c5f1807d4d8debbccc3936d2d889f171.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95

INDIAN INSTITUTE OF BANKING & FINANCE RISK MANAGEMENT MODULE C & D By M. Ravindran ravindran@iibf. org. in

Syllabus Module C: Treasury Management: Treasury management; concepts and functions; instruments in the treasury market; development of new financial products; control and supervision of Treasury management; linkage of domestic operations with foreign operations. Asset-liability management; Interest rate risk; interest rate futures; stock options; debt instruments; bond portfolio strategy; risk control and hedging instruments. Investments – Treasury bills – Money markets instruments such as CDs, CPs, IBPs; Securitisation and Forfaiting; Refinance and rediscounting facilities.

Syllabus Module D Capital Management and Profit Planning l Prudential Norms- Capital Adequacy-Basel IIAsset Classification-provisioning l Profit and Profitability-Historical Perspective of the Approach of Banks to profitability-Effects of NPA on profitability-A profitability Model-Share holders value Maximization & EVA-Profit Planning -Measures to improve profitability

Integrated Treasury refers to integration of money market, securities market and foreign exchange operations. Functions: -Meeting reserve requirements -Efficient merchant services -Global cash management -Optimizing profit by exploiting market opportunities in forex market, money market and securities market -Risk management -Assisting bank management in ALM
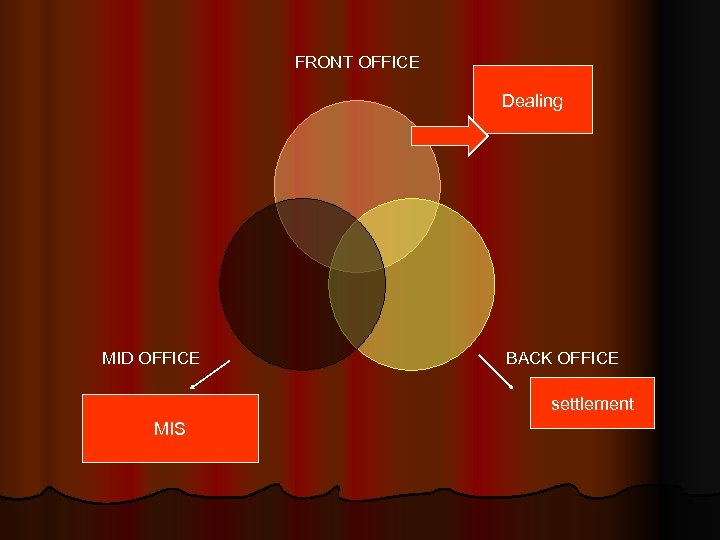
FRONT OFFICE Dealing MID OFFICE BACK OFFICE settlement MIS
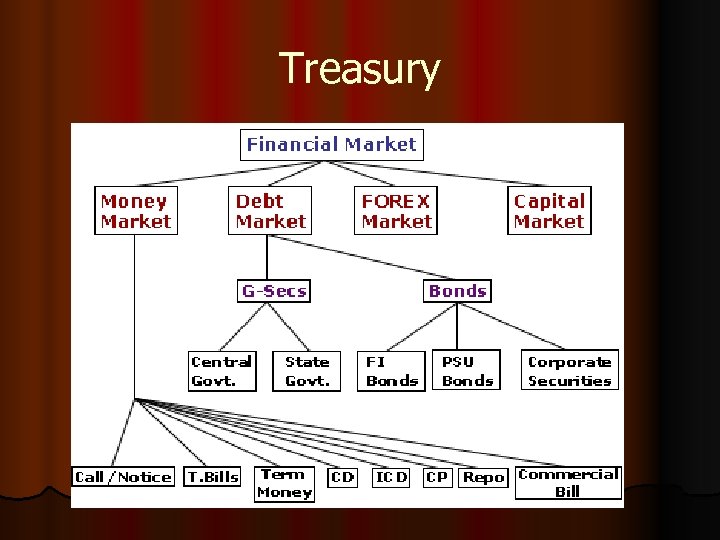
Treasury

Money Market l Certificate of Deposit (CD) l Commercial Paper (C. P) l Inter Bank Participation Certificates l Inter Bank term Money l Treasury Bills l Call Money

Certificate of Deposit CDs are short-term borrowings in the form of Usance Promissory Notes having a maturity of not less than 7 days up to a maximum of one year. l CD is subject to payment of Stamp Duty under Indian Stamp Act, 1899 (Central Act) l They are like bank term deposits accounts. Unlike traditional time deposits these are freely negotiable instruments and are often referred to as Negotiable Certificate of Deposits l

Features of CD l l l l Issued by all scheduled commercial banks except RRBs Minimum period 7 days Maximum period 1 year Minimum Amount Rs 1 lac and in multiples of Rs. 1 lac CDs are transferable by endorsement CRR & SLR are to be maintained CDs are to be stamped

