cd735ef324d2b16a321a6ec37f802a5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 Increasing presence of China in the Indian Ocean Strategy and Security implications for India Commodore RS Vasan IN (Retd) Head, Strategy and Security Studies Center for Asia Studies, Chennai
Increasing presence of China in the Indian Ocean Strategy and Security implications for India Commodore RS Vasan IN (Retd) Head, Strategy and Security Studies Center for Asia Studies, Chennai
 Maritime Challenges üLong Coast line 7516 Kms üFar flung Islands on both sides üNine maritime states üHeavy sea traffic along the Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs) around the sub-continent ü 13 Major and 200 minor ports üUnresolved maritime borders with Pakistan and Bangladesh üTroubled waters in the South. üAsymmetric threats
Maritime Challenges üLong Coast line 7516 Kms üFar flung Islands on both sides üNine maritime states üHeavy sea traffic along the Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs) around the sub-continent ü 13 Major and 200 minor ports üUnresolved maritime borders with Pakistan and Bangladesh üTroubled waters in the South. üAsymmetric threats
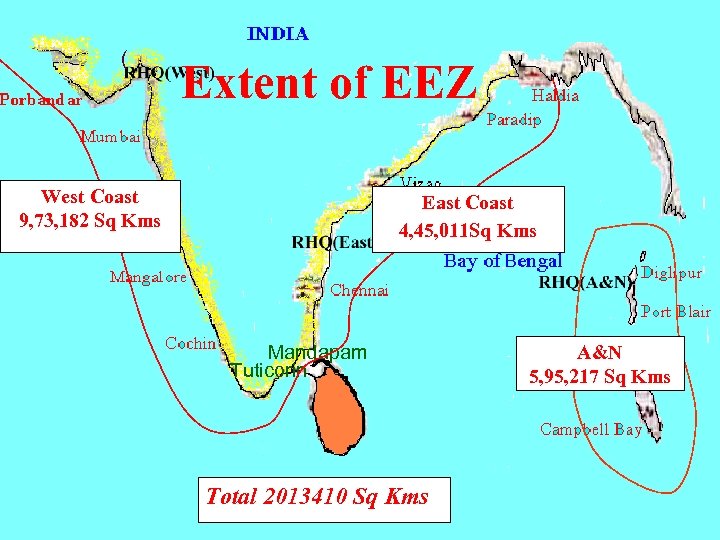 ( Extent of EEZ West Coast 9, 73, 182 Sq Kms East Coast 4, 45, 011 Sq Kms Mandapam Tuticorin Total 2013410 Sq Kms A&N 5, 95, 217 Sq Kms
( Extent of EEZ West Coast 9, 73, 182 Sq Kms East Coast 4, 45, 011 Sq Kms Mandapam Tuticorin Total 2013410 Sq Kms A&N 5, 95, 217 Sq Kms
 Security Challenges n. Illegal immigration n. Smuggling n. Poaching n. Gun running n. Refugees/Stow aways n. VNSAs n. Safety of lives and property n. Marine Pollution/Oil spills n. Off shore assets/ Islands/Port security
Security Challenges n. Illegal immigration n. Smuggling n. Poaching n. Gun running n. Refugees/Stow aways n. VNSAs n. Safety of lives and property n. Marine Pollution/Oil spills n. Off shore assets/ Islands/Port security
 Security Challenges ØIncreasing maritime and coastal trade ØSEZ including in port sector, Increased Private participation in maritime sector ØOff shore oil exploration and protection issues ØIssues of Governance of sensitive maritime boundaries. ØEnergy Security ØTerrorism and Piracy (Somalian waters) ØChina Factor? ?
