deb14ba9b4f47589b7980bf19ab3adb4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Infectious Diseases 2008
Infectious Diseases 2008
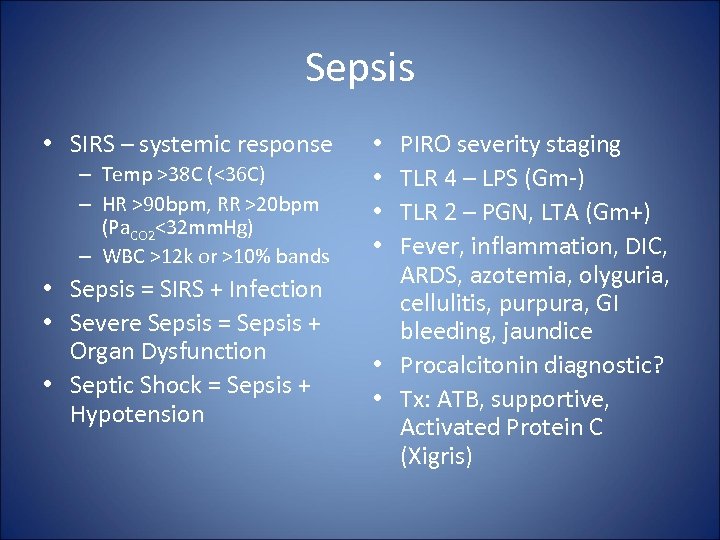 Sepsis • SIRS – systemic response – Temp >38 C (<36 C) – HR >90 bpm, RR >20 bpm (Pa. CO 2<32 mm. Hg) – WBC >12 k or >10% bands • Sepsis = SIRS + Infection • Severe Sepsis = Sepsis + Organ Dysfunction • Septic Shock = Sepsis + Hypotension PIRO severity staging TLR 4 – LPS (Gm-) TLR 2 – PGN, LTA (Gm+) Fever, inflammation, DIC, ARDS, azotemia, olyguria, cellulitis, purpura, GI bleeding, jaundice • Procalcitonin diagnostic? • Tx: ATB, supportive, Activated Protein C (Xigris) • •
Sepsis • SIRS – systemic response – Temp >38 C (<36 C) – HR >90 bpm, RR >20 bpm (Pa. CO 2<32 mm. Hg) – WBC >12 k or >10% bands • Sepsis = SIRS + Infection • Severe Sepsis = Sepsis + Organ Dysfunction • Septic Shock = Sepsis + Hypotension PIRO severity staging TLR 4 – LPS (Gm-) TLR 2 – PGN, LTA (Gm+) Fever, inflammation, DIC, ARDS, azotemia, olyguria, cellulitis, purpura, GI bleeding, jaundice • Procalcitonin diagnostic? • Tx: ATB, supportive, Activated Protein C (Xigris) • •
 Fever / Hyperthermia Fever Hyperthermia • Hypothalamic setpoint shifted up by PGE 2 stimulating EP-3 • Pyogenic cytokines • Pneumonia, drugs, PE, DVT, C. difficile, fungal infection, MI, NG tubes, IV catheters • Hypothalamic setpoint unchanged • Does not respond to NSAIDS • Heat stroke, hyperthyroidism, atropine, ecstasy, malignant hyperthermia, serotonin syndrome
Fever / Hyperthermia Fever Hyperthermia • Hypothalamic setpoint shifted up by PGE 2 stimulating EP-3 • Pyogenic cytokines • Pneumonia, drugs, PE, DVT, C. difficile, fungal infection, MI, NG tubes, IV catheters • Hypothalamic setpoint unchanged • Does not respond to NSAIDS • Heat stroke, hyperthyroidism, atropine, ecstasy, malignant hyperthermia, serotonin syndrome
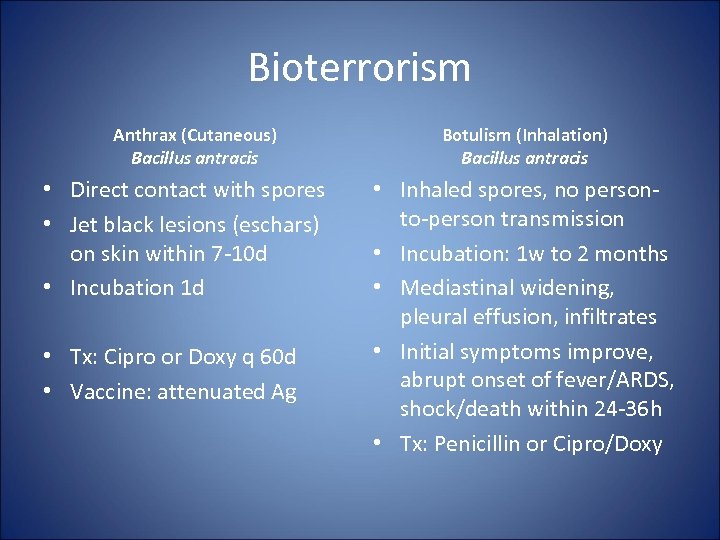 Bioterrorism Anthrax (Cutaneous) Bacillus antracis • Direct contact with spores • Jet black lesions (eschars) on skin within 7 -10 d • Incubation 1 d • Tx: Cipro or Doxy q 60 d • Vaccine: attenuated Ag Botulism (Inhalation) Bacillus antracis • Inhaled spores, no personto-person transmission • Incubation: 1 w to 2 months • Mediastinal widening, pleural effusion, infiltrates • Initial symptoms improve, abrupt onset of fever/ARDS, shock/death within 24 -36 h • Tx: Penicillin or Cipro/Doxy
Bioterrorism Anthrax (Cutaneous) Bacillus antracis • Direct contact with spores • Jet black lesions (eschars) on skin within 7 -10 d • Incubation 1 d • Tx: Cipro or Doxy q 60 d • Vaccine: attenuated Ag Botulism (Inhalation) Bacillus antracis • Inhaled spores, no personto-person transmission • Incubation: 1 w to 2 months • Mediastinal widening, pleural effusion, infiltrates • Initial symptoms improve, abrupt onset of fever/ARDS, shock/death within 24 -36 h • Tx: Penicillin or Cipro/Doxy
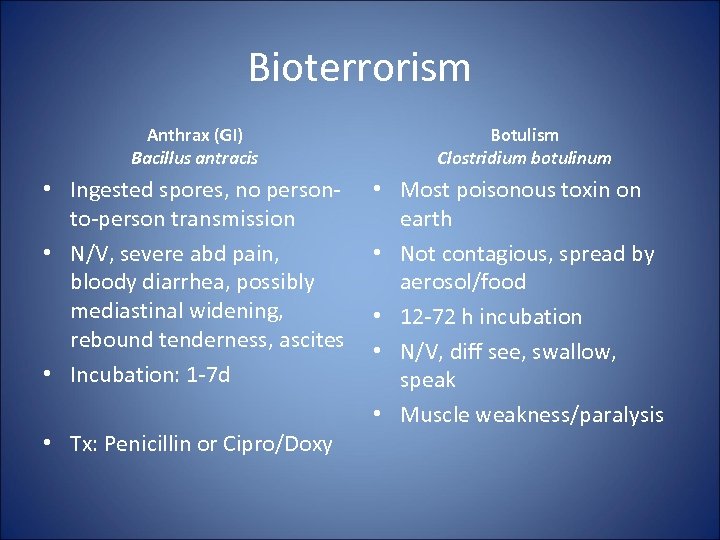 Bioterrorism Anthrax (GI) Bacillus antracis • Ingested spores, no personto-person transmission • N/V, severe abd pain, bloody diarrhea, possibly mediastinal widening, rebound tenderness, ascites • Incubation: 1 -7 d • Tx: Penicillin or Cipro/Doxy Botulism Clostridium botulinum • Most poisonous toxin on earth • Not contagious, spread by aerosol/food • 12 -72 h incubation • N/V, diff see, swallow, speak • Muscle weakness/paralysis
Bioterrorism Anthrax (GI) Bacillus antracis • Ingested spores, no personto-person transmission • N/V, severe abd pain, bloody diarrhea, possibly mediastinal widening, rebound tenderness, ascites • Incubation: 1 -7 d • Tx: Penicillin or Cipro/Doxy Botulism Clostridium botulinum • Most poisonous toxin on earth • Not contagious, spread by aerosol/food • 12 -72 h incubation • N/V, diff see, swallow, speak • Muscle weakness/paralysis
 Bioterrorism Cholera Vibrio cholerae • Rice-water diarrhea, dehydration, shock • Incubation 12 h-5 d • Food/water spread Glanders Burkholderia mallei • Affects horses, mules, donkeys • Enters cut skin, mucous membranes, inhalation
Bioterrorism Cholera Vibrio cholerae • Rice-water diarrhea, dehydration, shock • Incubation 12 h-5 d • Food/water spread Glanders Burkholderia mallei • Affects horses, mules, donkeys • Enters cut skin, mucous membranes, inhalation
 Bioterrorism Plague Yrsinia pestis • “Black Death”, infected fleas • Bubonic – 1 -10 cm buboes on skin w/ edema, flu-like symptoms w/ abd pain • Septicemic - secondary septicemia, thromboses in acral v. leading to necrosis • Penumonic – acute fulminant symptoms, nearly 100% mortality rate • Tx: Streptomycin or Doxycycline Q Fever Coxiella burnetii • Nonspecific febrile syndrome, pneumonia • Hepatitis, endocarditis, granulomatous complications • Tx: Doxycycline 14 -21 d
Bioterrorism Plague Yrsinia pestis • “Black Death”, infected fleas • Bubonic – 1 -10 cm buboes on skin w/ edema, flu-like symptoms w/ abd pain • Septicemic - secondary septicemia, thromboses in acral v. leading to necrosis • Penumonic – acute fulminant symptoms, nearly 100% mortality rate • Tx: Streptomycin or Doxycycline Q Fever Coxiella burnetii • Nonspecific febrile syndrome, pneumonia • Hepatitis, endocarditis, granulomatous complications • Tx: Doxycycline 14 -21 d
 Bioterrorism Smallpox Variola major Tularemia Francisella tularensis • Officially eradicated • Incubation 10 -14 d • High fever, HA, backache, vomiting, rash on palm/sole • Highly contagious • No tx, vaccine within 3 -5 d • One of most infectious bacteria in world • Tick/insect bites • Incubation 10 -14 d • Fever, chills, HA, cough, lethargy, skin ulcers, lymphadenopahty
Bioterrorism Smallpox Variola major Tularemia Francisella tularensis • Officially eradicated • Incubation 10 -14 d • High fever, HA, backache, vomiting, rash on palm/sole • Highly contagious • No tx, vaccine within 3 -5 d • One of most infectious bacteria in world • Tick/insect bites • Incubation 10 -14 d • Fever, chills, HA, cough, lethargy, skin ulcers, lymphadenopahty
