e2a53e79b35ff0941913e82bde16c2aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Independence & Nationalist Movements Southeast Asia Middle East Latin America
Independence & Nationalist Movements Southeast Asia Middle East Latin America
 Vietnam (Review) • Ho Chi Minh an educated, enlightened political leader that sought independence like Kwame Nkrumah and Gandhi • Used guerilla warfare and the military to gain independence like Simon Bolivar of Latin America • Fought Japanese, then French, then American forces • Independence complete by 1975
Vietnam (Review) • Ho Chi Minh an educated, enlightened political leader that sought independence like Kwame Nkrumah and Gandhi • Used guerilla warfare and the military to gain independence like Simon Bolivar of Latin America • Fought Japanese, then French, then American forces • Independence complete by 1975
 Vietminh Soldiers
Vietminh Soldiers
 Vietnamese POV • “People didn’t talk about the meaning of the war, ” he said. “We were really confused why the Americans tried to invade our homeland. We hadn’t done anything to them. ” • I asked Vu if the Vietnamese had understood that the United States perceived communism as a threat. • “People didn’t even know what communism was, ” Vu told me. “They just knew what was going on with their lives. ”
Vietnamese POV • “People didn’t talk about the meaning of the war, ” he said. “We were really confused why the Americans tried to invade our homeland. We hadn’t done anything to them. ” • I asked Vu if the Vietnamese had understood that the United States perceived communism as a threat. • “People didn’t even know what communism was, ” Vu told me. “They just knew what was going on with their lives. ”
 American POV • “The U. S. tried to inscribe the war in Vietnam into its Cold War campaign, ” Thomas Bass, a historian and journalism professor at University at Albany, State University of New York, told me. “North Vietnamese were evil communists, and the free and independent people of the South were to be protected. ” • “The country has been unified for 40 years, but the nation is yet to be reconciled, ” said Son Tran.
