363f05069864a77fd5dc3286c1d34f56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 80
 Information and Security Analytics Lecture #1 Unit #1: Data Management: Overview Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham May 27, 2010
Information and Security Analytics Lecture #1 Unit #1: Data Management: Overview Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham May 27, 2010
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -2 Objective of the Unit 0 This unit provides an overview of the developments in data management. It also provides an overview of data management, information management and knowledge management and illustrates a framework 0 Reference: Data Management Systems: Evolution and Interoperation, Thuraisingham, CRC Press, 1997
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -2 Objective of the Unit 0 This unit provides an overview of the developments in data management. It also provides an overview of data management, information management and knowledge management and illustrates a framework 0 Reference: Data Management Systems: Evolution and Interoperation, Thuraisingham, CRC Press, 1997
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -3 Outline of the Unit 0 What is Data Management? 0 Developments in Data Management 0 Current Status and Trends 0 Note on Data Administration 0 Data management, Information management, and Knowledge Management
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -3 Outline of the Unit 0 What is Data Management? 0 Developments in Data Management 0 Current Status and Trends 0 Note on Data Administration 0 Data management, Information management, and Knowledge Management
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -4 What is data management 0 One proposal: Data Management = Database System Management + Data Administration 0 Includes data analysis, data administration, database administration, auditing, data modeling, database system development, database application development 0 The tutorial will focus mainly on database system aspects of data management
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -4 What is data management 0 One proposal: Data Management = Database System Management + Data Administration 0 Includes data analysis, data administration, database administration, auditing, data modeling, database system development, database application development 0 The tutorial will focus mainly on database system aspects of data management
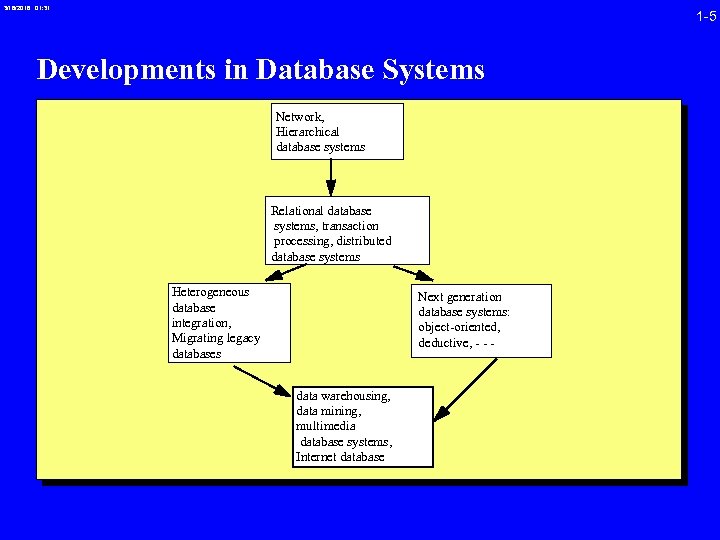 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -5 Developments in Database Systems Network, Hierarchical database systems Relational database systems, transaction processing, distributed database systems Heterogeneous database integration, Migrating legacy databases Next generation database systems: object-oriented, deductive, - - - data warehousing, data mining, multimedia database systems, Internet database
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -5 Developments in Database Systems Network, Hierarchical database systems Relational database systems, transaction processing, distributed database systems Heterogeneous database integration, Migrating legacy databases Next generation database systems: object-oriented, deductive, - - - data warehousing, data mining, multimedia database systems, Internet database
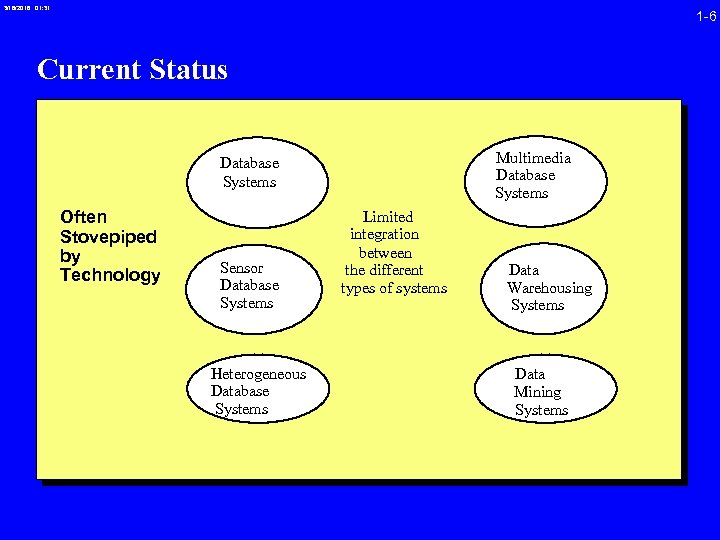 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -6 Current Status Multimedia Database Systems Often Stovepiped by Technology Sensor Database Systems Heterogeneous Database Systems Limited integration between the different types of systems Data Warehousing Systems Data Mining Systems
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -6 Current Status Multimedia Database Systems Often Stovepiped by Technology Sensor Database Systems Heterogeneous Database Systems Limited integration between the different types of systems Data Warehousing Systems Data Mining Systems
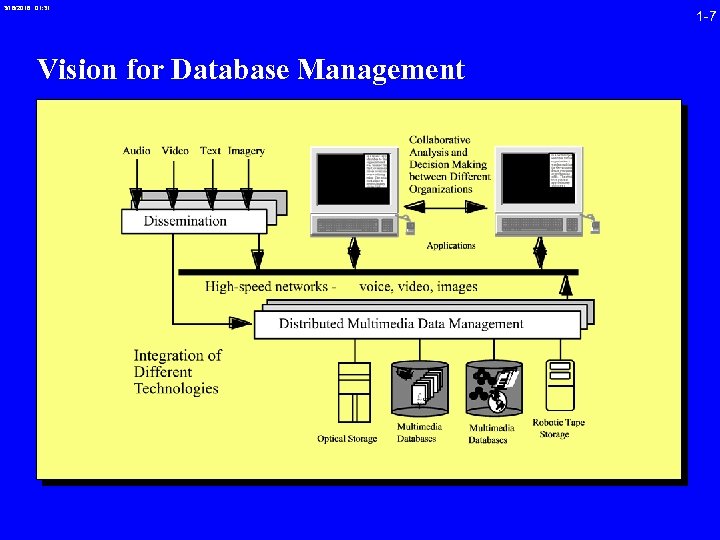 3/16/2018 01: 31 Vision for Database Management 1 -7
3/16/2018 01: 31 Vision for Database Management 1 -7
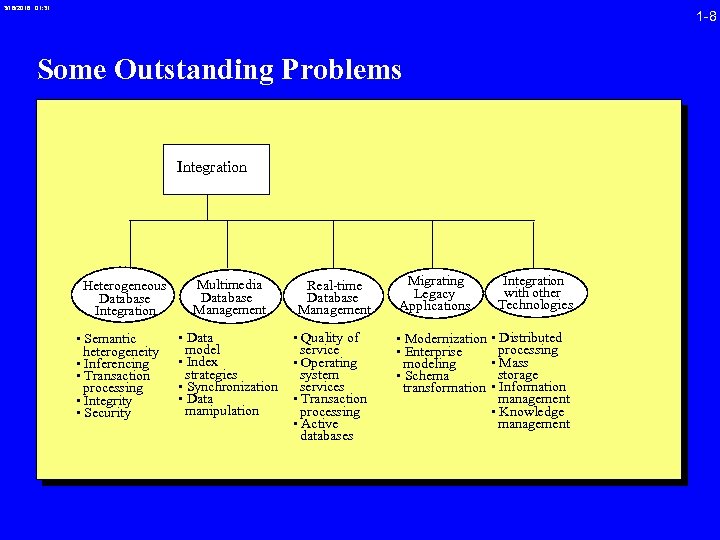 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -8 Some Outstanding Problems Integration Heterogeneous Database Integration • Semantic heterogeneity • Inferencing • Transaction processing • Integrity • Security Multimedia Database Management Real-time Database Management • Data model • Index strategies • Synchronization • Data manipulation • Quality of service • Operating system services • Transaction processing • Active databases Migrating Legacy Applications Integration with other Technologies • Modernization • Distributed processing • Enterprise • Mass modeling storage • Schema • Information transformation management • Knowledge management
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -8 Some Outstanding Problems Integration Heterogeneous Database Integration • Semantic heterogeneity • Inferencing • Transaction processing • Integrity • Security Multimedia Database Management Real-time Database Management • Data model • Index strategies • Synchronization • Data manipulation • Quality of service • Operating system services • Transaction processing • Active databases Migrating Legacy Applications Integration with other Technologies • Modernization • Distributed processing • Enterprise • Mass modeling storage • Schema • Information transformation management • Knowledge management
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -9 Some Current Trends in Data Management 0 Heterogeneous database integration - Query, transactions, semantics, security and integrity 0 Migrating legacy databases - Fine-grained encapsulation, distributed objects 0 Multimedia databases - Query, model, quality-of-service, index 0 Data Warehousing - Building a warehouse, query 0 Data Mining - Multimedia databases, web data mining 0 Data management for collaboration - Architecture, transactions 0 Web databases and digital libraries - Query, transactions, index, security
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -9 Some Current Trends in Data Management 0 Heterogeneous database integration - Query, transactions, semantics, security and integrity 0 Migrating legacy databases - Fine-grained encapsulation, distributed objects 0 Multimedia databases - Query, model, quality-of-service, index 0 Data Warehousing - Building a warehouse, query 0 Data Mining - Multimedia databases, web data mining 0 Data management for collaboration - Architecture, transactions 0 Web databases and digital libraries - Query, transactions, index, security
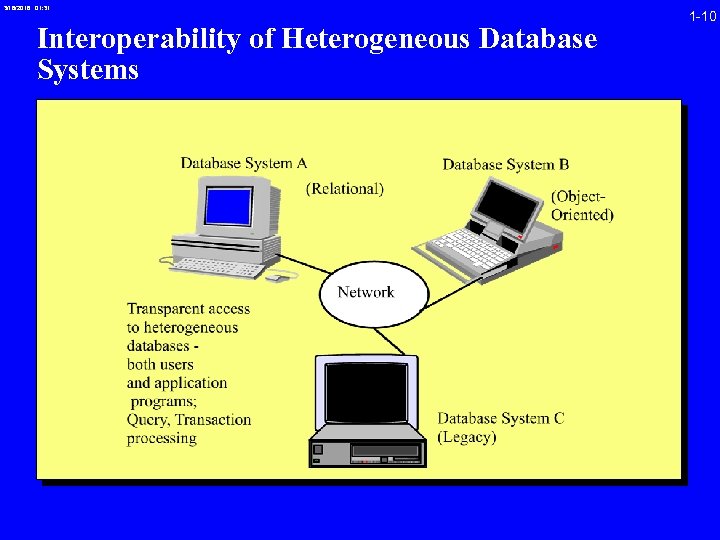 3/16/2018 01: 31 Interoperability of Heterogeneous Database Systems 1 -10
3/16/2018 01: 31 Interoperability of Heterogeneous Database Systems 1 -10
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -11 Note on Data Administration 0 Identifying the data - Data may be in files, paper, databases, etc. 0 Analyzing the data - Is the data of good quality? - Is the data complete? 0 Data standardization - Should one standardize all the data elements and metadata? - Repositories for handling semantic heterogeneity? 0 Data modeling - Structure the data, model the data and the processes
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -11 Note on Data Administration 0 Identifying the data - Data may be in files, paper, databases, etc. 0 Analyzing the data - Is the data of good quality? - Is the data complete? 0 Data standardization - Should one standardize all the data elements and metadata? - Repositories for handling semantic heterogeneity? 0 Data modeling - Structure the data, model the data and the processes
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -12 Data, Information and Knowledge Management 0 Data Management - Data: stored in databases, files or some media - Data management includes modeling, storing, retrieving and anbalyzing the data 0 Information Management - Information is what is obtained by making sense out of the data; E. g. , Data with context - Information management is about modeling, storing, retrieving and analyzing the information 0 Knowledge Management - Knowledge is what is obtained when the information is understood; it enables one to take actions - Knowledge management is about utilizing the knowledge to improve the business of an organization
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -12 Data, Information and Knowledge Management 0 Data Management - Data: stored in databases, files or some media - Data management includes modeling, storing, retrieving and anbalyzing the data 0 Information Management - Information is what is obtained by making sense out of the data; E. g. , Data with context - Information management is about modeling, storing, retrieving and analyzing the information 0 Knowledge Management - Knowledge is what is obtained when the information is understood; it enables one to take actions - Knowledge management is about utilizing the knowledge to improve the business of an organization
