8d290fca20cd06c6daab89c259c6414e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
Independent and Dependent Variables Continuous and Discrete Data Correlation
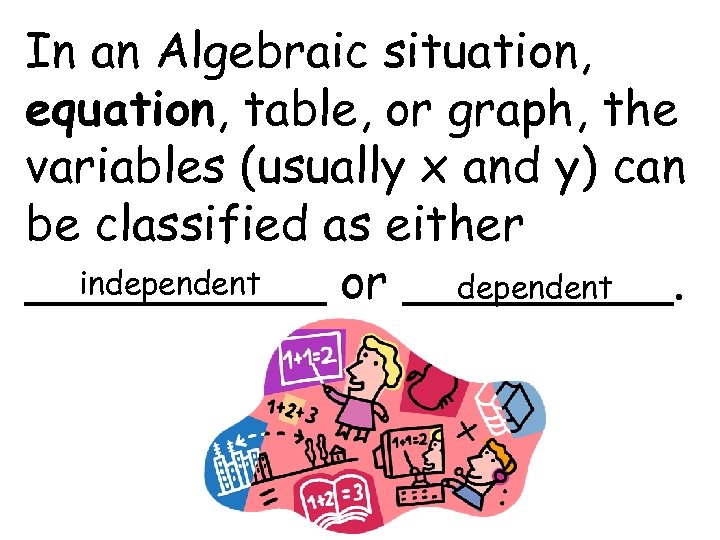
In an Algebraic situation, equation, table, or graph, the variables (usually x and y) can be classified as either independent _____ or _____. dependent
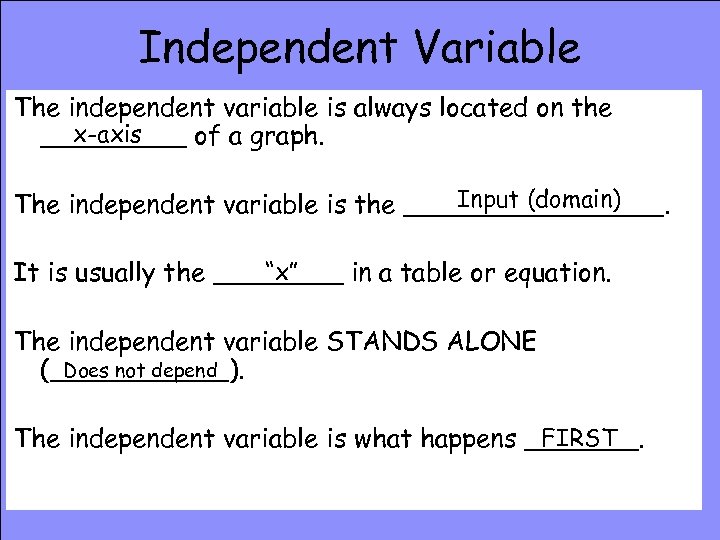
Independent Variable The independent variable is always located on the x-axis _____ of a graph. Input (domain) The independent variable is the ________. “x” It is usually the ____ in a table or equation. The independent variable STANDS ALONE Does not depend (______). FIRST The independent variable is what happens _______.

The variable in a function whose value you get to choose is the independent variable. The independent variable affects the value of the dependent variable.
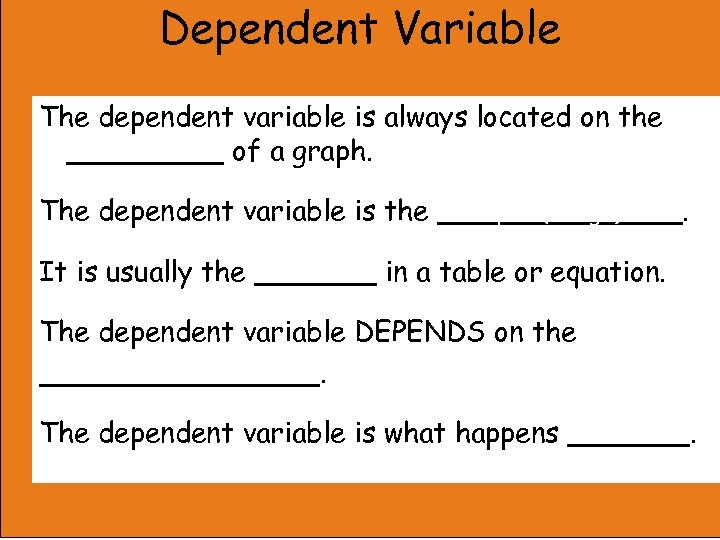
Dependent Variable The dependent variable is always located on the y-axis _____ of a graph. Output (Range) The dependent variable is the _______. “y” It is usually the _______ in a table or equation. The dependent variable DEPENDS on the independent variable ________. 2 nd The dependent variable is what happens _______.

