6c87b2d71ec2b1521266d666b8f6a61f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Informasi Teknologi muji@unila. ac. id
Informasi Teknologi muji@unila. ac. id
 Class 2 • Internet and Intranet • • • History and Function Email dan internet Browsing (if possible) Transfer File and File Saving Virus
Class 2 • Internet and Intranet • • • History and Function Email dan internet Browsing (if possible) Transfer File and File Saving Virus
 MISPREDICTIONS BY IT INDUSTRY LEADERS This “telephone” has too many shortcomings to be seriously considered as a means of communication. The device is inherently of no value to us. -Western Union internal memo, 1876 I think there is a world market for maybe five computers. -Thomas Watson, chairman of IBM, 1943 But what [is a microchip] good for? -Engineer at the Advanced Computing Systems Division of IBM, 1968 There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home. -Ken Olson, president, chairman, and founder of Digital Equipment Corp. , 1977 640 K ought to be enough for anybody. -Attributed to Bill Gates, chairman of Microsoft, 1981 Dell has a great business model, but that dog won’t scale. -John Shoemaker, head of Sun’s server division, 2000
MISPREDICTIONS BY IT INDUSTRY LEADERS This “telephone” has too many shortcomings to be seriously considered as a means of communication. The device is inherently of no value to us. -Western Union internal memo, 1876 I think there is a world market for maybe five computers. -Thomas Watson, chairman of IBM, 1943 But what [is a microchip] good for? -Engineer at the Advanced Computing Systems Division of IBM, 1968 There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home. -Ken Olson, president, chairman, and founder of Digital Equipment Corp. , 1977 640 K ought to be enough for anybody. -Attributed to Bill Gates, chairman of Microsoft, 1981 Dell has a great business model, but that dog won’t scale. -John Shoemaker, head of Sun’s server division, 2000
 Internet and Intranet • International network of network that are commercial (private) and publicly owned, connecting thousands of different network from more 200 countries around the world. (Managing digital Firm Page 17, K. C Laudon)
Internet and Intranet • International network of network that are commercial (private) and publicly owned, connecting thousands of different network from more 200 countries around the world. (Managing digital Firm Page 17, K. C Laudon)
 Internet and Intranet • An internal network based on internet and World Wide Web Standards (Managing digital Firm Page 24, K. C Laudon) • Extranet • Private Intranet that is accessible to authorized outsiders. (Managing digital Firm Page 24, K. C Laudon)
Internet and Intranet • An internal network based on internet and World Wide Web Standards (Managing digital Firm Page 24, K. C Laudon) • Extranet • Private Intranet that is accessible to authorized outsiders. (Managing digital Firm Page 24, K. C Laudon)
 Internet Map • Internet map: http: //www. caida. org/tools/visualization/mapnet/Backbone s/
Internet Map • Internet map: http: //www. caida. org/tools/visualization/mapnet/Backbone s/
 Internet History • • 1836 Telegraph, Patented. 1858 -1866 Transatlantic cable. Europe and US 1876 Telephone by Alexander Graham Bell 1957 Sputnik launch (USSR), Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) Inside US Do. D 1962 - 1968 Packet-switching (PS) networks initiate as foundation of data transfer in internet 1969 the birth of ARPANET by Do. D 1971 ARPANET expanded to 15 nodes (23 host), email were introduce 1972 the first public demonstration of ARPANET connecting 40 host, Telnet were introduce
Internet History • • 1836 Telegraph, Patented. 1858 -1866 Transatlantic cable. Europe and US 1876 Telephone by Alexander Graham Bell 1957 Sputnik launch (USSR), Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) Inside US Do. D 1962 - 1968 Packet-switching (PS) networks initiate as foundation of data transfer in internet 1969 the birth of ARPANET by Do. D 1971 ARPANET expanded to 15 nodes (23 host), email were introduce 1972 the first public demonstration of ARPANET connecting 40 host, Telnet were introduce
 Internet History (con’t) 1973 • The first International connection of ARPANET to University College of London (England) and Royal Radar Establishment (Norway) • Ethernet and FTP (file transfer protocol) format were initiate, the idea of internet emerged. 1974 • TCP (Transmission Control Program) used as standard in ARPANET network • Telenet, commercial version of ARPANET launched. 1976 • Networking networks expanding. • UUCP (Unix-to-Unix Co. Py) created by AT&T Bell Labs and distributed together with UNIX • UNIX as operating system still used until now.
Internet History (con’t) 1973 • The first International connection of ARPANET to University College of London (England) and Royal Radar Establishment (Norway) • Ethernet and FTP (file transfer protocol) format were initiate, the idea of internet emerged. 1974 • TCP (Transmission Control Program) used as standard in ARPANET network • Telenet, commercial version of ARPANET launched. 1976 • Networking networks expanding. • UUCP (Unix-to-Unix Co. Py) created by AT&T Bell Labs and distributed together with UNIX • UNIX as operating system still used until now.
