83635034690c1e19554ac9d607d1d17a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Indian Vocational Training System & Modular Employable Skills (MES) Skills for Global Economy Govt. of India SOUTH-SOUTH LEARNING EXCHANGE VISIT At Bangalore – 18. 2. 2009 DGET RDAT S. J. Amalan Regional Director & Director (Apex) (Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Orissa) DGE&T Ministry of Labour & Employment Govt. of India

Government of India Ministry of Labour and Employment Secretary Joint Secretary Director General of Employment & Training Directorate of Employment Directors of Training, Apprenticeship, Project, Women Occupation 2700 employees (280 Group A officers, 406 Group B officers, 1364 Group C employees & 650 Group D employees)
![Vocational Training Advisory Boards 1. National Council for Vocational Training [NCVT] 2. Central Apprenticeship Vocational Training Advisory Boards 1. National Council for Vocational Training [NCVT] 2. Central Apprenticeship](https://present5.com/presentation/83635034690c1e19554ac9d607d1d17a/image-3.jpg)
Vocational Training Advisory Boards 1. National Council for Vocational Training [NCVT] 2. Central Apprenticeship Council [CAC]

Vocational Training Schemes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Craftsmen Training Scheme Craft Instructors Training Apprenticeship Training Programme Advanced Vocational Training Scheme Training of Skilled Workers & Supervisors Training for Women – RVTIs Staff Training/Research - CSTARI Development of Instructional Materials - NIMI Hi-Tech Training Scheme Up-gradation of ITIs into Centers of Excellence (4540 crs-160 crs DF, 1580 crs WBF & 2800 crs DFL) 11. Up-gradation of 1396 Govt. ITI s through PPP (3665 cr) 12. Modular Employable Skills (MES) – SDI Scheme (550 crs DF)

Skill Training under DGET • 6500 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) – about 2000 in Govt. Sector – about 4500 in Private Sector • 1 Mn Seating Capacity • 50, 000 Skill Dev. Centres in the next 5 years • Needed 5, 000 ITI/VTPs in the country – (China has now 4, 000) • Industrial Training through Apprenticeship Scheme managed through Six RDATs in the country – about 1. 5 Million

NCVT Training Content • 70% of the training period is practical training • Theoretical training is given in subjects related to §Trade Theory, §Workshop Calculation & Science, §Engineering Drawing and §Social Studies (which also includes a module on Information Technology)

NCVT CERTIFICATE • SKILL COUNCIL REPRESENTED BY INDUSTRY ASSOCIATIONS, WORKERS, INSTITUTIONS, GOVERNMENT OF INDIA & STATE GOVERNMENTS • NATIONALLY ACCEPTED IN INDIA • INTERNATIONALLY ACCEPTED

Indian NCVT Skills WORLDS MOST KNOWN BRAND ON SKILL IN THE 21 ST CENTURY & BEYOND

THE WORLD WILL REQUIRE 470 MILLION SKILLED PERSONNEL IN THE AGE GROUP OF 16 TO 40 YEARS IN THE NEXT 25 YEARS INDIA HAS THE NUMBERS A GLOBAL OPPORTUNITY

Upgrading the Vocational Training System Studies & Recommendations

Commissions & Expert Groups have Analyzed the Vocational Training System in India and made Observations on the Strengths and Weaknesses and also made Recommendations for its Improvement • Working Group on Skill Development and Training for the X th Five year Plan (2002 -07) set up by Planning Commission (2001) • Task force on Employment Opportunities set up by Planning Commission under the chairmanship of Dr M S Ahluwalia (2001) • Second National Commission on Labour (2002) • Special Group on Targeting Ten Million Employment Opportunities per year set up by Planning Commission, under the Chairmanship of Dr S P Gupta(2002) • Expert Group on Upgradation of Training and Skill Development Programme, DGE&T, M/o Labour (2003) • 35 th meeting of National Council of Vocational Training held on 14 th Oct 2003