 Bioterrorism GB Sarin • Binary weapon – two nonlethal reagents mix to form sarin gas • Inhibit ACHe, phosphonate esters, light brown oil • If mild: dim vision, salivation, chest tightness • Tx: Atropine and 2 PAMCl VX 1000 x more toxic than GB Persists in soil for 6 d Binary weapon Inhibits ACHe, phosphonate esters, light brown oil • If severe: stop breathing, paralysis, seizures, LOC • •
Bioterrorism GB Sarin • Binary weapon – two nonlethal reagents mix to form sarin gas • Inhibit ACHe, phosphonate esters, light brown oil • If mild: dim vision, salivation, chest tightness • Tx: Atropine and 2 PAMCl VX 1000 x more toxic than GB Persists in soil for 6 d Binary weapon Inhibits ACHe, phosphonate esters, light brown oil • If severe: stop breathing, paralysis, seizures, LOC • •
 Bioterrorism Ricin • Waste leftover from processing castor beans • V/D, dehydration, hypotension, hallucinations, seizures, hematuria, multiple organ dysfunction • No tx available
Bioterrorism Ricin • Waste leftover from processing castor beans • V/D, dehydration, hypotension, hallucinations, seizures, hematuria, multiple organ dysfunction • No tx available
 Bioterrorism • Needs Immediate Treatment, Suspect … – Respiratory Symptoms • Acute: Cyanide – Also nerve agents, mustard, lewisite, phosgene, SEB • Delayed: Anthrax, Plague, Tularemia – Also Q Fever, SEB, ricin, mustard, lewisite, phosgene – Neurological Symptoms • Acute: Nerve agents – Also cyanide • Delayed: Botulism – Also VEE-CNS
Bioterrorism • Needs Immediate Treatment, Suspect … – Respiratory Symptoms • Acute: Cyanide – Also nerve agents, mustard, lewisite, phosgene, SEB • Delayed: Anthrax, Plague, Tularemia – Also Q Fever, SEB, ricin, mustard, lewisite, phosgene – Neurological Symptoms • Acute: Nerve agents – Also cyanide • Delayed: Botulism – Also VEE-CNS
 Bioterrorism • “Active” Research – – – – – Algeria Egypt India Iran Israel N. Korea Pakistan Syria Taiwan • “Secretly” Developing – China – Russia • “Former” Programs – – – Canada France Germany Japan S. Africa UK, US
Bioterrorism • “Active” Research – – – – – Algeria Egypt India Iran Israel N. Korea Pakistan Syria Taiwan • “Secretly” Developing – China – Russia • “Former” Programs – – – Canada France Germany Japan S. Africa UK, US
 Immunocompromised • Deficiencies in – – Complement IG/B-Cell Phagocyte T-cell • Clues – – – – Recurrent Neisseria inf Recurrent pneumonia Severe presentation Pneumocystis jiroveci Burkholderia cepacia Non-TB Mycobacteria Aspergillus
Immunocompromised • Deficiencies in – – Complement IG/B-Cell Phagocyte T-cell • Clues – – – – Recurrent Neisseria inf Recurrent pneumonia Severe presentation Pneumocystis jiroveci Burkholderia cepacia Non-TB Mycobacteria Aspergillus
 Complement Deficiency • Hereditary angioedema – C 1 inhibitor deficiency – Overactive complement – Minor stressors trigger attacks • C 5 -9 Deficiency – MAC lysis defect – Neisseria bacteremia • DAF and CD 59 – Paroxymal nocturnal hemoglobinuria • C 1, C 3, C 4 deficiency – Recurrent pyogenic sinus and respiratory infection • C 1 q deficiency – 90% have SLE
Complement Deficiency • Hereditary angioedema – C 1 inhibitor deficiency – Overactive complement – Minor stressors trigger attacks • C 5 -9 Deficiency – MAC lysis defect – Neisseria bacteremia • DAF and CD 59 – Paroxymal nocturnal hemoglobinuria • C 1, C 3, C 4 deficiency – Recurrent pyogenic sinus and respiratory infection • C 1 q deficiency – 90% have SLE
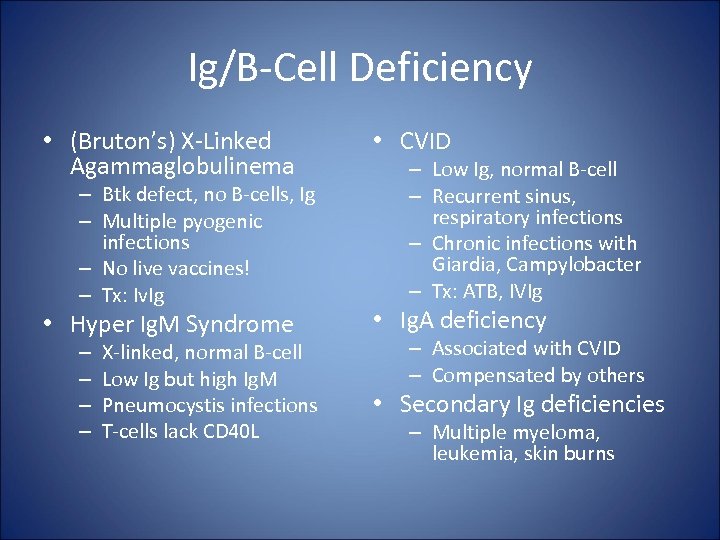 Ig/B-Cell Deficiency • (Bruton’s) X-Linked Agammaglobulinema • CVID • Hyper Ig. M Syndrome • Ig. A deficiency – Btk defect, no B-cells, Ig – Multiple pyogenic infections – No live vaccines! – Tx: Iv. Ig – – X-linked, normal B-cell Low Ig but high Ig. M Pneumocystis infections T-cells lack CD 40 L – Low Ig, normal B-cell – Recurrent sinus, respiratory infections – Chronic infections with Giardia, Campylobacter – Tx: ATB, IVIg – Associated with CVID – Compensated by others • Secondary Ig deficiencies – Multiple myeloma, leukemia, skin burns
Ig/B-Cell Deficiency • (Bruton’s) X-Linked Agammaglobulinema • CVID • Hyper Ig. M Syndrome • Ig. A deficiency – Btk defect, no B-cells, Ig – Multiple pyogenic infections – No live vaccines! – Tx: Iv. Ig – – X-linked, normal B-cell Low Ig but high Ig. M Pneumocystis infections T-cells lack CD 40 L – Low Ig, normal B-cell – Recurrent sinus, respiratory infections – Chronic infections with Giardia, Campylobacter – Tx: ATB, IVIg – Associated with CVID – Compensated by others • Secondary Ig deficiencies – Multiple myeloma, leukemia, skin burns
 Neutrophil Deficiency • Neutropenia – Causes • • Blacks have lower counts Chemotherapy patients Post-infection, sepsis Sulfa-drugs, β-lactams – Infections • • Mucositis Ecthyma gangrenosum Disseminated candidiasis Aspergillosis • Hereditary Cyclic N. – – AD, ELA 2 mutation Predictable cycles Aphtous stomatitis Tx: G-CSF, steroids • Chediak-Higashi Syndrome – AR, LYST mutation – Giant lysosomes, ineffective granulopoiesis – Oculocutaneous albinism
Neutrophil Deficiency • Neutropenia – Causes • • Blacks have lower counts Chemotherapy patients Post-infection, sepsis Sulfa-drugs, β-lactams – Infections • • Mucositis Ecthyma gangrenosum Disseminated candidiasis Aspergillosis • Hereditary Cyclic N. – – AD, ELA 2 mutation Predictable cycles Aphtous stomatitis Tx: G-CSF, steroids • Chediak-Higashi Syndrome – AR, LYST mutation – Giant lysosomes, ineffective granulopoiesis – Oculocutaneous albinism
 Neutrophil Deficiency • Job’s Syndrome – Hyper Ig. E, impaired chemotaxis – STAT 3 gene mutation – Facies, scoliosis, skin abscesses, sinusitis • Myeloperoxidase (MPO) – Makes pus green – Converts H 2 O 2 to HOCl – Deficiency impairs this • CGD – Defective NADPH oxidase, no respiratory burst, no killing – Infections with catalase positive organisms – NBT test
Neutrophil Deficiency • Job’s Syndrome – Hyper Ig. E, impaired chemotaxis – STAT 3 gene mutation – Facies, scoliosis, skin abscesses, sinusitis • Myeloperoxidase (MPO) – Makes pus green – Converts H 2 O 2 to HOCl – Deficiency impairs this • CGD – Defective NADPH oxidase, no respiratory burst, no killing – Infections with catalase positive organisms – NBT test