Security Challenges ØIncreasing maritime and coastal trade ØSEZ including in port sector, Increased Private participation in maritime sector ØOff shore oil exploration and protection issues ØIssues of Governance of sensitive maritime boundaries. ØEnergy Security ØTerrorism and Piracy (Somalian waters) ØChina Factor? ?
 Triggers and Trends Ø 70, 000 ships would transit the Straits in a few yrs. ØOver 43% of piracy attacks reported in the Malacca Straits last decade. Another 16% is reported in the Singapore ØSomalia overtaking Malacca Straits as hot spot for piracy attacks ØDead/missing crew has increased threefold since 2002 as per the IMB. ØThe cost due to piracy attacks was estimated to be at 16 billion per annum.
Triggers and Trends Ø 70, 000 ships would transit the Straits in a few yrs. ØOver 43% of piracy attacks reported in the Malacca Straits last decade. Another 16% is reported in the Singapore ØSomalia overtaking Malacca Straits as hot spot for piracy attacks ØDead/missing crew has increased threefold since 2002 as per the IMB. ØThe cost due to piracy attacks was estimated to be at 16 billion per annum.
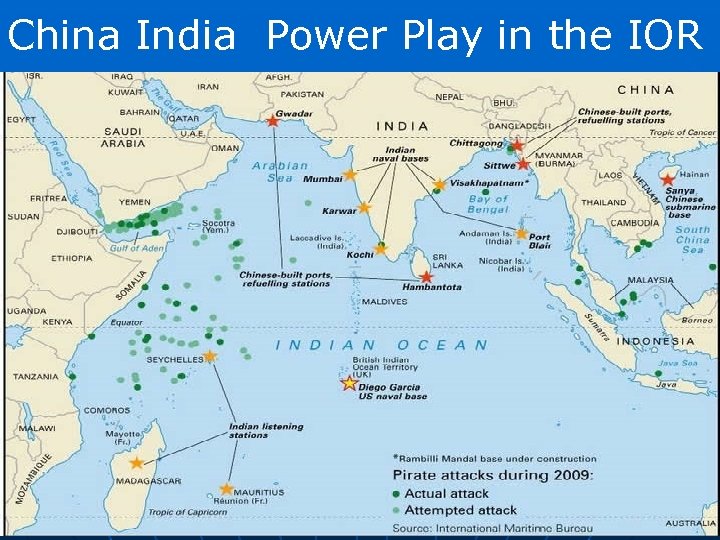 China India Power Play in the IOR
China India Power Play in the IOR
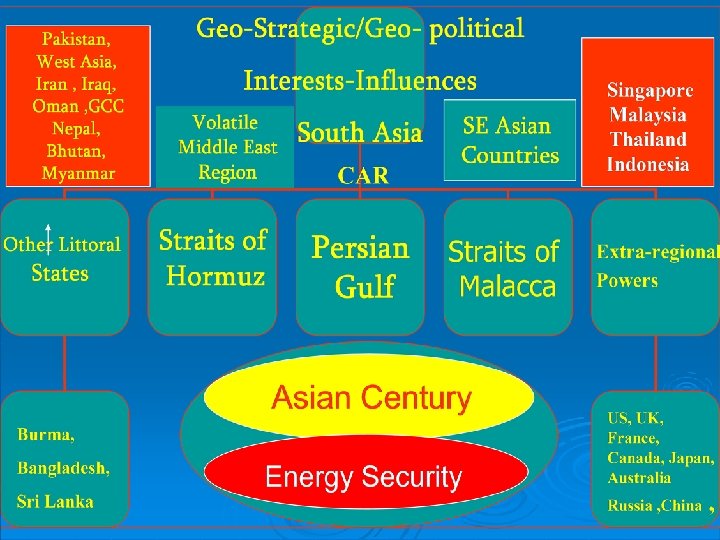
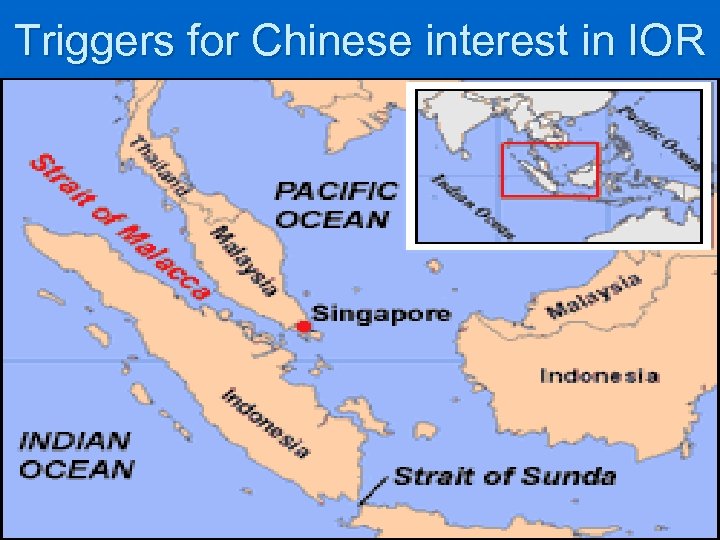 Triggers for Chinese interest in IOR
Triggers for Chinese interest in IOR
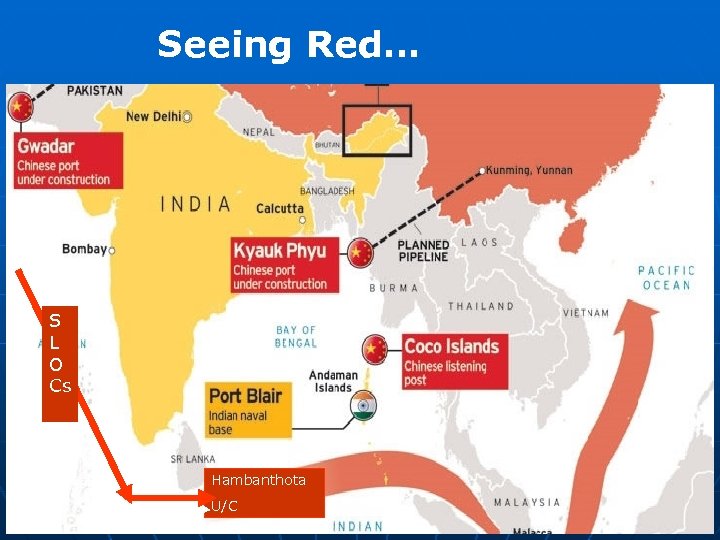 Seeing Red… S L O Cs Hambanthota U/C
Seeing Red… S L O Cs Hambanthota U/C
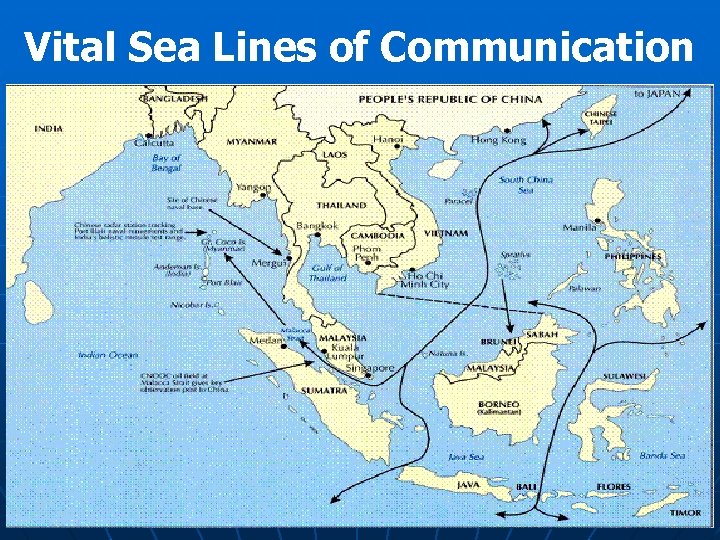 Vital Sea Lines of Communication
Vital Sea Lines of Communication
 ASIAN TRADE TRENDS v. China overtook Japan in Feb 2010 as the second largest economy v. SE Asian economies would grow at comparable rates. v. China export /import up by 30%+ during 20002009. v. China became top export destination of Singapore 7 yrs ago. v Indonesia’s FDI receipts in respect of China 67%.
ASIAN TRADE TRENDS v. China overtook Japan in Feb 2010 as the second largest economy v. SE Asian economies would grow at comparable rates. v. China export /import up by 30%+ during 20002009. v. China became top export destination of Singapore 7 yrs ago. v Indonesia’s FDI receipts in respect of China 67%.
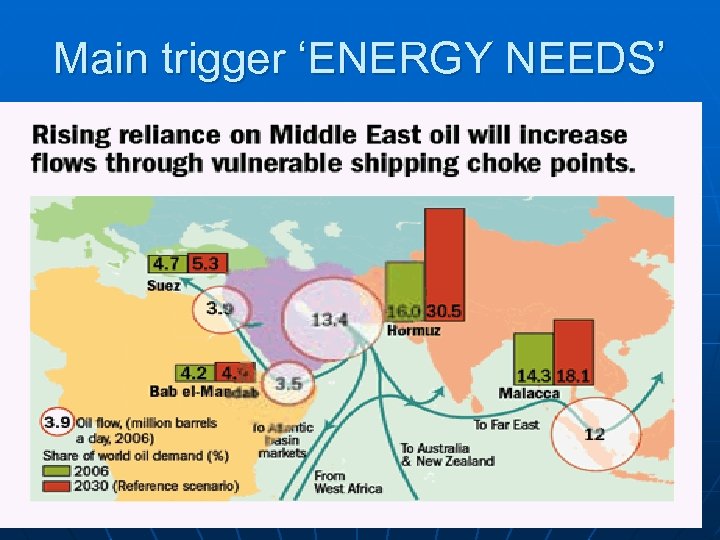 Main trigger ‘ENERGY NEEDS’
Main trigger ‘ENERGY NEEDS’
