e52d5eac114b7acbdc7971f72bd02a8b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Information and Decision Support Systems Chapter 10
Information and Decision Support Systems Chapter 10
 Chapter 10 Outline • Decision Making and Problem Solving • An Overview of Management Information Systems (MIS) • Functional Aspects of MIS • An Overview of Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Components of a DSS • Group Decision Support Systems (GDSSs) • Executive Support Systems (ESSs) 2
Chapter 10 Outline • Decision Making and Problem Solving • An Overview of Management Information Systems (MIS) • Functional Aspects of MIS • An Overview of Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Components of a DSS • Group Decision Support Systems (GDSSs) • Executive Support Systems (ESSs) 2
 Decision Making and Problem Solving
Decision Making and Problem Solving
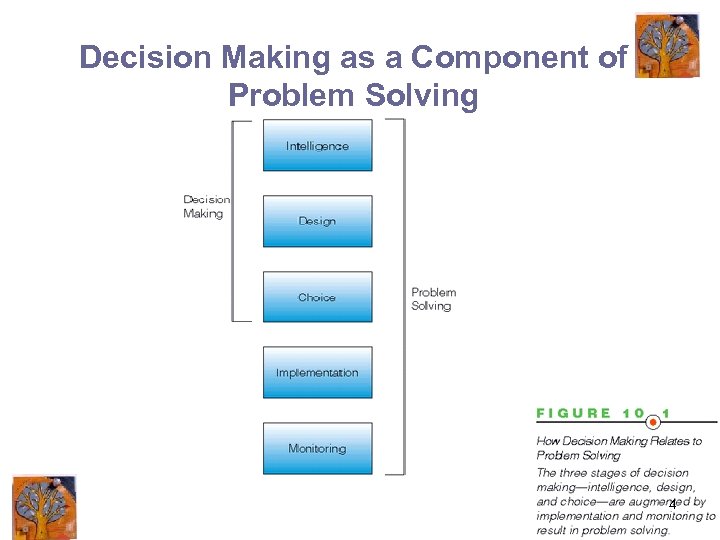 Decision Making as a Component of Problem Solving 4
Decision Making as a Component of Problem Solving 4
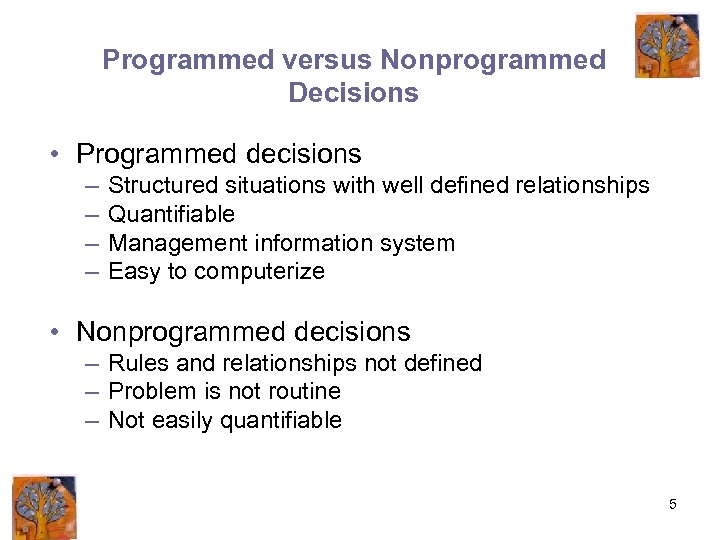 Programmed versus Nonprogrammed Decisions • Programmed decisions – – Structured situations with well defined relationships Quantifiable Management information system Easy to computerize • Nonprogrammed decisions – Rules and relationships not defined – Problem is not routine – Not easily quantifiable 5
Programmed versus Nonprogrammed Decisions • Programmed decisions – – Structured situations with well defined relationships Quantifiable Management information system Easy to computerize • Nonprogrammed decisions – Rules and relationships not defined – Problem is not routine – Not easily quantifiable 5