American POV • “The U. S. tried to inscribe the war in Vietnam into its Cold War campaign, ” Thomas Bass, a historian and journalism professor at University at Albany, State University of New York, told me. “North Vietnamese were evil communists, and the free and independent people of the South were to be protected. ” • “The country has been unified for 40 years, but the nation is yet to be reconciled, ” said Son Tran.
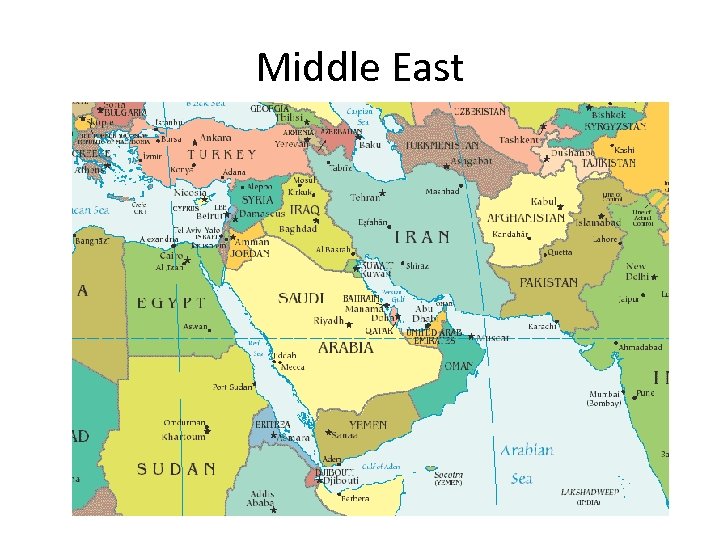 Middle East
Middle East
 Review: Ottoman Empire and Mandate System Ottoman Empire falls after WWI Turkey became a modern nation led by Mustafa Kemal Ataturk The Mandate system divided the Ottoman Empire’s Middle Eastern lands between the western powers, planting the seeds for future conflict in the region. ◦ France: Syria, Lebanon ◦ Britain: Palestine, Jordan, Iraq
Review: Ottoman Empire and Mandate System Ottoman Empire falls after WWI Turkey became a modern nation led by Mustafa Kemal Ataturk The Mandate system divided the Ottoman Empire’s Middle Eastern lands between the western powers, planting the seeds for future conflict in the region. ◦ France: Syria, Lebanon ◦ Britain: Palestine, Jordan, Iraq

 Egypt • Gained independence in 1922 but established a republic in the 1950’s • Gamal Abdul Nasser ◦ President 1956 to death in 1970 ◦ Promoted Pan-Arab nationalism ◦ Nationalized Suez Canal and led antiimperialist efforts in Africa and Middle East ◦ Established relationship with Soviet Union ◦ Built Aswan High Dam ◦ https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l 7 8 ki. UQ-I 5 Y
Egypt • Gained independence in 1922 but established a republic in the 1950’s • Gamal Abdul Nasser ◦ President 1956 to death in 1970 ◦ Promoted Pan-Arab nationalism ◦ Nationalized Suez Canal and led antiimperialist efforts in Africa and Middle East ◦ Established relationship with Soviet Union ◦ Built Aswan High Dam ◦ https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l 7 8 ki. UQ-I 5 Y
 Aswan High Dam
Aswan High Dam
