86b744fa89381c2c1222f615d69724b7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Increased Value, Decreased Time – Lean Project Delivery Shawn Klinge – Senior Lean Sensei Foth Companies – Green Bay, WI
Increased Value, Decreased Time – Lean Project Delivery Shawn Klinge – Senior Lean Sensei Foth Companies – Green Bay, WI
 Foth Overview v Consulting and engineering solutions through: 4 Foth Infrastructure & Environment, LLC 4 Foth Production Solutions, LLC 4 Foth Asset Management, LLC v 100% member-owned business founded in 1938 v Corporate headquarters in Green Bay, WI v Over 600 members
Foth Overview v Consulting and engineering solutions through: 4 Foth Infrastructure & Environment, LLC 4 Foth Production Solutions, LLC 4 Foth Asset Management, LLC v 100% member-owned business founded in 1938 v Corporate headquarters in Green Bay, WI v Over 600 members
 Agenda v Lean Project Delivery 4 Project Planning Process 4 Visual Workflow Management & Stand-up Meetings 4 Project Risk Process v Questions
Agenda v Lean Project Delivery 4 Project Planning Process 4 Visual Workflow Management & Stand-up Meetings 4 Project Risk Process v Questions
 Lean Project Delivery v More efficient utilization of Project Team v Provides time for strategy implementation v Integrates ALL Team members
Lean Project Delivery v More efficient utilization of Project Team v Provides time for strategy implementation v Integrates ALL Team members
 Project Planning
Project Planning
 The Project Planning Process v. Objective – Ø To generate a realistic project plan, including schedule, key milestone dates, “high level” budget and resource plan for the project. v. Key Outputs – Ø Project Budget and Resource Plan – High level Ø Project Milestone Schedule
The Project Planning Process v. Objective – Ø To generate a realistic project plan, including schedule, key milestone dates, “high level” budget and resource plan for the project. v. Key Outputs – Ø Project Budget and Resource Plan – High level Ø Project Milestone Schedule
 Milestones are… Key points in time in the project that are well understood, significant, and verifiable… 50, 000 ft view of project Examples: Commission reports Plan submittals to DOT Docket Meetings DNR Plan Submittals Construction Phase Complete
Milestones are… Key points in time in the project that are well understood, significant, and verifiable… 50, 000 ft view of project Examples: Commission reports Plan submittals to DOT Docket Meetings DNR Plan Submittals Construction Phase Complete
 Deliverables are… Any item that is tangible, actionable or transferable. DNR design report – – Soils reports Decision made – Public feedback– – Plan approvals ALL PROJECT VALUE IS EMBODIED IN DELIVERABLES A task is value-added only if it relates to a deliverable, and has a customer who needs it! Otherwise it is WASTE!
Deliverables are… Any item that is tangible, actionable or transferable. DNR design report – – Soils reports Decision made – Public feedback– – Plan approvals ALL PROJECT VALUE IS EMBODIED IN DELIVERABLES A task is value-added only if it relates to a deliverable, and has a customer who needs it! Otherwise it is WASTE!
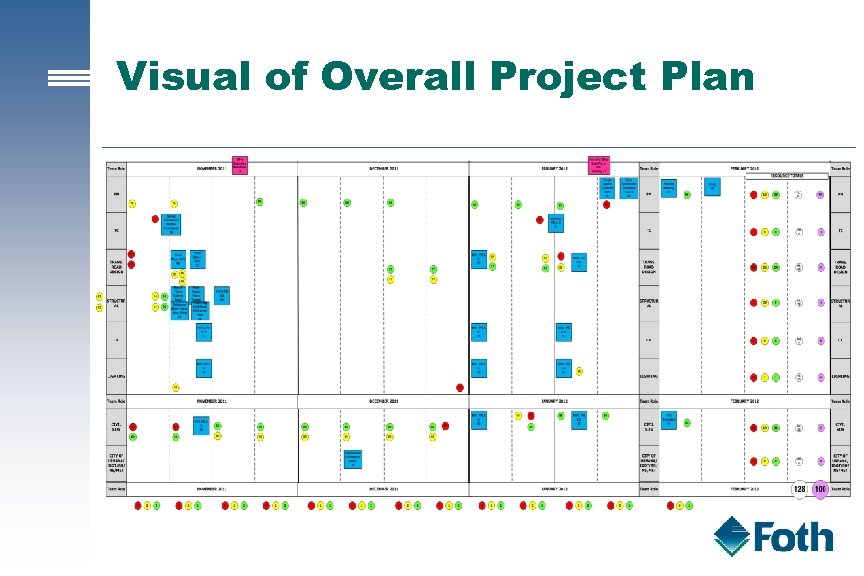 Visual of Overall Project Plan
Visual of Overall Project Plan
 Team working together to create!