 Gulf of Aden Challenge üSurge in Piracy off Somalia üIncreasing number of Hijackings at far off distances from coast üEach Navy despatching ships to area for protection of merchantmen üNo resolute action for Coordinated action üOrigins over land üBoth China and India despatched naval units and maintain presence
Gulf of Aden Challenge üSurge in Piracy off Somalia üIncreasing number of Hijackings at far off distances from coast üEach Navy despatching ships to area for protection of merchantmen üNo resolute action for Coordinated action üOrigins over land üBoth China and India despatched naval units and maintain presence
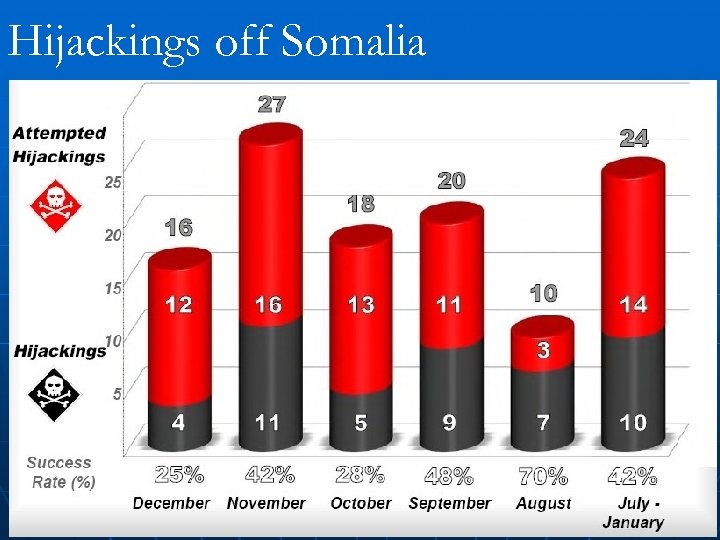 Hijackings off Somalia
Hijackings off Somalia
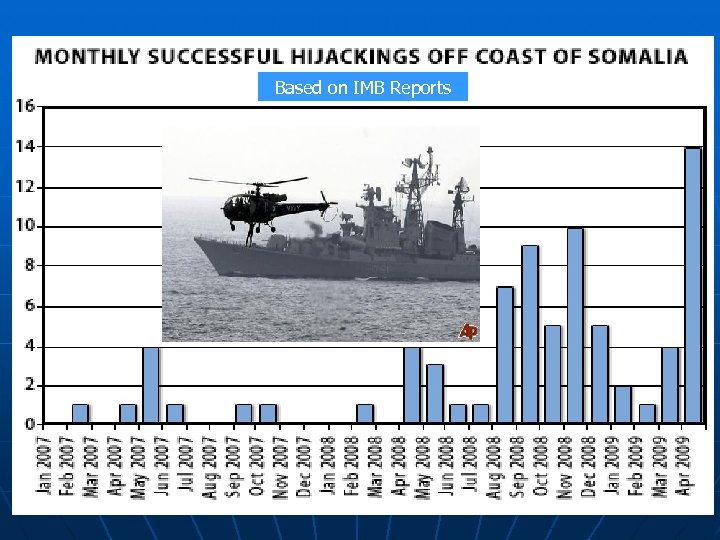 Based on IMB Reports
Based on IMB Reports
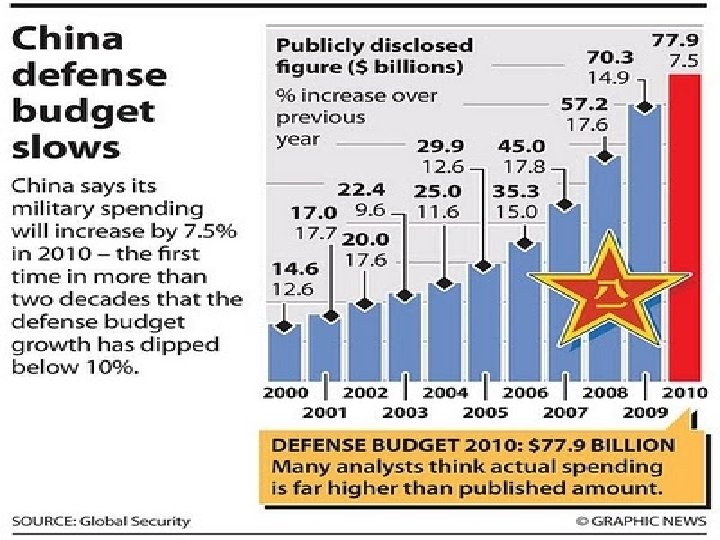
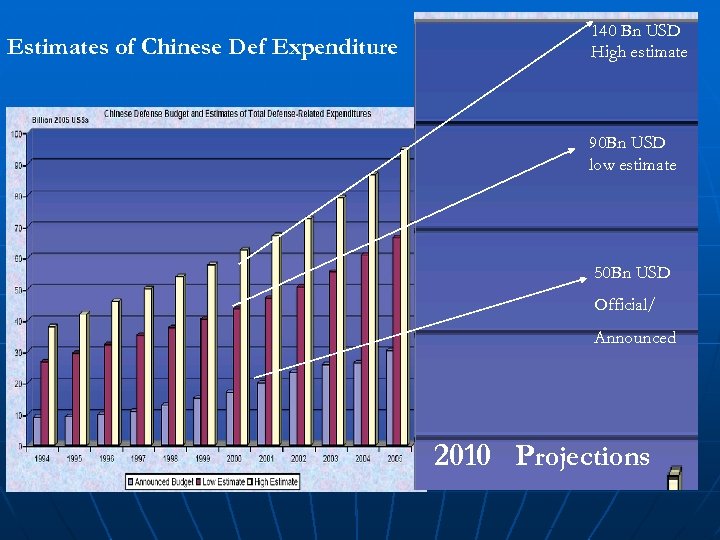 Estimates of Chinese Def Expenditure 140 Bn USD High estimate 90 Bn USD low estimate 50 Bn USD Official/ Announced 2010 Projections
Estimates of Chinese Def Expenditure 140 Bn USD High estimate 90 Bn USD low estimate 50 Bn USD Official/ Announced 2010 Projections
 Offshore Defence Strategy n n n n “Overall, our military strategy is defensive. We attack only after being attacked. But our operations are offensive. ” “Space or time will not limit our counter offensive. ” “We will not put boundaries on the limits of our offensives. ” “We will wait for the time and conditions that favor our forces when we do initiate offensive operations. ” “We will focus on the opposing force’s weaknesses. ” “We will use our own forces to eliminate the enemy’s forces” “Offensive operations against the enemy and defensive operations for our own force protection will be conducted simultaneously”
Offshore Defence Strategy n n n n “Overall, our military strategy is defensive. We attack only after being attacked. But our operations are offensive. ” “Space or time will not limit our counter offensive. ” “We will not put boundaries on the limits of our offensives. ” “We will wait for the time and conditions that favor our forces when we do initiate offensive operations. ” “We will focus on the opposing force’s weaknesses. ” “We will use our own forces to eliminate the enemy’s forces” “Offensive operations against the enemy and defensive operations for our own force protection will be conducted simultaneously”
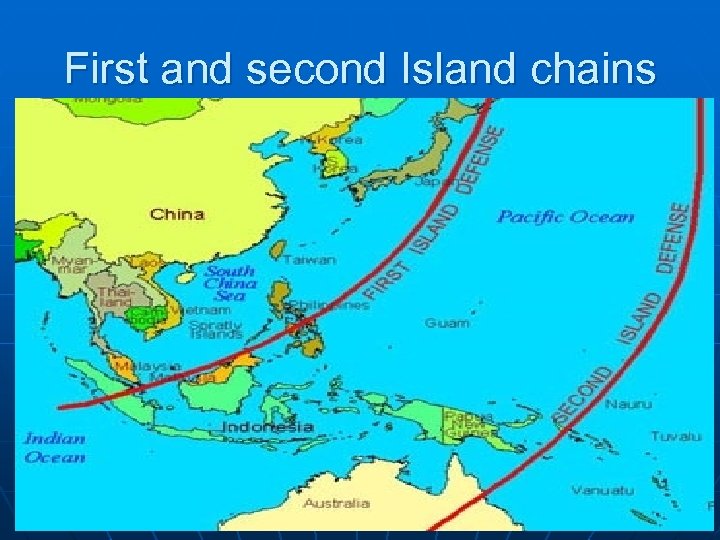 First and second Island chains
First and second Island chains