 Spleen “Deficiency” • Splenectomy – Trauma, ITP, Hairy cell leukemia, abscess • Hyposplenism – Autoimmune (Graves, Hashimoto, SLE) – Neoplasia (Hodgkin, CML, Sezary) – Amyloidosis – Alcoholism, elderly, Crohn’s, Sickle cell • Decrease in circulating activated B-cells (75%) • Risk of thalassemia > hodgkins > spherocytosis > ITP > sepsis • Infections – S. Pneumoniae (mostly) – Haemophilus, GNR, Neisseria (less common)
Spleen “Deficiency” • Splenectomy – Trauma, ITP, Hairy cell leukemia, abscess • Hyposplenism – Autoimmune (Graves, Hashimoto, SLE) – Neoplasia (Hodgkin, CML, Sezary) – Amyloidosis – Alcoholism, elderly, Crohn’s, Sickle cell • Decrease in circulating activated B-cells (75%) • Risk of thalassemia > hodgkins > spherocytosis > ITP > sepsis • Infections – S. Pneumoniae (mostly) – Haemophilus, GNR, Neisseria (less common)
 T-Cell Deficiency • Di. George’s – Deletion 22 q 11. 2 – No T-cells, hypocalcemia, velocardiofacial defects • SCID – Combined B/T-cell deficiency, lymphopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia – ADA, PNP, RAG 1/2, Jak 3 gene deficiencies • CD 4 T-cell Deficiency – HIV, <300 CD 4+/m. L • Wiskott-Aldrich – WASP protein – Pyogenic infections, purpura, eczema – High Ig. A, Ig. E, low Ig. M • Infections – Mycobacteria, norcardia, legionella, cryptococcus, histoplasma, pneumocystis, herpesvirus, cryptosporidium, toxoplasma
T-Cell Deficiency • Di. George’s – Deletion 22 q 11. 2 – No T-cells, hypocalcemia, velocardiofacial defects • SCID – Combined B/T-cell deficiency, lymphopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia – ADA, PNP, RAG 1/2, Jak 3 gene deficiencies • CD 4 T-cell Deficiency – HIV, <300 CD 4+/m. L • Wiskott-Aldrich – WASP protein – Pyogenic infections, purpura, eczema – High Ig. A, Ig. E, low Ig. M • Infections – Mycobacteria, norcardia, legionella, cryptococcus, histoplasma, pneumocystis, herpesvirus, cryptosporidium, toxoplasma
 Food Safety Milk pasteurization: 72 C for 15 s or 63 C for 30 m Botulism spores: kill with high heat + acidic Preservatives: weak acids, nitrites, sulfites, spices Radiation: γ-irradiation for spices, meats Survival: Cold – Listeria; Chlorine – Giardia, Cryptosporidum cysts; Anything home processed • Outbreaks: Listeria (microwaved hot dogs), Cyclospora (raspberries), Salmonella, ETEC • • •
Food Safety Milk pasteurization: 72 C for 15 s or 63 C for 30 m Botulism spores: kill with high heat + acidic Preservatives: weak acids, nitrites, sulfites, spices Radiation: γ-irradiation for spices, meats Survival: Cold – Listeria; Chlorine – Giardia, Cryptosporidum cysts; Anything home processed • Outbreaks: Listeria (microwaved hot dogs), Cyclospora (raspberries), Salmonella, ETEC • • •
 Tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bovis, africanum • Acid-fast, aerobic non-motile bacillus, reduce nitrates, produce niacin, slow growing • BACTEC blood culture, DAT tests using PCR • PPD (Mantoux) is killed tuberculin, positive if >15 mm, indicates prior infection (LTBI), need CXR • Risks: (normal) 1 st year: 3 -4%, lifetime: 5 -15% (HIV infected) 1 st year: 40%, +10% every year • Tx: test susceptibility, give multiple drugs INH + RIF + ETH (+ PZA), INH prophylaxis, hepatotoxicity
Tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bovis, africanum • Acid-fast, aerobic non-motile bacillus, reduce nitrates, produce niacin, slow growing • BACTEC blood culture, DAT tests using PCR • PPD (Mantoux) is killed tuberculin, positive if >15 mm, indicates prior infection (LTBI), need CXR • Risks: (normal) 1 st year: 3 -4%, lifetime: 5 -15% (HIV infected) 1 st year: 40%, +10% every year • Tx: test susceptibility, give multiple drugs INH + RIF + ETH (+ PZA), INH prophylaxis, hepatotoxicity
 Tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bovis, africanum • Infected aerosolized droplets, milk (M. bovis), replicates in middle/lower lobes alveolar space, Rasmussen’s aneurysm (pulmonary a. ), pleural effusion, sputum with PMNs • Spread to hilar lymph nodes in macrophages • Reactivate in upper lobes, cavities form • Can disseminate through blood (military TB), skin lesions, HA, abd pain, osteomyelitis
Tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bovis, africanum • Infected aerosolized droplets, milk (M. bovis), replicates in middle/lower lobes alveolar space, Rasmussen’s aneurysm (pulmonary a. ), pleural effusion, sputum with PMNs • Spread to hilar lymph nodes in macrophages • Reactivate in upper lobes, cavities form • Can disseminate through blood (military TB), skin lesions, HA, abd pain, osteomyelitis
 Leprosy Mycobacterium leprae • • Lepromatous Leprosy Poor TH 1 response Large # of bacteria in tissue Infectious, non self-limiting Tx: rifampicin (monthly) and dapsone (daily) - FREE • Thickened peripheral nerves • Loss of sensation, lesions, peripheral nerve damage, hair loss, disfigurement Tuberculoid Leprosy • • Strong TH 1 response Small # of bacteria Self-limiting Form granulomas
Leprosy Mycobacterium leprae • • Lepromatous Leprosy Poor TH 1 response Large # of bacteria in tissue Infectious, non self-limiting Tx: rifampicin (monthly) and dapsone (daily) - FREE • Thickened peripheral nerves • Loss of sensation, lesions, peripheral nerve damage, hair loss, disfigurement Tuberculoid Leprosy • • Strong TH 1 response Small # of bacteria Self-limiting Form granulomas
 AIDS HIV infection • Lenti- retrovirus, persistent viremia, infects Tcells and macrophages (CD 4 + CCR 5/CXCR 4) • CD 4 >500 asymptomatic, 200 -500 increased thrush, shingles, <200 opportunistic infections, <50 MAI, CMV CD 4 drops 10/month on average • Transmitted by breast milk (acute), blood, semen Risk: blood 95%, pregnancy 20 -33%, MSM 10%, needlestick 1 in 300 (1 in 2400 with therapy) Acute infection “mono”-like w/ rash, ulcers, and w/o tonsil hypertrophy and exudate.
