ca296cb90cc5b833240e40126a5f5bc6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 125
 Industrialization & Segregation Making America Grow and Divide
Industrialization & Segregation Making America Grow and Divide
 Timeline of Events ® 1826 ® Photography is invented ® 1837 ® Samuel Morse invents the telegraph ® 1846 ® Elias Howe invents the sewing machine
Timeline of Events ® 1826 ® Photography is invented ® 1837 ® Samuel Morse invents the telegraph ® 1846 ® Elias Howe invents the sewing machine
 Timeline of Events ® 1850 ® Henry Bessemer develops the process to make steel ® 1859 ® Charles Darwin’s Origin of the Species is published ® 1860 ® Internal combustion engine is invented
Timeline of Events ® 1850 ® Henry Bessemer develops the process to make steel ® 1859 ® Charles Darwin’s Origin of the Species is published ® 1860 ® Internal combustion engine is invented
 Timeline of Events ® 1865 ® Marshall Fields opens the first department store ® 1866 ® First labor union formed ~ National Labor Union ~ founded by William H. Sylvis ® “Jim Crow Laws” are in effect in the South
Timeline of Events ® 1865 ® Marshall Fields opens the first department store ® 1866 ® First labor union formed ~ National Labor Union ~ founded by William H. Sylvis ® “Jim Crow Laws” are in effect in the South
 Timeline of Events ® 1867 ® Dynamite is invented ® Christopher Sholes invents the typewriter ® 1868 ® Boss Tweed heads Tammany Hall and the Tweed Ring in New York City
Timeline of Events ® 1867 ® Dynamite is invented ® Christopher Sholes invents the typewriter ® 1868 ® Boss Tweed heads Tammany Hall and the Tweed Ring in New York City
 Timeline of Events ® 1869 ® Central Pacific & Union Pacific complete the transcontinental railroad ® Knights of Labor formed by Uriah Stephens ® 1870 ® Franco Prussian War breaks out ® F. W. Woolworth founds the chain store
Timeline of Events ® 1869 ® Central Pacific & Union Pacific complete the transcontinental railroad ® Knights of Labor formed by Uriah Stephens ® 1870 ® Franco Prussian War breaks out ® F. W. Woolworth founds the chain store
 Timeline of Events ® 1871 ® The Great Chicago Fire burns from October 8 th – 10 th ® 1872 ® Montgomery Ward begins mail order catalogs ® 1873 ® First electric motor is used
Timeline of Events ® 1871 ® The Great Chicago Fire burns from October 8 th – 10 th ® 1872 ® Montgomery Ward begins mail order catalogs ® 1873 ® First electric motor is used
 Timeline of Events ® 1875 ® British labor unions win right to strike ® 1876 ® Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone ® Rutherford B. Hayes is elected president ® Porfirio Diaz seizes power in Mexico
Timeline of Events ® 1875 ® British labor unions win right to strike ® 1876 ® Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone ® Rutherford B. Hayes is elected president ® Porfirio Diaz seizes power in Mexico
 Timeline of Events ® 1877 ® Phonograph is invented ® Munn v. Illinois establishes government regulation of railroads ® Mother Jones supports the Great Strike of 1877 ® Great Strike of 1877 occurs shutting down over 50, 000 miles of railroad lines
Timeline of Events ® 1877 ® Phonograph is invented ® Munn v. Illinois establishes government regulation of railroads ® Mother Jones supports the Great Strike of 1877 ® Great Strike of 1877 occurs shutting down over 50, 000 miles of railroad lines
 Timeline of Events ® 1878 ® Bicycle touring club is founded in Europe ® 1879 ® Thomas A. Edison invents a workable light bulb ® 1880 ® James A. Garfield is elected president
Timeline of Events ® 1878 ® Bicycle touring club is founded in Europe ® 1879 ® Thomas A. Edison invents a workable light bulb ® 1880 ® James A. Garfield is elected president
 Timeline of Events ® 1881 ® Chester A. Arthur succeeds Garfield after Garfield’s assassination ® Booker T. Washington heads Tuskegee Institute ® 1882 ® United States restricts Chinese immigration
Timeline of Events ® 1881 ® Chester A. Arthur succeeds Garfield after Garfield’s assassination ® Booker T. Washington heads Tuskegee Institute ® 1882 ® United States restricts Chinese immigration
 Timeline of Events ® 1883 ® Germany becomes the first nation to provide national health insurance ® Brooklyn Bridge is completed ® Time Zones are created by C. F. Dowd
Timeline of Events ® 1883 ® Germany becomes the first nation to provide national health insurance ® Brooklyn Bridge is completed ® Time Zones are created by C. F. Dowd
 Timeline of Events ® 1884 ® Grover Cleveland is elected president ® Berlin Conference meets to divide Africa among European nations ® First roller coaster opens at Coney Island, NY
Timeline of Events ® 1884 ® Grover Cleveland is elected president ® Berlin Conference meets to divide Africa among European nations ® First roller coaster opens at Coney Island, NY
 Timeline of Events ® 1885 ® Indian National Congress forms ® 1886 ® American Federation of Labor (AFL) is formed by Samuel Gompers ® Haymarket riot turns public sentiment against unions ® Sears Roebuck opens for catalog sales
Timeline of Events ® 1885 ® Indian National Congress forms ® 1886 ® American Federation of Labor (AFL) is formed by Samuel Gompers ® Haymarket riot turns public sentiment against unions ® Sears Roebuck opens for catalog sales
 Timeline of Events ® 1888 ® Benjamin Harrison is elected president ® Electric trolleys are first introduced in Richmond, Virginia ® George Eastman introduces the Kodak camera
Timeline of Events ® 1888 ® Benjamin Harrison is elected president ® Electric trolleys are first introduced in Richmond, Virginia ® George Eastman introduces the Kodak camera
 Timeline of Events ® 1889 ® Hull House is founded in Chicago by Jane Addams ® Barnum & Bailey Circus opens in London ® Johnstown flood occurs in Pennsylvania killing more than 2, 000 people
Timeline of Events ® 1889 ® Hull House is founded in Chicago by Jane Addams ® Barnum & Bailey Circus opens in London ® Johnstown flood occurs in Pennsylvania killing more than 2, 000 people
 Timeline of Events ® 1890 ® Colonization of sub-Saharan Africa peaks ® Congress passes the Sherman Anti. Trust Act ® 1891 ® Ida B. Wells campaigns against lynching
Timeline of Events ® 1890 ® Colonization of sub-Saharan Africa peaks ® Congress passes the Sherman Anti. Trust Act ® 1891 ® Ida B. Wells campaigns against lynching
 Timeline of Events ® 1892 ® Grover Cleveland is elected for a 2 nd term ® Ellis Island opens becoming the main immigration station on the east coast
Timeline of Events ® 1892 ® Grover Cleveland is elected for a 2 nd term ® Ellis Island opens becoming the main immigration station on the east coast
 Timeline of Events ® 1893 ® Women in New Zealand gain voting rights ® France establishes Indochina ® First Ferris wheel is unveiled in Chicago, Ill.
