c5688423b58b6a646295673c3663ac5c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

INF 245 Mobile applications Mobile Devices Ola Bø Fall 2007 Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 1

Introduction l Knowledge about mobile devices is relevant when choosing a device for an application Inputmechanism Screen -size Batteryoperating time Processor Radios Number sold Keyboard Screen Quality Accesories Size and Weight Ruggedized? Camera Software Memory Browser? GPS? Operatingsystem Who are the users? l. In some cases the device is not for us to choose. But we still need to have target devices to develop for. How do we choose the target? Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 2

Input-mechanisms I l Keypad l The standard for mobile phones is a 12 -digit keypad l We can enter all letters using multipress l or we can use T 9 (ca twice as quick as multitap). T 9 is also called dictionary supported predictive input T 9 Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 3

Input-mekanisms II l Pen based input l l l Soft Keyboard (simple, but slow) Letter Recognition– Pocket. PC (faster but more typing errors) Hand-writing recognition Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 4

Input-mechanisms III l Keyboard l l Standard for portable PC Accessory for smart phones and mobile phones l l Some smart phones have usable inbuilt keyboards l l may be wireless Thumb-keyboards Voice l l Voice recognition More advanced voice recognition may need a server – Voice gateway. l l Voice XML Problems l l Socially acceptable? Noisy environments? Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 5
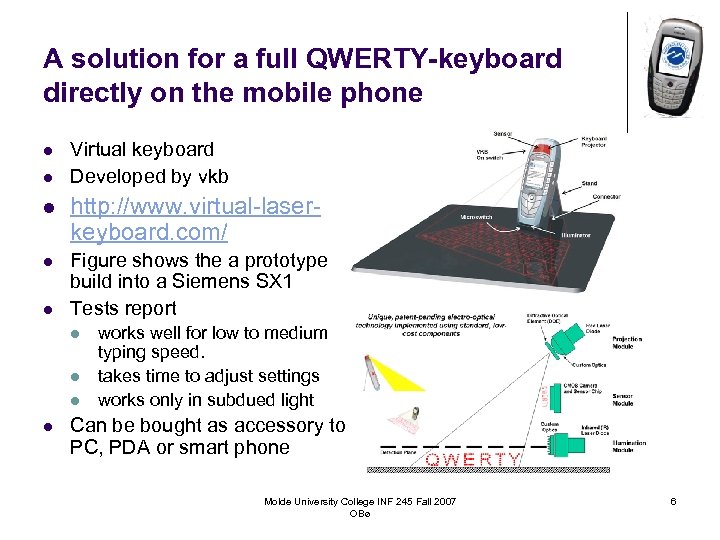
A solution for a full QWERTY-keyboard directly on the mobile phone l l Virtual keyboard Developed by vkb l http: //www. virtual-laserkeyboard. com/ l Figure shows the a prototype build into a Siemens SX 1 Tests report l l l works well for low to medium typing speed. takes time to adjust settings works only in subdued light Can be bought as accessory to PC, PDA or smart phone Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 6

Input mechanisms IV Digital Camera l l l Augmenting proportion of phones have a camera Augmenting number of pixels and camera featurs (auto focus, zoom, blitz) Applications l Used as a camera to make pictures l l Transfer to desktop, printer or lab Transfer to other persons or firms Blogging Used as a scanner to read bar codes l Places or things Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø Wikipedia the free encyclopedia 7
Input mechanisms V l GPS (Global Positioning System) l l Is beginning to be embedded in high end devices 2006/2007 Barcode scanner and/or RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader l Has been available on specialized devices for a number of years Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 8

Output mechanisms l Screen l l l Sound l l l varies widely from 96 x 68 black/white Nokia 1110 i to 240 x 320 262144 colors Nokia N 73 or 800 x 352+240 x 320 Nokia E 90 Improved sound generations Voice synthesis Projector? Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 9