 3/16/2018 01: 31 Data, Information and Knowledge Management: Alternative View: MITRE Model 1999/2000 Decision Support Knowledge Management Information Management Data Management Communication, Network, Operating System, Middleware 1 -13
3/16/2018 01: 31 Data, Information and Knowledge Management: Alternative View: MITRE Model 1999/2000 Decision Support Knowledge Management Information Management Data Management Communication, Network, Operating System, Middleware 1 -13
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -14 Information and Security Analytics Lecture #1 Unit #2: Database Systems Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham May 27, 2010
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -14 Information and Security Analytics Lecture #1 Unit #2: Database Systems Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham May 27, 2010
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -15 Objective of the Unit 0 This unit will provide an overview of the concepts and developments in database systems 0 Reference: Data Management Systems: Evolution and Interoperation, Thuraisingham, CRC Press, 1997
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -15 Objective of the Unit 0 This unit will provide an overview of the concepts and developments in database systems 0 Reference: Data Management Systems: Evolution and Interoperation, Thuraisingham, CRC Press, 1997
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -16 Outline of the Unit 0 Concepts in database systems 0 Types of database systems
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -16 Outline of the Unit 0 Concepts in database systems 0 Types of database systems
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -17 Concepts in Database Systems 0 Definition of a Database system 0 Early systems 0 Metadata 0 Architectural Issues - Schema, Functional 0 DBMS Design Issues 0 Other Issues - Database design, Administration
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -17 Concepts in Database Systems 0 Definition of a Database system 0 Early systems 0 Metadata 0 Architectural Issues - Schema, Functional 0 DBMS Design Issues 0 Other Issues - Database design, Administration
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -18 Database System 0 Consists of database, hardware, Database Management System (DBMS), and users 0 Database is the repository for persistent data 0 Hardware consists of secondary storage volumes, processors, and main memory 0 DBMS handles all users’ access to the database 0 Users include application programmers, end users, and the Database Administrator (DBA) 0 Need: Reduced redundancy, avoids inconsistency, ability to share data, enforce standards, apply security restrictions, maintain integrity, balance conflicting requirements 0 We have used the definition of a database management system given in C. J. Date’s Book (Addison Wesley, 1990)
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -18 Database System 0 Consists of database, hardware, Database Management System (DBMS), and users 0 Database is the repository for persistent data 0 Hardware consists of secondary storage volumes, processors, and main memory 0 DBMS handles all users’ access to the database 0 Users include application programmers, end users, and the Database Administrator (DBA) 0 Need: Reduced redundancy, avoids inconsistency, ability to share data, enforce standards, apply security restrictions, maintain integrity, balance conflicting requirements 0 We have used the definition of a database management system given in C. J. Date’s Book (Addison Wesley, 1990)
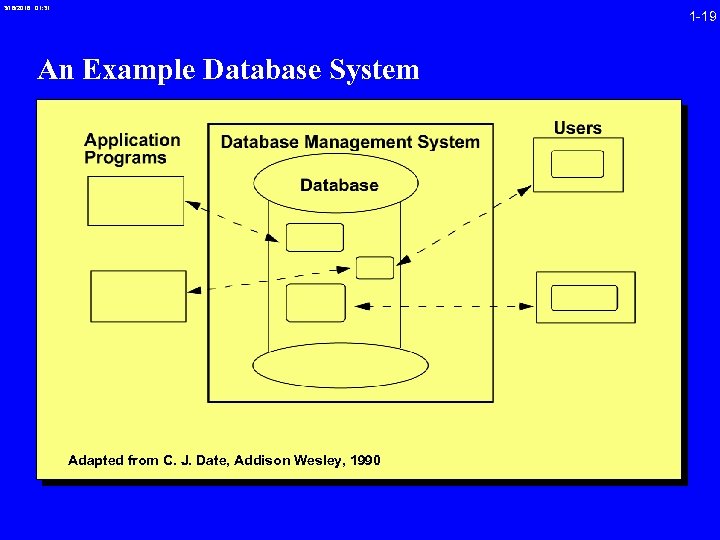 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -19 An Example Database System Adapted from C. J. Date, Addison Wesley, 1990
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -19 An Example Database System Adapted from C. J. Date, Addison Wesley, 1990
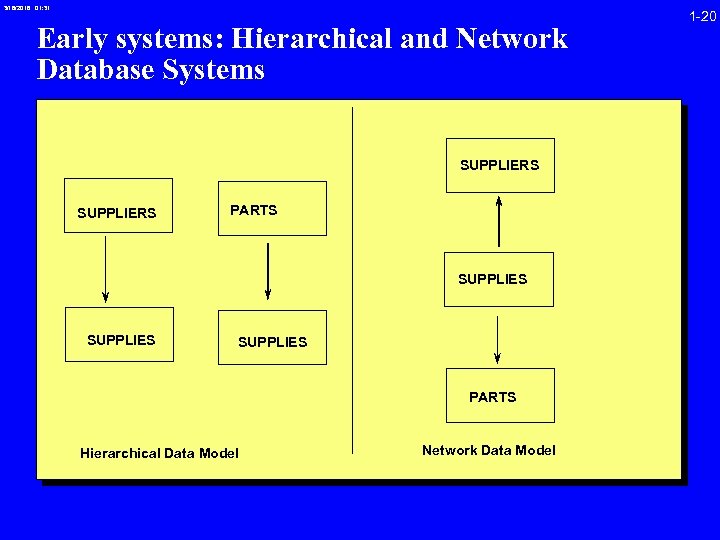 3/16/2018 01: 31 Early systems: Hierarchical and Network Database Systems SUPPLIERS PARTS SUPPLIES PARTS Hierarchical Data Model Network Data Model 1 -20
3/16/2018 01: 31 Early systems: Hierarchical and Network Database Systems SUPPLIERS PARTS SUPPLIES PARTS Hierarchical Data Model Network Data Model 1 -20
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -21 Metadata 0 Metadata describes the data in the database - Example: Database D consists of a relation EMP with attributes SS#, Name, and Salary 0 Metadatabase stores the metadata - Could be physically stored with the database 0 Metadatabase may also store constraints and administrative information 0 Metadata is also referred to as the schema or data dictionary
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -21 Metadata 0 Metadata describes the data in the database - Example: Database D consists of a relation EMP with attributes SS#, Name, and Salary 0 Metadatabase stores the metadata - Could be physically stored with the database 0 Metadatabase may also store constraints and administrative information 0 Metadata is also referred to as the schema or data dictionary
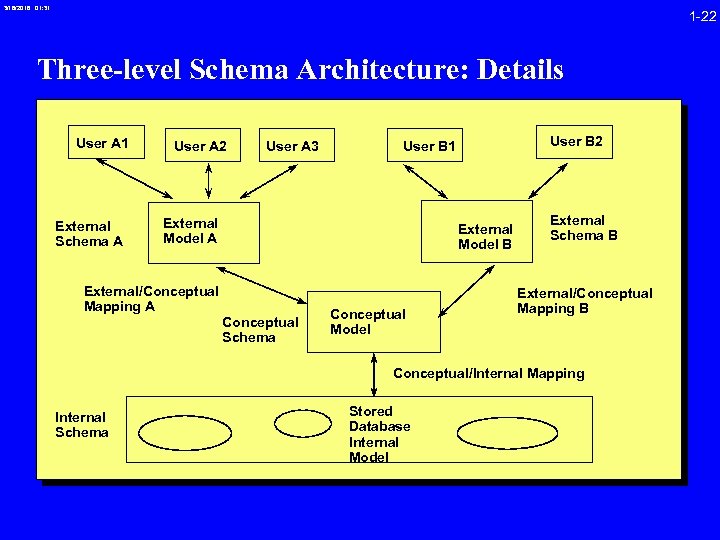 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -22 Three-level Schema Architecture: Details User A 1 External Schema A User A 2 User A 3 User B 2 User B 1 External Model A External Model B External/Conceptual Mapping A Conceptual Schema Conceptual Model External Schema B External/Conceptual Mapping B Conceptual/Internal Mapping Internal Schema Stored Database Internal Model
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -22 Three-level Schema Architecture: Details User A 1 External Schema A User A 2 User A 3 User B 2 User B 1 External Model A External Model B External/Conceptual Mapping A Conceptual Schema Conceptual Model External Schema B External/Conceptual Mapping B Conceptual/Internal Mapping Internal Schema Stored Database Internal Model
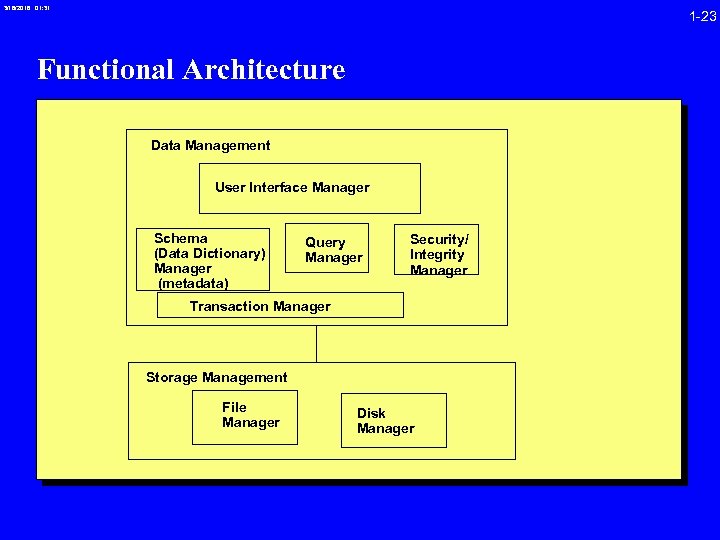 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -23 Functional Architecture Data Management User Interface Manager Schema (Data Dictionary) Manager (metadata) Query Manager Security/ Integrity Manager Transaction Manager Storage Management File Manager Disk Manager
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -23 Functional Architecture Data Management User Interface Manager Schema (Data Dictionary) Manager (metadata) Query Manager Security/ Integrity Manager Transaction Manager Storage Management File Manager Disk Manager
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -24 DBMS Design Issues 0 Query Processing - Optimization techniques 0 Transaction Management - Techniques for concurrency control and recovery 0 Metadata Management - Techniques for querying and updating the metadatabase 0 Security/Integrity Maintenance - Techniques for processing integrity constraints and enforcing access control rules 0 Storage management - Access methods and index strategies for efficient access to the database
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -24 DBMS Design Issues 0 Query Processing - Optimization techniques 0 Transaction Management - Techniques for concurrency control and recovery 0 Metadata Management - Techniques for querying and updating the metadatabase 0 Security/Integrity Maintenance - Techniques for processing integrity constraints and enforcing access control rules 0 Storage management - Access methods and index strategies for efficient access to the database
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -25 Other Issues 0 Database design - Generally a two-step process = Semantic data model to capture the entities of the application and the relationships between the entities = Generate the conceptual schema; theory of normal forms for relational databases - Research on object-oriented approaches for database design 0 Database Administration - Creating and deleting databases; backup and recovery, enforcing policies, auditing, etc.
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -25 Other Issues 0 Database design - Generally a two-step process = Semantic data model to capture the entities of the application and the relationships between the entities = Generate the conceptual schema; theory of normal forms for relational databases - Research on object-oriented approaches for database design 0 Database Administration - Creating and deleting databases; backup and recovery, enforcing policies, auditing, etc.
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -26 Types of Database Systems 0 Relational Database Systems 0 Object Database Systems 0 Deductive Database Systems 0 Other - Real-time, Secure, Parallel, Scientific, Temporal, Wireless, Functional, Entity-Relationship, Sensor/Stream Database Systems, etc.
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -26 Types of Database Systems 0 Relational Database Systems 0 Object Database Systems 0 Deductive Database Systems 0 Other - Real-time, Secure, Parallel, Scientific, Temporal, Wireless, Functional, Entity-Relationship, Sensor/Stream Database Systems, etc.
