4a7c8eaece21ce88e7ada2f9a2501c30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 industrialization 1865 -1920
industrialization 1865 -1920
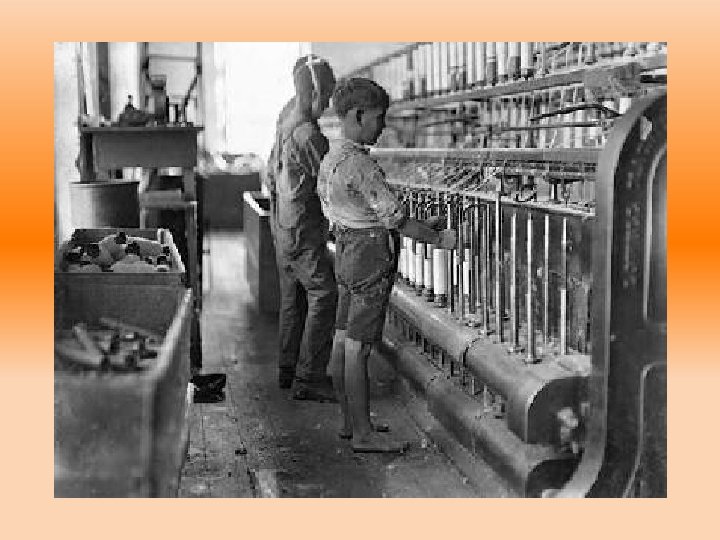




 the u. s. industrializes • Industrial Revolution began in the U. S. in the early 1800’s • At the beginning of the Civil War, the nation was still largely agrarian – 1. 3 out of 30 million worked in industry
the u. s. industrializes • Industrial Revolution began in the U. S. in the early 1800’s • At the beginning of the Civil War, the nation was still largely agrarian – 1. 3 out of 30 million worked in industry
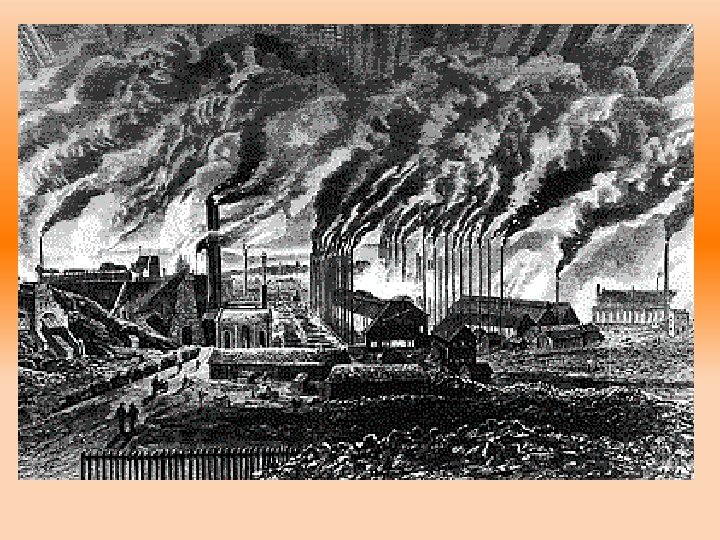
 • At the end of the Civil War, industry rapidly expanded • Millions left the farm to work in mines and factories
• At the end of the Civil War, industry rapidly expanded • Millions left the farm to work in mines and factories
 • By the 1900’s the U. S. was the world’s leading industrial nation • By 1914 the GNP was 8 times greater than pre. Civil War
• By the 1900’s the U. S. was the world’s leading industrial nation • By 1914 the GNP was 8 times greater than pre. Civil War
 1) natural resources • Abundance of raw materials was a necessity for industrial success – Water, timber, oil, coal, iron, copper – Companies didn’t have to import the resources
1) natural resources • Abundance of raw materials was a necessity for industrial success – Water, timber, oil, coal, iron, copper – Companies didn’t have to import the resources
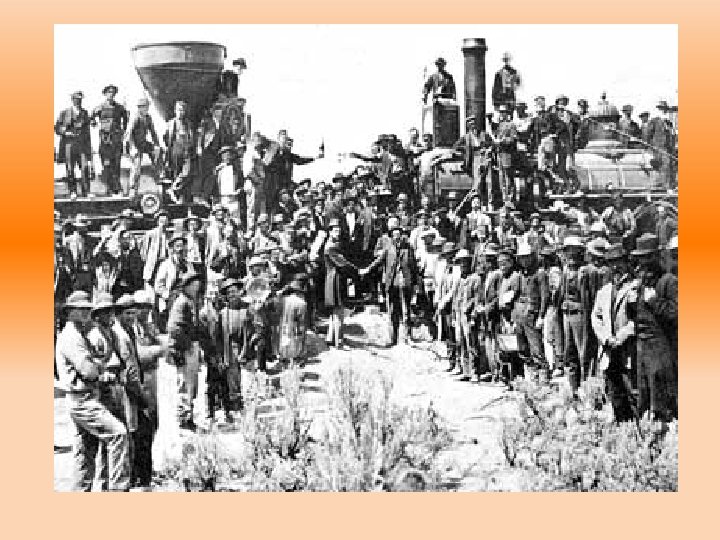
 • Transcontinental railroad brought resources from western settlements to eastern factories
• Transcontinental railroad brought resources from western settlements to eastern factories

 • Petroleum – Could be converted into kerosene (lamps and stoves) – By 1900’s, oil fields had been opened from Penn to Texas
• Petroleum – Could be converted into kerosene (lamps and stoves) – By 1900’s, oil fields had been opened from Penn to Texas
 2) workforce • Between 1860 and 1910 U. S. population tripled, providing a large workforce – Why? – PUSH/PULL factor: 1870 -1910: 20 million immigrants arrived
2) workforce • Between 1860 and 1910 U. S. population tripled, providing a large workforce – Why? – PUSH/PULL factor: 1870 -1910: 20 million immigrants arrived
 3) free enterprise How the government encouraged business to flourish… • Laissez-faire- French phrase meaning “let people do as they choose” (hands-off) • Supply/demand instead of government regulation • Low taxes created a profit motive • Attracted people of high ability and ambition into business. Entrepreneurs- People who risk their money in business
3) free enterprise How the government encouraged business to flourish… • Laissez-faire- French phrase meaning “let people do as they choose” (hands-off) • Supply/demand instead of government regulation • Low taxes created a profit motive • Attracted people of high ability and ambition into business. Entrepreneurs- People who risk their money in business
 4) new inventions (innovation) • Important inventions increased the nation’s productive capacity • Transportation and communication