Recommendation of Several Commissions are summed up as • Industry must have much greater involvement : – – – Management of ITIs Design of curriculum Selection of instructors Training of instructors in the Industry Providing equipment for training. • A new modular approach to vocational training – – Modular Concept with Credit System Multi-Skilling Latest technology Multi entry and multi exit • Vertical mobility of craftsmen and apprentices • Staff development and motivation. • Competency based certification system for workers without formal qualifications.
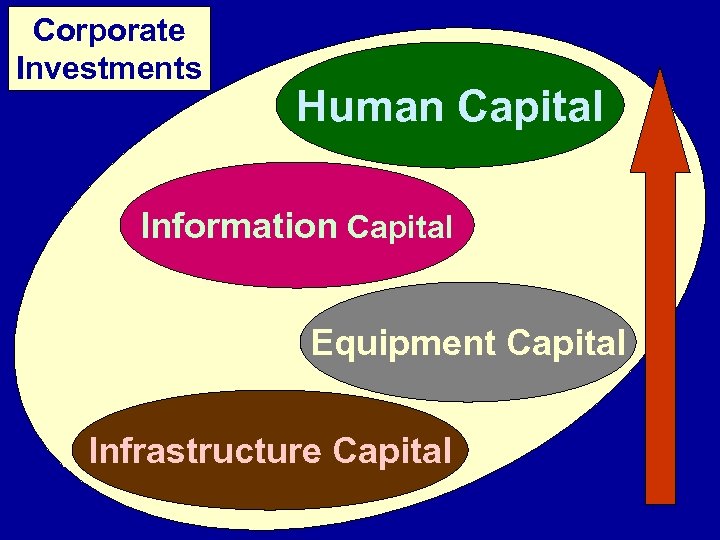
Corporate Investments Human Capital Information Capital Equipment Capital Infrastructure Capital

FORMAL, NON-FORMAL & INFORMAL TRAINING Indian NCVT Certification System • Formal Training (Indian NCVT-NTC, NAC, COE, . ) – Structural Programmes that enables participation in the next higher level of the (national) education system. • Non-Formal Training (Indian NCVT-MES, STC, . . ) – Not Recognized for entry into the next higher level of the (national) educational system. (Short-term demand driven programs) • Informal Training (Indian NCVT-MES, ……) – unstructured programmes/ skills acquired informally

Corporate Workforce Stake Holders Managers Engineers Supervisors Skilled Workforce
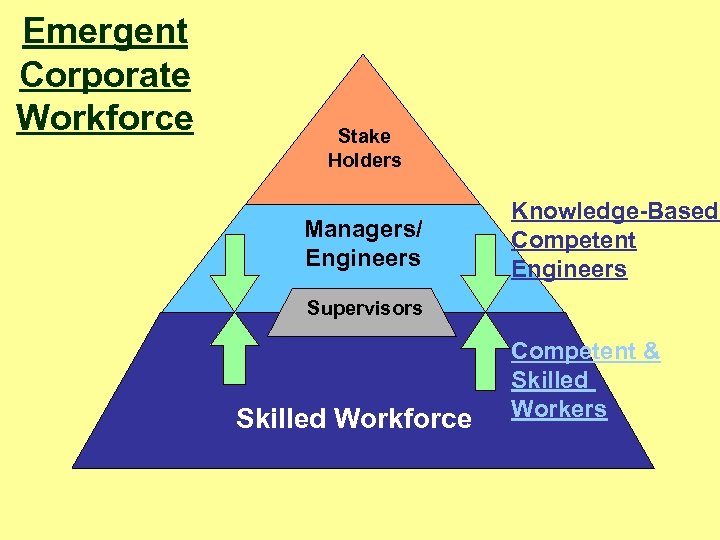
Emergent Corporate Workforce Stake Holders Managers/ Engineers Knowledge-Based Competent Engineers Supervisors Skilled Workforce Competent & Skilled Workers

