055a3aeb807800309c0f104b812cb8b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Information Architecture for Diverse Audiences Karyn Young Information Architect ibm. com/software
Information Architecture for Diverse Audiences Karyn Young Information Architect ibm. com/software
 Today's Presentation • Define today's challenges for information architects • The ibm. com approach to diverse audience design – – IA framework and background Process Guidelines Recent success
Today's Presentation • Define today's challenges for information architects • The ibm. com approach to diverse audience design – – IA framework and background Process Guidelines Recent success
 Three Information Architect’s Challenges • Designing for diverse audiences is designing for ebusiness 1. We inherit unplanned or brochureware architectures 2. E-business sites are a new level of complexity 3. E-business sites augment or replace human delivery systems
Three Information Architect’s Challenges • Designing for diverse audiences is designing for ebusiness 1. We inherit unplanned or brochureware architectures 2. E-business sites are a new level of complexity 3. E-business sites augment or replace human delivery systems
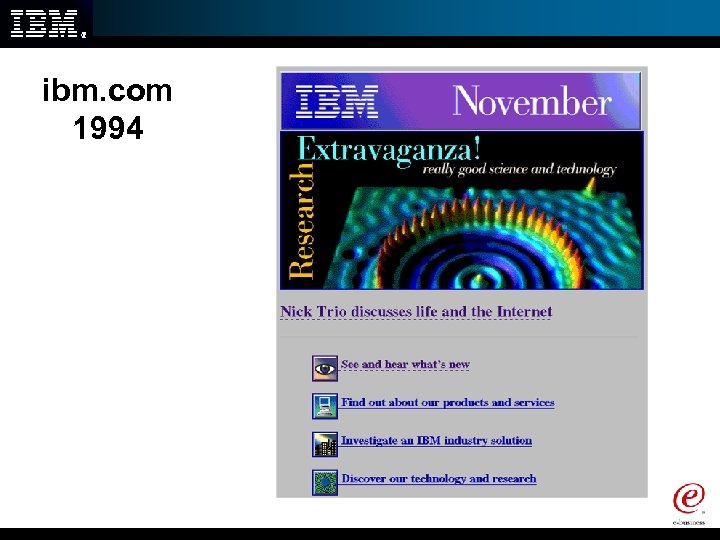 ibm. com 1994
ibm. com 1994
 ibm. com 1995
ibm. com 1995
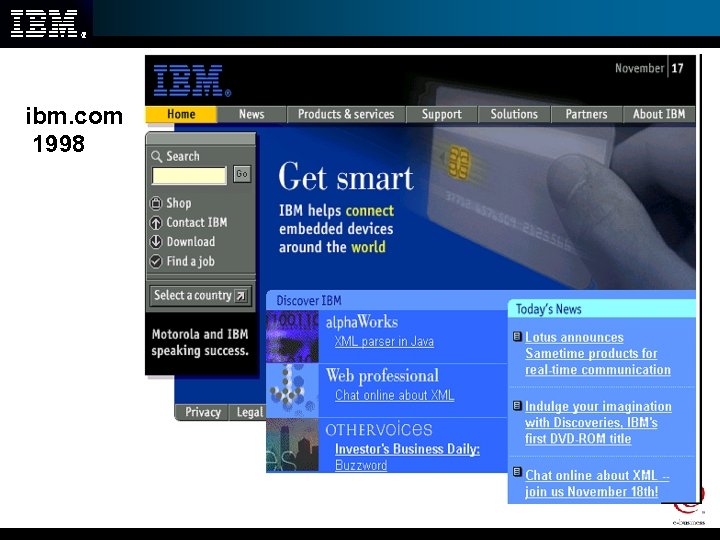 ibm. com 1998
ibm. com 1998
 Increasing Complexity • E-business sites support multiple audiences in accomplishing diverse tasks Common Web examples: • • Learning, evaluating, comparing, trying products Placing orders, reviewing order status Making changes to an account Maintaining, using, servicing, troubleshooting products
Increasing Complexity • E-business sites support multiple audiences in accomplishing diverse tasks Common Web examples: • • Learning, evaluating, comparing, trying products Placing orders, reviewing order status Making changes to an account Maintaining, using, servicing, troubleshooting products
 Augmenting and Replacing Humans • E-business sites may take the place of a: – – – Salesperson Technical salesperson Service representative Order taker Technical support representative And others