 Israel Zionism – Jewish nationalism, with emphasis on need for state in Holy Land Israel= ancient Jewish homeland After Diaspora, many Jews Diaspora faced persecution (Anti. Semitism) 19 th century: Jewish nationalists, or Zionists, Call for establishing a Jewish state in Palestine
Israel Zionism – Jewish nationalism, with emphasis on need for state in Holy Land Israel= ancient Jewish homeland After Diaspora, many Jews Diaspora faced persecution (Anti. Semitism) 19 th century: Jewish nationalists, or Zionists, Call for establishing a Jewish state in Palestine
 WWI and WWII 1917: Balfour Declaration gives British support for Jewish state in Palestine (also promised land to Arabs) Jews begin immigrating from Germany and Russia to escape persecution, increases after Holocaust Question: What to do after WWII?
WWI and WWII 1917: Balfour Declaration gives British support for Jewish state in Palestine (also promised land to Arabs) Jews begin immigrating from Germany and Russia to escape persecution, increases after Holocaust Question: What to do after WWII?
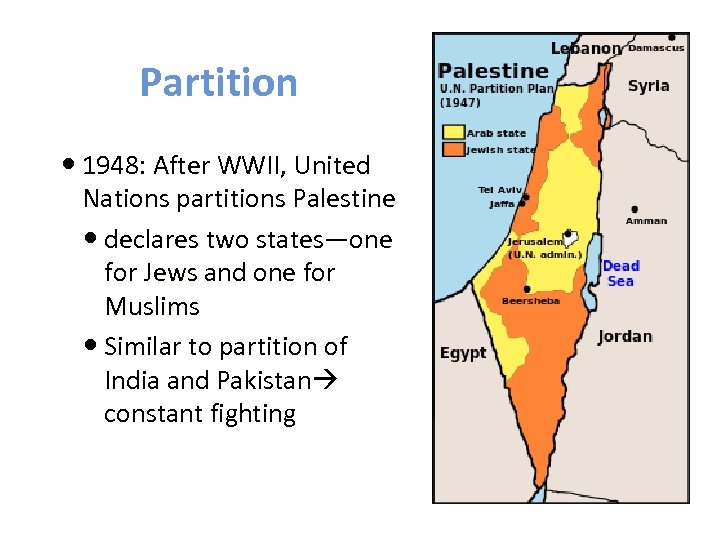 Partition 1948: After WWII, United Nations partitions Palestine declares two states—one for Jews and one for Muslims Similar to partition of India and Pakistan constant fighting
Partition 1948: After WWII, United Nations partitions Palestine declares two states—one for Jews and one for Muslims Similar to partition of India and Pakistan constant fighting
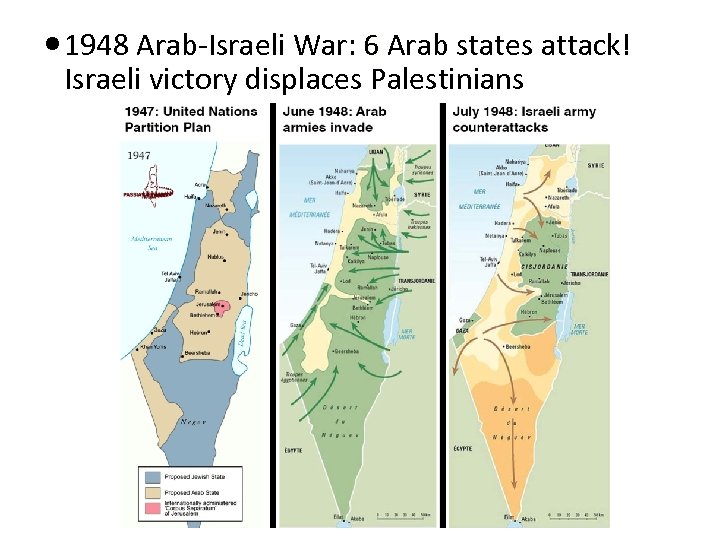 1948 Arab-Israeli War: 6 Arab states attack! Israeli victory displaces Palestinians
1948 Arab-Israeli War: 6 Arab states attack! Israeli victory displaces Palestinians
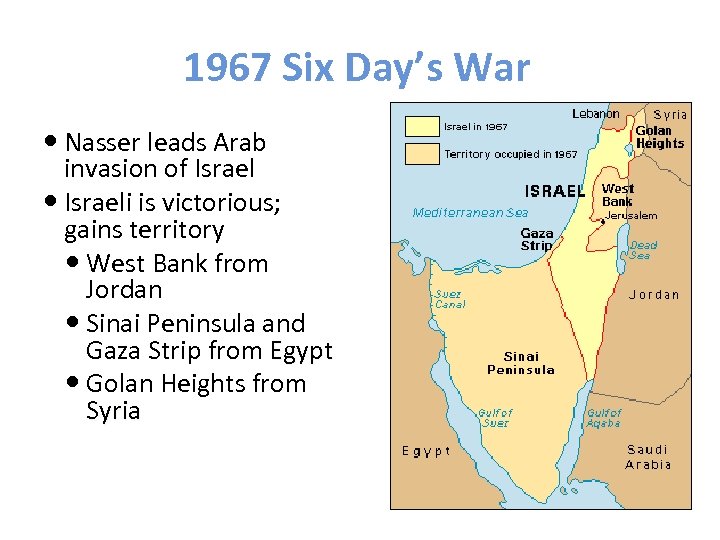 1967 Six Day’s War Nasser leads Arab invasion of Israeli is victorious; gains territory West Bank from Jordan Sinai Peninsula and Gaza Strip from Egypt Golan Heights from Syria
1967 Six Day’s War Nasser leads Arab invasion of Israeli is victorious; gains territory West Bank from Jordan Sinai Peninsula and Gaza Strip from Egypt Golan Heights from Syria
 Golda Meir Prime Minister of Israel After initial setbacks, led Israel to victory in 1973 Yom Kippur War ◦ Syrian invasion came as a surprise ◦ Sought support of United States to ensure victory "strong-willed, straight-talking, grey -bunned grandmother of the Jewish people"