 Missile Launch Ranges from China Hit any one, anywhere ØSuper sonic ASCM-YJ 62 on Luyang II DDGs, SSN 22 Sun burn on Sovremennyy, SSN 27 B/Sizzler on Kilo class Submarines ØBy Dec 09 deployed 1050 CSS 6 and 1150 CSS 7(SRBMs) ØASBMs based on CSS 5 MRBMs 1500 kms with manoeuvrable warhead
Missile Launch Ranges from China Hit any one, anywhere ØSuper sonic ASCM-YJ 62 on Luyang II DDGs, SSN 22 Sun burn on Sovremennyy, SSN 27 B/Sizzler on Kilo class Submarines ØBy Dec 09 deployed 1050 CSS 6 and 1150 CSS 7(SRBMs) ØASBMs based on CSS 5 MRBMs 1500 kms with manoeuvrable warhead
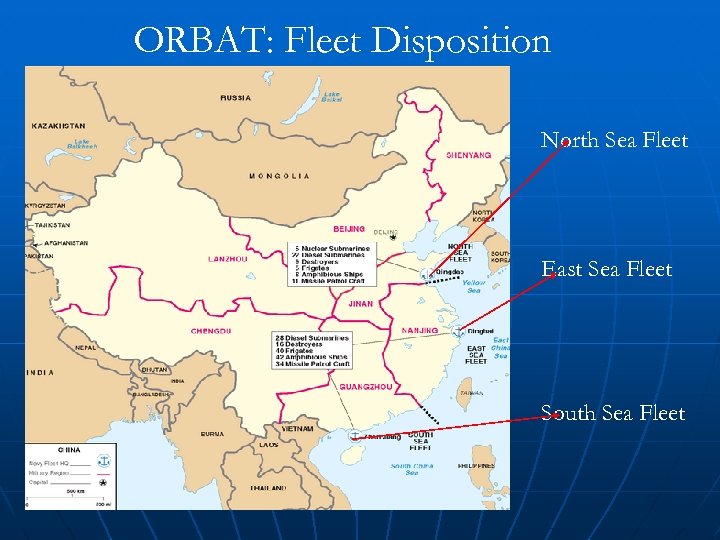 ORBAT: Fleet Disposition North Sea Fleet East Sea Fleet South Sea Fleet
ORBAT: Fleet Disposition North Sea Fleet East Sea Fleet South Sea Fleet
 PLAN Destroyers: 1 Type 052 C (Lanzhou class ) 1 Type 052 B (Guangzhou class) 2 Sovremenny class 1 Type 051 B (NATO codename: Luhai class) 2 Type 052 (NATO codename: Luhu class) 16 Luda class destroyers (some modernised, others mostly old tech) Total: 23 Frigates: 4 Type 053 H 2 G/Jangwei class 10 Type 053 H 3/Jangwei-II class 23 Jianghu-class (I+II+III, most old ships) Total: 37
PLAN Destroyers: 1 Type 052 C (Lanzhou class ) 1 Type 052 B (Guangzhou class) 2 Sovremenny class 1 Type 051 B (NATO codename: Luhai class) 2 Type 052 (NATO codename: Luhu class) 16 Luda class destroyers (some modernised, others mostly old tech) Total: 23 Frigates: 4 Type 053 H 2 G/Jangwei class 10 Type 053 H 3/Jangwei-II class 23 Jianghu-class (I+II+III, most old ships) Total: 37
 Type 051 C-DDG Luzhou
Type 051 C-DDG Luzhou
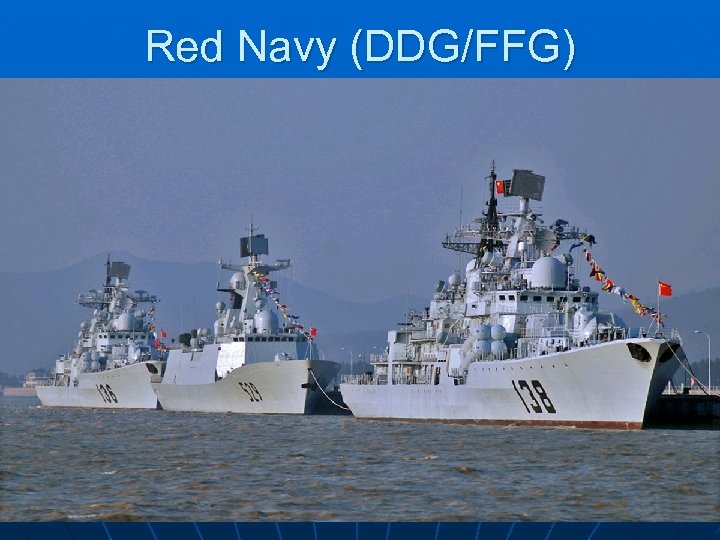 Red Navy (DDG/FFG)
Red Navy (DDG/FFG)
 Sentinels of the Deep PLAN Total: 54 subs 40 Type 035 Ming class and older Type 033 Romeo class diesel submarines 4 Russian-made Kilo class 5 indigenous Type 039 Song class diesel submarines 5 Type 091 Han class nuclear attack submarine (SSN) 1 Type 092 Xia class nuclear missile submarine (SSBN)
Sentinels of the Deep PLAN Total: 54 subs 40 Type 035 Ming class and older Type 033 Romeo class diesel submarines 4 Russian-made Kilo class 5 indigenous Type 039 Song class diesel submarines 5 Type 091 Han class nuclear attack submarine (SSN) 1 Type 092 Xia class nuclear missile submarine (SSBN)
 Sentinels of the sea (Type 094 -Jin Class) Hainan Island ?
Sentinels of the sea (Type 094 -Jin Class) Hainan Island ?