Augmenting and Replacing Humans • E-business sites may take the place of a: – – – Salesperson Technical salesperson Service representative Order taker Technical support representative And others
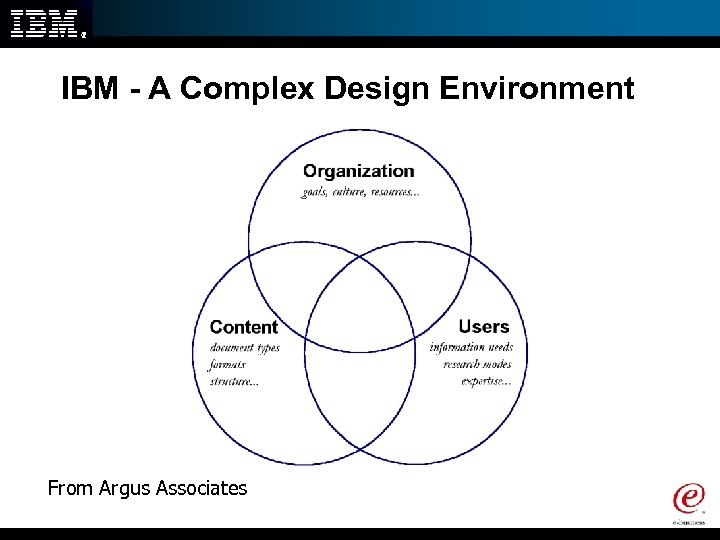 IBM - A Complex Design Environment From Argus Associates
IBM - A Complex Design Environment From Argus Associates
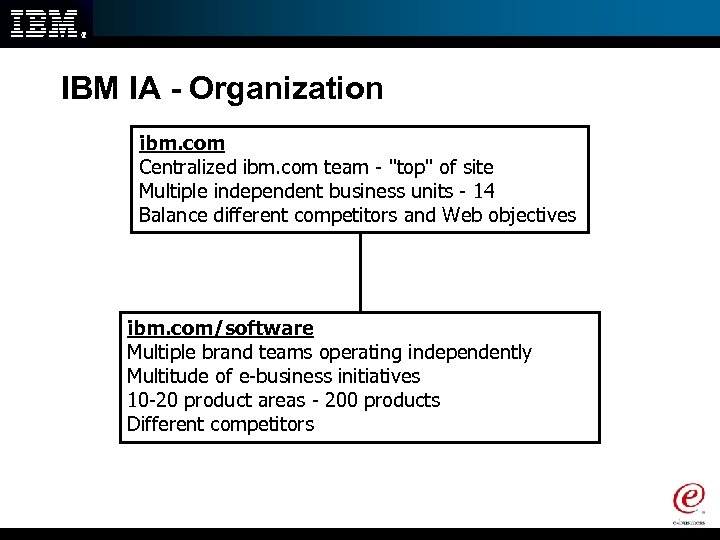 IBM IA - Organization ibm. com Centralized ibm. com team - "top" of site Multiple independent business units - 14 Balance different competitors and Web objectives ibm. com/software Multiple brand teams operating independently Multitude of e-business initiatives 10 -20 product areas - 200 products Different competitors
IBM IA - Organization ibm. com Centralized ibm. com team - "top" of site Multiple independent business units - 14 Balance different competitors and Web objectives ibm. com/software Multiple brand teams operating independently Multitude of e-business initiatives 10 -20 product areas - 200 products Different competitors
 IBM IA - Users ibm. com Several million visitors a week - main entry Audiences - home/home office, small business, large business, government, etc Research team - survey, focus groups, usability Who? What? Task accomplishment? ibm. com/software Roles - IT strategists, IT implementers, purchasers, consumers Growing focus on linking audiences, tasks, information needs Research - focus groups, interviews, usability
IBM IA - Users ibm. com Several million visitors a week - main entry Audiences - home/home office, small business, large business, government, etc Research team - survey, focus groups, usability Who? What? Task accomplishment? ibm. com/software Roles - IT strategists, IT implementers, purchasers, consumers Growing focus on linking audiences, tasks, information needs Research - focus groups, interviews, usability
 IBM IA - Content ibm. com 2. 5 million pages 70 countries, 16 languages Consistent design achieved Consistent content required next Different content requirements across products & consulting ibm. com/software 120, 000+ pages Country support - local challenges Understanding user content needs Structure content via templates Re-use of content via XML