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -27 Relational Database: Informal Overview 0 Collection of tables also called relations 0 Table has one or more columns also called attributes 0 Each table has zero or more rows also called tuples 0 Elements of a row take values from a pool of legal values 0 The values of one or more columns in a row uniquely identify the row. These columns form an identifier (also called key) 0 One identifier is designated as the unique identifier (also called primary key) 0 Querying relational databases using language called SQL (Structured Query Language)
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -27 Relational Database: Informal Overview 0 Collection of tables also called relations 0 Table has one or more columns also called attributes 0 Each table has zero or more rows also called tuples 0 Elements of a row take values from a pool of legal values 0 The values of one or more columns in a row uniquely identify the row. These columns form an identifier (also called key) 0 One identifier is designated as the unique identifier (also called primary key) 0 Querying relational databases using language called SQL (Structured Query Language)
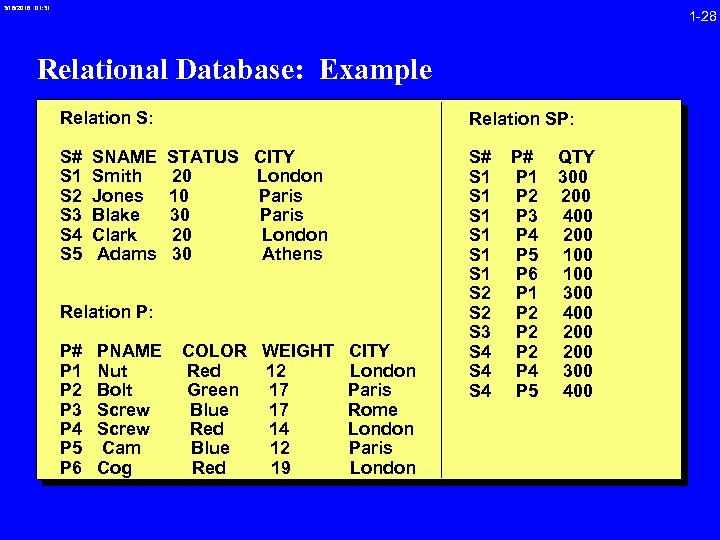 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -28 Relational Database: Example Relation S: S# S 1 S 2 S 3 S 4 S 5 SNAME Smith Jones Blake Clark Adams Relation SP: STATUS CITY 20 London 10 Paris 30 Paris 20 London 30 Athens Relation P: P# P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 P 6 PNAME Nut Bolt Screw Cam Cog COLOR WEIGHT CITY Red 12 London Green 17 Paris Blue 17 Rome Red 14 London Blue 12 Paris Red 19 London S# S 1 S 1 S 1 S 2 S 3 S 4 S 4 P# P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 P 6 P 1 P 2 P 2 P 4 P 5 QTY 300 200 400 200 100 300 400 200 300 400
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -28 Relational Database: Example Relation S: S# S 1 S 2 S 3 S 4 S 5 SNAME Smith Jones Blake Clark Adams Relation SP: STATUS CITY 20 London 10 Paris 30 Paris 20 London 30 Athens Relation P: P# P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 P 6 PNAME Nut Bolt Screw Cam Cog COLOR WEIGHT CITY Red 12 London Green 17 Paris Blue 17 Rome Red 14 London Blue 12 Paris Red 19 London S# S 1 S 1 S 1 S 2 S 3 S 4 S 4 P# P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 P 6 P 1 P 2 P 2 P 4 P 5 QTY 300 200 400 200 100 300 400 200 300 400
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -29 SQL: Data Manipulation 0 Select, Update, Delete, Insert Examples: SELECT S. S#, S. STATUS FROM S WHERE S. CITY = Paris SELECT * FROM S SELECT S. *, P. * FROM S, P WHERE S. CITY = P. CITY UPDATE P SET COLOR = ‘Yellow’ WEIGHT = WEIGHT + 5 CITY = NULL WHERE P# = P 2
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -29 SQL: Data Manipulation 0 Select, Update, Delete, Insert Examples: SELECT S. S#, S. STATUS FROM S WHERE S. CITY = Paris SELECT * FROM S SELECT S. *, P. * FROM S, P WHERE S. CITY = P. CITY UPDATE P SET COLOR = ‘Yellow’ WEIGHT = WEIGHT + 5 CITY = NULL WHERE P# = P 2
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -30 Features of Object-Oriented Database Systems Suitable for Advanced Applications 0 Objects (support for large and variable sized data blocks) 0 Class hierarchy (reusability) 0 Instance variables, composite and complex objects (complex data structures) 0 Methods, and message passing (object encapsulation) 0 Pointer swizzling (performance) 0 Tighter integration with programming languages (application program support) 0 Special mechanisms for long transactions and concurrency control, multimedia information management, schema management, versions management, storage management
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -30 Features of Object-Oriented Database Systems Suitable for Advanced Applications 0 Objects (support for large and variable sized data blocks) 0 Class hierarchy (reusability) 0 Instance variables, composite and complex objects (complex data structures) 0 Methods, and message passing (object encapsulation) 0 Pointer swizzling (performance) 0 Tighter integration with programming languages (application program support) 0 Special mechanisms for long transactions and concurrency control, multimedia information management, schema management, versions management, storage management
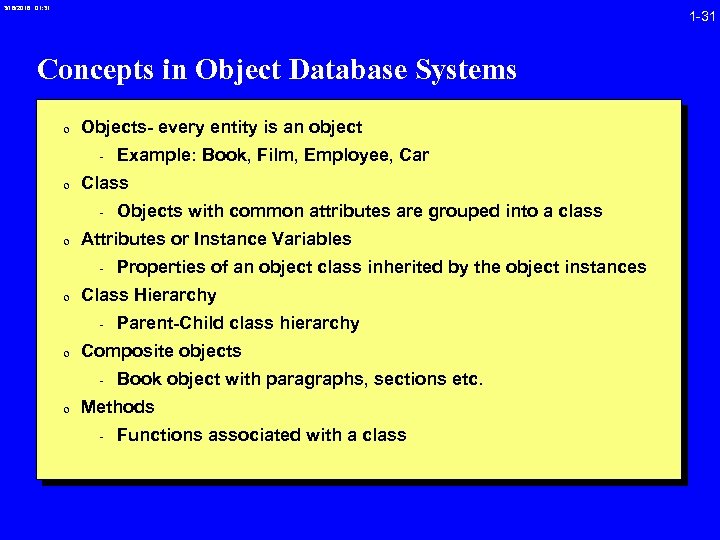 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -31 Concepts in Object Database Systems 0 Objects- every entity is an object - Example: Book, Film, Employee, Car 0 Class - Objects with common attributes are grouped into a class 0 Attributes or Instance Variables - Properties of an object class inherited by the object instances 0 Class Hierarchy - Parent-Child class hierarchy 0 Composite objects - Book object with paragraphs, sections etc. 0 Methods - Functions associated with a class
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -31 Concepts in Object Database Systems 0 Objects- every entity is an object - Example: Book, Film, Employee, Car 0 Class - Objects with common attributes are grouped into a class 0 Attributes or Instance Variables - Properties of an object class inherited by the object instances 0 Class Hierarchy - Parent-Child class hierarchy 0 Composite objects - Book object with paragraphs, sections etc. 0 Methods - Functions associated with a class
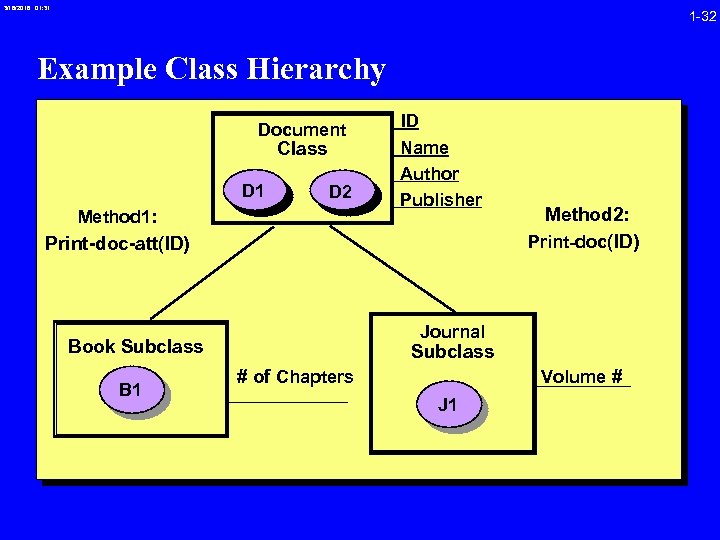 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -32 Example Class Hierarchy Document Class D 1 D 2 Method 1: ID Name Author Publisher Print-doc-att(ID) Journal Book Subclass B 1 Method 2: Print-doc(ID) Subclass Volume # # of Chapters J 1
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -32 Example Class Hierarchy Document Class D 1 D 2 Method 1: ID Name Author Publisher Print-doc-att(ID) Journal Book Subclass B 1 Method 2: Print-doc(ID) Subclass Volume # # of Chapters J 1
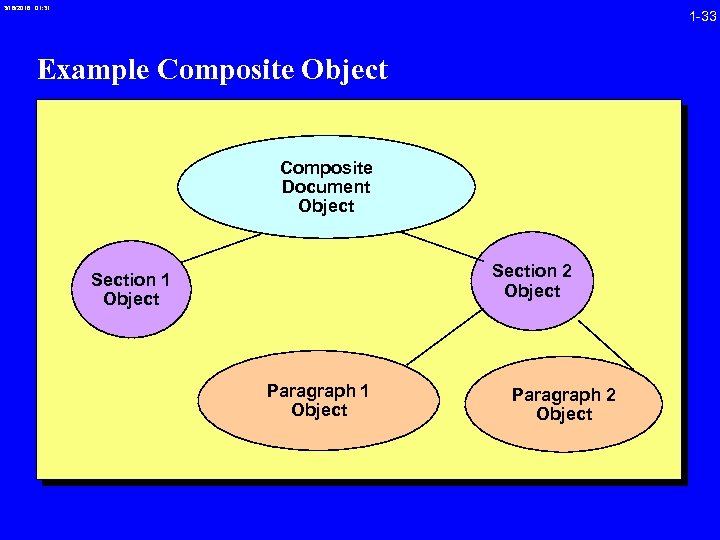 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -33 Example Composite Object Composite Document Object Section 2 Object Section 1 Object Paragraph 2 Object
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -33 Example Composite Object Composite Document Object Section 2 Object Section 1 Object Paragraph 2 Object
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -34 Deductive Database Systems 0 Database systems augmented with inference engines to deduce new data from existing data and rules 0 Example - Rule: parent of a parent is a grandparent - Data: John is Jane’s parent; Jane is Robert’s parent - From the above, infer John is Robert’s grandparent 0 Loose and tight coupling architectures between the database system and inference engine
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -34 Deductive Database Systems 0 Database systems augmented with inference engines to deduce new data from existing data and rules 0 Example - Rule: parent of a parent is a grandparent - Data: John is Jane’s parent; Jane is Robert’s parent - From the above, infer John is Robert’s grandparent 0 Loose and tight coupling architectures between the database system and inference engine
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -35 Current Status 0 Database Systems is a mature technology; numerous products and prototypes 0 Much work followed in distributed and heterogeneous databases 0 Current directions include web database management as well as data management support for novel applications including E-commerce, Bioinformatics and Geoinformatics 0 Work still continues on developing new kinds of database systems including stream/sensor database systems