Timeline of Events ® 1893 ® Women in New Zealand gain voting rights ® France establishes Indochina ® First Ferris wheel is unveiled in Chicago, Ill.
 Timeline of Events ® 1894 ® President Cleveland sends federal troops to Illinois to end the Pullman strike ® 1895 ® Marconi invents the radio ® X-rays are first used ® Motion pictures are invented
Timeline of Events ® 1894 ® President Cleveland sends federal troops to Illinois to end the Pullman strike ® 1895 ® Marconi invents the radio ® X-rays are first used ® Motion pictures are invented
 Timeline of Events ® 1896 ® First modern Olympic Games are held in Athens, Greece ® William Mc. Kinley is elected president ® Supreme Court established “separate but equal” doctrine in Plessy v. Ferguson ® 1898 ® Hawaii is annexed by the U. S.
Timeline of Events ® 1896 ® First modern Olympic Games are held in Athens, Greece ® William Mc. Kinley is elected president ® Supreme Court established “separate but equal” doctrine in Plessy v. Ferguson ® 1898 ® Hawaii is annexed by the U. S.
 Timeline of Events ® 1899 ® German psychoanalyst, Sigmund Freud, publishes The Interpretation of Dreams ® 1900 ® William Mc. Kinley is reelected
Timeline of Events ® 1899 ® German psychoanalyst, Sigmund Freud, publishes The Interpretation of Dreams ® 1900 ® William Mc. Kinley is reelected
 Timeline of Events ® 1901 ® The Commonwealth of Australia is founded ® William Mc. Kinley is assassinated and Theodore Roosevelt becomes president ® 1903 ® Wright Brothers fly the first airplane in Kittyhawk, North Carolina ® First World Series for baseball held ~ Boston Pilgrims beat the Pittsburgh Pirates
Timeline of Events ® 1901 ® The Commonwealth of Australia is founded ® William Mc. Kinley is assassinated and Theodore Roosevelt becomes president ® 1903 ® Wright Brothers fly the first airplane in Kittyhawk, North Carolina ® First World Series for baseball held ~ Boston Pilgrims beat the Pittsburgh Pirates
 Timeline of Events ® 1904 ® Theodore Roosevelt elected president ® 1905 ® William Haywood founds the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) or Wobblies ® Workers revolt in St. Petersburg, Russia ® Niagara Movement founded by W. E. B. Dubois
Timeline of Events ® 1904 ® Theodore Roosevelt elected president ® 1905 ® William Haywood founds the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) or Wobblies ® Workers revolt in St. Petersburg, Russia ® Niagara Movement founded by W. E. B. Dubois
 Timeline of Events ® 1906 ® San Francisco is hit by an earthquake on April 18 th ® 1907 ® Gentlemen’s Agreement with Japan ® 1908 ® Oil is discovered in Persia ® Henry Ford introduces the Model T ® William H. Taft is elected president
Timeline of Events ® 1906 ® San Francisco is hit by an earthquake on April 18 th ® 1907 ® Gentlemen’s Agreement with Japan ® 1908 ® Oil is discovered in Persia ® Henry Ford introduces the Model T ® William H. Taft is elected president
 Timeline of Events ® 1909 ® Pauline Newman founds the ILGWU (International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union) ® W. E. B. Du Bois founds the NAACP ® 1910 ® The appearance of Halley’s Comet causes widespread panic ® Mexican Revolution begins
Timeline of Events ® 1909 ® Pauline Newman founds the ILGWU (International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union) ® W. E. B. Du Bois founds the NAACP ® 1910 ® The appearance of Halley’s Comet causes widespread panic ® Mexican Revolution begins
 Timeline of Events ® 1911 ® Triangle Shirtwaist fire occurs killing 146 women ® 1912 ® Woodrow Wilson is elected president ® Qing dynasty in China is overthrown
Timeline of Events ® 1911 ® Triangle Shirtwaist fire occurs killing 146 women ® 1912 ® Woodrow Wilson is elected president ® Qing dynasty in China is overthrown
 Expansion of Industry ®Natural Resources ® U. S. after Civil War ~ agricultural nation ® By 1920 s ~ leading industrial nation ®Reasons ® Wealth for expansion of natural resources ® Government support of business ® Growing urban population providing cheap labor and markets for new products
Expansion of Industry ®Natural Resources ® U. S. after Civil War ~ agricultural nation ® By 1920 s ~ leading industrial nation ®Reasons ® Wealth for expansion of natural resources ® Government support of business ® Growing urban population providing cheap labor and markets for new products
 Black Gold ® 1840 s ® Kerosene came into use ® Abraham Gesner ~ Canadian geologist discovered how to distill the fuel from oil or coal ® 1859 ® Edwin L. Drake used a steam engine to drill for oil near Titusville, PA making the removal of oil more practical
Black Gold ® 1840 s ® Kerosene came into use ® Abraham Gesner ~ Canadian geologist discovered how to distill the fuel from oil or coal ® 1859 ® Edwin L. Drake used a steam engine to drill for oil near Titusville, PA making the removal of oil more practical
 Black Gold ®A boom spread through Kentucky, Illinois, Ohio, Indiana, and eventually Texas ®Petroleum refining industries were established in Cleveland Pittsburgh ®Gasoline was not considered usable so was thrown away
Black Gold ®A boom spread through Kentucky, Illinois, Ohio, Indiana, and eventually Texas ®Petroleum refining industries were established in Cleveland Pittsburgh ®Gasoline was not considered usable so was thrown away