Golda Meir Prime Minister of Israel After initial setbacks, led Israel to victory in 1973 Yom Kippur War ◦ Syrian invasion came as a surprise ◦ Sought support of United States to ensure victory "strong-willed, straight-talking, grey -bunned grandmother of the Jewish people"
 Camp David 1977: Israeli PM Begin and Egypt’s Sadat sign Camp David Accords ◦ Israel pulls out of Sinai, Egypt recognizes Israel’s right to exist ◦ Sadat later assassinated
Camp David 1977: Israeli PM Begin and Egypt’s Sadat sign Camp David Accords ◦ Israel pulls out of Sinai, Egypt recognizes Israel’s right to exist ◦ Sadat later assassinated
 Palestinian Nationalism Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) led by Yassir Arafat until death in 2004 2000—intifada (uprising) movement of Palestinians against Israeli military 2003 “Roadmap to Peace, ” but still disagreement, including recent wars
Palestinian Nationalism Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) led by Yassir Arafat until death in 2004 2000—intifada (uprising) movement of Palestinians against Israeli military 2003 “Roadmap to Peace, ” but still disagreement, including recent wars
 Divisions among Palestinians Fatah party led by Mahmoud Abbas in West Bank= more peaceful Hamas— Hamas considered a terrorist group; controls Gaza Hezbollah— Hezbollah militant Shia group backed by Syria
Divisions among Palestinians Fatah party led by Mahmoud Abbas in West Bank= more peaceful Hamas— Hamas considered a terrorist group; controls Gaza Hezbollah— Hezbollah militant Shia group backed by Syria
 Israel-Gaza War • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=VQ dehzx. Ug. VQ
Israel-Gaza War • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=VQ dehzx. Ug. VQ

 Iran Persian, Shia 1941: Mohammed Reza Pahlavi installed by British and Soviets 1953: American and British came to the Shah's aid After the Shah fled the country, the British MI 6 and American CIA organized a coup d’etat to oust the nationalist and democratically elected PM Mohammad Mossadegh
