2d8a920fac14a84a70e87a5e99b7ddb5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Industry & INCOSE Perspectives On SOS Architecting Critical Success Factors Paul Robitaille Director & Corporate Fellow – Systems Engineering Lockheed Martin Corporation President, INCOSE paul. robitaille@lmco. com 1
Industry & INCOSE Perspectives On SOS Architecting Critical Success Factors Paul Robitaille Director & Corporate Fellow – Systems Engineering Lockheed Martin Corporation President, INCOSE paul. robitaille@lmco. com 1
 Agenda - Definition of Architecture & Attributes of System & SOS Architectures - Observed Limitations in current practice - Key SOS Architecting Success Factors - Activities In Work to Advance the Practice 2
Agenda - Definition of Architecture & Attributes of System & SOS Architectures - Observed Limitations in current practice - Key SOS Architecting Success Factors - Activities In Work to Advance the Practice 2
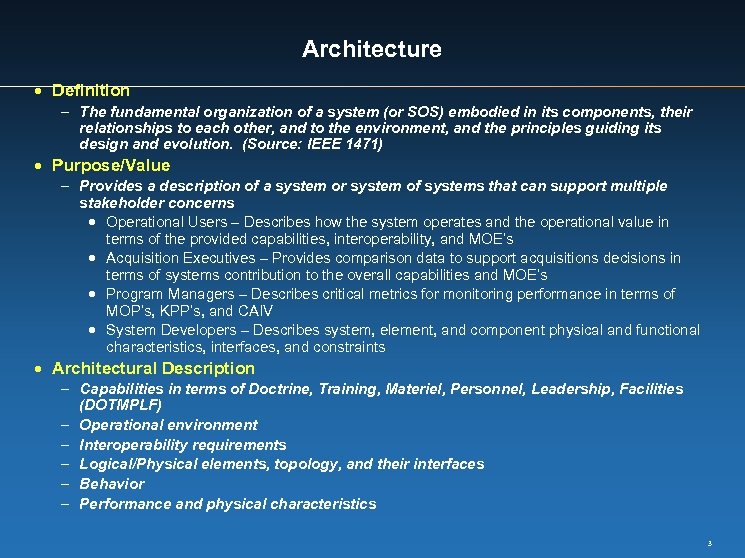 Architecture · Definition - The fundamental organization of a system (or SOS) embodied in its components, their relationships to each other, and to the environment, and the principles guiding its design and evolution. (Source: IEEE 1471) · Purpose/Value - Provides a description of a system or system of systems that can support multiple stakeholder concerns · Operational Users – Describes how the system operates and the operational value in terms of the provided capabilities, interoperability, and MOE’s · Acquisition Executives – Provides comparison data to support acquisitions decisions in terms of systems contribution to the overall capabilities and MOE’s · Program Managers – Describes critical metrics for monitoring performance in terms of MOP’s, KPP’s, and CAIV · System Developers – Describes system, element, and component physical and functional characteristics, interfaces, and constraints · Architectural Description - Capabilities in terms of Doctrine, Training, Materiel, Personnel, Leadership, Facilities (DOTMPLF) - Operational environment - Interoperability requirements - Logical/Physical elements, topology, and their interfaces - Behavior - Performance and physical characteristics 3
Architecture · Definition - The fundamental organization of a system (or SOS) embodied in its components, their relationships to each other, and to the environment, and the principles guiding its design and evolution. (Source: IEEE 1471) · Purpose/Value - Provides a description of a system or system of systems that can support multiple stakeholder concerns · Operational Users – Describes how the system operates and the operational value in terms of the provided capabilities, interoperability, and MOE’s · Acquisition Executives – Provides comparison data to support acquisitions decisions in terms of systems contribution to the overall capabilities and MOE’s · Program Managers – Describes critical metrics for monitoring performance in terms of MOP’s, KPP’s, and CAIV · System Developers – Describes system, element, and component physical and functional characteristics, interfaces, and constraints · Architectural Description - Capabilities in terms of Doctrine, Training, Materiel, Personnel, Leadership, Facilities (DOTMPLF) - Operational environment - Interoperability requirements - Logical/Physical elements, topology, and their interfaces - Behavior - Performance and physical characteristics 3
 Observed Architecting Limitations (DOD Context) · Inability to support capabilities-based planning processes with a useful architecture description of ends, ways, and means expressed as the full range of DOTMLPF architecture alternatives · Inability to support systems acquisition and portfolio planning/investment processes with an unambiguous way to compare architecture alternatives · Inability to integrate architecture descriptions with other systems engineering artifacts such as requirements specifications and engineering analyses · In general, not focusing on client-valued support to core organizational processes · In general, not producing results in the language of those who need them Although “pockets of good practice” do exist, architecting in general is failing to meet the expectations of its clients 4