Team working together to create!
 Project Planning Exercise
Project Planning Exercise
 Visual Workflow Management
Visual Workflow Management
 Visual Workflow Management v. Objective – Ø Creation and use of Visual Workflow Management Boards and the concurrent utilization of Stand-up Coordination Meetings v. Key Outputs – Ø Focus on near-term tasks Ø Opportunity for rapid feedback on status, plans, and priorities Ø Team members are personally engaged and committed to project activities and commitments Ø Critical project information easily available to ALL team members in a visual format
Visual Workflow Management v. Objective – Ø Creation and use of Visual Workflow Management Boards and the concurrent utilization of Stand-up Coordination Meetings v. Key Outputs – Ø Focus on near-term tasks Ø Opportunity for rapid feedback on status, plans, and priorities Ø Team members are personally engaged and committed to project activities and commitments Ø Critical project information easily available to ALL team members in a visual format
 Tasks are… Action items that directly create tangible progress towards completion of deliverables. - Define pavement removal limits - Approve preliminary plans - Obtain temporary easements - Survey existing utilities - Hold public information meeting–
Tasks are… Action items that directly create tangible progress towards completion of deliverables. - Define pavement removal limits - Approve preliminary plans - Obtain temporary easements - Survey existing utilities - Hold public information meeting–
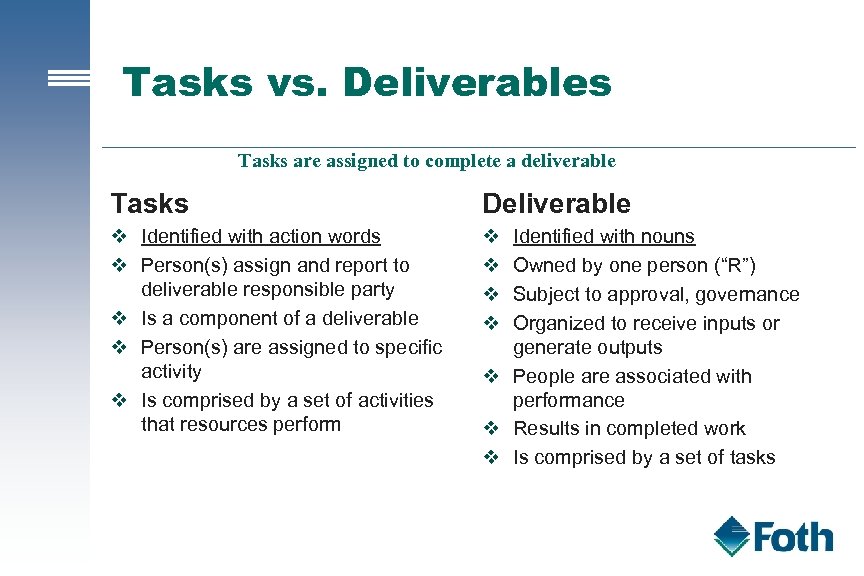 Tasks vs. Deliverables Tasks are assigned to complete a deliverable Tasks Deliverable v Identified with action words v Person(s) assign and report to deliverable responsible party v Is a component of a deliverable v Person(s) are assigned to specific activity v Is comprised by a set of activities that resources perform v v Identified with nouns Owned by one person (“R”) Subject to approval, governance Organized to receive inputs or generate outputs v People are associated with performance v Results in completed work v Is comprised by a set of tasks