 Internet History (con’t) 1977 • E-mail become more popular • Internet became reality with 100 connected host. • THEORYNET became the fist network that provide email to more than 100 researcher. • Email format and specifications became standard • Public demonstration of ARPANET/Packet Radio Net/ SATNET Internet protocols through gateways. 1979 • News Groups introduced • USENET created with UUCP and still used until today • ARPA created Internet Configuration Control Board.
Internet History (con’t) 1977 • E-mail become more popular • Internet became reality with 100 connected host. • THEORYNET became the fist network that provide email to more than 100 researcher. • Email format and specifications became standard • Public demonstration of ARPANET/Packet Radio Net/ SATNET Internet protocols through gateways. 1979 • News Groups introduced • USENET created with UUCP and still used until today • ARPA created Internet Configuration Control Board.
 Internet History (con’t) 1981 • Various private and commercial network started to combine and connected. • BITNET ("Because It's Time NETwork”) started as first cooperative network at City University (New York) with first connection to Yale University 1982 • TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) dan Internet Protocol (IP) ), became future data communication standard. 1983 • Internet became bigger and bigger • Name server created, host naming with alphabet characters started. • Internet Activities Board (IAB) created replacing ICCB • Berkeley Labs launch UNIX 4. 2 BSD with TCP/IP
Internet History (con’t) 1981 • Various private and commercial network started to combine and connected. • BITNET ("Because It's Time NETwork”) started as first cooperative network at City University (New York) with first connection to Yale University 1982 • TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) dan Internet Protocol (IP) ), became future data communication standard. 1983 • Internet became bigger and bigger • Name server created, host naming with alphabet characters started. • Internet Activities Board (IAB) created replacing ICCB • Berkeley Labs launch UNIX 4. 2 BSD with TCP/IP
 Internet History (con’t) 1984 • Host connected reach 1000 hosts • Domain Name Server (DNS) implemented, host naming become less complicated 123. 456. 789. 10 = www. myuniversity. mydept. mynetwork. mycountry (www. unila. ac. id). 1986 • Internet power become reality with 5000 host connected and 241 news groups. • Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) created. 1987 • Internet commercialization, host number increased to 28. 000 • UUNET established provided commercial UUCP and Usenet access.
Internet History (con’t) 1984 • Host connected reach 1000 hosts • Domain Name Server (DNS) implemented, host naming become less complicated 123. 456. 789. 10 = www. myuniversity. mydept. mynetwork. mycountry (www. unila. ac. id). 1986 • Internet power become reality with 5000 host connected and 241 news groups. • Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) created. 1987 • Internet commercialization, host number increased to 28. 000 • UUNET established provided commercial UUCP and Usenet access.
 Internet History (con’t) 1988 • Introduction of Internet Relay Chat (IRC) 1989 • Host increase to 100, 000 hosts. • The first relay between commercial email and internet • Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and Internet Research Task Force (IRTF) established under IAB 1990 • Host increase to 300, 000 Hosts and 1, 000 News groups • ARPANET existence decrease • The World (world. std. com) the first company that provide internet service through dial up
Internet History (con’t) 1988 • Introduction of Internet Relay Chat (IRC) 1989 • Host increase to 100, 000 hosts. • The first relay between commercial email and internet • Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and Internet Research Task Force (IRTF) established under IAB 1990 • Host increase to 300, 000 Hosts and 1, 000 News groups • ARPANET existence decrease • The World (world. std. com) the first company that provide internet service through dial up
 Internet History (con’t) 1991 • Friendly User Interface ke WWW created. • Gopher created by Paul Lindner and Mark P. Mc. Cahill from university of Minnesota. • World-Wide Web (WWW) standard established by CERN; Tim Berners-Lee 1992 • Multimedia change the face of internet • Host number increase to 1 million, News groups reach 4, 000 • Established of Internet Society (ISOC) • The first MBONE audio multicast (March) dan video multicast (November). • "Surfing the Internet" introduced by by Jean Armour Polly.
Internet History (con’t) 1991 • Friendly User Interface ke WWW created. • Gopher created by Paul Lindner and Mark P. Mc. Cahill from university of Minnesota. • World-Wide Web (WWW) standard established by CERN; Tim Berners-Lee 1992 • Multimedia change the face of internet • Host number increase to 1 million, News groups reach 4, 000 • Established of Internet Society (ISOC) • The first MBONE audio multicast (March) dan video multicast (November). • "Surfing the Internet" introduced by by Jean Armour Polly.