Commercial Paper l Commercial Paper (CP) is an unsecured money market instrument issued in the form of a promissory note. l Who can issue Commercial Paper (CP) Highly rated corporate borrowers, primary dealers (PDs) and all-India financial institutions (FIs)

Eligibility for issue of CP the tangible net worth of the company, as per the latest audited balance sheet, is not less than Rs. 4 crore; b) the working capital (fund-based) limit of the company has been sanctioned by banks c) borrowal account of the company is classified as a Standard Asset by the financing bank/s. a)

Rating Requirement l l l l All eligible participants should obtain the credit rating for issuance of Commercial Paper Credit Rating Information Services of India Ltd. (CRISIL) Investment Information and Credit Rating Agency of India Ltd. (ICRA) Credit Analysis and Research Ltd. (CARE) Fitch Ratings Duff & Phelps Credit Rating India Pvt. Ltd. (DCR India) The minimum credit rating shall be P-2 of CRISIL or such equivalent rating by other agencies

Features l CP can be issued for maturities between a minimum of 7 days and a maximum upto one year from the date of issue. l Minimum issue price Rs. 5 lakhs and in multiples of Rs. 5 lakhs l Issued in demat form only

To whom issued CP is issued to Ø individuals, Ø banking companies, Ø other corporate bodies registered or incorporated in India and unincorporated bodies, Ø Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) Ø Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs).

CP-Yield calculation l Yield = (Face value-Price)*365*100 ----------------Price *No of days to maturity Face value 5 lakhs price 4, 92, 711 for 90 days Find out yield 500000 -492711*365*100 -----------------= 6% 492711*90

Calculation of price-CP PRICE= Face Value ------( 1+Yield *No of days -----------365*100) Face Value Rs. 500000 for 90 days at 6% 500000 ------1(6*90/365*100) = Rs 492711

Meaning of Repo It is a transaction in which two parties agree to sell and repurchase the same securitya t a mutually decided future date and a price l The Repo/Reverse Repo transaction can only be done at Mumbai between parties approved by RBI and in securities as approved by RBI (Treasury Bills, Central/State Govt securities). l

Repo Uses of Repo It helps banks to invest surplus cash It helps banks to raise funds at better rates An SLR surplus and CRR deficit bank can use the Repo deals as a convenient way of adjusting SLR/CRR positions simultaneously. RBI uses Repo and Reverse repo as instruments for liquidity adjustment in the system

Coupon rate and Yield The difference between coupon rate and yield arises because the market price of a security might be different from the face value of the security. Since coupon payments are calculated on the face value, the coupon rate is different from the yield.

Example l 10% Aug 2015 10 year Govt Bond l Face Value RS. 1000 l Market Value Rs. 1200 l In this case Coupon rate is 10% l Yield is 8. 33% = 1200*10 -------1000

Call Money The money that is lent for one day is known as "Call Money", If it exceeds one day (but less than 15 days) it is referred to as "Notice Money".

Call Money Market Banks borrow in this market for the following purpose l To fill the gaps or temporary mismatches in funds l To meet the CRR & SLR mandatory requirements as stipulated by the Central bank l To meet sudden demand for funds arising out of large outflows.

Factors influencing interest rates The factors which govern the interest rates are mostly economy related and are commonly referred to as macroeconomic factors. Some of these factors are: 1) Demand for money 2) Government borrowings 3) Supply of money 4) Inflation rate 5) The Reserve Bank of India and the Government policies which determine some of the variables mentioned above.

Gilt edged securities The term government securities encompass all Bonds & T-bills issued by the Central Government, and state governments. These securities are normally referred to, as "giltedged" as repayments of principal as well as interest are totally secured by sovereign guarantee.

Treasury Bills Treasury bills, commonly referred to as T-Bills are issued by Government of India against their short term borrowing requirements with maturities ranging between 14 to 364 days. All these are issued at a discount-to-face value. For example a Treasury bill of Rs. 100. 00 face value issued for Rs. 91. 50 gets redeemed at the end of it's tenure at Rs. 100.

Who can invest in T-Bill Banks, Primary Dealers, State Governments, Provident Funds, Financial Institutions, Insurance Companies, NBFCs, FIIs (as per prescribed norms), NRIs & OCBs can invest in T-Bills.

What is auction of Securities Auction is a process of calling of bids with an objective of arriving at the market price. It is basically a price discovery mechanism

Debenture l. A Debenture is a debt security issued by a company (called the Issuer), which offers to pay interest in lieu of the money borrowed for a certain period. l These are long-term debt instruments issued by private sector companies. These are issued in denominations as low as Rs 1000 and have maturities ranging between one and ten years.