Tasks vs. Deliverables Tasks are assigned to complete a deliverable Tasks Deliverable v Identified with action words v Person(s) assign and report to deliverable responsible party v Is a component of a deliverable v Person(s) are assigned to specific activity v Is comprised by a set of activities that resources perform v v Identified with nouns Owned by one person (“R”) Subject to approval, governance Organized to receive inputs or generate outputs v People are associated with performance v Results in completed work v Is comprised by a set of tasks
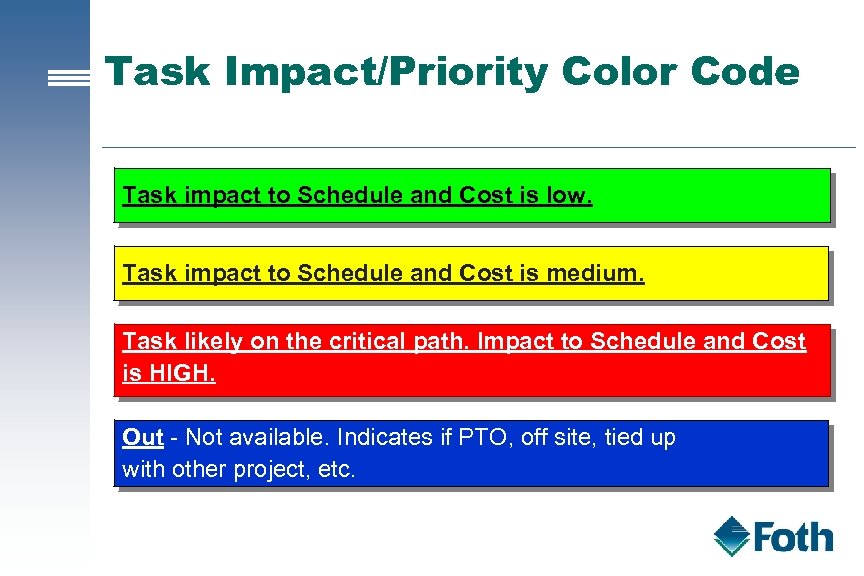 Task Impact/Priority Color Code Task impact to Schedule and Cost is low. Task impact to Schedule and Cost is medium. Task likely on the critical path. Impact to Schedule and Cost is HIGH. Out - Not available. Indicates if PTO, off site, tied up with other project, etc.
Task Impact/Priority Color Code Task impact to Schedule and Cost is low. Task impact to Schedule and Cost is medium. Task likely on the critical path. Impact to Schedule and Cost is HIGH. Out - Not available. Indicates if PTO, off site, tied up with other project, etc.
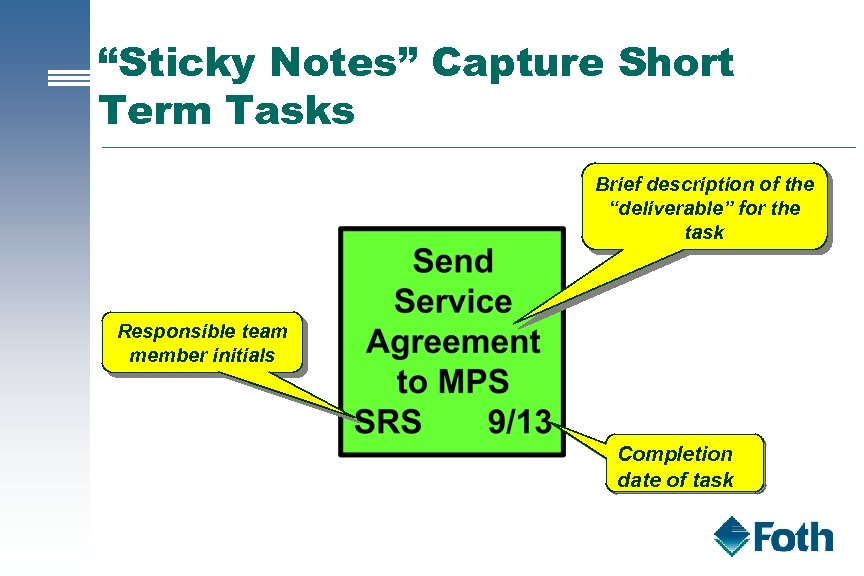 “Sticky Notes” Capture Short Term Tasks Brief description of the “deliverable” for the task Responsible team member initials Completion date of task
“Sticky Notes” Capture Short Term Tasks Brief description of the “deliverable” for the task Responsible team member initials Completion date of task
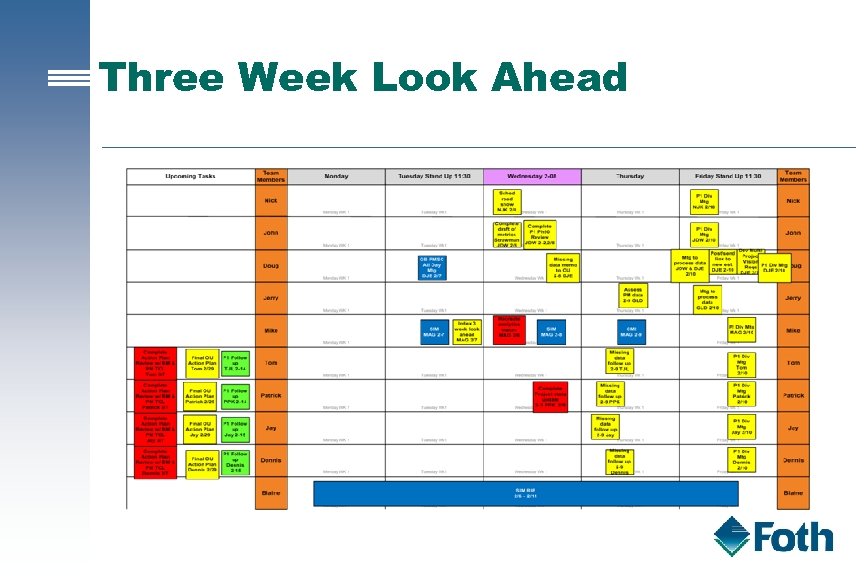 Three Week Look Ahead
Three Week Look Ahead
 Visual Workflow Management Exercise
Visual Workflow Management Exercise
 Stand-up Meetings
Stand-up Meetings
