a301d3ed69f35bfeb2c69fb26efb3e28.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Indian Financial System -An Overview 1
Indian Financial System -An Overview 1
 Indian Financial System – An Overview FUNCTIONS • • Collection of SAVINGS & Distribution for INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT. Stimulating CAPITAL FORMATION & ACCELERATING THE ECONNOMIC GROWTH STRUCTURES 1. Regulatory Bodies (RBI/SEBI/IRDA/PFRDA) 2. Financial Intermediotories 3. Financial Markets 4. Financial Assets / Instruments PHASES * Upto 1951 Pvt. Sector * 1951 to 1990 Public Sector * Early Ninties Privatisation * Present Status Globalisation 2
Indian Financial System – An Overview FUNCTIONS • • Collection of SAVINGS & Distribution for INDUSTRIAL INVESTMENT. Stimulating CAPITAL FORMATION & ACCELERATING THE ECONNOMIC GROWTH STRUCTURES 1. Regulatory Bodies (RBI/SEBI/IRDA/PFRDA) 2. Financial Intermediotories 3. Financial Markets 4. Financial Assets / Instruments PHASES * Upto 1951 Pvt. Sector * 1951 to 1990 Public Sector * Early Ninties Privatisation * Present Status Globalisation 2
 Indian Financial System – An Overview Process of Capital Formation Involves three distinct, although inter-related activities. (i) Savings: The ability by which resources are set aside and become available for other purpose. (ii) Finance: The activity by which claims to resources are either assembled from abroad, deposits or notes and then placed in the hands of the investor. (iii) Investments: The activity by which resources are actually committed to production. The financial system is a link between the savers (savings – surplus economic units) and the investors (savings – deficit economic units). It is made up of all those channels through which savings become available for investment. 3
Indian Financial System – An Overview Process of Capital Formation Involves three distinct, although inter-related activities. (i) Savings: The ability by which resources are set aside and become available for other purpose. (ii) Finance: The activity by which claims to resources are either assembled from abroad, deposits or notes and then placed in the hands of the investor. (iii) Investments: The activity by which resources are actually committed to production. The financial system is a link between the savers (savings – surplus economic units) and the investors (savings – deficit economic units). It is made up of all those channels through which savings become available for investment. 3
 Indian Financial System – An Overview • Orderly mechanism & structure in economy. • Mobilises the monetary resources/capital from surplus sectors. • Distributes resources to needy sectors. • Transformation of savings into investment & consumption. • Financial Markets – Places where the above activities take place. 4
Indian Financial System – An Overview • Orderly mechanism & structure in economy. • Mobilises the monetary resources/capital from surplus sectors. • Distributes resources to needy sectors. • Transformation of savings into investment & consumption. • Financial Markets – Places where the above activities take place. 4
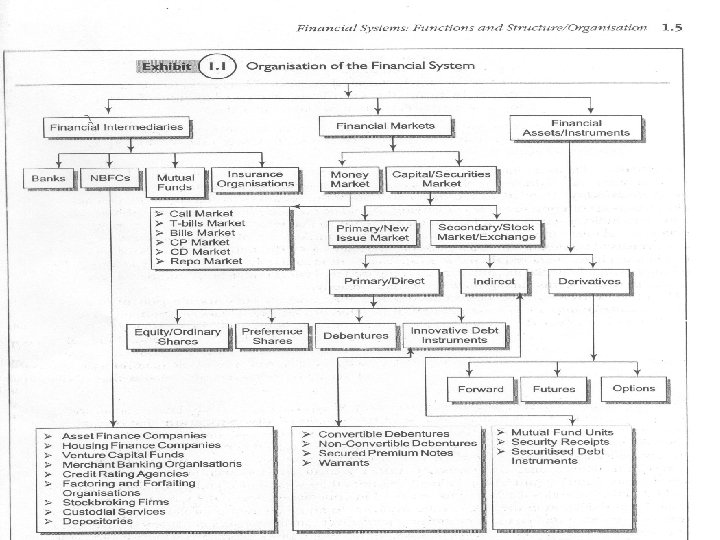
 Indian Financial System – An Overview ORGANISATION Financial System consists of What they do Who They Are Financial Intermediaries (a) Collect Savings (b) Issue claim against themselves (c) Use Funds, thus raised, to purchase ownership or debt-claims Notes: Characteristics of claims issued against self & debt-claims are absolutely different. (ii) Financial Markets (a) Not a Source of funds (b) Act as a facilitating organisation and link saver & investor (c) Based on nature of work they are classified as (1) Money Market (2) Capital/Security Markets. Call Market T-Bill Market CP-Market Report Market Stock Exchange (iii) Financial Asset/Instrument/ Security (a) Financial Product – innovation (b) Three broad categories (1) Direct/Primary e. g. Share, Debt. , Pref. Share etc. (2) Indirect MF, Security Receipts, Securitized Debt Investment. (3) Derivatives Forward, Future, Options. Shares, Debt Instruments Debentures etc. Banks, NBFC, MF insurance organisations etc. 5