Difference between debenture and bond Long-term debt securities issued by the Government of India or any of the State Government’s or undertakings owned by them or by development financial institutions are called as bonds. Instruments issued by other entities are called debentures.

Current yield It is calculated by dividing the coupon rate by the purchase price of the bond. For e. g: If an investor buys a 10% Rs 100 debenture of ABC company at Rs 90, his current Yield on the instrument would be computed as: Current Yield = (10%*100)/90 X 100 , That is 11. 11% p. a.

Primary Dealers l Primary Dealers can be referred to as Merchant Bankers to Government of India, comprising the first tier of the government securities market. These were formed during the year 1994 -96 to strengthen the market infrastructure

What role do Primary Dealers play? The role of Primary Dealers is to; (i) commit participation as Principals in Government of India issues through bidding in auctions (ii) provide underwriting services (iii) offer firm buy - sell / bid ask quotes for T-Bills & dated securities (v) Development of Secondary Debt Market

OMO or Open Market Operations is a market regulating mechanism often resorted to by Reserve Bank of India. Under OMO Operations Reserve Bank of India as a market regulator keeps buying or/and selling securities through it's open market window. It's decision to sell or/and buy securities is influenced by factors such as overall liquidity in the system etc

YIELD CURVE The relationship between time and yield on a homogenous risk class of securities is called the Yield Curve. The relationship represents the time value of money showing that people would demand a positive rate of return on the money they are willing to part today for a payback into the future

SHAPE OF YIELD CURVE A yield curve can be positive, neutral or flat. A positive yield curve, which is most natural, is when the slope of the curve is positive, i. e. the yield at the longer end is higher than that at the shorter end of the time axis. This results, as people demand higher compensation for parting their money for a longer time into the future. A neutral yield curve is that which has a zero slope, i. e. is flat across time. T his occurs when people are willing to accept more or less the same returns across maturities. The negative yield curve (also called an inverted yield curve) is one of which the slope is negative, i. e. the long term yield is lower than the short term yield
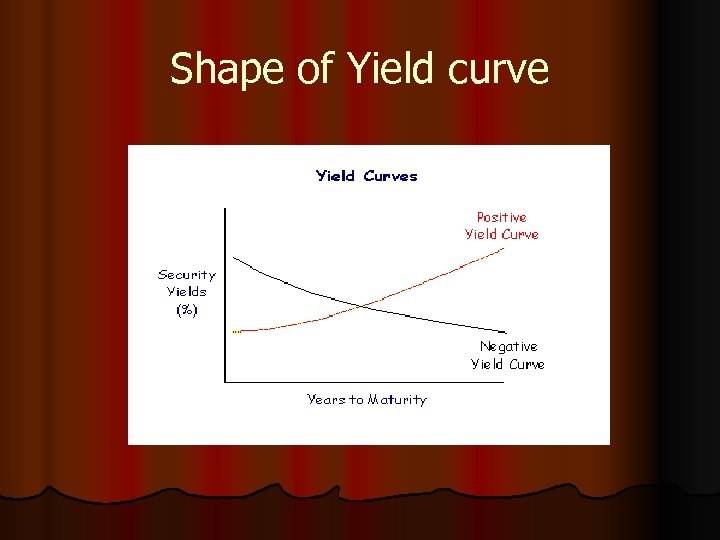
Shape of Yield curve