IBM IA - Content ibm. com 2. 5 million pages 70 countries, 16 languages Consistent design achieved Consistent content required next Different content requirements across products & consulting ibm. com/software 120, 000+ pages Country support - local challenges Understanding user content needs Structure content via templates Re-use of content via XML
 Information Architecture Design Guidelines 1. Support the people your business cares about "Users" 2. In the way they need to be supported - "Context" 3. In accomplishing what they need and want to do "Tasks" • Getting it right requires a process
Information Architecture Design Guidelines 1. Support the people your business cares about "Users" 2. In the way they need to be supported - "Context" 3. In accomplishing what they need and want to do "Tasks" • Getting it right requires a process
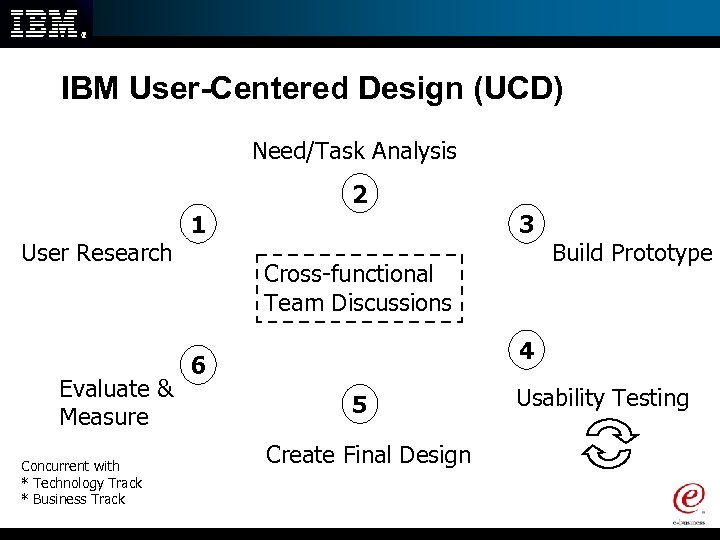 IBM User-Centered Design (UCD) Need/Task Analysis 2 User Research Evaluate & Measure Concurrent with * Technology Track * Business Track 1 3 Cross-functional Team Discussions Build Prototype 4 6 5 Create Final Design Usability Testing
IBM User-Centered Design (UCD) Need/Task Analysis 2 User Research Evaluate & Measure Concurrent with * Technology Track * Business Track 1 3 Cross-functional Team Discussions Build Prototype 4 6 5 Create Final Design Usability Testing
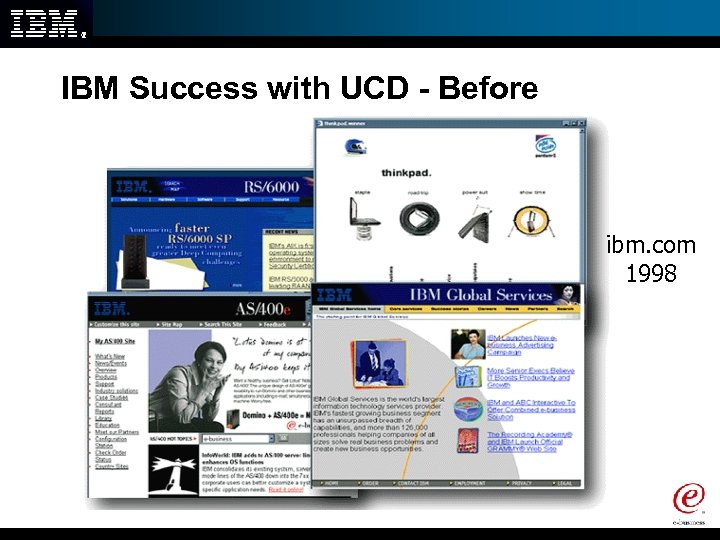 IBM Success with UCD - Before ibm. com 1998
IBM Success with UCD - Before ibm. com 1998
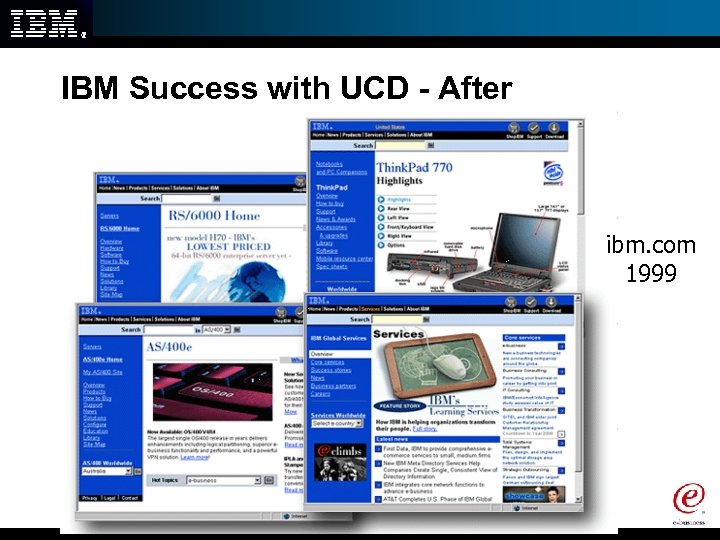 IBM Success with UCD - After ibm. com 1999
IBM Success with UCD - After ibm. com 1999
 Focusing on the User Research in UCD • Who are your users • How do they define themselves? – Audiences – Job role – Language/Culture (International) • Today vs. tomorrow
Focusing on the User Research in UCD • Who are your users • How do they define themselves? – Audiences – Job role – Language/Culture (International) • Today vs. tomorrow
 Focusing on the User Research in UCD • What is the context or situation for your users? • Example questions to ask – – – What is their comfort level with technology? Are they pressured for time? How do they use the Web? When? Browser? Cell Phone? Pager? Do they already know about your company? Your products? What challenges might they face? (Accessibility)
