inflam. diseases (2).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88
 Inflammatory diseases of female generative organs. Particularity of duration among girls. Lecture : Antonova G. A.
Inflammatory diseases of female generative organs. Particularity of duration among girls. Lecture : Antonova G. A.
 n For the septic process it is not enough only going infection because of in the organism of woman there special mechanism, protecting women from diseases. These are processes of a common and local character. There are two tites of infections of sexual organs: septic and specific. Septic infections may be due to trauma of sexual organs. It is possible mechanic trauma- medical abortion, sounding of uterine cavity, termal trauma, chemical trauma.
n For the septic process it is not enough only going infection because of in the organism of woman there special mechanism, protecting women from diseases. These are processes of a common and local character. There are two tites of infections of sexual organs: septic and specific. Septic infections may be due to trauma of sexual organs. It is possible mechanic trauma- medical abortion, sounding of uterine cavity, termal trauma, chemical trauma.
 Classification of inflammatory diseases of septic etiology: According to clinical duration : n Acute - duration of its 2 - 3 weeks n Sub-acute - till 6 weeks n chronic – more than 6 weeks According to localization: n inflammation of external sexual organs n inflammation of internal sexual organs n
Classification of inflammatory diseases of septic etiology: According to clinical duration : n Acute - duration of its 2 - 3 weeks n Sub-acute - till 6 weeks n chronic – more than 6 weeks According to localization: n inflammation of external sexual organs n inflammation of internal sexual organs n
 Diagnostic of inflammatory diseases of generative tract. n n n n clinical picture examination in speculum colposcopy bacteriological examination Microscopy Bi- manual examination
Diagnostic of inflammatory diseases of generative tract. n n n n clinical picture examination in speculum colposcopy bacteriological examination Microscopy Bi- manual examination
 Particularity duration of inflammatory diseases among girls n n There are prevalence of external sexual organs inflammations vulvitis. Sometimes vulva- vaginitis are possible. External sexual organs are – vulva and Bartholian glands. Internal sexual organs arevagina, uterus, cervix, uterine tubes, ovaries.
Particularity duration of inflammatory diseases among girls n n There are prevalence of external sexual organs inflammations vulvitis. Sometimes vulva- vaginitis are possible. External sexual organs are – vulva and Bartholian glands. Internal sexual organs arevagina, uterus, cervix, uterine tubes, ovaries.
 Clinic of vulvitis : n n n Hyperemia and edema of external sexual organs, purulent discharges, Hyperemia of the internal surface of femurs. Complaints are: pruritus , itching at the external sexual organs , weakness. As a rule girls have secondary colpitis due to spreading infection from vagina in cases of heavy discharges.
Clinic of vulvitis : n n n Hyperemia and edema of external sexual organs, purulent discharges, Hyperemia of the internal surface of femurs. Complaints are: pruritus , itching at the external sexual organs , weakness. As a rule girls have secondary colpitis due to spreading infection from vagina in cases of heavy discharges.
 Treatment of vulvitis: n n Bed rest To treat condition , that is reason of vulvitis. Toilet of external sexual organs, using a slight solution of potassium permanganate, t -rae chamomile, 3% sol. of boric acid. In cases of severe itching to use anesthetic ointment.
Treatment of vulvitis: n n Bed rest To treat condition , that is reason of vulvitis. Toilet of external sexual organs, using a slight solution of potassium permanganate, t -rae chamomile, 3% sol. of boric acid. In cases of severe itching to use anesthetic ointment.
 Acute endometritis n n It is inflammation of endometrium. As a rule it occurs on 3 -4 day after abortion or another intra uterine intervention Temperature is high, pulse rate is frequent, there is headache, there is disturbance of a common condition. The duration of disease 7— 8 days.
Acute endometritis n n It is inflammation of endometrium. As a rule it occurs on 3 -4 day after abortion or another intra uterine intervention Temperature is high, pulse rate is frequent, there is headache, there is disturbance of a common condition. The duration of disease 7— 8 days.
 Acute endometritis : n After a chill temperature of body will be 39° and high. Uterus is big, after a temperature decreasing it will be heavy discharges from vagina.
Acute endometritis : n After a chill temperature of body will be 39° and high. Uterus is big, after a temperature decreasing it will be heavy discharges from vagina.