LIBOR stands for the London Interbank Offered Rate and is the rate of interest at which banks borrow funds from other banks, in marketable size, in the London interbank market. l LIBOR is the most widely used "benchmark" or reference rate for short term interest rates. It is compiled by the British Bankers Association as a free service and released to the market at about 11. 00[London time] each day. l
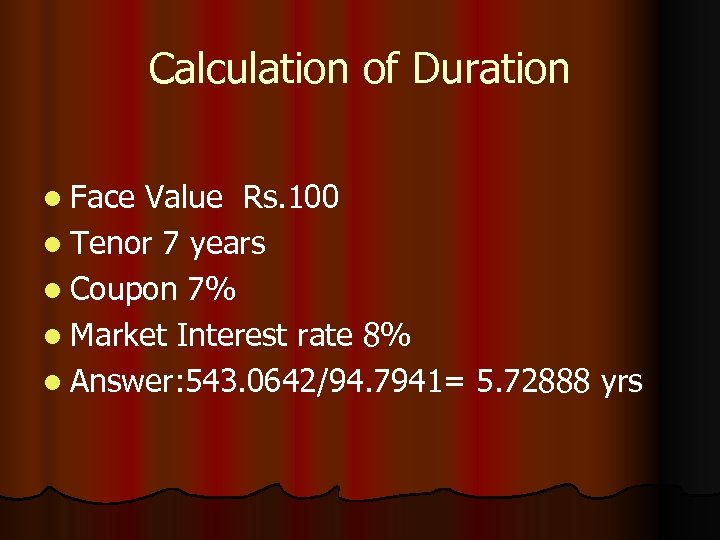
Calculation of Duration l Face Value Rs. 100 l Tenor 7 years l Coupon 7% l Market Interest rate 8% l Answer: 543. 0642/94. 7941= 5. 72888 yrs
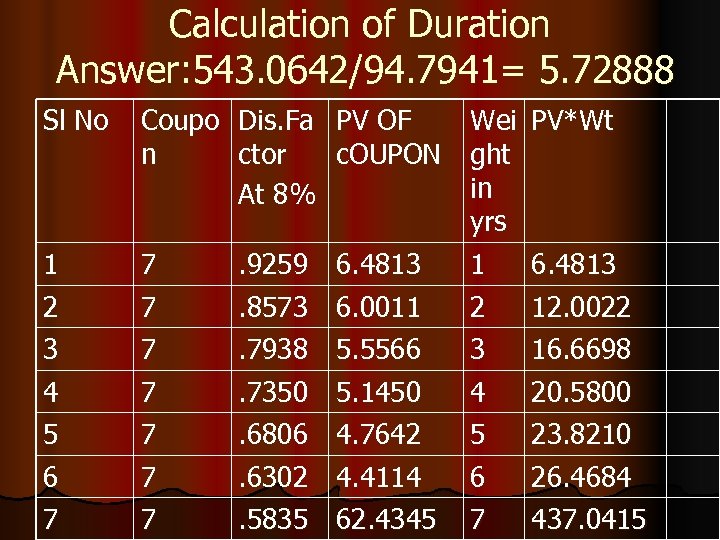
Calculation of Duration Answer: 543. 0642/94. 7941= 5. 72888 Sl No Coupo Dis. Fa PV OF n ctor c. OUPON At 8% Wei PV*Wt ght in yrs 1 2 7 7 1 2 6. 4813 12. 0022 3 4 7 7 16. 6698 20. 5800 5 6 7 7 . 7350 5. 1450. 6806 4. 7642. 6302 4. 4114 3 4 5 6 23. 8210 26. 4684 7 7 . 5835 62. 4345 7 437. 0415 . 9259 6. 4813. 8573 6. 0011. 7938 5. 5566

CRR & SLR The minimum and maximum levels of CRR are prescribed at 3% and 20% of demand term liabilities (DTL) of the bank, respectively, under Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934. The minimum and maximum SLR are prescribed at 25% and 40% of DTL respectively, under Banking Regulation Act of 1949. The CRR and SLR are to be maintained on fortnightly basis.

Demand Time Liabilities l l l Main components of DTL are: Demand deposits (held in current and savings accounts, margin money for LCs, overdue fixed deposits etc. ) Time deposits (in fixed deposits, recurring deposits, reinvestment deposits etc. ) Overseas borrowings Foreign outward remittances in transit (FC liabilities net of FC assets) Other demand time liabilities (accrued interest, credit balances in suspense account etc. )

SLR is to be maintained in the form of the following assets: l Cash balances (excluding balances maintained for CRR) l Gold (valued at price not exceeding current market price) l Approved securities valued as per norms prescribed by RBI.

Va. R Value at Risk (Va. R) is the most probable loss that we may incur in normal market conditions over a given period due to the volatility of a factor, exchange rates, interest rates or commodity prices. The probability of loss is expressed as a percentage – Va. R at 95% confidence level, implies a 5% probability of incurring the loss; at 99% confidence level the Va. R implies 1% probability of the stated loss. The loss is generally stated in absolute amounts for a given transaction value (or value of a investment portfolio).

Va. R The Va. R is an estimate of potential loss, always for a given period, at a given confidence level. . A Va. R of 5 p in USD / INR rate for a 30 - day period at 95% confidence level means that Rupee is likely to lose 5 p in exchange value with 5% probability, or in other words, Rupee is likely to depreciate by maximum 5 p on 1. 5 days of the period (30*5% ). A Va. R of Rs. 100, 000 at 99% confidence level for one week for a investment portfolio of Rs. 10, 000 similarly means that the market value of the portfolio is most likely to drop by maximum Rs. 100, 000 with 1% probability over one week, or , 99% of the time the portfolio will stand at or above its current value.

Exchange Rate Quotation Exchange Quotations : There are two methods l Exchange rate is expressed as the price per unit of foreign currency in terms of the home currency is known as the “Home currency quotation” or “Direct Quotation” l Exchange rate is expressed as the price per unit of home currency in terms of the foreign currency is known as the “Foreign Currency Quotation” or “Indirect Quotation” l Direct Quotation is used in New York and other foreign exchange markets and Indirect Quotation is used in London foreign exchange market. l

Principles l Direct Quotation: Buy Low, Sell High: 1 USD= Rs. 42. 60 42. 65 l Indirect Quotation: Buy High, Sell Low: Rs. 100 = USD 2. 5600 – 2. 5650

Spot and Forward Transactions l ‘A’ Bank agrees to buy from ‘B’ Bank USD 100000. The actual exchange of currencies i. e. payment of rupees and receipt of US Dollars, under the contract may take place : l on the same day or l two days later or l some day later, say after a month.

