9b420b551f14dfc3a9d51b4dae0ea65c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
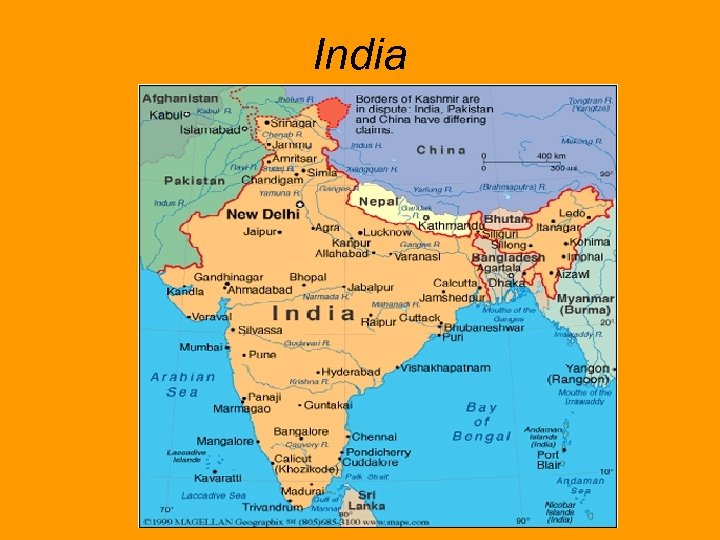
India

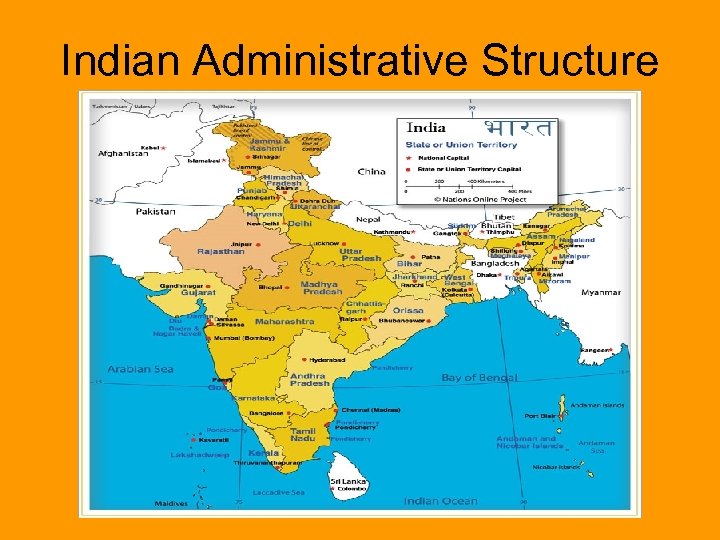
Indian Administrative Structure

Basics • Over 1 Billion people • Opening to the world economically since 1991 • Importance of the US-Indian-Chinese relationship in the future

Paradoxes 1. Democracy and Inequality 2. Religion and Separation of Church and State 3. Indian Economic Model 4. Wealth and Poverty 5. Diversity 6. National vs Regional

Paradox One: Democracy and Inequality • Largest democracy in the World • But… – Economic inequality – Social inequality (due to lingering Hindu caste system)

Paradox Two: Religion and Separation of Church and State • Religion: 80% Hindu • But… a national ideology of separation of church and state… • But the Bharatiya Janata and “Hindu nationalism” or Hindutva

Prime Minister 2004 -2014 • Manmohan Singh • The first Sikh PM • From Congress Party

Leader of Congress Party • Sonja Gandhi • Roman Catholic • Born in Italy

Three Presidents of India First “Untouchable” Pres. First Muslim Pres. First Woman Pres. 2007 -2012

Paradox Three: Indian Economic Model • East Asian Model: Authoritarian and capitalist • India: Democratic with a socialist economy (until 1991 when economic reforms began)