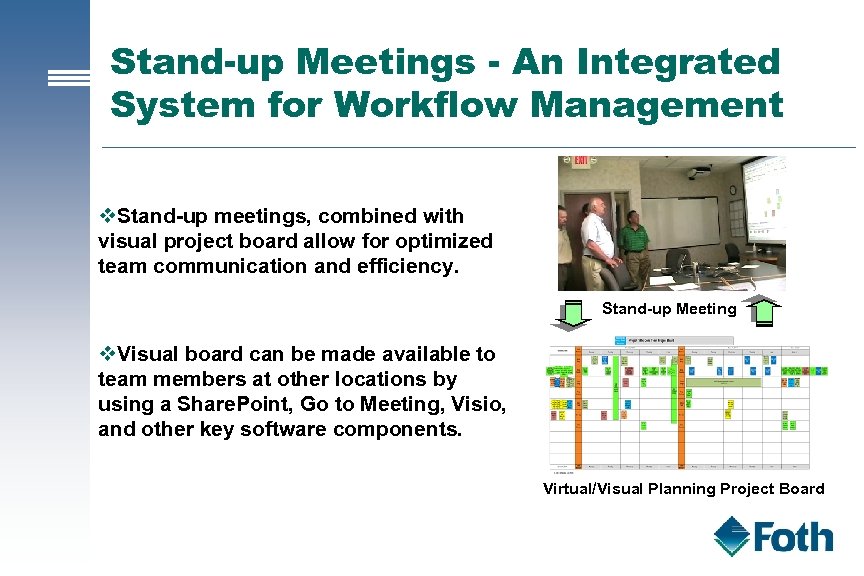 Stand-up Meetings - An Integrated System for Workflow Management v. Stand-up meetings, combined with visual project board allow for optimized team communication and efficiency. Stand-up Meeting v. Visual board can be made available to team members at other locations by using a Share. Point, Go to Meeting, Visio, and other key software components. Virtual/Visual Planning Project Board
Stand-up Meetings - An Integrated System for Workflow Management v. Stand-up meetings, combined with visual project board allow for optimized team communication and efficiency. Stand-up Meeting v. Visual board can be made available to team members at other locations by using a Share. Point, Go to Meeting, Visio, and other key software components. Virtual/Visual Planning Project Board
 Powerful Benefits of Stand-Up Coordination Meetings Ø Shared language among the team Ø Real-time reallocation of resources Ø Focus on value-creating activities Ø Sets a clear work plan for each day Ø Mechanism for behavioral change leading to a transformation of the “Culture” Ø Team identity and emotional commitment
Powerful Benefits of Stand-Up Coordination Meetings Ø Shared language among the team Ø Real-time reallocation of resources Ø Focus on value-creating activities Ø Sets a clear work plan for each day Ø Mechanism for behavioral change leading to a transformation of the “Culture” Ø Team identity and emotional commitment
 How to Conduct a Stand-up Meeting 1. Should be held either at starting time, or just before lunch hour. 2. Should last for no more than 1 – 1 ½ minutes times the number of attendees(15 minutes MAXIMUM duration at first; the team can always agree to a longer duration later). 3. Team members with active tasks should attend – off-site people can “virtual” process – overseas people can be connected through designated “liaison. ” 4. The meeting leader (anyone) should ask three simple questions: • • • What progress have you made since the last meeting? How will you work toward your next key milestone? What do you need from others to meet this goal?