4) new inventions (innovation) • Important inventions increased the nation’s productive capacity • Transportation and communication
 Alexander Graham Bell – 1876 Bell “invented” the telephone – Really Antonio Meucci – Revolutionized business and personal communication
Alexander Graham Bell – 1876 Bell “invented” the telephone – Really Antonio Meucci – Revolutionized business and personal communication
 Thomas Edison – Invented the phonograph, battery, motion picture – Also stole other peoples’ ideas – Companies merged in 1889 to form the Edison General Electric Company- now GE
Thomas Edison – Invented the phonograph, battery, motion picture – Also stole other peoples’ ideas – Companies merged in 1889 to form the Edison General Electric Company- now GE
 • Impact of Technology (other significant inventions) – Thaddeus Lowe- Ice Machine – Gustavus Swift- refrigerated railroad car 1870’s – Power driven sewing machine – Mass production of shoes – Cyrus Field laid telegraph cable across Atlantic Ocean
• Impact of Technology (other significant inventions) – Thaddeus Lowe- Ice Machine – Gustavus Swift- refrigerated railroad car 1870’s – Power driven sewing machine – Mass production of shoes – Cyrus Field laid telegraph cable across Atlantic Ocean
 railroads • 1865 - 35, 000 miles of track • 1900 - 200, 000 miles of track • Pacific Railway Act– 1862 signed by Lincoln – Construction of a transcontinental RR by two corporations(Union Pacific & Central Pacific)
railroads • 1865 - 35, 000 miles of track • 1900 - 200, 000 miles of track • Pacific Railway Act– 1862 signed by Lincoln – Construction of a transcontinental RR by two corporations(Union Pacific & Central Pacific)
 land grant system • Land grants given to many railroad companies to encourage RR. • RR companies would then sell the land to settlers
land grant system • Land grants given to many railroad companies to encourage RR. • RR companies would then sell the land to settlers
 robber barons • What is a robber baron? • Where did railroad barons get their wealth? – Swindling investors and taxpayers – Bribing gov. officials – Cheating on their contracts and debts
robber barons • What is a robber baron? • Where did railroad barons get their wealth? – Swindling investors and taxpayers – Bribing gov. officials – Cheating on their contracts and debts
 • Jay Gould– Practiced “insider trading” – He used information he received as a railroad owner to manipulate stock prices for his benefit • James J. Hill – Entrepreneur who was not a robber baron – He built and operated the Great Northern Railroad from MN to WA. – Used no federal grants or subsidies
• Jay Gould– Practiced “insider trading” – He used information he received as a railroad owner to manipulate stock prices for his benefit • James J. Hill – Entrepreneur who was not a robber baron – He built and operated the Great Northern Railroad from MN to WA. – Used no federal grants or subsidies
 14. 3 big business Businesses: Pre- Civil War vs. Early 1900 s What changed?
