580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Influence of native-language phonology How are words stored? Abstract phonological representation Details omitted, only contrastive info stored Exemplar Details retained
Influence of native-language phonology How are words stored? Abstract phonological representation Details omitted, only contrastive info stored Exemplar Details retained
 Influence of native-language phonology How are words recognized? Abstract phonological representation Details stripped and then compared with other abstract entries in the mental lexicon
Influence of native-language phonology How are words recognized? Abstract phonological representation Details stripped and then compared with other abstract entries in the mental lexicon
 Influence of native-language phonology How are words recognized? Abstract phonological representation Details stripped and then compared with other abstract entries in the mental lexicon Examplar model Concrete, detailed word compared to other exemplar store with details
Influence of native-language phonology How are words recognized? Abstract phonological representation Details stripped and then compared with other abstract entries in the mental lexicon Examplar model Concrete, detailed word compared to other exemplar store with details
 Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language
Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language
![Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e] Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e]](https://present5.com/presentation/580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264/image-5.jpg) Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e] and [ɛ] [netə] granddaughter [nɛtə] clean
Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e] and [ɛ] [netə] granddaughter [nɛtə] clean
![Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e] Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e]](https://present5.com/presentation/580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264/image-6.jpg) Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e] and [ɛ] [netə] granddaughter [nɛtə] clean In Spanish [e] and [ɛ] are allophones of the same phoneme
Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [e] and [ɛ] [netə] granddaughter [nɛtə] clean In Spanish [e] and [ɛ] are allophones of the same phoneme
![Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [o] Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [o]](https://present5.com/presentation/580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264/image-7.jpg) Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [o] and [ɔ] [donə] he gives [dɔnə] lady In Spanish [o] and [ɔ] are allophones of the same phoneme
Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [o] and [ɔ] [donə] he gives [dɔnə] lady In Spanish [o] and [ɔ] are allophones of the same phoneme
![Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [s] Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [s]](https://present5.com/presentation/580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264/image-8.jpg) Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [s] and [z] [kazə] house [kasə] he hunts In Spanish [s] and [z] are allophones of the same phoneme
Influence of native-language phonology Let's look at how bilinguals process language Catalan distinguishes [s] and [z] [kazə] house [kasə] he hunts In Spanish [s] and [z] are allophones of the same phoneme
 Influence of native-language phonology They compare two groups of speakers' Spanish/Catalan bilinguals who are Catalan dominant Spanish/Catalan bilinguals who are Spanish dominant
Influence of native-language phonology They compare two groups of speakers' Spanish/Catalan bilinguals who are Catalan dominant Spanish/Catalan bilinguals who are Spanish dominant
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not?
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not?
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not? If you hear the same word a second time RT goes down This is evidence that you heard the word previously
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not? If you hear the same word a second time RT goes down This is evidence that you heard the word previously
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not? If you hear the same word a second time RT goes down This is evidence that you heard the word previously If a Catalan speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [nɛtə] again, there would be a priming effect
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not? If you hear the same word a second time RT goes down This is evidence that you heard the word previously If a Catalan speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [nɛtə] again, there would be a priming effect
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not? If you hear the same word a second time RT goes down This is evidence that you heard the word previously If a Catalan speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [nɛtə] again, there would be a priming effect If a Catalan speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [netə], there would not be a priming effect
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan Is the word you heard real or not? If you hear the same word a second time RT goes down This is evidence that you heard the word previously If a Catalan speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [nɛtə] again, there would be a priming effect If a Catalan speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [netə], there would not be a priming effect
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan If a monolingual Spanish speaker heard [netə] and later on heard [netə], there would be a priming effect
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan If a monolingual Spanish speaker heard [netə] and later on heard [netə], there would be a priming effect
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan If a monolingual Spanish speaker heard [netə] and later on heard [netə], there would be a priming effect If a monolingual Spanish speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [netə], would there be a priming effect because the words are phonologically identical?
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan If a monolingual Spanish speaker heard [netə] and later on heard [netə], there would be a priming effect If a monolingual Spanish speaker heard [nɛtə] and later on heard [netə], would there be a priming effect because the words are phonologically identical?
 Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan But the participants where bilingual so that would be different, right?
Influence of native-language phonology Lexical decision task done in Catalan But the participants where bilingual so that would be different, right?
