1f1508086f6099d668ced6f5dda952d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

“Infectious Diseases Laboratory Quality Control – Essential Component for Public Health Improvement. ” Kalashnikova T. (GISK RF; CDC/CAR) Musabaev E. (Ref. Lab. Uzbekistan) Usmanov R. (Ref. Lab. Kyrgyztan) Kuchuk T. (Ref. Lab. Kyrgyztan) Ongarbaev A. (Ref. Lab. Uzbekistan) Mustafaeva E. (Ref. Lab. Uzbekistan) Suleymenova S. (Ref. Lab. Kazakhstan ) Jumagulova A. ( CDC/CAR) Favorov M. (CDC/CAR)

Actuality High level of Infectious Disease Necessity of further improving current public health measures for control and prophylaxis of infectious disease. Objective Results of Laboratory Diagnosis

Main issues of laboratory work in countries of the former Soviet Union • Increase in the number and type of laboratories • Absence of Quality Control measures for • Progress in using highly laboratory effective laboratory investigations methods ( ELISA , PCR) There is mismatch between clinicalepidemiological diagnoses and the results of serological tests.

Goals • To develop a training module for quality control (QC) measures and implement QC program in the laboratory servises of Central Asia countries.

Objectives ® Knowledge : ® Training course for establishing the proper laboratory conditions and quality control measures for laboratory investigations ® Teach on screening and other blood banks related lab issues ® Use quality control manual developed by USAID/CDC ® Improve Skills: ® Conduct a “wet” day, part of the training course ® Conduct ELIZA testing ® Group to group results comparison in order to mistakes identification and problems solving technique. ® Competence: ® ® Establish of the Reference laboratories Comprehensive laboratory documentation Reference panels for various markers Introduction of external quality control for the countries

Methods ® Four-day courses for teaching with focus on: Quality control methodology for pre-analytical stage and analytical assay for laboratory investigation; principles for making and using biological standards; laboratory safety; demonstrate epidemiological and prevention principles using viral hepatitis A through E as models. ® Wet lab day: conduct ELIZA tests using CDC design reference panel; compare results among groups of participants; find out the mistakes made by participants ® Reference laboratory on site training: develop laboratory guideline documents; develop reference panels for markers for different infectious diseases; monitor quality of laboratories in Republics

Develop knowledge Seven quality control training seminars were held in various regions of Central Asia Kirgyzia (1998) Uzbekistan (1999, 2000 and 2001) Kazakhstan (2000 and 2001) Turkmenistan (2000) 196 participants attended from the laboratories of various Republic oblasts. Blood banks Infection hospitals Private laboratories Sanitary Epidemiological Stations Lectures for quality control measures were included in seminars for epidemiologists and clinicians from Central Asia.

Establish the proper conditions and quality control measures for the stages of laboratory investigations Pre-analytical stage • Ways to prevent clerical mistakes Analytical stage • Conditions – The forms of direction – The forms of marking for samples • – The forms of the registration • Standards for handling samples – – obtaining serum extraction transportation storage – checking equipment – checking each lot of laboratory test kit Quality Control – develop reference samples panel of markers for different infectious disease – how to utilize reference samples for quality control of tests
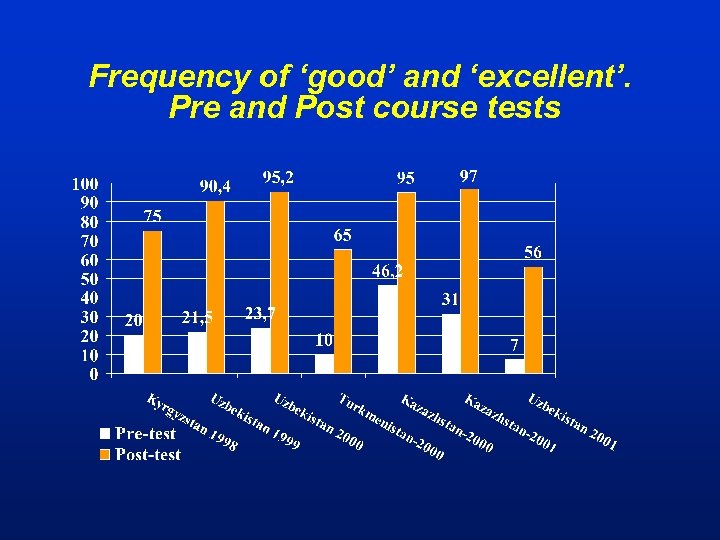
Frequency of ‘good’ and ‘excellent’. Pre and Post course tests

Establishing of Reference Laboratory staff Laboratory Layout • • Chief Laboratory workers Assistants Laboratory Procedures Guidelines • • Quality assurance of pre-analytical stage of laboratory research (Kyrgyztan , 2000) Instructions for pre-analytical stage (Kazakstan , 2000) Quality Control guidelines (Kyrgyztan, 2001) Instructions for in-house laboratory quality control (Uzbekistan, 2001) Rooms for Serology Rooms for receiving samples Rooms for staff Utility and Autoclave rooms Equipment • • Refrigerators Incubators Computers Plate washers Readers Automatic pipetmen Backup generators