 Problem Solving Approaches • Optimization: find the best solution • Satisficing: find a good solution • Heuristics: rules of thumb 6
Problem Solving Approaches • Optimization: find the best solution • Satisficing: find a good solution • Heuristics: rules of thumb 6
 Optimization, Satisficing, and Heuristic Approaches 7
Optimization, Satisficing, and Heuristic Approaches 7
 An Overview of Management Information Systems
An Overview of Management Information Systems
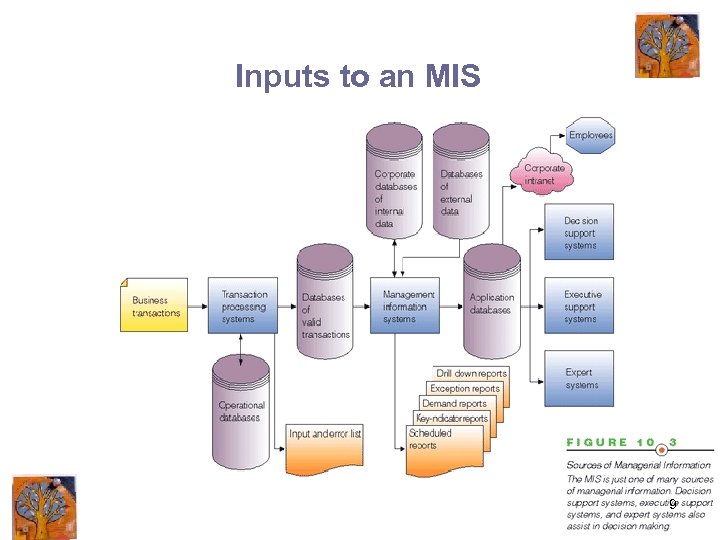 Inputs to an MIS 9
Inputs to an MIS 9
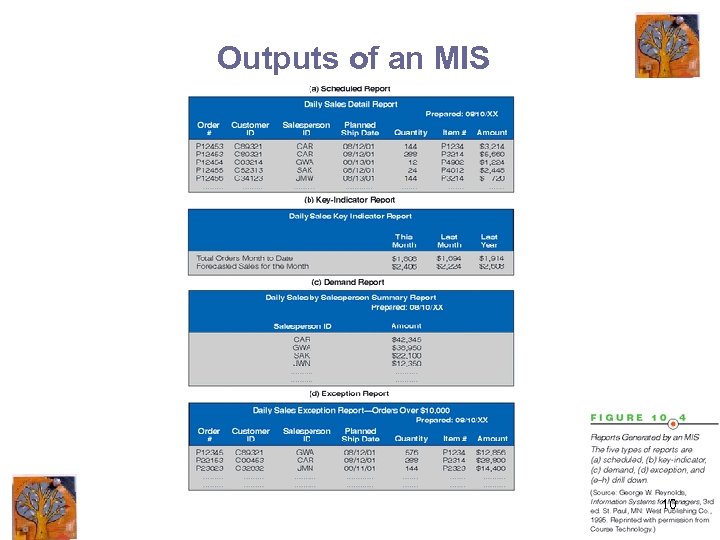 Outputs of an MIS 10
Outputs of an MIS 10
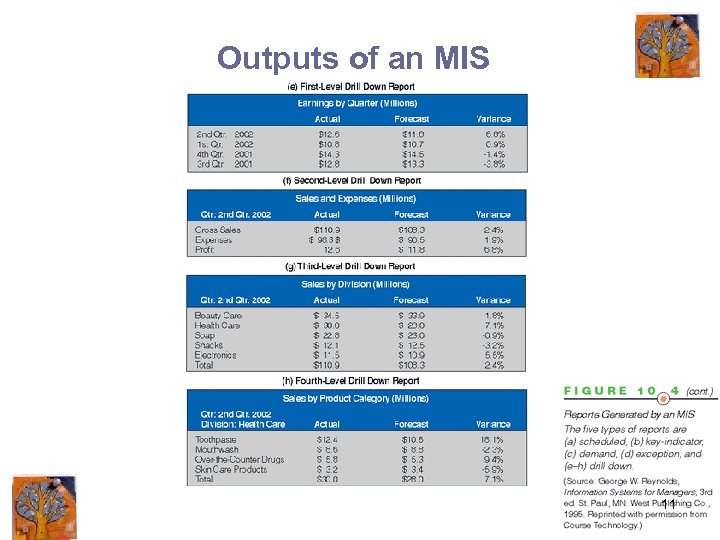 Outputs of an MIS 11
Outputs of an MIS 11
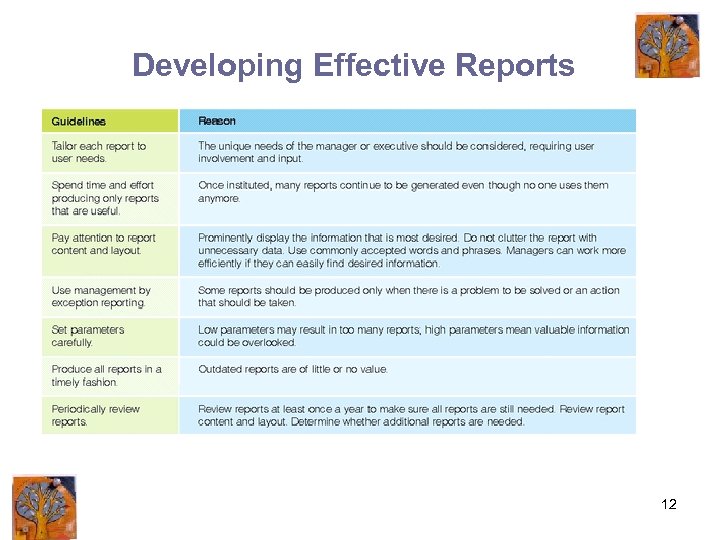 Developing Effective Reports 12
Developing Effective Reports 12
 Characteristics of an MIS • • • Fixed format, standard reports Hard-copy or soft-copy reports Uses internal data User-developed reports Users must request formal reports from IS department 13
Characteristics of an MIS • • • Fixed format, standard reports Hard-copy or soft-copy reports Uses internal data User-developed reports Users must request formal reports from IS department 13
 Functional Aspects of the MIS
Functional Aspects of the MIS
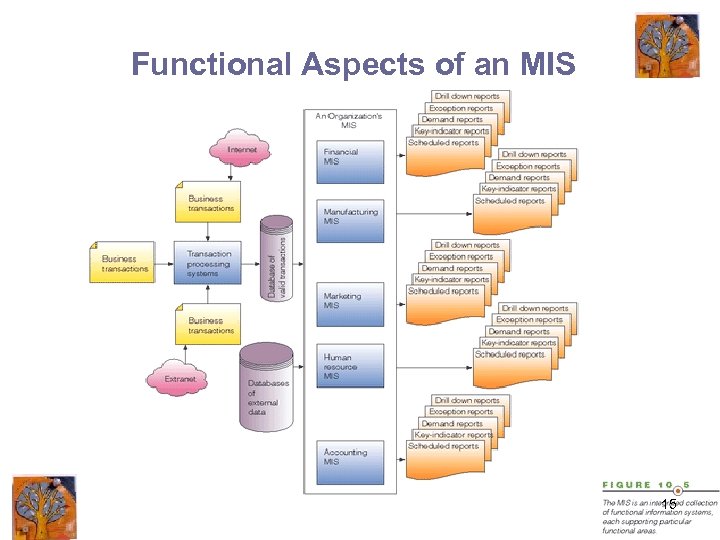 Functional Aspects of an MIS 15
Functional Aspects of an MIS 15
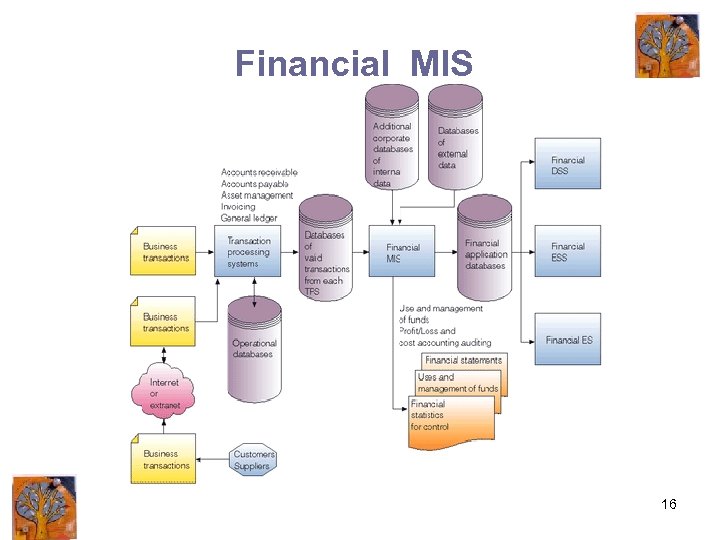 Financial MIS 16
Financial MIS 16
 Manufacturing MIS • Design engineering • Process control – Computer-assisted manufacturing (CAM) – Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) – Flexible manufacturing system • Quality control and testing 17
