1131fcfd517469937e90a3db8d07bf4f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Industrial Revolution WORLD HISTORY UNIT IV: CHAPTER 9
Industrial Revolution WORLD HISTORY UNIT IV: CHAPTER 9
 Beginnings of Industrialization What is the Industrial Revolution? Began in England in the mid-1700 s Major increase in machine-made goods Led to creation of factories Expanded to Europe and America What type of goods were made first? Textiles (cloth)
Beginnings of Industrialization What is the Industrial Revolution? Began in England in the mid-1700 s Major increase in machine-made goods Led to creation of factories Expanded to Europe and America What type of goods were made first? Textiles (cloth)
 Beginnings of Industrialization Started with Agricultural Revolution Wealthy landowners buy up land, build fences around them (enclosures) New farming methods created Jethro Tull – seed drill 1701 Increased crop yields Crop Rotation – change crops each year to restore nutrients
Beginnings of Industrialization Started with Agricultural Revolution Wealthy landowners buy up land, build fences around them (enclosures) New farming methods created Jethro Tull – seed drill 1701 Increased crop yields Crop Rotation – change crops each year to restore nutrients
 Beginnings of Industrialization Robert Bakewell – selective breeding, avg weight of sheep doubles in 86 years Many farmers lose their jobs, forced to move into urban areas, work in factories Industrialization begins – the process of developing machine production of goods It requires many natural resources
Beginnings of Industrialization Robert Bakewell – selective breeding, avg weight of sheep doubles in 86 years Many farmers lose their jobs, forced to move into urban areas, work in factories Industrialization begins – the process of developing machine production of goods It requires many natural resources
 Beginnings of Industrialization Water and coal power the machines Iron Ore used to construct machines, buildings Rivers used for transportation Harbors used to ship goods Britain had all of these resources, plus a strong national bank to give loans to start businesses. Growing trade =more demand
Beginnings of Industrialization Water and coal power the machines Iron Ore used to construct machines, buildings Rivers used for transportation Harbors used to ship goods Britain had all of these resources, plus a strong national bank to give loans to start businesses. Growing trade =more demand
 Beginnings of Industrialization Britain was first to industrialize due to having ALL factors of production Land, In Labor, Capital other words, they had the natural resources, enough people to work, and enough wealth to continue producing Textiles (cloth): wool, linen, cotton were being produced by new inventions
Beginnings of Industrialization Britain was first to industrialize due to having ALL factors of production Land, In Labor, Capital other words, they had the natural resources, enough people to work, and enough wealth to continue producing Textiles (cloth): wool, linen, cotton were being produced by new inventions
 Inventor Chart Inventor Eli Whitney Invention Cotton Gin
Inventor Chart Inventor Eli Whitney Invention Cotton Gin
 Inventions Promote Industry 1733: John Kay creates flying shuttle 1764: James Hargreaves invents spinning wheel called “Spinning Jenny” Both created huge boosts in production of cotton textiles 1769: Richard Arkwright invents water frame, uses water power from streams to drive spinning wheel
Inventions Promote Industry 1733: John Kay creates flying shuttle 1764: James Hargreaves invents spinning wheel called “Spinning Jenny” Both created huge boosts in production of cotton textiles 1769: Richard Arkwright invents water frame, uses water power from streams to drive spinning wheel
 Spinning Jenny
Spinning Jenny
 Inventions Promote Industry England’s cotton came from plantations in America (the south) Removing seeds from raw cotton was hard work 1793 American inventor Eli Whitney invents cotton gin to clean cotton Cotton production skyrockets 1790: 1. 5 m lbs 1810: 85 m lbs
Inventions Promote Industry England’s cotton came from plantations in America (the south) Removing seeds from raw cotton was hard work 1793 American inventor Eli Whitney invents cotton gin to clean cotton Cotton production skyrockets 1790: 1. 5 m lbs 1810: 85 m lbs