Paradox Four: Wealth and Poverty Bangalore India’s Silicon Valley Slums of any city

Paradox Five: Diversity • 80% Hindu, but… • 22 Official languages now • Over 140 million Muslims (the nation in the world with the third largest Muslim population)

Paradox Six: National vs. Regional • Two major national parties: – Congress Party – BJP – Also, minor party: Communist Party Marxist • 2009: 35 regional parties in Parliament • Lok Sabha Party-wise

Political Culture 1. 2. 3. 4. Geography Agrarian economy Population Religion 1. 2. 3. 4. Hindu: 81% Muslim: 13% Christian 2. 3% Sikh: 1. 9%

Hindu Caste System 1. Priests – Brahmins 2. Warriors – Kahtriyas 3. Landowners/merchants – Vaishyas 4. Small Farmers – Sudras Outcastes, sub-castes, backward tribes, and “Untouchables” or Dalits or Harijans Bhimrao Ambedkar
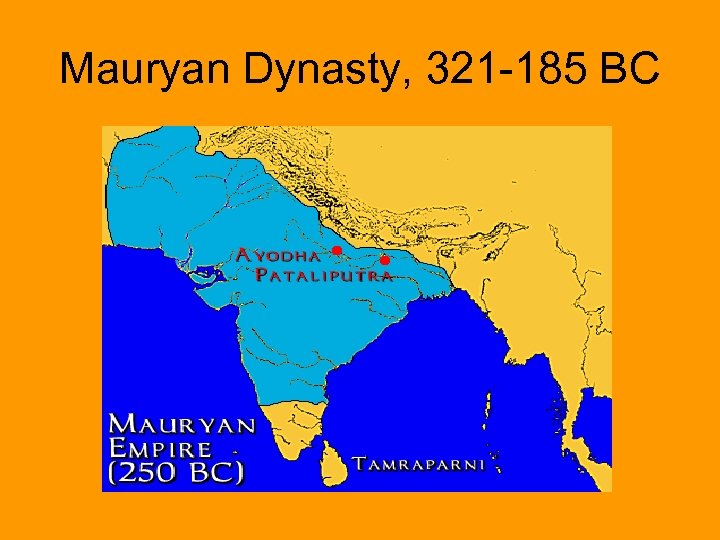
Mauryan Dynasty, 321 -185 BC
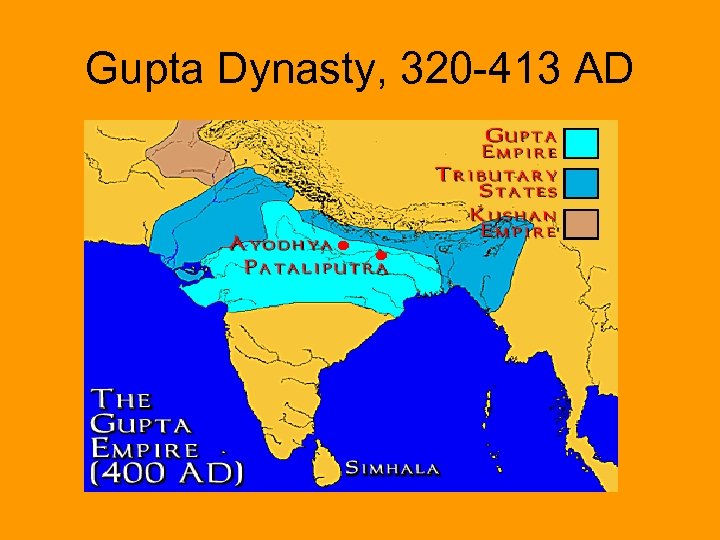
Gupta Dynasty, 320 -413 AD
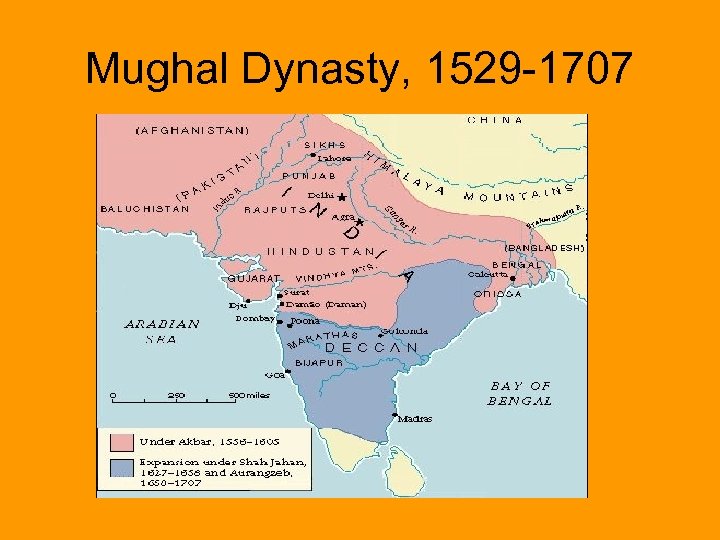
Mughal Dynasty, 1529 -1707
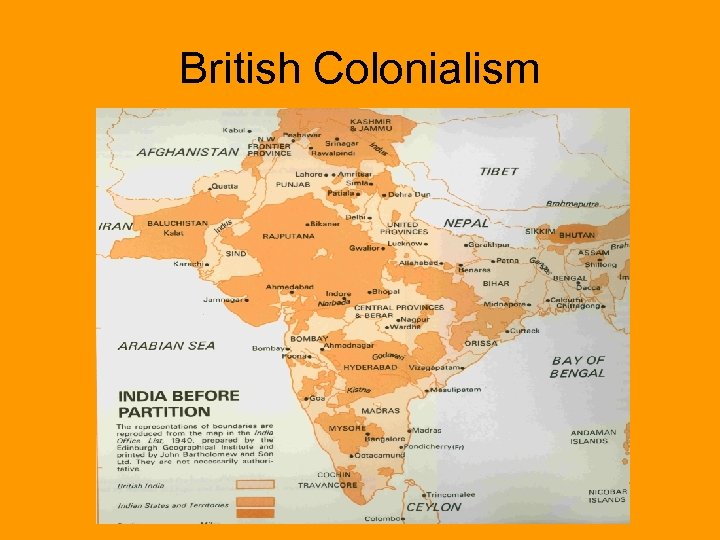
British Colonialism

