 Indirect Speech
Indirect Speech
 n n Речь, которая передает подлинные слова какого-либо лица, называется прямой речью. Речь, в которой передается содержание того, что было кемто сказано, называется косвенной. Лена говорит Нине: «Я хочу обедать» . предложение, прямая речь вводящее в прямую речь Lena tells Nina, “I want to have dinner. ” Лена говорит Нине, что она хочет обедать. главное предложение придаточное изъяснительное предложение Lena tells Nina that she wants to have dinner.
n n Речь, которая передает подлинные слова какого-либо лица, называется прямой речью. Речь, в которой передается содержание того, что было кемто сказано, называется косвенной. Лена говорит Нине: «Я хочу обедать» . предложение, прямая речь вводящее в прямую речь Lena tells Nina, “I want to have dinner. ” Лена говорит Нине, что она хочет обедать. главное предложение придаточное изъяснительное предложение Lena tells Nina that she wants to have dinner.
 При изменении прямой речи в косвенную соблюдаются правила согласования времен. В косвенной речи глагол не меняется, если: 1. Глагол, который вводит КР, употреблен в настоящем или будущем времени: He says he went there yesterday. 2. Сообщается о законе природы, общеизвестной истине, постоянном факте: The teacher said that the sun sets in the west.
При изменении прямой речи в косвенную соблюдаются правила согласования времен. В косвенной речи глагол не меняется, если: 1. Глагол, который вводит КР, употреблен в настоящем или будущем времени: He says he went there yesterday. 2. Сообщается о законе природы, общеизвестной истине, постоянном факте: The teacher said that the sun sets in the west.
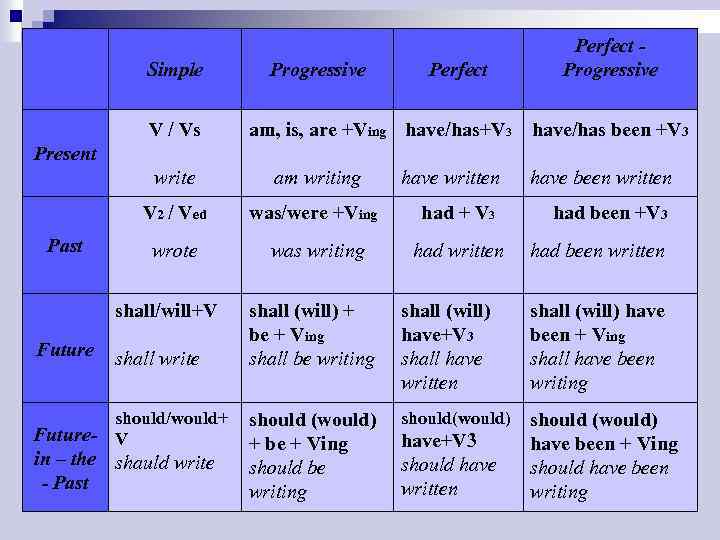 Simple V / Vs Progressive Perfect am, is, are +Ving have/has+V 3 Perfect Progressive have/has been +V 3 Present write V 2 / Ved Past am writing wrote shall/will+V Future shall write should/would+ Future- V in – the shauld write - Past have written have been written was/were +Ving had + V 3 had been +V 3 was writing had written had been written shall (will) + be + Ving shall be writing shall (will) have+V 3 shall have written shall (will) have been + Ving shall have been writing should (would) + be + Ving should be writing should(would) should (would) have been + Ving should have been writing have+V 3 should have written
Simple V / Vs Progressive Perfect am, is, are +Ving have/has+V 3 Perfect Progressive have/has been +V 3 Present write V 2 / Ved Past am writing wrote shall/will+V Future shall write should/would+ Future- V in – the shauld write - Past have written have been written was/were +Ving had + V 3 had been +V 3 was writing had written had been written shall (will) + be + Ving shall be writing shall (will) have+V 3 shall have written shall (will) have been + Ving shall have been writing should (would) + be + Ving should be writing should(would) should (would) have been + Ving should have been writing have+V 3 should have written
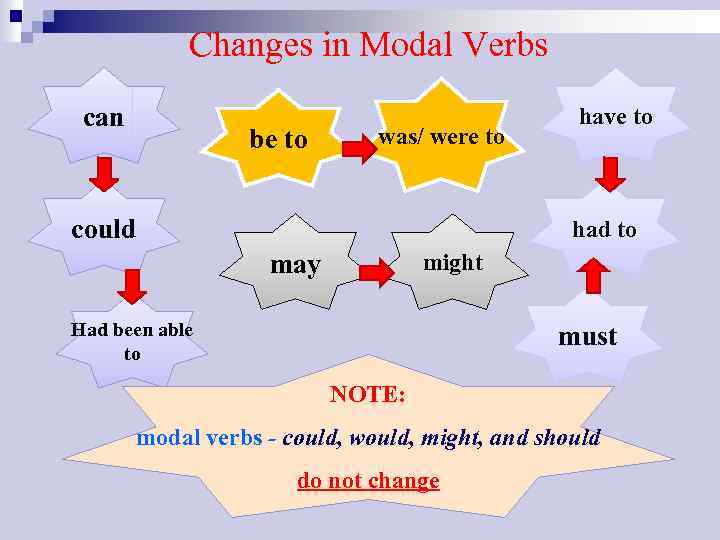 Changes in Modal Verbs can be to was/ were to could have to had to may might Had been able to must NOTE: modal verbs - could, would, might, and should do not change
Changes in Modal Verbs can be to was/ were to could have to had to may might Had been able to must NOTE: modal verbs - could, would, might, and should do not change
 В утвердительных и отрицательных предложениях (statements) происходят также следующие изменения: now then today that day tomorrow the next day the day after tomorrow two days later ago before next (year) the next/ following (year) last week the previous week/ a week before here this that these those come go She said: “I lived in Rostov two years ago. ” She said she had lived in Rostov two years before. n