Indian Financial System – An Overview ORGANISATION Financial System consists of What they do Who They Are Financial Intermediaries (a) Collect Savings (b) Issue claim against themselves (c) Use Funds, thus raised, to purchase ownership or debt-claims Notes: Characteristics of claims issued against self & debt-claims are absolutely different. (ii) Financial Markets (a) Not a Source of funds (b) Act as a facilitating organisation and link saver & investor (c) Based on nature of work they are classified as (1) Money Market (2) Capital/Security Markets. Call Market T-Bill Market CP-Market Report Market Stock Exchange (iii) Financial Asset/Instrument/ Security (a) Financial Product – innovation (b) Three broad categories (1) Direct/Primary e. g. Share, Debt. , Pref. Share etc. (2) Indirect MF, Security Receipts, Securitized Debt Investment. (3) Derivatives Forward, Future, Options. Shares, Debt Instruments Debentures etc. Banks, NBFC, MF insurance organisations etc. 5
 Indian Financial System – An Overview Pre 1951 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Control of Money Lenders No Laws / Total Private Sector No Regulatory Bodies Hardly any industrialization Banks – Traditional lenders for Trade and that too short term Main concentration on Traditional Agriculture Narrow industrial securities market (i. e. Gold/Bullion/Metal but largely linked to London Market) Absence of intermediatory institutions in long-term financing of industry Industry had limited access to outside saving/resources 6
Indian Financial System – An Overview Pre 1951 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Control of Money Lenders No Laws / Total Private Sector No Regulatory Bodies Hardly any industrialization Banks – Traditional lenders for Trade and that too short term Main concentration on Traditional Agriculture Narrow industrial securities market (i. e. Gold/Bullion/Metal but largely linked to London Market) Absence of intermediatory institutions in long-term financing of industry Industry had limited access to outside saving/resources 6
 Indian Financial System – An Overview 1951 to 1990 7
Indian Financial System – An Overview 1951 to 1990 7
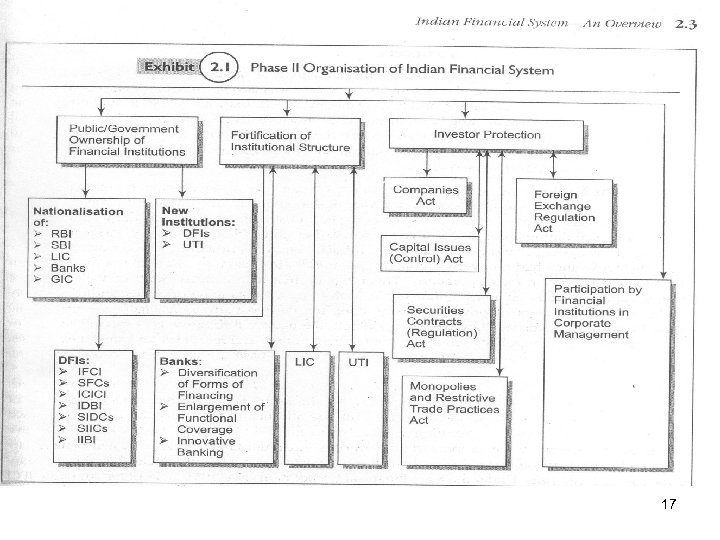
 Indian Financial System – An Overview 1951 -1990 i. Public ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Nationalisation RBI 1948 SBI LIC Banks 1956 (take-over of Imperial Bank of India) 1956 (Merges of over 250 Life Insurance Companies) 1969 (14 major banks with Deposits of over Rs. 50 Crs. nationalised) 1980 (6 more Banks) Insurance 1972 (General Insurance Corp. GIC by New India, Oriental, united and National 8
Indian Financial System – An Overview 1951 -1990 i. Public ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Nationalisation RBI 1948 SBI LIC Banks 1956 (take-over of Imperial Bank of India) 1956 (Merges of over 250 Life Insurance Companies) 1969 (14 major banks with Deposits of over Rs. 50 Crs. nationalised) 1980 (6 more Banks) Insurance 1972 (General Insurance Corp. GIC by New India, Oriental, united and National 8
 Indian Financial System – An Overview 1951 -1990 i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Development • • Directing the Capital in confirmity with Planning priorities Encouragement to new entrepreneurs and small set-ups Development of Backward Region IFCI (1948) (Industrial Finance Corporation of India) State Finance Corporation (1951) Purely Mortgage institution IDBI (1964) As subsidiary of RBI to provide Project / Term Finance ICICI (1966) Channellising of Foreign Currency Loan from World Bank to Pvt. Sector and underwriting of Capital issues. • SIDC’s & State Industrial Investment Corporation (SIIC) State Level Corporations for SME sector • UTI (1964) to enable small investors to share Industrial Growth • Industrial Reconstruction Corporation of India (IRCI) (1971) to take care of rehabilitation of sick-mills promoted by IDBI, Banks & LIC. IRCI name changed to Industrial Investment Bank of India (IIBI) in 1997. 9