Amritsar Massacre, April 1919 Eduard Thony painting

Indian National Congress Jawaharlal Nehru and Mohandas Gandhi

Gandhi’s Impact on the INC • Extremists vs. moderates • Ending factional struggle • Mass movement • Non-violence – Gandhi’s writings • Independence Now

Muslim League Mohammed Ali Jinnah
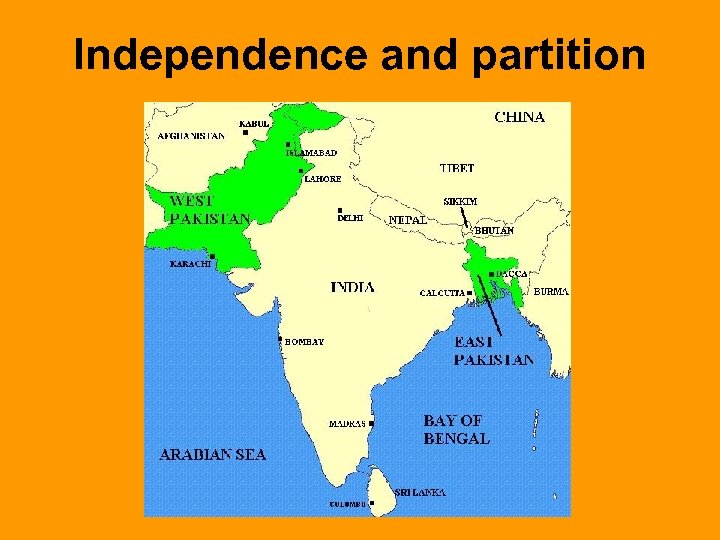
Independence and partition
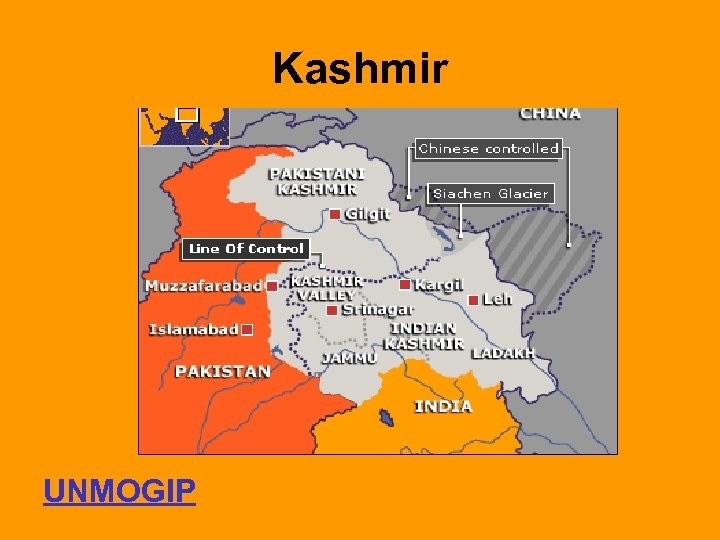
Kashmir UNMOGIP