 Treatment. Bed rest. Ice on the abdomen. Anti- bacterial treatment. Infusion therapy. desensebilizated treatment gently uterus contracted drugs. Immunomodulator’s For imrovement of lochia going away- spasmolytic drugs Vitamino- therapy intrauterine lavage
Treatment. Bed rest. Ice on the abdomen. Anti- bacterial treatment. Infusion therapy. desensebilizated treatment gently uterus contracted drugs. Immunomodulator’s For imrovement of lochia going away- spasmolytic drugs Vitamino- therapy intrauterine lavage
 Hyperbolic oxygenation (HBO) n n n n Anti- hypoxic effect antiparetic effect detoxication uterotonic effect Immunocorregic effect Increasing of regenerative processes Decreasing of the medicamental therapy volume
Hyperbolic oxygenation (HBO) n n n n Anti- hypoxic effect antiparetic effect detoxication uterotonic effect Immunocorregic effect Increasing of regenerative processes Decreasing of the medicamental therapy volume
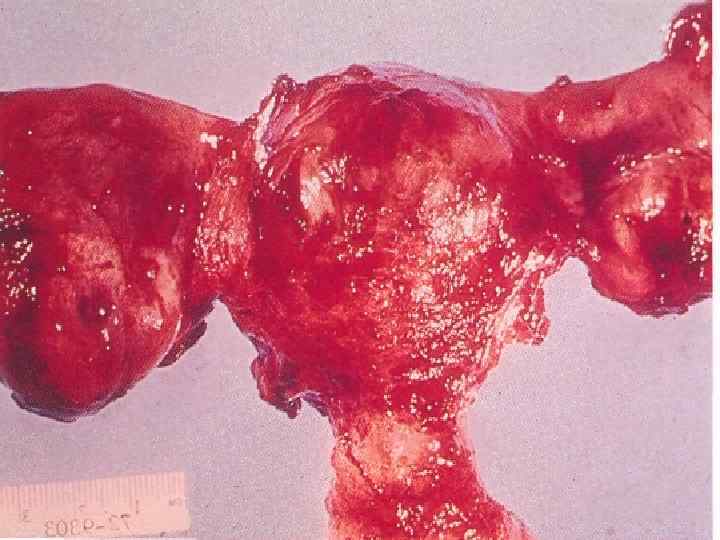
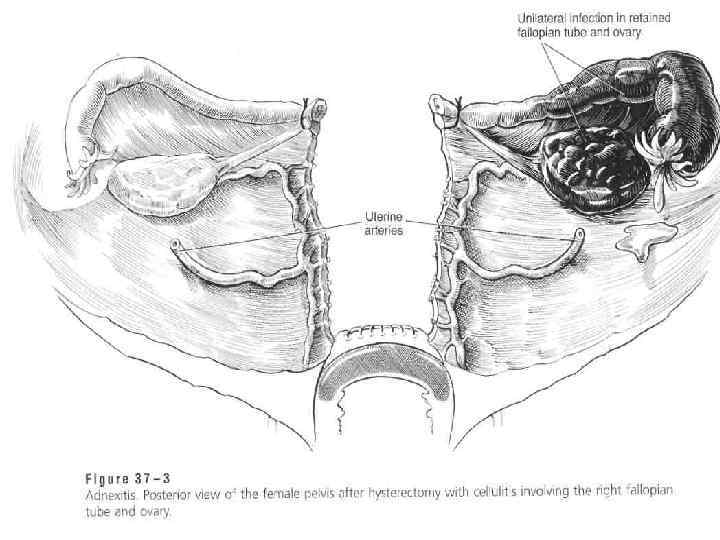
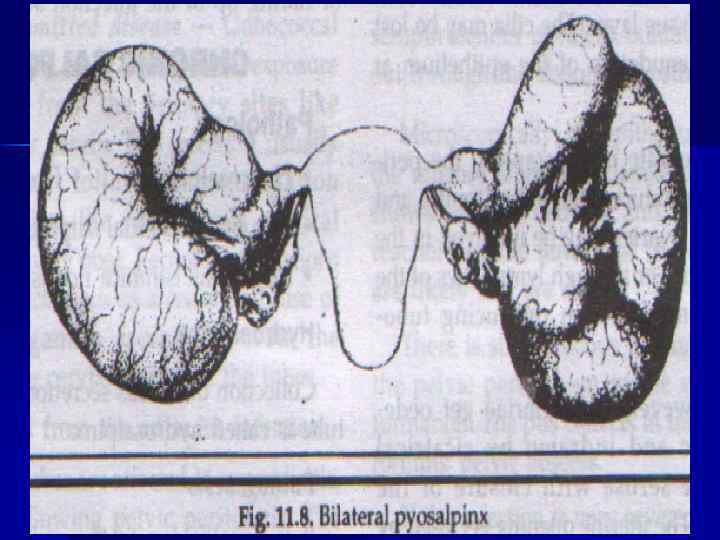
 n Such disease are possible as salpingitis, oophoritis, together of its – adnexitis. As a rule, this process is on one side It is possible catarrhal and purulent salpingitis. Sactosalpinx is oblitirated tube with fluid inside. Pyosalpinx – tube is full, of pus.
n Such disease are possible as salpingitis, oophoritis, together of its – adnexitis. As a rule, this process is on one side It is possible catarrhal and purulent salpingitis. Sactosalpinx is oblitirated tube with fluid inside. Pyosalpinx – tube is full, of pus.
 n Sometime, in a heavy cases it is possible to have pyovarum, due to that it is possible to have amilodosis of kidney, Sometimes is possible a tubo- ovarian abscess formation.
n Sometime, in a heavy cases it is possible to have pyovarum, due to that it is possible to have amilodosis of kidney, Sometimes is possible a tubo- ovarian abscess formation.