Manufacturing MIS • Design engineering • Process control – Computer-assisted manufacturing (CAM) – Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) – Flexible manufacturing system • Quality control and testing 17
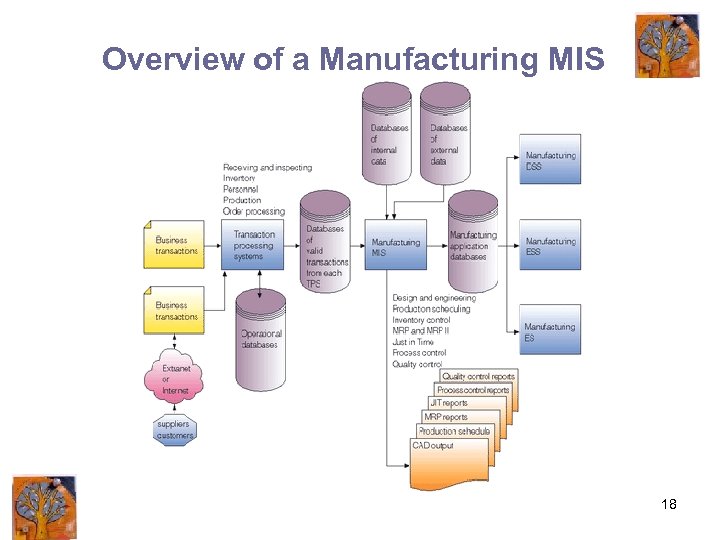 Overview of a Manufacturing MIS 18
Overview of a Manufacturing MIS 18
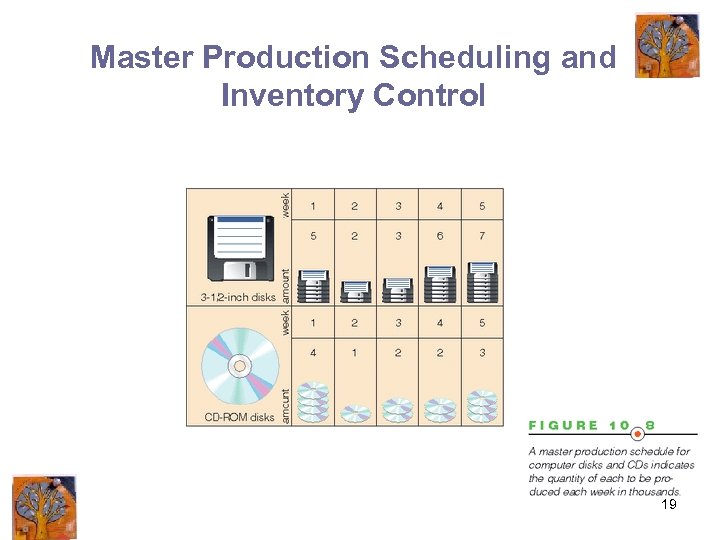 Master Production Scheduling and Inventory Control 19
Master Production Scheduling and Inventory Control 19
 Quality Control and Testing 20
Quality Control and Testing 20
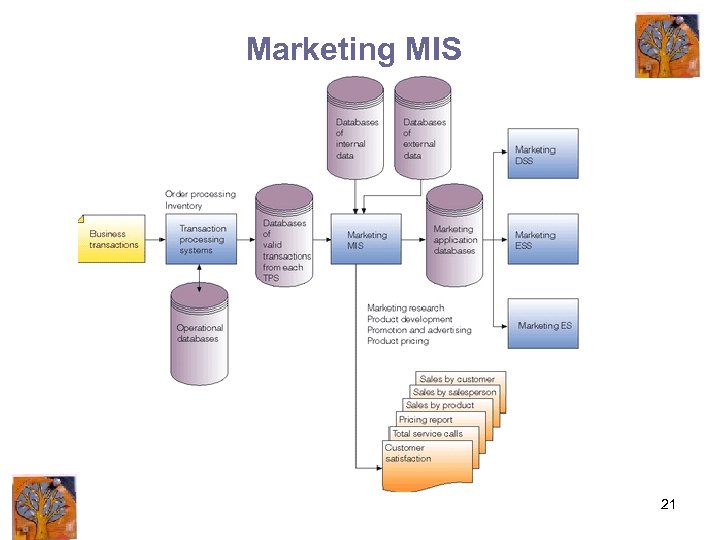 Marketing MIS 21
Marketing MIS 21
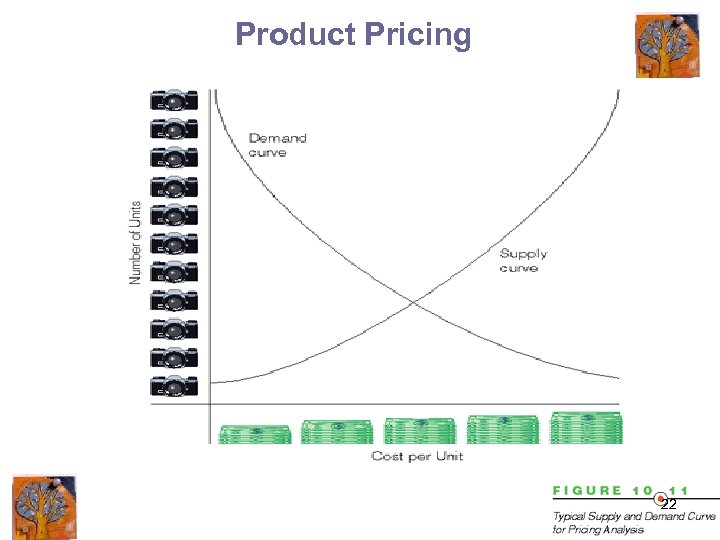 Product Pricing 22
Product Pricing 22
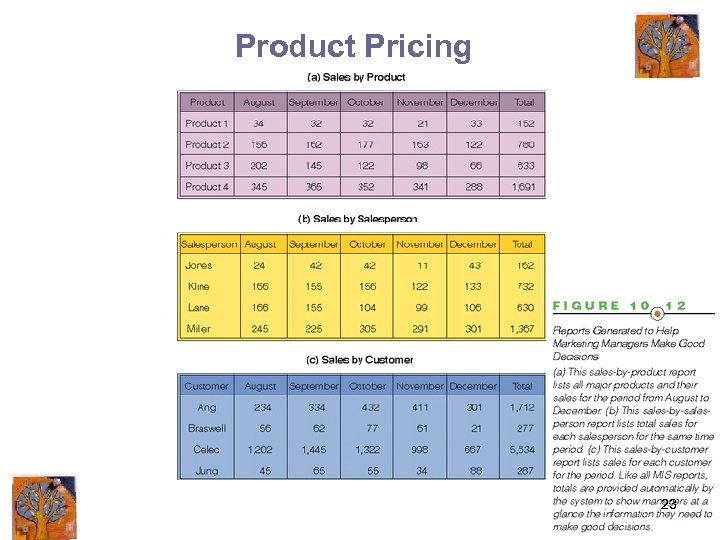 Product Pricing 23
Product Pricing 23
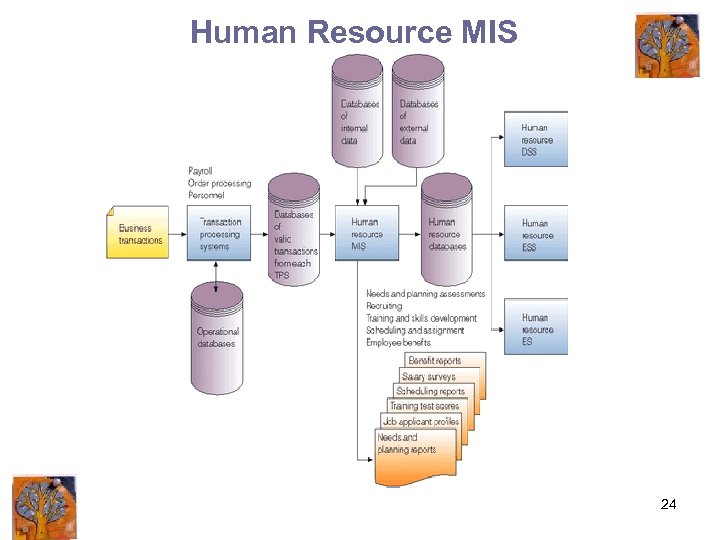 Human Resource MIS 24
Human Resource MIS 24
 Other MIS • Accounting management information systems • Geographic information systems (GIS) 25
Other MIS • Accounting management information systems • Geographic information systems (GIS) 25
 Characteristics of Decision Support Systems • Handle large amounts of data from various sources • Provide report and presentation flexibility • Offer both textual and graphical orientation • Support drill down analysis 26
Characteristics of Decision Support Systems • Handle large amounts of data from various sources • Provide report and presentation flexibility • Offer both textual and graphical orientation • Support drill down analysis 26
 An Overview of Decision Support Systems
An Overview of Decision Support Systems
 Characteristics of a DSS • Perform complex, sophisticated analysis • Optimization, satisficing, heuristics – Simulation – What-if analysis – Goal-seeking analysis 28