 Internet History (con’t) 1993 • WWW revolution, 2 Million hosts and 600 WWW sites. • Business and Media really take notice of the Internet. • White house and United Nations on-line. • Mosaic popularity in internet as front end for WWW evolved to Netscape the most popular WWW browser at that time. 1994 • Internet commercialization started, 3 million host 10. 000 www sites and 10. 00 newsgroup • ARPANET/Internet 25 th year anniversary. • Local community started to connect directly to internet, US senate start to give information server access. • Internet Became life standard, the first Cyberbank opened
Internet History (con’t) 1993 • WWW revolution, 2 Million hosts and 600 WWW sites. • Business and Media really take notice of the Internet. • White house and United Nations on-line. • Mosaic popularity in internet as front end for WWW evolved to Netscape the most popular WWW browser at that time. 1994 • Internet commercialization started, 3 million host 10. 000 www sites and 10. 00 newsgroup • ARPANET/Internet 25 th year anniversary. • Local community started to connect directly to internet, US senate start to give information server access. • Internet Became life standard, the first Cyberbank opened
 Internet History (con’t) 1995 • 6. 5 Million Hosts, 100, 000 WWW Sites. • dial-up systems (by Compuserve, America Online, Prodigy) selling internet access • Domain name registration is not free any more. • Search Engine technology introduced. 1996 • Microsoft entering internet business, 12. 8 Million hosts and 0. 5 million WWW sites. • Telephone Technology through internet (VO-IP) became threat to telecommunication industry, they plead to US senate to banned this technology. (US Senate only banned this technology only for 1 year) • WWW wars between netscape dan microsoft started.
Internet History (con’t) 1995 • 6. 5 Million Hosts, 100, 000 WWW Sites. • dial-up systems (by Compuserve, America Online, Prodigy) selling internet access • Domain name registration is not free any more. • Search Engine technology introduced. 1996 • Microsoft entering internet business, 12. 8 Million hosts and 0. 5 million WWW sites. • Telephone Technology through internet (VO-IP) became threat to telecommunication industry, they plead to US senate to banned this technology. (US Senate only banned this technology only for 1 year) • WWW wars between netscape dan microsoft started.
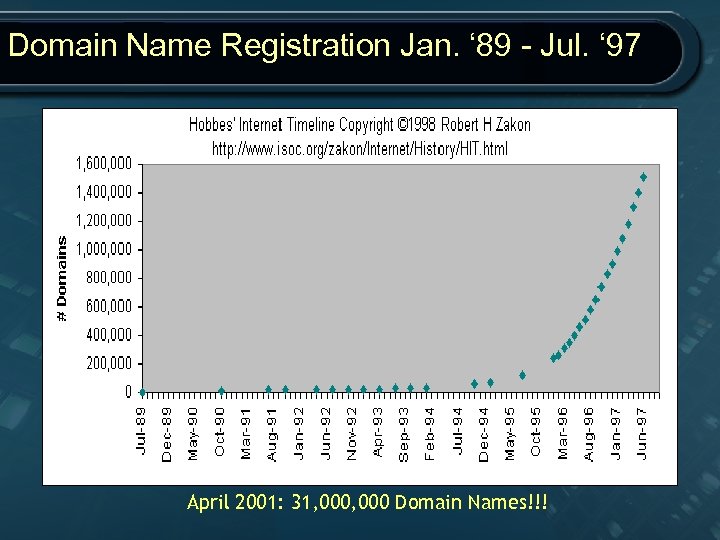 Domain Name Registration Jan. ‘ 89 - Jul. ‘ 97 April 2001: 31, 000 Domain Names!!!
Domain Name Registration Jan. ‘ 89 - Jul. ‘ 97 April 2001: 31, 000 Domain Names!!!
 September 2002 The Internet Reached Two Important Milestones: Ø 200, 000 IP Hosts > 840, 000 Users
September 2002 The Internet Reached Two Important Milestones: Ø 200, 000 IP Hosts > 840, 000 Users
 Internet Growth Trends • 2005 • The sky is the limits • Use search engine to find more information