 Potent force in the making Ø Ø Ø Type 093, SSN, new nuclear powered attack submarine Type 094, SSBN, new nuclear powered ballistic missile submarine Type 039, Song class SSK, ddvanced diesel electric attack submarine Proj 636, Yuanzheng SSK, imported advanced Russian Kilo diesel electric attack submarine Yuan Class SSK, new advanced diesel electric attack submarine with Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) Capabilities
Potent force in the making Ø Ø Ø Type 093, SSN, new nuclear powered attack submarine Type 094, SSBN, new nuclear powered ballistic missile submarine Type 039, Song class SSK, ddvanced diesel electric attack submarine Proj 636, Yuanzheng SSK, imported advanced Russian Kilo diesel electric attack submarine Yuan Class SSK, new advanced diesel electric attack submarine with Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) Capabilities
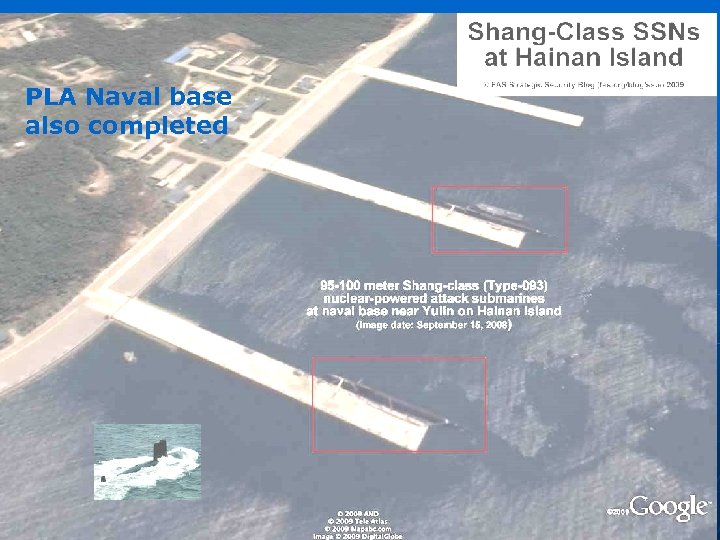 PLA Naval base also completed
PLA Naval base also completed
 Han class sub
Han class sub
 052 Class
052 Class
 Special Ops: PLAN
Special Ops: PLAN
 All eyes on Varyag ØCould also start commencing indigenous aircraft carrier programme by end of this year (2010) Ø Plans to train 50 pilots including from Varyag in a four year programme
All eyes on Varyag ØCould also start commencing indigenous aircraft carrier programme by end of this year (2010) Ø Plans to train 50 pilots including from Varyag in a four year programme
 Blue water navy in the making? ØBases in China, Dependency ports in IOR, ASBMs, Modernisation ØOTH targeting capabilitiy with Sky Wave and Surface Wave OTH Radars ØSatellites for long range surveillance for precision attacks with ASBMs Ø‘Informatisation’ for Integrated Joint Ops (Concept in 2004) ØUp to five new SSBNs JIN 094 class and 095 advanced SSNs, 13 Song class Diesel electric submarines(YJ 82 ASCM) follow on is Yuan class(AIP)- 15 more planned in addition to four existing – All likely to be capable of launching CH-SS_NX 13 ASCM on acceptance ØSurface combatants with long range HHQ 9 LRSAMs on LUYANG(052 C) and SA-N-20 LRSAM (Russian) on LUzhou( 051 C), 6 Jiangkai II(054 A) FFG with medium range HHQ-16 VLSAMs ØHoubei Type 0222 missile patorl boats for local defence carrying up to eight YJ 83 ASCMs ØDevelopment of AEW&C based on KJ-200 and KJ 2000(IL 76) ØCyber space initiatives-
Blue water navy in the making? ØBases in China, Dependency ports in IOR, ASBMs, Modernisation ØOTH targeting capabilitiy with Sky Wave and Surface Wave OTH Radars ØSatellites for long range surveillance for precision attacks with ASBMs Ø‘Informatisation’ for Integrated Joint Ops (Concept in 2004) ØUp to five new SSBNs JIN 094 class and 095 advanced SSNs, 13 Song class Diesel electric submarines(YJ 82 ASCM) follow on is Yuan class(AIP)- 15 more planned in addition to four existing – All likely to be capable of launching CH-SS_NX 13 ASCM on acceptance ØSurface combatants with long range HHQ 9 LRSAMs on LUYANG(052 C) and SA-N-20 LRSAM (Russian) on LUzhou( 051 C), 6 Jiangkai II(054 A) FFG with medium range HHQ-16 VLSAMs ØHoubei Type 0222 missile patorl boats for local defence carrying up to eight YJ 83 ASCMs ØDevelopment of AEW&C based on KJ-200 and KJ 2000(IL 76) ØCyber space initiatives-
 Concept of ops (CONOPS) India n n n CBG Both Sea Control and Denial forces LND Amphibious forces Layered defence using marine police wing, Coast Guard and the Navy Integrated Coastal defence network
Concept of ops (CONOPS) India n n n CBG Both Sea Control and Denial forces LND Amphibious forces Layered defence using marine police wing, Coast Guard and the Navy Integrated Coastal defence network
 Concept of Operations (CONOPS) Shore based and integral aviation for surveillance n NCW/NCO n Satellite n
Concept of Operations (CONOPS) Shore based and integral aviation for surveillance n NCW/NCO n Satellite n
 Indian Navy Surface: Total 36 1 Carrier 3 type 15 5 Rajput (with Brahmos capability) 3 Type 16 3 Talwars 3 Type 16 A 3 Type 25 A 13 Veer Submarines : Total 14 10 kilos (upgraded with klub N) can strike surface 4 HDW 209
Indian Navy Surface: Total 36 1 Carrier 3 type 15 5 Rajput (with Brahmos capability) 3 Type 16 3 Talwars 3 Type 16 A 3 Type 25 A 13 Veer Submarines : Total 14 10 kilos (upgraded with klub N) can strike surface 4 HDW 209
 INDIAN NAVY Submarines: Total 17 2 Vela (Foxtrot) Class 4 Shishumer Class(HDW) 10 (Kilo) Sindhogush 1 Akula Class on lease Air craft carriers Viraat Vikramaditya ADS U/C
INDIAN NAVY Submarines: Total 17 2 Vela (Foxtrot) Class 4 Shishumer Class(HDW) 10 (Kilo) Sindhogush 1 Akula Class on lease Air craft carriers Viraat Vikramaditya ADS U/C
 Maritime Capability Perspective Plan n n 11 th through 13 th plan aimed at balanced growth in ship building, submarine construction and aviation development About 20 percent of def budget expected for Navy (capital to revenue about 60: 40) Six Scorpene at MDL first delivery 2012 last in 2017? Mod Plans include induction of major surface combatants, surveillance platforms , ASW/ASV platforms, multi role helicopters, space based surveillance and satellite communications, NCW
Maritime Capability Perspective Plan n n 11 th through 13 th plan aimed at balanced growth in ship building, submarine construction and aviation development About 20 percent of def budget expected for Navy (capital to revenue about 60: 40) Six Scorpene at MDL first delivery 2012 last in 2017? Mod Plans include induction of major surface combatants, surveillance platforms , ASW/ASV platforms, multi role helicopters, space based surveillance and satellite communications, NCW
 Maritime Capability Perspective Plan U/C Aircraft Carrier, 2 HDW submarines, and six Scorpene. Total 32 ships and subs u/c n Building of ships by non PSUs due to heavy orders n 15 yrs indigenous plan n R&D both by DRDO and Indian Industries n Opportunities for Marine Eng Equipment and Technologies exist for Indian Industry n n Vikramaditya by 2012?
Maritime Capability Perspective Plan U/C Aircraft Carrier, 2 HDW submarines, and six Scorpene. Total 32 ships and subs u/c n Building of ships by non PSUs due to heavy orders n 15 yrs indigenous plan n R&D both by DRDO and Indian Industries n Opportunities for Marine Eng Equipment and Technologies exist for Indian Industry n n Vikramaditya by 2012?