How to Conduct a Stand-up Meeting 1. Should be held either at starting time, or just before lunch hour. 2. Should last for no more than 1 – 1 ½ minutes times the number of attendees(15 minutes MAXIMUM duration at first; the team can always agree to a longer duration later). 3. Team members with active tasks should attend – off-site people can “virtual” process – overseas people can be connected through designated “liaison. ” 4. The meeting leader (anyone) should ask three simple questions: • • • What progress have you made since the last meeting? How will you work toward your next key milestone? What do you need from others to meet this goal?
 Project Risk and Mitigation
Project Risk and Mitigation
 Risk ID & Mitigation Event v. Objective – Ø To perform proactive risk identification and mitigation for the project. v. Key Outputs – Ø Prioritized List of Risk Issues Ø Action Assignments for Risk Mitigation
Risk ID & Mitigation Event v. Objective – Ø To perform proactive risk identification and mitigation for the project. v. Key Outputs – Ø Prioritized List of Risk Issues Ø Action Assignments for Risk Mitigation
 Risk Mitigation – A Critical Opportunity for Risk Management v Safety Risk Ø Ø Ø Is team unaware of unusual safety conditions Confined space/Lock out – Tag Out/Fall protection/PPE Requirements for “Safety in Design” v Contract Risk Ø Ø Ø Missing the target Misinterpreting customer needs Errors in project estimates v Technical Risk Ø Ø Ø Technical feasibility issues Excessive design iterations Planning for “discovery” v Schedule Risk Ø Ø Ø Lack of needed resources Disruptive changes to requirements Supplier/material lead time v Cost/Quality Risk: Ø Ø Ø Critical-to-Quality issues Critical-to-Cost issues Installation issues
Risk Mitigation – A Critical Opportunity for Risk Management v Safety Risk Ø Ø Ø Is team unaware of unusual safety conditions Confined space/Lock out – Tag Out/Fall protection/PPE Requirements for “Safety in Design” v Contract Risk Ø Ø Ø Missing the target Misinterpreting customer needs Errors in project estimates v Technical Risk Ø Ø Ø Technical feasibility issues Excessive design iterations Planning for “discovery” v Schedule Risk Ø Ø Ø Lack of needed resources Disruptive changes to requirements Supplier/material lead time v Cost/Quality Risk: Ø Ø Ø Critical-to-Quality issues Critical-to-Cost issues Installation issues