 Eli Whitney Cotton Gin
Eli Whitney Cotton Gin
 Improvement in Transportation 1765: James Watt invents faster and more efficient steam engine that uses less fuel He partners with an entrepreneur (person who takes on the risks of starting a new business) to sell more machines Robert Fulton orders a steam engine and uses it on water in 1807
Improvement in Transportation 1765: James Watt invents faster and more efficient steam engine that uses less fuel He partners with an entrepreneur (person who takes on the risks of starting a new business) to sell more machines Robert Fulton orders a steam engine and uses it on water in 1807
 Railways Emerge 1804: Richard Trevithick creates a locomotive with a steam engine Others improve his design 1821: George Stephenson creates first railway line from Yorkshire coal fields to port of Stockton (27 miles) Entrepreneurs create more lines to connect cities – Fastest train designed by Stephenson “rocket” went 24 mph
Railways Emerge 1804: Richard Trevithick creates a locomotive with a steam engine Others improve his design 1821: George Stephenson creates first railway line from Yorkshire coal fields to port of Stockton (27 miles) Entrepreneurs create more lines to connect cities – Fastest train designed by Stephenson “rocket” went 24 mph

 George Stephenson design
George Stephenson design
 George Stephenson design
George Stephenson design
 Development of Cities People earned more in factories than on farms Allowed them to heat their homes, eat better food, clothe themselves Factories pulled more and more people from farmlands (rural areas) to cities (urban areas) This process is called “urbanization”
Development of Cities People earned more in factories than on farms Allowed them to heat their homes, eat better food, clothe themselves Factories pulled more and more people from farmlands (rural areas) to cities (urban areas) This process is called “urbanization”
 England leads industrialization London, capital of England, had the most people, and most workers. It had twice as many people as Paris Other cities in England also expand Manchester, Cities Birmingham, Sheffield expand too fast for their own good No development plans, no sanitation codes, no building codes
England leads industrialization London, capital of England, had the most people, and most workers. It had twice as many people as Paris Other cities in England also expand Manchester, Cities Birmingham, Sheffield expand too fast for their own good No development plans, no sanitation codes, no building codes

 Development of Cities Most cities lacked adequate housing, police, education, sewer, and road systems – Factories cause pollution Many workers live in dark, dirty shelters Whole families live in one bedroom Garbage piled on streets, sicknesses (such as cholera) spread rapidly 1842: avg working-class life-span 17 years
Development of Cities Most cities lacked adequate housing, police, education, sewer, and road systems – Factories cause pollution Many workers live in dark, dirty shelters Whole families live in one bedroom Garbage piled on streets, sicknesses (such as cholera) spread rapidly 1842: avg working-class life-span 17 years




 Development of Cities Rich factory owners and merchants lived outside of the inner city (suburbs) Houses were larger, conditions better Working conditions for factory workers were awful Owners wanted their machines running as long as possible each day Avg worker: 14 hour days, 6 days/week
Development of Cities Rich factory owners and merchants lived outside of the inner city (suburbs) Houses were larger, conditions better Working conditions for factory workers were awful Owners wanted their machines running as long as possible each day Avg worker: 14 hour days, 6 days/week
 Life of a Worker Factories often dirty, dark, dangerous Many people injured on the job, did not have any rights to sue No gov’t programs to offer aid to workers Coal mines most dangerous job of all Cheapest labor was women and children, often put to work in mines Many in poverty – Few with wealth