Interpretation of Quotation The market quotation for a currency consists of the spot rate and the forward margin. The outright forward rate has to be calculated by loading the forward margin into the spot rate. For example US Dollar is quoted as under in the inter-bank market on a given day as under : l Spot 1 USD = Rs. 44. 1000/1300 l Spot/November 0200/0500 l Spot/December 1500/1800 l

TT Buying Rate l l TT Buying Rate (TT stands for Telegraphic Transfer) This is the rate applied when the transaction does not involve any delay in realization of the foreign exchange by the bank. In other words, the nostro account of the bank would already have been credited. The rate is calculated by deducting from the inter-bank buying rate the exchange margin as determined by the Bank.

Bills Buying Rate l This is the rate to be applied when a foreign bill is purchased. When a bill is purchased, the proceeds will be realized by the Bank after the bill is presented to the drawee at the overseas center. In the case of a usance bill the proceeds will be realized on the due date of the bill which includes the transit period and the usance period of the bill.

Problem You would like to import machinery from USA worth USD 100000 to be payable to the overseas supplier on 31 st Oct [a] Spot Rate USD = Rs. 45. 8500/8600 Forward Premium September 0. 2950/3000 October 0. 5400/5450 November 0. 7600/7650 [b] exchange margin 0. 125% [c] Last two digits in multiples of nearest 25 paise l Calculate the rate to be quoted by the bank ?

Solution This is an example Forward Sale Contract. Inter Bank Spot Selling Rate Rs. 45. 8600 Add Forward Margin . 5450 ------- 46. 4050 Add Exchange Margin . 0580 -------Forward Rate 46. 4630 Rounded Off to multiple of 25 paise Rs. 4625 Amount Payable to the bank Rs. 46, 250

Swap l. A swap agreement between two parties commits each counterparty to exchange an amount of funds, determined by a formula, at regular intervals, until the swap expires. l In the case of a currency swap, there is an initial exchange of currency and a reverse exchange at maturity.

Mechanics l Firm A needs fixed rate loan –AAA rated l Firm B needs floating rate -A rated l Firm A enjoys an absolute advantage in both credit markets. Firm A Fixedrate finance Floatingrate finance Firm B 9% 11% LIBOR +0. 0% +1%

Mechanics STEP ! Firm A will borrow at Fixed rate 9% Firm B will borrow at floating rate (LIBOR +1)% STEP 2 Firm A will pay Floating rate [LIBOR] to Firm B will Pay Fixed rate [9. 5%] only Gain Net interest cost LIBOR-. 5% Net Interest cost 9+[ 1%+0. 5%]=10. 5%
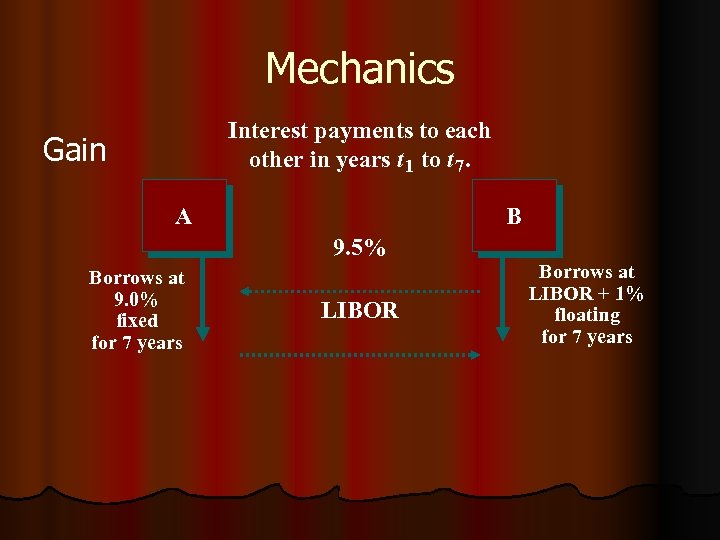
Mechanics Interest payments to each other in years t 1 to t 7. Gain A B 9. 5% Borrows at 9. 0% fixed for 7 years LIBOR Borrows at LIBOR + 1% floating for 7 years