AIDS HIV infection • Lenti- retrovirus, persistent viremia, infects Tcells and macrophages (CD 4 + CCR 5/CXCR 4) • CD 4 >500 asymptomatic, 200 -500 increased thrush, shingles, <200 opportunistic infections, <50 MAI, CMV CD 4 drops 10/month on average • Transmitted by breast milk (acute), blood, semen Risk: blood 95%, pregnancy 20 -33%, MSM 10%, needlestick 1 in 300 (1 in 2400 with therapy) Acute infection “mono”-like w/ rash, ulcers, and w/o tonsil hypertrophy and exudate.
 AIDS HIV infection • Presents with unexplained anemia, leukopenia, recurrent pneumococcal pneumonias, Kaposi’s sarcoma, thrush, wasting, STD, fever • Screen: ELISA, Confirm: Western Blot, Viral Load: PCR, Severity: CD 4 Count • HAART Treatment: NRTI (AZT, 3 TC), NNRTI (nevirapine, efavirenz), protease inhibitors (ritonavir, nelfinavir) • Opportunistic Infections: CMV, MAC, PCP, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptococcosis, Candida, PML
AIDS HIV infection • Presents with unexplained anemia, leukopenia, recurrent pneumococcal pneumonias, Kaposi’s sarcoma, thrush, wasting, STD, fever • Screen: ELISA, Confirm: Western Blot, Viral Load: PCR, Severity: CD 4 Count • HAART Treatment: NRTI (AZT, 3 TC), NNRTI (nevirapine, efavirenz), protease inhibitors (ritonavir, nelfinavir) • Opportunistic Infections: CMV, MAC, PCP, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptococcosis, Candida, PML
 Gonorrhea Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Gm- diplococci • Infect columnar/cuboidal epi, PMN response, pharynx, anorectal, conjunctivitis • Spread via sex and perinatally • Dysuria w/o frequency or urgency, pain, discharge, cervicitis (PID complication) • Dx by culturing swab for diplococci • Tx with Ceftriaxone IM/cefixime PO
Gonorrhea Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Gm- diplococci • Infect columnar/cuboidal epi, PMN response, pharynx, anorectal, conjunctivitis • Spread via sex and perinatally • Dysuria w/o frequency or urgency, pain, discharge, cervicitis (PID complication) • Dx by culturing swab for diplococci • Tx with Ceftriaxone IM/cefixime PO
 Chlamydia C. trachomatis, psittaci, pneumoniae • Intracellular membrane-bound inclusions • Dx with culture, DFA (Micro. Trak), ELISA, annual screen sexually active women <25 yo • Tx Azithromycin x 1 or Doxycycline bid x 7 d, abstinence x 7 d after treatment
Chlamydia C. trachomatis, psittaci, pneumoniae • Intracellular membrane-bound inclusions • Dx with culture, DFA (Micro. Trak), ELISA, annual screen sexually active women <25 yo • Tx Azithromycin x 1 or Doxycycline bid x 7 d, abstinence x 7 d after treatment
 Chlamydia C. trachomatis, psittaci, pneumoniae LGV (STD) • Endemic in Africa/SE Asia/ India/S. America • Painless ulcer (heals) to lymphadenopathy (scars) to ulceration of genetalia • Tx: Doxycycline po bid x 21 d Urethritis • • NGU 7 -14 d incubation Dysuria, scant discharge Complications – PID, ectopic pregnancy – Reiter’s syndrome (arthritis)
Chlamydia C. trachomatis, psittaci, pneumoniae LGV (STD) • Endemic in Africa/SE Asia/ India/S. America • Painless ulcer (heals) to lymphadenopathy (scars) to ulceration of genetalia • Tx: Doxycycline po bid x 21 d Urethritis • • NGU 7 -14 d incubation Dysuria, scant discharge Complications – PID, ectopic pregnancy – Reiter’s syndrome (arthritis)
 Trichomonas Vaginalis • Flagellated motile protozoa • Yellow, purulent, frothy, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, itch, dysuria, lower abd pain • Tx: Metronidazole (ok in pregnancy)
Trichomonas Vaginalis • Flagellated motile protozoa • Yellow, purulent, frothy, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, itch, dysuria, lower abd pain • Tx: Metronidazole (ok in pregnancy)
 Bacterial Vaginosis Gardnerella or Mobiluncus • Mild to moderate thin, gray, adherent vaginal discharge with odor, itch • Clue cells (squamous cells stippled with bacteria) • +Whiff test (fishy smell in KOH) • Tx: Flagyl/Clindamycin (+Metronidazole in pregnant women)
Bacterial Vaginosis Gardnerella or Mobiluncus • Mild to moderate thin, gray, adherent vaginal discharge with odor, itch • Clue cells (squamous cells stippled with bacteria) • +Whiff test (fishy smell in KOH) • Tx: Flagyl/Clindamycin (+Metronidazole in pregnant women)
 Herpes Simplex HSV-1/2 Vesicular lesions, grouped, painful ulcers Incubation 6 days, primary disease lasts 3 wks Recurrence in 90% of patients Dx by Tzanck smear (Wright stain) showing multinucleated giant cells • Tx: Acyclovir • •
Herpes Simplex HSV-1/2 Vesicular lesions, grouped, painful ulcers Incubation 6 days, primary disease lasts 3 wks Recurrence in 90% of patients Dx by Tzanck smear (Wright stain) showing multinucleated giant cells • Tx: Acyclovir • •
 Syphilis Treponema pallidum • 1⁰ - localized painless chancres (ulcerated, nontender, hard, smooth clean base) • 2⁰ (25% untreated) – 3 -6 wks after chancre, generalized rash on palms/soles, condylomata lata (flat warts), minimally pruritic • Latency – High Ab titers, 30% progress to 3⁰ • 3⁰ - “gummas” (granulomatous lesions) neurosyphilis: general paresis (insanity), tabes dorsalis (demyelination of posterior columns - sensation), Argyll Robertson pupil (nonreactive to light), gun-barrel sight
Syphilis Treponema pallidum • 1⁰ - localized painless chancres (ulcerated, nontender, hard, smooth clean base) • 2⁰ (25% untreated) – 3 -6 wks after chancre, generalized rash on palms/soles, condylomata lata (flat warts), minimally pruritic • Latency – High Ab titers, 30% progress to 3⁰ • 3⁰ - “gummas” (granulomatous lesions) neurosyphilis: general paresis (insanity), tabes dorsalis (demyelination of posterior columns - sensation), Argyll Robertson pupil (nonreactive to light), gun-barrel sight