Life of a Worker Factories often dirty, dark, dangerous Many people injured on the job, did not have any rights to sue No gov’t programs to offer aid to workers Coal mines most dangerous job of all Cheapest labor was women and children, often put to work in mines Many in poverty – Few with wealth
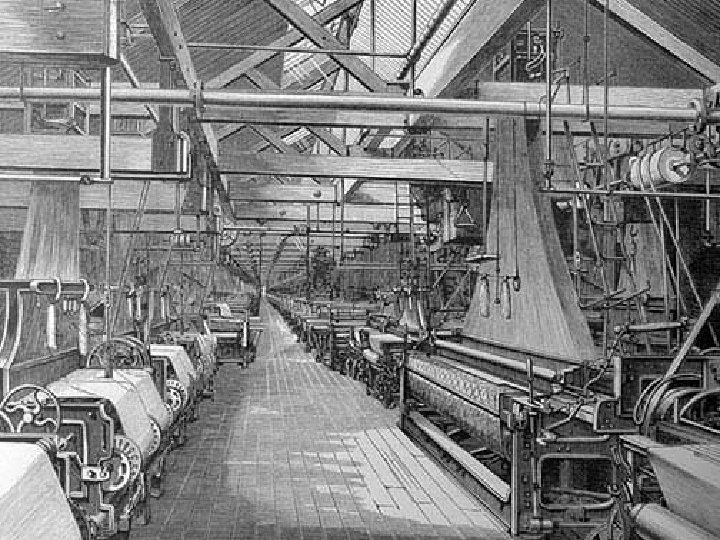

 Tensions Develop Most new money belonged to middleclass(factory owners, shippers, merchants) Landowners/Aristocrats no longer at the top of society, many middle class are wealthier Middle class expands gradually Many people still considered workingclass, lived/worked in horrid conditions
Tensions Develop Most new money belonged to middleclass(factory owners, shippers, merchants) Landowners/Aristocrats no longer at the top of society, many middle class are wealthier Middle class expands gradually Many people still considered workingclass, lived/worked in horrid conditions
 Child Labor Children as young as 6 work from 6 am to 8 pm, 6 days a week ½ hour for lunch, 1 hr for dinner Supervisors beat them to keep them awake Kids were often injured on the job Dust, cotton particles, etc filled their lungs often caused them to cough
Child Labor Children as young as 6 work from 6 am to 8 pm, 6 days a week ½ hour for lunch, 1 hr for dinner Supervisors beat them to keep them awake Kids were often injured on the job Dust, cotton particles, etc filled their lungs often caused them to cough




 Luddites Some working-class people got angry at their conditions in Northern England They call themselves the Luddites after a mythical person named Ned Ludd They destroyed machines and whole factories in 1811
Luddites Some working-class people got angry at their conditions in Northern England They call themselves the Luddites after a mythical person named Ned Ludd They destroyed machines and whole factories in 1811

 Long-Term Effects Ppl in industrialized countries can afford goods that would’ve been luxuries in the past Extreme pollution that lasted for years Working/living conditions eventually improved over the decades Profits from factories produced tax money for the gov’t Gov’t then invested in urban improvement
Long-Term Effects Ppl in industrialized countries can afford goods that would’ve been luxuries in the past Extreme pollution that lasted for years Working/living conditions eventually improved over the decades Profits from factories produced tax money for the gov’t Gov’t then invested in urban improvement
 Sec 3: Industrialization Spreads The US had many of the same resources as Britain Early on, British blockade and trade policy forced US to develop separately and more slowly Northern states experienced faster industrialization than southern ones Southern states remained highly agricultural
Sec 3: Industrialization Spreads The US had many of the same resources as Britain Early on, British blockade and trade policy forced US to develop separately and more slowly Northern states experienced faster industrialization than southern ones Southern states remained highly agricultural
 American Industrialization Cultural changes cause a conflict in US South: Slavery North: Abolition Country expands territory quickly American Civil War breaks out Ends 1865, Lincoln assassinated Last 1/3 of 19 th century there is a huge boom in technology that expands industry
American Industrialization Cultural changes cause a conflict in US South: Slavery North: Abolition Country expands territory quickly American Civil War breaks out Ends 1865, Lincoln assassinated Last 1/3 of 19 th century there is a huge boom in technology that expands industry
 American Industrialization
American Industrialization
 European Industrialization of Europe takes longer because of French Revolution, Napoleon, etc Belgium: First continental country to industrialize, designs were brought by British engineers Germany: Had been divided in 1800 s, pockets of industry start to appear By late 1800 s industrial & military giant
European Industrialization of Europe takes longer because of French Revolution, Napoleon, etc Belgium: First continental country to industrialize, designs were brought by British engineers Germany: Had been divided in 1800 s, pockets of industry start to appear By late 1800 s industrial & military giant