HUMAN CAPITAL The need of the corporate world • Competent Human Beings are required – Competent Skilled Wealth Creating Human Beings – Competent Knowledgeable Wealth Managing Human Beings
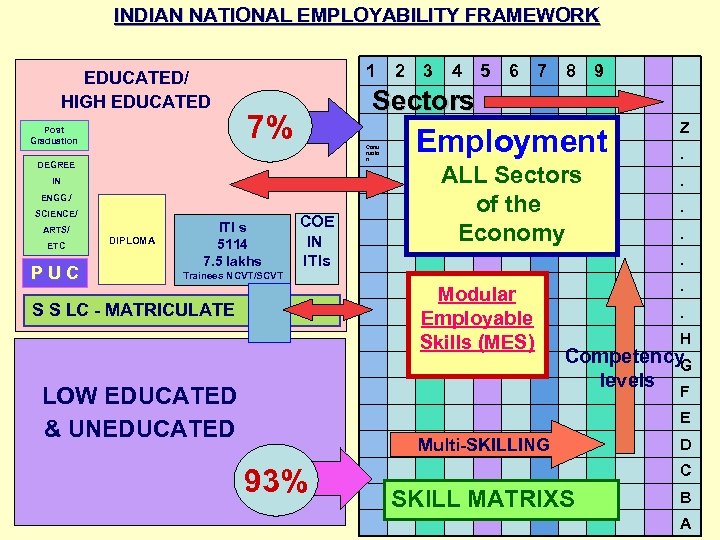
INDIAN NATIONAL EMPLOYABILITY FRAMEWORK EDUCATED/ HIGH EDUCATED Post Graduation 1 Const ructio n DEGREE IN ENGG. / ARTS/ ETC PUC DIPLOMA ITI s 5114 7. 5 lakhs 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sectors 7% SCIENCE/ 2 COE IN ITIs Employment ALL Sectors of the Economy Modular Employable Skills (MES) LOW EDUCATED & UNEDUCATED . . . Trainees NCVT/SCVT S S LC - MATRICULATE Z . . H Competency G levels F E Multi-SKILLING 93% D C SKILL MATRIXS B A
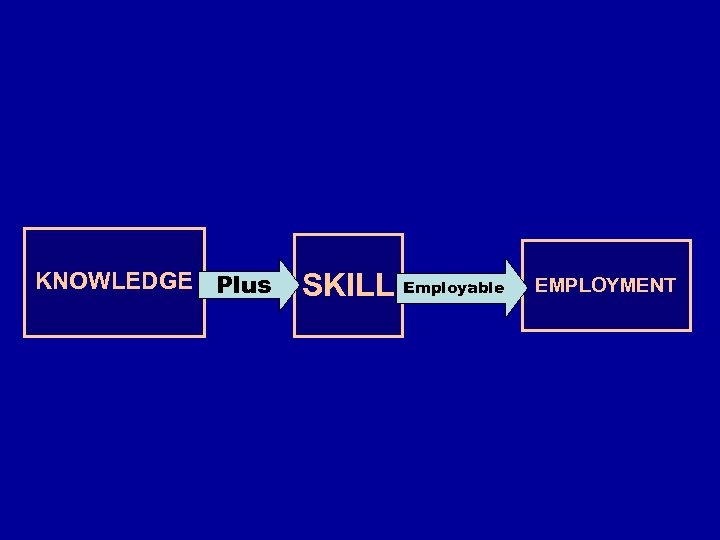
KNOWLEDGE Plus SKILL Employable EMPLOYMENT
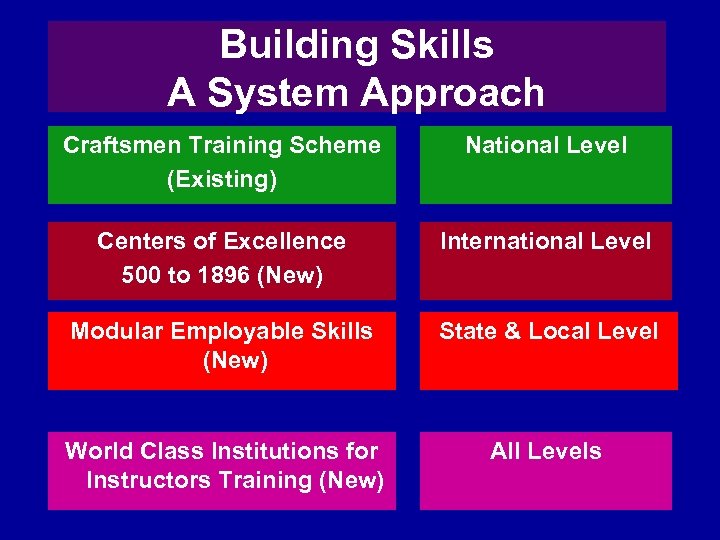
Building Skills A System Approach Craftsmen Training Scheme (Existing) National Level Centers of Excellence 500 to 1896 (New) International Level Modular Employable Skills (New) State & Local Level World Class Institutions for Instructors Training (New) All Levels