Government Structure • Indian Constitution • President • Parliament – Rajya Sabha – Lok Sabha • Prime Minister
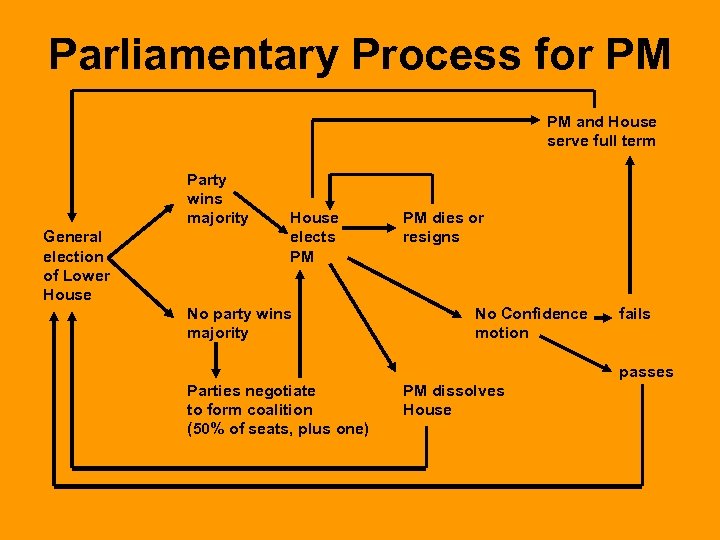
Parliamentary Process for PM PM and House serve full term Party wins majority General election of Lower House elects PM No party wins majority PM dies or resigns No Confidence motion fails passes Parties negotiate to form coalition (50% of seats, plus one) PM dissolves House
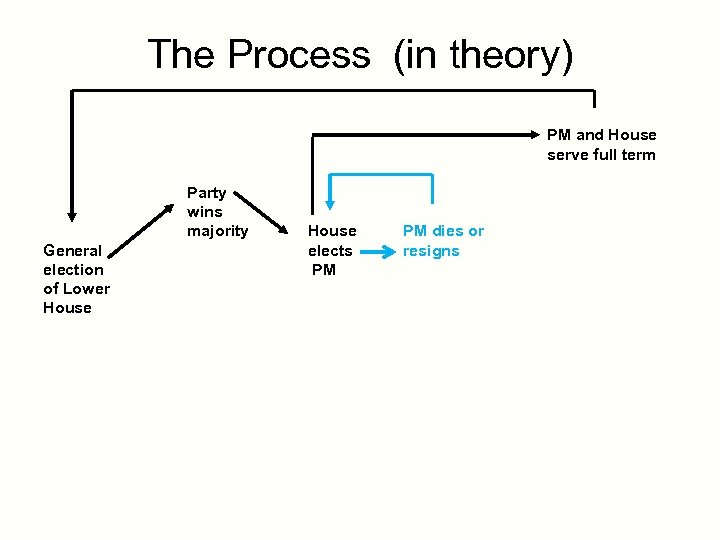
The Process (in theory) PM and House serve full term Party wins majority General election of Lower House elects PM PM dies or resigns
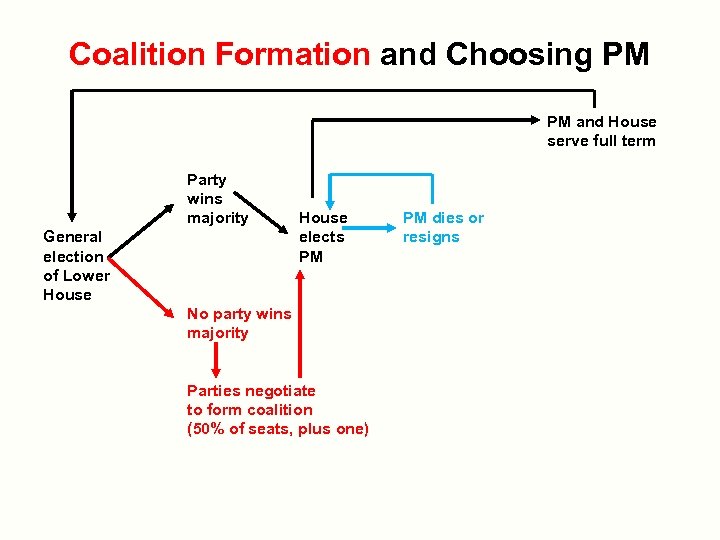