 European Industrialization of Europe takes longer because of French Revolution, Napoleon, etc Belgium: First continental country to industrialize, designs were brought by British engineers Germany: Had been divided in 1800 s, pockets of industry start to appear By late 1800 s industrial & military giant
European Industrialization of Europe takes longer because of French Revolution, Napoleon, etc Belgium: First continental country to industrialize, designs were brought by British engineers Germany: Had been divided in 1800 s, pockets of industry start to appear By late 1800 s industrial & military giant
 European Industrialization Many places in Europe do not industrialize Geography (mountains, land formations) prevented countries from being able to Social structure, monarchs, etc prevent industrial growth Transportation (lack of railroads, waterways, roads etc) was limited
European Industrialization Many places in Europe do not industrialize Geography (mountains, land formations) prevented countries from being able to Social structure, monarchs, etc prevent industrial growth Transportation (lack of railroads, waterways, roads etc) was limited
 Global Industrialization widened the gap btwn industrialized (rich) and nonindustrialized (poor) nations Less-industrialized countries keep providing food and raw supplies to industrialized ones Industrialized countries sell back the products to poorer countries for profit Britain starts to exploit poorer nations
Global Industrialization widened the gap btwn industrialized (rich) and nonindustrialized (poor) nations Less-industrialized countries keep providing food and raw supplies to industrialized ones Industrialized countries sell back the products to poorer countries for profit Britain starts to exploit poorer nations
 Imperialism Soon after, US, Russia, Japan all begin to do the same as Britain Imperialism emerges This is when a country extends its rule over many other lands using wealth and a strong economy Industrialization led directly to Imperialism
Imperialism Soon after, US, Russia, Japan all begin to do the same as Britain Imperialism emerges This is when a country extends its rule over many other lands using wealth and a strong economy Industrialization led directly to Imperialism
 Imperialism
Imperialism
 Western Dominated World Between 1700 -1900, huge changes in agriculture, industry, communication, and technology make Western Europe and the US far more advanced than anywhere else Despite early hardships, the populations health and wealth both rose dramatically in all industrialized nations Middle class emerged
Western Dominated World Between 1700 -1900, huge changes in agriculture, industry, communication, and technology make Western Europe and the US far more advanced than anywhere else Despite early hardships, the populations health and wealth both rose dramatically in all industrialized nations Middle class emerged
 Sec 4: Reforming the Industrial World The emerging middle class meant a wider gap between the rich and poor Two opinions about gov’t develop Business leaders opinion: gov’t should stay out of business and economics Reformers opinion: gov’t needs to help improve the conditions for the poor, more rights for workers
Sec 4: Reforming the Industrial World The emerging middle class meant a wider gap between the rich and poor Two opinions about gov’t develop Business leaders opinion: gov’t should stay out of business and economics Reformers opinion: gov’t needs to help improve the conditions for the poor, more rights for workers
 What is “economics” anyway? Economics: helps us analyze how goods are produced, distributed, & consumed. Basic economic principles: Supply: How much of a good is available? Demand: How much desire there is for the good? Distribution: Where is the product made & and where is it going to go? Price: What do I have to give up to get it?
What is “economics” anyway? Economics: helps us analyze how goods are produced, distributed, & consumed. Basic economic principles: Supply: How much of a good is available? Demand: How much desire there is for the good? Distribution: Where is the product made & and where is it going to go? Price: What do I have to give up to get it?