Iran Persian, Shia 1941: Mohammed Reza Pahlavi installed by British and Soviets 1953: American and British came to the Shah's aid After the Shah fled the country, the British MI 6 and American CIA organized a coup d’etat to oust the nationalist and democratically elected PM Mohammad Mossadegh
 Protests Shah decides to westernize and institute reforms in education, land, women’s rights These reforms infuriated Islamic fundamentalists who wanted sharia law 1977: secular and religious demonstrations, strikes demonstrations against the Shah
Protests Shah decides to westernize and institute reforms in education, land, women’s rights These reforms infuriated Islamic fundamentalists who wanted sharia law 1977: secular and religious demonstrations, strikes demonstrations against the Shah
 1979: Iranian Revolution Demonstrations reach a “tipping point” and military point cannot contain Shah flees Ayatollah Khomeini established a Shiite caliphate or theocracy Modernization and westernization reversed women lost rights Comparison: Women gained rights in China after the revolution while women lost rights in the Iranian revolution
1979: Iranian Revolution Demonstrations reach a “tipping point” and military point cannot contain Shah flees Ayatollah Khomeini established a Shiite caliphate or theocracy Modernization and westernization reversed women lost rights Comparison: Women gained rights in China after the revolution while women lost rights in the Iranian revolution
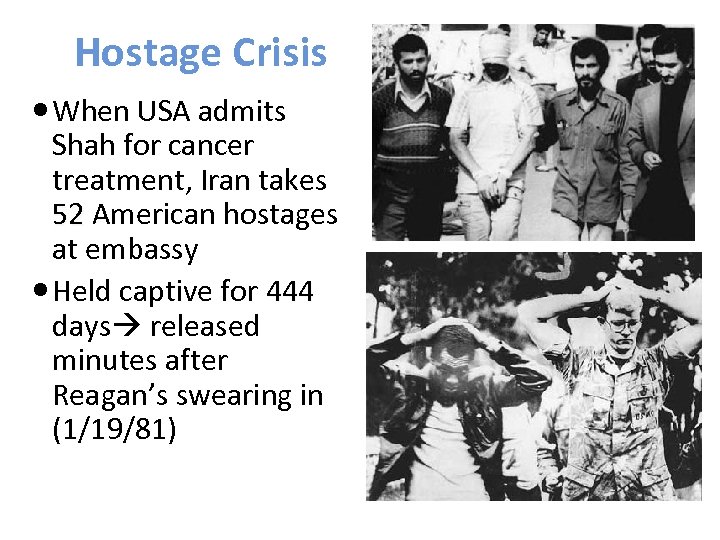 Hostage Crisis When USA admits Shah for cancer treatment, Iran takes 52 American hostages at embassy Held captive for 444 days released minutes after Reagan’s swearing in (1/19/81)
Hostage Crisis When USA admits Shah for cancer treatment, Iran takes 52 American hostages at embassy Held captive for 444 days released minutes after Reagan’s swearing in (1/19/81)
 Iran-Iraq War 1980 -8 1980: Iran invades Iraq USA supports Iraq and Saddam Hussein! Current conflict over Iran’s nuclear program Iran as largest state sponsor of terrorism – funding radicals in Iraq, Syria, Yemen, Israel
