, 1993 Fisher et al, 1995 Krupka, 1995 Grishman, 1995 Aberdeen et al, 1993 Lin, 1995 Turmo, 2002 Weischedel et al, 1995 Aone et al, 1998 Childs et al, 1995 Miller et al, 1998 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Parsing Semantics Discourse indepth understanding template merging Chunking Pattern matching Gramm relations interp Partial Parsing semantic interpretation procedures pattern matching Pattern matching template merging - sintactico-semantic parsing Adaptive Information Extraction
![Examples of IE systems Knowledge [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER Examples of IE systems Knowledge [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER](https://present5.com/presentation/d6f6deb1763e2a18d10697670ba88e3e/image-67.jpg) Examples of IE systems Knowledge [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER HASTEN PROTEUS ALEMBIC TURBIO PIE PLUM IE 2 Parsing Semantics Treebank grammar hand-crafted stratified general grammar General grammar -expressions semantic network concept nodes (Auto. Slog) hand-crafted IE rules concept nodes (CRYSTAL) Phrasal grammar E-graphs IE rules (Ex. DISCO) hand-crafted gram relations IE rules (EVIUS) General grammar hand-crafted IE rules LOUELLA SIFT Discourse decision trees hand-crafted rules decision trees Statistical models for syntactic-semantic parsing & coreference resolution learned from PTB and on-domain annotated texts Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems Knowledge [Turmo, 2002] System La. SIE-II LOLITA CIRCUS FASTUS BADGER HASTEN PROTEUS ALEMBIC TURBIO PIE PLUM IE 2 Parsing Semantics Treebank grammar hand-crafted stratified general grammar General grammar -expressions semantic network concept nodes (Auto. Slog) hand-crafted IE rules concept nodes (CRYSTAL) Phrasal grammar E-graphs IE rules (Ex. DISCO) hand-crafted gram relations IE rules (EVIUS) General grammar hand-crafted IE rules LOUELLA SIFT Discourse decision trees hand-crafted rules decision trees Statistical models for syntactic-semantic parsing & coreference resolution learned from PTB and on-domain annotated texts Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
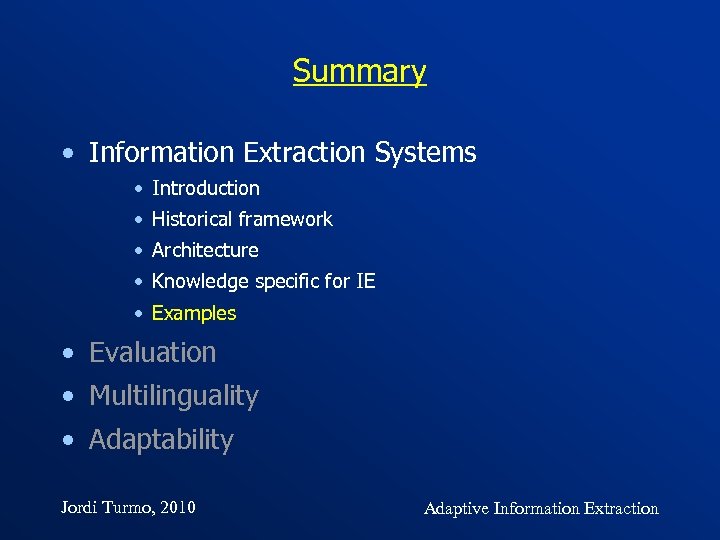
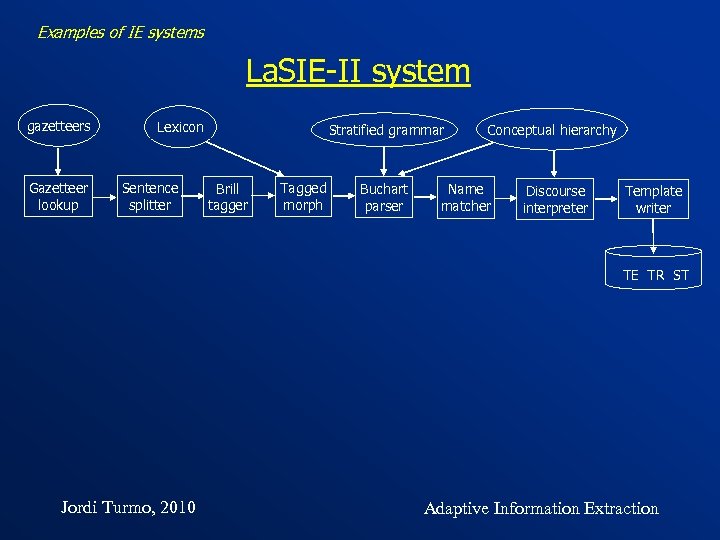 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Template writer TE TR ST Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Template writer TE TR ST Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
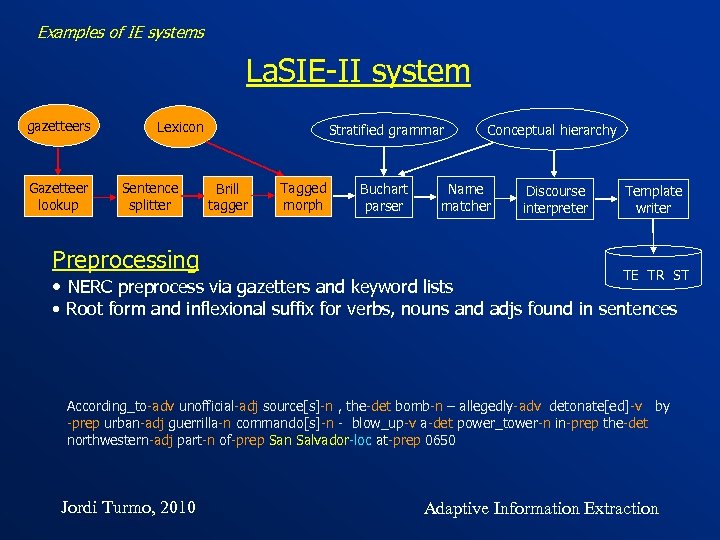 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Preprocessing Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher • NERC preprocess via gazetters and keyword lists Template writer TE TR ST • Root form and inflexional suffix for verbs, nouns and adjs found in sentences According_to-adv unofficial-adj source[s]-n , the-det bomb-n – allegedly-adv detonate[ed]-v by -prep urban-adj guerrilla-n commando[s]-n - blow_up-v a-det power_tower-n in-prep the-det northwestern-adj part-n of-prep San Salvador-loc at-prep 0650 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Preprocessing Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher • NERC preprocess via gazetters and keyword lists Template writer TE TR ST • Root form and inflexional suffix for verbs, nouns and adjs found in sentences According_to-adv unofficial-adj source[s]-n , the-det bomb-n – allegedly-adv detonate[ed]-v by -prep urban-adj guerrilla-n commando[s]-n - blow_up-v a-det power_tower-n in-prep the-det northwestern-adj part-n of-prep San Salvador-loc at-prep 0650 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
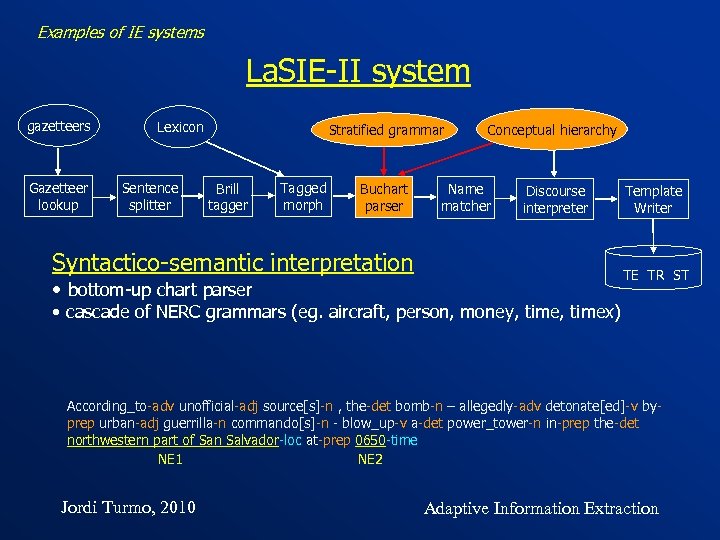 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Syntactico-semantic interpretation • bottom-up chart parser Template Writer TE TR ST • cascade of NERC grammars (eg. aircraft, person, money, timex) According_to-adv unofficial-adj source[s]-n , the-det bomb-n – allegedly-adv detonate[ed]-v byprep urban-adj guerrilla-n commando[s]-n - blow_up-v a-det power_tower-n in-prep the-det northwestern part of San Salvador-loc at-prep 0650 -time NE 2 NE 1 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Syntactico-semantic interpretation • bottom-up chart parser Template Writer TE TR ST • cascade of NERC grammars (eg. aircraft, person, money, timex) According_to-adv unofficial-adj source[s]-n , the-det bomb-n – allegedly-adv detonate[ed]-v byprep urban-adj guerrilla-n commando[s]-n - blow_up-v a-det power_tower-n in-prep the-det northwestern part of San Salvador-loc at-prep 0650 -time NE 2 NE 1 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
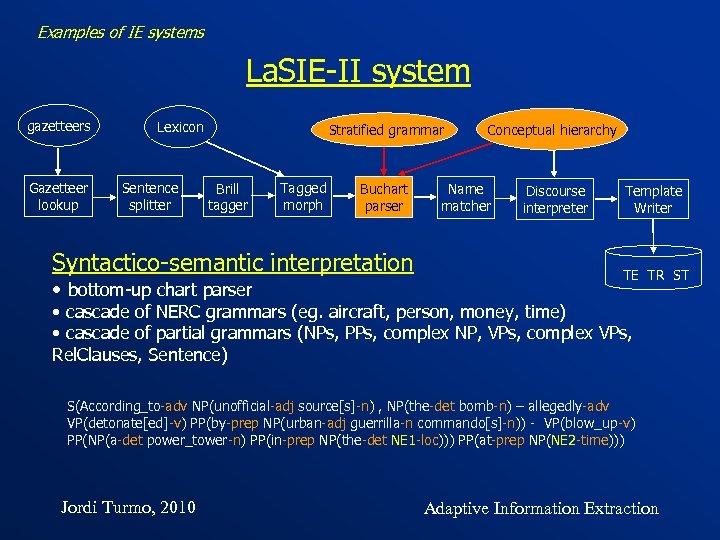 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Syntactico-semantic interpretation • bottom-up chart parser Name matcher Template Writer TE TR ST • cascade of NERC grammars (eg. aircraft, person, money, time) • cascade of partial grammars (NPs, PPs, complex NP, VPs, complex VPs, Rel. Clauses, Sentence) S(According_to-adv NP(unofficial-adj source[s]-n) , NP(the-det bomb-n) – allegedly-adv VP(detonate[ed]-v) PP(by-prep NP(urban-adj guerrilla-n commando[s]-n)) - VP(blow_up-v) PP(NP(a-det power_tower-n) PP(in-prep NP(the-det NE 1 -loc))) PP(at-prep NP(NE 2 -time))) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Syntactico-semantic interpretation • bottom-up chart parser Name matcher Template Writer TE TR ST • cascade of NERC grammars (eg. aircraft, person, money, time) • cascade of partial grammars (NPs, PPs, complex NP, VPs, complex VPs, Rel. Clauses, Sentence) S(According_to-adv NP(unofficial-adj source[s]-n) , NP(the-det bomb-n) – allegedly-adv VP(detonate[ed]-v) PP(by-prep NP(urban-adj guerrilla-n commando[s]-n)) - VP(blow_up-v) PP(NP(a-det power_tower-n) PP(in-prep NP(the-det NE 1 -loc))) PP(at-prep NP(NE 2 -time))) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