 Different Economic Approaches Depending on where you are, the economy can be handled by governments in many different ways Laissez-faire economics: This economic policy lets owners of industries set their own working conditions, run themselves, and do as they please The term literally means “let do” and the gov’t keeps its hands off of the economy
Different Economic Approaches Depending on where you are, the economy can be handled by governments in many different ways Laissez-faire economics: This economic policy lets owners of industries set their own working conditions, run themselves, and do as they please The term literally means “let do” and the gov’t keeps its hands off of the economy
 Laissez-Faire and Free Trade If a gov’t uses laissez-faire, they are supporting “free trade” This means nations should trade freely, without any rules or regulations from gov’ts (no taxes, laws, or limitations) Many believed this would allow economies to grow and be successful Adam Smith wrote a book called “Wealth of Nations and supported free trade ”
Laissez-Faire and Free Trade If a gov’t uses laissez-faire, they are supporting “free trade” This means nations should trade freely, without any rules or regulations from gov’ts (no taxes, laws, or limitations) Many believed this would allow economies to grow and be successful Adam Smith wrote a book called “Wealth of Nations and supported free trade ”
 Adam Smith
Adam Smith
 Adam Smith (Wealth of Nations Smith Adam ) Supports economic liberty (freedom) Created 3 economic laws 1. ) the law of self interest (people work for their own good 2. ) the law of competition (competition forces people to make better products) 3. ) the law of supply/demand (enough goods are produced at a low price to meet demand
Adam Smith (Wealth of Nations Smith Adam ) Supports economic liberty (freedom) Created 3 economic laws 1. ) the law of self interest (people work for their own good 2. ) the law of competition (competition forces people to make better products) 3. ) the law of supply/demand (enough goods are produced at a low price to meet demand
 Laissez-Faire economic system too and Capitalism is an It uses some laissez-faire principles What is capitalism? Land, labor and capital (factors of production) are privately owned – NOT run by the gov’t Money is invested in business ventures to make profits Today, we are capitalist but have many regulations on economics as well
Laissez-Faire economic system too and Capitalism is an It uses some laissez-faire principles What is capitalism? Land, labor and capital (factors of production) are privately owned – NOT run by the gov’t Money is invested in business ventures to make profits Today, we are capitalist but have many regulations on economics as well
 Laissez-Faire and Capitalism
Laissez-Faire and Capitalism
 Capitalists vs Socialists Capitalists like Smith disagreed that the gov’t should help poor working class folk He thought if gov’t made laws about minimum wages and working conditions that it would slowdown economic growth Not everyone believed in laissez-faire Others thought gov’t shouldintervene in private business to help the lower-class
Capitalists vs Socialists Capitalists like Smith disagreed that the gov’t should help poor working class folk He thought if gov’t made laws about minimum wages and working conditions that it would slowdown economic growth Not everyone believed in laissez-faire Others thought gov’t shouldintervene in private business to help the lower-class
 Utilitarianism Jeremy Bantham creates this idea that states ppl should judge ideas, institutions, and actions on the basis of how useful they are He said if we want to judge how useful gov’t is, it is only useful if it provides as much good as possible to as many ppl as possible
Utilitarianism Jeremy Bantham creates this idea that states ppl should judge ideas, institutions, and actions on the basis of how useful they are He said if we want to judge how useful gov’t is, it is only useful if it provides as much good as possible to as many ppl as possible
 Jeremy Bantham
Jeremy Bantham
 Utilitarianism led the utilitarian John Stuart Mill movement in the 1800 s Mill questioned unregulated capitalism He believed it was wrong that workers should lead deprived lives that bordered on starvation He wanted to help ordinary workers He wanted gov’t to make reforms to lower the gap between rich and poor
Utilitarianism led the utilitarian John Stuart Mill movement in the 1800 s Mill questioned unregulated capitalism He believed it was wrong that workers should lead deprived lives that bordered on starvation He wanted to help ordinary workers He wanted gov’t to make reforms to lower the gap between rich and poor
 John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill
 Socialism an economic system, but its Socialism is very different from capitalism In socialism, all factors of production are owned by the public (gov’t), and operate for the welfare of everyone equally It is considered overly optimistic because it requires humans to be fair and equal Socialists believe the economy should be controlled by the gov’t (opp. of free trade)
Socialism an economic system, but its Socialism is very different from capitalism In socialism, all factors of production are owned by the public (gov’t), and operate for the welfare of everyone equally It is considered overly optimistic because it requires humans to be fair and equal Socialists believe the economy should be controlled by the gov’t (opp. of free trade)
 Socialism that if the gov’t controls Socialists believe the economy and regulates businesses with laws, everyone will be equal In America, we have some socialized systems – for instance, education Many western countries have socialized healthcare systems, which means that hospitals are run by the government and people don’t need insurance for care
Socialism that if the gov’t controls Socialists believe the economy and regulates businesses with laws, everyone will be equal In America, we have some socialized systems – for instance, education Many western countries have socialized healthcare systems, which means that hospitals are run by the government and people don’t need insurance for care
 Socialism and socialism was called Karl Marx A radical form of Marxism – named after Karl Marx wrote a book called the “Communist Manifesto” In it, he argued the “haves” which were the rich middle-class bourgeoisie would be attacked by the “have-nots” or “proletariat” because of the unfairness He called this class warfare
Socialism and socialism was called Karl Marx A radical form of Marxism – named after Karl Marx wrote a book called the “Communist Manifesto” In it, he argued the “haves” which were the rich middle-class bourgeoisie would be attacked by the “have-nots” or “proletariat” because of the unfairness He called this class warfare
 Communism and Karl Marx
Communism and Karl Marx
 Communism practice extreme socialism Countries that have dictators and are called Communists This term comes from the idea that everyone would live on a “commune, ” where the land, resources, and production of goods would be given out equally to all – a“Utopian Society” The problem is that everyone is equally poor and has no freedoms
Communism practice extreme socialism Countries that have dictators and are called Communists This term comes from the idea that everyone would live on a “commune, ” where the land, resources, and production of goods would be given out equally to all – a“Utopian Society” The problem is that everyone is equally poor and has no freedoms
 Communism – Join the Party!