Characteristics of a DSS • Perform complex, sophisticated analysis • Optimization, satisficing, heuristics – Simulation – What-if analysis – Goal-seeking analysis 28
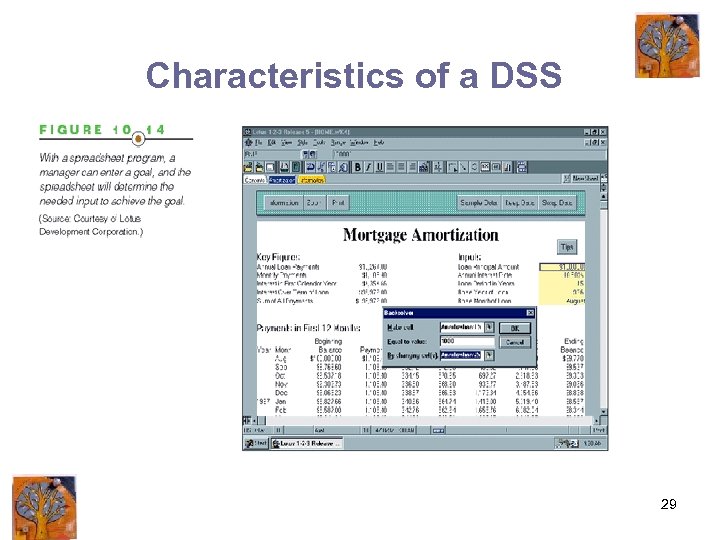 Characteristics of a DSS 29
Characteristics of a DSS 29
 Capabilities of a DSS • Support all problem-solving phases • Support different decision frequencies • Support different problem structures • Support various decision-making levels 30
Capabilities of a DSS • Support all problem-solving phases • Support different decision frequencies • Support different problem structures • Support various decision-making levels 30
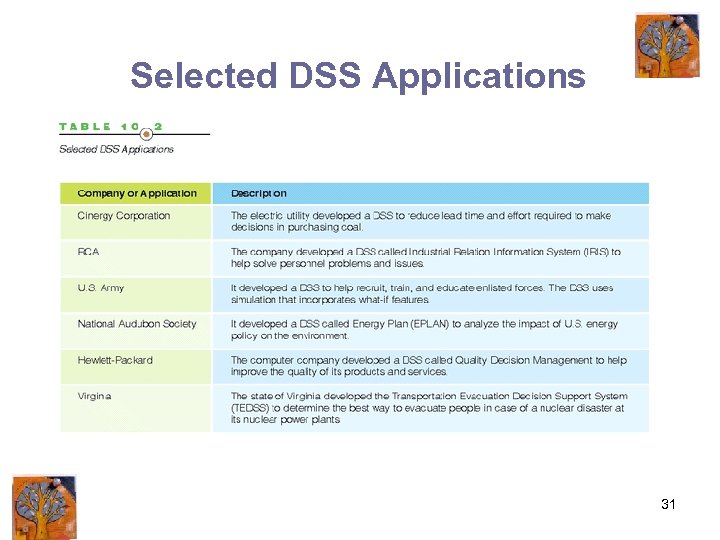 Selected DSS Applications 31
Selected DSS Applications 31
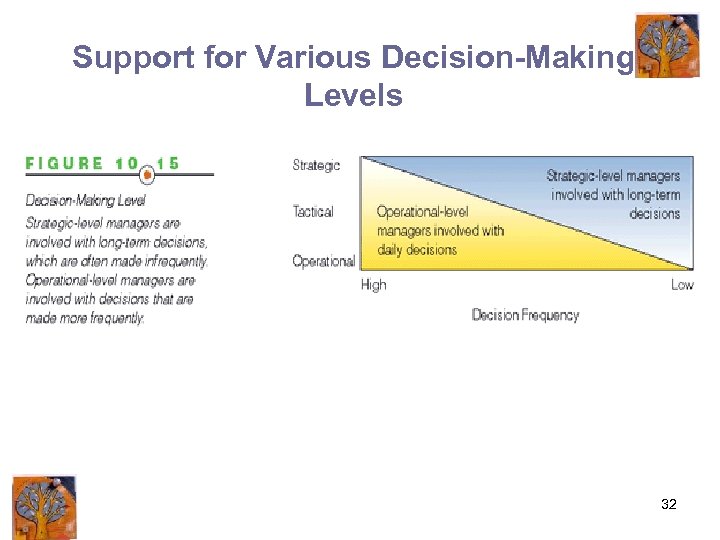 Support for Various Decision-Making Levels 32
Support for Various Decision-Making Levels 32
 Comparison of DSSs and MISs 33
Comparison of DSSs and MISs 33
 Comparison of DSSs and MISs 34
Comparison of DSSs and MISs 34
 Components of a DSS
Components of a DSS
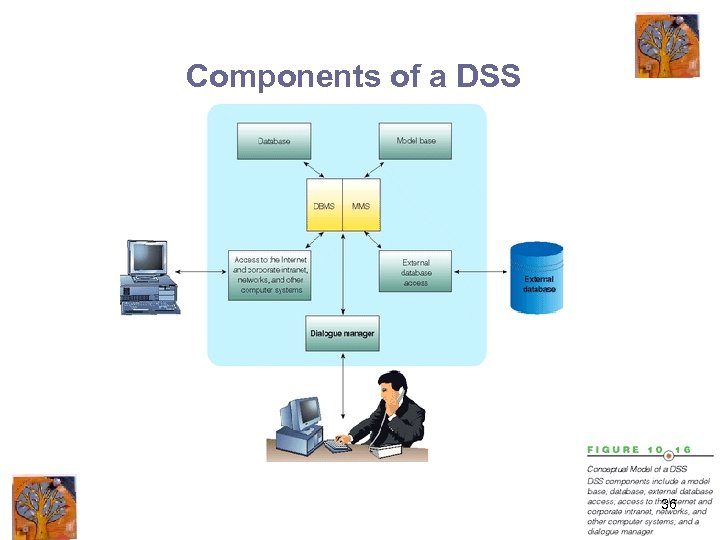 Components of a DSS 36
Components of a DSS 36
 The Model Base • Financial models – Cash flow – Internal rate of return • Statistical analysis models – Summary statistics – Trend projections – Hypothesis testing • Graphical models • Project management models 37
The Model Base • Financial models – Cash flow – Internal rate of return • Statistical analysis models – Summary statistics – Trend projections – Hypothesis testing • Graphical models • Project management models 37
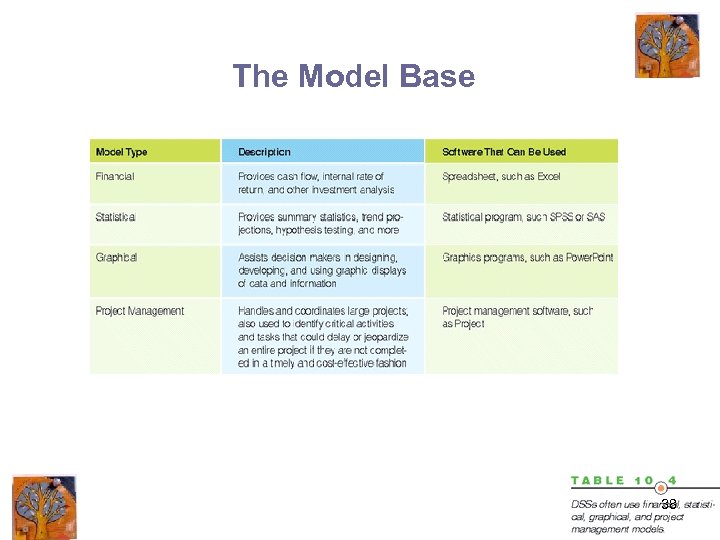 The Model Base 38
The Model Base 38