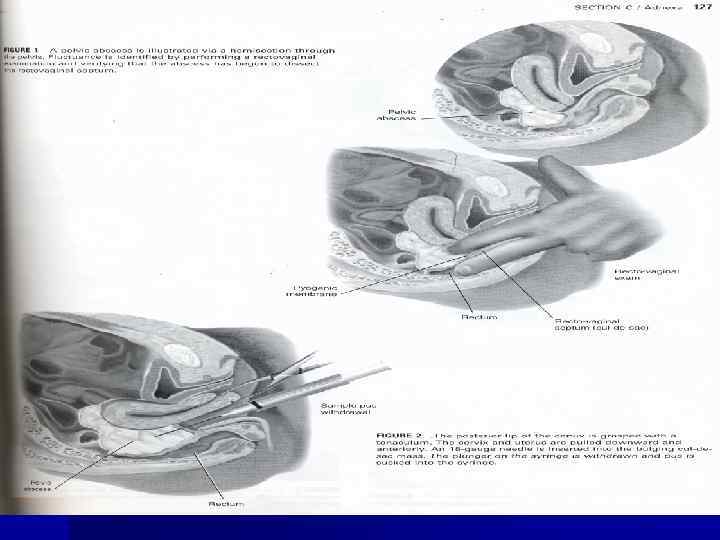
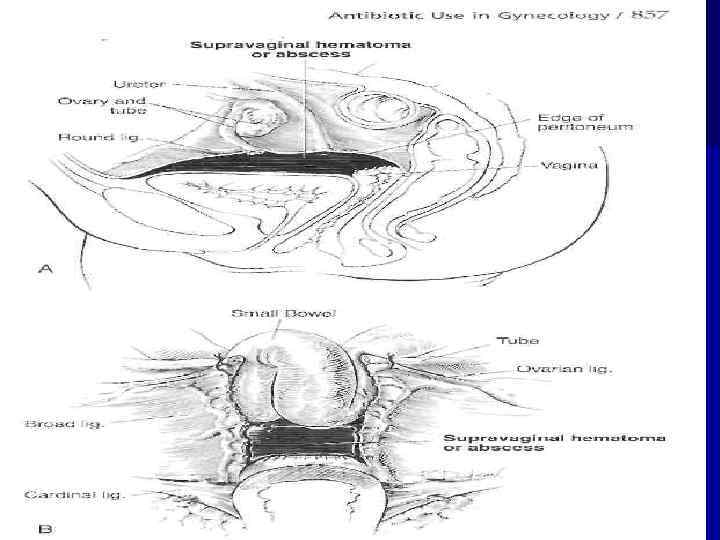
 n In cases of going infection on a peritonium is possible to have a post partum septic pelvioperitonitis. Fluid is collected behind of uterus and uterus is going to anterior part of a pelvis. Exudate may be serous or purulent. During vaginal examination the posterior fornix will be flattened.
n In cases of going infection on a peritonium is possible to have a post partum septic pelvioperitonitis. Fluid is collected behind of uterus and uterus is going to anterior part of a pelvis. Exudate may be serous or purulent. During vaginal examination the posterior fornix will be flattened.
 n In cases of pelvio-peritonitis there is such clinic as, rapid pulse rate, nausea, delay of gases. In cases of adherences formation, the process will be located and it will be fluid.
n In cases of pelvio-peritonitis there is such clinic as, rapid pulse rate, nausea, delay of gases. In cases of adherences formation, the process will be located and it will be fluid.
 n The upper borderline in this cases will be because of adherences.
n The upper borderline in this cases will be because of adherences.
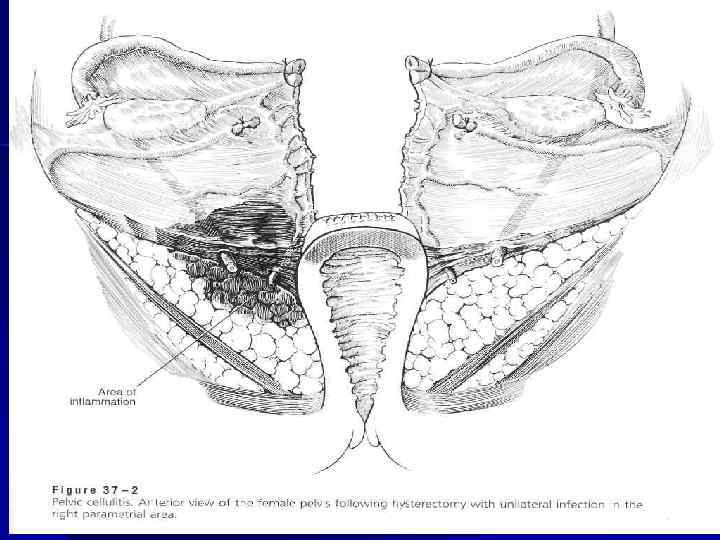
 n In the cases of spreading infection through the lymphatic vessels it is possible to have a parametritis. It is possible to have a lateral parametritis, anterior parametritis, posterior parametritis. In cases of inflammation of the all cellular tissue of small pelvis it is pelvio-cellulitis.