Wireless communications l Three solutions: l Two cooperating devices e. g. a mobile computer and a mobile phone. § l l l Can be connected using a cable, IR (infrared) or Blue. Tooth Accessory (e. g. wlan-card) Integrated solution (radio integrated in the device) Several radios integrated in the device We are moving in this direction. Why? Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 10

Classification of mobile devices Is this illustration too simple? From Mallick (2003) Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 11

Web-phones l Mobile phones l l Wireless internet applications But display and keyboard are limited l l l Voice SMS only suitable for applications with limited sets of data Contains a wireless modem Long battery service time Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø Nokia 1110 i 12

Low end smart phones l l Similar to web-phones in size and screen Smart phones can run local applications l Applications can be downloaded via radio l l l This is called OTA (Over The Air)-provisioning Common applications: Games J 2 ME is the standard programming platform for this kind of devices. (300 000 devices sold until autumn 2004) Primary use: SMS and Telephony Simple to use Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 13
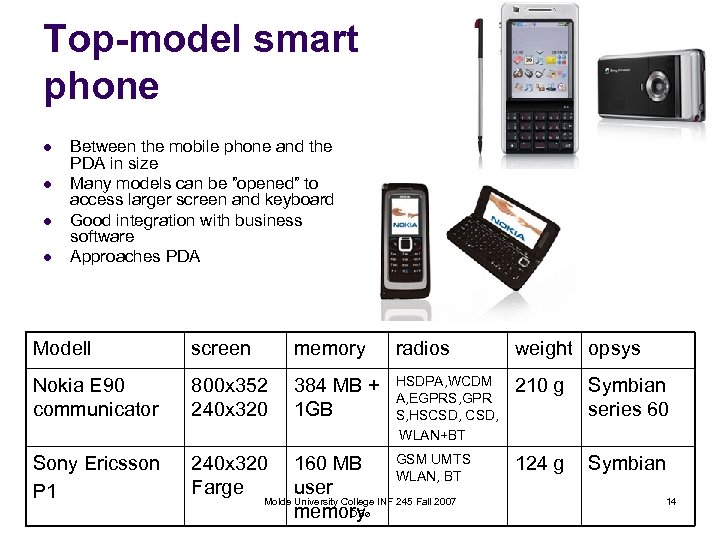
Top-model smart phone l l Between the mobile phone and the PDA in size Many models can be ”opened” to access larger screen and keyboard Good integration with business software Approaches PDA Modell screen memory radios weight opsys Nokia E 90 communicator 800 x 352 240 x 320 384 MB + 1 GB HSDPA, WCDM A, EGPRS, GPR S, HSCSD, WLAN+BT 210 g Symbian series 60 Sony Ericsson P 1 240 x 320 Farge 124 g Symbian GSM UMTS 160 MB WLAN, BT user Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø memory 14

Top-end smart phones Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 15

Handheld PCs l l l l Designed as Laptops, but smaller From 1980 Psion Windows CE -> Handheld PC Often ½ VGA i. e. 480 x 320 Instant on/off weight ca 0, 5 kg Squeezed between PDA and mini-portable Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 16

Tablet PC l l Smaller than laptop l weight can be a problem Touch-screen and pen-input l Not as precise as a mouse. l l l Same storage and computing power as a laptop Advantage over laptop l l Consequences? Can easily be used with one hand without a desk. Advantage over mobile phone l Screen size and computing power Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 17

Notebook/laptop l Advantages: l l l Same operating system and functionality as a desktop l But the computer power is often reduced – why? Can use the same applications Connectivity: an augmenting number of radios are integrated WLAN, Blue. Tooth: Standard in new devices l EDGE, UMTS: Can be added using a card Drawbacks: l l l Weight, Fragility, Battery capacity, Size Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 18