Indian Financial System – An Overview 1951 -1990 i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Development • • Directing the Capital in confirmity with Planning priorities Encouragement to new entrepreneurs and small set-ups Development of Backward Region IFCI (1948) (Industrial Finance Corporation of India) State Finance Corporation (1951) Purely Mortgage institution IDBI (1964) As subsidiary of RBI to provide Project / Term Finance ICICI (1966) Channellising of Foreign Currency Loan from World Bank to Pvt. Sector and underwriting of Capital issues. • SIDC’s & State Industrial Investment Corporation (SIIC) State Level Corporations for SME sector • UTI (1964) to enable small investors to share Industrial Growth • Industrial Reconstruction Corporation of India (IRCI) (1971) to take care of rehabilitation of sick-mills promoted by IDBI, Banks & LIC. IRCI name changed to Industrial Investment Bank of India (IIBI) in 1997. 9
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. • NCC (1968) National Credit Council to assess the demand of Credit & determine priorities for grant of Loans, advances, investment & requirements of priority sector (presently 40%) • Credit Guarantee Scheme (1960) for SSI Finance upto 75% of defaulted amount or guarantee amount whichever is lower with ceiling of Rs. 7. 5 Lacs for W/Cap & Rs. 2. 5 Lacs for T/L per borrower. • Agriculture Finance Corp. (AFC) for financing agriculture projects and help Banks. Lead Districts (580) Service Area Approach. Scrapped in 2006. • ARC (1963) Agriculture Refinance Corp. for refinance of medium & long term loans. • Export Credit Guarantee Corporation ECGC (1964) FOR Export Performance 10
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. • NCC (1968) National Credit Council to assess the demand of Credit & determine priorities for grant of Loans, advances, investment & requirements of priority sector (presently 40%) • Credit Guarantee Scheme (1960) for SSI Finance upto 75% of defaulted amount or guarantee amount whichever is lower with ceiling of Rs. 7. 5 Lacs for W/Cap & Rs. 2. 5 Lacs for T/L per borrower. • Agriculture Finance Corp. (AFC) for financing agriculture projects and help Banks. Lead Districts (580) Service Area Approach. Scrapped in 2006. • ARC (1963) Agriculture Refinance Corp. for refinance of medium & long term loans. • Export Credit Guarantee Corporation ECGC (1964) FOR Export Performance 10
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Commercial Banks • • Continued old way of Deposit – Banking & short term credit to trade Selective Credit Control (Control through quantum, rate of interest margin etc). Extensive Branch Expansion. (4000 in 1969 now over 5, 000) Refinance Facility to share risk & also cost of Banks’ funds (Nationalisation. Objectives of Madame Indira Gandhi) Ø Ø Ø Better needs of Economic development Create job opportunities Fulfilment of Plan objectives Servicing maximum population by Branch expansion Setting up Committees. Tandon (1974) to regulate Bank Credit & follow-up Bank Credit to Priority Sector. (substantial increase) 11
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Commercial Banks • • Continued old way of Deposit – Banking & short term credit to trade Selective Credit Control (Control through quantum, rate of interest margin etc). Extensive Branch Expansion. (4000 in 1969 now over 5, 000) Refinance Facility to share risk & also cost of Banks’ funds (Nationalisation. Objectives of Madame Indira Gandhi) Ø Ø Ø Better needs of Economic development Create job opportunities Fulfilment of Plan objectives Servicing maximum population by Branch expansion Setting up Committees. Tandon (1974) to regulate Bank Credit & follow-up Bank Credit to Priority Sector. (substantial increase) 11
