 Information Architecture
Information Architecture
 Information architecture is the science — some would insist art — of defining the design of organization and navigation systems to help people find and manage information successfully From Design Matters. http: //stc-on. org/id/informationarchitecture/2006/07/25/what-why-and-how-of-informationarchitecture/#more-128
Information architecture is the science — some would insist art — of defining the design of organization and navigation systems to help people find and manage information successfully From Design Matters. http: //stc-on. org/id/informationarchitecture/2006/07/25/what-why-and-how-of-informationarchitecture/#more-128
 Information Architecture Overall design of the site Must connect with the user’s context Don’t let sites just grow – No order to pages – Information is scattered Based on content and functionality
Information Architecture Overall design of the site Must connect with the user’s context Don’t let sites just grow – No order to pages – Information is scattered Based on content and functionality
 Information architecture Without an effective and efficient architecture, the site will not support a person’s needs. Must be user-centered (UCD). Reflect the user’s information needs and not the organization’s.
Information architecture Without an effective and efficient architecture, the site will not support a person’s needs. Must be user-centered (UCD). Reflect the user’s information needs and not the organization’s.
 Information architecture About – The site structure – Overall organization – Navigation Not about – The page layout – Color choices – Creating content
Information architecture About – The site structure – Overall organization – Navigation Not about – The page layout – Color choices – Creating content
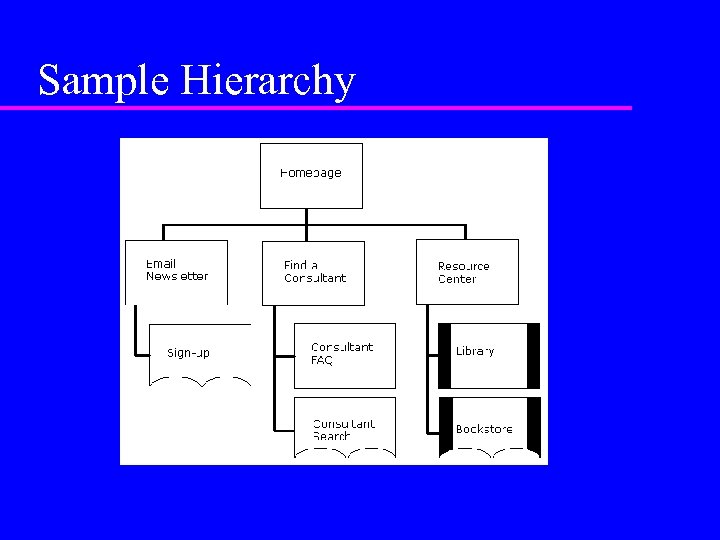 Sample Hierarchy
Sample Hierarchy
 Show overall structure
Show overall structure
 Navigation is visual Keep reader oriented Provide cues to location on the web site – Nav bar marking – Bread crumbs Design problems – Complex system is hard to maintain – Reader must understand your coding
Navigation is visual Keep reader oriented Provide cues to location on the web site – Nav bar marking – Bread crumbs Design problems – Complex system is hard to maintain – Reader must understand your coding
 Designing Navigation Always have way to homepage Don’t rely on the back button Build a hierarchy – Construct in user terms – Don’t construct in system terms Avoid menu-menu scheme
Designing Navigation Always have way to homepage Don’t rely on the back button Build a hierarchy – Construct in user terms – Don’t construct in system terms Avoid menu-menu scheme
 Doing the initial design Figure out the categories – User-based, not system-based Draw it out. Your mind will not work for a very complicated site. – Post-it notes – Paper sketches – Software is ok, but often clunky
Doing the initial design Figure out the categories – User-based, not system-based Draw it out. Your mind will not work for a very complicated site. – Post-it notes – Paper sketches – Software is ok, but often clunky
 Knowing what to design We started the way I had started with my first webpage: we pored over the documentation to discover who the audience was and what their key needs were. We wrote the names of three people who we thought would use the site, and wrote their needs underneath each of the names. Dave, the CEO who wanted to know if he should buy the product. Jill, the potential employee who wanted to know if it was a cool place to work. Carla, the investor who wanted to know if this was a hot buy.
Knowing what to design We started the way I had started with my first webpage: we pored over the documentation to discover who the audience was and what their key needs were. We wrote the names of three people who we thought would use the site, and wrote their needs underneath each of the names. Dave, the CEO who wanted to know if he should buy the product. Jill, the potential employee who wanted to know if it was a cool place to work. Carla, the investor who wanted to know if this was a hot buy.
 Conceptual model Which of these does the IA control and why? – The implementation model is how the product works from a technical point of view. – The mental model is how the user thinks the product works. – The conceptual model is the message the designer or IA sends to the user
Conceptual model Which of these does the IA control and why? – The implementation model is how the product works from a technical point of view. – The mental model is how the user thinks the product works. – The conceptual model is the message the designer or IA sends to the user
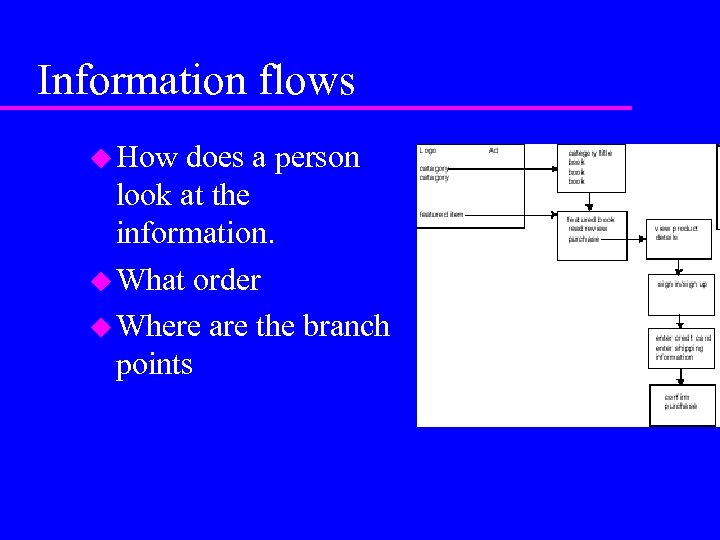 Information flows How does a person look at the information. What order Where are the branch points
Information flows How does a person look at the information. What order Where are the branch points
 Site map Drawing of the entire site Don’t be afraid to use a wall and Post-its Software is not a good way to go – Often huge and constantly updated – Need to keep big picture
Site map Drawing of the entire site Don’t be afraid to use a wall and Post-its Software is not a good way to go – Often huge and constantly updated – Need to keep big picture
 Wirefames Simple mock up of the page
Wirefames Simple mock up of the page
 End
End