n In the cases of spreading infection through the lymphatic vessels it is possible to have a parametritis. It is possible to have a lateral parametritis, anterior parametritis, posterior parametritis. In cases of inflammation of the all cellular tissue of small pelvis it is pelvio-cellulitis.
 n In cases of parametritis the infection is sрreading through the cervical injuring or the place of placenta attachment.
n In cases of parametritis the infection is sрreading through the cervical injuring or the place of placenta attachment.
 n High temperature, in case if the fluid be purulent is during 1— 2 weeks. At 12— 14% of all patient there is hectic temperature, infiltration will be soft. If the parametrium would not be cut the pus is going through the large ishia’s foramen, on femours.
n High temperature, in case if the fluid be purulent is during 1— 2 weeks. At 12— 14% of all patient there is hectic temperature, infiltration will be soft. If the parametrium would not be cut the pus is going through the large ishia’s foramen, on femours.
 n It is possible to have thrombophlebtis of the big veins of pelvis and low extremities – thrombophlebitic form of diseases, particulary, if a women willl have varicous veins.
n It is possible to have thrombophlebtis of the big veins of pelvis and low extremities – thrombophlebitic form of diseases, particulary, if a women willl have varicous veins.
 n If there is no of supuration of thromb, through 1— 2 weeks the process will be finished.
n If there is no of supuration of thromb, through 1— 2 weeks the process will be finished.
 n Metrothrombophlebitis is in cases, when endometritis is not finished at 7 -8 days. There is a rapid pulse rate ( Malar’s symptom ) in this cases. The picture of septico- pyemia is in this cases.
n Metrothrombophlebitis is in cases, when endometritis is not finished at 7 -8 days. There is a rapid pulse rate ( Malar’s symptom ) in this cases. The picture of septico- pyemia is in this cases.
 Peritonitis: n The role of uterus as a place of infection is due to presence in uterine cavity of cloth, decidua tissue, that are the food for microorganisms. At the same time there is a wide surface in uterus for resorption of bacterial toxins and possibility going of toxins in blood circulation.
Peritonitis: n The role of uterus as a place of infection is due to presence in uterine cavity of cloth, decidua tissue, that are the food for microorganisms. At the same time there is a wide surface in uterus for resorption of bacterial toxins and possibility going of toxins in blood circulation.
 Etiology of peritonitis: n n Leading role intestinal rode, staphylococcus, protea take place. In the last time there is a role of anaerobic bacteria, which are conditionally – pathogenic and have a resistance to antibiotics and anti- bacterial medicine.
Etiology of peritonitis: n n Leading role intestinal rode, staphylococcus, protea take place. In the last time there is a role of anaerobic bacteria, which are conditionally – pathogenic and have a resistance to antibiotics and anti- bacterial medicine.
 n As a rule at an exudate there is high level of potassium, but in blood circulation – deficiency of its. Its makes more sever intestinal paresis, bradycardia, arythmia.
n As a rule at an exudate there is high level of potassium, but in blood circulation – deficiency of its. Its makes more sever intestinal paresis, bradycardia, arythmia.
 Classification of peritonitis. n n n 1. According to etiology 2. according to character of exudates ( serous, serous- fibrinous, purulent, hemorragical) 3. according to spreading (local and common) 4. according to clinic picture: The first phase — reactive, II — toxic, III — terminal.
Classification of peritonitis. n n n 1. According to etiology 2. according to character of exudates ( serous, serous- fibrinous, purulent, hemorragical) 3. according to spreading (local and common) 4. according to clinic picture: The first phase — reactive, II — toxic, III — terminal.
 n During vaginal examination the palpation of uterus and adnexa is not possible because of very painful Fornex posterior is tender. During of rectal examination there is flattened of rectum. Continuation of this stage of peritonitis is 2 -3 days.
n During vaginal examination the palpation of uterus and adnexa is not possible because of very painful Fornex posterior is tender. During of rectal examination there is flattened of rectum. Continuation of this stage of peritonitis is 2 -3 days.
 n Treatment in cases of peritonitis should be surgical. During 2 -4 hours should be before – operation preparing.
n Treatment in cases of peritonitis should be surgical. During 2 -4 hours should be before – operation preparing.