В утвердительных и отрицательных предложениях (statements) происходят также следующие изменения: now then today that day tomorrow the next day the day after tomorrow two days later ago before next (year) the next/ following (year) last week the previous week/ a week before here this that these those come go She said: “I lived in Rostov two years ago. ” She said she had lived in Rostov two years before. n
 STATEMENTS IN REPORTED SPEECH Если после глагола to say есть указание на то к кому эта речь обращена, то глагол to say меняется на to tell. Jeff said to Ann: « I am going to Glasgow. » Jeff told Ann he was going to Glasgow. Союз that часто опускается после глаголов to say, to think, to know. She remembered she had asked him about it. n
STATEMENTS IN REPORTED SPEECH Если после глагола to say есть указание на то к кому эта речь обращена, то глагол to say меняется на to tell. Jeff said to Ann: « I am going to Glasgow. » Jeff told Ann he was going to Glasgow. Союз that часто опускается после глаголов to say, to think, to know. She remembered she had asked him about it. n
 STATEMENTS IN REPORTED SPEECH Утвердительные предложения вводятся в косвенной речи следующими глаголами: v admit – признавать v complain – жаловаться v decide – решить v deny – отрицать v explain – объяснять v promise – обещать v remind – напомнить v reply – ответить v warn – предупредить v think – думать, полагать say (to) tell
STATEMENTS IN REPORTED SPEECH Утвердительные предложения вводятся в косвенной речи следующими глаголами: v admit – признавать v complain – жаловаться v decide – решить v deny – отрицать v explain – объяснять v promise – обещать v remind – напомнить v reply – ответить v warn – предупредить v think – думать, полагать say (to) tell
 Expressions with say, tell, ask TO SAY TO TELL TO ASK good morning/afternoon, something/ nothing, a prayer, so, a few words the truth, a lie, a secret, a story, a joke, the time, the difference, sb the way, one’s fortune, one from another a favour, the time, a question, the price
Expressions with say, tell, ask TO SAY TO TELL TO ASK good morning/afternoon, something/ nothing, a prayer, so, a few words the truth, a lie, a secret, a story, a joke, the time, the difference, sb the way, one’s fortune, one from another a favour, the time, a question, the price
 Необходимо обратить внимание на перевод подобных предложений He said he was writing a letter then. Он сказал, что пишет письмо сейчас. The teacher said : « The holidays will begin in a week. » The teacher said the holidays would begin a week later. Учительница сказала, что каникулы начнутся через неделю.
Необходимо обратить внимание на перевод подобных предложений He said he was writing a letter then. Он сказал, что пишет письмо сейчас. The teacher said : « The holidays will begin in a week. » The teacher said the holidays would begin a week later. Учительница сказала, что каникулы начнутся через неделю.
 Change these statements into the Reported Speech:
Change these statements into the Reported Speech:
 Вопросы в косвенной речи GENERAL QUESTIONS n Если вопрос общий (начинается с вспомогательного глагола), то придаточное предложение присоединяется к главному при помощи союзов if или whether: If/ Whether Прямой порядок слов “Do you like ice-cream? ” asked Tom. do Tim asked if I liked ice-cream.