Focusing on the User Research in UCD • What is the context or situation for your users? • Example questions to ask – – – What is their comfort level with technology? Are they pressured for time? How do they use the Web? When? Browser? Cell Phone? Pager? Do they already know about your company? Your products? What challenges might they face? (Accessibility)
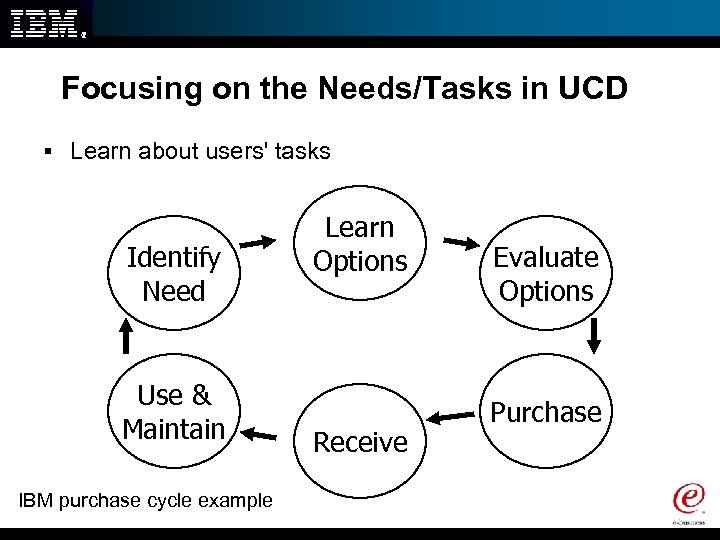 Focusing on the Needs/Tasks in UCD § Learn about users' tasks Identify Need Use & Maintain IBM purchase cycle example Learn Options Receive Evaluate Options Purchase
Focusing on the Needs/Tasks in UCD § Learn about users' tasks Identify Need Use & Maintain IBM purchase cycle example Learn Options Receive Evaluate Options Purchase
 User Research and Need/Task Analysis Techniques • Common Web user research - away from user site – Traditional market research techniques – Usability evaluations • Less common Web user research - at user site – Observe, listen to, and talk with users – Interview users Adapted from User and Task Analysis for Interface Design, Jo. Ann Hackos and Janice Redish
User Research and Need/Task Analysis Techniques • Common Web user research - away from user site – Traditional market research techniques – Usability evaluations • Less common Web user research - at user site – Observe, listen to, and talk with users – Interview users Adapted from User and Task Analysis for Interface Design, Jo. Ann Hackos and Janice Redish
 IBM's latest iteration ibm. com 2000
IBM's latest iteration ibm. com 2000
 Referenced Books/Links • IBM User-Centered Design – User Centered Design: Technologies and Techniques, by Karel Vredenburg and Scott Isensee, published spring 2001 – www. ibm. com/easy • User Understanding – User and Task Analysis for Interface Design, by Jo. Ann Hackos & Janice C. Redish – The Inmates are Running the Asylum, by Alan Cooper • Accessibility information – www. w 3 c. org