 Bessemer Steel Process ®Steel ~ made by removing carbon from iron to make it lighter and more flexible ®Problem ~ how to make it easier ®Iron ore deposits found in Mesabi Range of Minnesota ~ 3 miles wide and 100 miles long
Bessemer Steel Process ®Steel ~ made by removing carbon from iron to make it lighter and more flexible ®Problem ~ how to make it easier ®Iron ore deposits found in Mesabi Range of Minnesota ~ 3 miles wide and 100 miles long
 Bessemer Steel Process ® Developed independently by British manufacturer, Henry Bessemer and American iron maker William Kelly around 1850 ® Involved injecting air into molten iron to remove the carbon and other impurities ® By 1880 s America was producing 90% of the nation’s steel
Bessemer Steel Process ® Developed independently by British manufacturer, Henry Bessemer and American iron maker William Kelly around 1850 ® Involved injecting air into molten iron to remove the carbon and other impurities ® By 1880 s America was producing 90% of the nation’s steel
 Bessemer Steel Process
Bessemer Steel Process
 New Uses for Steel ®Railroads ~ biggest customer ~ used steel for track ®Joseph Glidden ~ barbed wire ®John Deere ~ steel plow ®Cyrus Mc. Cormick ~ mechanical reaper
New Uses for Steel ®Railroads ~ biggest customer ~ used steel for track ®Joseph Glidden ~ barbed wire ®John Deere ~ steel plow ®Cyrus Mc. Cormick ~ mechanical reaper
 New Uses for Steel ®Innovations ®Brooklyn in construction Bridge ~ 1883 ~ 1595 feet across the East River in New York City ®William Le Baron Jenney ~ constructed the first skyscraper ~ Home Insurance Building in Chicago
New Uses for Steel ®Innovations ®Brooklyn in construction Bridge ~ 1883 ~ 1595 feet across the East River in New York City ®William Le Baron Jenney ~ constructed the first skyscraper ~ Home Insurance Building in Chicago
 New Uses for Steel
New Uses for Steel
 New Uses for Steel
New Uses for Steel
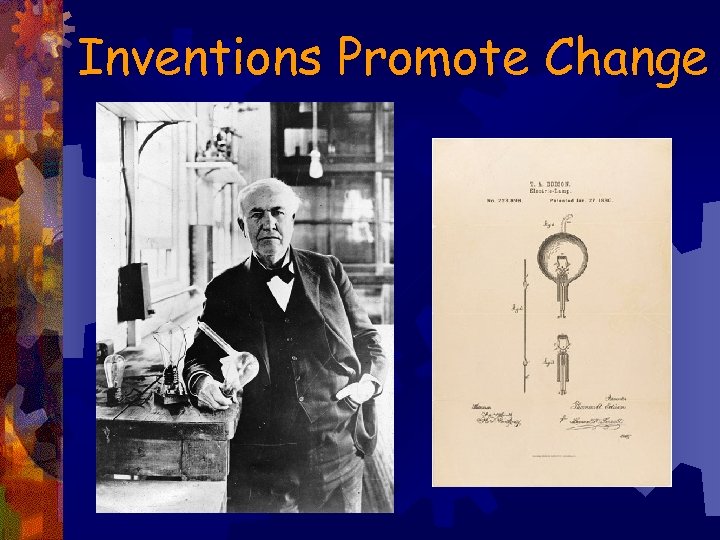
 Inventions Promote Change ® 1876 ®Thomas Alva Edison established the world’s first research lab in Menlo Park, NJ ® 1880 ®Incandescent ® 1880 s ®Invents Light Bulb a system for producing & distributing electricity
Inventions Promote Change ® 1876 ®Thomas Alva Edison established the world’s first research lab in Menlo Park, NJ ® 1880 ®Incandescent ® 1880 s ®Invents Light Bulb a system for producing & distributing electricity
 Inventions Promote Change
Inventions Promote Change
 Inventions Promote Change ®George Westinghouse assists in making electricity safer and less expensive ® 1890 s ~ electric streetcars made urban travel cheaper and efficient ®Also ran fans and printing presses
Inventions Promote Change ®George Westinghouse assists in making electricity safer and less expensive ® 1890 s ~ electric streetcars made urban travel cheaper and efficient ®Also ran fans and printing presses
 Inventions Promote Change
Inventions Promote Change
 Inventions Promote Change ® 1867 ® Christopher typewriter Sholes invented the ® 1876 ® Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas Watson invented the telephone ® opens a way for worldwide communications ® Women ® 1870 in the workforce ~ 5% and by 1910 ~ 40%
Inventions Promote Change ® 1867 ® Christopher typewriter Sholes invented the ® 1876 ® Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas Watson invented the telephone ® opens a way for worldwide communications ® Women ® 1870 in the workforce ~ 5% and by 1910 ~ 40%
 Inventions Promote Change
Inventions Promote Change
 The Age of Railroads ®Made local transit reliable and westward expansion possible for business as well as people ®Assisted in settling the West and developing the country ®Huge land grants were given to the railroads by the federal government
The Age of Railroads ®Made local transit reliable and westward expansion possible for business as well as people ®Assisted in settling the West and developing the country ®Huge land grants were given to the railroads by the federal government
 National Network ® 1856 ® Railroads extend to the Mississippi River ® 1859 ® Crossed over into Missouri ® 1869 ® Central Pacific and Union Pacific meet at Promontory, Utah on May 10, 1869 creating the first transcontinental railroad
National Network ® 1856 ® Railroads extend to the Mississippi River ® 1859 ® Crossed over into Missouri ® 1869 ® Central Pacific and Union Pacific meet at Promontory, Utah on May 10, 1869 creating the first transcontinental railroad
 National Network
National Network
 National Network
National Network
 National Network
National Network
 Railroad Time ® 1869 ® Professor C. F. Dowd proposed that the earth’s surface be divided into 24 time zones ® United States had 4 time zones ~ Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific ® 1918 ® Finally adopted by the U. S. Congress
Railroad Time ® 1869 ® Professor C. F. Dowd proposed that the earth’s surface be divided into 24 time zones ® United States had 4 time zones ~ Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific ® 1918 ® Finally adopted by the U. S. Congress
 New Towns and Markets ®Railroad promoted trade and interdependence ®Cities like Chicago, Minneapolis, Abilene, Flagstaff, Denver and Seattle will grow, prosper and become diverse
New Towns and Markets ®Railroad promoted trade and interdependence ®Cities like Chicago, Minneapolis, Abilene, Flagstaff, Denver and Seattle will grow, prosper and become diverse