Basel I to Basel II l Minimum capital requirements → 3 Pillars l New credit risk approaches l Market risk - unchanged l Add operational risk portion
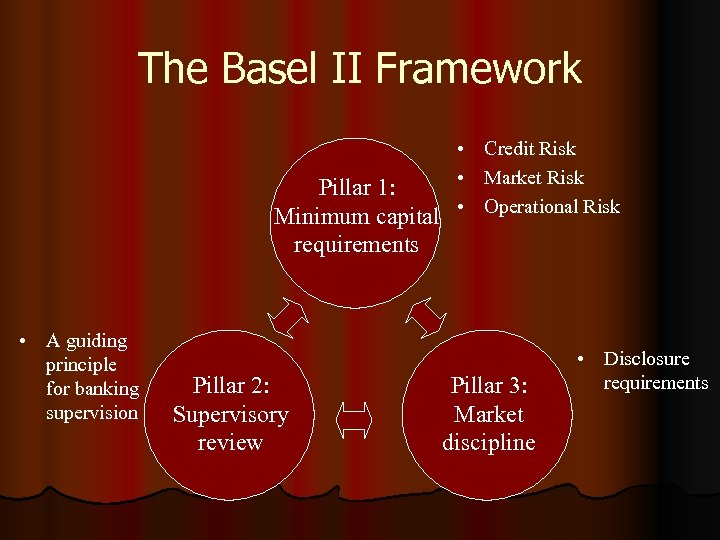
The Basel II Framework Pillar 1: Minimum capital requirements • A guiding principle for banking supervision Pillar 2: Supervisory review • Credit Risk • Market Risk • Operational Risk Pillar 3: Market discipline • Disclosure requirements

Pillar 1: Minimum Capital Requirements l The calculation of regulatory minimum capital requirements:

The Capital and Assets Definition of capital: l Tier 1 capital + Tier 2 capital + adjustments Total risk-weighted assets are determined by: l multiplying the capital requirements for market risk and operational risk by 12. 5 l and adding the resulting figures to the sum of risk-weighted assets for credit risk.

Credit Risk l Standardised Approach l Foundation IRB Approach l Advanced IRB Approach

Credit Risk Standardised Approach l In determining the risk weights in the standardised approach, banks may use assessments by external credit assessment institutions.
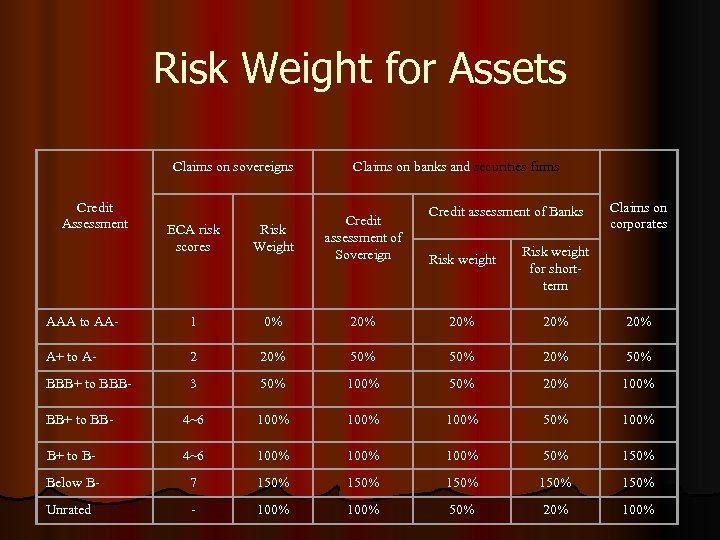
Risk Weight for Assets Claims on sovereigns Credit Assessment Claims on banks and securities firms Credit assessment of Banks Claims on corporates ECA risk scores Risk Weight Credit assessment of Sovereign Risk weight for shortterm AAA to AA- 1 0% 20% 20% A+ to A- 2 20% 50% BBB+ to BBB- 3 50% 100% 50% 20% 100% BB+ to BB- 4~6 100% 50% 100% B+ to B- 4~6 100% 50% 150% Below B- 7 150% 150% Unrated - 100% 50% 20% 100%

Credit Risk - IRB Approach l In the internal ratings-based(IRB) approach, it’s based on banks’ internal assessment. l The approach combines the quantitative inputs provides by banks and formula specified by the Committee.

Credit Risk - IRB Approach Four quantitative inputs (risk components): l Probability of default (PD) l Loss given default (LGD) l Exposure at default (EAD) l Maturity (M) Use formula of the Committee to calculate the minimum requirements.