Referenced Books/Links • IBM User-Centered Design – User Centered Design: Technologies and Techniques, by Karel Vredenburg and Scott Isensee, published spring 2001 – www. ibm. com/easy • User Understanding – User and Task Analysis for Interface Design, by Jo. Ann Hackos & Janice C. Redish – The Inmates are Running the Asylum, by Alan Cooper • Accessibility information – www. w 3 c. org
 IA Links • • http: //webbusiness. cio. com/archive/closer. html - Web critiques with an IA slant www. nathan. com (Nathan Shedroff) - excellent pointer to many Web-related design resources, check out Nathan's "Unified Field Theory of Design" paper www. useit. com (Jakob Nielsen) - Executive summaries on usability-related topics in the Alertbox newsletter www. usableweb. com - The site says it all: "Usable Web is a collection of links about human factors, user interface issues, and usable design specific to the World Wide Web". www. creativegood. com - There's usually some interesting research here and a newsletter www. webreview. com - As the site says: "cross-training for Web teams". There are sections on authoring, design, development, e-commerce, multimedia and backend. www. webmonkey. com - Another source of information for Web teams. http: //www. tomalak. org (Tomalak's Realm) - Excellent Web news source -- links to IA articles
IA Links • • http: //webbusiness. cio. com/archive/closer. html - Web critiques with an IA slant www. nathan. com (Nathan Shedroff) - excellent pointer to many Web-related design resources, check out Nathan's "Unified Field Theory of Design" paper www. useit. com (Jakob Nielsen) - Executive summaries on usability-related topics in the Alertbox newsletter www. usableweb. com - The site says it all: "Usable Web is a collection of links about human factors, user interface issues, and usable design specific to the World Wide Web". www. creativegood. com - There's usually some interesting research here and a newsletter www. webreview. com - As the site says: "cross-training for Web teams". There are sections on authoring, design, development, e-commerce, multimedia and backend. www. webmonkey. com - Another source of information for Web teams. http: //www. tomalak. org (Tomalak's Realm) - Excellent Web news source -- links to IA articles
 Questions? Comments? keyoung@us. ibm. com
Questions? Comments? keyoung@us. ibm. com