 Syphilis Treponema pallidum • Congenital: affects muscle, skin, bones; saber shins, saddle nose, Hutchinson’s teeth • Dx: non-specific VDRL, RPR (negative in 1⁰, 3⁰), specific FTA-ABS test (confirmatory) • Tx: (1⁰, 2⁰) Benzathine – Penicillin G IM x 1 (latent) Benzathine PCN G q week x 3 (neurosyphilis) IV PCN G q 4 h
Syphilis Treponema pallidum • Congenital: affects muscle, skin, bones; saber shins, saddle nose, Hutchinson’s teeth • Dx: non-specific VDRL, RPR (negative in 1⁰, 3⁰), specific FTA-ABS test (confirmatory) • Tx: (1⁰, 2⁰) Benzathine – Penicillin G IM x 1 (latent) Benzathine PCN G q week x 3 (neurosyphilis) IV PCN G q 4 h
 Chancroid H. ducreyi • Painful ulcer/ragged edges, painful inguinal lymphadenopathy • Often associated with HIV infection • Incubation 4 -7 d • Tx: Azithromycin x 1 or Ceftriaxone IM x 1
Chancroid H. ducreyi • Painful ulcer/ragged edges, painful inguinal lymphadenopathy • Often associated with HIV infection • Incubation 4 -7 d • Tx: Azithromycin x 1 or Ceftriaxone IM x 1
 Donovanosis Klebsiella granulomatis • Painless destructive ulcers • No lymphadenopathy • Tx: Doxycycline (+aminoglycoside)
Donovanosis Klebsiella granulomatis • Painless destructive ulcers • No lymphadenopathy • Tx: Doxycycline (+aminoglycoside)
 TORCH Syndrome • Mother asymtomatic but baby has: small size, hepatosplenomegaly, rash (thrombocytopenia), CNS defects (encephalitis, seizures), jaundice • • • Toxoplasma Other (syphilis, HIV) Rubella CMV HSV
TORCH Syndrome • Mother asymtomatic but baby has: small size, hepatosplenomegaly, rash (thrombocytopenia), CNS defects (encephalitis, seizures), jaundice • • • Toxoplasma Other (syphilis, HIV) Rubella CMV HSV
 TORCH Syndrome Toxoplasmosis • Detect Ig. G for previous infection, positive immunity • If not immune: monitor for Ig. M (acute), avoid undercooked meat, garden soil, wash fruits and vegetables, handwashing • Treat infected infants aggressively Other (syphilis) • Test all pregnant mothers • If positive, treat monther with penicillin, if allergic to PCN then desensitize • Infected babies commonly show bone lesions, screen CSF for neurosyphilis
TORCH Syndrome Toxoplasmosis • Detect Ig. G for previous infection, positive immunity • If not immune: monitor for Ig. M (acute), avoid undercooked meat, garden soil, wash fruits and vegetables, handwashing • Treat infected infants aggressively Other (syphilis) • Test all pregnant mothers • If positive, treat monther with penicillin, if allergic to PCN then desensitize • Infected babies commonly show bone lesions, screen CSF for neurosyphilis
 TORCH Syndrome Other (HIV) • Reduce transmission by – Anti-HIV therapy (zidovudine) during pregnancy and at birth – Give infant antiretroviral therapy for 16 weeks – Cesarean delivery – No breast feeding Rubella • Vaccinate mother • Highest risk when mother infected in 1 st trimester, no risk after 16 weeks • Infected infant has patent ductus arteriosus
TORCH Syndrome Other (HIV) • Reduce transmission by – Anti-HIV therapy (zidovudine) during pregnancy and at birth – Give infant antiretroviral therapy for 16 weeks – Cesarean delivery – No breast feeding Rubella • Vaccinate mother • Highest risk when mother infected in 1 st trimester, no risk after 16 weeks • Infected infant has patent ductus arteriosus
 TORCH Syndrome CMV HSV • Dangerous if mother not immune before pregnancy • If mother not immune, 40% transmission • 15% infected infants have neurological symptoms (hearing loss, MR) • Education, handwashing, no vaccine • Perinatal infection by reactivated herpes lesions • Reduce transmission by Cesarean section • Can treat mother with acyclovir around birth time to reduce transmission • Treat infected infants with antiviral therapy
TORCH Syndrome CMV HSV • Dangerous if mother not immune before pregnancy • If mother not immune, 40% transmission • 15% infected infants have neurological symptoms (hearing loss, MR) • Education, handwashing, no vaccine • Perinatal infection by reactivated herpes lesions • Reduce transmission by Cesarean section • Can treat mother with acyclovir around birth time to reduce transmission • Treat infected infants with antiviral therapy
 Other Congenital • GBS – Perinatal infection (50%), anogenital screening – Concern in newborn (meningitis), infant (sepsis) • VSV – Primary infection during pregnancy very serious, especially during first 20 weeks (later is mild) – VZV Ig given within 96 h of exposure, no vaccine – Fetal infection results in short limbs, skin scars, CNS • B 19 – Most maternal infections do not lead to fetal infection – Infant symptoms: death, anemia w/ blueberry rash
Other Congenital • GBS – Perinatal infection (50%), anogenital screening – Concern in newborn (meningitis), infant (sepsis) • VSV – Primary infection during pregnancy very serious, especially during first 20 weeks (later is mild) – VZV Ig given within 96 h of exposure, no vaccine – Fetal infection results in short limbs, skin scars, CNS • B 19 – Most maternal infections do not lead to fetal infection – Infant symptoms: death, anemia w/ blueberry rash
 Endocarditis • Infection of the endocardial surface or valves • Surface disrupted, platelets/fibrin deposit on exposed collagen forming sterile thrombus, transient bacteremia infect sterile thrombus on low pressure side (Venturi effect), thrombus grows, Ab cannot clear infection • Once established, require ATB to cure • Two types, native or prosthetic valve endoc.
Endocarditis • Infection of the endocardial surface or valves • Surface disrupted, platelets/fibrin deposit on exposed collagen forming sterile thrombus, transient bacteremia infect sterile thrombus on low pressure side (Venturi effect), thrombus grows, Ab cannot clear infection • Once established, require ATB to cure • Two types, native or prosthetic valve endoc.