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. LIC Mobilised massive long term funds & single largest organisation with large long term savings. Dominant role in underwriting issues and direct push of industrial activities. LIC helped in price stabilization during downswing (e. g. mid 2008 when market faced crisis due to turmoil in global finance market). Premium Amount (Rs. in Crs. ) Rs. 87108 Crs. * Life Insurance Policies Nos. 5. 09 Crs. Nos. of Agents/Selling fore 10, 000+ Rent Income Rs. 7000 Crs. p. a. * The largest Pvt. Sector ICICI prudential is Rs. 6813 Crs. (less than 10%) 12
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. LIC Mobilised massive long term funds & single largest organisation with large long term savings. Dominant role in underwriting issues and direct push of industrial activities. LIC helped in price stabilization during downswing (e. g. mid 2008 when market faced crisis due to turmoil in global finance market). Premium Amount (Rs. in Crs. ) Rs. 87108 Crs. * Life Insurance Policies Nos. 5. 09 Crs. Nos. of Agents/Selling fore 10, 000+ Rent Income Rs. 7000 Crs. p. a. * The largest Pvt. Sector ICICI prudential is Rs. 6813 Crs. (less than 10%) 12
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. PROTECTION TO INVESTORS • • Building up confidence of investors shattered due to distrust in Pvt. Ltd. Redesigning Legal & Administrative set up of Companies. * Ban on Forward Trading * Abolition of Managing Agency System STEPS TAKEN (LEGAL/ADMINISRTATIVE) Companies Act 1956 to regulate Companies, Capital Structure. Capital Issues (Control) Act, 1947 implemented through CCI in MOF to regulate Capital Issues & Foreign Investment (repealled in 1992) Securities Contract (Regulation) Act, 1956 enforced through Directorate of Stock Exchange under MOF to regulate Capital Market. MRTPA (1970) to avoid (a) concentration of economic power and (b) Control monopolistic and restrictive trade practices. FERA (1973) to regulate foreign investment & foreign business. 13
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. PROTECTION TO INVESTORS • • Building up confidence of investors shattered due to distrust in Pvt. Ltd. Redesigning Legal & Administrative set up of Companies. * Ban on Forward Trading * Abolition of Managing Agency System STEPS TAKEN (LEGAL/ADMINISRTATIVE) Companies Act 1956 to regulate Companies, Capital Structure. Capital Issues (Control) Act, 1947 implemented through CCI in MOF to regulate Capital Issues & Foreign Investment (repealled in 1992) Securities Contract (Regulation) Act, 1956 enforced through Directorate of Stock Exchange under MOF to regulate Capital Market. MRTPA (1970) to avoid (a) concentration of economic power and (b) Control monopolistic and restrictive trade practices. FERA (1973) to regulate foreign investment & foreign business. 13
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Participation of Corporate Management • By Financial Institutions (IDBI, IFCI, ICICI, IRBI, SFC, SIIC etc. • By LIC • By GIC • Through conversion of Loans into Equity. (NOMINEE DIRECTORS – enjoy protection) 14
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Participation of Corporate Management • By Financial Institutions (IDBI, IFCI, ICICI, IRBI, SFC, SIIC etc. • By LIC • By GIC • Through conversion of Loans into Equity. (NOMINEE DIRECTORS – enjoy protection) 14
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies (i) Institutional Structure * Banks, LIC, UTI, Collected Savings directly from investors * DFI/PFI like IDBI, IFCI, ICICI, SFCs etc. got funds from sponsers like RBI/GOVT. * Term Finance moved to Big Industries (ii) Distributive Mechanism FIs were incapable of handling growing needs of industries (iii) Form of Financing * Term Loan (Debt) was main part of financial structure with little part of equity Capital * Sometimes Institution became more sympathetic & permitted more than desired finance in case of strain / default. * Position of IFCI, IDBI, ICICI, & most of the SFCs became precarious. 15