14. 3 big business Businesses: Pre- Civil War vs. Early 1900 s What changed?
 role of corporations • Corporation – an organization owned by many people but treated by law as though it were a single person – Can own property, pay taxes, make contracts, sue and be sued – Owned by stockholders
role of corporations • Corporation – an organization owned by many people but treated by law as though it were a single person – Can own property, pay taxes, make contracts, sue and be sued – Owned by stockholders
 • Stockholder: they own shares of ownership called stock – Before 1830 s, entrepreneurs had to acquire a charter from the state – After, states began passing general incorporation laws (allowing companies to issue stock)
• Stockholder: they own shares of ownership called stock – Before 1830 s, entrepreneurs had to acquire a charter from the state – After, states began passing general incorporation laws (allowing companies to issue stock)
 With the money raised from stock sales, corporations could : – invest in new technology – hire a large workforce – purchase machinery (+ efficiency) Economies of sale – When corporations make goods more cheaply because they produce so much so quickly using large manufacturing facilities – What happens to ‘mom and pop’ stores? Fixed costs vs. Operating costs
With the money raised from stock sales, corporations could : – invest in new technology – hire a large workforce – purchase machinery (+ efficiency) Economies of sale – When corporations make goods more cheaply because they produce so much so quickly using large manufacturing facilities – What happens to ‘mom and pop’ stores? Fixed costs vs. Operating costs
 Andrew Carnegie – Born in Scotland – Immigrated in 1848 – Rags to Riches story • Vertical integration- • Horizontal integration- Andrew Carnegie, know for Carnegie Steel Company
Andrew Carnegie – Born in Scotland – Immigrated in 1848 – Rags to Riches story • Vertical integration- • Horizontal integration- Andrew Carnegie, know for Carnegie Steel Company
 • Monopoly- when a single company achieves control of an entire market
• Monopoly- when a single company achieves control of an entire market
 trusts In 1882 Standard Oil formed the first trust- • a new way of merging business that did not violate the laws against owing other companies http: //www. library. gsu. edu/spcollima ges/labor/19 clabor/Labor%20 Prints/7940_21. jpg
trusts In 1882 Standard Oil formed the first trust- • a new way of merging business that did not violate the laws against owing other companies http: //www. library. gsu. edu/spcollima ges/labor/19 clabor/Labor%20 Prints/7940_21. jpg
 14. 4 UNIONS The Assembly Line
14. 4 UNIONS The Assembly Line
 Life of a Worker • Life for industrial workers was difficult: – Assembly line= BORING! – Health issues • Rise in the standard of living • Deflation- - companies want to pay less $$, workers organize in union
Life of a Worker • Life for industrial workers was difficult: – Assembly line= BORING! – Health issues • Rise in the standard of living • Deflation- - companies want to pay less $$, workers organize in union
 TYPES OF UNIONS • Differences between trade workers and common laborers: Trade Common • 1830 s: craft workers began to form trade unions – For workers with specific skills – Trade unions are different from industrial unions – Industrial unions:
TYPES OF UNIONS • Differences between trade workers and common laborers: Trade Common • 1830 s: craft workers began to form trade unions – For workers with specific skills – Trade unions are different from industrial unions – Industrial unions:
 Management vs. Labor “Tools” of Management M lockout M blacklisting M open shop “Tools” of Labor M boycotts M sympathy demonstration s and picketing M closed shops M organized strikes
Management vs. Labor “Tools” of Management M lockout M blacklisting M open shop “Tools” of Labor M boycotts M sympathy demonstration s and picketing M closed shops M organized strikes
 MARXIST Theory • Karl Marx and his ideas on capitalism – Class struggle between workers & owners – Revolt by workers will overthrow government – New government will redistribute property evenly • Some extreme ideas included anarchism
MARXIST Theory • Karl Marx and his ideas on capitalism – Class struggle between workers & owners – Revolt by workers will overthrow government – New government will redistribute property evenly • Some extreme ideas included anarchism
 The Great Railroad Strike of 1877: - wages were cut, 80, 000 workers walk off job! - 100 people dead, millions in property damage
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877: - wages were cut, 80, 000 workers walk off job! - 100 people dead, millions in property damage
 Goals of the Knights of Labor 8 hr workday. No child and labor. = pay for men and women. Safety codes. No contract foreign labor. Support arbitration Injury to one is the concern of us all!!