Iran-Iraq War 1980 -8 1980: Iran invades Iraq USA supports Iraq and Saddam Hussein! Current conflict over Iran’s nuclear program Iran as largest state sponsor of terrorism – funding radicals in Iraq, Syria, Yemen, Israel
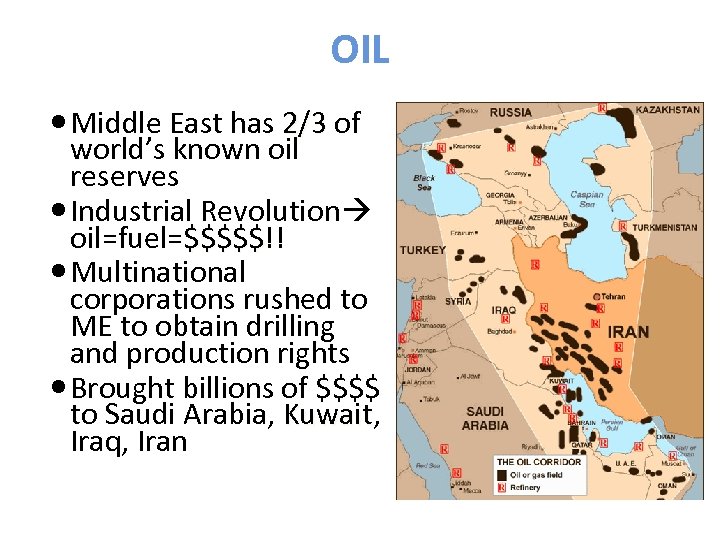 OIL Middle East has 2/3 of world’s known oil reserves Industrial Revolution oil=fuel=$$$$$!! $$$$$ Multinational corporations rushed to ME to obtain drilling and production rights Brought billions of $$$$ to Saudi Arabia, Kuwait Iraq, Iran
OIL Middle East has 2/3 of world’s known oil reserves Industrial Revolution oil=fuel=$$$$$!! $$$$$ Multinational corporations rushed to ME to obtain drilling and production rights Brought billions of $$$$ to Saudi Arabia, Kuwait Iraq, Iran
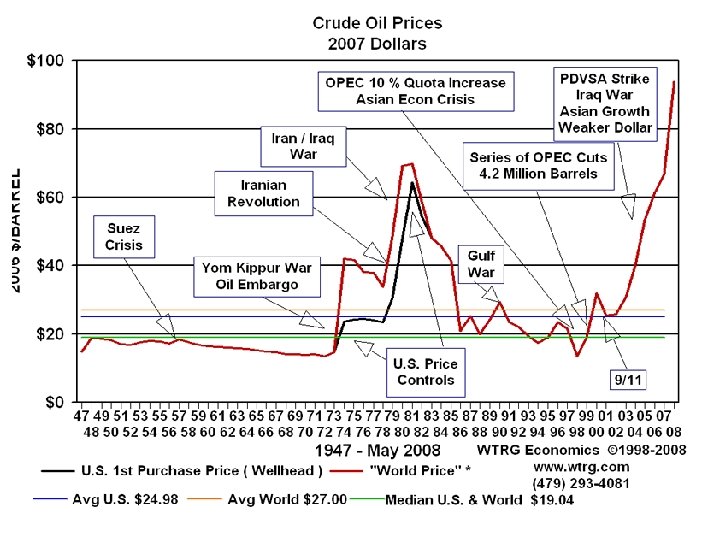
 OPEC Organization of Petroleum-Exporting Countries Cartel formed in 1960, controls ¾ of world’s petroleum Cut supply in 1970 s, driving up the price of gasoline and leading to shortages
OPEC Organization of Petroleum-Exporting Countries Cartel formed in 1960, controls ¾ of world’s petroleum Cut supply in 1970 s, driving up the price of gasoline and leading to shortages
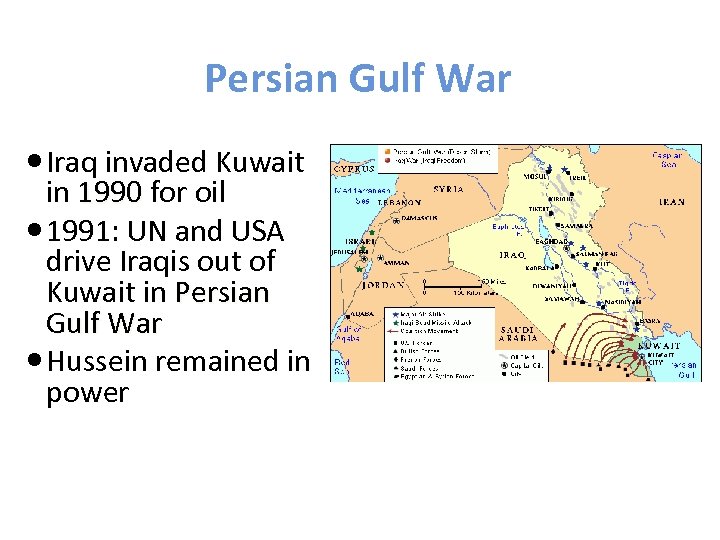 Persian Gulf War Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990 for oil 1991: UN and USA drive Iraqis out of Kuwait in Persian Gulf War Hussein remained in power
Persian Gulf War Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990 for oil 1991: UN and USA drive Iraqis out of Kuwait in Persian Gulf War Hussein remained in power

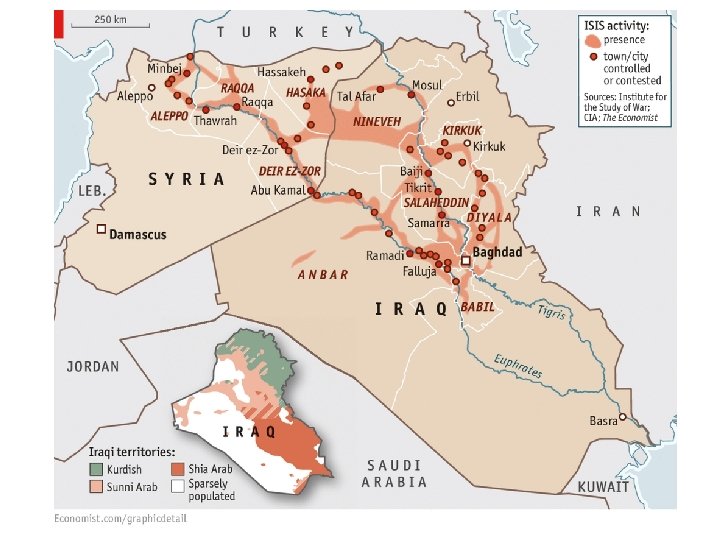
 Iraq War April 2003: USA led coalition ousts Saddam Hussein from power over concerns about “weapons of mass destruction” destruction 2004: democratic government formed 2005: sectional conflict between Shia, Sunni, and Kurds leads to civil war 2007: USA troop surge improves conditions USA leaves Iraq in 2011 ISIS now controls large parts of Iraq and Syria Iran funding Shia militiants
Iraq War April 2003: USA led coalition ousts Saddam Hussein from power over concerns about “weapons of mass destruction” destruction 2004: democratic government formed 2005: sectional conflict between Shia, Sunni, and Kurds leads to civil war 2007: USA troop surge improves conditions USA leaves Iraq in 2011 ISIS now controls large parts of Iraq and Syria Iran funding Shia militiants