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies (i) Institutional Structure * Banks, LIC, UTI, Collected Savings directly from investors * DFI/PFI like IDBI, IFCI, ICICI, SFCs etc. got funds from sponsers like RBI/GOVT. * Term Finance moved to Big Industries (ii) Distributive Mechanism FIs were incapable of handling growing needs of industries (iii) Form of Financing * Term Loan (Debt) was main part of financial structure with little part of equity Capital * Sometimes Institution became more sympathetic & permitted more than desired finance in case of strain / default. * Position of IFCI, IDBI, ICICI, & most of the SFCs became precarious. 15
 Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Small & New Enterprises * System was unable to meet the financial requirements. * Very costly to raise funds from the market. New Issues Marketing / Management Absence of right – type Merchant Banking Institutions. 16
Indian Financial System – An Overview i. Pu blic ownership of Financial Institution ii. Strengthening of Institutional Structure iii. Protection to Investors iv. Participation of Corporate Management v. Organisational Deficiencies. Small & New Enterprises * System was unable to meet the financial requirements. * Very costly to raise funds from the market. New Issues Marketing / Management Absence of right – type Merchant Banking Institutions. 16
 17
17
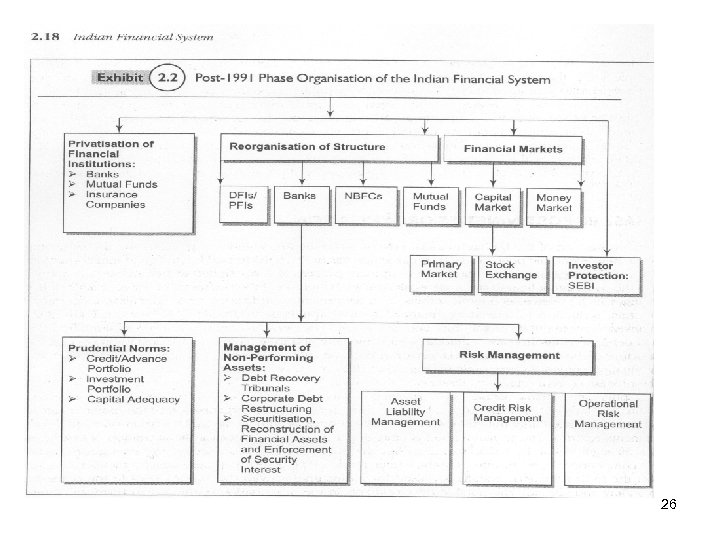
 Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 s IMPORTANT DEVELOPMENTS Development Financial Institutions : (DFIs) • Started providing Working Capital also • Set up CREDIT RATING AGENCIES CRISIL(IPO IN 1993 -94; standard & poor acquires 9. 68% in 1996 -97 S & P acquires shares / holding upto 58. 46%) ICRA Set up in 1991 by leading FIs/Banks/Fin. Ser. Cos. And Moody’s CARE Set-up by IFCI/Banks. FITCH a 100% subsidiary of FITCH Group. • • Privatisation of DFI Reduction in Govt. holding & Public Participation e. g. IFCI Ltd. , IDBI Ltd. , ICICI Ltd. Conversion into Banking / Merger into Banking Companies IDBI Bank & ICICI Bank Issuance of Bond by DFIs without Govt. ’s Guarantees to mobilise resources. • Reduction in holding of Govt. in Banks, i. e. Public Participation / Listing • 18
Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 s IMPORTANT DEVELOPMENTS Development Financial Institutions : (DFIs) • Started providing Working Capital also • Set up CREDIT RATING AGENCIES CRISIL(IPO IN 1993 -94; standard & poor acquires 9. 68% in 1996 -97 S & P acquires shares / holding upto 58. 46%) ICRA Set up in 1991 by leading FIs/Banks/Fin. Ser. Cos. And Moody’s CARE Set-up by IFCI/Banks. FITCH a 100% subsidiary of FITCH Group. • • Privatisation of DFI Reduction in Govt. holding & Public Participation e. g. IFCI Ltd. , IDBI Ltd. , ICICI Ltd. Conversion into Banking / Merger into Banking Companies IDBI Bank & ICICI Bank Issuance of Bond by DFIs without Govt. ’s Guarantees to mobilise resources. • Reduction in holding of Govt. in Banks, i. e. Public Participation / Listing • 18
 Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 INDUSTRIES • • Rise & Growth of Service Sector industries. Reliance & Dependance on technology. E-mail & mobile made sea-change in communication, data collection etc. Computerisation – a catch phrase and inevitable need of an hour. Dependent on Capital Market rather than only Debts dependancy. Scalability of operations through globally competitive size. Broad basing of Board. Professional Management. NBFC • • NBFC under RBI governance to finance retail assets and mobilise small/medium sized savings. Very large NBFCs are emerging (Shri Ram Transport Finance, Birla, Tata Finance, Sundaram Finance, Reliance Finance, DLF, Religare etc. 19
Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 INDUSTRIES • • Rise & Growth of Service Sector industries. Reliance & Dependance on technology. E-mail & mobile made sea-change in communication, data collection etc. Computerisation – a catch phrase and inevitable need of an hour. Dependent on Capital Market rather than only Debts dependancy. Scalability of operations through globally competitive size. Broad basing of Board. Professional Management. NBFC • • NBFC under RBI governance to finance retail assets and mobilise small/medium sized savings. Very large NBFCs are emerging (Shri Ram Transport Finance, Birla, Tata Finance, Sundaram Finance, Reliance Finance, DLF, Religare etc. 19
 Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 Commercial Bank • • • Govt. holding reduced even by upto 40% Setting up of Universal Banks (from CASA to Corp. Finance) One-stop Banking. Capital Adequacy. (Basel II accepted) 9% Assets classification (Regular, Problem, Anxiety, Causing, Non-Performing) and Provisioning norms identified/reviewed & revised. NPA classification – substandard, Doubtful & Loss Assets. Focus on Non-Fund Business like L/C, Guarantees, Acceptance, FOREX etc. Promoting Signature-based and consultancy services like Project Counselling, Merchant Banking, New Issues Management, Capital Market related activities, Merger & Acquisitions, debt syndication, trusteeship of debts, sponsoring Mutual Funds, Wealth Management, Sales & Services of insurance (both life & non-life) products etc. New Private Sector Banks (AXIS, YES, HDFC, KOTAK MAHINDRA etc. ) CAMELS’ Rating (C-Capital Adequacy, A-Asset Quality, M-Management, EEarning, L-Liquidity, & S-Systems & controls). 20
Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 Commercial Bank • • • Govt. holding reduced even by upto 40% Setting up of Universal Banks (from CASA to Corp. Finance) One-stop Banking. Capital Adequacy. (Basel II accepted) 9% Assets classification (Regular, Problem, Anxiety, Causing, Non-Performing) and Provisioning norms identified/reviewed & revised. NPA classification – substandard, Doubtful & Loss Assets. Focus on Non-Fund Business like L/C, Guarantees, Acceptance, FOREX etc. Promoting Signature-based and consultancy services like Project Counselling, Merchant Banking, New Issues Management, Capital Market related activities, Merger & Acquisitions, debt syndication, trusteeship of debts, sponsoring Mutual Funds, Wealth Management, Sales & Services of insurance (both life & non-life) products etc. New Private Sector Banks (AXIS, YES, HDFC, KOTAK MAHINDRA etc. ) CAMELS’ Rating (C-Capital Adequacy, A-Asset Quality, M-Management, EEarning, L-Liquidity, & S-Systems & controls). 20
 Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 Mutual Funds § • • • Bifurcation of UTI and UTI (AMC) put under SEBI. Banks, Broking Houses, Finance Companies Insurance Companies, Pvt. Sector in Foreign collaboration, FII and Merchant Banks set up Mutual Funds with a varieties of schemes. Helps small investors in big way Backbone of Capital Markets Mutual Funds, AIG, Baroda Pioneer, Birla Sunlife, Canara Robeco, DBS Chola, Edelweiss, Fidelity, Fortis, Franklin, HSBC, HDFC, ICICI Prudential, IDFC, ING, JM, Kotak, LIC, Magnum, Mirae, Morgan, Quantum, Reliance, Religare, Sahara, Sundaram BNP, Tata Tourus, UTI etc. Mutual Funds Investment Schemes (over 1000 in Nos. ) Equity Diversified Equity Index Equity Tax Planning Equity Banking Equity FMCG Equity Pharma Equity Technology Equity Speciality Cash Funds Balanced Funds Hybrid – Equity Oriented Hybrid – Debt Oriented Hybrid – Asset Allocation Hybrid Arbitrage Bond Funds Debt Medium Term/Short Term Institutional Hybrid Monthly Income Gilt Medium & Long Term Debt Liquid Plus 21
Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 Mutual Funds § • • • Bifurcation of UTI and UTI (AMC) put under SEBI. Banks, Broking Houses, Finance Companies Insurance Companies, Pvt. Sector in Foreign collaboration, FII and Merchant Banks set up Mutual Funds with a varieties of schemes. Helps small investors in big way Backbone of Capital Markets Mutual Funds, AIG, Baroda Pioneer, Birla Sunlife, Canara Robeco, DBS Chola, Edelweiss, Fidelity, Fortis, Franklin, HSBC, HDFC, ICICI Prudential, IDFC, ING, JM, Kotak, LIC, Magnum, Mirae, Morgan, Quantum, Reliance, Religare, Sahara, Sundaram BNP, Tata Tourus, UTI etc. Mutual Funds Investment Schemes (over 1000 in Nos. ) Equity Diversified Equity Index Equity Tax Planning Equity Banking Equity FMCG Equity Pharma Equity Technology Equity Speciality Cash Funds Balanced Funds Hybrid – Equity Oriented Hybrid – Debt Oriented Hybrid – Asset Allocation Hybrid Arbitrage Bond Funds Debt Medium Term/Short Term Institutional Hybrid Monthly Income Gilt Medium & Long Term Debt Liquid Plus 21