Internet Growth Trends • 2005 • The sky is the limits • Use search engine to find more information
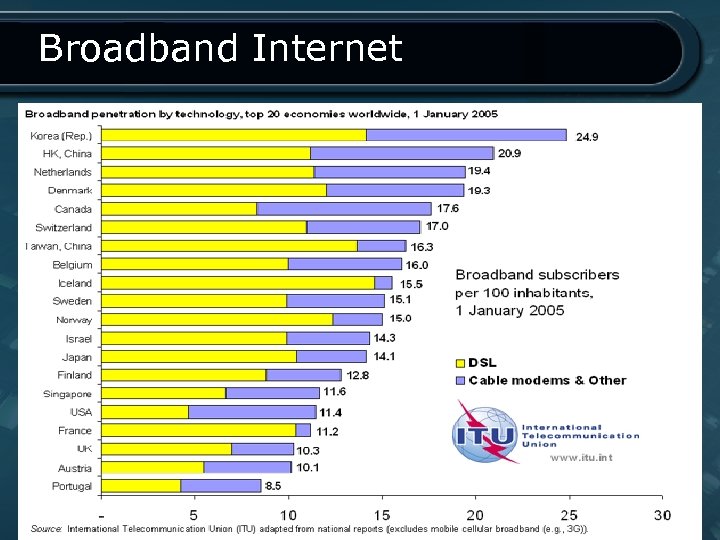 Broadband Internet
Broadband Internet
 Internet Growth Trends • • • 1977: 111 hosts on Internet 1981: 213 hosts 1983: 562 hosts 1984: 1, 000 hosts 1986: 5, 000 hosts 1987: 10, 000 hosts 1989: 100, 000 hosts 1992: 1, 000 hosts 2001: 150 – 175 million hosts 2002: over 200 million hosts By 2010, about 80% of the planet will be on the Internet
Internet Growth Trends • • • 1977: 111 hosts on Internet 1981: 213 hosts 1983: 562 hosts 1984: 1, 000 hosts 1986: 5, 000 hosts 1987: 10, 000 hosts 1989: 100, 000 hosts 1992: 1, 000 hosts 2001: 150 – 175 million hosts 2002: over 200 million hosts By 2010, about 80% of the planet will be on the Internet
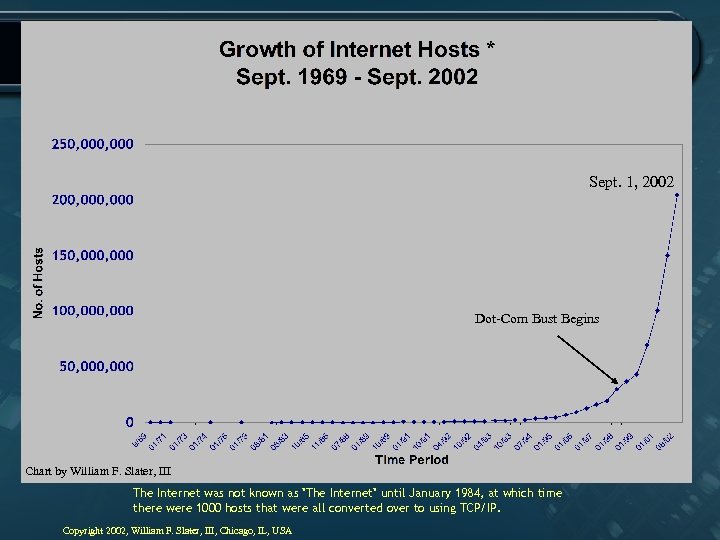 Sept. 1, 2002 Dot-Com Bust Begins Chart by William F. Slater, III The Internet was not known as "The Internet" until January 1984, at which time there were 1000 hosts that were all converted over to using TCP/IP. Copyright 2002, William F. Slater, III, Chicago, IL, USA
Sept. 1, 2002 Dot-Com Bust Begins Chart by William F. Slater, III The Internet was not known as "The Internet" until January 1984, at which time there were 1000 hosts that were all converted over to using TCP/IP. Copyright 2002, William F. Slater, III, Chicago, IL, USA
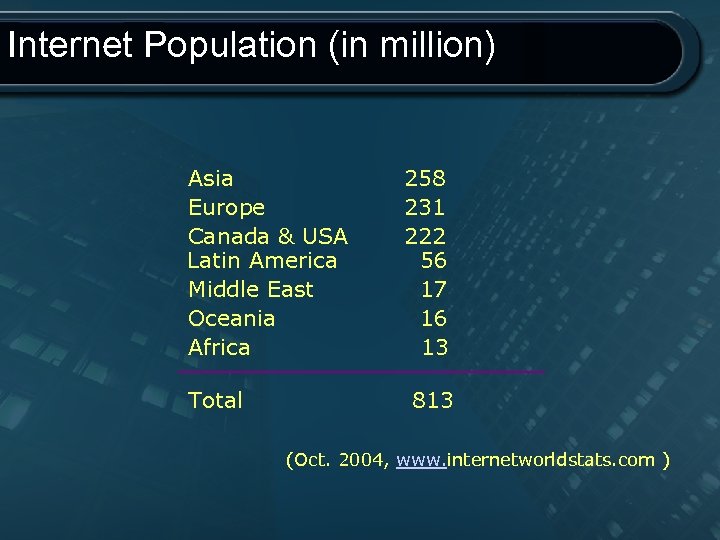 Internet Population (in million) Asia 258 Europe 231 Canada & USA 222 Latin America 56 Middle East 17 Oceania 16 Africa 13 Total 813 (Oct. 2004, www. internetworldstats. com )
Internet Population (in million) Asia 258 Europe 231 Canada & USA 222 Latin America 56 Middle East 17 Oceania 16 Africa 13 Total 813 (Oct. 2004, www. internetworldstats. com )
 Email and internet • INTERNET naming based on TCP/IP protocol • IP (Internet Protocol) • Based on 4 column between 0 and 255 and each column separated by dot. • xxx • 167. 205. 136. 1 • 35. 8. 7. 92 • This technology called IPv 4 (Internet Protocol Version 4)
Email and internet • INTERNET naming based on TCP/IP protocol • IP (Internet Protocol) • Based on 4 column between 0 and 255 and each column separated by dot. • xxx • 167. 205. 136. 1 • 35. 8. 7. 92 • This technology called IPv 4 (Internet Protocol Version 4)
 Email and internet (con’t) • IP address management in the world being distributed and manage by Inter. NIC where it will distributed to ISP (Internet Service Provider), • ISP will distributed to its user and customer. • DNS (domain name system) used to give flexibility to translate ip address number to non number identification. • 167. 205. 136. 1 = www. unila. ac. id • 208. 150. 216. 210 = www. kompas. com
Email and internet (con’t) • IP address management in the world being distributed and manage by Inter. NIC where it will distributed to ISP (Internet Service Provider), • ISP will distributed to its user and customer. • DNS (domain name system) used to give flexibility to translate ip address number to non number identification. • 167. 205. 136. 1 = www. unila. ac. id • 208. 150. 216. 210 = www. kompas. com