Coalition Formation and Choosing PM PM and House serve full term Party wins majority General election of Lower House elects PM No party wins majority Parties negotiate to form coalition (50% of seats, plus one) PM dies or resigns
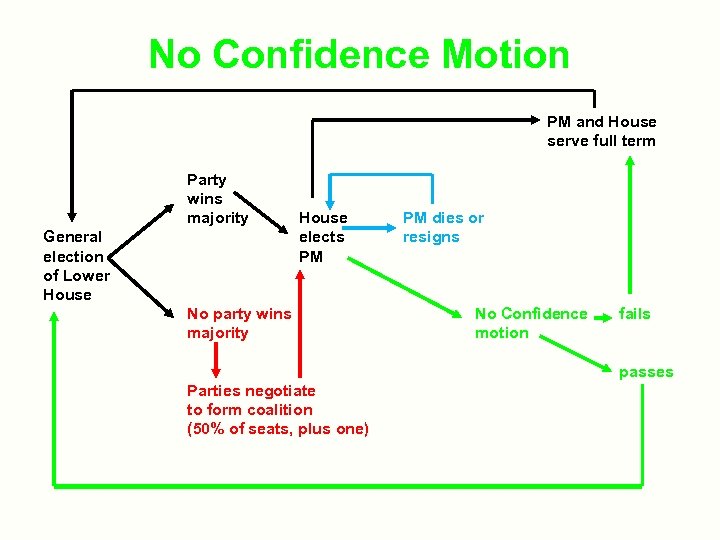
No Confidence Motion PM and House serve full term Party wins majority General election of Lower House elects PM No party wins majority PM dies or resigns No Confidence motion fails passes Parties negotiate to form coalition (50% of seats, plus one)
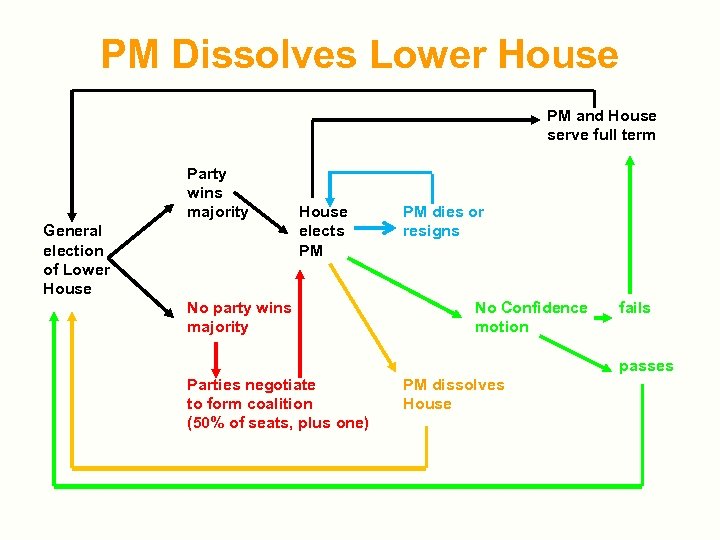
PM Dissolves Lower House PM and House serve full term Party wins majority General election of Lower House elects PM No party wins majority PM dies or resigns No Confidence motion fails passes Parties negotiate to form coalition (50% of seats, plus one) PM dissolves House