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -35 Current Status 0 Database Systems is a mature technology; numerous products and prototypes 0 Much work followed in distributed and heterogeneous databases 0 Current directions include web database management as well as data management support for novel applications including E-commerce, Bioinformatics and Geoinformatics 0 Work still continues on developing new kinds of database systems including stream/sensor database systems
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -36 Information and Security Analytics Lecture #1 Unit #3: Distributed and Heterogeneous Database Systems Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham May 27, 2010
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -36 Information and Security Analytics Lecture #1 Unit #3: Distributed and Heterogeneous Database Systems Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham May 27, 2010
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -37 Objective of the Unit 0 This unit provides an overview of concepts in distributed and heterogeneous databases. In particular, definitions and functions, are discussed 0 Reference: - Data Management Systems: Evolution and Interoperation, Thuraisingham, CRC Press, 1997 - Heterogeneous Information Exchange and Organizational Hubs, Kluwer, 2002, Editors: Bestougeff, Dubois and Thuraisingham
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -37 Objective of the Unit 0 This unit provides an overview of concepts in distributed and heterogeneous databases. In particular, definitions and functions, are discussed 0 Reference: - Data Management Systems: Evolution and Interoperation, Thuraisingham, CRC Press, 1997 - Heterogeneous Information Exchange and Organizational Hubs, Kluwer, 2002, Editors: Bestougeff, Dubois and Thuraisingham
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -38 Outline of the Unit 0 Distributed Database Systems - Architecture, Data Distribution, Functions 0 Heterogeneous Database Integration 0 Federated Database Management 0 Client-Server Database Management 0 Migrating Legacy Databases 0 Current Status and Directions
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -38 Outline of the Unit 0 Distributed Database Systems - Architecture, Data Distribution, Functions 0 Heterogeneous Database Integration 0 Federated Database Management 0 Client-Server Database Management 0 Migrating Legacy Databases 0 Current Status and Directions
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -39 A Definition of a Distributed Database System 0 A collection of database systems connected via a network 0 The software that is responsible for interconnection is a Distributed Database Management System (DDBMS) 0 Each DBMS executes local applications and should be involved in at least one global application (Ceri and Pelagetti) 0 Homogeneous environment
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -39 A Definition of a Distributed Database System 0 A collection of database systems connected via a network 0 The software that is responsible for interconnection is a Distributed Database Management System (DDBMS) 0 Each DBMS executes local applications and should be involved in at least one global application (Ceri and Pelagetti) 0 Homogeneous environment
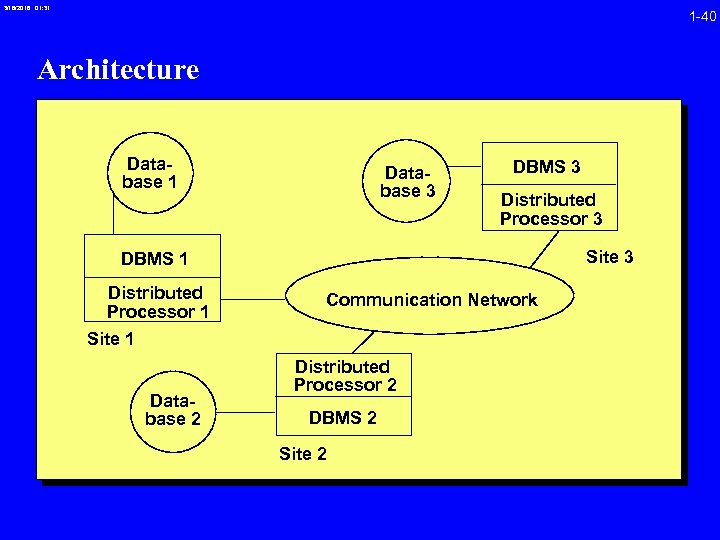 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -40 Architecture Database 1 Database 3 DBMS 3 Distributed Processor 3 Site 3 DBMS 1 Distributed Processor 1 Communication Network Site 1 Database 2 Distributed Processor 2 DBMS 2 Site 2
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -40 Architecture Database 1 Database 3 DBMS 3 Distributed Processor 3 Site 3 DBMS 1 Distributed Processor 1 Communication Network Site 1 Database 2 Distributed Processor 2 DBMS 2 Site 2
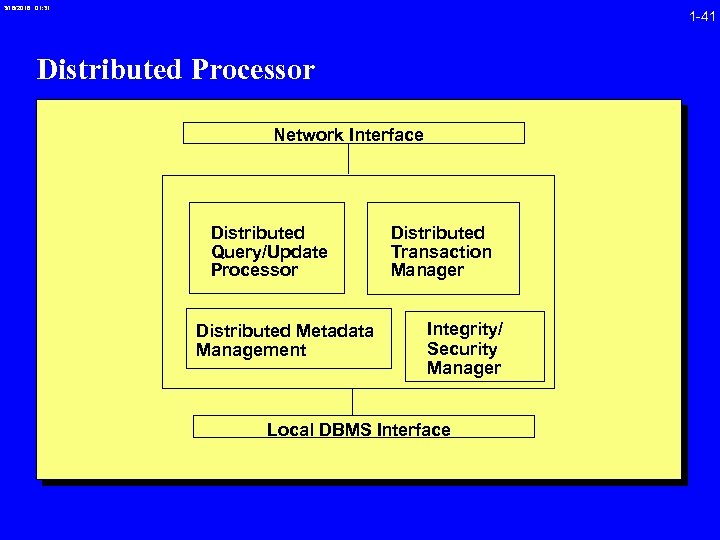 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -41 Distributed Processor Network Interface Distributed Query/Update Processor Distributed Metadata Management Distributed Transaction Manager Integrity/ Security Manager Local DBMS Interface
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -41 Distributed Processor Network Interface Distributed Query/Update Processor Distributed Metadata Management Distributed Transaction Manager Integrity/ Security Manager Local DBMS Interface
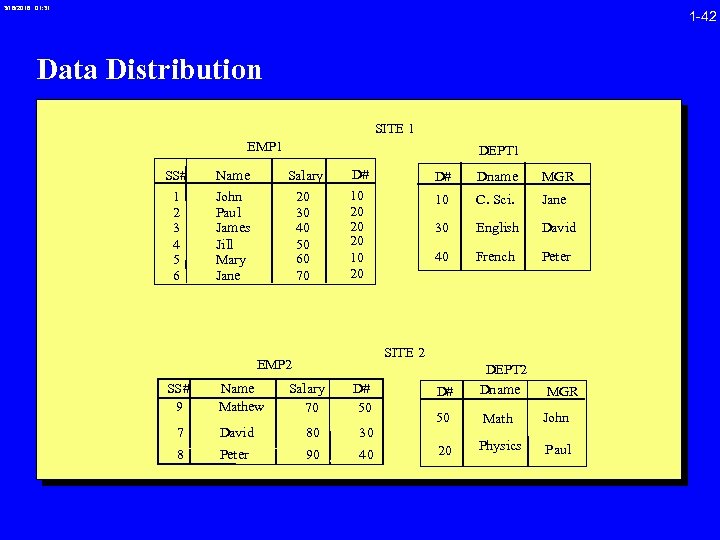 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -42 Data Distribution SITE 1 EMP 1 DEPT 1 SS# Name Salary D# D# Dname MGR 1 2 3 4 5 6 John Paul James Jill Mary Jane 20 30 40 50 60 70 10 20 20 20 10 C. Sci. Jane 30 English David 40 French Peter D# DEPT 2 Dname MGR 50 Math John 20 Physics Paul SITE 2 EMP 2 SS# 9 Name Mathew Salary 70 D# 50 7 David 80 30 8 Peter 90 40
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -42 Data Distribution SITE 1 EMP 1 DEPT 1 SS# Name Salary D# D# Dname MGR 1 2 3 4 5 6 John Paul James Jill Mary Jane 20 30 40 50 60 70 10 20 20 20 10 C. Sci. Jane 30 English David 40 French Peter D# DEPT 2 Dname MGR 50 Math John 20 Physics Paul SITE 2 EMP 2 SS# 9 Name Mathew Salary 70 D# 50 7 David 80 30 8 Peter 90 40
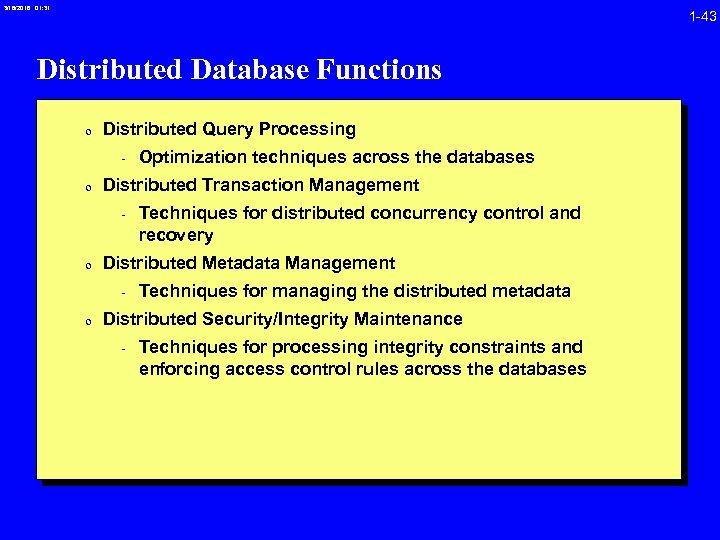 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -43 Distributed Database Functions 0 Distributed Query Processing - Optimization techniques across the databases 0 Distributed Transaction Management - Techniques for distributed concurrency control and recovery 0 Distributed Metadata Management - Techniques for managing the distributed metadata 0 Distributed Security/Integrity Maintenance - Techniques for processing integrity constraints and enforcing access control rules across the databases
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -43 Distributed Database Functions 0 Distributed Query Processing - Optimization techniques across the databases 0 Distributed Transaction Management - Techniques for distributed concurrency control and recovery 0 Distributed Metadata Management - Techniques for managing the distributed metadata 0 Distributed Security/Integrity Maintenance - Techniques for processing integrity constraints and enforcing access control rules across the databases
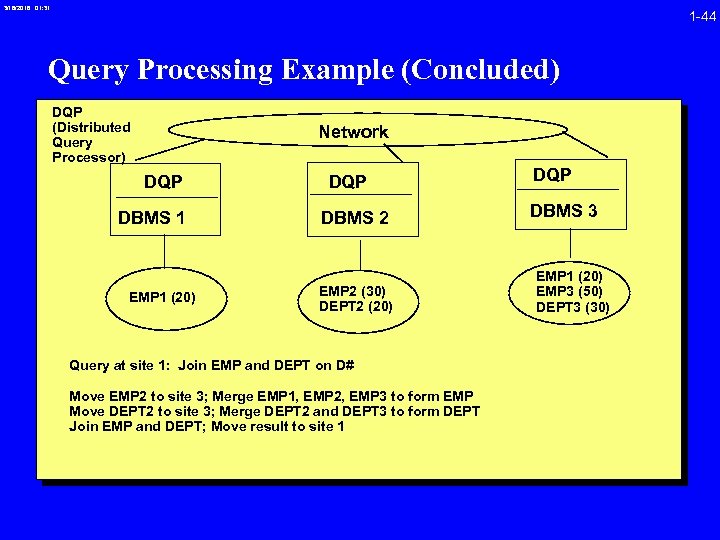 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -44 Query Processing Example (Concluded) DQP (Distributed Query Processor) Network DQP DBMS 1 EMP 1 (20) DQP DBMS 2 EMP 2 (30) DEPT 2 (20) Query at site 1: Join EMP and DEPT on D# Move EMP 2 to site 3; Merge EMP 1, EMP 2, EMP 3 to form EMP Move DEPT 2 to site 3; Merge DEPT 2 and DEPT 3 to form DEPT Join EMP and DEPT; Move result to site 1 DQP DBMS 3 EMP 1 (20) EMP 3 (50) DEPT 3 (30)
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -44 Query Processing Example (Concluded) DQP (Distributed Query Processor) Network DQP DBMS 1 EMP 1 (20) DQP DBMS 2 EMP 2 (30) DEPT 2 (20) Query at site 1: Join EMP and DEPT on D# Move EMP 2 to site 3; Merge EMP 1, EMP 2, EMP 3 to form EMP Move DEPT 2 to site 3; Merge DEPT 2 and DEPT 3 to form DEPT Join EMP and DEPT; Move result to site 1 DQP DBMS 3 EMP 1 (20) EMP 3 (50) DEPT 3 (30)