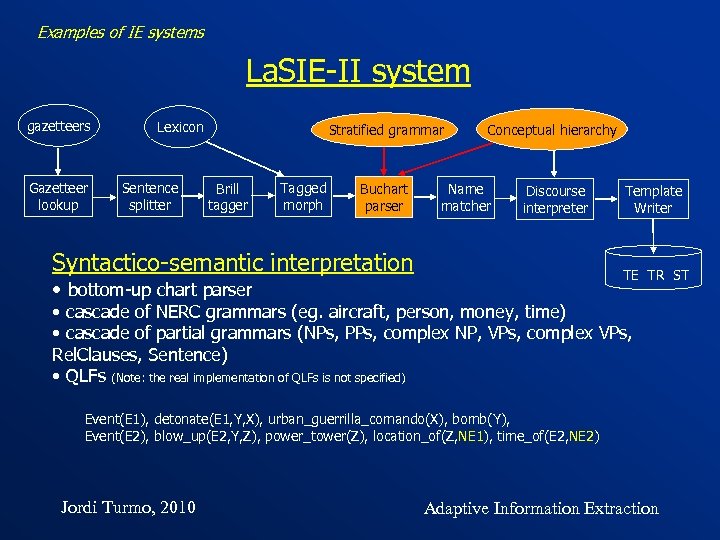 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Syntactico-semantic interpretation Template Writer TE TR ST • bottom-up chart parser • cascade of NERC grammars (eg. aircraft, person, money, time) • cascade of partial grammars (NPs, PPs, complex NP, VPs, complex VPs, Rel. Clauses, Sentence) • QLFs (Note: the real implementation of QLFs is not specified) Event(E 1), detonate(E 1, Y, X), urban_guerrilla_comando(X), bomb(Y), Event(E 2), blow_up(E 2, Y, Z), power_tower(Z), location_of(Z, NE 1), time_of(E 2, NE 2) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Syntactico-semantic interpretation Template Writer TE TR ST • bottom-up chart parser • cascade of NERC grammars (eg. aircraft, person, money, time) • cascade of partial grammars (NPs, PPs, complex NP, VPs, complex VPs, Rel. Clauses, Sentence) • QLFs (Note: the real implementation of QLFs is not specified) Event(E 1), detonate(E 1, Y, X), urban_guerrilla_comando(X), bomb(Y), Event(E 2), blow_up(E 2, Y, Z), power_tower(Z), location_of(Z, NE 1), time_of(E 2, NE 2) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
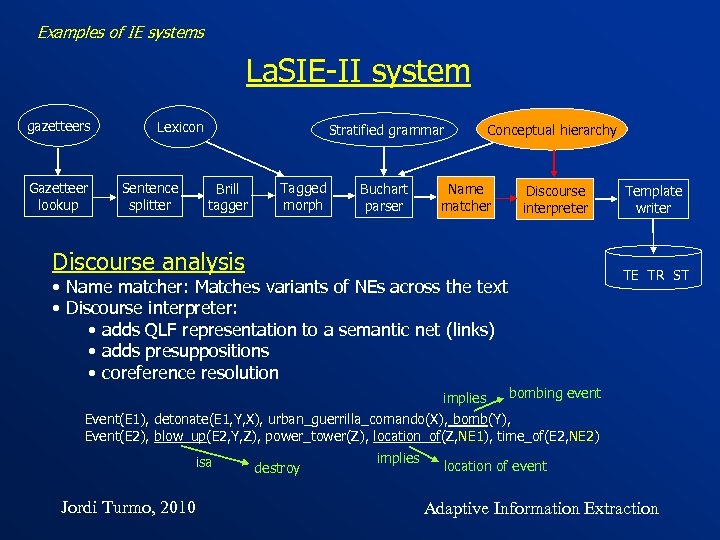 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Discourse analysis TE TR ST • Name matcher: Matches variants of NEs across the text • Discourse interpreter: • adds QLF representation to a semantic net (links) • adds presuppositions • coreference resolution implies Template writer bombing event Event(E 1), detonate(E 1, Y, X), urban_guerrilla_comando(X), bomb(Y), Event(E 2), blow_up(E 2, Y, Z), power_tower(Z), location_of(Z, NE 1), time_of(E 2, NE 2) isa Jordi Turmo, 2010 destroy implies location of event Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Tagged morph Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Name matcher Discourse analysis TE TR ST • Name matcher: Matches variants of NEs across the text • Discourse interpreter: • adds QLF representation to a semantic net (links) • adds presuppositions • coreference resolution implies Template writer bombing event Event(E 1), detonate(E 1, Y, X), urban_guerrilla_comando(X), bomb(Y), Event(E 2), blow_up(E 2, Y, Z), power_tower(Z), location_of(Z, NE 1), time_of(E 2, NE 2) isa Jordi Turmo, 2010 destroy implies location of event Adaptive Information Extraction
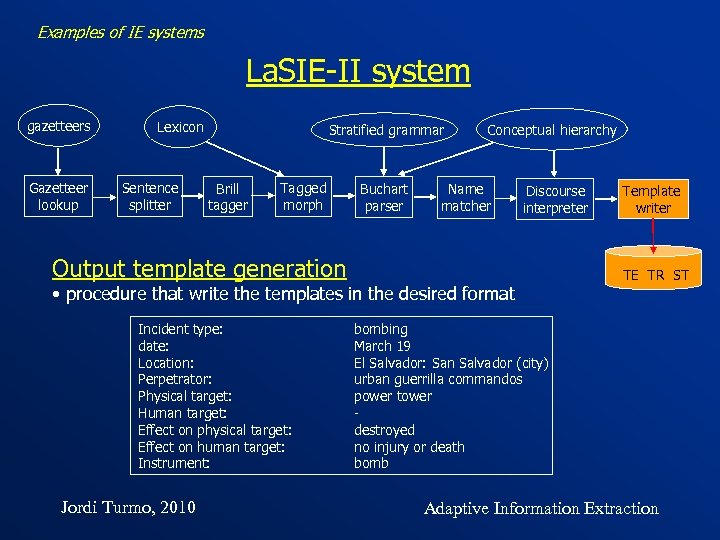 Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Tagged morph Name matcher Output template generation • procedure that write the templates in the desired format Incident type: date: Location: Perpetrator: Physical target: Human target: Effect on physical target: Effect on human target: Instrument: Jordi Turmo, 2010 Template writer TE TR ST bombing March 19 El Salvador: San Salvador (city) urban guerrilla commandos power tower destroyed no injury or death bomb Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems La. SIE-II system gazetteers Gazetteer lookup Lexicon Sentence splitter Stratified grammar Brill tagger Conceptual hierarchy Buchart parser Discourse interpreter Tagged morph Name matcher Output template generation • procedure that write the templates in the desired format Incident type: date: Location: Perpetrator: Physical target: Human target: Effect on physical target: Effect on human target: Instrument: Jordi Turmo, 2010 Template writer TE TR ST bombing March 19 El Salvador: San Salvador (city) urban guerrilla commandos power tower destroyed no injury or death bomb Adaptive Information Extraction