1996 Election • Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) • Congress Party • National Front 160 136 110 • National Front forms government

Nehru Dynasty Jawaharlal Nehru 1947 -1964 Indira Gandhi 1966 -1977 1980 -1984 Rajiv Gandhi 1984 -1989

Congress Party INC

Congress’ Ideology • Secularism • Socialist economics 1947 -1991 • Economic Reform 1991 -present
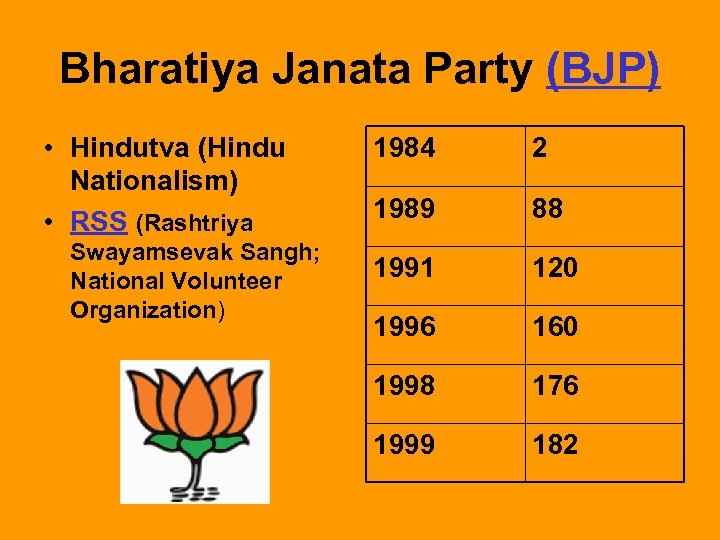
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) • Hindutva (Hindu Nationalism) • RSS (Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh; National Volunteer Organization) 1984 2 1989 88 1991 120 1996 160 1998 176 1999 182

Others • Leftist parties – AITC (All India Trinamool Congress (West Bengal, Manipur, Tripura and Arunachal Pradesh) – Communist Party of India (Marxist) • Regional parties – AIADMK (All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhigam) Tamil Nadu state – Telugu Desam Party (Andrha Pradesh) – Samajwadi Party (Uttar Pradesh) • Caste-based Parties – Bahujan Samaj Party
9b420b551f14dfc3a9d51b4dae0ea65c.ppt