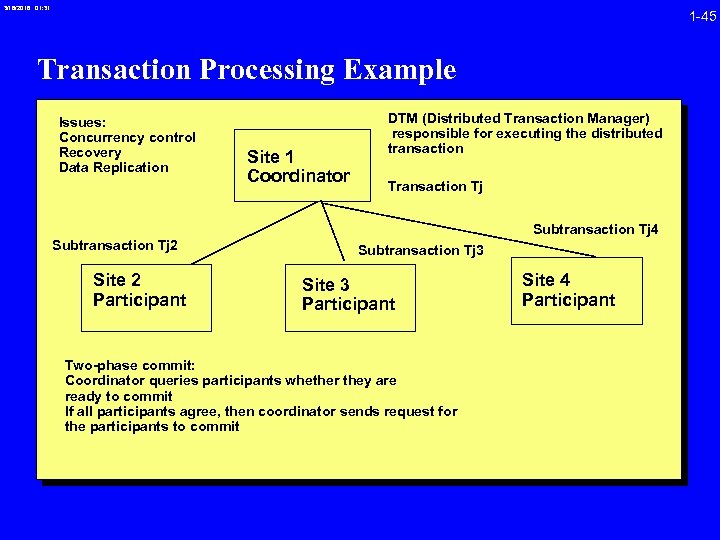 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -45 Transaction Processing Example Issues: Concurrency control Recovery Data Replication Site 1 Coordinator DTM (Distributed Transaction Manager) responsible for executing the distributed transaction Tj Subtransaction Tj 4 Subtransaction Tj 2 Site 2 Participant Subtransaction Tj 3 Site 3 Participant Two-phase commit: Coordinator queries participants whether they are ready to commit If all participants agree, then coordinator sends request for the participants to commit Site 4 Participant
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -45 Transaction Processing Example Issues: Concurrency control Recovery Data Replication Site 1 Coordinator DTM (Distributed Transaction Manager) responsible for executing the distributed transaction Tj Subtransaction Tj 4 Subtransaction Tj 2 Site 2 Participant Subtransaction Tj 3 Site 3 Participant Two-phase commit: Coordinator queries participants whether they are ready to commit If all participants agree, then coordinator sends request for the participants to commit Site 4 Participant
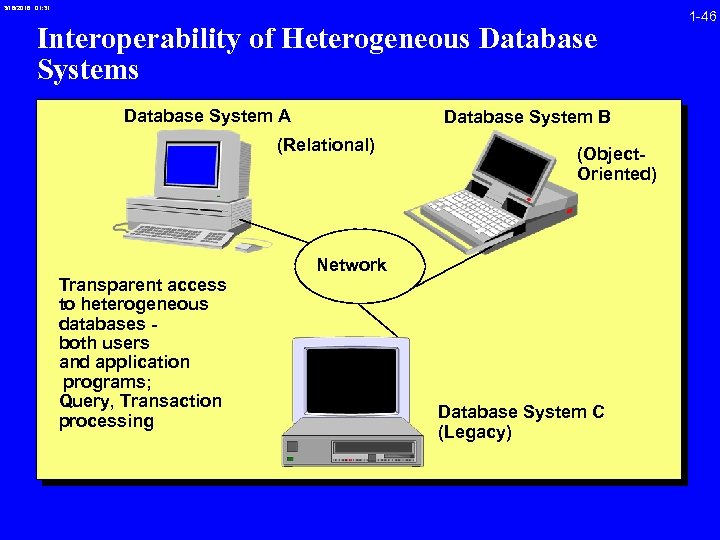 3/16/2018 01: 31 Interoperability of Heterogeneous Database System A Database System B (Relational) Transparent access to heterogeneous databases both users and application programs; Query, Transaction processing (Object. Oriented) Network Database System C (Legacy) 1 -46
3/16/2018 01: 31 Interoperability of Heterogeneous Database System A Database System B (Relational) Transparent access to heterogeneous databases both users and application programs; Query, Transaction processing (Object. Oriented) Network Database System C (Legacy) 1 -46
 3/16/2018 01: 31 Technical Issues on the Interoperability of Heterogeneous Database Systems 0 Heterogeneity with respect to data models, schema, query processing, query languages, transaction management, semantics, integrity, and security policies 0 Interoperability based on client-server architectures 0 Federated database management - Collection of cooperating, autonomous, and possibly heterogeneous component database systems, each belonging to one or more federations 1 -47
3/16/2018 01: 31 Technical Issues on the Interoperability of Heterogeneous Database Systems 0 Heterogeneity with respect to data models, schema, query processing, query languages, transaction management, semantics, integrity, and security policies 0 Interoperability based on client-server architectures 0 Federated database management - Collection of cooperating, autonomous, and possibly heterogeneous component database systems, each belonging to one or more federations 1 -47
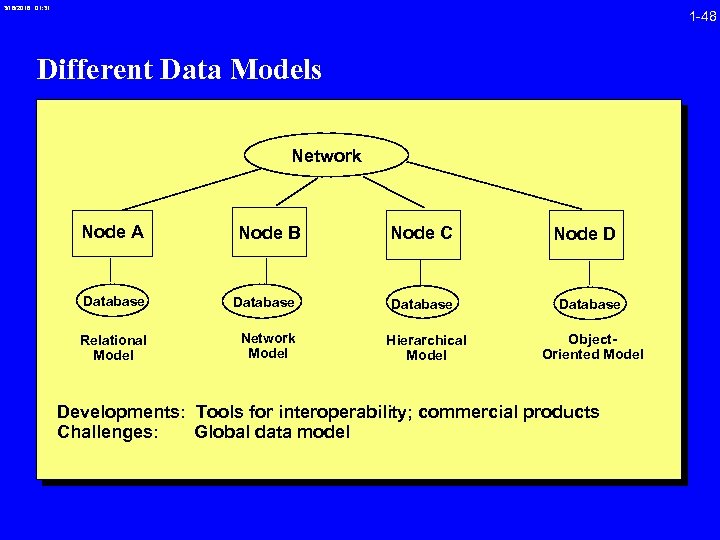 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -48 Different Data Models Network Node A Node B Database Relational Model Network Model Node C Database Hierarchical Model Node D Database Object. Oriented Model Developments: Tools for interoperability; commercial products Challenges: Global data model
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -48 Different Data Models Network Node A Node B Database Relational Model Network Model Node C Database Hierarchical Model Node D Database Object. Oriented Model Developments: Tools for interoperability; commercial products Challenges: Global data model
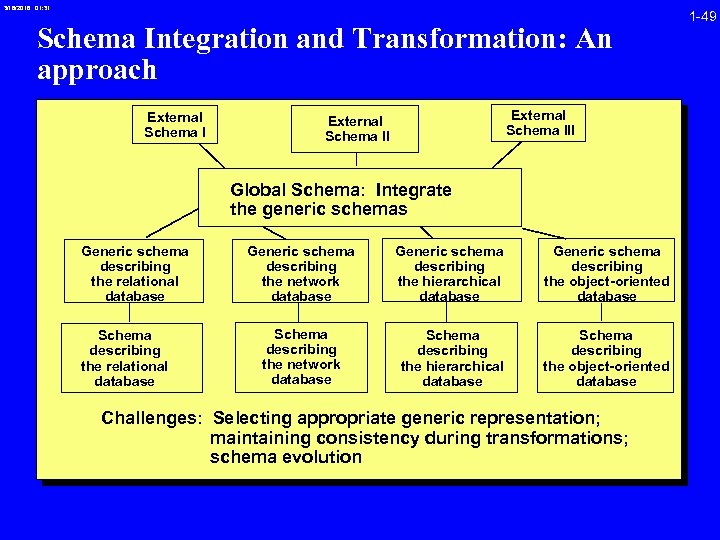 3/16/2018 01: 31 Schema Integration and Transformation: An approach External Schema III External Schema II Global Schema: Integrate the generic schemas Generic schema describing the relational database Schema describing the relational database Generic schema describing the network database Generic schema describing the hierarchical database Generic schema describing the object-oriented database Schema describing the network database Schema describing the hierarchical database Schema describing the object-oriented database Challenges: Selecting appropriate generic representation; maintaining consistency during transformations; schema evolution 1 -49
3/16/2018 01: 31 Schema Integration and Transformation: An approach External Schema III External Schema II Global Schema: Integrate the generic schemas Generic schema describing the relational database Schema describing the relational database Generic schema describing the network database Generic schema describing the hierarchical database Generic schema describing the object-oriented database Schema describing the network database Schema describing the hierarchical database Schema describing the object-oriented database Challenges: Selecting appropriate generic representation; maintaining consistency during transformations; schema evolution 1 -49
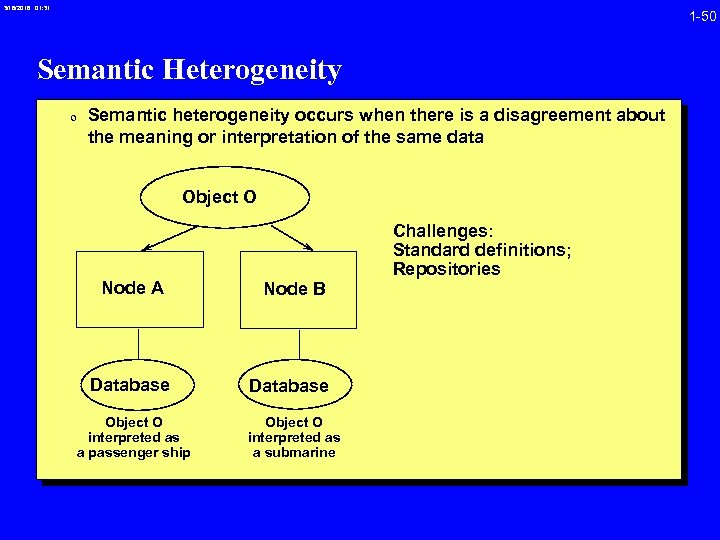 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -50 Semantic Heterogeneity 0 Semantic heterogeneity occurs when there is a disagreement about the meaning or interpretation of the same data Object O Node A Database Object O interpreted as a passenger ship Node B Database Object O interpreted as a submarine Challenges: Standard definitions; Repositories
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -50 Semantic Heterogeneity 0 Semantic heterogeneity occurs when there is a disagreement about the meaning or interpretation of the same data Object O Node A Database Object O interpreted as a passenger ship Node B Database Object O interpreted as a submarine Challenges: Standard definitions; Repositories
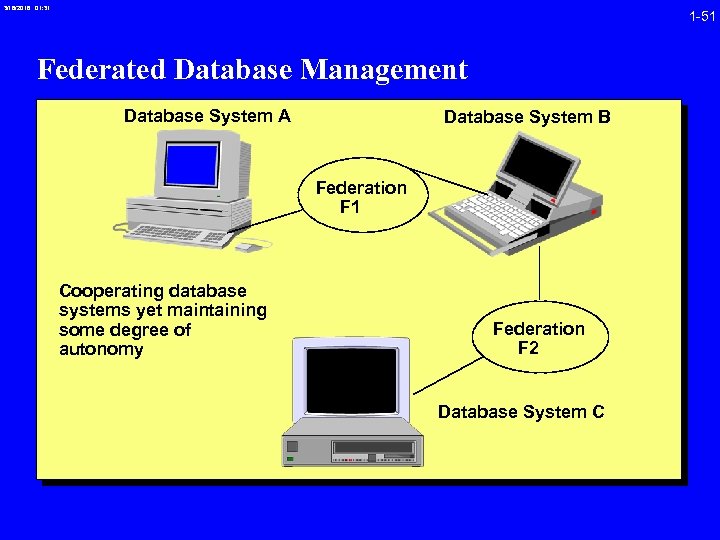 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -51 Federated Database Management Database System A Database System B Federation F 1 Cooperating database systems yet maintaining some degree of autonomy Federation F 2 Database System C
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -51 Federated Database Management Database System A Database System B Federation F 1 Cooperating database systems yet maintaining some degree of autonomy Federation F 2 Database System C
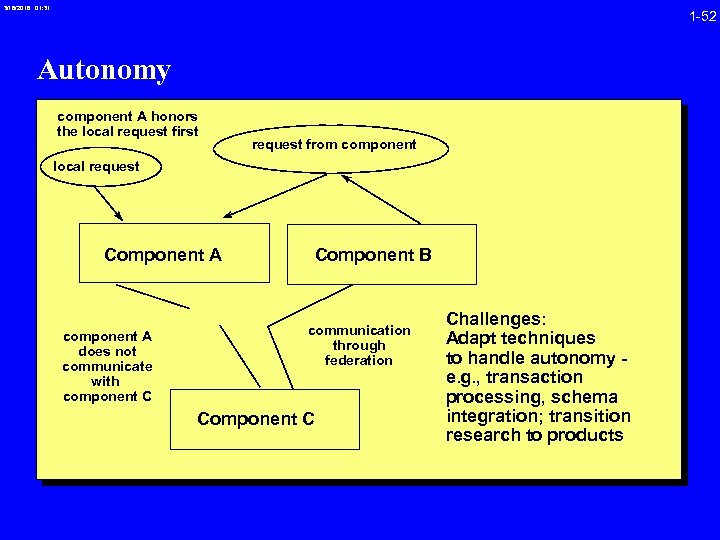 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -52 Autonomy component A honors the local request first request from component local request Component A component A does not communicate with component C Component B communication through federation Component C Challenges: Adapt techniques to handle autonomy e. g. , transaction processing, schema integration; transition research to products
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -52 Autonomy component A honors the local request first request from component local request Component A component A does not communicate with component C Component B communication through federation Component C Challenges: Adapt techniques to handle autonomy e. g. , transaction processing, schema integration; transition research to products
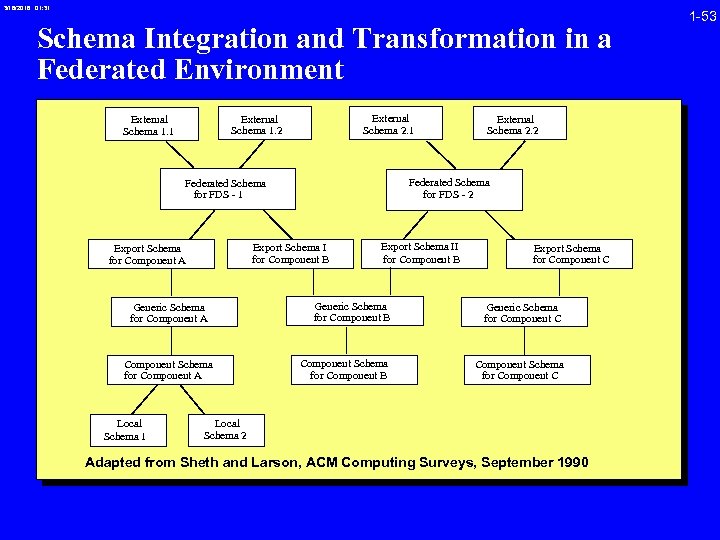 3/16/2018 01: 31 Schema Integration and Transformation in a Federated Environment External Schema 1. 1 External Schema 2. 1 External Schema 1. 2 Federated Schema for FDS - 1 Export Schema I for Component B Export Schema for Component A Generic Schema for Component A Component Schema for Component A Local Schema 1 External Schema 2. 2 Export Schema II for Component B Export Schema for Component C Generic Schema for Component B Generic Schema for Component C Component Schema for Component B Component Schema for Component C Local Schema 2 Adapted from Sheth and Larson, ACM Computing Surveys, September 1990 1 -53