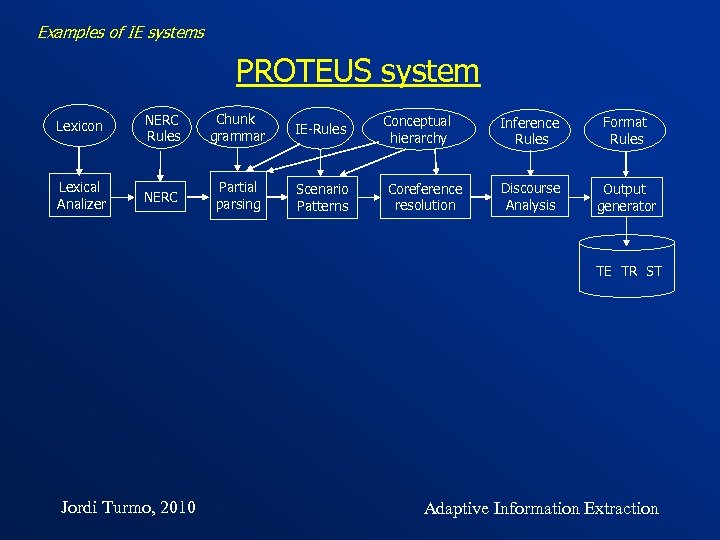 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
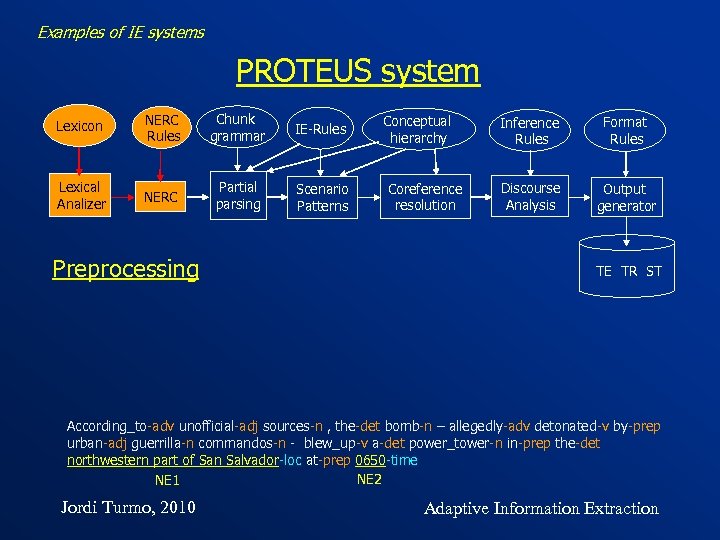 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Preprocessing Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST According_to-adv unofficial-adj sources-n , the-det bomb-n – allegedly-adv detonated-v by-prep urban-adj guerrilla-n commandos-n - blew_up-v a-det power_tower-n in-prep the-det northwestern part of San Salvador-loc at-prep 0650 -time NE 2 NE 1 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Preprocessing Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST According_to-adv unofficial-adj sources-n , the-det bomb-n – allegedly-adv detonated-v by-prep urban-adj guerrilla-n commandos-n - blew_up-v a-det power_tower-n in-prep the-det northwestern part of San Salvador-loc at-prep 0650 -time NE 2 NE 1 Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
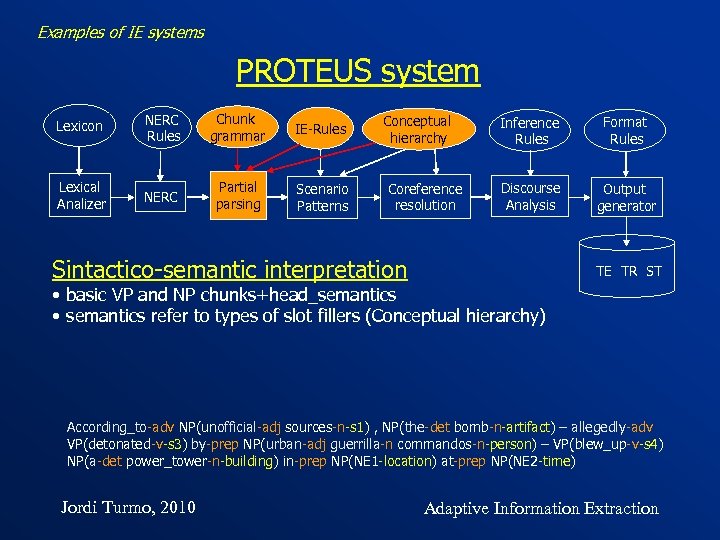 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Sintactico-semantic interpretation Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST • basic VP and NP chunks+head_semantics • semantics refer to types of slot fillers (Conceptual hierarchy) According_to-adv NP(unofficial-adj sources-n-s 1) , NP(the-det bomb-n-artifact) – allegedly-adv VP(detonated-v-s 3) by-prep NP(urban-adj guerrilla-n commandos-n-person) – VP(blew_up-v-s 4) NP(a-det power_tower-n-building) in-prep NP(NE 1 -location) at-prep NP(NE 2 -time) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Sintactico-semantic interpretation Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST • basic VP and NP chunks+head_semantics • semantics refer to types of slot fillers (Conceptual hierarchy) According_to-adv NP(unofficial-adj sources-n-s 1) , NP(the-det bomb-n-artifact) – allegedly-adv VP(detonated-v-s 3) by-prep NP(urban-adj guerrilla-n commandos-n-person) – VP(blew_up-v-s 4) NP(a-det power_tower-n-building) in-prep NP(NE 1 -location) at-prep NP(NE 2 -time) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
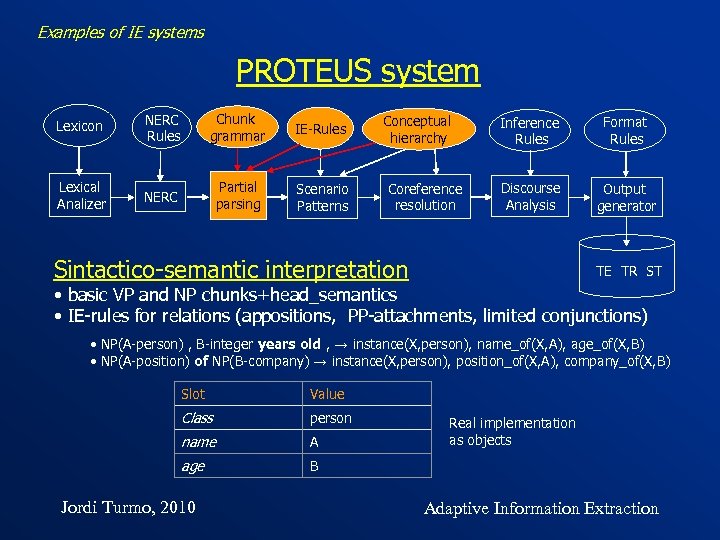 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator Sintactico-semantic interpretation TE TR ST • basic VP and NP chunks+head_semantics • IE-rules for relations (appositions, PP-attachments, limited conjunctions) • NP(A-person) , B-integer years old , → instance(X, person), name_of(X, A), age_of(X, B) • NP(A-position) of NP(B-company) → instance(X, person), position_of(X, A), company_of(X, B) Slot Value Class person name A age B Jordi Turmo, 2010 Real implementation as objects Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator Sintactico-semantic interpretation TE TR ST • basic VP and NP chunks+head_semantics • IE-rules for relations (appositions, PP-attachments, limited conjunctions) • NP(A-person) , B-integer years old , → instance(X, person), name_of(X, A), age_of(X, B) • NP(A-position) of NP(B-company) → instance(X, person), position_of(X, A), company_of(X, B) Slot Value Class person name A age B Jordi Turmo, 2010 Real implementation as objects Adaptive Information Extraction