Communism – Join the Party!
 Communism gap btwn rich and poor fails Over time, the has not widened as Marx predicted Religion, nationalism, desire for democracy all have influence on economy Governments often pass reforms before turning to communism Most communist leaders have twisted Marxist ideas: Stalin, Castro, Mao Zedong, etc.
Communism gap btwn rich and poor fails Over time, the has not widened as Marx predicted Religion, nationalism, desire for democracy all have influence on economy Governments often pass reforms before turning to communism Most communist leaders have twisted Marxist ideas: Stalin, Castro, Mao Zedong, etc.
 Reforms in Industrialization To get reforms, factory workers form unions A union is a group of workers that operate as a single whole They bargain for better pay, shorter work days, and better conditions If factory owners refuse, they can strike – or protest and refuse to work Skilled workers have an edge in unions
Reforms in Industrialization To get reforms, factory workers form unions A union is a group of workers that operate as a single whole They bargain for better pay, shorter work days, and better conditions If factory owners refuse, they can strike – or protest and refuse to work Skilled workers have an edge in unions
 Labor Reform try to outlaw strikes Laws Originally, gov’ts Eventually, unions are allowed and make progress 1833: Child labor law makes it illegal to hire kids under age 9 1842: No kids work in mines 1847: Limited work day to 10 hrs for women and children 1904: Child labor ends
Labor Reform try to outlaw strikes Laws Originally, gov’ts Eventually, unions are allowed and make progress 1833: Child labor law makes it illegal to hire kids under age 9 1842: No kids work in mines 1847: Limited work day to 10 hrs for women and children 1904: Child labor ends
 European Imperialism in Africa, 1870 -1898 In this lesson, students will be able to define the following terms: “Scramble for Africa” Berlin Conference of 1884 -1885 Effects of European Imperialism on Africa E. Napp
European Imperialism in Africa, 1870 -1898 In this lesson, students will be able to define the following terms: “Scramble for Africa” Berlin Conference of 1884 -1885 Effects of European Imperialism on Africa E. Napp
 European powers engaged in a “Scramble for Africa” starting in the 1870 s. By 1890, most of Africa came under European control. E. Napp
European powers engaged in a “Scramble for Africa” starting in the 1870 s. By 1890, most of Africa came under European control. E. Napp
 By 1890, only Ethiopia and Liberia remained independent. E. Napp
By 1890, only Ethiopia and Liberia remained independent. E. Napp
 The major European powers to acquire African territories were Great Britain, France, Germany, Belgium, Portugal, and Italy. E. Napp
The major European powers to acquire African territories were Great Britain, France, Germany, Belgium, Portugal, and Italy. E. Napp
 The French acquired much of northwestern Africa above the Sahara, as well as Central Africa. E. Napp
The French acquired much of northwestern Africa above the Sahara, as well as Central Africa. E. Napp
 King Leopold, the king of Belgium, ruled the Congo like his own private estate. Natives that did not supply enough rubber had their hands cut off. While the king profited, the people of the Belgian Congo suffered greatly. E. Napp
King Leopold, the king of Belgium, ruled the Congo like his own private estate. Natives that did not supply enough rubber had their hands cut off. While the king profited, the people of the Belgian Congo suffered greatly. E. Napp
 The British established colonies in West Africa and along the length of most of East Africa from Egypt to South Africa. E. Napp
The British established colonies in West Africa and along the length of most of East Africa from Egypt to South Africa. E. Napp
 Sometimes European imperialists came into conflict with one another. Disputes among the imperial powers were worked out at the Berlin Conference of 1884 -1885. At the Berlin Conference, the remainder of Africa was divided up. E. Napp