 Data-driven versus Model-driven DSS • Data-driven DSS - primarily performs qualitative analysis based on the company’s databases • Model-driven DSS - primarily performs mathematical or quantitative analysis 39
Data-driven versus Model-driven DSS • Data-driven DSS - primarily performs qualitative analysis based on the company’s databases • Model-driven DSS - primarily performs mathematical or quantitative analysis 39
 Group Decision Support Systems
Group Decision Support Systems
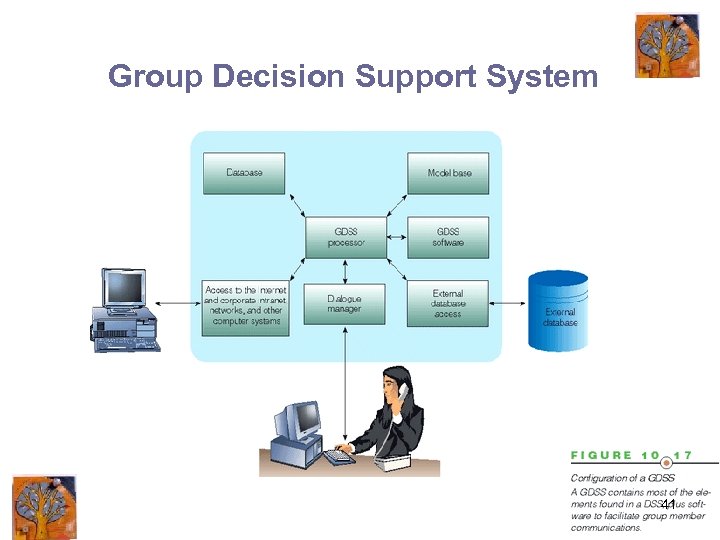 Group Decision Support System 41
Group Decision Support System 41
 Characteristics of a GDSS • • Special design Ease of use Flexibility Decision-making support Anonymous input Reduction of negative group behavior Parallel communication Automated record keeping 42
Characteristics of a GDSS • • Special design Ease of use Flexibility Decision-making support Anonymous input Reduction of negative group behavior Parallel communication Automated record keeping 42
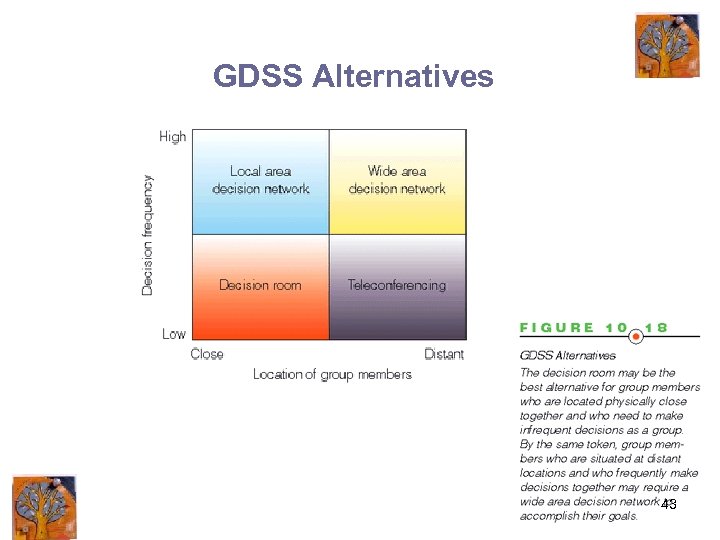 GDSS Alternatives 43
GDSS Alternatives 43
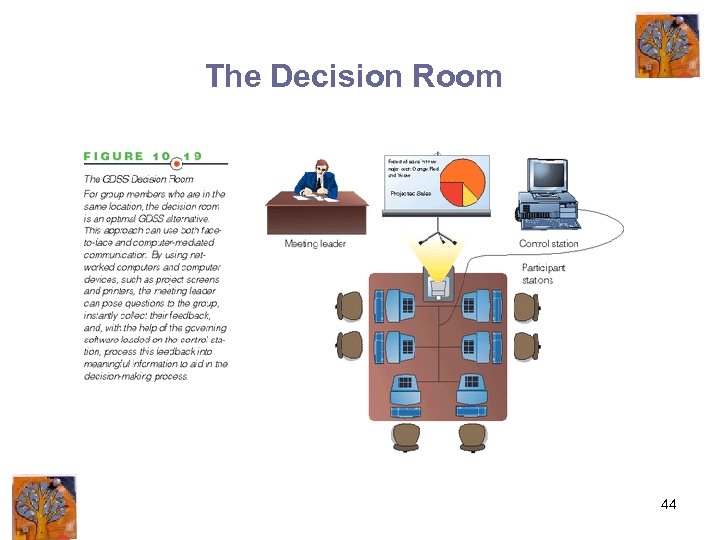 The Decision Room 44
The Decision Room 44
 Executive Support Systems 45
Executive Support Systems 45
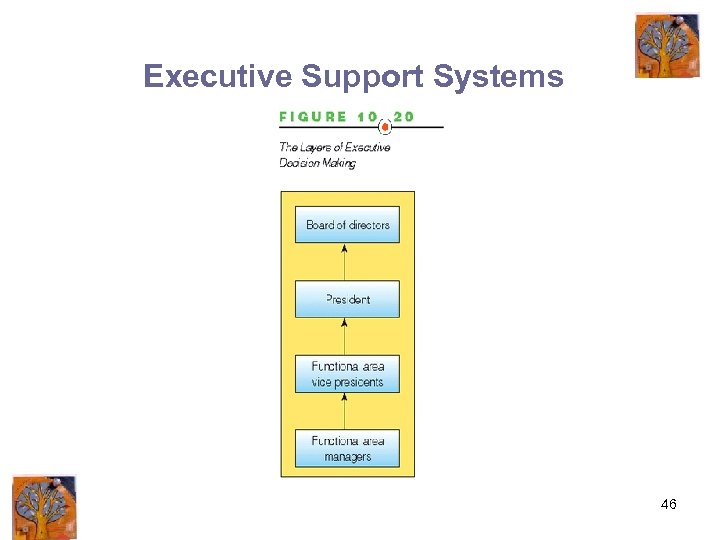 Executive Support Systems 46
Executive Support Systems 46
 Executive Support Systems (ESS) in Perspective • • Tailored to individual executives Easy to use Drill down capabilities Support need for external data Can help when uncertainty is high Future-oriented Linked to value-added processes 47
Executive Support Systems (ESS) in Perspective • • Tailored to individual executives Easy to use Drill down capabilities Support need for external data Can help when uncertainty is high Future-oriented Linked to value-added processes 47