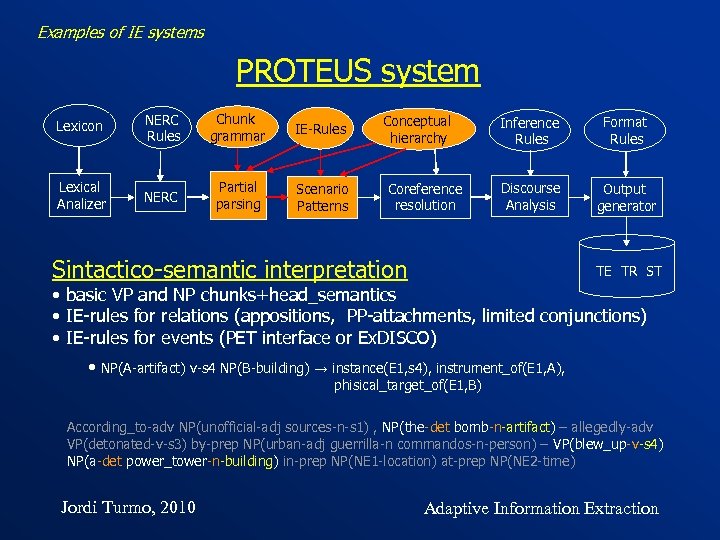 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator Sintactico-semantic interpretation TE TR ST • basic VP and NP chunks+head_semantics • IE-rules for relations (appositions, PP-attachments, limited conjunctions) • IE-rules for events (PET interface or Ex. DISCO) • NP(A-artifact) v-s 4 NP(B-building) → instance(E 1, s 4), instrument_of(E 1, A), phisical_target_of(E 1, B) According_to-adv NP(unofficial-adj sources-n-s 1) , NP(the-det bomb-n-artifact) – allegedly-adv VP(detonated-v-s 3) by-prep NP(urban-adj guerrilla-n commandos-n-person) – VP(blew_up-v-s 4) NP(a-det power_tower-n-building) in-prep NP(NE 1 -location) at-prep NP(NE 2 -time) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator Sintactico-semantic interpretation TE TR ST • basic VP and NP chunks+head_semantics • IE-rules for relations (appositions, PP-attachments, limited conjunctions) • IE-rules for events (PET interface or Ex. DISCO) • NP(A-artifact) v-s 4 NP(B-building) → instance(E 1, s 4), instrument_of(E 1, A), phisical_target_of(E 1, B) According_to-adv NP(unofficial-adj sources-n-s 1) , NP(the-det bomb-n-artifact) – allegedly-adv VP(detonated-v-s 3) by-prep NP(urban-adj guerrilla-n commandos-n-person) – VP(blew_up-v-s 4) NP(a-det power_tower-n-building) in-prep NP(NE 1 -location) at-prep NP(NE 2 -time) Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
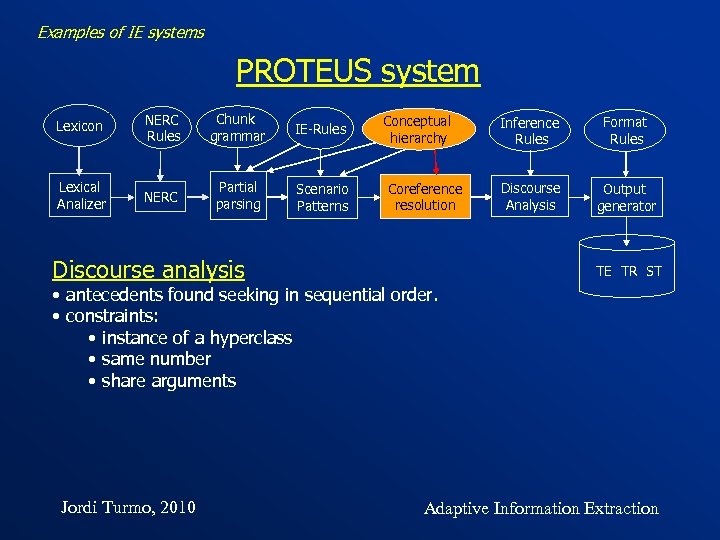 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Discourse analysis Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST • antecedents found seeking in sequential order. • constraints: • instance of a hyperclass • same number • share arguments Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Discourse analysis Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST • antecedents found seeking in sequential order. • constraints: • instance of a hyperclass • same number • share arguments Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
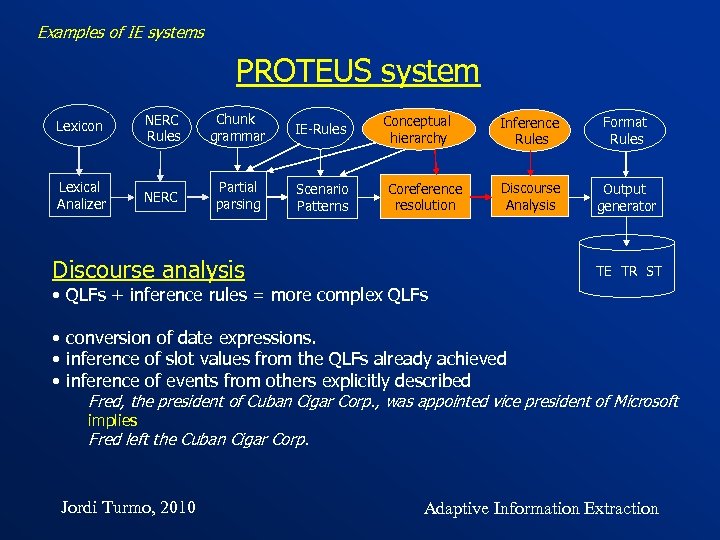 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator Discourse analysis TE TR ST • QLFs + inference rules = more complex QLFs • conversion of date expressions. • inference of slot values from the QLFs already achieved • inference of events from others explicitly described Fred, the president of Cuban Cigar Corp. , was appointed vice president of Microsoft implies Fred left the Cuban Cigar Corp. Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator Discourse analysis TE TR ST • QLFs + inference rules = more complex QLFs • conversion of date expressions. • inference of slot values from the QLFs already achieved • inference of events from others explicitly described Fred, the president of Cuban Cigar Corp. , was appointed vice president of Microsoft implies Fred left the Cuban Cigar Corp. Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