Sometimes European imperialists came into conflict with one another. Disputes among the imperial powers were worked out at the Berlin Conference of 1884 -1885. At the Berlin Conference, the remainder of Africa was divided up. E. Napp
 European imperialism had many effects on Africa. European colonization had both positive and negative effects on Africa. E. Napp
European imperialism had many effects on Africa. European colonization had both positive and negative effects on Africa. E. Napp
 A positive effect of European imperialism was the introduction of modern transportation and communication systems, such as telegraphs, railroads, and telephones. E. Napp
A positive effect of European imperialism was the introduction of modern transportation and communication systems, such as telegraphs, railroads, and telephones. E. Napp
 The introduction of European medicine and improved nutrition led to an expansion of population. E. Napp
The introduction of European medicine and improved nutrition led to an expansion of population. E. Napp
 However, there were many negative effects of European Imperialism on African peoples were treated as inferior to Europeans. E. Napp
However, there were many negative effects of European Imperialism on African peoples were treated as inferior to Europeans. E. Napp
 Europeans divided Africa and ignored the tribal, ethnic, and cultural boundaries of the African people. This has led to tribal conflicts in many African nations that continue to this day. E. Napp
Europeans divided Africa and ignored the tribal, ethnic, and cultural boundaries of the African people. This has led to tribal conflicts in many African nations that continue to this day. E. Napp
 Questions for Reflection: • What was the “Scramble for Africa”? • Why did the Berlin Conference occur? • What European nations gained control of Africa? • What were the positive effects of European imperialism on Africa? • What were the negative effects of European imperialism on Africa? E. Napp
Questions for Reflection: • What was the “Scramble for Africa”? • Why did the Berlin Conference occur? • What European nations gained control of Africa? • What were the positive effects of European imperialism on Africa? • What were the negative effects of European imperialism on Africa? E. Napp
 How to prepare • Re-Read Chapter 9 in textbook • Pay close attention to names not mentioned in lecture from text and charts / pictures etc… • Know your lecture notes well • 28 m/c questions, 8 matching
How to prepare • Re-Read Chapter 9 in textbook • Pay close attention to names not mentioned in lecture from text and charts / pictures etc… • Know your lecture notes well • 28 m/c questions, 8 matching
 Test Review – 28 M/C, 8 matching • 8 inventors – What they did • Adam Smith – Economic principles • Elizabeth Gaskell, Charles Dickens, Alex de Tocqueville, Karl Marx, Jane Addams, Jeremy Bentham. • Vocabulary words from text • Notes – general questions
Test Review – 28 M/C, 8 matching • 8 inventors – What they did • Adam Smith – Economic principles • Elizabeth Gaskell, Charles Dickens, Alex de Tocqueville, Karl Marx, Jane Addams, Jeremy Bentham. • Vocabulary words from text • Notes – general questions
 Essay Question • 1 of these 3 will be your essay question • Scramble for Africa, Why England for the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, or Difference between Socialism and Laissez-faire Capitalism.
Essay Question • 1 of these 3 will be your essay question • Scramble for Africa, Why England for the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, or Difference between Socialism and Laissez-faire Capitalism.
 Essay Explain the “Scramble for Africa during the late 1800’s citing the positive and negative impact.
Essay Explain the “Scramble for Africa during the late 1800’s citing the positive and negative impact.
 Essay Contrast Laissez-Faire Capitalism with Socialism (examples to illustrate)
Essay Contrast Laissez-Faire Capitalism with Socialism (examples to illustrate)
 Essay Why did the “Industrial Revolution” start in England during the mid 1700’s citing multiple reasons for this.
Essay Why did the “Industrial Revolution” start in England during the mid 1700’s citing multiple reasons for this.