 Email and internet (con’t) • DNS concepts can be describe as • maiser. unila. ac. id • 1. 2. 3. 4 • 4 = country code • . id = Indonesia • . uk = United Kingdom (peter@jerk. edu. uk) • . us = United States (peter@mars. nasa. go) • . jp = Japan (shien@maca. ac. jp) • . au = Australia (bob@landiv. mil. au) • . sg = Singapore (head@intel. com)
Email and internet (con’t) • DNS concepts can be describe as • maiser. unila. ac. id • 1. 2. 3. 4 • 4 = country code • . id = Indonesia • . uk = United Kingdom (peter@jerk. edu. uk) • . us = United States (peter@mars. nasa. go) • . jp = Japan (shien@maca. ac. jp) • . au = Australia (bob@landiv. mil. au) • . sg = Singapore (head@intel. com)
 Email and internet (con’t) • maiser. unila. ac. id • 1. 2. 3. 4 • . ac / the third column = institution type • . ac. = Academic (admin@maiser. unila. ac. id) • . edu. = Education (admin@grep. mit. edu) • . mil. = militer (pentagon-info@mil. us) • . com/co. = commercial (snake@petshop. com) • . gov/go. = government (alatas@rty. deplu. gov. id) • . org / or = organization (info@golkar. org) • . net. = Internet Service Provider (server@idola. net. id) • . tv. = television • Web = web provide company • Sch = school
Email and internet (con’t) • maiser. unila. ac. id • 1. 2. 3. 4 • . ac / the third column = institution type • . ac. = Academic (admin@maiser. unila. ac. id) • . edu. = Education (admin@grep. mit. edu) • . mil. = militer (pentagon-info@mil. us) • . com/co. = commercial (snake@petshop. com) • . gov/go. = government (alatas@rty. deplu. gov. id) • . org / or = organization (info@golkar. org) • . net. = Internet Service Provider (server@idola. net. id) • . tv. = television • Web = web provide company • Sch = school
 Email and internet (con’t) • maiser. unila. ac. id • 1. 2. 3. 4 • . unila / 2 nd column = institution name • . itb. = Institut Teknologi Bandung (info@nic. itb. ac. id) • . ui. = Universitas Indonesia (puskom@ui. ac. di) • . bppt. = BPPT (info@bppt. go. id) • . ptme = PT. Metrodata Elektronik (sales@ptme. com) • . republika = Koran Republika (kontak@republika. co. id) • Maiser. / 1 st column = machine/host name/sub institution • Webmaster@unila. ac. id maiser = komputer mail server • Info@cnrg. itb. ac. id cnrg = computer network research group • Info@xxx. oke. edu xxx = komputer xxx
Email and internet (con’t) • maiser. unila. ac. id • 1. 2. 3. 4 • . unila / 2 nd column = institution name • . itb. = Institut Teknologi Bandung (info@nic. itb. ac. id) • . ui. = Universitas Indonesia (puskom@ui. ac. di) • . bppt. = BPPT (info@bppt. go. id) • . ptme = PT. Metrodata Elektronik (sales@ptme. com) • . republika = Koran Republika (kontak@republika. co. id) • Maiser. / 1 st column = machine/host name/sub institution • Webmaster@unila. ac. id maiser = komputer mail server • Info@cnrg. itb. ac. id cnrg = computer network research group • Info@xxx. oke. edu xxx = komputer xxx