 Taliban, Al Qaeda, Osama bin Laden 1980: Soviet Union sent thousands of troops to Afghanistan at request of Marxist leader Many Afghans opposed communism civil war Becomes the Soviet Union’s Vietnam USA helps arm and train the mujahideen “holy warriors” to oust Soviets 1996: 14 years of fighting and 2 million lives later, Taliban takes over
Taliban, Al Qaeda, Osama bin Laden 1980: Soviet Union sent thousands of troops to Afghanistan at request of Marxist leader Many Afghans opposed communism civil war Becomes the Soviet Union’s Vietnam USA helps arm and train the mujahideen “holy warriors” to oust Soviets 1996: 14 years of fighting and 2 million lives later, Taliban takes over
 The Taliban and Al Qaeda Islamic fundamentalist regime imposed strict Islamic law and restrictions on women Taliban provided safe haven for Osama bin Laden Bin Laden—Saudi leader of international terrorist network Al Qaeda ◦ Al Qaeda angered over USA support of Israel, troop Israel presence in Saudi Arabia, Arabia globalization
The Taliban and Al Qaeda Islamic fundamentalist regime imposed strict Islamic law and restrictions on women Taliban provided safe haven for Osama bin Laden Bin Laden—Saudi leader of international terrorist network Al Qaeda ◦ Al Qaeda angered over USA support of Israel, troop Israel presence in Saudi Arabia, Arabia globalization
 9/11/01 September 11, 2001: Al Qaeda hijacks four planes, flies two into World Trade Centers in NYC 3, 000 casualties USA declares war on terror, invades Afghanistan to oust Taliban Al Qaeda continues to carry out smaller-scale attacks, became involved in Iraq 5/1/11—Osama bin Laden 5/1/11 killed by U. S. Navy Seals in Pakistan
9/11/01 September 11, 2001: Al Qaeda hijacks four planes, flies two into World Trade Centers in NYC 3, 000 casualties USA declares war on terror, invades Afghanistan to oust Taliban Al Qaeda continues to carry out smaller-scale attacks, became involved in Iraq 5/1/11—Osama bin Laden 5/1/11 killed by U. S. Navy Seals in Pakistan