 Septic shock: n n The frequency of septic shock is from 3 till 10% among all post abortion diseases. Etiology – gram- negative microorganisms: intestinal rode, protea, clebsiella.
Septic shock: n n The frequency of septic shock is from 3 till 10% among all post abortion diseases. Etiology – gram- negative microorganisms: intestinal rode, protea, clebsiella.
 n n Pathogenesis: in cases of distoying of bacterium it will be endotoxin. It cause generalized injuring of endotelium, disturbed the system of hemostasis. It will be generated disturbance of microcirculation. Decreasing of BP will be as a result of disturbance of micro- circulation.
n n Pathogenesis: in cases of distoying of bacterium it will be endotoxin. It cause generalized injuring of endotelium, disturbed the system of hemostasis. It will be generated disturbance of microcirculation. Decreasing of BP will be as a result of disturbance of micro- circulation.
 n - It will be vasoconstriction , particular at post capillary’s after that vasodilatation and increasing of a capillary permeability – tissue ( cells) hypoxia and anoxia, hypofusional acidosis.
n - It will be vasoconstriction , particular at post capillary’s after that vasodilatation and increasing of a capillary permeability – tissue ( cells) hypoxia and anoxia, hypofusional acidosis.
 n Clinic: n as a rule, acute clinic after manipulation at the focus of infection, when microorganisms very active are going in blood. BP is going down without blood lost.
n Clinic: n as a rule, acute clinic after manipulation at the focus of infection, when microorganisms very active are going in blood. BP is going down without blood lost.
 Phases of septic shock: n n Hyperdinamic , or wearm : MBP is going down on 10 -12 мм of Hg (80 -90). Continuation of it - 15 -20 minutes, till 1 -2 hours. Hypodinamic, or cool: prolonged going down of BP, from some hours tills some days. After that may be ARI, progressive DIC syndrome.
Phases of septic shock: n n Hyperdinamic , or wearm : MBP is going down on 10 -12 мм of Hg (80 -90). Continuation of it - 15 -20 minutes, till 1 -2 hours. Hypodinamic, or cool: prolonged going down of BP, from some hours tills some days. After that may be ARI, progressive DIC syndrome.
 n Terminal stage: anuria, respiratory and cardiac insufficiency. Terminal stage may be in 6 -8 hours. часов.
n Terminal stage: anuria, respiratory and cardiac insufficiency. Terminal stage may be in 6 -8 hours. часов.
 Diagnosis is based on: n n 1. Presence of high temperature with chills, after that sharp decreasing of temperature Presence of a septic place in genitalia 3. going down of BP, without correction with blood lost ( more than on 40 mm from initial) 4. tachicardia ( more 90 baets in one minute)
Diagnosis is based on: n n 1. Presence of high temperature with chills, after that sharp decreasing of temperature Presence of a septic place in genitalia 3. going down of BP, without correction with blood lost ( more than on 40 mm from initial) 4. tachicardia ( more 90 baets in one minute)
 Ways of infection spreading: n n n - hematogenic - lymphatic - intracanicular - combined Intracanicular way very often may be in cases of gonorrhea
Ways of infection spreading: n n n - hematogenic - lymphatic - intracanicular - combined Intracanicular way very often may be in cases of gonorrhea
 Gonorrhea. Exeter is gonococci, situated intracellular ( intra lucocytes), gram- negative. Gonococci may situated and extra cells on the superficial of multilayer flat epithelium. It is possible of fagocytosis of gonococci by trichomonads.
Gonorrhea. Exeter is gonococci, situated intracellular ( intra lucocytes), gram- negative. Gonococci may situated and extra cells on the superficial of multilayer flat epithelium. It is possible of fagocytosis of gonococci by trichomonads.
 In the cases of acute gonorrhea exiters have the same form and size , in cases of chronic duration and non rational treatment by antibiotics it is possible to see polymorphism of gonococci, formation of L - forms, pathogenic form , without sensitivity to the medicaments. Gonococci may be killed at the closed cavities because of its toxins, in cases of dryness, temperature more than 55 graduce of С, action of antibiotics.
In the cases of acute gonorrhea exiters have the same form and size , in cases of chronic duration and non rational treatment by antibiotics it is possible to see polymorphism of gonococci, formation of L - forms, pathogenic form , without sensitivity to the medicaments. Gonococci may be killed at the closed cavities because of its toxins, in cases of dryness, temperature more than 55 graduce of С, action of antibiotics.
 Multilayer epithelium of vagina has resistance to gonococci; gonococci infection likes columnar epithelium of cervical channel. Multilayer epithelium of vagina is injuring in cases of rather old age of women and children. As compare as septic infections for the development of gonorrhea it is not necessary of injuring of epithelium and “ hills” for infection.
Multilayer epithelium of vagina has resistance to gonococci; gonococci infection likes columnar epithelium of cervical channel. Multilayer epithelium of vagina is injuring in cases of rather old age of women and children. As compare as septic infections for the development of gonorrhea it is not necessary of injuring of epithelium and “ hills” for infection.