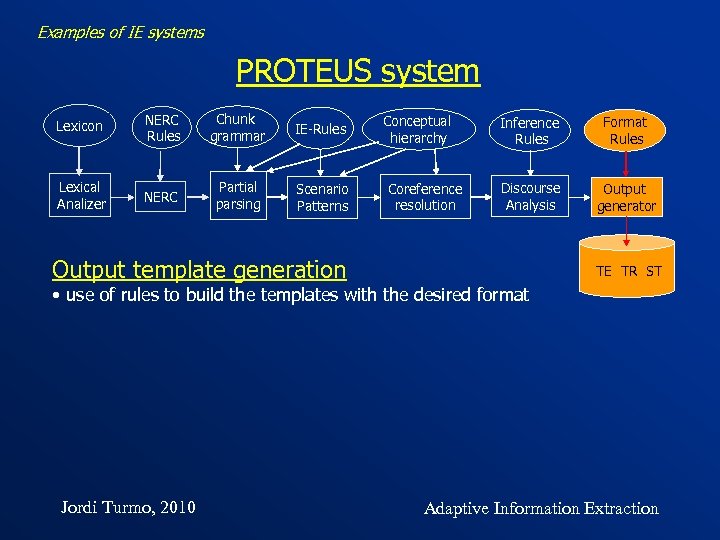 Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Output template generation Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST • use of rules to build the templates with the desired format Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems PROTEUS system Lexicon NERC Rules Chunk grammar IE-Rules Lexical Analizer NERC Partial parsing Scenario Patterns Output template generation Conceptual hierarchy Coreference resolution Inference Rules Format Rules Discourse Analysis Output generator TE TR ST • use of rules to build the templates with the desired format Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
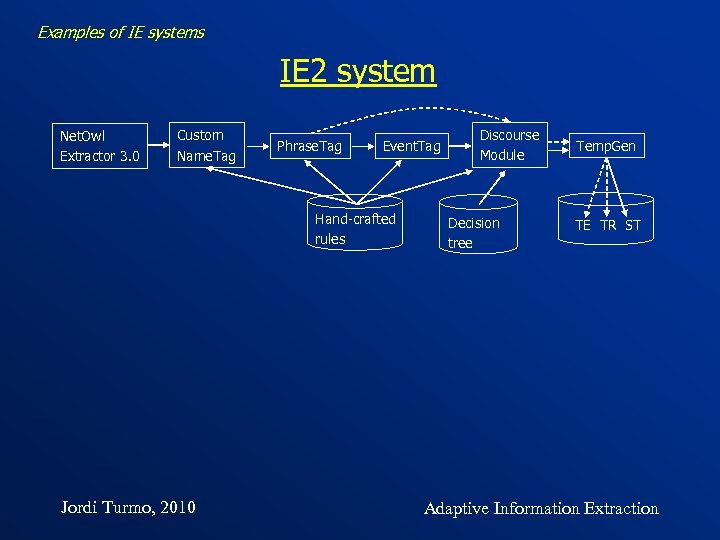 Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Jordi Turmo, 2010 Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Jordi Turmo, 2010 Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Adaptive Information Extraction
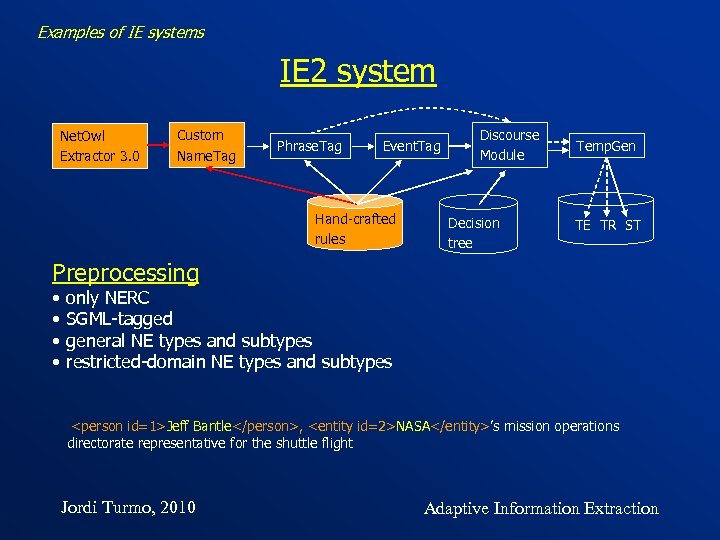 Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Preprocessing • • only NERC SGML-tagged general NE types and subtypes restricted-domain NE types and subtypes
Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Preprocessing • • only NERC SGML-tagged general NE types and subtypes restricted-domain NE types and subtypes
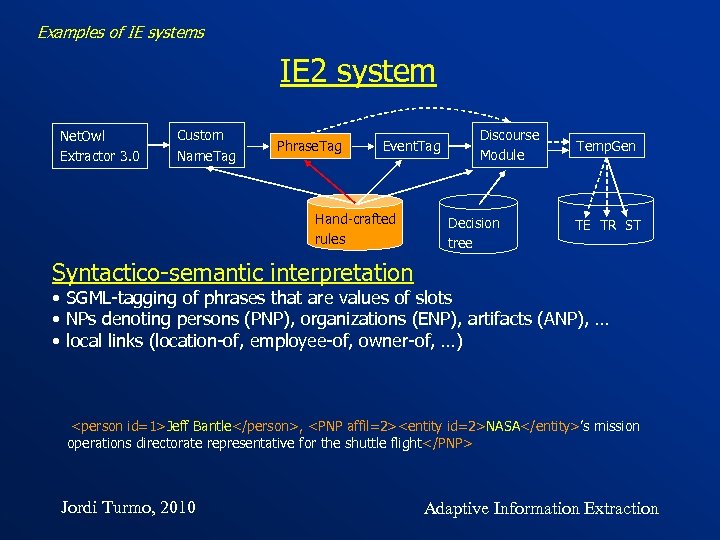 Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Syntactico-semantic interpretation • SGML-tagging of phrases that are values of slots • NPs denoting persons (PNP), organizations (ENP), artifacts (ANP), … • local links (location-of, employee-of, owner-of, …)
Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Syntactico-semantic interpretation • SGML-tagging of phrases that are values of slots • NPs denoting persons (PNP), organizations (ENP), artifacts (ANP), … • local links (location-of, employee-of, owner-of, …)
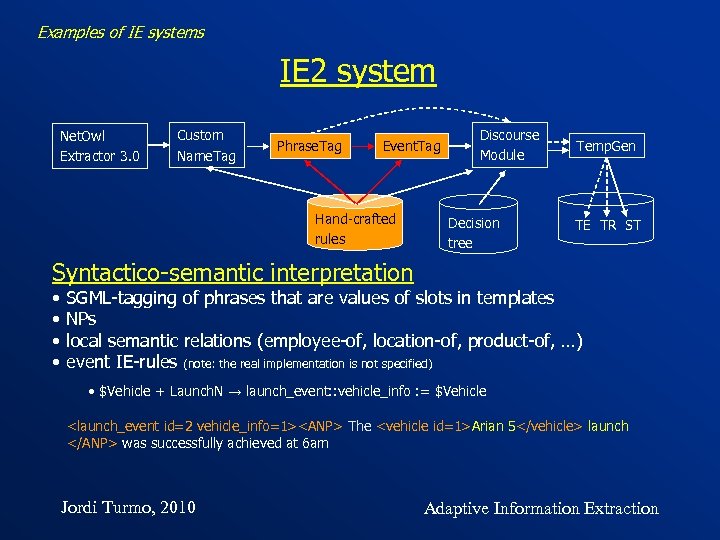 Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Syntactico-semantic interpretation • • SGML-tagging of phrases that are values of slots in templates NPs local semantic relations (employee-of, location-of, product-of, …) event IE-rules (note: the real implementation is not specified) • $Vehicle + Launch. N → launch_event: : vehicle_info : = $Vehicle
Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Syntactico-semantic interpretation • • SGML-tagging of phrases that are values of slots in templates NPs local semantic relations (employee-of, location-of, product-of, …) event IE-rules (note: the real implementation is not specified) • $Vehicle + Launch. N → launch_event: : vehicle_info : = $Vehicle
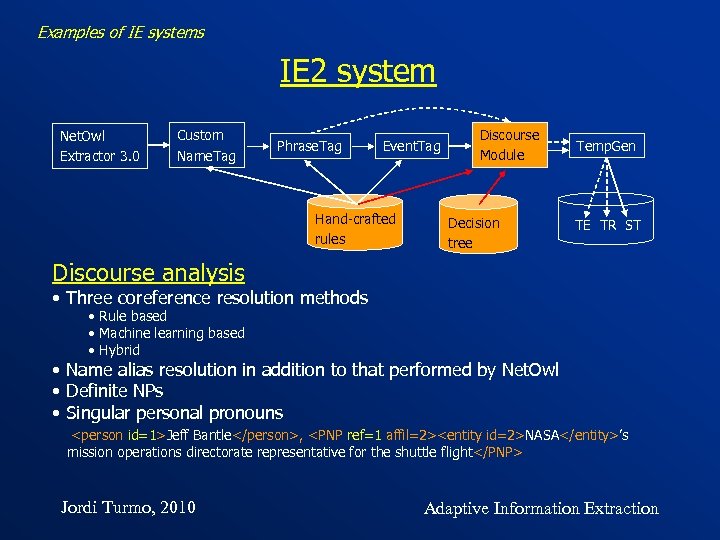 Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Discourse analysis • Three coreference resolution methods • Rule based • Machine learning based • Hybrid • Name alias resolution in addition to that performed by Net. Owl • Definite NPs • Singular personal pronouns
Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Discourse analysis • Three coreference resolution methods • Rule based • Machine learning based • Hybrid • Name alias resolution in addition to that performed by Net. Owl • Definite NPs • Singular personal pronouns