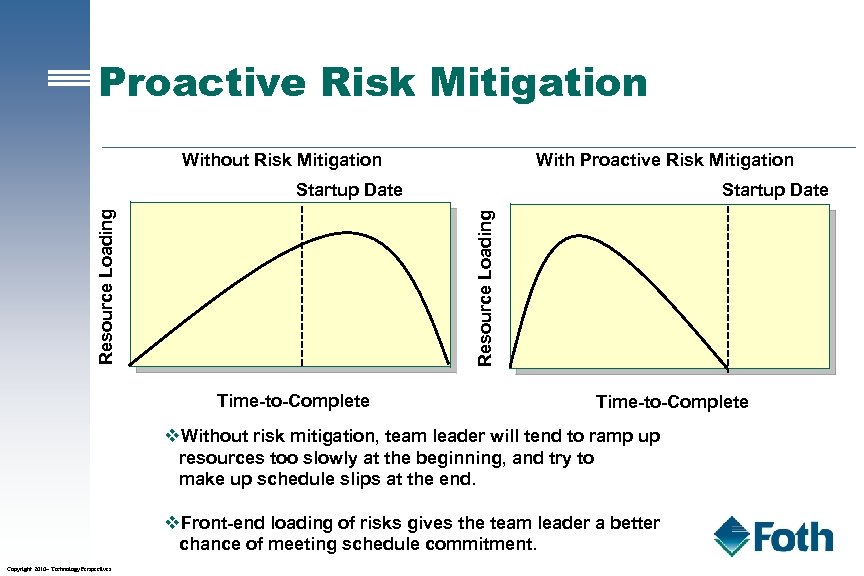 Proactive Risk Mitigation Without Risk Mitigation With Proactive Risk Mitigation Startup Date Resource Loading Startup Date Time-to-Complete v. Without risk mitigation, team leader will tend to ramp up resources too slowly at the beginning, and try to make up schedule slips at the end. v. Front-end loading of risks gives the team leader a better chance of meeting schedule commitment. Copyright 2010– Technology Perspectives
Proactive Risk Mitigation Without Risk Mitigation With Proactive Risk Mitigation Startup Date Resource Loading Startup Date Time-to-Complete v. Without risk mitigation, team leader will tend to ramp up resources too slowly at the beginning, and try to make up schedule slips at the end. v. Front-end loading of risks gives the team leader a better chance of meeting schedule commitment. Copyright 2010– Technology Perspectives
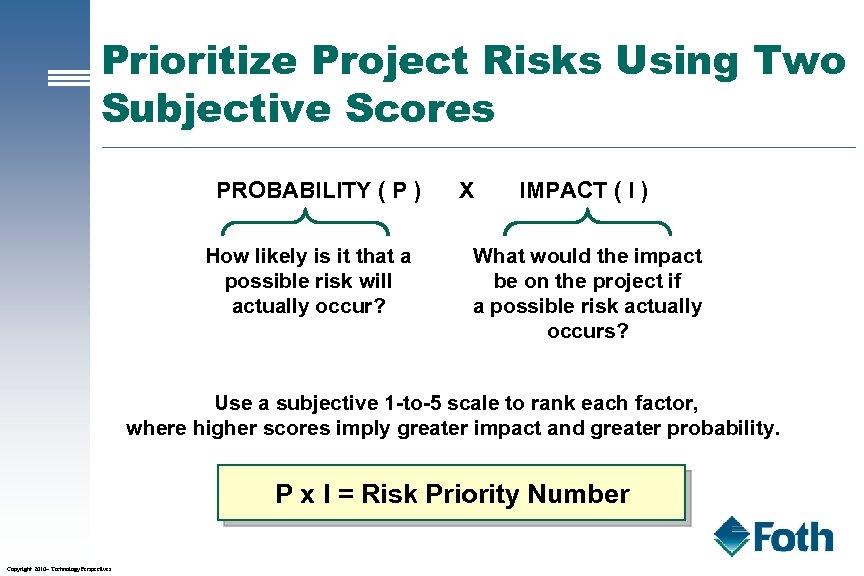 Prioritize Project Risks Using Two Subjective Scores PROBABILITY ( P ) How likely is it that a possible risk will actually occur? X IMPACT ( I ) What would the impact be on the project if a possible risk actually occurs? Use a subjective 1 -to-5 scale to rank each factor, where higher scores imply greater impact and greater probability. P x I = Risk Priority Number Copyright 2010– Technology Perspectives
Prioritize Project Risks Using Two Subjective Scores PROBABILITY ( P ) How likely is it that a possible risk will actually occur? X IMPACT ( I ) What would the impact be on the project if a possible risk actually occurs? Use a subjective 1 -to-5 scale to rank each factor, where higher scores imply greater impact and greater probability. P x I = Risk Priority Number Copyright 2010– Technology Perspectives
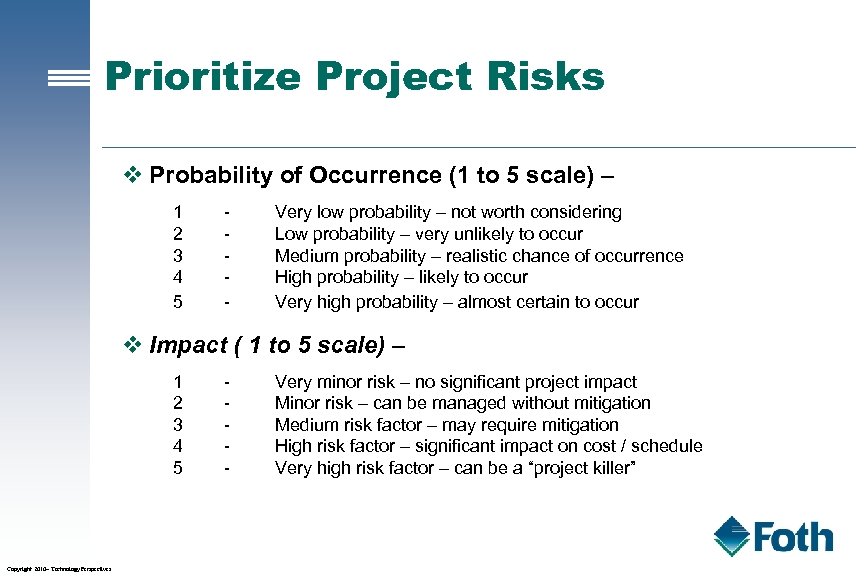 Prioritize Project Risks v Probability of Occurrence (1 to 5 scale) – 1 2 3 4 5 - Very low probability – not worth considering Low probability – very unlikely to occur Medium probability – realistic chance of occurrence High probability – likely to occur Very high probability – almost certain to occur v Impact ( 1 to 5 scale) – 1 2 3 4 5 Copyright 2010– Technology Perspectives - Very minor risk – no significant project impact Minor risk – can be managed without mitigation Medium risk factor – may require mitigation High risk factor – significant impact on cost / schedule Very high risk factor – can be a “project killer”