 Clinic: Infection will appear in 3 -4 days after contamination n continuation of incubational period from 7 to 15 days till 3 weeks n gonococci are going at the sub-epithelial layer. n In case of death of exiter endotoxin is produced , causing generative – destructive changes of epithelium with proliferation of connected tissue. n
Clinic: Infection will appear in 3 -4 days after contamination n continuation of incubational period from 7 to 15 days till 3 weeks n gonococci are going at the sub-epithelial layer. n In case of death of exiter endotoxin is produced , causing generative – destructive changes of epithelium with proliferation of connected tissue. n
 In cases of a process progress it is possible formation of scars, that leads to a uterine tubes conclusion, infertility, stricture of uretra and disturbance of urination.
In cases of a process progress it is possible formation of scars, that leads to a uterine tubes conclusion, infertility, stricture of uretra and disturbance of urination.
 Through a blood endotoxin may injure articulations, peripheral nervous, internal membranes of heart.
Through a blood endotoxin may injure articulations, peripheral nervous, internal membranes of heart.
 The true immunity in case of gonorrhea is not: it is possible to have the repeated onset of diseases. Clinic appearance of gonorrhea may be bright expressed, small expressed and torpid.
The true immunity in case of gonorrhea is not: it is possible to have the repeated onset of diseases. Clinic appearance of gonorrhea may be bright expressed, small expressed and torpid.
 Classification: According to duration of disease there are 2 forms: 1. Fresh ( continuation of diseases is till 3 months месяцев): 1) acute - not more 2 weeks 2) sub-acute - continuation of process is 2 -8 weeks 3) torpid – small symptoms, but gonococcus are present. 2. Chronic- continuation is more than 2 months.
Classification: According to duration of disease there are 2 forms: 1. Fresh ( continuation of diseases is till 3 months месяцев): 1) acute - not more 2 weeks 2) sub-acute - continuation of process is 2 -8 weeks 3) torpid – small symptoms, but gonococcus are present. 2. Chronic- continuation is more than 2 months.
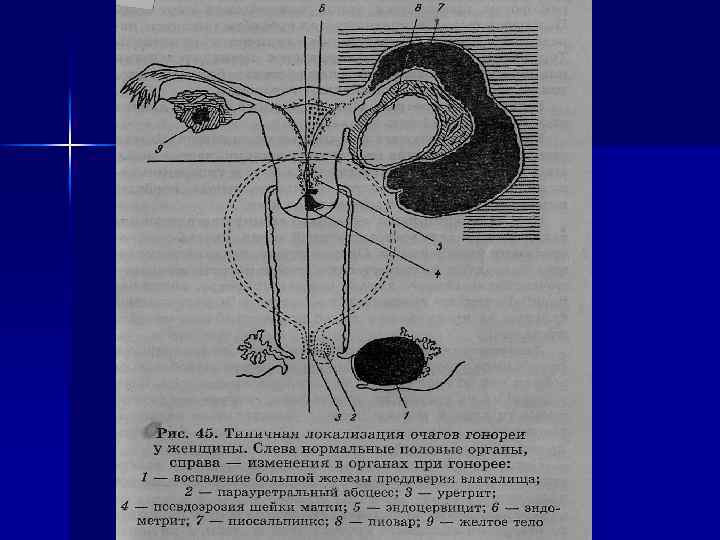
 According to degree of spreading there are 2 forms of gonorrhea: Gonorrhea of the low department of urea-sexual organs: gonorrhea of uretra, para-uretral ways, vulva, vagina, Bartoliniev glands, and uterine cervix ( cervical channel). It is watched more often at 60 -65 % of cases. 2. Ascendant gonorrhea - gonorrhea of endometrium, uterine tubes, ovaries and pelvic peritoneum. Frequency is 35 -40 %.
According to degree of spreading there are 2 forms of gonorrhea: Gonorrhea of the low department of urea-sexual organs: gonorrhea of uretra, para-uretral ways, vulva, vagina, Bartoliniev glands, and uterine cervix ( cervical channel). It is watched more often at 60 -65 % of cases. 2. Ascendant gonorrhea - gonorrhea of endometrium, uterine tubes, ovaries and pelvic peritoneum. Frequency is 35 -40 %.
 Boderline between the upper and low part department is internal os of uterine cervix.
Boderline between the upper and low part department is internal os of uterine cervix.
 Diagnostic 1) It may be uretritis with bi- lateral bartolinitis 2) Endocervisitis among women with primary infertility, didn’t have any diagnostic intervations, making a uterine cervix trauma; 3) bi- lateral salpingitis, salpingo- oophoritis among of women without of history of abortions, labour’s, intra uterine manipulations with uretritis and endocervisitis connection
Diagnostic 1) It may be uretritis with bi- lateral bartolinitis 2) Endocervisitis among women with primary infertility, didn’t have any diagnostic intervations, making a uterine cervix trauma; 3) bi- lateral salpingitis, salpingo- oophoritis among of women without of history of abortions, labour’s, intra uterine manipulations with uretritis and endocervisitis connection
 Methods of examination: 1. microscopic 2. bacterioscopy 3. cultural 4. serological.