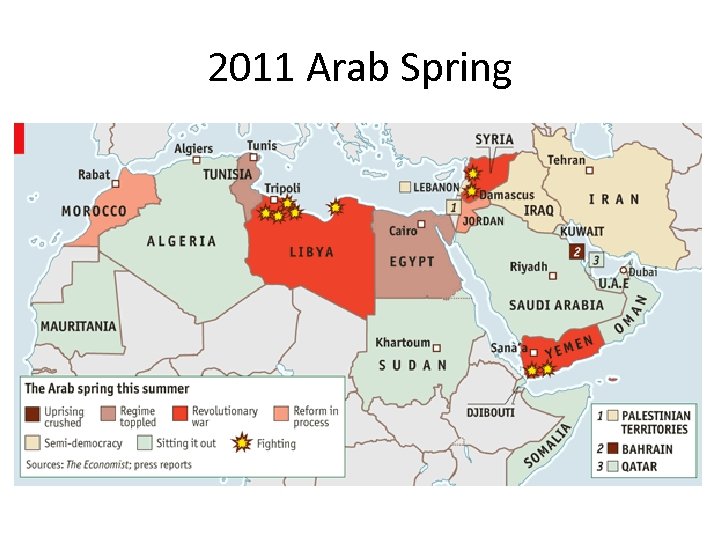 2011 Arab Spring
2011 Arab Spring
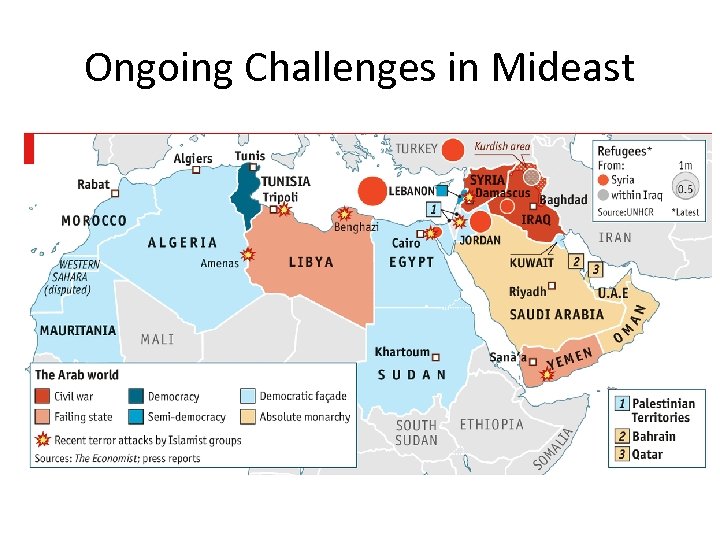 Ongoing Challenges in Mideast
Ongoing Challenges in Mideast
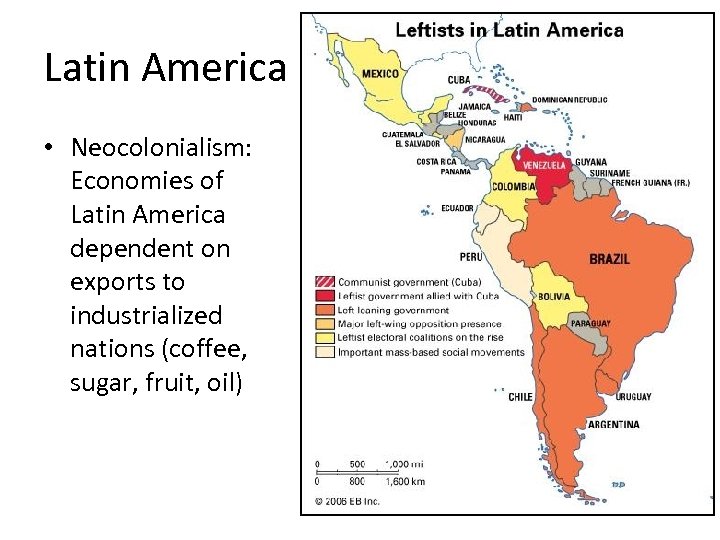 Latin America • Neocolonialism: Economies of Latin America dependent on exports to industrialized nations (coffee, sugar, fruit, oil)
Latin America • Neocolonialism: Economies of Latin America dependent on exports to industrialized nations (coffee, sugar, fruit, oil)
 Mexico • Revolution of 1910 (Zapata and Poncho Villa) • Created a constitution based on land reform • One party politics (PRI) from 1917 until 2000 election
Mexico • Revolution of 1910 (Zapata and Poncho Villa) • Created a constitution based on land reform • One party politics (PRI) from 1917 until 2000 election
 Venezuela • Socialist president Hugo Chavez nationalizes industries
Venezuela • Socialist president Hugo Chavez nationalizes industries
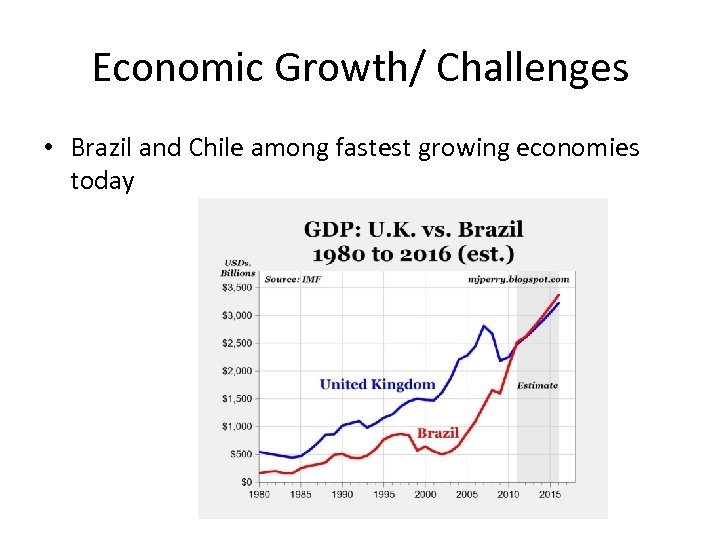 Economic Growth/ Challenges • Brazil and Chile among fastest growing economies today
Economic Growth/ Challenges • Brazil and Chile among fastest growing economies today
 • 19 year old libertarian Kim Kataguiri • President Dilma Rousseff
• 19 year old libertarian Kim Kataguiri • President Dilma Rousseff
 • A widening kickback scandal at Petrobras, the state oil company, is one of several complaints undermining the administration. Kataguiri and others are striking a chord with Brazilians fed up with soaring inflation, a high and growing tax burden, and those who blame government intervention for hobbling Brazil's economy, which grew just 0. 1 percent last year and is expected to shrink in 2015.
• A widening kickback scandal at Petrobras, the state oil company, is one of several complaints undermining the administration. Kataguiri and others are striking a chord with Brazilians fed up with soaring inflation, a high and growing tax burden, and those who blame government intervention for hobbling Brazil's economy, which grew just 0. 1 percent last year and is expected to shrink in 2015.