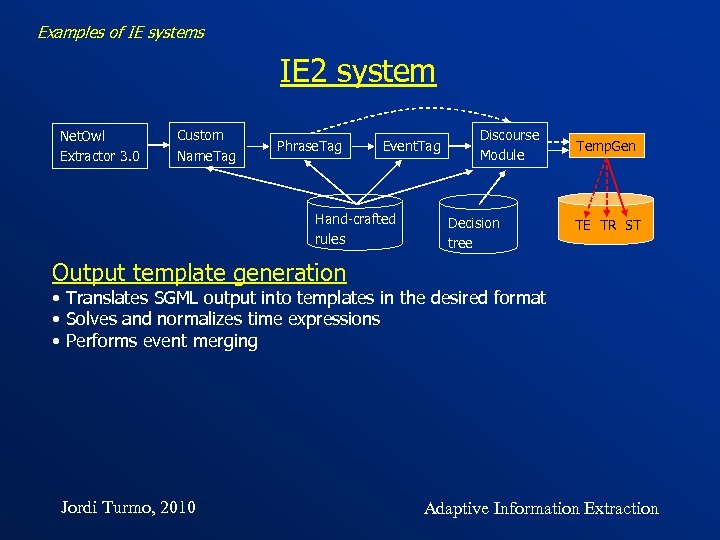 Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Output template generation • Translates SGML output into templates in the desired format • Solves and normalizes time expressions • Performs event merging Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems IE 2 system Net. Owl Extractor 3. 0 Custom Name. Tag Phrase. Tag Event. Tag Hand-crafted rules Discourse Module Decision tree Temp. Gen TE TR ST Output template generation • Translates SGML output into templates in the desired format • Solves and normalizes time expressions • Performs event merging Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
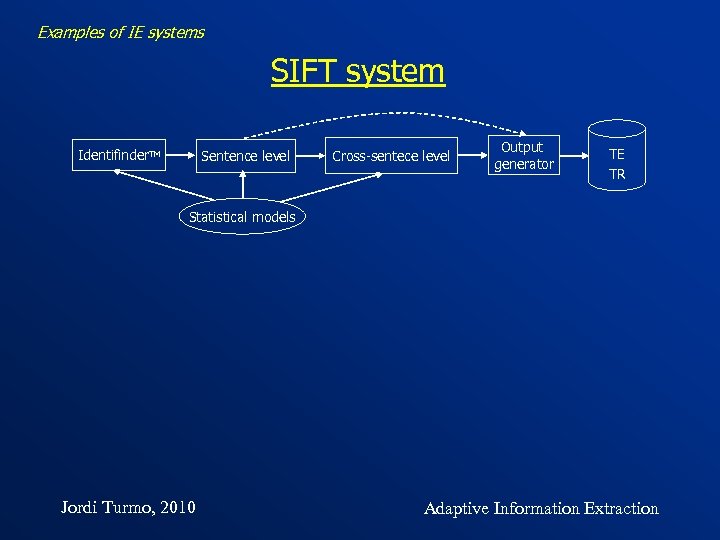 Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
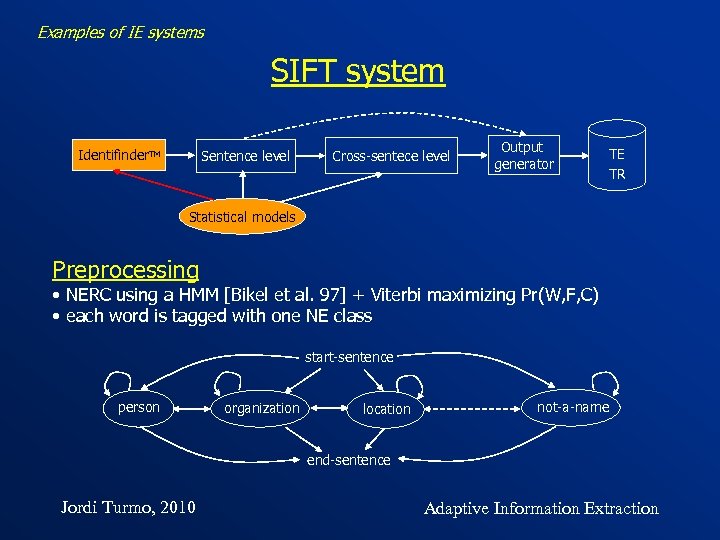 Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Preprocessing • NERC using a HMM [Bikel et al. 97] + Viterbi maximizing Pr(W, F, C) • each word is tagged with one NE class start-sentence person organization location not-a-name end-sentence Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Preprocessing • NERC using a HMM [Bikel et al. 97] + Viterbi maximizing Pr(W, F, C) • each word is tagged with one NE class start-sentence person organization location not-a-name end-sentence Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
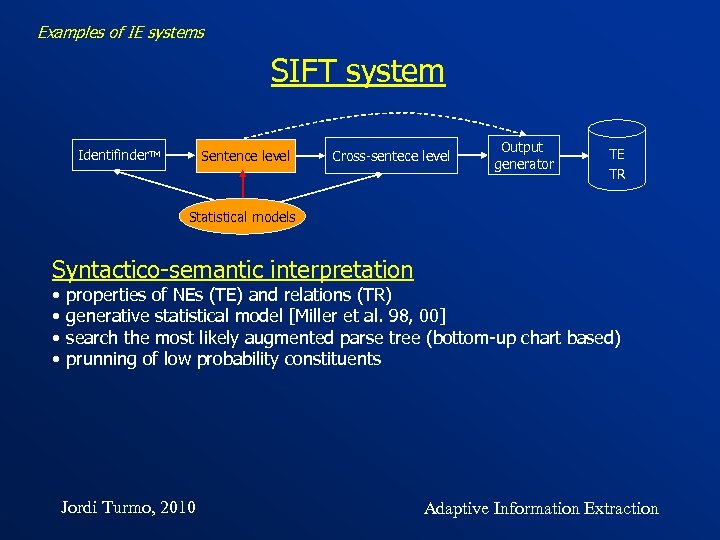 Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Syntactico-semantic interpretation • • properties of NEs (TE) and relations (TR) generative statistical model [Miller et al. 98, 00] search the most likely augmented parse tree (bottom-up chart based) prunning of low probability constituents Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Syntactico-semantic interpretation • • properties of NEs (TE) and relations (TR) generative statistical model [Miller et al. 98, 00] search the most likely augmented parse tree (bottom-up chart based) prunning of low probability constituents Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
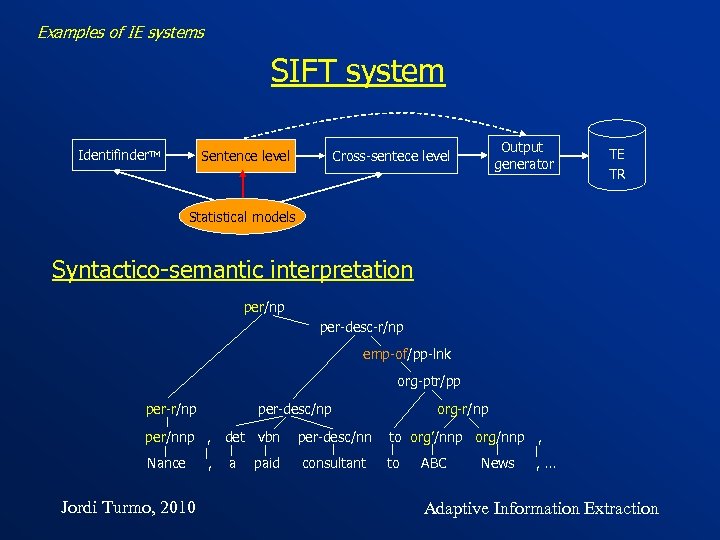 Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Output generator Cross-sentece level TE TR Statistical models Syntactico-semantic interpretation per/np per-desc-r/np emp-of/pp-lnk org-ptr/pp per-r/np per-desc/np per/nnp , det vbn Nance Jordi Turmo, 2010 , a paid per-desc/nn consultant org-r/np to org’/nnp org/nnp , to ABC News , … Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Output generator Cross-sentece level TE TR Statistical models Syntactico-semantic interpretation per/np per-desc-r/np emp-of/pp-lnk org-ptr/pp per-r/np per-desc/np per/nnp , det vbn Nance Jordi Turmo, 2010 , a paid per-desc/nn consultant org-r/np to org’/nnp org/nnp , to ABC News , … Adaptive Information Extraction
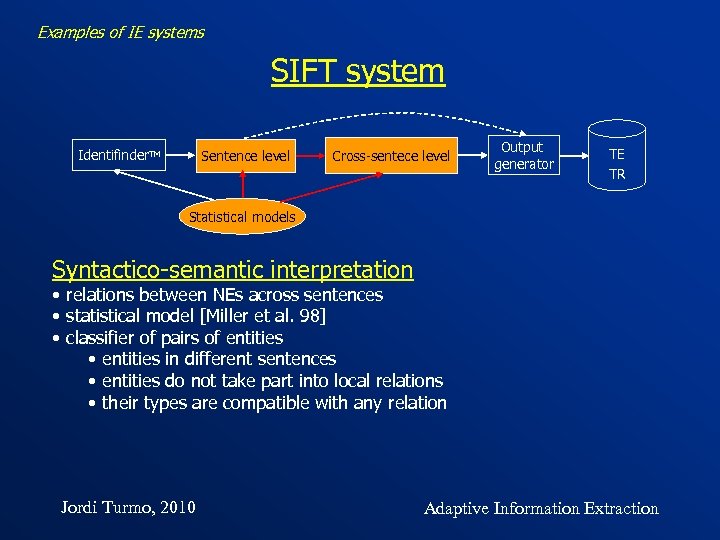 Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Syntactico-semantic interpretation • relations between NEs across sentences • statistical model [Miller et al. 98] • classifier of pairs of entities • entities in different sentences • entities do not take part into local relations • their types are compatible with any relation Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems SIFT system Identifinder. TM Sentence level Cross-sentece level Output generator TE TR Statistical models Syntactico-semantic interpretation • relations between NEs across sentences • statistical model [Miller et al. 98] • classifier of pairs of entities • entities in different sentences • entities do not take part into local relations • their types are compatible with any relation Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