 Force structuring two CBG, LND forces, well defined submarine force, shore based LRMR, ASW, ASV, integral helicopters n Translates to a force consisting of three aircraft carriers, 35 frigates/destroyers, four supprt ships, about 100 LND units, about 20 subs, amphibious ships n 2 carriers by 2014 and the third to join by 2019? n Seven frigates and four Destroyers approved to be built by DPSUs by 2021 @ Rs 45, 000 crores n Present level is of 130 ships plans to get it up to 160 n
Force structuring two CBG, LND forces, well defined submarine force, shore based LRMR, ASW, ASV, integral helicopters n Translates to a force consisting of three aircraft carriers, 35 frigates/destroyers, four supprt ships, about 100 LND units, about 20 subs, amphibious ships n 2 carriers by 2014 and the third to join by 2019? n Seven frigates and four Destroyers approved to be built by DPSUs by 2021 @ Rs 45, 000 crores n Present level is of 130 ships plans to get it up to 160 n
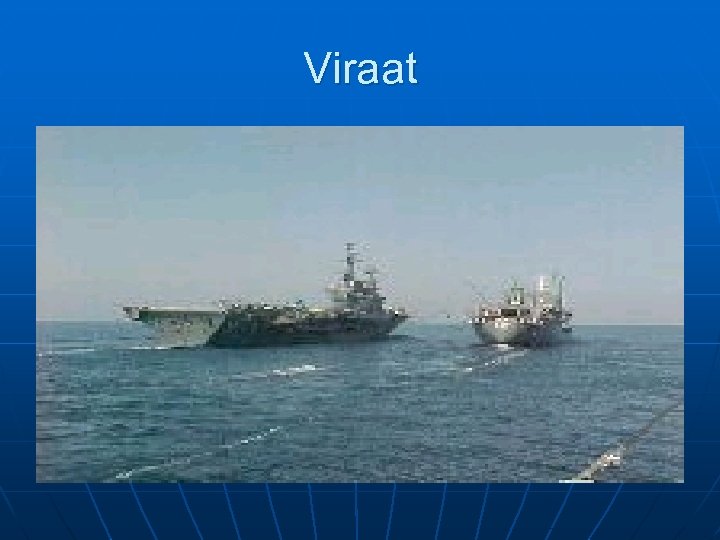 Viraat
Viraat
 Vikramaditya Many Questions Still ?
Vikramaditya Many Questions Still ?
 Sindhuvijay
Sindhuvijay
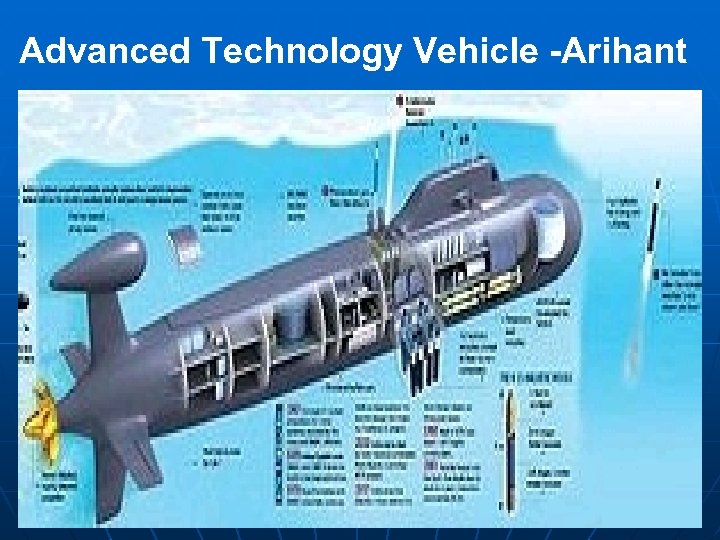 Advanced Technology Vehicle -Arihant
Advanced Technology Vehicle -Arihant
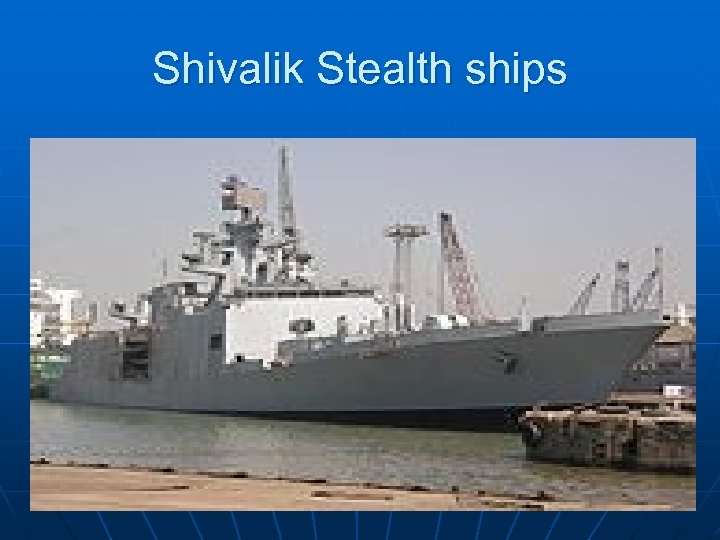 Shivalik Stealth ships
Shivalik Stealth ships
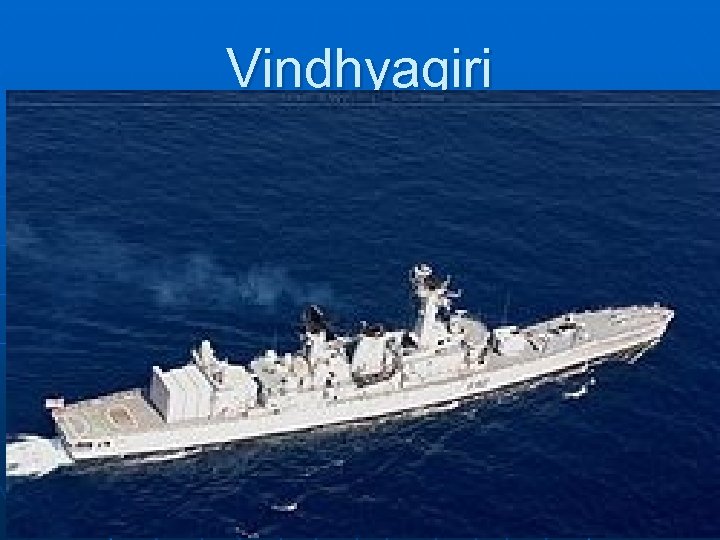 Vindhyagiri
Vindhyagiri
 INS Shishumar
INS Shishumar
 Talwar
Talwar
 Charlie Class sub-Chakra
Charlie Class sub-Chakra
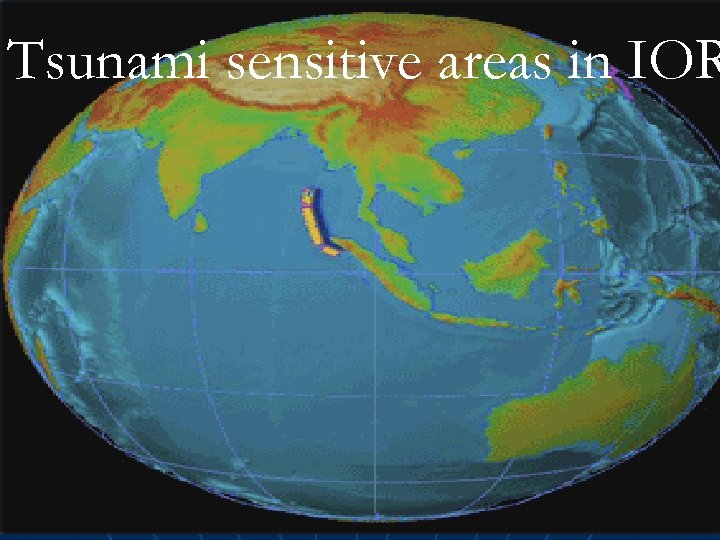 Tsunami sensitive areas in IOR
Tsunami sensitive areas in IOR
 China’s IOR Ambitions Energy/SLOC protection n “Warm water Ports” referred to also as dependency ports in IOR for future (Gwadar, Hambanthota, Myanmar) n Containment of India n Protection of own ships from Piracy-Somalia/Gulf of Aden n Enablement of operation Carrier Task Force n
China’s IOR Ambitions Energy/SLOC protection n “Warm water Ports” referred to also as dependency ports in IOR for future (Gwadar, Hambanthota, Myanmar) n Containment of India n Protection of own ships from Piracy-Somalia/Gulf of Aden n Enablement of operation Carrier Task Force n
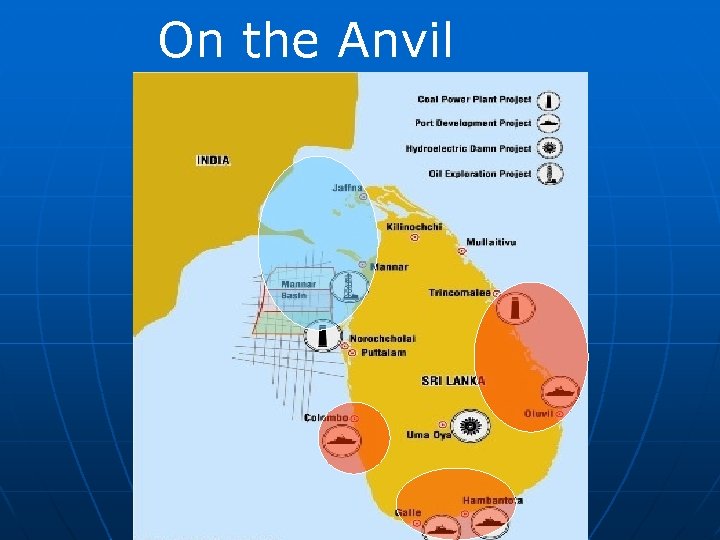 On the Anvil
On the Anvil
 Economic Developments n n n Post war - Hong Kong-based conglomerate Huichen Investment Holdings Ltd. investing $28 million to develop SEZ located in Mirigama, 55 km (34 miles) from Colombo port and 40 km from the international airport. Hambantota Port Development Project (worth US$1 billion) Norochcholai Coal Power Plant Project (worth US$855 million) Colombo-Katunayake Expressway (worth US$248. 2 million) 2006 to 2008, Chinese aid to Sri Lanka grew fivefold, replacing Japan as Sri Lanka ’s largest donor. Interest free loans, subsidised loans
Economic Developments n n n Post war - Hong Kong-based conglomerate Huichen Investment Holdings Ltd. investing $28 million to develop SEZ located in Mirigama, 55 km (34 miles) from Colombo port and 40 km from the international airport. Hambantota Port Development Project (worth US$1 billion) Norochcholai Coal Power Plant Project (worth US$855 million) Colombo-Katunayake Expressway (worth US$248. 2 million) 2006 to 2008, Chinese aid to Sri Lanka grew fivefold, replacing Japan as Sri Lanka ’s largest donor. Interest free loans, subsidised loans