 Pullman ® 1880 ® George M. Pullman build a factory for manufacturing sleepers and other railroad cars in Illinois ® Built a town nearby for his workers ® Residents lived in clean, wellconstructed brick houses and apartment buildings ® Town had doctors, offices, and an athletic field
Pullman ® 1880 ® George M. Pullman build a factory for manufacturing sleepers and other railroad cars in Illinois ® Built a town nearby for his workers ® Residents lived in clean, wellconstructed brick houses and apartment buildings ® Town had doctors, offices, and an athletic field
 Pullman
Pullman
 Pullman ® 1880 ® George M. Pullman build a factory for manufacturing sleepers and other railroad cars in Illinois ® Built a town nearby for his workers ® Residents lived in clean, wellconstructed brick houses and apartment buildings ® Town had doctors, offices, and an athletic field
Pullman ® 1880 ® George M. Pullman build a factory for manufacturing sleepers and other railroad cars in Illinois ® Built a town nearby for his workers ® Residents lived in clean, wellconstructed brick houses and apartment buildings ® Town had doctors, offices, and an athletic field
 Credit Mobilier ® One of the most infamous schemes ® Union Pacific stockholders formed a construction company in 1864 ® Gave the company the contract to lay track at 2 to 3 times the actual cost and pocketed the profits ® Donated shares of stocks to 20 representatives in Congress
Credit Mobilier ® One of the most infamous schemes ® Union Pacific stockholders formed a construction company in 1864 ® Gave the company the contract to lay track at 2 to 3 times the actual cost and pocketed the profits ® Donated shares of stocks to 20 representatives in Congress
 Credit Mobilier ® Investigation took place because of reports in the New York Sun ® Officers of the Union Pacific had taken up to $23 million in stocks, bonds and cash ® Those implicated were Vice President Schuyler Colfax, and Congressman James Garfield ® Most received a slap on the wrist and were able to keep their profits
Credit Mobilier ® Investigation took place because of reports in the New York Sun ® Officers of the Union Pacific had taken up to $23 million in stocks, bonds and cash ® Those implicated were Vice President Schuyler Colfax, and Congressman James Garfield ® Most received a slap on the wrist and were able to keep their profits
 The Grange & Railroads ®Farmers did not like railroad corruption ®Grange ® Founded in 1867 by farmers ® Demanded governmental control over the railroad industry
The Grange & Railroads ®Farmers did not like railroad corruption ®Grange ® Founded in 1867 by farmers ® Demanded governmental control over the railroad industry
 The Grange The Patrons of Husbandry
The Grange The Patrons of Husbandry
 Railroad Abuses ®Farmers Angry for many reasons ® Upset by misuse of government land grants ® Price fixing by different railroad companies ® Charging different customers different prices (more for short hauls than for long hauls)
Railroad Abuses ®Farmers Angry for many reasons ® Upset by misuse of government land grants ® Price fixing by different railroad companies ® Charging different customers different prices (more for short hauls than for long hauls)
 Granger Laws ®Grangers took political action ®Sponsored state and local candidates ®Convinced local and state legislators to pass the Granger Laws which established maximum freight and passenger rates and prohibited discrimination
Granger Laws ®Grangers took political action ®Sponsored state and local candidates ®Convinced local and state legislators to pass the Granger Laws which established maximum freight and passenger rates and prohibited discrimination
 Munn v. Illinois ® 1877 ®Supreme Court upheld the Granger Laws by a vote of 7 to 2 ®States won the right to regulate railroads for the benefit of farmers and consumers ®Helped to established the federal government’s right to regulate private industry to serve public interest
Munn v. Illinois ® 1877 ®Supreme Court upheld the Granger Laws by a vote of 7 to 2 ®States won the right to regulate railroads for the benefit of farmers and consumers ®Helped to established the federal government’s right to regulate private industry to serve public interest
 Interstate Commerce Act ® 1886 ® Supreme Court ruled states could not set rates on interstate commerce ® 1887 ® Passed by Congress in ® Established the federal government’s right to supervise railroad activities ® Created a 5 member ICC ~ Interstate Commerce Commission
Interstate Commerce Act ® 1886 ® Supreme Court ruled states could not set rates on interstate commerce ® 1887 ® Passed by Congress in ® Established the federal government’s right to supervise railroad activities ® Created a 5 member ICC ~ Interstate Commerce Commission
 Interstate Commerce Act ® 1897 ® Supreme Court ruled that it could not set maximum railroad rates ® 1906 ® Regained power to be effective
Interstate Commerce Act ® 1897 ® Supreme Court ruled that it could not set maximum railroad rates ® 1906 ® Regained power to be effective
 Panic of 1893 ® Financial problems played a huge role in the Panic of 1893 ® Worst depression of the time ® 600 banks and 15, 000 businesses failed ® 4 million people out of jobs ® 25% of the railroads were taken over by financial companies
Panic of 1893 ® Financial problems played a huge role in the Panic of 1893 ® Worst depression of the time ® 600 banks and 15, 000 businesses failed ® 4 million people out of jobs ® 25% of the railroads were taken over by financial companies