The variable in a function whose value is determined by the independent variable.

Let’s Practice! 1. A student’s grade depends on how much she studies. Time studying Independent variable: _____ grade Dependent variable: ______ 2. The height of a plant and the amount you water it. Amount watered Independent variable: ______ height Dependent variable: _______

3. The amount of money you make and the number of hours you work. Hours worked Independent variable: _______ Amount of money Dependent variable: _______ 4. The number of sodas you buy and the total money spent. Number of sodas Independent variable: _______ Total money Dependent variable: ________ 5. The number of houses you can paint depends on how much time you have. Amount of time Independent variable: _______ Number of houses Dependent variable: ________
Continuous Data continuously Data that is continuous is data that _____ happens. You can usually tell that your data is measuring continuous if you are _____ something (i. e. time, distance, length, height, etc. ). If your connect data is continuous, then you will _____ the points on your graph.
Discrete Data You can tell that your data is discrete if counting or measuring in whole numbers you are ____________ (i. e. number of people, cars, or stories of a building). If your data is discrete, then NOT connect you will _______ the points on your graph.

• Graphs of each situation

Let’s Practice Look at the situations given in examples 1 -5. Decide if the situation would best be classified as either discrete or continuous data. 1. A student’s grade depends on how much she studies. continuous 2. The height of a plant and the amount you water it. continuous 3. The amount of money you make and the number of hours you work. discrete 4. The number of sodas you buy and the total money spent. discrete 5. The number of houses you can paint depends on how much time you have. continuous
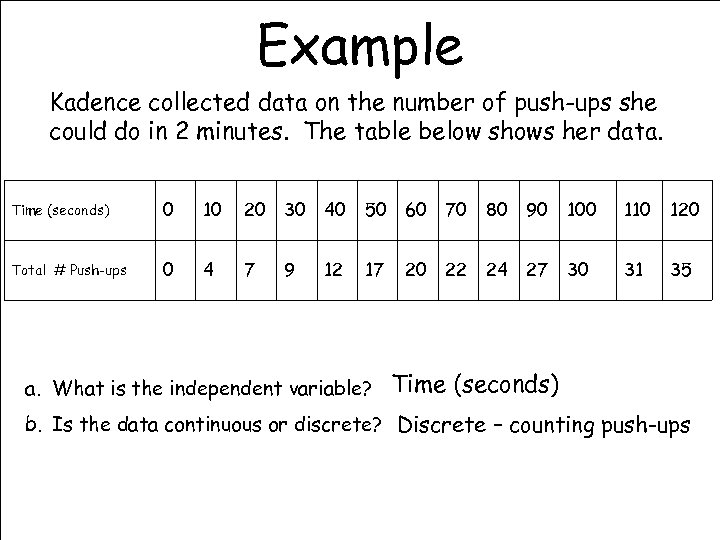
Example Kadence collected data on the number of push-ups she could do in 2 minutes. The table below shows her data. Time (seconds) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Total # Push-ups 0 4 7 9 12 17 20 22 24 27 30 31 35 a. What is the independent variable? Time (seconds) b. Is the data continuous or discrete? Discrete – counting push-ups

Correlation • It is the relationship that exists between two variables (Independent and dependent).
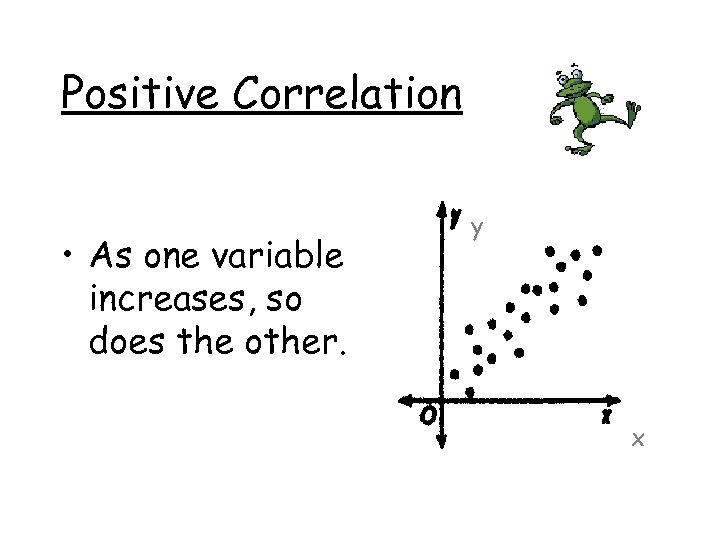
Positive Correlation • As one variable increases, so does the other. y x