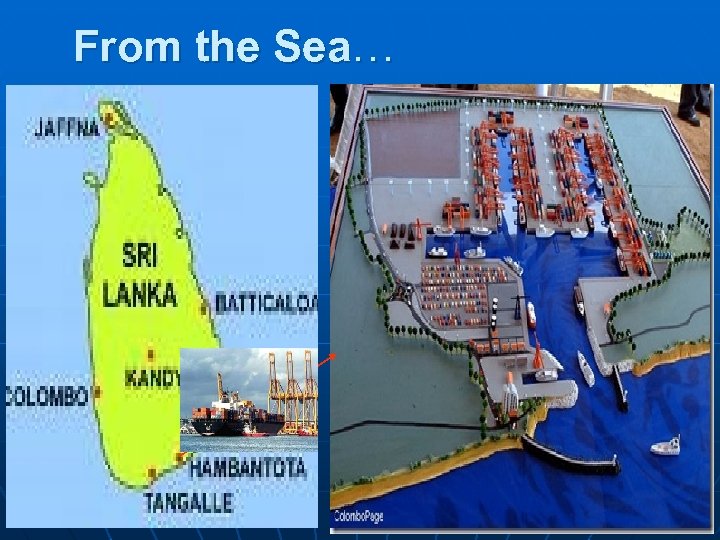 From the Sea…
From the Sea…
 . . Over land. . Colombo Kattunayake Highway and many investments in projects and infrastructure
. . Over land. . Colombo Kattunayake Highway and many investments in projects and infrastructure
 Hambanthota. . n n n n Three times the size of Colombo Service and Industrial Port 12 berths bunkering and refueling LNG refinery Aviation fuel storage Dry docks 6000 direct and 50, 000 indirect job creation
Hambanthota. . n n n n Three times the size of Colombo Service and Industrial Port 12 berths bunkering and refueling LNG refinery Aviation fuel storage Dry docks 6000 direct and 50, 000 indirect job creation
![Artist’s view of Hambanthota ‘Over 200 ships sail this route [daily] and we want Artist’s view of Hambanthota ‘Over 200 ships sail this route [daily] and we want](https://present5.com/presentation/cd735ef324d2b16a321a6ec37f802a5a/image-59.jpg) Artist’s view of Hambanthota ‘Over 200 ships sail this route [daily] and we want to attract them… Our vision is to consolidate the position of Sri Lanka as the premier maritime logistic centre of the Asian region. ’ Dr. Priyath Bandu Wickrama Chairman Sri Lanka Port Authority
Artist’s view of Hambanthota ‘Over 200 ships sail this route [daily] and we want to attract them… Our vision is to consolidate the position of Sri Lanka as the premier maritime logistic centre of the Asian region. ’ Dr. Priyath Bandu Wickrama Chairman Sri Lanka Port Authority
 Shape of things to come….
Shape of things to come….
 From the Air…… Shape of things to come
From the Air…… Shape of things to come
 Some figures about the airport coming up near Hambanthota. US$210 mn ØExtent of land: 2, 000 hectares in total. ØInitial construction covers an extent of 800 hectares. ØAerodrome design: Designed to meet the ICAO specification for code 4 F. ØRunway Length: 3, 500 metres in length with a width of 75 metres. Taxiways: 60 metre long taxiway from the runway centre line to the edge of the apron. ØApron: 10 parking positions initially with the total being 80. Air Field Capacity: Annual Service Volume of the aerodrome at short and medium/long term planning horizons will be 30, 000 and 60, 000 movements respectively. ØTerminal and related buildings: Proposed 10, 000 square metres to accommodate 800 peak hours and 100 domestic passengers both ways.
Some figures about the airport coming up near Hambanthota. US$210 mn ØExtent of land: 2, 000 hectares in total. ØInitial construction covers an extent of 800 hectares. ØAerodrome design: Designed to meet the ICAO specification for code 4 F. ØRunway Length: 3, 500 metres in length with a width of 75 metres. Taxiways: 60 metre long taxiway from the runway centre line to the edge of the apron. ØApron: 10 parking positions initially with the total being 80. Air Field Capacity: Annual Service Volume of the aerodrome at short and medium/long term planning horizons will be 30, 000 and 60, 000 movements respectively. ØTerminal and related buildings: Proposed 10, 000 square metres to accommodate 800 peak hours and 100 domestic passengers both ways.