 Indian Financial System – An Overview Securities/Capital Market Primary Market - Phenominal increase in number of investors. - New intermediatories i. e. Merchant Bankers, Lead Manager & Book-Builders, Underwriters, Bankers to Issue, Registrar to Issue, Share Transfer Agents, Portfolio Managers, Depositories, FIIs, Custodians, Rating Agencies, etc. are playing important role. - FIIs are allowed to invest & participate in public issues of Debt & Equities within sectoral limits fixed by the Govt. 22
Indian Financial System – An Overview Securities/Capital Market Primary Market - Phenominal increase in number of investors. - New intermediatories i. e. Merchant Bankers, Lead Manager & Book-Builders, Underwriters, Bankers to Issue, Registrar to Issue, Share Transfer Agents, Portfolio Managers, Depositories, FIIs, Custodians, Rating Agencies, etc. are playing important role. - FIIs are allowed to invest & participate in public issues of Debt & Equities within sectoral limits fixed by the Govt. 22
 Indian Financial System – An Overview Secondary Market - Over 90% Securities Dematerialised. - Depository Act 1996; 2 Depositories NSDC & CDSL. - Settlement Cycle reduced from 15 days to T + 2. - Clearing & Settlement by Clearing Corp. - Securities related derivatives introduced. - Future, Option, Arbitrage, Hedging permitted. 23
Indian Financial System – An Overview Secondary Market - Over 90% Securities Dematerialised. - Depository Act 1996; 2 Depositories NSDC & CDSL. - Settlement Cycle reduced from 15 days to T + 2. - Clearing & Settlement by Clearing Corp. - Securities related derivatives introduced. - Future, Option, Arbitrage, Hedging permitted. 23
 Indian Financial System – An Overview Money Market - Primary Dealers Money Market Mutual Funds came up Call/Notice Market Treasury Bills Market Commercial Paper Market (CP) Certificate of Deposit Market (CD) Repo Market FOREX Market 24
Indian Financial System – An Overview Money Market - Primary Dealers Money Market Mutual Funds came up Call/Notice Market Treasury Bills Market Commercial Paper Market (CP) Certificate of Deposit Market (CD) Repo Market FOREX Market 24
 Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 Organisational Structure • • • Boards of PSU Banks reorganised. Regulation / guidelines for Statutory Auditors. Most of the Banks entrusted Business Plan / Restructure of Organisations to Globally acclaimed Consultants like KPMG, PWC, E & Y etc. CAPITAL MARKET • • NSE set up as FIRST automated Exchange. (turnover now is Rs. 65000 Crs. p. d. ) Total 2500 + V-SATs in 191 cities; 1242 Members (1096 Corporates) Depositories Promoters’ Participants Centers No. of Clients NSDL IDBI, UTI, NSE, SBI etc. 282 1015 1 Cr. CDSL BSE, HDFC, SBI, BOB etc. 483 6469 60. 37 Lacs • Custodian * Stock Holding Corp. of India. • • OTC Regional Stock Exchanges 25
Indian Financial System – An Overview POST 1990 Organisational Structure • • • Boards of PSU Banks reorganised. Regulation / guidelines for Statutory Auditors. Most of the Banks entrusted Business Plan / Restructure of Organisations to Globally acclaimed Consultants like KPMG, PWC, E & Y etc. CAPITAL MARKET • • NSE set up as FIRST automated Exchange. (turnover now is Rs. 65000 Crs. p. d. ) Total 2500 + V-SATs in 191 cities; 1242 Members (1096 Corporates) Depositories Promoters’ Participants Centers No. of Clients NSDL IDBI, UTI, NSE, SBI etc. 282 1015 1 Cr. CDSL BSE, HDFC, SBI, BOB etc. 483 6469 60. 37 Lacs • Custodian * Stock Holding Corp. of India. • • OTC Regional Stock Exchanges 25
 26
26
 27
27
 Indian Financial System – An Overview GLOBAL FINANCIAL SYSTEMS IBRD (World Bank) Long-Term Capital Assistance IFCI To finance PRIVATE enterprises in the form of loans & equity IDA Affiliate of World Bank Soft – Loan window of the Bank. Mainly for developing & under-developed nations. Re-payment period upto 50 years Govt. & Private, both, eligible. MIGA (1988) Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency – an affiliate of World Bank Provides guarantee for investment in needy countries. ABD (1966) Under the aegis of ECAFE (Economic Commission for Asia & Far East) promote investment in Asia & Far East and also finance priority area. Also co-ordinates with U. N. agencies. 28