Example of positive correlation… The longer you exercise, the more calories you burn. *As exercise increases, calories burned increases Can you think of one?
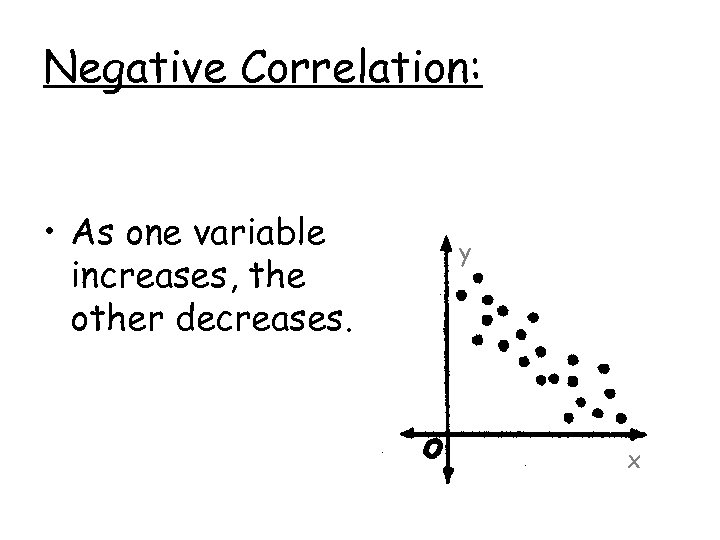
Negative Correlation: • As one variable increases, the other decreases. y x

Example of negative correlation… The longer the air conditioner is turned on, the colder the temperature. *As time increases, the temperature decreases Can you think of one?
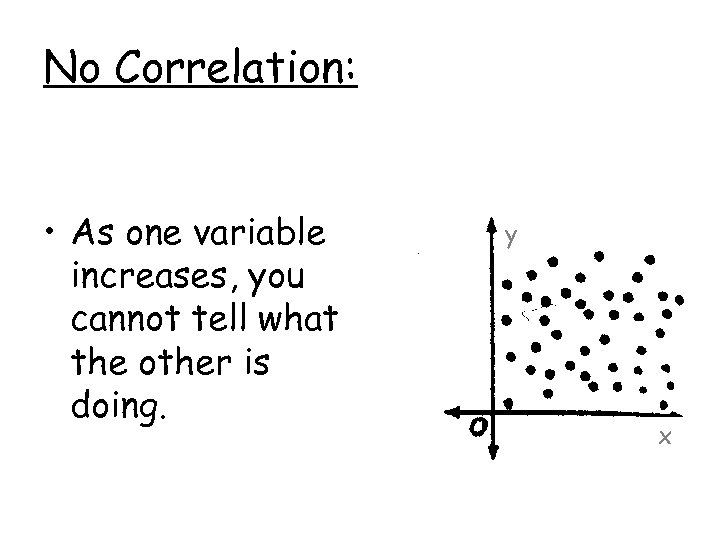
No Correlation: • As one variable increases, you cannot tell what the other is doing. y x

Example of no correlation… The number of students in the classroom and the average height. *As the number of students increases, you cannot tell what the average height will do. Can you think of one?

Everything… The amount of time you spend in an airplane and the distance between your departure and your destination. 1. What are the independent and dependent variables? Independent: Distance Dependent: Time 2. Would this situation represent a discrete or continuous situation? Continuous 3. What type of correlation is represented in this situation? Negative correlation

Everything again… The number of times you dip a wick into hot wax and the diameter of a handmade candle 1. What are the independent and dependent variables? Independent: The number of dips Dependent: diameter of candle 2. Would this situation represent a discrete or continuous situation? Discrete 3. What type of correlation is represented in this situation? Positive correlation
8d290fca20cd06c6daab89c259c6414e.ppt