Credit Risk - IRB Approach Data Input Foundation IRB Advanced IRB Probability of default (PD) Loss given default (LGD) Exposure at default (EAD) From banks Set by the Committee From banks Maturity (M) From banks Set by the Committee or from banks From banks

Market Risk l Standardised method - the standards of the Committee l Internal models - use banks’ internal assessments - Value at Risk (Va. R)

Operational Risk l The risk of losses results from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and system, or external events. l Basic Indicator Approach l Standardised Approach l Advanced Measurement Approaches(AMA)

Operational Risk Basic Indicator Approach l GI = average annual gross income(three years, excepted the negative amounts) l α = 15%

Operational Risk Standardised Approach l GI 1 -8 = average annual gross income from business line from one to eight (three years, excepted the negative amounts) l β = A fixed percentage set by the Committee
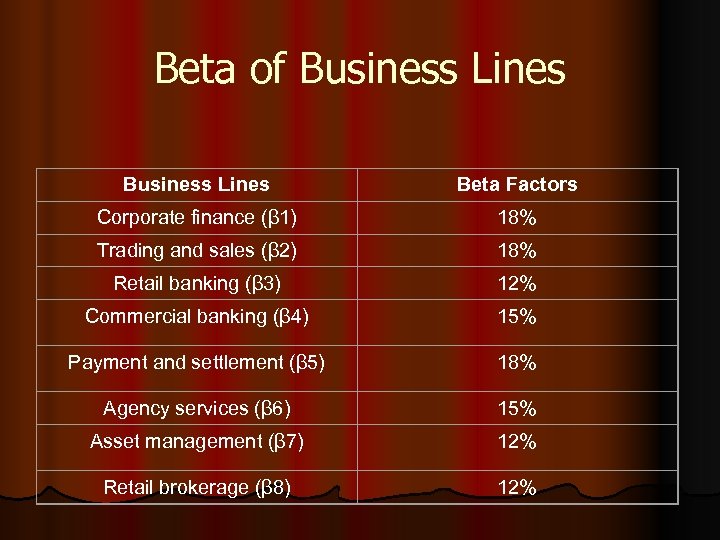
Beta of Business Lines Beta Factors Corporate finance (β 1) 18% Trading and sales (β 2) 18% Retail banking (β 3) 12% Commercial banking (β 4) 15% Payment and settlement (β 5) 18% Agency services (β 6) 15% Asset management (β 7) 12% Retail brokerage (β 8) 12%

Operational Risk - Advanced Measurement Approaches l Under the AMA, the regulatory capital requirement will equal the risk measure generated by the bank’s internal operational risk measurement system using the quantitative and qualitative criteria for the AMA. l Use of the AMA is subject to supervisory approval.

Pillar 2: Supervisory Review l Principle 1: Banks should have a process for assessing and maintaining their overall capital adequacy. l Principle 2: Supervisors should review and evaluate banks’ internal capital adequacy assessments and strategies.

Supervisory Review l Principle 3: Supervisors should expect banks to operate above the minimum regulatory capital ratios. l Principle 4: Supervisors should intervene at an early stage to prevent capital from falling below the minimum levels.

Pillar 3: Market Discipline l The purpose of pillar three is to complement the pillar one and pillar two. l Develop a set of disclosure requirements to allow market participants to assess information about a bank’s risk profile and level of capitalization.

Minimum Capital Adequacy Ratios l Tier one capital to total risk weighted credit exposures to be not less than 4 %; l Total capital (i. e. tier one plus tier two less certain deductions) to total risk weighted credit exposures to be not less than 8%

Calculation of Capital Tier One Capital l the ordinary share capital (or equity) of the bank; and l audited revenue reserves e. g. . retained earnings; less l current year's losses; l future tax benefits; and l intangible assets, e. g. goodwill.

Calculation of Capital Upper Tier Two Capital l l Un-audited retained earnings; revaluation reserves; general provisions for bad debts; perpetual cumulative preference shares (i. e. preference shares with no maturity date whose dividends accrue for future payment even if the bank's financial condition does not support immediate payment); perpetual subordinated debt (i. e. debt with no maturity date which ranks in priority behind all creditors except shareholders).

Calculation of Capital Lower Tier Two Capital l Subordinated debt with a term of at least 5 years; l Sedeemable preference shares which may not be redeemed for at least 5 years.

Restrictions l Tier two capital may not exceed 100% of tier one capital; l Lower tier two capital may not exceed 50% of tier one capital; l Lower tier two capital is amortized on a straight line basis over the last five years of its life.

Total Capital This is the sum of tier 1 and tier 2 capital less the following deductions: l equity investments in subsidiaries; l shareholdings in other banks that exceed 10 percent of that bank's capital; l unrealized revaluation losses on securities holdings.