 Influence of native-language phonology Diamonds: priming effect for repeated words Same for Catalan and Spanish dominant
Influence of native-language phonology Diamonds: priming effect for repeated words Same for Catalan and Spanish dominant
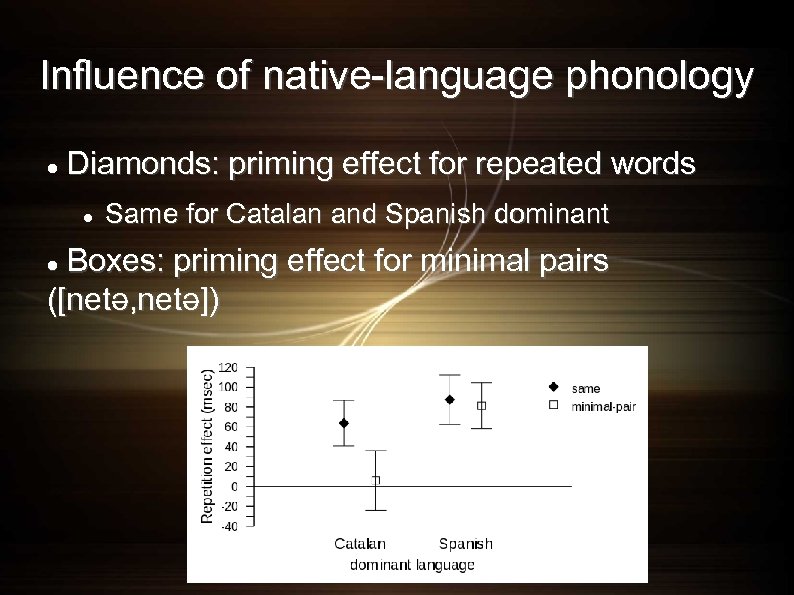 Influence of native-language phonology Diamonds: priming effect for repeated words Same for Catalan and Spanish dominant Boxes: priming effect for minimal pairs ([netə, netə])
Influence of native-language phonology Diamonds: priming effect for repeated words Same for Catalan and Spanish dominant Boxes: priming effect for minimal pairs ([netə, netə])
![Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [netə, netə] are minimal Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [netə, netə] are minimal](https://present5.com/presentation/580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264/image-19.jpg) Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [netə, netə] are minimal pairs
Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [netə, netə] are minimal pairs
![Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [nɛtə, netə] are minimal Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [nɛtə, netə] are minimal](https://present5.com/presentation/580eb5eb241a5fcbf9c3d40e9c981264/image-20.jpg) Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [nɛtə, netə] are minimal pairs Spanish dominant process [netə, netə] as being the same word, even though they speak Catalan
Influence of native-language phonology Catalan dominants have no priming because [nɛtə, netə] are minimal pairs Spanish dominant process [netə, netə] as being the same word, even though they speak Catalan
 Influence of native-language phonology If word recognition is exemplar (detailed) the Spanish speakers should have correctly matched [nɛtə, netə]
Influence of native-language phonology If word recognition is exemplar (detailed) the Spanish speakers should have correctly matched [nɛtə, netə]
 Influence of native-language phonology If word recognition is exemplar (detailed) the Spanish speakers should have correctly matched [nɛtə, netə] If word recognition is abstract, Spanish speakers would use their native phonology, strip irrelevant differences such [ɛ, e], and perceive [nɛtə, netə] to be identical
Influence of native-language phonology If word recognition is exemplar (detailed) the Spanish speakers should have correctly matched [nɛtə, netə] If word recognition is abstract, Spanish speakers would use their native phonology, strip irrelevant differences such [ɛ, e], and perceive [nɛtə, netə] to be identical
 Influence of native-language phonology If word recognition is exemplar (detailed) the Spanish speakers should have correctly matched [nɛtə, netə] If word recognition is abstract, Spanish speakers would use their native phonology, strip irrelevant differences such [ɛ, e], and perceive [nɛtə, netə] to be identical This is evidence for abstract phonological storage
Influence of native-language phonology If word recognition is exemplar (detailed) the Spanish speakers should have correctly matched [nɛtə, netə] If word recognition is abstract, Spanish speakers would use their native phonology, strip irrelevant differences such [ɛ, e], and perceive [nɛtə, netə] to be identical This is evidence for abstract phonological storage