 Big Business and Labor ®Andrew Carnegie ~ Carnegie Steel ®John D. Rockefeller ~ Standard Oil ®J. P. Morgan ~ United States Steel and J. P. Morgan Banking ®Cornelius Vanderbilt ~ Vanderbilt Railroad
Big Business and Labor ®Andrew Carnegie ~ Carnegie Steel ®John D. Rockefeller ~ Standard Oil ®J. P. Morgan ~ United States Steel and J. P. Morgan Banking ®Cornelius Vanderbilt ~ Vanderbilt Railroad
 Big Business and Labor Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefeller
Big Business and Labor Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefeller
 Big Business and Labor J. P. Morgan Cornelius Vanderbilt
Big Business and Labor J. P. Morgan Cornelius Vanderbilt
 Big Business and Labor ® Andrew Carnegie ® Born in Scotland came to the U. S. in 1848 ® In 1850 he began working for the local superintendent of the Pennsylvania Railroad ® Was given the chance to purchase stock in the company ® Used the money to buy more stock and by 1865 he left his job with the Pennsylvania Railroad
Big Business and Labor ® Andrew Carnegie ® Born in Scotland came to the U. S. in 1848 ® In 1850 he began working for the local superintendent of the Pennsylvania Railroad ® Was given the chance to purchase stock in the company ® Used the money to buy more stock and by 1865 he left his job with the Pennsylvania Railroad
 Big Business and Labor ® Andrew Carnegie ® In 1873 he entered the steel business ® By 1899 Carnegie Steel Company manufactured more steel than all the factories in Great Britain ® Success due to his management practices ® Incorporated new machinery and techniques ® Attracted talented people by offering them stock in the company ® Encourage competition among his assistants
Big Business and Labor ® Andrew Carnegie ® In 1873 he entered the steel business ® By 1899 Carnegie Steel Company manufactured more steel than all the factories in Great Britain ® Success due to his management practices ® Incorporated new machinery and techniques ® Attracted talented people by offering them stock in the company ® Encourage competition among his assistants
 Carnegie Steel
Carnegie Steel
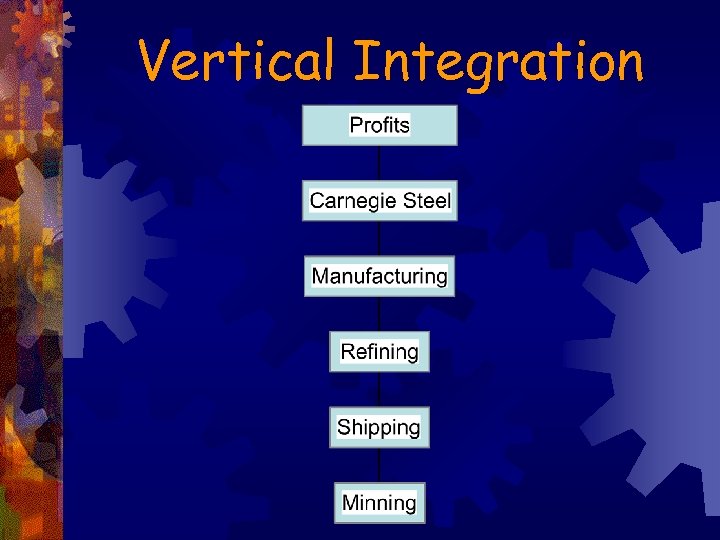
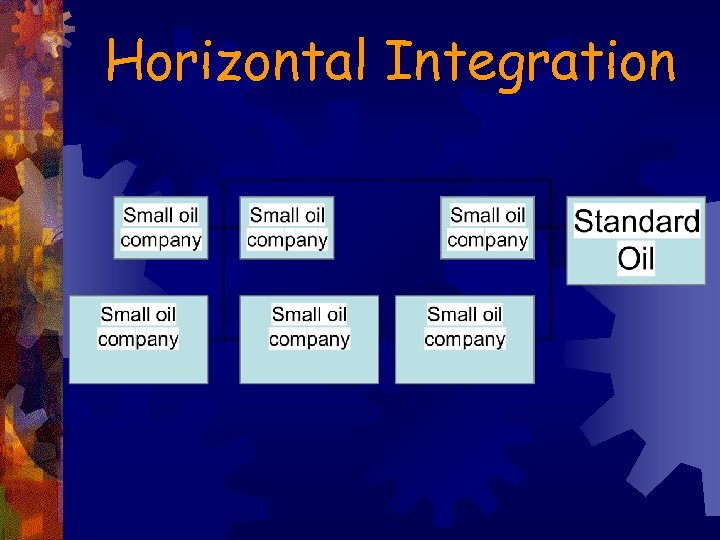
 Integration ® Vertical Integration - control all phases of development from the ground up ® Was less expensive to own mines, railroads, and processing plants than to pay rent for them ® Horizontal Integration – companies producing similar product merge ® Carnegie gained control over his suppliers and limited his competition
Integration ® Vertical Integration - control all phases of development from the ground up ® Was less expensive to own mines, railroads, and processing plants than to pay rent for them ® Horizontal Integration – companies producing similar product merge ® Carnegie gained control over his suppliers and limited his competition
 Vertical Integration
Vertical Integration
 Horizontal Integration
Horizontal Integration
 Social Darwinism ®Charles ® English Darwin naturalist ® Developed theory of biological evolution ® Wrote Origin of the Species, published in 1859 ® Explained the process of natural selection which weeded out less –suited individuals and enabled the best adapted to survive
Social Darwinism ®Charles ® English Darwin naturalist ® Developed theory of biological evolution ® Wrote Origin of the Species, published in 1859 ® Explained the process of natural selection which weeded out less –suited individuals and enabled the best adapted to survive
 Social Darwinism ® Herbert Spencer used Darwin’s theories to explain the evolution of human society ® Economists used Social Darwinism to explain laissez-faire economics ® William G. Sumner, a professor at Yale, promoted theory for business failures and successes
Social Darwinism ® Herbert Spencer used Darwin’s theories to explain the evolution of human society ® Economists used Social Darwinism to explain laissez-faire economics ® William G. Sumner, a professor at Yale, promoted theory for business failures and successes
 Robber Barons ®John D. Rockefeller ® Rockefeller sold oil cheaper than others and gave railroad friends discounts on oil if they shipped only his oil ® Standard Oil had lower prices ® Bought out competitors ® Joined the companies in trust agreements ® Horizontal Consolidation - creation of one large business from smaller ones
Robber Barons ®John D. Rockefeller ® Rockefeller sold oil cheaper than others and gave railroad friends discounts on oil if they shipped only his oil ® Standard Oil had lower prices ® Bought out competitors ® Joined the companies in trust agreements ® Horizontal Consolidation - creation of one large business from smaller ones
 Standard Oil Company
Standard Oil Company
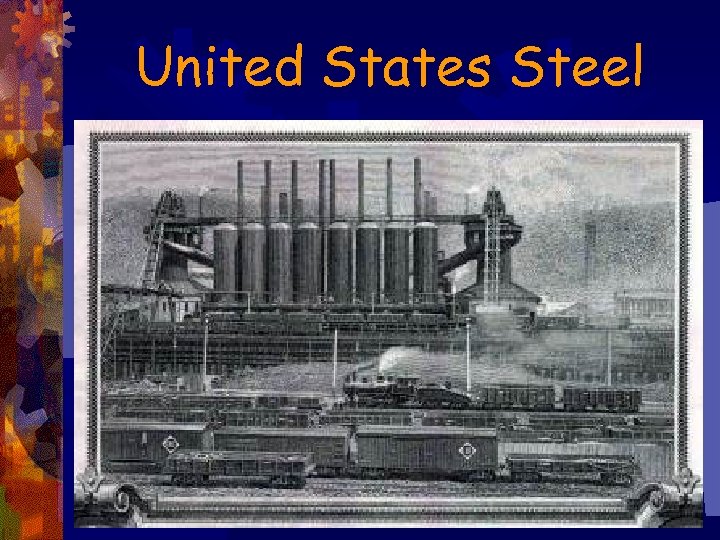
 Robber Barons ®J. P. Morgan ® Investment Banker ® Bought Carnegie Steel for $500 million ® Created U. S. Steel - the first billion dollar corporation in the world ® Controlled over 60% of steel production in the U. S.
Robber Barons ®J. P. Morgan ® Investment Banker ® Bought Carnegie Steel for $500 million ® Created U. S. Steel - the first billion dollar corporation in the world ® Controlled over 60% of steel production in the U. S.
 United States Steel
United States Steel
 Robber Barons ® These industrialists were called robber barons because of the tactics they used to create their companies. ® Industrialists were also philanthropists ® Rockefeller gave away $500 million, established the Rockefeller foundation, University of Chicago, and created a medical institute that helped cure yellow fever