Observed Architecting Limitations (DOD Context) · Inability to support capabilities-based planning processes with a useful architecture description of ends, ways, and means expressed as the full range of DOTMLPF architecture alternatives · Inability to support systems acquisition and portfolio planning/investment processes with an unambiguous way to compare architecture alternatives · Inability to integrate architecture descriptions with other systems engineering artifacts such as requirements specifications and engineering analyses · In general, not focusing on client-valued support to core organizational processes · In general, not producing results in the language of those who need them Although “pockets of good practice” do exist, architecting in general is failing to meet the expectations of its clients 4
 Proposed Critical Success Factors Ensure the architecture definition can be used to answer the specific questions under study for the stakeholders: 1. Data-centric, not product centric approach – yielding actionable architectures 2. Unambiguous, clear, and semantically rich views – (Remember Zachman’s principles!) 3. Identify the core set of architecture elements 4. Support executable architecture development & analysis 5. Be useful for more than just IT architecting 6. Support cost-benefit analyses 7. Enable federating / linking of architectures 8. Support structured / object modeling methodologies 9. Seamlessly fit within the broader set of SE process (Reference: Ring, Current State of Do. DAF / CADM v 1. 0 Architecting) 5
Proposed Critical Success Factors Ensure the architecture definition can be used to answer the specific questions under study for the stakeholders: 1. Data-centric, not product centric approach – yielding actionable architectures 2. Unambiguous, clear, and semantically rich views – (Remember Zachman’s principles!) 3. Identify the core set of architecture elements 4. Support executable architecture development & analysis 5. Be useful for more than just IT architecting 6. Support cost-benefit analyses 7. Enable federating / linking of architectures 8. Support structured / object modeling methodologies 9. Seamlessly fit within the broader set of SE process (Reference: Ring, Current State of Do. DAF / CADM v 1. 0 Architecting) 5
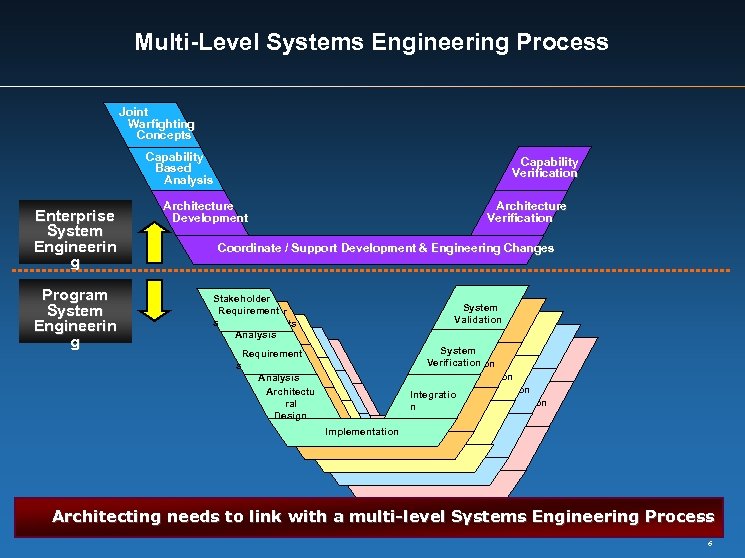 Multi-Level Systems Engineering Process Joint Warfighting Concepts Capability Based Analysis Enterprise System Engineerin g Program System Engineerin g Capability Verification Architecture Development Architecture Verification Coordinate / Support Development & Engineering Changes Stakeholder Requirement Stakeholder s Requirements Analysis Requirement s Analysis Architectu ral Synthesi Design s Synthesi s s. Implementation Synthesi s System Validation System Verification Integration Integration n Unit Test Architecting needs to link with a multi-level Systems Engineering Process 6
Multi-Level Systems Engineering Process Joint Warfighting Concepts Capability Based Analysis Enterprise System Engineerin g Program System Engineerin g Capability Verification Architecture Development Architecture Verification Coordinate / Support Development & Engineering Changes Stakeholder Requirement Stakeholder s Requirements Analysis Requirement s Analysis Architectu ral Synthesi Design s Synthesi s s. Implementation Synthesi s System Validation System Verification Integration Integration n Unit Test Architecting needs to link with a multi-level Systems Engineering Process 6