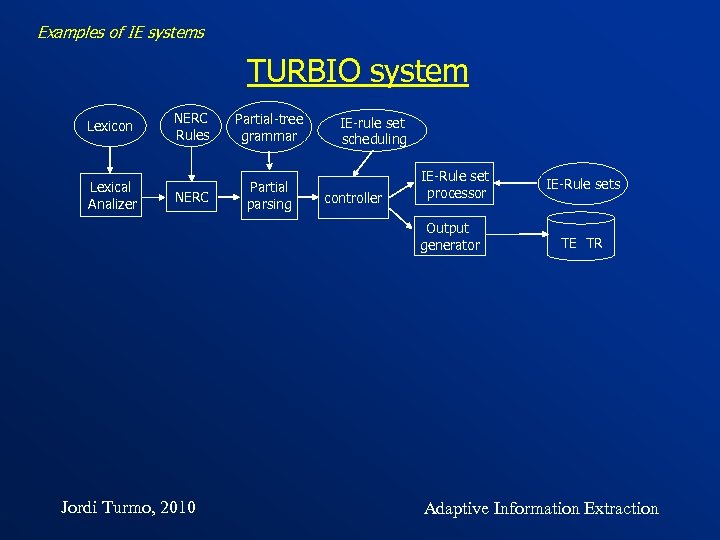 Examples of IE systems TURBIO system Lexicon Lexical Analizer NERC Rules Partial-tree grammar NERC Partial parsing IE-rule set scheduling controller IE-Rule set processor Output generator Jordi Turmo, 2010 IE-Rule sets TE TR Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems TURBIO system Lexicon Lexical Analizer NERC Rules Partial-tree grammar NERC Partial parsing IE-rule set scheduling controller IE-Rule set processor Output generator Jordi Turmo, 2010 IE-Rule sets TE TR Adaptive Information Extraction
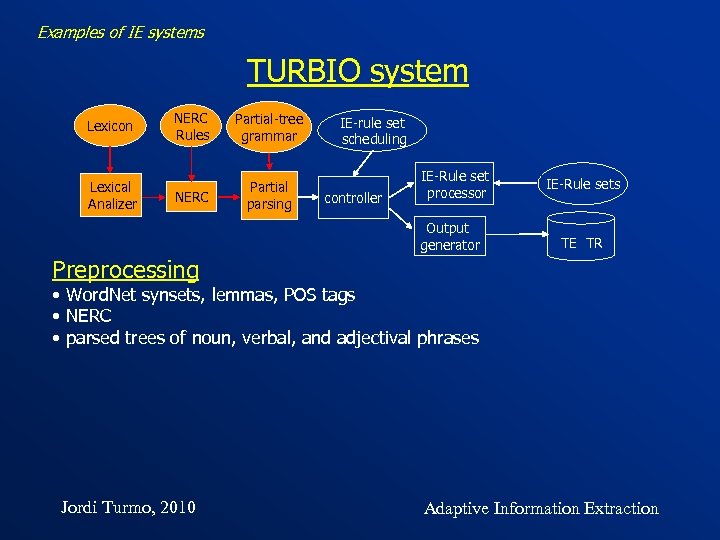 Examples of IE systems TURBIO system Lexicon Lexical Analizer NERC Rules Partial-tree grammar NERC Partial parsing IE-rule set scheduling controller IE-Rule set processor Output generator IE-Rule sets TE TR Preprocessing • Word. Net synsets, lemmas, POS tags • NERC • parsed trees of noun, verbal, and adjectival phrases Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems TURBIO system Lexicon Lexical Analizer NERC Rules Partial-tree grammar NERC Partial parsing IE-rule set scheduling controller IE-Rule set processor Output generator IE-Rule sets TE TR Preprocessing • Word. Net synsets, lemmas, POS tags • NERC • parsed trees of noun, verbal, and adjectival phrases Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
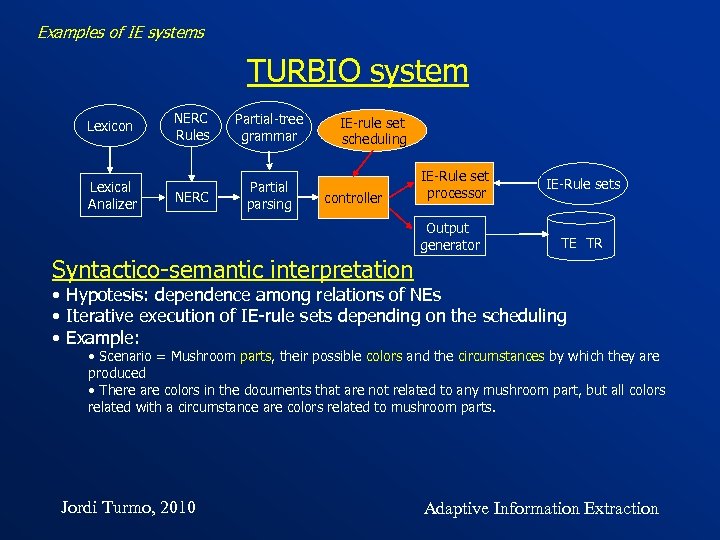 Examples of IE systems TURBIO system Lexicon Lexical Analizer NERC Rules Partial-tree grammar NERC Partial parsing IE-rule set scheduling controller IE-Rule set processor Output generator IE-Rule sets TE TR Syntactico-semantic interpretation • Hypotesis: dependence among relations of NEs • Iterative execution of IE-rule sets depending on the scheduling • Example: • Scenario = Mushroom parts, their possible colors and the circumstances by which they are produced • There are colors in the documents that are not related to any mushroom part, but all colors related with a circumstance are colors related to mushroom parts. Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction
Examples of IE systems TURBIO system Lexicon Lexical Analizer NERC Rules Partial-tree grammar NERC Partial parsing IE-rule set scheduling controller IE-Rule set processor Output generator IE-Rule sets TE TR Syntactico-semantic interpretation • Hypotesis: dependence among relations of NEs • Iterative execution of IE-rule sets depending on the scheduling • Example: • Scenario = Mushroom parts, their possible colors and the circumstances by which they are produced • There are colors in the documents that are not related to any mushroom part, but all colors related with a circumstance are colors related to mushroom parts. Jordi Turmo, 2010 Adaptive Information Extraction