Robber Barons ® These industrialists were called robber barons because of the tactics they used to create their companies. ® Industrialists were also philanthropists ® Rockefeller gave away $500 million, established the Rockefeller foundation, University of Chicago, and created a medical institute that helped cure yellow fever
 University of Chicago
University of Chicago
 Robber Barons ® Carnegie gave away about 90% of his wealth which still supports the arts and learning today ® Carnegie Hall ® Carnegie Music Institute ® Carnegie Mellon University ® 2, 811 libraries throughout the world
Robber Barons ® Carnegie gave away about 90% of his wealth which still supports the arts and learning today ® Carnegie Hall ® Carnegie Music Institute ® Carnegie Mellon University ® 2, 811 libraries throughout the world
 Carnegie Philanthropy
Carnegie Philanthropy
 Sherman Antitrust Act ® 1890 ® Made it illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade between states or with other countries ® Not easy to prosecute companies that violated the act ® Used more against labor unions than big business
Sherman Antitrust Act ® 1890 ® Made it illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade between states or with other countries ® Not easy to prosecute companies that violated the act ® Used more against labor unions than big business
 The South ® In a strangle hold by the North which controlled 90% of the railroads ® Remained agricultural and at the mercy of the railroads ® Did have hopes in forestry, mining, tobacco, furniture and textile industries
The South ® In a strangle hold by the North which controlled 90% of the railroads ® Remained agricultural and at the mercy of the railroads ® Did have hopes in forestry, mining, tobacco, furniture and textile industries
 Labor Unions Emerge ® Long Hours and Danger Steel mills demanded 7 day work weeks ® Seamstresses worked 12 hour days, 6 days a week ® Employees were not entitled to vacation, sick leave, unemployment compensation or reimbursement for injuries suffered on the job ® ® 1882 675 workers killed in on the job accidents each week ® 1890 – 1910 ~ women working went from 4 to 8 million ® 20% of the boys, 10% of the girls under 15 worked ®
Labor Unions Emerge ® Long Hours and Danger Steel mills demanded 7 day work weeks ® Seamstresses worked 12 hour days, 6 days a week ® Employees were not entitled to vacation, sick leave, unemployment compensation or reimbursement for injuries suffered on the job ® ® 1882 675 workers killed in on the job accidents each week ® 1890 – 1910 ~ women working went from 4 to 8 million ® 20% of the boys, 10% of the girls under 15 worked ®
 Child Labor
Child Labor
 Child Labor
Child Labor
 Child Labor
Child Labor
 Child Labor
Child Labor
 Early Labor Organizations ® National Labor Union (NLU) ® First large scale national organization ® Formed in 1866 by William H. Sylvis ® 640, 000 members ® 1868 – Congress passed 8 hour work day for government workers ® Colored National Labor Union ® Created because blacks were not admitted to the NLU
Early Labor Organizations ® National Labor Union (NLU) ® First large scale national organization ® Formed in 1866 by William H. Sylvis ® 640, 000 members ® 1868 – Congress passed 8 hour work day for government workers ® Colored National Labor Union ® Created because blacks were not admitted to the NLU
 Early Labor Organizations ® Noble Order of the Knights of Labor Organized in 1869 by Uriah Stephens ® Focused on industrial workers ® Motto ~ “An injury to one is the concern of all” ® Supported 8 hour work day ® Advocated equal pay for equal work by men and women ® Advocated arbitration ® 1886 – 700, 000 members ® Declined after the failure of a series of strikes ®
Early Labor Organizations ® Noble Order of the Knights of Labor Organized in 1869 by Uriah Stephens ® Focused on industrial workers ® Motto ~ “An injury to one is the concern of all” ® Supported 8 hour work day ® Advocated equal pay for equal work by men and women ® Advocated arbitration ® 1886 – 700, 000 members ® Declined after the failure of a series of strikes ®
 Early Labor Organizations
Early Labor Organizations
 Craft Unions ® American Federation of Labor ® Founded by Samuel Gompers who led the Cigar Maker’s International Union in 1886 ® Focused on collective bargaining to reach written agreements ® Used strikes as a major tactic ® Able to increase wages for workers and decrease the work week as well
Craft Unions ® American Federation of Labor ® Founded by Samuel Gompers who led the Cigar Maker’s International Union in 1886 ® Focused on collective bargaining to reach written agreements ® Used strikes as a major tactic ® Able to increase wages for workers and decrease the work week as well
 American Federation of Labor
American Federation of Labor
 Industrial Unionism ® American Railway Union ® First attempt to form a industrial union of skilled and unskilled workers ® Founded by Eugene V. Debs ® 1894 ~ won a strike for higher wages ® Membership 150, 000 within 2 months ® Added momentum to union organizing
Industrial Unionism ® American Railway Union ® First attempt to form a industrial union of skilled and unskilled workers ® Founded by Eugene V. Debs ® 1894 ~ won a strike for higher wages ® Membership 150, 000 within 2 months ® Added momentum to union organizing