 Capabilities of an ESS • • • Support for defining an overall vision Support for strategic planning Support for strategic organizing & staffing Support for strategic control Support for crisis management 48
Capabilities of an ESS • • • Support for defining an overall vision Support for strategic planning Support for strategic organizing & staffing Support for strategic control Support for crisis management 48
 Summary • Management information system - an integrated collection of people, procedures, databases, and devices that provide managers and decision-makers with information to help achieve organizational goals • Decision-making phase: includes intelligence, design, and choice • Problem solving: also includes implementation and monitoring • Decision approaches: optimization, satisficing, and heuristic 49
Summary • Management information system - an integrated collection of people, procedures, databases, and devices that provide managers and decision-makers with information to help achieve organizational goals • Decision-making phase: includes intelligence, design, and choice • Problem solving: also includes implementation and monitoring • Decision approaches: optimization, satisficing, and heuristic 49
 Summary • Decision support system (DSS) - an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices working to support managerial decision making • Group decision support system (GDSS) - also called a computerized collaborative work system, consists of most of the elements in a DSS, plus software needed to provide effective support in group decision-making settings • Executive support systems (ESSs) - specialized decision support systems designed to meet the needs of senior management 50
Summary • Decision support system (DSS) - an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices working to support managerial decision making • Group decision support system (GDSS) - also called a computerized collaborative work system, consists of most of the elements in a DSS, plus software needed to provide effective support in group decision-making settings • Executive support systems (ESSs) - specialized decision support systems designed to meet the needs of senior management 50
 Principles and Learning Objectives • Good decision-making and problem-solving skills are the key to developing effective information and decision support systems. – Define the stages of decision making. – Discuss the importance of implementation and monitoring in problem solving. 51
Principles and Learning Objectives • Good decision-making and problem-solving skills are the key to developing effective information and decision support systems. – Define the stages of decision making. – Discuss the importance of implementation and monitoring in problem solving. 51
 Principles and Learning Objectives • The management information system (MIS) must provide the right information to the right person in the right fashion at the right time. – Define the term MIS and clearly distinguish the difference between a TPS and an MIS. – Discuss information systems in the functional areas of business organizations. 52