 Related Development Research Activities - DODAF V 2. 0 WG · Delivery of Version 1. 5 1 st Quarter 2007 · V 2. 0 - ensure required SE information is included to support stakeholder needs - DOD OUSD AT&L – DOD SOSE Guide Book – with support from INCOSE - Model Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) · Develop model based SE methods and techniques to facilitate SE-Design communications - ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 WG 42 · New Group dedicated to architecture & linked to WG 7 (Life cycle processes) · Fast tracked IEEE 1471 into ISO/IEC 25961 which is planned for update - Object Management Group (OMG) · Drive detailed requirements for standard architecture representations (e. g. Sys. ML, UML Profile for DODAF/MODAF) for SE/So. SE - LM - Extending the SE Vee Model to Address SOS SE - Net Centric Operations Industry Consortium (NCOIC) · Support standard frameworks for interoperability and net centric strategies 7
Related Development Research Activities - DODAF V 2. 0 WG · Delivery of Version 1. 5 1 st Quarter 2007 · V 2. 0 - ensure required SE information is included to support stakeholder needs - DOD OUSD AT&L – DOD SOSE Guide Book – with support from INCOSE - Model Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) · Develop model based SE methods and techniques to facilitate SE-Design communications - ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 WG 42 · New Group dedicated to architecture & linked to WG 7 (Life cycle processes) · Fast tracked IEEE 1471 into ISO/IEC 25961 which is planned for update - Object Management Group (OMG) · Drive detailed requirements for standard architecture representations (e. g. Sys. ML, UML Profile for DODAF/MODAF) for SE/So. SE - LM - Extending the SE Vee Model to Address SOS SE - Net Centric Operations Industry Consortium (NCOIC) · Support standard frameworks for interoperability and net centric strategies 7
 INCOSE Architecture Working Group (AWG) Core Leadership Team · Dr. Harry Crisp INCOSE Fellow · Mr. Hillary Sillitto INCOSE UK Chapter President Head of Integration Authority, MOD · Mr. Dennis De. Voti, P. E. Deputy Commissioning Officer NYC Transit - CPM · Mr. Sanford Friedenthal INCOSE Liaison to the OMG Chair, OMG Systems Engineering Domain Special Interest Group (SE DISG) Lockheed Martin · Mr. Dwayne Hardy American Systems Corporation Advisor to the Do. D Open Systems Joint Task Force (OSJTF) · Dr. Barry Boehm Professor of Software Engineering Director, USC Center for Software Engineering University of Southern California · Mr. James Martin INCOSE Head of Standards The Aerospace Corporation · Dr. Charles Dickerson Chair, INCOSE Architecture Working Group Technical Fellow, BAE Systems · Dr. William Crossley Associate Professor – Purdue University · Stuart Arnold Qinetiq 8
INCOSE Architecture Working Group (AWG) Core Leadership Team · Dr. Harry Crisp INCOSE Fellow · Mr. Hillary Sillitto INCOSE UK Chapter President Head of Integration Authority, MOD · Mr. Dennis De. Voti, P. E. Deputy Commissioning Officer NYC Transit - CPM · Mr. Sanford Friedenthal INCOSE Liaison to the OMG Chair, OMG Systems Engineering Domain Special Interest Group (SE DISG) Lockheed Martin · Mr. Dwayne Hardy American Systems Corporation Advisor to the Do. D Open Systems Joint Task Force (OSJTF) · Dr. Barry Boehm Professor of Software Engineering Director, USC Center for Software Engineering University of Southern California · Mr. James Martin INCOSE Head of Standards The Aerospace Corporation · Dr. Charles Dickerson Chair, INCOSE Architecture Working Group Technical Fellow, BAE Systems · Dr. William Crossley Associate Professor – Purdue University · Stuart Arnold Qinetiq 8
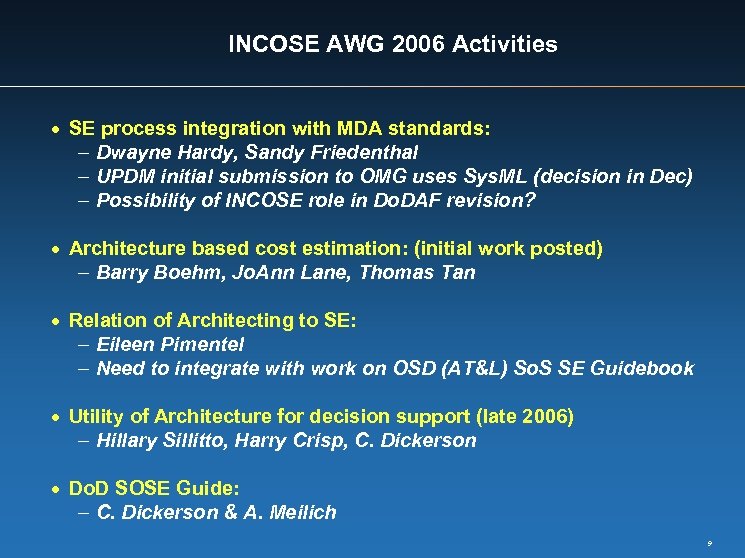 INCOSE AWG 2006 Activities · SE process integration with MDA standards: - Dwayne Hardy, Sandy Friedenthal - UPDM initial submission to OMG uses Sys. ML (decision in Dec) - Possibility of INCOSE role in Do. DAF revision? · Architecture based cost estimation: (initial work posted) - Barry Boehm, Jo. Ann Lane, Thomas Tan · Relation of Architecting to SE: - Eileen Pimentel - Need to integrate with work on OSD (AT&L) So. S SE Guidebook · Utility of Architecture for decision support (late 2006) - Hillary Sillitto, Harry Crisp, C. Dickerson · Do. D SOSE Guide: - C. Dickerson & A. Meilich 9