 American Railway Union
American Railway Union
 Socialism and the IWW ® ® ® ® Debs and others in an attempt to organize turned to socialism Socialism ~ an extreme form of communism advocated the overthrow of communism 1905 ~ Industrial Workers of the World or Wobblies organized William “Big Bill” Haywood was the leader Included miners, lumberers, and cannery and dock workers Membership never topped 100, 000 Gave dignity and a sense of solidarity to unskilled workers
Socialism and the IWW ® ® ® ® Debs and others in an attempt to organize turned to socialism Socialism ~ an extreme form of communism advocated the overthrow of communism 1905 ~ Industrial Workers of the World or Wobblies organized William “Big Bill” Haywood was the leader Included miners, lumberers, and cannery and dock workers Membership never topped 100, 000 Gave dignity and a sense of solidarity to unskilled workers
 Wobblies
Wobblies
 Labor in the West ® 1903 ~ Japanese and Mexican workers organize a successful strike in the sugarbeet fields of Ventura County, CA ® State Federation of Labor in Wyoming supported a union of Chinese and Japanese miners who wanted the same treatment and wages as other miners
Labor in the West ® 1903 ~ Japanese and Mexican workers organize a successful strike in the sugarbeet fields of Ventura County, CA ® State Federation of Labor in Wyoming supported a union of Chinese and Japanese miners who wanted the same treatment and wages as other miners
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Great Strike of 1877 July 1877 ® Workers for the B&O Baltimore and Ohio Railroad struck to protest a wage cut (2 nd in 2 months) ® Work stoppage spread to other lines ® Freight and passenger traffic stopped on over 50, 000 miles of track for over a week ® Rutherford B. Hayes was asked to intervene because it was impeding interstate traffic ® Federal troops were sent in to end the strike ®
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Great Strike of 1877 July 1877 ® Workers for the B&O Baltimore and Ohio Railroad struck to protest a wage cut (2 nd in 2 months) ® Work stoppage spread to other lines ® Freight and passenger traffic stopped on over 50, 000 miles of track for over a week ® Rutherford B. Hayes was asked to intervene because it was impeding interstate traffic ® Federal troops were sent in to end the strike ®
 The Great Strike of 1877
The Great Strike of 1877
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Haymarket Affair ® May 4, 1886 ® 3000 people gathered at Chicago’s Haymarket Square to protest police brutality ® 6 workers were killed at the Mc. Cormick Harvester plant the day before ® Rain began to fall and the people were leaving when the police arrived ® Someone tossed a bomb in the police line
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Haymarket Affair ® May 4, 1886 ® 3000 people gathered at Chicago’s Haymarket Square to protest police brutality ® 6 workers were killed at the Mc. Cormick Harvester plant the day before ® Rain began to fall and the people were leaving when the police arrived ® Someone tossed a bomb in the police line
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Haymarket Affair ® Police fired on the workers ® 7 police and several workers were killed ® 3 speakers at the demonstration and 5 other radicals were charged with inciting a riot ® All 8 were convicted, 4 were hanged, and 1 committed suicide in prison ® Public will begin to turn against labor unions after this event
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Haymarket Affair ® Police fired on the workers ® 7 police and several workers were killed ® 3 speakers at the demonstration and 5 other radicals were charged with inciting a riot ® All 8 were convicted, 4 were hanged, and 1 committed suicide in prison ® Public will begin to turn against labor unions after this event
 The Haymarket Riot
The Haymarket Riot
 The Haymarket Riot
The Haymarket Riot
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Homestead Strike ® June 29, 1892 ® Took place at the Carnegie Steel Company’s Homestead Plant in PA ® Henry Clay Frick, the president of the company announced a wage cut ® Frick hired Pinkerton Detective Agents to protect the plant
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Homestead Strike ® June 29, 1892 ® Took place at the Carnegie Steel Company’s Homestead Plant in PA ® Henry Clay Frick, the president of the company announced a wage cut ® Frick hired Pinkerton Detective Agents to protect the plant
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Homestead Strike ® Resulting fight left 3 detective and 9 workers dead ® July 12, 1892 ~ Pennsylvania National Guardsmen arrive ® Strike ends in November ® Takes 45 years for steel workers to mobilize once again
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Homestead Strike ® Resulting fight left 3 detective and 9 workers dead ® July 12, 1892 ~ Pennsylvania National Guardsmen arrive ® Strike ends in November ® Takes 45 years for steel workers to mobilize once again
 The Homestead Strike
The Homestead Strike
 The Homestead Strike
The Homestead Strike
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Pullman Company Strike ® Pullman Company laid off 3000 workers during the Panic of 1893 ® Cut wages of the 2800 workers who were left by 25 to 50% but not the cost of housing ® Strike called in 1894 after the economy improved and the company did not restore wages ® Debs asked for arbitration, company said no