 Endocarditis NVE • Native Valve Endocarditis • Viridans strep most common (followed by S. aureus, Strep, Entero) • If culture negative, can be HACEK, intracellular pathogens, fungi PVE • Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis • Coagulase negative Staph most common in early PVE • Late PVE similar to NVE but coag neg staph still common • Platelets still deposit • Infection of surgical site leads to ring abscess
Endocarditis NVE • Native Valve Endocarditis • Viridans strep most common (followed by S. aureus, Strep, Entero) • If culture negative, can be HACEK, intracellular pathogens, fungi PVE • Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis • Coagulase negative Staph most common in early PVE • Late PVE similar to NVE but coag neg staph still common • Platelets still deposit • Infection of surgical site leads to ring abscess
 Endocarditis Fever + murmur, persistent bacteremia Insidious onset of non-specific symptoms History of heart disease, dental work Small red lesions on palms/soles, Janeway are non-tender, Osler’s is tender • Roth spots – retinal hemorrhage w/ central pallor • Splinter hemorrhages under nails • Anemia, elevated ESR, TEE echo • •
Endocarditis Fever + murmur, persistent bacteremia Insidious onset of non-specific symptoms History of heart disease, dental work Small red lesions on palms/soles, Janeway are non-tender, Osler’s is tender • Roth spots – retinal hemorrhage w/ central pallor • Splinter hemorrhages under nails • Anemia, elevated ESR, TEE echo • •
 Endocarditis • Dx: Duke – microbes on valve OR 2 major OR 1 major & 3 minor OR 5 minor • Tx: IV Bactericidal for >4 weeks (Viridans) IV PCN + aminoglycoside (Culture-neg) IV Ceftriaxone (MRSA) Vancomycin + Gentamycin + Rifampin (Entero) Ampicillin + Gentamycin (Fungi) Amphotericin B + SURGERY (2+ embolic event) SURGERY • Prophylaxis: Amoxicillin
Endocarditis • Dx: Duke – microbes on valve OR 2 major OR 1 major & 3 minor OR 5 minor • Tx: IV Bactericidal for >4 weeks (Viridans) IV PCN + aminoglycoside (Culture-neg) IV Ceftriaxone (MRSA) Vancomycin + Gentamycin + Rifampin (Entero) Ampicillin + Gentamycin (Fungi) Amphotericin B + SURGERY (2+ embolic event) SURGERY • Prophylaxis: Amoxicillin
 Respiratory Diseases Rhinitis Influenza • Rhinovirus, parainfluenza, RSV, coronavirus, others • Rhinorrhea, little cellular damage, self-limiting • Symptoms peak days 3 -4, persist 1 -2 weeks • Late August to early spring, unrelated to temp • Leading infectious cause of death in US • Type A shifts H+N antigens easily, B less so • Vaccine: 2 A strains, 1 B • Amantadine resistance is prevalent
Respiratory Diseases Rhinitis Influenza • Rhinovirus, parainfluenza, RSV, coronavirus, others • Rhinorrhea, little cellular damage, self-limiting • Symptoms peak days 3 -4, persist 1 -2 weeks • Late August to early spring, unrelated to temp • Leading infectious cause of death in US • Type A shifts H+N antigens easily, B less so • Vaccine: 2 A strains, 1 B • Amantadine resistance is prevalent
 Respiratory Diseases Typical Pneumonia Streptococcus pneumoniae • Rusty sputum, unilobar • Aspirated into alveolar space, fills with fluid and PMN, then fills with blood (2 -3 d), then fill with fibrin, then resolve w/o scarring • Asplenic, sickle-cell, agammaglobulinemia at risk • Vaccine has 23 serotypes Atypical Pneumonia Mycoplasma pneumoniae • Dry cough, myringitis • Inhaled, attaches to respiratory cell, bronchitis infiltrated by plasma cells, lasts 2 -6 wks • Similar to Chlamydophila • Unusual over age 40 • Ig. M cold agglutinins
Respiratory Diseases Typical Pneumonia Streptococcus pneumoniae • Rusty sputum, unilobar • Aspirated into alveolar space, fills with fluid and PMN, then fills with blood (2 -3 d), then fill with fibrin, then resolve w/o scarring • Asplenic, sickle-cell, agammaglobulinemia at risk • Vaccine has 23 serotypes Atypical Pneumonia Mycoplasma pneumoniae • Dry cough, myringitis • Inhaled, attaches to respiratory cell, bronchitis infiltrated by plasma cells, lasts 2 -6 wks • Similar to Chlamydophila • Unusual over age 40 • Ig. M cold agglutinins
 Respiratory Diseases Aspiration Pneumonia • Chronic, foul sputum • Polymicrobial anaerobic, microaerophilic aspirated into lung • Alcoholics, seizures, tracheoesophageal fistula are risk factors • Tx: Clindamycin PO x 3 wks
Respiratory Diseases Aspiration Pneumonia • Chronic, foul sputum • Polymicrobial anaerobic, microaerophilic aspirated into lung • Alcoholics, seizures, tracheoesophageal fistula are risk factors • Tx: Clindamycin PO x 3 wks
 Acute Bacterial Meningitis • S. pneumoniae – vaccine covers most types • N. meningitidis – B cause half infections – vaccine does not have B • H. influenzae – type b vaccine • L. monocytogenes – neonates + elderly • <4 w GBS, <18 y H. flu, 1850 y S. pneu, >50 y L. mono • Stiff neck, Kernig’s sign (leg extension resisted when supine), Brudzinski’s sign (neck flex causes hip flex) • Dx: CNS leukocytosis, positive culture • Tx: Ceftriaxone (+Vanco if community acquired) (+ampicillin if immunocompromised) + Dexamethasone
Acute Bacterial Meningitis • S. pneumoniae – vaccine covers most types • N. meningitidis – B cause half infections – vaccine does not have B • H. influenzae – type b vaccine • L. monocytogenes – neonates + elderly • <4 w GBS, <18 y H. flu, 1850 y S. pneu, >50 y L. mono • Stiff neck, Kernig’s sign (leg extension resisted when supine), Brudzinski’s sign (neck flex causes hip flex) • Dx: CNS leukocytosis, positive culture • Tx: Ceftriaxone (+Vanco if community acquired) (+ampicillin if immunocompromised) + Dexamethasone
 Acute Viral Meningitis • Enterovirus – Kids > 2 wks old – Summer months – Hand-foot-mouth disease, herpangina • HSV-2 – Aseptic meningitis – Genital warts • HIV – Aseptic meningitis • Mucosal to viremia to BBB crossing to subarachnoid space to CSF to inflammation • Dx: LP <1000, mostly lymphocytes • Tx: (enterov) nothing (HSV-2) acyclovir (HIV) HAART
Acute Viral Meningitis • Enterovirus – Kids > 2 wks old – Summer months – Hand-foot-mouth disease, herpangina • HSV-2 – Aseptic meningitis – Genital warts • HIV – Aseptic meningitis • Mucosal to viremia to BBB crossing to subarachnoid space to CSF to inflammation • Dx: LP <1000, mostly lymphocytes • Tx: (enterov) nothing (HSV-2) acyclovir (HIV) HAART
 Chronic Meningitis • Fungal – CSF glucose normal, protein >60, WBC <500 • Tuberculosis – CSF protein >>100 – AFB smear, +culture • Chronic symptoms with gradual neurologic decline • Dx: history, PE, LP • Tx: most likely diagnosis
Chronic Meningitis • Fungal – CSF glucose normal, protein >60, WBC <500 • Tuberculosis – CSF protein >>100 – AFB smear, +culture • Chronic symptoms with gradual neurologic decline • Dx: history, PE, LP • Tx: most likely diagnosis
 Intracranial Abscess • Frontal: sinus, teeth Temporal: ear, jaw, sinus Cerebellum: ear, jaw • Neurologic deficit • 1 -3 d: early cerebritis 4 -9 d: late cerebritis 10 -13 d: early capsule – Strep, GNR, Bacteroides, >14 d: late capsule S. aureus, Fusobacter • Dx: MRI/CT c contrast • MCA: blood, lung, heart • Tx: Surgical drainage, – Staph, Strep, Fusobacter, manage ICP, culture Actinomyces, Anaerobes Metronidazole + ceph + • Beneath wound naf/vanco – Clostridium, Staph, Strep
Intracranial Abscess • Frontal: sinus, teeth Temporal: ear, jaw, sinus Cerebellum: ear, jaw • Neurologic deficit • 1 -3 d: early cerebritis 4 -9 d: late cerebritis 10 -13 d: early capsule – Strep, GNR, Bacteroides, >14 d: late capsule S. aureus, Fusobacter • Dx: MRI/CT c contrast • MCA: blood, lung, heart • Tx: Surgical drainage, – Staph, Strep, Fusobacter, manage ICP, culture Actinomyces, Anaerobes Metronidazole + ceph + • Beneath wound naf/vanco – Clostridium, Staph, Strep
 Viral Encephalitis • Non-treatable – EEEV, WEEV, VEEV, St. Louis Encephalitis, West Nile, Polio, Rabies, HIV, Measles • Treatable – HSV-1/2, VZV • Altered mental status, decrease LOC, seizures • Enter brain via blood, retrograde transport, exposed CN-I • Dx: EEG, MRI, LP/PCR • Tx: Acyclovir if treatable