Backup Honda generator Don’t use expensive kits for confirmation before you purchase generator
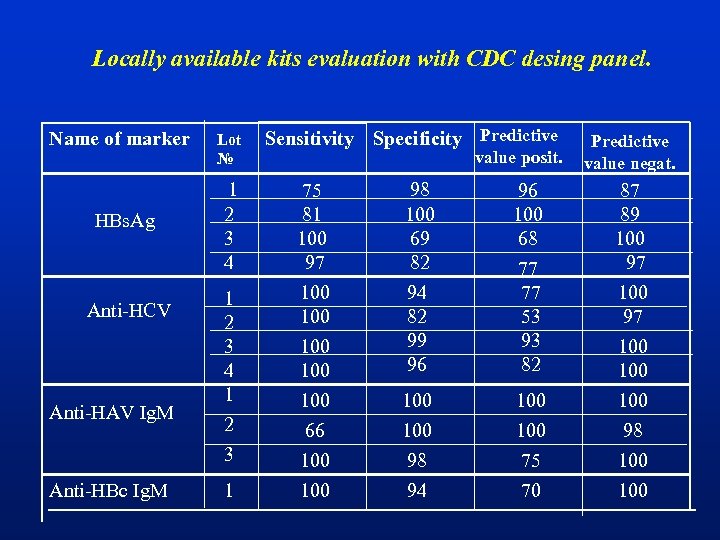
Locally available kits evaluation with CDC desing panel. Name of marker HBs. Ag Anti-HCV Anti-HAV Ig. M Anti-HBc Ig. M Lot № Sensitivity Specificity Predictive value posit. 1 2 3 4 75 81 100 97 98 100 69 82 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 100 100 100 66 100 94 82 99 96 96 100 68 77 77 53 93 82 100 98 94 100 75 70 1 Predictive value negat. 87 89 100 97 100 100 98 100
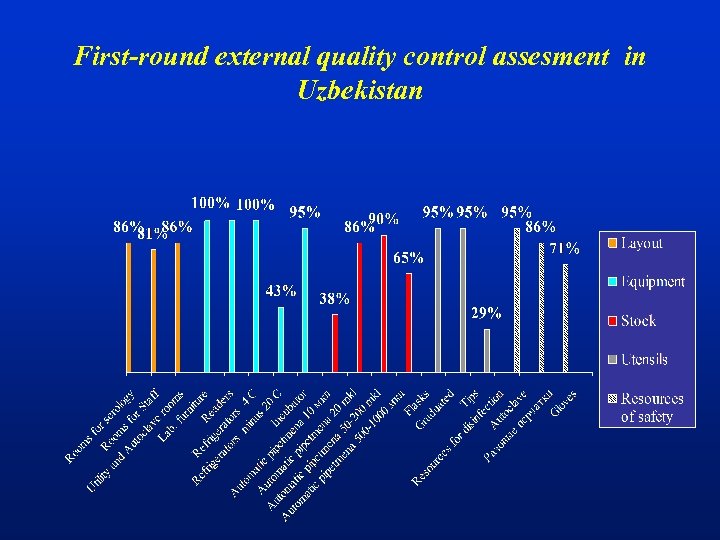
First-round external quality control assesment in Uzbekistan
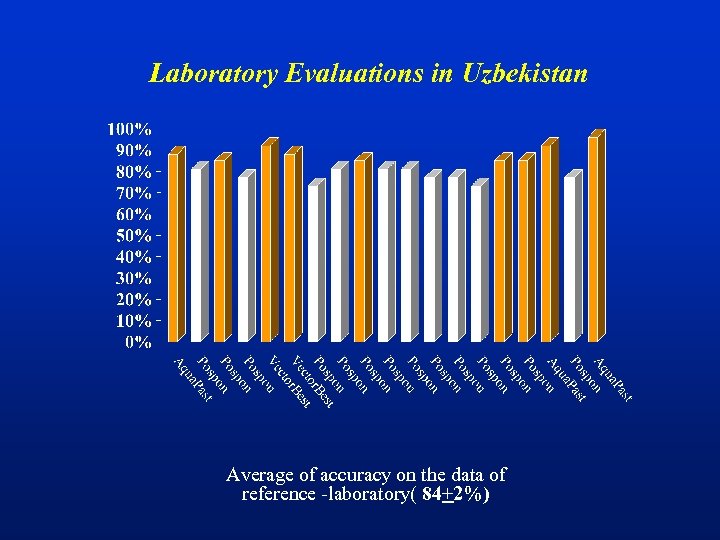
Laboratory Evaluations in Uzbekistan Average of accuracy on the data of reference -laboratory( 84+2%)

Сonclusion The training module to establish quality control principles in the region has been developed Building quality control for infection diseases laboratories in: – Sentinal surveillance for viral hepatitis in Kyrgyztan. – Control of diagnostic reagents (kits) for viral hepatitis under national licensing praktices in Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan. – The outside quality assessment on the state level in Uzbekistan Establishing the system of quality control laboratory procedure in Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan extending program to Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan

Recommendations: Promote training of trainers program for quality control project in Central Asia. Strengthen reference laboratory role in establishing external and internal laboratory control within countries of the region. Training module adoption to HIV diagnostic laboratories. Establishing quality control program for Polymerize Cheng Reaction technology laboratories.
1f1508086f6099d668ced6f5dda952d4.ppt