INCOSE AWG 2006 Activities · SE process integration with MDA standards: - Dwayne Hardy, Sandy Friedenthal - UPDM initial submission to OMG uses Sys. ML (decision in Dec) - Possibility of INCOSE role in Do. DAF revision? · Architecture based cost estimation: (initial work posted) - Barry Boehm, Jo. Ann Lane, Thomas Tan · Relation of Architecting to SE: - Eileen Pimentel - Need to integrate with work on OSD (AT&L) So. S SE Guidebook · Utility of Architecture for decision support (late 2006) - Hillary Sillitto, Harry Crisp, C. Dickerson · Do. D SOSE Guide: - C. Dickerson & A. Meilich 9
 INCOSE AWG Web Site · The web site is now operational on INCOSE Connect · Relation of the web site to the AWG and INCOSE - Core working group/leaders (contributors to BOK; write authority) - Community of practice (AWG members have read access) - Community of interest (access of all INCOSE TBD) · Leaders are responsible for posting a focus area - Visibility as an incentive for progress · Ultimately the AWG web site should provide an open portal to a broader international community 10
INCOSE AWG Web Site · The web site is now operational on INCOSE Connect · Relation of the web site to the AWG and INCOSE - Core working group/leaders (contributors to BOK; write authority) - Community of practice (AWG members have read access) - Community of interest (access of all INCOSE TBD) · Leaders are responsible for posting a focus area - Visibility as an incentive for progress · Ultimately the AWG web site should provide an open portal to a broader international community 10
 SE Shared Vision Project · INCOSE Led Project to develop a consensus, community shared vision for Systems Engineering · A follow-up comment adjudication meeting will be held on January 27 -30 in conjunction with the INCOSE International Workshop in Albuquerque, NM · Community Review Period From 30 October – 15 December 2006 - Version 2. 0 of SE Vision (PDF) - Review Guidance Sheet (MS Word) - Comment Submittal Sheet (Excel) 11
SE Shared Vision Project · INCOSE Led Project to develop a consensus, community shared vision for Systems Engineering · A follow-up comment adjudication meeting will be held on January 27 -30 in conjunction with the INCOSE International Workshop in Albuquerque, NM · Community Review Period From 30 October – 15 December 2006 - Version 2. 0 of SE Vision (PDF) - Review Guidance Sheet (MS Word) - Comment Submittal Sheet (Excel) 11
 SE Vision V 2. 0 Findings Grand Challenges: · Multi-Dimensional mathematical model manager · Evolutionary computational and generic algorithms to help explore the trade space · Quantitative risk management based on decision theory · Value and preference model to translate diverse stakeholder requirements · More comprehensive collaborative integrated development toolset that will support distributed large scale system and SOS development Maybe not Grand Challenges, but still Challenges needing work: · So. S “Grade” Baseline Management Techniques · Risk based processes with supporting measures and improved risk management techniques 12
SE Vision V 2. 0 Findings Grand Challenges: · Multi-Dimensional mathematical model manager · Evolutionary computational and generic algorithms to help explore the trade space · Quantitative risk management based on decision theory · Value and preference model to translate diverse stakeholder requirements · More comprehensive collaborative integrated development toolset that will support distributed large scale system and SOS development Maybe not Grand Challenges, but still Challenges needing work: · So. S “Grade” Baseline Management Techniques · Risk based processes with supporting measures and improved risk management techniques 12
 Questions? 13
Questions? 13