Methods of examination: 1. microscopic 2. bacterioscopy 3. cultural 4. serological.
 Methods of provocation: 1. Chemical 2. Biological 3. Теrmal 4. Меchanical 5. Аlimenatar 6. Combined
Methods of provocation: 1. Chemical 2. Biological 3. Теrmal 4. Меchanical 5. Аlimenatar 6. Combined
 Treatment By broad specters antibiotics In cases of torpid form with the aim of stimulation of the protected forces are using gonovaccine, pyrogenic drugs( pyrogrnal, prodigazone).
Treatment By broad specters antibiotics In cases of torpid form with the aim of stimulation of the protected forces are using gonovaccine, pyrogenic drugs( pyrogrnal, prodigazone).
 Criteria of completely curable. Absence of gonococcocus in smear, in 7 -10 days, наgive the 1 provocation, after that in 24, 48 and 72 hours in all focuses. Examination is performing during 2 -3 мonthes. At the days of menstruation smear should be taken. Woman is completely cure in cases of absence of complains and absence of gonoccocus in smear.
Criteria of completely curable. Absence of gonococcocus in smear, in 7 -10 days, наgive the 1 provocation, after that in 24, 48 and 72 hours in all focuses. Examination is performing during 2 -3 мonthes. At the days of menstruation smear should be taken. Woman is completely cure in cases of absence of complains and absence of gonoccocus in smear.
 Tricomoniasis. The forms of trichomoniasis: 1)fresh: acute, subacute, torpid form 2)chronic, which has torpid duration and duration of diseases more 2 мonths; 3) trichomonadocaring
Tricomoniasis. The forms of trichomoniasis: 1)fresh: acute, subacute, torpid form 2)chronic, which has torpid duration and duration of diseases more 2 мonths; 3) trichomonadocaring
 The place of infection is vagina, endocervix, not often - uretrа, bladder, ductcts of Bartoliniev ‘s glands. But it is possible to have trichomonad to the uterine cavity, uterine tubes and abdominal cavity.
The place of infection is vagina, endocervix, not often - uretrа, bladder, ductcts of Bartoliniev ‘s glands. But it is possible to have trichomonad to the uterine cavity, uterine tubes and abdominal cavity.
 Cinic At the acute and subacute stages there are complains on itching, fluid purulent discharges, painful urination. и There is hyperimia of vaginal mucouse, edema, heavy fluid discharges.
Cinic At the acute and subacute stages there are complains on itching, fluid purulent discharges, painful urination. и There is hyperimia of vaginal mucouse, edema, heavy fluid discharges.
 Diagnosis is found on the dates of specific clinic dates and microscopy of native and painted slaids from the places of infection.
Diagnosis is found on the dates of specific clinic dates and microscopy of native and painted slaids from the places of infection.
 Principles of treatment: 1) treatment of woman together with her partner. 2)sexual life is not possible at the time of treatment 3) using of special drugs again of trichomonada together with hygiene procedure.
Principles of treatment: 1) treatment of woman together with her partner. 2)sexual life is not possible at the time of treatment 3) using of special drugs again of trichomonada together with hygiene procedure.
 The more effective medicine is metranidazolum- (trichopol, flagil, orvagil, clion) and tinadozolum (fazizin).
The more effective medicine is metranidazolum- (trichopol, flagil, orvagil, clion) and tinadozolum (fazizin).
 Treatment is successful in cases of trichomonad absence from different places after menstruation during of 3 menstrual cycles.
Treatment is successful in cases of trichomonad absence from different places after menstruation during of 3 menstrual cycles.
 Genital chlamidiosis. Urea- genital chlamidiosis is the more spreading infection, going through a sexual ways. Due to absence of good results of treatment, complications it is very big treat for reproductive health.
Genital chlamidiosis. Urea- genital chlamidiosis is the more spreading infection, going through a sexual ways. Due to absence of good results of treatment, complications it is very big treat for reproductive health.
 n There are 60 % of women without symptoms of gonorrhea, but having chronic inflammatory diseases have chlamidiosis.
n There are 60 % of women without symptoms of gonorrhea, but having chronic inflammatory diseases have chlamidiosis.
 n Exiter of this diseases is - Chlamidia trachomatis. Its has many seroutypes
n Exiter of this diseases is - Chlamidia trachomatis. Its has many seroutypes
 n It is obligate intra- cellular parasite , which has 3 types of existence: elementary and reticular ( initial bodies) and intermedial forms.
n It is obligate intra- cellular parasite , which has 3 types of existence: elementary and reticular ( initial bodies) and intermedial forms.
 n Elementary bodies make adherence to the cell’s surface and going inside on a type of fagocitosis. Elemental body is going to initial, that make a process of development.
n Elementary bodies make adherence to the cell’s surface and going inside on a type of fagocitosis. Elemental body is going to initial, that make a process of development.