Вопросы в косвенной речи GENERAL QUESTIONS n Если вопрос общий (начинается с вспомогательного глагола), то придаточное предложение присоединяется к главному при помощи союзов if или whether: If/ Whether Прямой порядок слов “Do you like ice-cream? ” asked Tom. do Tim asked if I liked ice-cream.
 “Did you see an elephant at the Zoo? ” She wondered if I had seen an elephant at the Zoo. “Does he usually clean his room? ” Mother was interested if Mike usually cleaned his room. “Will Pat perform at the concert? ” Children were interested if Pat would perform at the concert. “Have you done your homework? ” Father wanted to know if I had done my homework “Can you come in two days? ” The teacher asked if he could come two days later?
“Did you see an elephant at the Zoo? ” She wondered if I had seen an elephant at the Zoo. “Does he usually clean his room? ” Mother was interested if Mike usually cleaned his room. “Will Pat perform at the concert? ” Children were interested if Pat would perform at the concert. “Have you done your homework? ” Father wanted to know if I had done my homework “Can you come in two days? ” The teacher asked if he could come two days later?
 SPECIAL QUESTIONS n Если вопрос специальный (начинается с вопросительного слова when/ how/ where/ why/ how many, etc. ), то придаточное предложение присоединяется к главному при помощи вопросительного слова. Порядок слов меняется на прямой Вопрос. слово Прямой порядок слов Lilly, where did you spend the holidays? They asked Lilly where she had spent the holidays. did
SPECIAL QUESTIONS n Если вопрос специальный (начинается с вопросительного слова when/ how/ where/ why/ how many, etc. ), то придаточное предложение присоединяется к главному при помощи вопросительного слова. Порядок слов меняется на прямой Вопрос. слово Прямой порядок слов Lilly, where did you spend the holidays? They asked Lilly where she had spent the holidays. did
 What have you just done? The teacher asked what I had done. How did the doctor examine her? He was interested how the doctor had examined her. Where will they spend their holidays? She wondered where they would spend their holidays. When does she go to the swimming pool? Jack wanted to know when she went to the swimming pool.
What have you just done? The teacher asked what I had done. How did the doctor examine her? He was interested how the doctor had examined her. Where will they spend their holidays? She wondered where they would spend their holidays. When does she go to the swimming pool? Jack wanted to know when she went to the swimming pool.
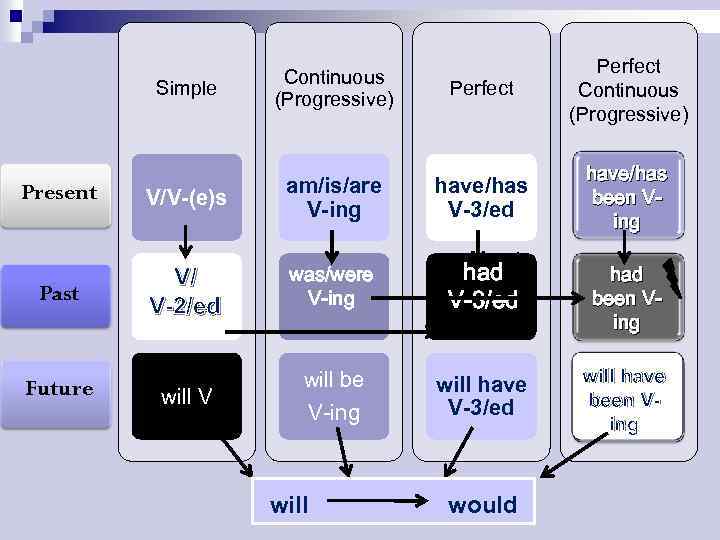 Simple Continuous (Progressive) Perfect Continuous (Progressive) Present V/V-(e)s am/is/are V-ing have/has V-3/ed have/has been Ving Past V/ V-2/ed was/were V-ing had V-3/ed had been Ving will V will be V-ing will have V-3/ed will have been Ving Future will would
Simple Continuous (Progressive) Perfect Continuous (Progressive) Present V/V-(e)s am/is/are V-ing have/has V-3/ed have/has been Ving Past V/ V-2/ed was/were V-ing had V-3/ed had been Ving will V will be V-ing will have V-3/ed will have been Ving Future will would
 Косвенные просьбы и приказания Повелительные предложения вводятся следующими глаголами: To tell, to order, to ask. Robert, «Сome here!» Robert asked Nancy to come here. Bob to Dan, «Don’t be late!» Bob told Dan not to be late.