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Pullman Company Strike ® Pullman Company laid off 3000 workers during the Panic of 1893 ® Cut wages of the 2800 workers who were left by 25 to 50% but not the cost of housing ® Strike called in 1894 after the economy improved and the company did not restore wages ® Debs asked for arbitration, company said no
 Strikes Turn Violent ® The Pullman Company Strike ® ARU began to boycott Pullman trains ® Pullman hired strikebreakers ® Strike became violent ® Cleveland sent in federal troops ® Debs was jailed ® Pullman fired most of the strikers and railroads blacklisted many others
Strikes Turn Violent ® The Pullman Company Strike ® ARU began to boycott Pullman trains ® Pullman hired strikebreakers ® Strike became violent ® Cleveland sent in federal troops ® Debs was jailed ® Pullman fired most of the strikers and railroads blacklisted many others
 The Pullman Strike
The Pullman Strike
 Women Organize ® Mother Jones ® Mary Harris Jones ~ most prominent organizer in the women’s labor movement ® Supported the Great Strike of 1877 ® Organized for the Union Mine Workers of America (UMW) ® 1903 led 80 mill children on a march to Theodore Roosevelt’s home which helped influence the passage of child labor laws
Women Organize ® Mother Jones ® Mary Harris Jones ~ most prominent organizer in the women’s labor movement ® Supported the Great Strike of 1877 ® Organized for the Union Mine Workers of America (UMW) ® 1903 led 80 mill children on a march to Theodore Roosevelt’s home which helped influence the passage of child labor laws
 Mother Jones
Mother Jones
 Women Organize ® International Ladies’ Garment Workers Union (ILGWU) ® Organized in 1909 ® Pauline Newman founder was an immigrant from Lithuania in 1901 ® Was 16 years old when she organized the union ® Supported the “Uprising of the 20, 000” which improved working conditions for some strikers
Women Organize ® International Ladies’ Garment Workers Union (ILGWU) ® Organized in 1909 ® Pauline Newman founder was an immigrant from Lithuania in 1901 ® Was 16 years old when she organized the union ® Supported the “Uprising of the 20, 000” which improved working conditions for some strikers
 ILGWU
ILGWU
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire ® On March 25, 1911, a fire broke out in the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory ® Spread swiftly through the oil-soaked machines and piles of cloth ® 8 th, 9 th, and 10 th floors were engulfed ® All doors except one were locked to prevent theft and that door was blocked by the fire ® The factory had no sprinkler system ® The single fire escape collapsed almost immediately
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire ® On March 25, 1911, a fire broke out in the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory ® Spread swiftly through the oil-soaked machines and piles of cloth ® 8 th, 9 th, and 10 th floors were engulfed ® All doors except one were locked to prevent theft and that door was blocked by the fire ® The factory had no sprinkler system ® The single fire escape collapsed almost immediately
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire ® The fire department’s ladders only reached to the 6 th floor ® 146 women were killed ® Many found huddled with their faces raised to a small window ® Public was outraged ® Factory owners were brought up on charges of manslaughter ® State of NY set up a task force to study factory working conditions
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire ® The fire department’s ladders only reached to the 6 th floor ® 146 women were killed ® Many found huddled with their faces raised to a small window ® Public was outraged ® Factory owners were brought up on charges of manslaughter ® State of NY set up a task force to study factory working conditions
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
 Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
 Management and Government Pressure Unions ® Management refused to recognize unions as they became more powerful ® Many employers forbade union meetings, fired union members, and made new workers sign “yellow dog contracts” (promising not to join unions) ® Sherman Antitrust Act began to be used against labor unions with the help of many industrial leaders and the courts ® Legal limitations made it difficult for unions to be effective
Management and Government Pressure Unions ® Management refused to recognize unions as they became more powerful ® Many employers forbade union meetings, fired union members, and made new workers sign “yellow dog contracts” (promising not to join unions) ® Sherman Antitrust Act began to be used against labor unions with the help of many industrial leaders and the courts ® Legal limitations made it difficult for unions to be effective
 Management and Government Pressure Unions ® Even with all the pressure, workers viewed unions as a powerful tool ® 1904 ® AFL had about 1, 700, 000 members in its affiliated unions ® Eve of WWI ® AFL membership was about 2 million
Management and Government Pressure Unions ® Even with all the pressure, workers viewed unions as a powerful tool ® 1904 ® AFL had about 1, 700, 000 members in its affiliated unions ® Eve of WWI ® AFL membership was about 2 million