Prioritize Project Risks v Probability of Occurrence (1 to 5 scale) – 1 2 3 4 5 - Very low probability – not worth considering Low probability – very unlikely to occur Medium probability – realistic chance of occurrence High probability – likely to occur Very high probability – almost certain to occur v Impact ( 1 to 5 scale) – 1 2 3 4 5 Copyright 2010– Technology Perspectives - Very minor risk – no significant project impact Minor risk – can be managed without mitigation Medium risk factor – may require mitigation High risk factor – significant impact on cost / schedule Very high risk factor – can be a “project killer”
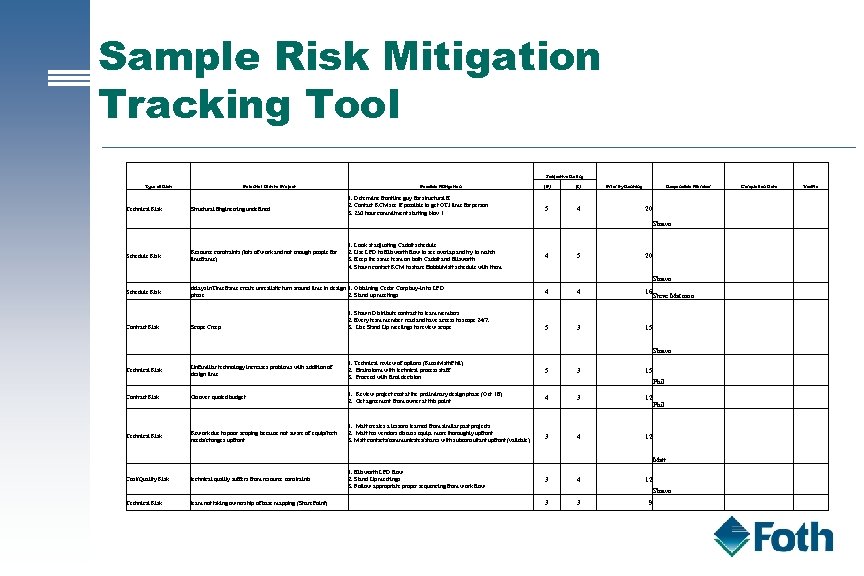 Sample Risk Mitigation Tracking Tool Subjective Rating Type of Risk Technical Risk Potential Risk to Project Structural Engineering undefined Possible Mitigation 1. Determine frontline guy for structural E 2. Contact RCM see if possible to get OTJ time for person 3. 250 hour commitment starting Nov 1 (P) (I) 5 4 Priority Ranking Responsible Member Completion Date Yes/No 20 Shawn delays in. Timeframe create unrealistic turn around time in design 1. Obtaining Cedar Corp buy-in to LPD phase 2. Stand up meetings Contract Risk Technical Risk Scope Creep 1. Shawn Distribute contract to team members 2. Every team member read and have access to scope 24/7. 3. Use Stand Up meetings to review scope 16 5 3 Unfamiliar technology increases problems with addition of design time 5 Go over quoted budget 1. Review project cost at the preliminary design phase (Oct 18) 2. Get agreement from owner at this point 4 1. Matt creates a lessons learned from similar past projects 2. Matt has vendors discuss equip. more thoroughly upfront 3. Matt contacts/communicates/shares with subconsultant upfront (validate) Cost/Quality Risk technical quality suffers from resource constraints 1. Ellsworth LPD flow 2. Stand Up meetings 3. Follow appropriate proper sequencing from work flow Technical Risk team not taking ownership of base mapping (Share. Point) Phil 15 1. Technical review of options (Russ/Matt/Phil) 2. Brainstorm with technical process staff 3. Proceed with final decision Rework due to poor scoping because not aware of equip/tech needs/changes upfront Shawn 4 20 4 Steve Marmon Phil 5 Matt Schedule Risk 4 Shawn Resource constraints (lots of work and not enough people for timeframe) Shawn 1. Look at adjusting Cadott schedule 2. Use LPD to Ellsworth flow to see overlap and try to match 3. Keep the same team on both Cadott and Ellsworth 4. Shawn contact RCM to share Bobbi/Matt schedule with them Schedule Risk 3 3 3 4 3 3 15 12 12 12 9