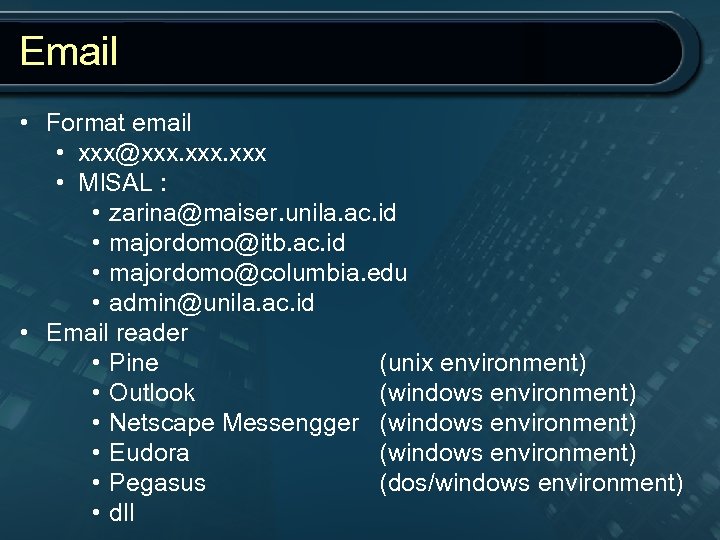 Email • Format email • xxx@xxx. xxx • MISAL : • zarina@maiser. unila. ac. id • majordomo@itb. ac. id • majordomo@columbia. edu • admin@unila. ac. id • Email reader • Pine (unix environment) • Outlook (windows environment) • Netscape Messengger (windows environment) • Eudora (windows environment) • Pegasus (dos/windows environment) • dll
Email • Format email • xxx@xxx. xxx • MISAL : • zarina@maiser. unila. ac. id • majordomo@itb. ac. id • majordomo@columbia. edu • admin@unila. ac. id • Email reader • Pine (unix environment) • Outlook (windows environment) • Netscape Messengger (windows environment) • Eudora (windows environment) • Pegasus (dos/windows environment) • dll
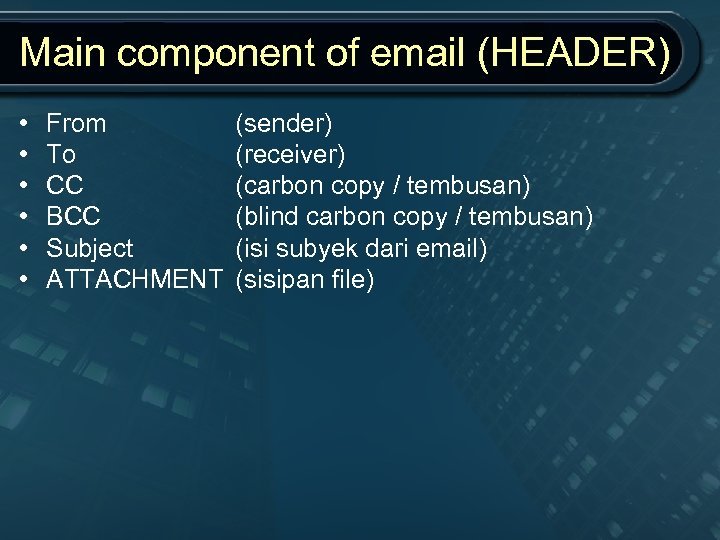 Main component of email (HEADER) • • • From To CC BCC Subject ATTACHMENT (sender) (receiver) (carbon copy / tembusan) (blind carbon copy / tembusan) (isi subyek dari email) (sisipan file)
Main component of email (HEADER) • • • From To CC BCC Subject ATTACHMENT (sender) (receiver) (carbon copy / tembusan) (blind carbon copy / tembusan) (isi subyek dari email) (sisipan file)
 Email Internal Universitas Lampung • Telnet ke email server menggunakan • Telnet client (windows XP) • Server telnet + email : maiser. unila. ac. id • Web based email • http: //webmail. unila. ac. id server utama • http: //students. unila. ac. id internal webmail
Email Internal Universitas Lampung • Telnet ke email server menggunakan • Telnet client (windows XP) • Server telnet + email : maiser. unila. ac. id • Web based email • http: //webmail. unila. ac. id server utama • http: //students. unila. ac. id internal webmail
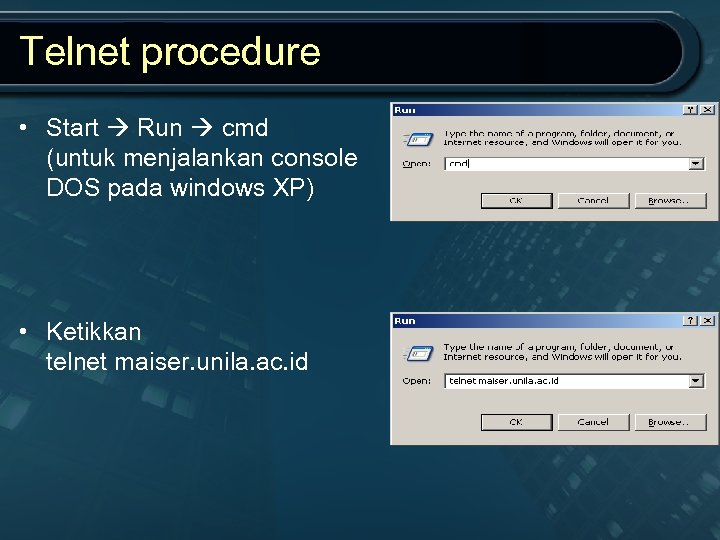 Telnet procedure • Start Run cmd (untuk menjalankan console DOS pada windows XP) • Ketikkan telnet maiser. unila. ac. id
Telnet procedure • Start Run cmd (untuk menjalankan console DOS pada windows XP) • Ketikkan telnet maiser. unila. ac. id
 Virus • 1949 - Theories for self-replicating programs are first developed • 1981 - Apple Viruses 1, 2, and 3 are some of the first viruses "in the wild, " or public domain. Found on the Apple II operating system, the viruses spread through Texas A&M via pirated computer games. • 1983 - Fred Cohen, while working on his dissertation, formally defines a computer virus as "a computer program that can affect other computer programs by modifying them in such a way as to include a (possibly evolved) copy of itself. " • 1986 - Two programmers named Basit and Amjad replace the executable code in the boot sector of a floppy disk with their own code designed to infect each 360 kb floppy accessed on any drive. Infected floppies had "© Brain" for a volume label.