3/16/2018 01: 31 Schema Integration and Transformation in a Federated Environment External Schema 1. 1 External Schema 2. 1 External Schema 1. 2 Federated Schema for FDS - 1 Export Schema I for Component B Export Schema for Component A Generic Schema for Component A Component Schema for Component A Local Schema 1 External Schema 2. 2 Export Schema II for Component B Export Schema for Component C Generic Schema for Component B Generic Schema for Component C Component Schema for Component B Component Schema for Component C Local Schema 2 Adapted from Sheth and Larson, ACM Computing Surveys, September 1990 1 -53
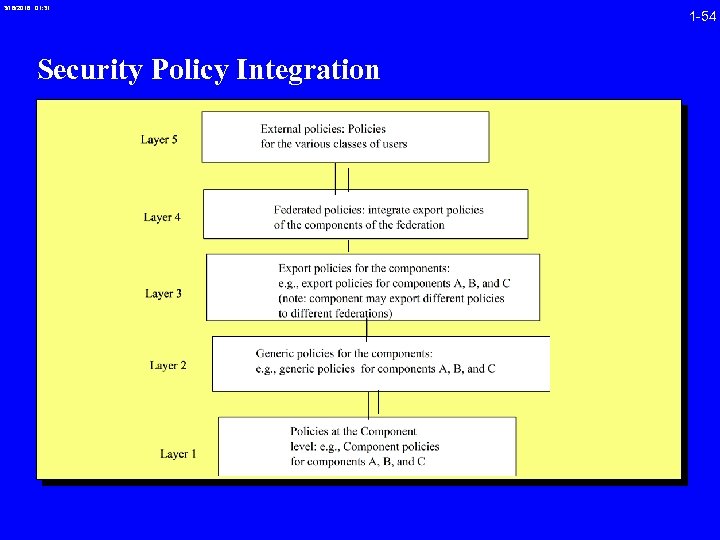 3/16/2018 01: 31 Security Policy Integration 1 -54
3/16/2018 01: 31 Security Policy Integration 1 -54
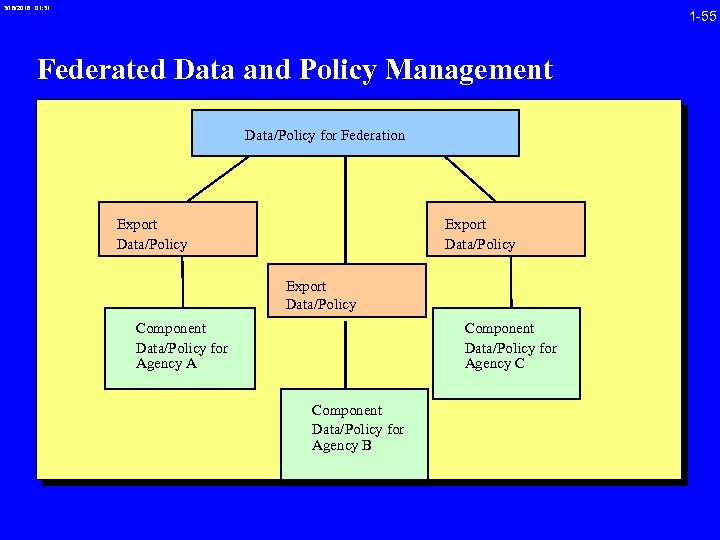 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -55 Federated Data and Policy Management Data/Policy for Federation Export Data/Policy Component Data/Policy for Agency A Component Data/Policy for Agency C Component Data/Policy for Agency B
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -55 Federated Data and Policy Management Data/Policy for Federation Export Data/Policy Component Data/Policy for Agency A Component Data/Policy for Agency C Component Data/Policy for Agency B
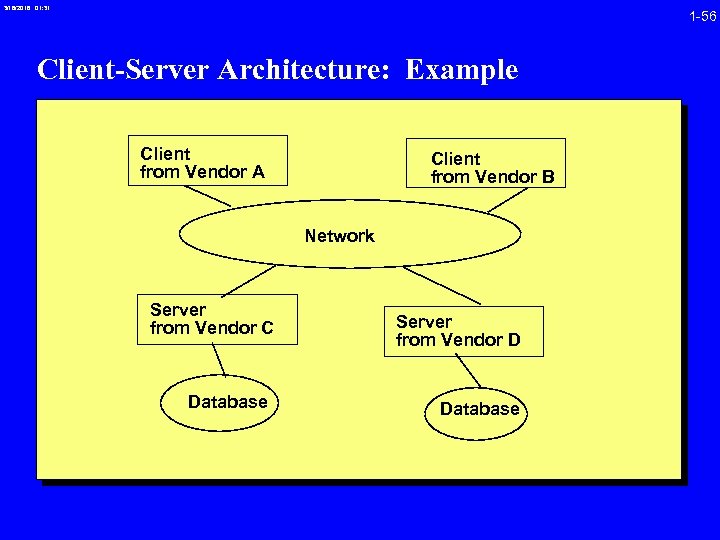 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -56 Client-Server Architecture: Example Client from Vendor A Client from Vendor B Network Server from Vendor C Database Server from Vendor D Database
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -56 Client-Server Architecture: Example Client from Vendor A Client from Vendor B Network Server from Vendor C Database Server from Vendor D Database
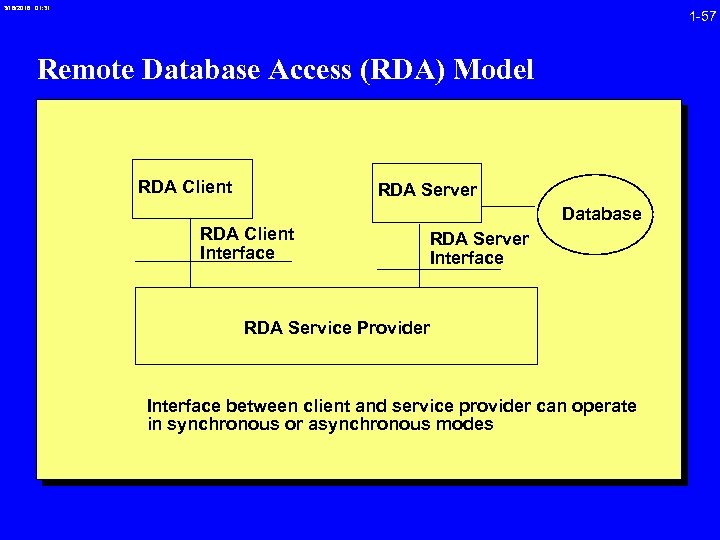 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -57 Remote Database Access (RDA) Model RDA Client RDA Server Database RDA Client Interface RDA Server Interface RDA Service Provider Interface between client and service provider can operate in synchronous or asynchronous modes
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -57 Remote Database Access (RDA) Model RDA Client RDA Server Database RDA Client Interface RDA Server Interface RDA Service Provider Interface between client and service provider can operate in synchronous or asynchronous modes
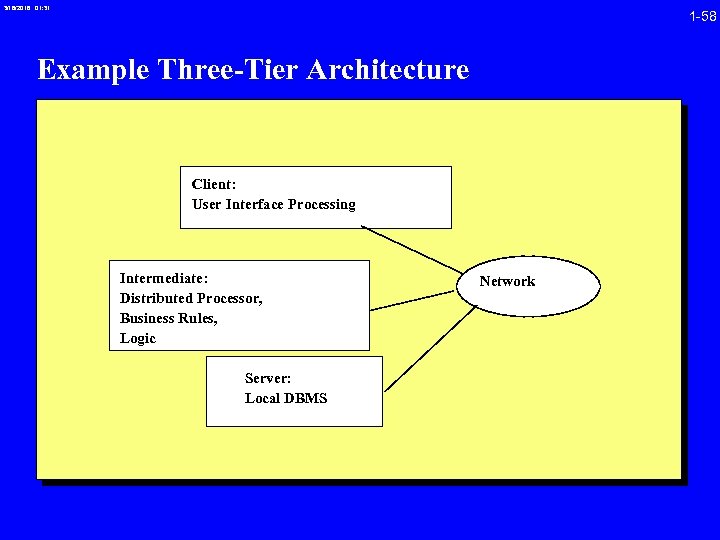 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -58 Example Three-Tier Architecture Client: User Interface Processing Intermediate: Distributed Processor, Business Rules, Logic Server: Local DBMS Network
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -58 Example Three-Tier Architecture Client: User Interface Processing Intermediate: Distributed Processor, Business Rules, Logic Server: Local DBMS Network
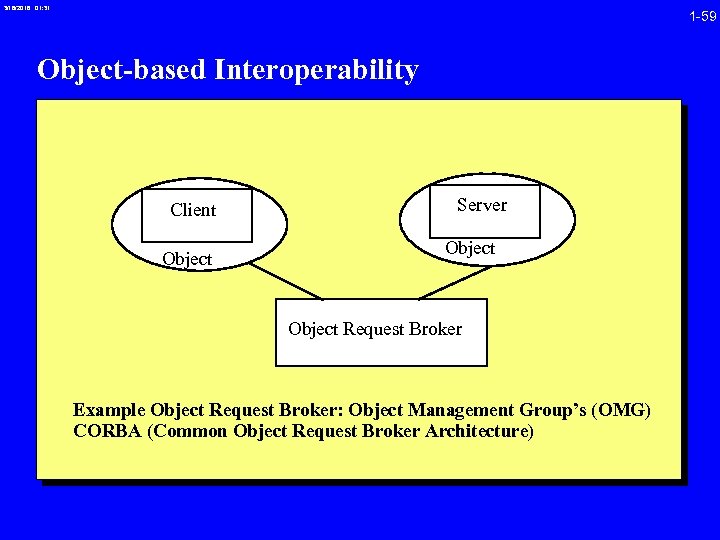 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -59 Object-based Interoperability Client Object Server Object Request Broker Example Object Request Broker: Object Management Group’s (OMG) CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture)
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -59 Object-based Interoperability Client Object Server Object Request Broker Example Object Request Broker: Object Management Group’s (OMG) CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture)
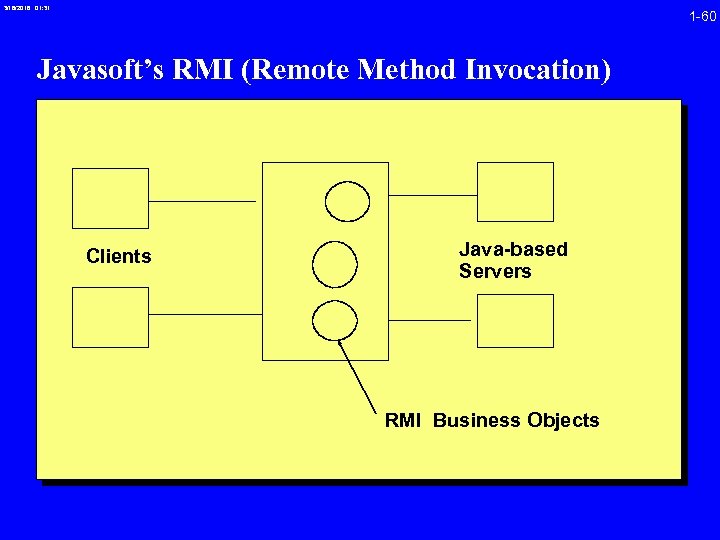 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -60 Javasoft’s RMI (Remote Method Invocation) Clients Java-based Servers RMI Business Objects
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -60 Javasoft’s RMI (Remote Method Invocation) Clients Java-based Servers RMI Business Objects
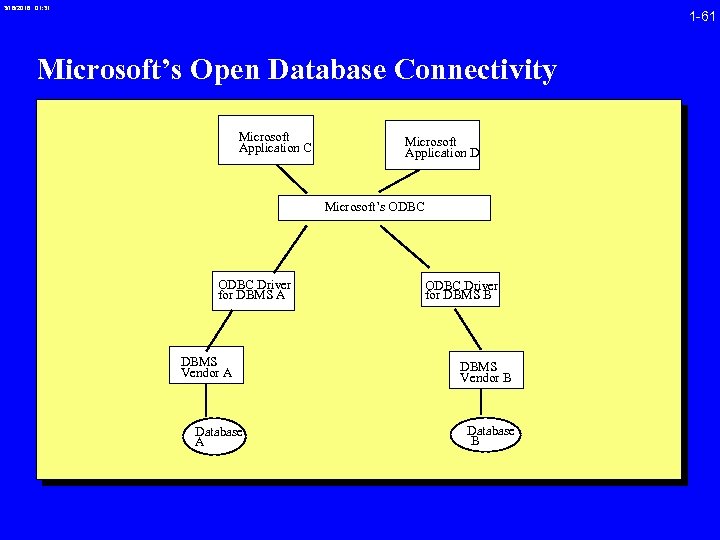 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -61 Microsoft’s Open Database Connectivity Microsoft Application C Microsoft Application D Microsoft’s ODBC Driver for DBMS A DBMS Vendor A Database A ODBC Driver for DBMS B DBMS Vendor B Database B
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -61 Microsoft’s Open Database Connectivity Microsoft Application C Microsoft Application D Microsoft’s ODBC Driver for DBMS A DBMS Vendor A Database A ODBC Driver for DBMS B DBMS Vendor B Database B
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -62 Overview: Migrating Legacy Systems 0 Many of the current systems and applications may become obsolete 0 Need an approach to migrate these systems to new architectures 0 Evolutionary approach: incremental transition of today's systems into more flexible systems 0 Extensible system architecture ultimately replaces today's hardware and software architecture 0 Open systems approach, standards
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -62 Overview: Migrating Legacy Systems 0 Many of the current systems and applications may become obsolete 0 Need an approach to migrate these systems to new architectures 0 Evolutionary approach: incremental transition of today's systems into more flexible systems 0 Extensible system architecture ultimately replaces today's hardware and software architecture 0 Open systems approach, standards
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -63 Migrating Legacy Database and Applications 0 Build business model in a sub-domain and relate data to existing databases and systems. 0 Wrap existing systems to provide access as needed. 0 Incorporate middle tier services and begin migrating workflow. 0 Gradually migrate business logic and rely on business objects for end-user systems.
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -63 Migrating Legacy Database and Applications 0 Build business model in a sub-domain and relate data to existing databases and systems. 0 Wrap existing systems to provide access as needed. 0 Incorporate middle tier services and begin migrating workflow. 0 Gradually migrate business logic and rely on business objects for end-user systems.
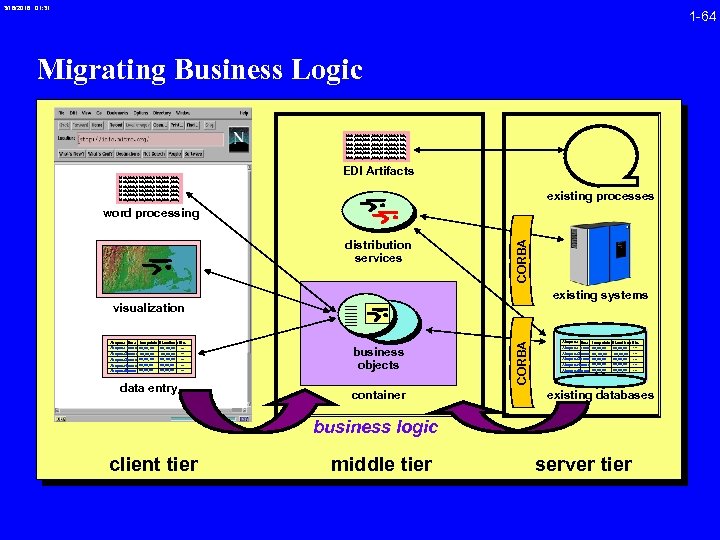 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -64 Migrating Business Logic blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, EDI Artifacts existing processes distribution services CORBA word processing existing systems Airspace time turnpoints Airspace nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 2 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 3 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 4 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 5 nn: nn xx, xx Elevations Etc. . . . xx, xx, xx. . . data entry business objects container CORBA visualization Airspace time turnpoints Airspace nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 2 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 3 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 4 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 5 nn: nn xx, xx Elevations Etc. . . . xx, xx, xx. . . existing databases business logic client tier middle tier server tier