MES ‘Womb to Tomb’ INSTITUTIONALISATION OF LIFELONG LEARNING

Modular Employable Skills(MES) for Lifelong Learning 1. MINIMUM SKILL SETS WHICH WILL MAKE A PERSON EMPLOYABLE / CAN MAKE ECONOMIC CONTRIBUTION / PRODUCE WEALTH / SUPPORT WEALTH CREATION 2. Training done by Vocational Training Providers (VTP) 3. Assessment carried out by Independent Agency from Industry/Employer Organization/Assessing bodies which have been appointed by the Government. 10 National Bodies Appointed 4. Government reimburses the Assessment cost and the Training cost, and the Trainee gets back the training fee and assessment fees on passing the
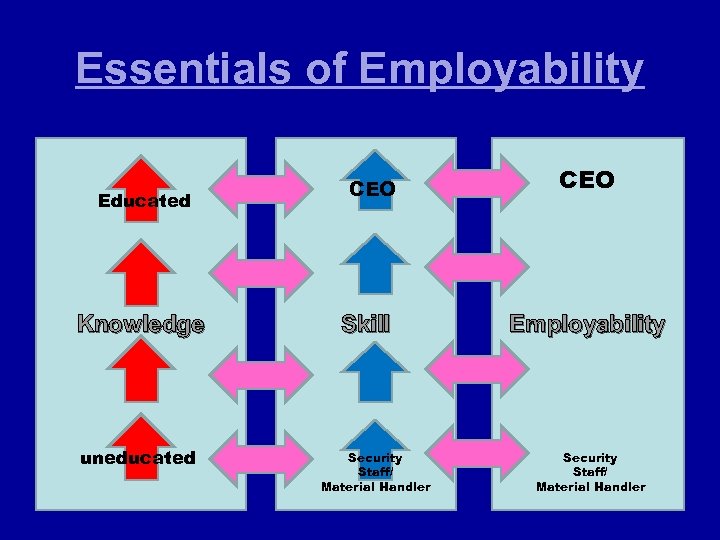
Essentials of Employability Educated Knowledge uneducated CEO Skill Security Staff/ Material Handler CEO Employability Security Staff/ Material Handler

MES-Common Plug-in Board for 1. INDUSTRY 2. PERSON 3. INSTITUTION

MES CURRICULUM DESIGN 1. Industry/ Sector Panels Identify the Employment Matrix / Job Matrix 2. Arrange the Job Skills in a vertical and horizontal formation according to there position or depending on competencies or multiskilling, learning complexities, etc. 3. PWD Skill Council for Job Skills & Placements 4. The Sectorial Panels will use a Common Format for each MES Module

MES SECTORS AND MODULES 1. We have identified 40 Sectors 2. Presently 340 MES have been designed and we have set a target of about 2000 in the next year 3. 25 Skill Sector Panels are in operation

Every Person can be made Employable

MES SKILL n’ JOB FAIR • • • In the Pilot phase during 2008 1 fair in every month at the same location 100 Industries/Employers/etc. will participate in each Fair 1, 000 MES graduates will participate in each fair Learning/Skilling/Re-learning/Re-skilling will be done for the persons till employment/self-employment is secured for 100% of the persons is engineered Learning/Skilling Institutions, about 700 of them have been registered MES will give Recognition of the Initiation of the Choice of Skill by a person at the entry level About 100 Fairs have been planned in the three states for the year 2008 -2009 A target of 1, 000 persons trained and certified is being planned for the year 2008 -2009

Challenges in Skill Development 1. Skill Recognition and the Social Angle 2. Skill Mobility & Apt Deployment 3. Skill Development Models for Public Private Partnership 4. Skill Curriculum, Norms & Certification a Government Activity 5. Industry bodies for Curriculum Development and Assessment 6. Skill Brand Building “Indian NCVT Skills” 7. Skill Currency or IND-SKILL Dollars – Century’s largest FOREX earner.

Assessing Body - MES 1. AB State Assessment Cell - 5 member committee - 3 year term - Name & Address 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Separate Bank Account Fees in favor of ___ payable at ___ Engagement of Assessing Agency/Coordinators/Assessors Application forms from AB Stationery / Advertisements Letter to RDAT with above details and readiness to take up Assessments in the State by the State Cell Chairman for writing to allotted VTP List of Trained Candidates for Testing to be sent to RDAT Assessment dates fixed with VTPs/Industry Assessment Sheets with Marks and details sent to RDAT Results declared by RDAT Reimbursement of Assessment fees to AB Reimbursement of Training Fees to the Vocational Training Provider (VTP)

High Energy and High Quality Human Being for World Economy • Reliability/Dependability • Repeatability/Uniformity in performance • Competency/Professional Expertise
INFRA-STRUCTURE AND INTRA-STRUCTURE

Professional Humility Oneness is better than Correctness • For Human networking for higher productivity • For Continuous Learning • For Tremendous Output

World in the hands of WHOM (High Quality Human Being) • • • SKILL in the hands of WHOM Knowledge in the hands of WHOM Power in the hands of WHOM AUTHORITY in the hands of WHOM KNIFE in the hands of WHOM – Doctor – Robber

Difference to any Industry Situation is the AVERAGE Quality of Human Beings • LOW QUALITY HUMAN BEINGS • MEDIUM QUALITY HUMAN BEINGS • HIGH QUALITY HUMAN BEINGS

WORLD CLASS Professionals • 50% Paid for Out-put • 50% Paid for In-put

EDUSAT

Thank You sjamalan@yahoo. co. in
83635034690c1e19554ac9d607d1d17a.ppt