Virus • 1949 - Theories for self-replicating programs are first developed • 1981 - Apple Viruses 1, 2, and 3 are some of the first viruses "in the wild, " or public domain. Found on the Apple II operating system, the viruses spread through Texas A&M via pirated computer games. • 1983 - Fred Cohen, while working on his dissertation, formally defines a computer virus as "a computer program that can affect other computer programs by modifying them in such a way as to include a (possibly evolved) copy of itself. " • 1986 - Two programmers named Basit and Amjad replace the executable code in the boot sector of a floppy disk with their own code designed to infect each 360 kb floppy accessed on any drive. Infected floppies had "© Brain" for a volume label.
 Virus (con’t) • 1988 - Jerusalem, is unleashed. Activated every Friday the 13 th, the virus affects both. EXE and. COM files and deletes any programs run on that day. • 1990 - Symantec launches Norton Anti. Virus, one of the first anti-virus programs developed by a large company. • 1991 - Tequila is the first widespread polymorphic virus found in the wild. Polymorphic viruses make detection difficult for virus scanners by changing their appearance with each new infection. • 1992 - 1300 viruses are in existence, an increase of 420% from December of 1990.
Virus (con’t) • 1988 - Jerusalem, is unleashed. Activated every Friday the 13 th, the virus affects both. EXE and. COM files and deletes any programs run on that day. • 1990 - Symantec launches Norton Anti. Virus, one of the first anti-virus programs developed by a large company. • 1991 - Tequila is the first widespread polymorphic virus found in the wild. Polymorphic viruses make detection difficult for virus scanners by changing their appearance with each new infection. • 1992 - 1300 viruses are in existence, an increase of 420% from December of 1990.
 Virus (con’t) • 1999 - The Melissa virus, W 97 M/Melissa, executes a macro in a document attached to an email, which forwards the document to 50 people in the user's Outlook address book. The virus also infects other Word documents and subsequently mails them out as attachments. Melissa spread faster than any other previous virus. • 2000 - The Love Bug, also known as the ILOVEYOU virus, sends itself out via Outlook, much like Melissa. The virus comes as a VBS attachment and deletes files, including MP 3, MP 2, and JPG. It also sends usernames and passwords to the virus' author. W 97 M. Resume. A, a new variation of the Melissa virus, is determined to be in the wild. The "resume" virus acts much like Melissa, using a Word macro to infect Outlook and spread itself.
Virus (con’t) • 1999 - The Melissa virus, W 97 M/Melissa, executes a macro in a document attached to an email, which forwards the document to 50 people in the user's Outlook address book. The virus also infects other Word documents and subsequently mails them out as attachments. Melissa spread faster than any other previous virus. • 2000 - The Love Bug, also known as the ILOVEYOU virus, sends itself out via Outlook, much like Melissa. The virus comes as a VBS attachment and deletes files, including MP 3, MP 2, and JPG. It also sends usernames and passwords to the virus' author. W 97 M. Resume. A, a new variation of the Melissa virus, is determined to be in the wild. The "resume" virus acts much like Melissa, using a Word macro to infect Outlook and spread itself.
 Virus (con’t) • 2001 • The Anna Kournikova virus, also known as VBS/SST. • It spreads by sending copies of itself to the entire address book in Microsoft Outlook. • It is believed that this virus was created with a so-called virus creation kit, a program which can enable even a novice programmer to create these malicious programs. • The Code Red I and II worms attacked computer networks in July and August. • According to Computer Economics they affected over 700, 000 computers and caused upwards of 2 billion in damages. • A worm spreads through external and (then) internal computer networks, as opposed to a virus which infects computers via email and certain websites. • Code Red took advantage of a vulnerability in Microsoft's Windows 2000 and Windows NT server software. • Microsoft developed a patch to protect networks against the worm, and admits that they too were attacked. Other major companies affected include AT&T, and the AP.
Virus (con’t) • 2001 • The Anna Kournikova virus, also known as VBS/SST. • It spreads by sending copies of itself to the entire address book in Microsoft Outlook. • It is believed that this virus was created with a so-called virus creation kit, a program which can enable even a novice programmer to create these malicious programs. • The Code Red I and II worms attacked computer networks in July and August. • According to Computer Economics they affected over 700, 000 computers and caused upwards of 2 billion in damages. • A worm spreads through external and (then) internal computer networks, as opposed to a virus which infects computers via email and certain websites. • Code Red took advantage of a vulnerability in Microsoft's Windows 2000 and Windows NT server software. • Microsoft developed a patch to protect networks against the worm, and admits that they too were attacked. Other major companies affected include AT&T, and the AP.