Viral Encephalitis • Non-treatable – EEEV, WEEV, VEEV, St. Louis Encephalitis, West Nile, Polio, Rabies, HIV, Measles • Treatable – HSV-1/2, VZV • Altered mental status, decrease LOC, seizures • Enter brain via blood, retrograde transport, exposed CN-I • Dx: EEG, MRI, LP/PCR • Tx: Acyclovir if treatable
 Subdural Empyema • Bacteriology – Strep, Staph, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, anerobes, GNR – Usually polymicrobial • Inflammatory Source – 50 -80% frontal/ethmoid – 10 -20% mastoid/AOM – 5% hematogenous • Altered mental status, focal neuro signs, seizures, like rapidly expanding mass lesion • Reach via emissary vessels or osteomyelitis • Dx: MRI • Tx: Burr holes, craniotomy, manage ICP Metronidazole + Ceftriaxone + Naf/Vanco
Subdural Empyema • Bacteriology – Strep, Staph, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, anerobes, GNR – Usually polymicrobial • Inflammatory Source – 50 -80% frontal/ethmoid – 10 -20% mastoid/AOM – 5% hematogenous • Altered mental status, focal neuro signs, seizures, like rapidly expanding mass lesion • Reach via emissary vessels or osteomyelitis • Dx: MRI • Tx: Burr holes, craniotomy, manage ICP Metronidazole + Ceftriaxone + Naf/Vanco
 Epidural Abscess Intracranial Spinal • Intracranial epidural abscess spills over into subdural space • 81% associated with subdural empyema, similar bacteriology, diagnositic, treatment • Mainly S. aureus (60 -90%) • Abscess covers 4 -5 vertebra but can extend entire length • Focal pain, radiculopathy, increasing paralysis • Bacteria enter space by osteomyelitis or hematogenous • Dx: MRI, myelogram • Tx: Surgical drainage Metro + 3 rd gen ceph + Vanco
Epidural Abscess Intracranial Spinal • Intracranial epidural abscess spills over into subdural space • 81% associated with subdural empyema, similar bacteriology, diagnositic, treatment • Mainly S. aureus (60 -90%) • Abscess covers 4 -5 vertebra but can extend entire length • Focal pain, radiculopathy, increasing paralysis • Bacteria enter space by osteomyelitis or hematogenous • Dx: MRI, myelogram • Tx: Surgical drainage Metro + 3 rd gen ceph + Vanco
 Nosocomial Precautions • Standard: gloves, do not recap needles – Infectious: blood, CSF, amniotic/vaginal fluid, semen – Low Risk: saliva, sputum, urine, feces • Surgery: double glove, cover shoes, (face shield) • Contact: gown (+gloves) – VRE, MRSA, C. difficile • Droplet: surgical mask – Influenza, Mumps, Meningococcal Meningitis • Airborne: N-95 mask (particles <5 microns) – TB, Chicken Pox
Nosocomial Precautions • Standard: gloves, do not recap needles – Infectious: blood, CSF, amniotic/vaginal fluid, semen – Low Risk: saliva, sputum, urine, feces • Surgery: double glove, cover shoes, (face shield) • Contact: gown (+gloves) – VRE, MRSA, C. difficile • Droplet: surgical mask – Influenza, Mumps, Meningococcal Meningitis • Airborne: N-95 mask (particles <5 microns) – TB, Chicken Pox
 Nosocomial Risks and Numbers • Accidental contaminated needlestick – 1: 300 HIV (therapy decrease risk 8 -fold) – 1: 30 Hepatitis C – 1: 3 Hepatitis B (without therapy) • Bacterial drug resistance – 63% S. aureus in hospitals are MRSA (2007) – 80% E. faecium in this area are VRE • Bacteruria occurs in 100% of patients with indwelling urinary catheters after 30 days
Nosocomial Risks and Numbers • Accidental contaminated needlestick – 1: 300 HIV (therapy decrease risk 8 -fold) – 1: 30 Hepatitis C – 1: 3 Hepatitis B (without therapy) • Bacterial drug resistance – 63% S. aureus in hospitals are MRSA (2007) – 80% E. faecium in this area are VRE • Bacteruria occurs in 100% of patients with indwelling urinary catheters after 30 days
 UTIs • We prevent UTIs by emptying bladder, valves, normal flora distally, lack glucose, Tamm-Horsfall protein (prevent E. coli attachment) • Lower UTI vs Upper UTI – Lower UTI is the lower poles and the bladder, upper UTI is the upper poles and the kidneys • Uncomplicated vs Complicated – Uncomplicated is adult female who Is not pregnant with normal urinary tract anatomy/fxn • E. coli most common cause of UTIs
UTIs • We prevent UTIs by emptying bladder, valves, normal flora distally, lack glucose, Tamm-Horsfall protein (prevent E. coli attachment) • Lower UTI vs Upper UTI – Lower UTI is the lower poles and the bladder, upper UTI is the upper poles and the kidneys • Uncomplicated vs Complicated – Uncomplicated is adult female who Is not pregnant with normal urinary tract anatomy/fxn • E. coli most common cause of UTIs
 UTIs Lower UTI • Cystitis – – – Dysuria, frequency, urgency Pyuria tested by urine dipstick Hematuria, bacteruria Uncomplicated tx Cipro x 3 d Complicated tx Cipro x 7 -14 d • Urethritis – Usually due to STD • Prostatitis – Avoid rectal exam if acute – Acute tx: TMP-SMX x 14 d – Chronic difficult to treat Upper UTI • Fever common symptom • Pyelonephritis – – – 85% E. coli, 15% entero Dysuria, frequency, urgency Fever, CVA/flank tenderness, N/V “urosepsis” appear septic Tx ampi + aminoglycoside x 14 d • Renal Abscess – – Rare complication in DM Can be caused by S. aureus Dx CT/Ultrasound Tx anti-staph PCN, cephalosporin
UTIs Lower UTI • Cystitis – – – Dysuria, frequency, urgency Pyuria tested by urine dipstick Hematuria, bacteruria Uncomplicated tx Cipro x 3 d Complicated tx Cipro x 7 -14 d • Urethritis – Usually due to STD • Prostatitis – Avoid rectal exam if acute – Acute tx: TMP-SMX x 14 d – Chronic difficult to treat Upper UTI • Fever common symptom • Pyelonephritis – – – 85% E. coli, 15% entero Dysuria, frequency, urgency Fever, CVA/flank tenderness, N/V “urosepsis” appear septic Tx ampi + aminoglycoside x 14 d • Renal Abscess – – Rare complication in DM Can be caused by S. aureus Dx CT/Ultrasound Tx anti-staph PCN, cephalosporin
 Other UTIs Catheter-related UTI Pregnancy • Most common nosocomial infection • Indwelling = Foley cath • Mostly by E. coli, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterococci • Can lead to “urosepsis” • Tx: change the catheter broad spectrum ATB x 3 -5 d • 5% develop asymptomatic bacteruria • Screened at 1 st visit and 28 th week (or 16 th week once) • Associated with premature labor, stillbirth, low infant birth weights • Tx amoxicillin, TMP-SMX, cephalosporin to eradicate
Other UTIs Catheter-related UTI Pregnancy • Most common nosocomial infection • Indwelling = Foley cath • Mostly by E. coli, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterococci • Can lead to “urosepsis” • Tx: change the catheter broad spectrum ATB x 3 -5 d • 5% develop asymptomatic bacteruria • Screened at 1 st visit and 28 th week (or 16 th week once) • Associated with premature labor, stillbirth, low infant birth weights • Tx amoxicillin, TMP-SMX, cephalosporin to eradicate
 Cellulitis Staph. aureus | Strep. pyogenes • Source: anterior nares • Source: nasopharynx • Virulence: hemolytic • Virulence: M-protein toxin and leukocidin and hyaluronidase • Entry by infected oil gland, puncture, bite, rash • High risk: poor lymph drainage, blood supply, neutropenia, hypogammaglobulinemia • Tx: elevate extremity, local heat, ATB • Variants • Impetigo – confined to dermis with crusting • Erysipelas – rapidly spreads, raised borders • Furuncles – local abscesses from infected gland • Carbuncle – several connected furuncles
Cellulitis Staph. aureus | Strep. pyogenes • Source: anterior nares • Source: nasopharynx • Virulence: hemolytic • Virulence: M-protein toxin and leukocidin and hyaluronidase • Entry by infected oil gland, puncture, bite, rash • High risk: poor lymph drainage, blood supply, neutropenia, hypogammaglobulinemia • Tx: elevate extremity, local heat, ATB • Variants • Impetigo – confined to dermis with crusting • Erysipelas – rapidly spreads, raised borders • Furuncles – local abscesses from infected gland • Carbuncle – several connected furuncles