Principles and Learning Objectives • The management information system (MIS) must provide the right information to the right person in the right fashion at the right time. – Define the term MIS and clearly distinguish the difference between a TPS and an MIS. – Discuss information systems in the functional areas of business organizations. 52
 Principles and Learning Objectives • Decision support systems (DSSs) are used when the problems are more unstructured. – List and discuss important characteristics of DSSs that give them the potential to be effective management support tools. – Identify and describe the basic components of a DSS. 53
Principles and Learning Objectives • Decision support systems (DSSs) are used when the problems are more unstructured. – List and discuss important characteristics of DSSs that give them the potential to be effective management support tools. – Identify and describe the basic components of a DSS. 53
 Principles and Learning Objectives • Specialized support systems, such as group decision support systems (GDSSs) and executive support systems (ESSs), use the overall approach of a DSS in situations such as group and executive decision making. – State the goals of a GDSS and identify the characteristics that distinguish it from a DSS. – Identify the fundamental uses of an ESS and list the characteristics of such a system. 54
Principles and Learning Objectives • Specialized support systems, such as group decision support systems (GDSSs) and executive support systems (ESSs), use the overall approach of a DSS in situations such as group and executive decision making. – State the goals of a GDSS and identify the characteristics that distinguish it from a DSS. – Identify the fundamental uses of an ESS and list the characteristics of such a system. 54
 End of Chapter 10
End of Chapter 10