 Virus (con’t) • 2004 - Trojan. Xombe, Randex, Bizex, Witty, MP 3 Concept, Sasser, Mac OS X, W 64. Rugrat. 3344, Symb/Cabir-A, JS/Scob. A, WCE/Duts-A, W 32/Amus-A, • 2004 - social engineering taking the lead in propagation techniques. Trojan. Xombe was sent out to a wide audience. • It posed as a message from Microsoft Windows Update asking you to run the attached revision to XP Service Pack 1. • In February it was demonstrated that virus writers were starting to ply their craft for money. A German magazine managed to buy a list of infected IP addresses from a distributor of the virus Randex. These IP addresses were for sale to spammers who could use the infected machines as mail zombies. • In April saw the Sasser worm which is the first to effectively use the LSASS Windows vulnerability; a vulnerability that allowed the worm to spread via an open FTP port instead of through E-mail • In June Symb/Cabir-A appeared to infect Nokia Series 60 mobile phones. The worm is designed to spread to nearby Bluetoothenabled devices.
Virus (con’t) • 2004 - Trojan. Xombe, Randex, Bizex, Witty, MP 3 Concept, Sasser, Mac OS X, W 64. Rugrat. 3344, Symb/Cabir-A, JS/Scob. A, WCE/Duts-A, W 32/Amus-A, • 2004 - social engineering taking the lead in propagation techniques. Trojan. Xombe was sent out to a wide audience. • It posed as a message from Microsoft Windows Update asking you to run the attached revision to XP Service Pack 1. • In February it was demonstrated that virus writers were starting to ply their craft for money. A German magazine managed to buy a list of infected IP addresses from a distributor of the virus Randex. These IP addresses were for sale to spammers who could use the infected machines as mail zombies. • In April saw the Sasser worm which is the first to effectively use the LSASS Windows vulnerability; a vulnerability that allowed the worm to spread via an open FTP port instead of through E-mail • In June Symb/Cabir-A appeared to infect Nokia Series 60 mobile phones. The worm is designed to spread to nearby Bluetoothenabled devices.
 Virus (con’t) • 2005 - Bropia, Troj/Bank. Ash, Commwarrior, Chod • In 2005 the end of January saw the Bropia Worm which targets MSN Messenger for spreading. • The 9 th of February then saw Troj/Bank. Ash, the first Trojan to attack the new (still in beta) Microsoft Anti. Spyware product. • This Trojan also was reported to go after various British on-line banking services. • The start of March saw distribution of another mobile phone worm: Commwarrior, which spread via MMS messaging. • The end of March/start of April saw variants of Chod appear. This is a sophisticated worm that spreads via E-mail and the MSN Messaging client.
Virus (con’t) • 2005 - Bropia, Troj/Bank. Ash, Commwarrior, Chod • In 2005 the end of January saw the Bropia Worm which targets MSN Messenger for spreading. • The 9 th of February then saw Troj/Bank. Ash, the first Trojan to attack the new (still in beta) Microsoft Anti. Spyware product. • This Trojan also was reported to go after various British on-line banking services. • The start of March saw distribution of another mobile phone worm: Commwarrior, which spread via MMS messaging. • The end of March/start of April saw variants of Chod appear. This is a sophisticated worm that spreads via E-mail and the MSN Messaging client.
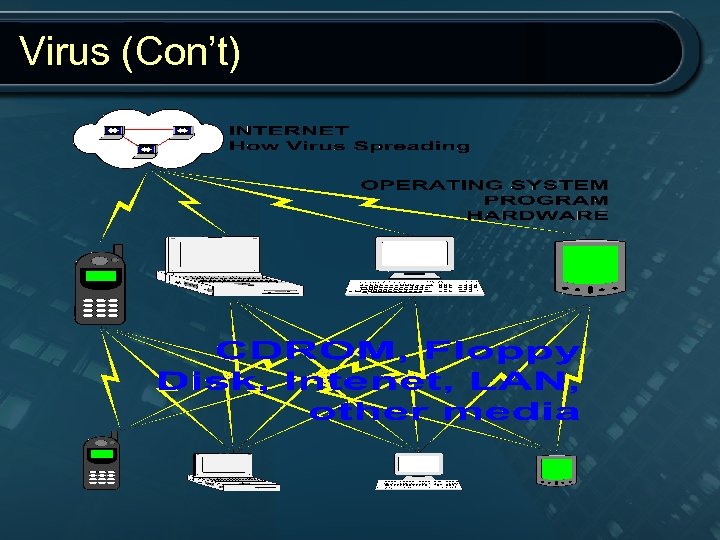 Virus (Con’t)
Virus (Con’t)