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -64 Migrating Business Logic blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah, EDI Artifacts existing processes distribution services CORBA word processing existing systems Airspace time turnpoints Airspace nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 2 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 3 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 4 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 5 nn: nn xx, xx Elevations Etc. . . . xx, xx, xx. . . data entry business objects container CORBA visualization Airspace time turnpoints Airspace nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 2 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 3 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 4 nn: nn xx, xx Airspace 5 nn: nn xx, xx Elevations Etc. . . . xx, xx, xx. . . existing databases business logic client tier middle tier server tier
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -66 Application vs. Database Migration 0 Extract schema from the legacy code - Use reengineering tools 0 Extract metadata associated with the data 0 Deal with incomplete data and fill in the gaps 0 Build schemas in the target system from the extracted schema 0 Build the database
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -66 Application vs. Database Migration 0 Extract schema from the legacy code - Use reengineering tools 0 Extract metadata associated with the data 0 Deal with incomplete data and fill in the gaps 0 Build schemas in the target system from the extracted schema 0 Build the database
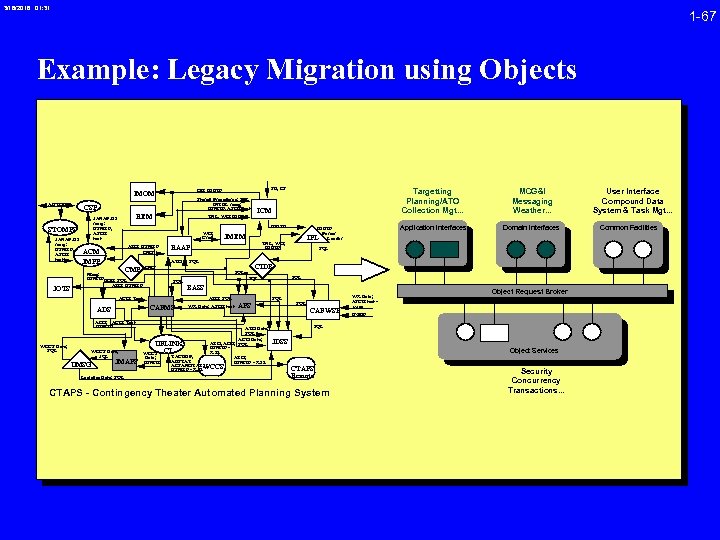 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -67 Example: Legacy Migration using Objects AUTODIN STOMPS JANAP 128 mesg: USMTF, ASCII text TNL, WO; IDBTF REM ATO; USMTF CMS ACM JMPP CMS Mesg: USMTF EOB; SQL ATO; USMTF ATO ACO; Text USMTF WCCS Data; JQL UMSG JMAPS Logistics Data; SQL UFLINK CI WCCS Data; USMTF SQL CIDB SQL BASS ATO; SQL CAFMS ADS SQL WX Data; ASCII text APS ATO Data; SQL ACO Data; ATO, ACO; SQL USMTF X. 25 ATO; USMTF - X. 25 TACREP, ABSTAT ACSAMSTAT; USMTF - X. 25 WCCS Domain Interfaces IPL TNL, WO; IDBTF SQL IDBTF Parser Loader JMEM MCG&I Messaging Weather. . . Application Interfaces ICM RAAP ACO; Text WCCS Data; SQL Targetting Planning/ATO Collection Mgt. . . IDBTF WO; Cmd CMP JOTS Stored Procedures; SQL INTEL mesg; USMTF, ASCII text CSP JANAP 128 mesg: USMTF, ASCII text SB, CS OB; IDBTF IMOM SQL CAFWSP WX Data; ASCII text AWN UGDF Object Request Broker SQL JDSS Object Services CTAPS Remote CTAPS - Contingency Theater Automated Planning System Security Concurrency Transactions. . . User Interface Compound Data System & Task Mgt. . . Common Facilities
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -67 Example: Legacy Migration using Objects AUTODIN STOMPS JANAP 128 mesg: USMTF, ASCII text TNL, WO; IDBTF REM ATO; USMTF CMS ACM JMPP CMS Mesg: USMTF EOB; SQL ATO; USMTF ATO ACO; Text USMTF WCCS Data; JQL UMSG JMAPS Logistics Data; SQL UFLINK CI WCCS Data; USMTF SQL CIDB SQL BASS ATO; SQL CAFMS ADS SQL WX Data; ASCII text APS ATO Data; SQL ACO Data; ATO, ACO; SQL USMTF X. 25 ATO; USMTF - X. 25 TACREP, ABSTAT ACSAMSTAT; USMTF - X. 25 WCCS Domain Interfaces IPL TNL, WO; IDBTF SQL IDBTF Parser Loader JMEM MCG&I Messaging Weather. . . Application Interfaces ICM RAAP ACO; Text WCCS Data; SQL Targetting Planning/ATO Collection Mgt. . . IDBTF WO; Cmd CMP JOTS Stored Procedures; SQL INTEL mesg; USMTF, ASCII text CSP JANAP 128 mesg: USMTF, ASCII text SB, CS OB; IDBTF IMOM SQL CAFWSP WX Data; ASCII text AWN UGDF Object Request Broker SQL JDSS Object Services CTAPS Remote CTAPS - Contingency Theater Automated Planning System Security Concurrency Transactions. . . User Interface Compound Data System & Task Mgt. . . Common Facilities
 3/16/2018 01: 31 Example Lessons Learned: Experience with CORBA 0 CORBA provides an evolvable system integration platform 0 CORBA provides a path for legacy migration - Applications can be coarsely wrapped as CORBA objects, providing 100% reuse = Wrapping is a relatively straight forward technique = Need to dig to uncover hidden dependencies = Does not address duplication of common functions - Applications can be reengineered to replace duplicated functions with CORBA based common services = Substantially more difficult than coarse wrapping 1 -68
3/16/2018 01: 31 Example Lessons Learned: Experience with CORBA 0 CORBA provides an evolvable system integration platform 0 CORBA provides a path for legacy migration - Applications can be coarsely wrapped as CORBA objects, providing 100% reuse = Wrapping is a relatively straight forward technique = Need to dig to uncover hidden dependencies = Does not address duplication of common functions - Applications can be reengineered to replace duplicated functions with CORBA based common services = Substantially more difficult than coarse wrapping 1 -68
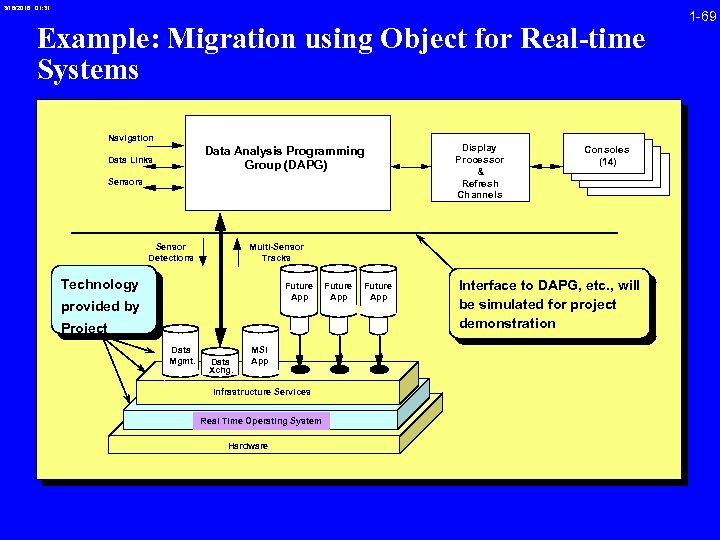 3/16/2018 01: 31 Example: Migration using Object for Real-time Systems Navigation Data Analysis Programming Group (DAPG) Data Links Sensor Detections Consoles (14) Multi-Sensor Tracks Technology Future App provided by Project Data Mgmt. Display Processor & Refresh Channels Data Xchg. MSI App Infrastructure Services Real Time Operating System Hardware Future App Interface to DAPG, etc. , will be simulated for project demonstration 1 -69
3/16/2018 01: 31 Example: Migration using Object for Real-time Systems Navigation Data Analysis Programming Group (DAPG) Data Links Sensor Detections Consoles (14) Multi-Sensor Tracks Technology Future App provided by Project Data Mgmt. Display Processor & Refresh Channels Data Xchg. MSI App Infrastructure Services Real Time Operating System Hardware Future App Interface to DAPG, etc. , will be simulated for project demonstration 1 -69
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -70 Current Status and Directions 0 Developments - Several prototypes and some commercial products - Tools for schema integration and transformation - Standards for interoperable database systems 0 Challenges being addressed - Semantic heterogeneity - Autonomy and federation - Global transaction management - Integrity and Security 0 New challenges - Scale - Web data management
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -70 Current Status and Directions 0 Developments - Several prototypes and some commercial products - Tools for schema integration and transformation - Standards for interoperable database systems 0 Challenges being addressed - Semantic heterogeneity - Autonomy and federation - Global transaction management - Integrity and Security 0 New challenges - Scale - Web data management
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -71 Information and Security Analytics Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham The University of Texas at Dallas Lecture #1 Unit #4 Data Warehousing May 28, 2010
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -71 Information and Security Analytics Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham The University of Texas at Dallas Lecture #1 Unit #4 Data Warehousing May 28, 2010
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -72 Outline 0 Data Warehousing 0 Data Warehouse to Data Mining
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -72 Outline 0 Data Warehousing 0 Data Warehouse to Data Mining
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -73 What is a Data Warehouse? 0 A Data Warehouse is a: - Subject-oriented - Integrated - Nonvolatile - Time variant - Collection of data in support of management’s decisions - From: Building the Data Warehouse by W. H. Inmon, John Wiley and Sons 0 Integration of heterogeneous data sources into a repository 0 Summary reports, aggregate functions, etc.