Sample Risk Mitigation Tracking Tool Subjective Rating Type of Risk Technical Risk Potential Risk to Project Structural Engineering undefined Possible Mitigation 1. Determine frontline guy for structural E 2. Contact RCM see if possible to get OTJ time for person 3. 250 hour commitment starting Nov 1 (P) (I) 5 4 Priority Ranking Responsible Member Completion Date Yes/No 20 Shawn delays in. Timeframe create unrealistic turn around time in design 1. Obtaining Cedar Corp buy-in to LPD phase 2. Stand up meetings Contract Risk Technical Risk Scope Creep 1. Shawn Distribute contract to team members 2. Every team member read and have access to scope 24/7. 3. Use Stand Up meetings to review scope 16 5 3 Unfamiliar technology increases problems with addition of design time 5 Go over quoted budget 1. Review project cost at the preliminary design phase (Oct 18) 2. Get agreement from owner at this point 4 1. Matt creates a lessons learned from similar past projects 2. Matt has vendors discuss equip. more thoroughly upfront 3. Matt contacts/communicates/shares with subconsultant upfront (validate) Cost/Quality Risk technical quality suffers from resource constraints 1. Ellsworth LPD flow 2. Stand Up meetings 3. Follow appropriate proper sequencing from work flow Technical Risk team not taking ownership of base mapping (Share. Point) Phil 15 1. Technical review of options (Russ/Matt/Phil) 2. Brainstorm with technical process staff 3. Proceed with final decision Rework due to poor scoping because not aware of equip/tech needs/changes upfront Shawn 4 20 4 Steve Marmon Phil 5 Matt Schedule Risk 4 Shawn Resource constraints (lots of work and not enough people for timeframe) Shawn 1. Look at adjusting Cadott schedule 2. Use LPD to Ellsworth flow to see overlap and try to match 3. Keep the same team on both Cadott and Ellsworth 4. Shawn contact RCM to share Bobbi/Matt schedule with them Schedule Risk 3 3 3 4 3 3 15 12 12 12 9
 Risk Mitigation Exercise
Risk Mitigation Exercise
 Lean Project Delivery Questions? ? ?
Lean Project Delivery Questions? ? ?