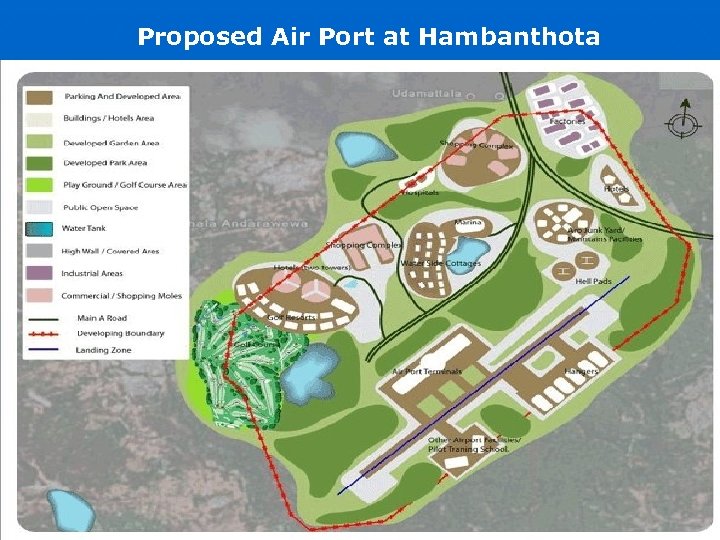 Proposed Air Port at Hambanthota
Proposed Air Port at Hambanthota
 What it portends for future n n n n Direct flights from China Strategic Air Lift Capability Support to PLA Navy on IOR missions Economic Development Air and Sea bridge to IOR (Port +Air port) Dual Use in future Hambanthota bids for hosting 2018 CWG
What it portends for future n n n n Direct flights from China Strategic Air Lift Capability Support to PLA Navy on IOR missions Economic Development Air and Sea bridge to IOR (Port +Air port) Dual Use in future Hambanthota bids for hosting 2018 CWG
 Factoring Sri Lanka in China’s equations n n With the geo strategic importance of Sri Lanka it would assume greater importance for global players post LTTE defeat Many developments and investments in ports/Airports/transport sector particularly by China increases China’s leverage Chinese overtures in the neighbourhood is discomforting to India What is today an economic investment of huge proportions is expected to pay dividends for investors particularly China in increasing its IOR ambitions and also provides leverages for future use both for commercial and military use
Factoring Sri Lanka in China’s equations n n With the geo strategic importance of Sri Lanka it would assume greater importance for global players post LTTE defeat Many developments and investments in ports/Airports/transport sector particularly by China increases China’s leverage Chinese overtures in the neighbourhood is discomforting to India What is today an economic investment of huge proportions is expected to pay dividends for investors particularly China in increasing its IOR ambitions and also provides leverages for future use both for commercial and military use
 India’s Maritime Posturing of concern to China Cooperative arrangements with maritime forces of Japan, Vietnam, US, UK, France, Australia, Singapore, Thailand etc. , n Maldives security pact n Regional Initiatives- SAARC, ARF, MILAN, Bilateral agreements n Indian Ocean Region Symposium n Launch of INS Arihant –ATV n Modernisation of India’s maritime assets n Infrastructure improvements n
India’s Maritime Posturing of concern to China Cooperative arrangements with maritime forces of Japan, Vietnam, US, UK, France, Australia, Singapore, Thailand etc. , n Maldives security pact n Regional Initiatives- SAARC, ARF, MILAN, Bilateral agreements n Indian Ocean Region Symposium n Launch of INS Arihant –ATV n Modernisation of India’s maritime assets n Infrastructure improvements n
 Invitation for engagement/intervention Areas of concern: India n n n n Strategic Location Regional power dynamics Economic opportunity Technological prowess Democracy Countervailing force to China’s adventures in the area Historical baggage Nuclear power
Invitation for engagement/intervention Areas of concern: India n n n n Strategic Location Regional power dynamics Economic opportunity Technological prowess Democracy Countervailing force to China’s adventures in the area Historical baggage Nuclear power
 Extra regional powers interests/role n n n n China –Energy, Spheres of influence (SOP) to counter India's influence France- Strategic presence in IOR, bases in Diego Suareg +Reunion Island Japan- Increased interest in IOR, Greater interaction with the maritime forces of India (CG) for protection of mercantile marine traffic from piracy. Benign support? US- Diego Garcia, Mobile fleets in areas around the world (CTF 150 and 151 ) for preemption and energy security. Global policing UK - Play supporting role for US initiatives while retaining space for its own initiatives, Norway –Peace brokering Russia - Slowly trying to regain lost space
Extra regional powers interests/role n n n n China –Energy, Spheres of influence (SOP) to counter India's influence France- Strategic presence in IOR, bases in Diego Suareg +Reunion Island Japan- Increased interest in IOR, Greater interaction with the maritime forces of India (CG) for protection of mercantile marine traffic from piracy. Benign support? US- Diego Garcia, Mobile fleets in areas around the world (CTF 150 and 151 ) for preemption and energy security. Global policing UK - Play supporting role for US initiatives while retaining space for its own initiatives, Norway –Peace brokering Russia - Slowly trying to regain lost space
 n Conclusion …. cont’d n n China’s remote presence already visible around India Areas of interest in IOR would continue to be under satellite surveillance and other ISR means China’s virtual presence felt alreay on many Govt and private internet sites China’s actual presence due to continuous deployment of its ships in Gulf of Aden and by way of its work force in projects around IOR countries Land divides and Oceans unite nations. From being a neighbour sharing land borders China is now a maritime neighbour as well connected through narrow Malacca straits
n Conclusion …. cont’d n n China’s remote presence already visible around India Areas of interest in IOR would continue to be under satellite surveillance and other ISR means China’s virtual presence felt alreay on many Govt and private internet sites China’s actual presence due to continuous deployment of its ships in Gulf of Aden and by way of its work force in projects around IOR countries Land divides and Oceans unite nations. From being a neighbour sharing land borders China is now a maritime neighbour as well connected through narrow Malacca straits
 n n Conclusion n n IOR would continue to hold interest for West and the rest including China The 21 st century would witness acute competition between the two Asian neighbours impacting security and safety in IOR Force level augmentation, modernisation and greater power play inevitable in the region Conflict for supremacy in IOR and cooperation (anti piracy/counter terrorism) where convenient would continue India would continue to enjoy the geo strategic advantage in the short term Cooperative initiatives, collaborative efforts are inescapable for taking on the scourge of piracy and maritime terrorism.
n n Conclusion n n IOR would continue to hold interest for West and the rest including China The 21 st century would witness acute competition between the two Asian neighbours impacting security and safety in IOR Force level augmentation, modernisation and greater power play inevitable in the region Conflict for supremacy in IOR and cooperation (anti piracy/counter terrorism) where convenient would continue India would continue to enjoy the geo strategic advantage in the short term Cooperative initiatives, collaborative efforts are inescapable for taking on the scourge of piracy and maritime terrorism.
 Options for India n n n n Engaging China’s neighbours and those weary of China’s military ambitions -Kautilya’s Arthashastra prescriptions Strengthening and operationalising second strike capability Greater use of space for surveillance Cyber warfare Sustained support for Modernisation Engaging immediate neighbourhood Overcoming vacuum in political leadership Keeping counters in place and all options open Strengthening A&N even more-
Options for India n n n n Engaging China’s neighbours and those weary of China’s military ambitions -Kautilya’s Arthashastra prescriptions Strengthening and operationalising second strike capability Greater use of space for surveillance Cyber warfare Sustained support for Modernisation Engaging immediate neighbourhood Overcoming vacuum in political leadership Keeping counters in place and all options open Strengthening A&N even more-
 Thank You
Thank You