Goals of the Knights of Labor 8 hr workday. No child and labor. = pay for men and women. Safety codes. No contract foreign labor. Support arbitration Injury to one is the concern of us all!!
 Anarchists: Haymarket Riot (1886) Union leaders called for a nationwide for 8 hour work day Police entered the square, someone threw a bomb
Anarchists: Haymarket Riot (1886) Union leaders called for a nationwide for 8 hour work day Police entered the square, someone threw a bomb
 The Pullman Strike • American Railway Union led by Eugene Debs was formed against Pullman Palace Car Company. • Workers needed to live in the town of Pullman and buy goods from the company store • Pullman slashed wages • President Grover Cleveland issues injunction
The Pullman Strike • American Railway Union led by Eugene Debs was formed against Pullman Palace Car Company. • Workers needed to live in the town of Pullman and buy goods from the company store • Pullman slashed wages • President Grover Cleveland issues injunction
 American Federation of Labor (AFL) “plain and simple” union Wants higher wages/better conditions Mediated disputes between management and labor rather than strike. Pushed for closed shops. Samuel Gompers
American Federation of Labor (AFL) “plain and simple” union Wants higher wages/better conditions Mediated disputes between management and labor rather than strike. Pushed for closed shops. Samuel Gompers
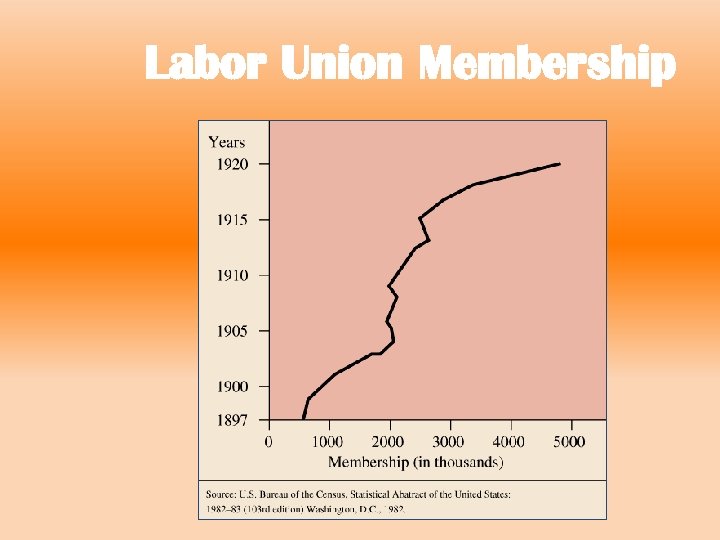 Labor Union Membership
Labor Union Membership
 WOMEN IN THE WORKFORCE -More women after CW -Paid less $ -Excluded from joining unions except: 1/3: domestic servants 1/3: teacher, nurses, secretaries 1/3: industrial workers
WOMEN IN THE WORKFORCE -More women after CW -Paid less $ -Excluded from joining unions except: 1/3: domestic servants 1/3: teacher, nurses, secretaries 1/3: industrial workers
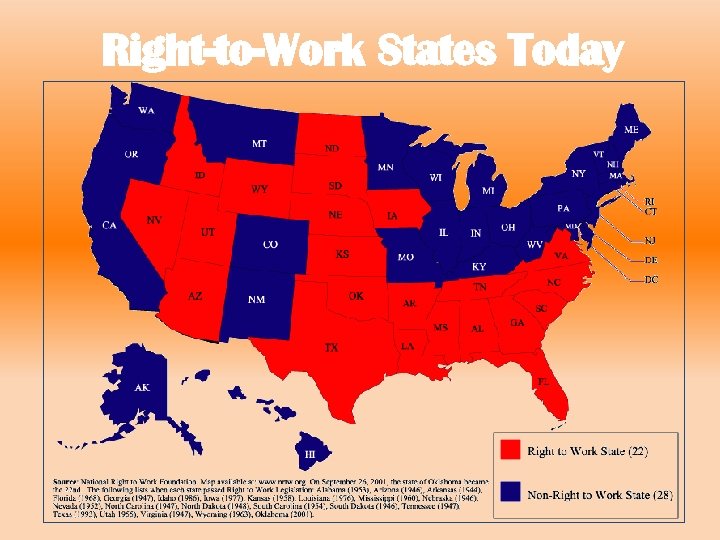 Right-to-Work States Today
Right-to-Work States Today