Trends – convergence and improvement l More and more technologies are melting together l Mobile phone + PDA + GPS + digital camera + mp 3 and video-player l EDGE + UMTS + Blue. Tooth + WLAN + GPS l l l in the same device roaming between networks Cheap devices steadily gets more functionality All devices gets faster processor and more memory All devices gets a colour screen with augmenting number of pixels and colour depth Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 19
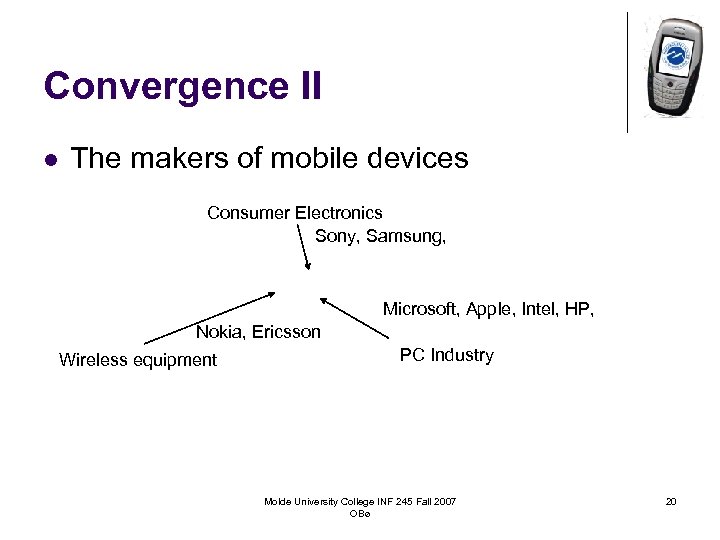
Convergence II l The makers of mobile devices Consumer Electronics Sony, Samsung, Microsoft, Apple, Intel, HP, Nokia, Ericsson Wireless equipment PC Industry Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 20

Accessories l Mobile printers l Canon PIXMA i. P 90 v Weight ~ 2 kg Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 21

Conclusion l There is a substansial heterogeneity in mobile devices, but we also see some convergence l Consequence: If you develop an application that must be available for many different diveces it is often more expensive to adapt the application to all the units than it costs to develop it for the first device (Schlickum 2005) l Testing demands a great number of units and is expensive. Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 22

Exercise Petrine’s Pizza wishes to make it possible to order Pizza from mobile equipment. The custormers should get an answer confirming that the order is received. What kind of mobile devices should this application be made for? Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 23

Exercise The maintenance workers of a manufacturing company are servicing machines in production facilities in a number of sites within a large area. For each service job there is an operating procedure and possibly drawings of the equipment to be serviced. The part inventory database and the log for service jobs should also be available and updatable. The service jobs are done regularly on a weekly to yearly schedule. The maintenance is done partly in places that are difficult to access demanding climbing ladders or passing through narrow openings. It is an advantage if the mobile equipment is available when the work is being carried out. The workers also need to communicate with each others and with the maintenance managers. Some of the work places ar without GSM or WLAN coverage. Suggest mobile devices suitable for supporting the maintenance work and explain why the selected devices are suitable. Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 24

Exercise You are working with an application to support ornithologists. The main goal of the application is to enable registration of birds in an area. The date being registered are species, number of adults, number of eggs/offspring, date, time and comment. The registered information shall be transferred to a central data base. In rare cases, the ornithologist is in doubt as to which species he is observing. Therefore images and sounds for all species should be available on the mobile device. Some of the areas being observed are outside the coverage area of mobile networks. Choose a suitable mobile device and explain why this device is appropriate. Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 25

Oppgave After testing opinion using a questionnaire there is a substantial amount of supplementary work punching the questionnaires into the database of results. The cost and number of errors committed can be reduced by registering the answer directly into the database while the respondent is answering. Suggest mobile devices that are practical for the employees of the opinion testing agency when the testing is being done by walking from door to door in an area or by stopping people in the street. What is the difference between this work situation and that of the mobile maintenance workers? Can the kind of questions asked in the questionnaire have any influence on what may be regarded as suitable equipment. Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 26

References Mallick, Martin (2003) Mobile and Wireless Design Essentials Molde University College INF 245 Fall 2007 OBø 27
c5688423b58b6a646295673c3663ac5c.ppt