Косвенные просьбы и приказания Повелительные предложения вводятся следующими глаголами: To tell, to order, to ask. Robert, «Сome here!» Robert asked Nancy to come here. Bob to Dan, «Don’t be late!» Bob told Dan not to be late.
 Ada: « Tim will phone us. » Ada said Tim would phone them. Jack: «Does this bus go to the British museum? » The girl asked if that bus went to the museum. Susan: «Can you tell me the way to the station? » Susan asked if the policeman could tell her the way to the station. Pete : «What did you do yesterday? » Pete asked Hellen what she had done the day before. Nick said: «Let ’s go for a walk. » Nick invited his friends to go for a walk.
Ada: « Tim will phone us. » Ada said Tim would phone them. Jack: «Does this bus go to the British museum? » The girl asked if that bus went to the museum. Susan: «Can you tell me the way to the station? » Susan asked if the policeman could tell her the way to the station. Pete : «What did you do yesterday? » Pete asked Hellen what she had done the day before. Nick said: «Let ’s go for a walk. » Nick invited his friends to go for a walk.
 Mary said: “Tim helps his Granny every day. ” Mary said Tim helped his Granny every day. Jill said: “I went to the Bolshoi Theatre last week”. Jill said she had gone to the Bolshoi the previous week. Bob asked: “Are they playing computer games ? ” Bob asked if they were playing computer games. Sue asked: “What book have you read lately? ” Sue asked what book you had read lately. John said: “ Don’t go there!” John told Pat not to go there.
Mary said: “Tim helps his Granny every day. ” Mary said Tim helped his Granny every day. Jill said: “I went to the Bolshoi Theatre last week”. Jill said she had gone to the Bolshoi the previous week. Bob asked: “Are they playing computer games ? ” Bob asked if they were playing computer games. Sue asked: “What book have you read lately? ” Sue asked what book you had read lately. John said: “ Don’t go there!” John told Pat not to go there.
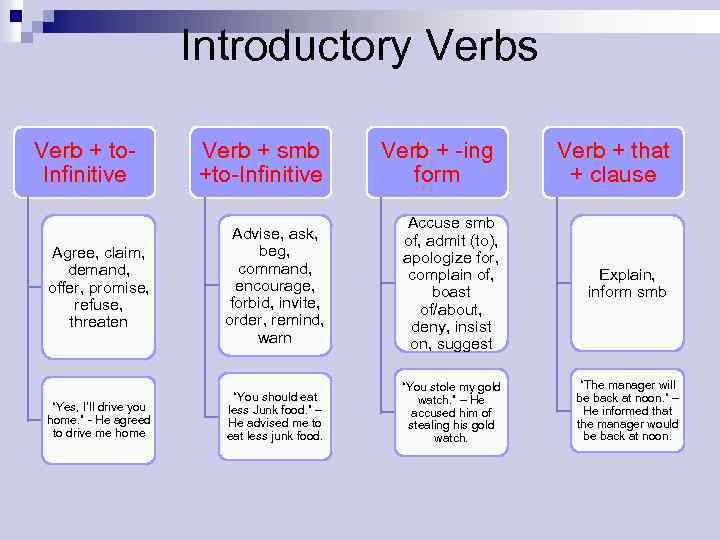 Introductory Verbs Verb + to. Infinitive Verb + smb +to-Infinitive Verb + -ing form Verb + that + clause Agree, claim, demand, offer, promise, refuse, threaten Advise, ask, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, order, remind, warn Accuse smb of, admit (to), apologize for, complain of, boast of/about, deny, insist on, suggest Explain, inform smb “Yes, I’ll drive you home. ” - He agreed to drive me home “You should eat less Junk food. ” – He advised me to eat less junk food. “You stole my gold watch. ” – He accused him of stealing his gold watch. “The manager will be back at noon. ” – He informed that the manager would be back at noon.
Introductory Verbs Verb + to. Infinitive Verb + smb +to-Infinitive Verb + -ing form Verb + that + clause Agree, claim, demand, offer, promise, refuse, threaten Advise, ask, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, order, remind, warn Accuse smb of, admit (to), apologize for, complain of, boast of/about, deny, insist on, suggest Explain, inform smb “Yes, I’ll drive you home. ” - He agreed to drive me home “You should eat less Junk food. ” – He advised me to eat less junk food. “You stole my gold watch. ” – He accused him of stealing his gold watch. “The manager will be back at noon. ” – He informed that the manager would be back at noon.