 Skin and Soft Tissue Diseases Synergistic Gangrene • Clostridium perfringens is synergistic with GNR, S. aureus causing cellulitis • Necrosis of blood vessels, gangrene of subcutaneous tissue, spreads rapidly • Tx: Surgical removal Toxin-Cased Skin Inflammation • Toxic Shock Syndrome: – Staphylcoccus protein – Desquamation of skin of hands, feet, tongue – Hypotension, organ failure • Scarlet Fever – Streptococcus toxin – Diffuse red rash • Scalded-skin syndrome – Staphylococcal toxin – Dehydration, infection
Skin and Soft Tissue Diseases Synergistic Gangrene • Clostridium perfringens is synergistic with GNR, S. aureus causing cellulitis • Necrosis of blood vessels, gangrene of subcutaneous tissue, spreads rapidly • Tx: Surgical removal Toxin-Cased Skin Inflammation • Toxic Shock Syndrome: – Staphylcoccus protein – Desquamation of skin of hands, feet, tongue – Hypotension, organ failure • Scarlet Fever – Streptococcus toxin – Diffuse red rash • Scalded-skin syndrome – Staphylococcal toxin – Dehydration, infection
 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Anthrax • Bacillus anthracis, a soil bacterium • Marked edema, necrosis surrounding black ulcer • 20% fatal if untreated • Common in underdevelopd world Pasteurella Multocida • Gm- coccobacillus • Cat bites • Pain/swelling at bite can spread to joints and bone • Tx: opening bite, cleaning, PCN
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Anthrax • Bacillus anthracis, a soil bacterium • Marked edema, necrosis surrounding black ulcer • 20% fatal if untreated • Common in underdevelopd world Pasteurella Multocida • Gm- coccobacillus • Cat bites • Pain/swelling at bite can spread to joints and bone • Tx: opening bite, cleaning, PCN
 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Lymphocutaneous Granulomas Lyme Disease • Mycobacterium manium or Sporothrix schenckii • Painful papule can ulcerate, spread along lymphatics • M. marinum: exposure to fresh/brackish water • S. schenckii: exposure to plants (rose thorns, hay) • Tx: (fungus) Itraconazole (bac) rifampin+ethambutol • Borrelia burgdorferi • Deer tick bite, expanding disc of redness clearing in center (bulls-eye), lethargy, fever, can progress to arthritis and CNS symptoms • Tx: PCN, tetracycline
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Lymphocutaneous Granulomas Lyme Disease • Mycobacterium manium or Sporothrix schenckii • Painful papule can ulcerate, spread along lymphatics • M. marinum: exposure to fresh/brackish water • S. schenckii: exposure to plants (rose thorns, hay) • Tx: (fungus) Itraconazole (bac) rifampin+ethambutol • Borrelia burgdorferi • Deer tick bite, expanding disc of redness clearing in center (bulls-eye), lethargy, fever, can progress to arthritis and CNS symptoms • Tx: PCN, tetracycline
 GI Infections • Transmission: Feces, Food, Fluids, Fingers, Fomites, Fornication, Flies • Lactose+ (CSEEK) Citrobacter, Serratia, E. coli, Enterobacter, Kleb • Lactose- (invas) Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia • Lactose- (opportunistic) Proteus • Non-motile Gm- rod: Shigella, Kleb, Yersinia
GI Infections • Transmission: Feces, Food, Fluids, Fingers, Fomites, Fornication, Flies • Lactose+ (CSEEK) Citrobacter, Serratia, E. coli, Enterobacter, Kleb • Lactose- (invas) Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia • Lactose- (opportunistic) Proteus • Non-motile Gm- rod: Shigella, Kleb, Yersinia
 Vibrios • Vibrio cholerae – Cholera toxin: increase c. AMP results in water loss and dehydration – Rice water diarrhea, no fever, no inflammation – Halophilic, Gulf Coast – Spread via contaminated food/water • Vibrio parahemolyticus – Improperly cooked seafood, oysters – GI year-round, wound infections and septicemia in summer • Vibrio vulnificus – Very virulent – Eating oysters can cause sepsis
Vibrios • Vibrio cholerae – Cholera toxin: increase c. AMP results in water loss and dehydration – Rice water diarrhea, no fever, no inflammation – Halophilic, Gulf Coast – Spread via contaminated food/water • Vibrio parahemolyticus – Improperly cooked seafood, oysters – GI year-round, wound infections and septicemia in summer • Vibrio vulnificus – Very virulent – Eating oysters can cause sepsis
 Pathogenic E. coil • ETEC (-toxigenic) – Traveler’s diarrhea – Contaminated food/H 2 O – Toxins cause diarrhea • LT ↑c. AMP, ST ↑c. GMP • EPEC (-pathgenic) – Infant diarrhea – Effacing of microvilli, increased signal transd. – Oral/fecal, hands, foods • EHEC (-hemorrhagic) – Bloody diarrhea – Fever, HUS (hemolytic anemia, oliguric RF, thrombocytopenia) – E. coli O 157: H 7 – Shiga-like toxin, Stx – Burgers, apple juice – Do not give ATB • EAEC (-adhesive)
Pathogenic E. coil • ETEC (-toxigenic) – Traveler’s diarrhea – Contaminated food/H 2 O – Toxins cause diarrhea • LT ↑c. AMP, ST ↑c. GMP • EPEC (-pathgenic) – Infant diarrhea – Effacing of microvilli, increased signal transd. – Oral/fecal, hands, foods • EHEC (-hemorrhagic) – Bloody diarrhea – Fever, HUS (hemolytic anemia, oliguric RF, thrombocytopenia) – E. coli O 157: H 7 – Shiga-like toxin, Stx – Burgers, apple juice – Do not give ATB • EAEC (-adhesive)
 Invasive Enteric Pathogens • Shigella – S. dysenteriae (developing countries, shiga toxin stops protein synthesis), sonnei (US), flexneri, boydii – Resistant to acid – 70% <15 yo kids – Invade colon, multiply intracellularly • Salmonella – S. typhi (humans), choleraesuis (pigs), typhimurium (US) – Typhoid fever – Bacteria invade and divide in macrophages – Carrier in gallbladder – Tx (typhi) ampicillin, cefriaxone, bactrim
Invasive Enteric Pathogens • Shigella – S. dysenteriae (developing countries, shiga toxin stops protein synthesis), sonnei (US), flexneri, boydii – Resistant to acid – 70% <15 yo kids – Invade colon, multiply intracellularly • Salmonella – S. typhi (humans), choleraesuis (pigs), typhimurium (US) – Typhoid fever – Bacteria invade and divide in macrophages – Carrier in gallbladder – Tx (typhi) ampicillin, cefriaxone, bactrim
 Invasive Enteric Pathogens • Yersinia – Y. enterocolitica and pseudotuberculosis – Resist phagocytosis – Blood transfusion disease (grow at 4 C) – Belgian chocolates – Mimic appendicitis – Tx: Cipro, TMP-SMX, third gen ceph • Camphylobacter – Small Gm- commas – C. jejuni (most common US gastroenteritis, poultry, unpasteurized milk, water) C. fetus (spread to blood) C. upsaliensis (uncommon) – Damage jejunum mucosa, ulceration, self-limited – Guillan-Barre sequale
Invasive Enteric Pathogens • Yersinia – Y. enterocolitica and pseudotuberculosis – Resist phagocytosis – Blood transfusion disease (grow at 4 C) – Belgian chocolates – Mimic appendicitis – Tx: Cipro, TMP-SMX, third gen ceph • Camphylobacter – Small Gm- commas – C. jejuni (most common US gastroenteritis, poultry, unpasteurized milk, water) C. fetus (spread to blood) C. upsaliensis (uncommon) – Damage jejunum mucosa, ulceration, self-limited – Guillan-Barre sequale
 Helicobacter • H. pylori Spiral Gm- rods Corkscrew motility Urease production Peptic/duodenal ulcers, gastritis, carcinoma, MALT lymphoma – Fecal-oral transmission – Dx ELISA, urease breath test, silver stain, biopsy – Tx proton pump inhibitor + tetra + metro + bismuth – – • H. cinaedi – Gastroenteritis, septicemia, proctitis, cellulitis, sepsis in ICH – Homosexual men – Tx amp and/or gent • H. fennelliae – Gastroenteritis, septicemia, proctitis – Homosexual men – Tx amp and/or gent
Helicobacter • H. pylori Spiral Gm- rods Corkscrew motility Urease production Peptic/duodenal ulcers, gastritis, carcinoma, MALT lymphoma – Fecal-oral transmission – Dx ELISA, urease breath test, silver stain, biopsy – Tx proton pump inhibitor + tetra + metro + bismuth – – • H. cinaedi – Gastroenteritis, septicemia, proctitis, cellulitis, sepsis in ICH – Homosexual men – Tx amp and/or gent • H. fennelliae – Gastroenteritis, septicemia, proctitis – Homosexual men – Tx amp and/or gent