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -73 What is a Data Warehouse? 0 A Data Warehouse is a: - Subject-oriented - Integrated - Nonvolatile - Time variant - Collection of data in support of management’s decisions - From: Building the Data Warehouse by W. H. Inmon, John Wiley and Sons 0 Integration of heterogeneous data sources into a repository 0 Summary reports, aggregate functions, etc.
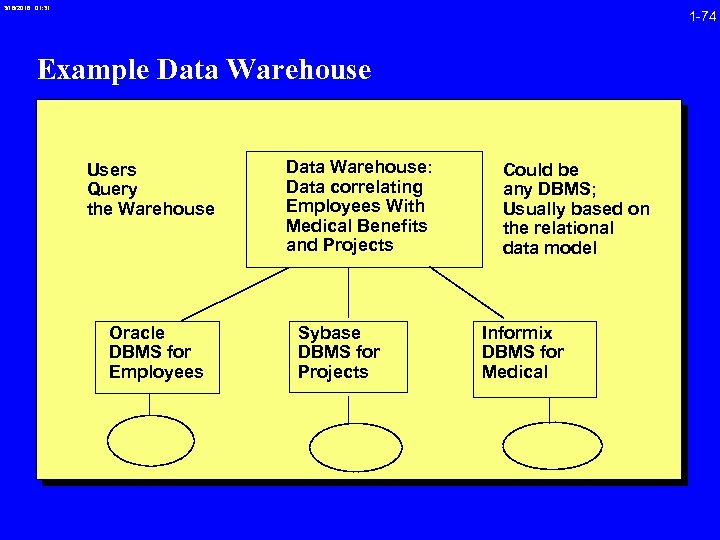 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -74 Example Data Warehouse Users Query the Warehouse Oracle DBMS for Employees Data Warehouse: Data correlating Employees With Medical Benefits and Projects Sybase DBMS for Projects Could be any DBMS; Usually based on the relational data model Informix DBMS for Medical
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -74 Example Data Warehouse Users Query the Warehouse Oracle DBMS for Employees Data Warehouse: Data correlating Employees With Medical Benefits and Projects Sybase DBMS for Projects Could be any DBMS; Usually based on the relational data model Informix DBMS for Medical
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -75 Some Data Warehousing Technologies 0 Heterogeneous Database Integration 0 Statistical Databases 0 Data Modeling 0 Metadata 0 Access Methods and Indexing 0 Language Interface 0 Database Administration 0 Parallel Database Management
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -75 Some Data Warehousing Technologies 0 Heterogeneous Database Integration 0 Statistical Databases 0 Data Modeling 0 Metadata 0 Access Methods and Indexing 0 Language Interface 0 Database Administration 0 Parallel Database Management
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -76 Data Warehouse Design 0 Appropriate Data Model is key to designing the Warehouse 0 Higher Level Model in stages - Stage 1: Corporate data model - Stage 2: Enterprise data model - Stage 3: Warehouse data model 0 Middle-level data model - A model for possibly for each subject area in the higher level model 0 Physical data model - Include features such as keys in the middle-level model 0 Need to determine appropriate levels of granularity of data in order to build a good data warehouse
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -76 Data Warehouse Design 0 Appropriate Data Model is key to designing the Warehouse 0 Higher Level Model in stages - Stage 1: Corporate data model - Stage 2: Enterprise data model - Stage 3: Warehouse data model 0 Middle-level data model - A model for possibly for each subject area in the higher level model 0 Physical data model - Include features such as keys in the middle-level model 0 Need to determine appropriate levels of granularity of data in order to build a good data warehouse
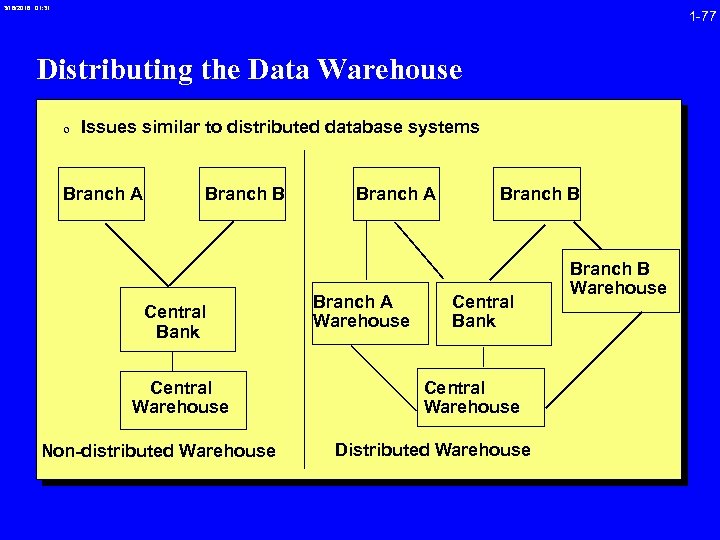 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -77 Distributing the Data Warehouse 0 Issues similar to distributed database systems Branch A Branch B Central Bank Central Warehouse Non-distributed Warehouse Branch A Warehouse Branch B Central Bank Central Warehouse Distributed Warehouse Branch B Warehouse
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -77 Distributing the Data Warehouse 0 Issues similar to distributed database systems Branch A Branch B Central Bank Central Warehouse Non-distributed Warehouse Branch A Warehouse Branch B Central Bank Central Warehouse Distributed Warehouse Branch B Warehouse
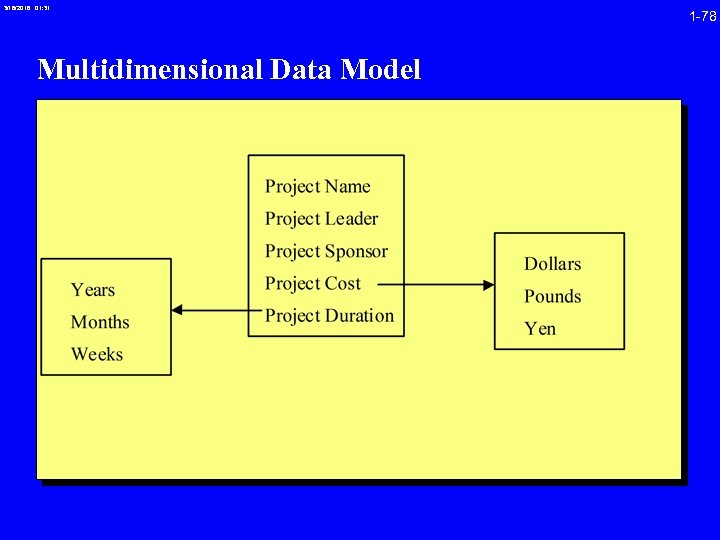 3/16/2018 01: 31 Multidimensional Data Model 1 -78
3/16/2018 01: 31 Multidimensional Data Model 1 -78
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -79 Indexing for Data Warehousing 0 Bit-Maps 0 Multi-level indexing 0 Storing parts or all of the index files in main memory 0 Dynamic indexing
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -79 Indexing for Data Warehousing 0 Bit-Maps 0 Multi-level indexing 0 Storing parts or all of the index files in main memory 0 Dynamic indexing
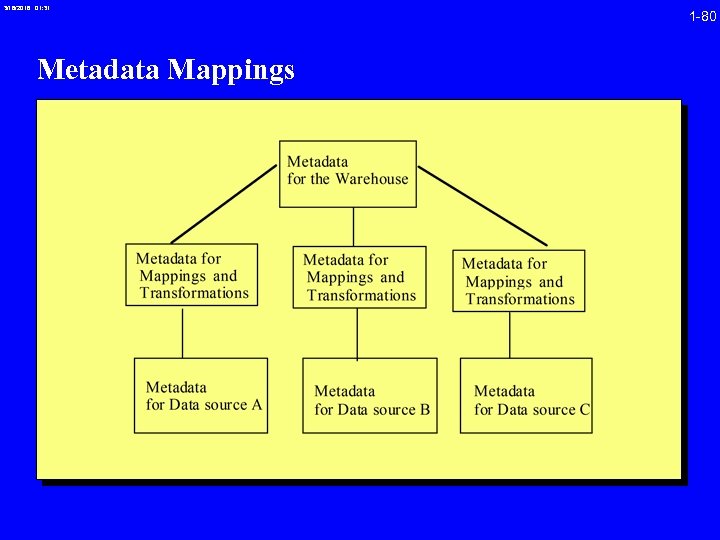 3/16/2018 01: 31 Metadata Mappings 1 -80
3/16/2018 01: 31 Metadata Mappings 1 -80
 3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -81 Data Mining Information Harvesting Knowledge Mining Data Mining Knowledge Discovery in Databases Data Dredging Data Archaeology Data Pattern Processing Database Mining Siftware Knowledge Extraction The process of discovering meaningful new correlations, patterns, and trends by sifting through large amounts of data, often previously unknown, using pattern recognition technologies and statistical and mathematical techniques (Thuraisingham 1998)
3/16/2018 01: 31 1 -81 Data Mining Information Harvesting Knowledge Mining Data Mining Knowledge Discovery in Databases Data Dredging Data Archaeology Data Pattern Processing Database Mining Siftware Knowledge Extraction The process of discovering meaningful new correlations, patterns, and trends by sifting through large amounts of data, often previously unknown, using pattern recognition technologies and statistical and mathematical techniques (Thuraisingham 1998)