Module D Capital Management

Capital Management & Profit Planning

Basel II Tier I-Core Capital Paid up capital , Free Reserves and unallocated surpluses Tier II-Supplementary Capital Subordinated debt of more than 5 years maturity , loan loss reserve, revaluation reserve, investment fluctuation reserve, limited life preference sharerestricted to 100% of tier I capital Tier III Capital subordinated debt with shot term maturity [min 2 years] for market risk

Total Risk weighted Assets l Risk weighted assets of credit risk plus l 12. 5* Capital requirement for market risk plus l 12. 5* capital requirement for operational risk

Three pillars l First Pillar-minimum capital requirements l Second pillar-supervisory process l Third pillar-market discipline
![Capital Charge for Credit Risk Standardized Approach Internal rating based approach [1]Foundation Approach [2]Advanced Capital Charge for Credit Risk Standardized Approach Internal rating based approach [1]Foundation Approach [2]Advanced](https://present5.com/presentation/c5f1807d4d8debbccc3936d2d889f171/image-87.jpg)
Capital Charge for Credit Risk Standardized Approach Internal rating based approach [1]Foundation Approach [2]Advanced IRB Approach
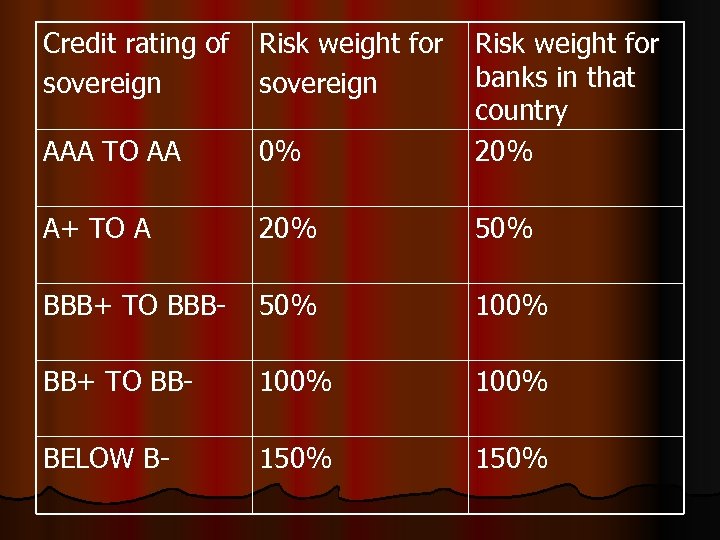
Credit rating of sovereign Risk weight for sovereign AAA TO AA 0% Risk weight for banks in that country 20% A+ TO A 20% 50% BBB+ TO BBB- 50% 100% BB+ TO BB- 100% BELOW B- 150%
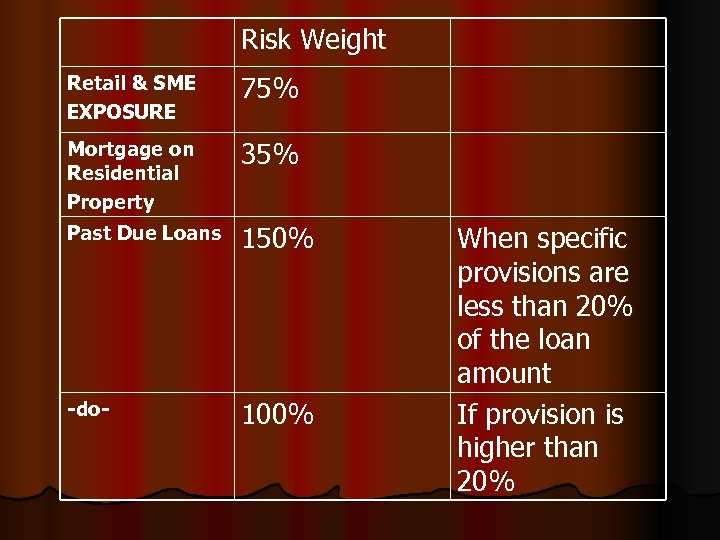
Risk Weight Retail & SME EXPOSURE 75% Mortgage on Residential Property 35% Past Due Loans 150% -do- 100% When specific provisions are less than 20% of the loan amount If provision is higher than 20%

Capital Charge for Operational Risk l The Basic Indicator Approach l The Standardized Approach l Advanced Management Approach

Standardized Approach for Operational Risk l l Beta factor- a fixed percentage set by Basel committee Maximum 18% Minimum 12% Banks activities are divided into 8 business linescorporate finance, trading, retail banking, commercial banking, payment &settlement, agency services, asset management, retail brokering

Asset Classification l Standard Assets l Sub Standard Assets l Doubtful Assts l Loss Assets

Provisioning l Standard Assts 0. 40% l Substandardl Secured -provision 10% l Unsecured[realisable value is not more than 10% of o/s] –provision 20%

Provision Doubtful I- first 12 months Provision 20% realizable value of security plus 100% shortfall of security Doubtful II-further 24 months Provision 30% realizable value of security plus 100% shortfall of security Doubtful III-for over 36 months 100% provision Loss Assets 100%

Thank you With Best Wishes ravindran@iibf. org. in
c5f1807d4d8debbccc3936d2d889f171.ppt