Indian Financial System – An Overview GLOBAL FINANCIAL SYSTEMS IBRD (World Bank) Long-Term Capital Assistance IFCI To finance PRIVATE enterprises in the form of loans & equity IDA Affiliate of World Bank Soft – Loan window of the Bank. Mainly for developing & under-developed nations. Re-payment period upto 50 years Govt. & Private, both, eligible. MIGA (1988) Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency – an affiliate of World Bank Provides guarantee for investment in needy countries. ABD (1966) Under the aegis of ECAFE (Economic Commission for Asia & Far East) promote investment in Asia & Far East and also finance priority area. Also co-ordinates with U. N. agencies. 28
 Indian Financial System – An Overview GLOBAL FINANCIAL SYSTEMS International Financial Markets MONEY STOCK BOND LOAN Main Players Commercial Banks Corporations Non Bank Financial Institutions. Central Bank and other Govt. Agencies. Venture Funds/PE Funds Hedge Funds University Funds Trusts & Foundations and charitable Societies Endowments. HNI. 29
Indian Financial System – An Overview GLOBAL FINANCIAL SYSTEMS International Financial Markets MONEY STOCK BOND LOAN Main Players Commercial Banks Corporations Non Bank Financial Institutions. Central Bank and other Govt. Agencies. Venture Funds/PE Funds Hedge Funds University Funds Trusts & Foundations and charitable Societies Endowments. HNI. 29
 Global Financial System – An Overview Functions of Financial Market • • • Price Discovery Liquidity Cost of Transactions (saver search & information costs) Transfer of savings from one sector to other Reflects as Barometer for economic growth Financial Assets • • Treasury Bonds Debt Bonus Equity (with/without Voting Rights) Commercial Paper/Debentures etc. Euro & Petro Bonds. Gold/Silver Deep Discount Bond/Coss Border Bonds /instruments. 30
Global Financial System – An Overview Functions of Financial Market • • • Price Discovery Liquidity Cost of Transactions (saver search & information costs) Transfer of savings from one sector to other Reflects as Barometer for economic growth Financial Assets • • Treasury Bonds Debt Bonus Equity (with/without Voting Rights) Commercial Paper/Debentures etc. Euro & Petro Bonds. Gold/Silver Deep Discount Bond/Coss Border Bonds /instruments. 30
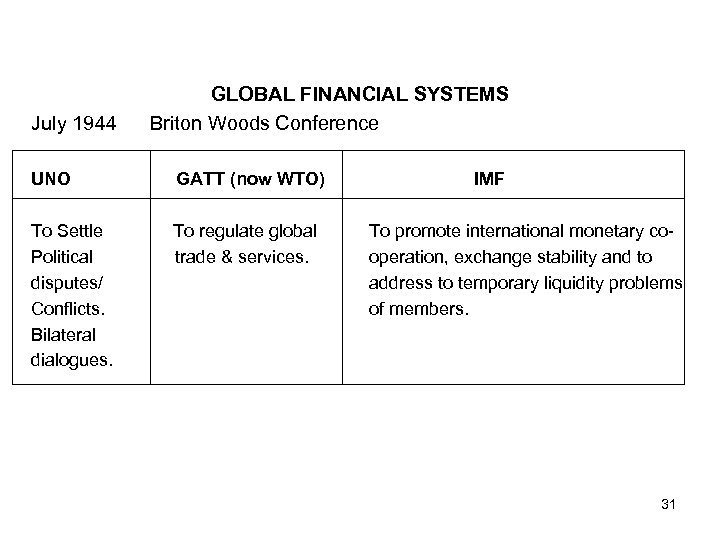 July 1944 GLOBAL FINANCIAL SYSTEMS Briton Woods Conference UNO GATT (now WTO) To Settle Political disputes/ Conflicts. Bilateral dialogues. To regulate global trade & services. IMF To promote international monetary cooperation, exchange stability and to address to temporary liquidity problems of members. 31
July 1944 GLOBAL FINANCIAL SYSTEMS Briton Woods Conference UNO GATT (now WTO) To Settle Political disputes/ Conflicts. Bilateral dialogues. To regulate global trade & services. IMF To promote international monetary cooperation, exchange stability and to address to temporary liquidity problems of members. 31
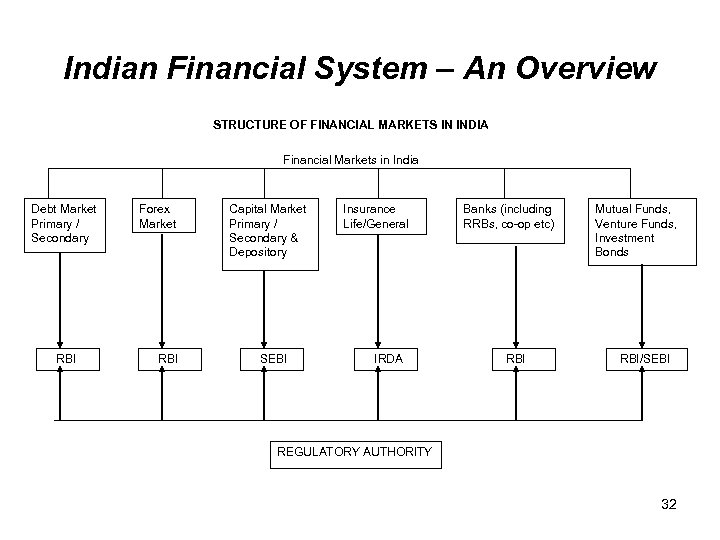 Indian Financial System – An Overview STRUCTURE OF FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA Financial Markets in India Debt Market Primary / Secondary RBI Forex Market RBI Capital Market Primary / Secondary & Depository SEBI Insurance Life/General IRDA Banks (including RRBs, co-op etc) RBI Mutual Funds, Venture Funds, Investment Bonds RBI/SEBI REGULATORY AUTHORITY 32
Indian Financial System – An Overview STRUCTURE OF FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA Financial Markets in India Debt Market Primary / Secondary RBI Forex Market RBI Capital Market Primary / Secondary & Depository SEBI Insurance Life/General IRDA Banks (including RRBs, co-op etc) RBI Mutual Funds, Venture Funds, Investment Bonds RBI/SEBI REGULATORY AUTHORITY 32