 Using a way of binaural dividing at the vacuoles of a master there is cumulation of initial cells ( vegetated form). After that in the way of fragmentation it will be elemental body ( spor’s form), than cam b very close to a new cells. n Continuation of a cycle of development is 48 -72 hours. n
Using a way of binaural dividing at the vacuoles of a master there is cumulation of initial cells ( vegetated form). After that in the way of fragmentation it will be elemental body ( spor’s form), than cam b very close to a new cells. n Continuation of a cycle of development is 48 -72 hours. n
 n There is very big influence of immune answer of organism in cases of В chlamidiosis development. Repeated cycles of intra- cellular development and infection of new cells make stimulation of immune process and increase the degree of cells injuring.
n There is very big influence of immune answer of organism in cases of В chlamidiosis development. Repeated cycles of intra- cellular development and infection of new cells make stimulation of immune process and increase the degree of cells injuring.
 n Intra cellular there are peresisted association of chlamidia, without growing and development. It is the main mechanism in a chlamidiosis pathogenesis.
n Intra cellular there are peresisted association of chlamidia, without growing and development. It is the main mechanism in a chlamidiosis pathogenesis.
 n Clinic. There are sub-acute, chronic, persisted forms of diseases, more rarely – acute. In the cases of acute forms there is hyperemia of urino- sexual way mucous, mucous- purulent discharges.
n Clinic. There are sub-acute, chronic, persisted forms of diseases, more rarely – acute. In the cases of acute forms there is hyperemia of urino- sexual way mucous, mucous- purulent discharges.
 Women with not expressed symptoms of diseases don’t have any complains, discharges from sexual , way, hyperemia of mucous. n It is possible to have carriage of chlamidia. There is no any changes during examination. n
Women with not expressed symptoms of diseases don’t have any complains, discharges from sexual , way, hyperemia of mucous. n It is possible to have carriage of chlamidia. There is no any changes during examination. n
 Chlamidia has localization in places, where is columnar epithilium. n Methods of diagnostic: n The strick immuno- fluorescent, polymeraze- linked reaction, immunoenzyme analysis, serological, microscopy. n
Chlamidia has localization in places, where is columnar epithilium. n Methods of diagnostic: n The strick immuno- fluorescent, polymeraze- linked reaction, immunoenzyme analysis, serological, microscopy. n
 n n Treatment: Tetracyclins, macrolids, sulfanilamids, anti- fungal medicine- nistatin, levorin. The course of tetracycline treatment is from 7 -10 till 14 -20 days (on 0, 5 gr. х 4 times in day). Erytromycin on 250 mg х 4 times dayly during 21 days, or on 500 mg х 2 times per day during 14 - 15 days. Rondomycin (metacycline) and doxacyclin ( vibromycin) at the 1 day is prescribed on 200 мг once, than 100 mg once dayly during 14 days.
n n Treatment: Tetracyclins, macrolids, sulfanilamids, anti- fungal medicine- nistatin, levorin. The course of tetracycline treatment is from 7 -10 till 14 -20 days (on 0, 5 gr. х 4 times in day). Erytromycin on 250 mg х 4 times dayly during 21 days, or on 500 mg х 2 times per day during 14 - 15 days. Rondomycin (metacycline) and doxacyclin ( vibromycin) at the 1 day is prescribed on 200 мг once, than 100 mg once dayly during 14 days.
 n It is possible to use azytromycin ( sumamed) on 500 мg daily 1 day, than 250 mg the next 9 days pefloxacin (аbactal) оn 600 мg х 1 time in day during 7 days; ryphampicin оn 600 мg daily, after that оn 300 мg х 2 times 7 days.
n It is possible to use azytromycin ( sumamed) on 500 мg daily 1 day, than 250 mg the next 9 days pefloxacin (аbactal) оn 600 мg х 1 time in day during 7 days; ryphampicin оn 600 мg daily, after that оn 300 мg х 2 times 7 days.
 n It is very useful stimulated therapy, using pyrogenal, decaris, metyluracil, biostimulators. Desensebilizated therapy, enzymes.
n It is very useful stimulated therapy, using pyrogenal, decaris, metyluracil, biostimulators. Desensebilizated therapy, enzymes.
 Genital candidosis. n Exiter is candidaa. It is possible injuring of any age women, but particular – pregnant women and puerpera’s.
Genital candidosis. n Exiter is candidaa. It is possible injuring of any age women, but particular – pregnant women and puerpera’s.


 Thank You for attention!
Thank You for attention!


