d3ce7a04d87471bfd9400ae354eaf24d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Incorporating Sustainable Development Objectives into ICT Enabled Land Administration Systems Expert Group Meeting 9 -11 November 2005 Geomatics The University of Melbourne Australia’s International Science Linkages Program Centre for SDIs and Land Administration SDI Requirements of LA Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
Background • Internationally SDI concept has focussed on National SDIs; • However, SDIs are increasingly focussing on large-scale people relevant data (land parcel based data or build environmental data); • A central aspect in understanding these developments is the evolution of mapping, and the growth of land administration systems and national mapping initiatives in different countries. Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
Role of SDI • Starting from the current initiatives to implement SDI as a mechanism to facilitate access/sharing of spatial data hosted in distributed GISs (the conventional concept); • through the access and chain of web services offered by distributed GISs, making use of Internet technologies; • To a new business paradigm where ‘SDI’ is emerging as a ‘virtual jurisdiction’ or ‘virtual enterprise’ to promote the jurisdiction enterprise partnership of SI-organisations (Public/Private) to provide wider scope of data and services, of size and complexity that is beyond their individual capacity. • The development of such SDI requires an integrated platform to support the chaining of services across participating SIorganisations.
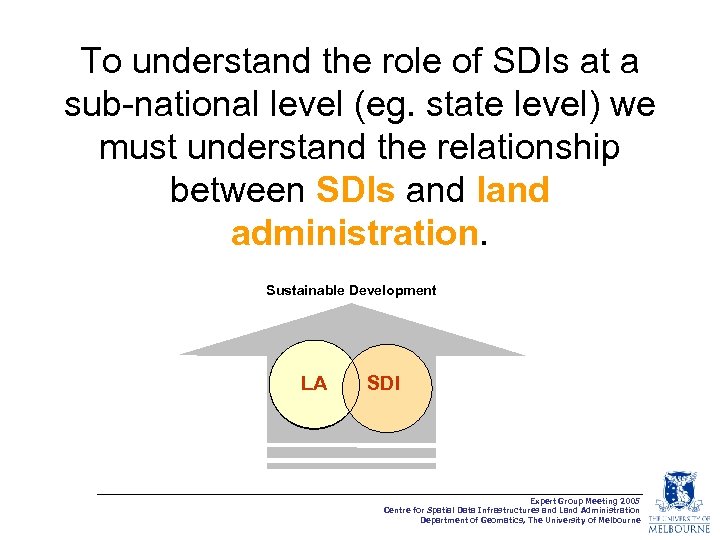
To understand the role of SDIs at a sub-national level (eg. state level) we must understand the relationship between SDIs and land administration. Sustainable Development LA SDI Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
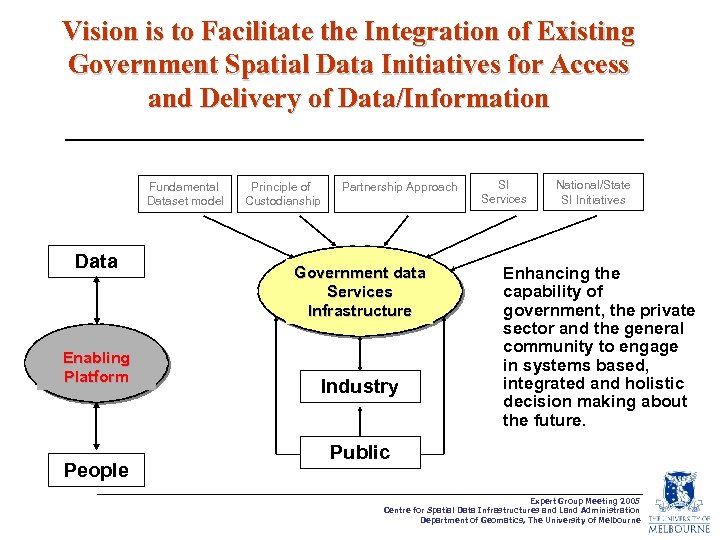
Vision is to Facilitate the Integration of Existing Government Spatial Data Initiatives for Access and Delivery of Data/Information Fundamental Dataset model Data Enabling Platform Connecting people to data and services People Principle of Custodianship Partnership Approach Government data Services Infrastructure Industry SI Services National/State SI Initiatives Enhancing the capability of government, the private sector and the general community to engage in systems based, integrated and holistic decision making about the future. Public Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne

The Role of Sub-National Government and the Private Sector in Future SDIs Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
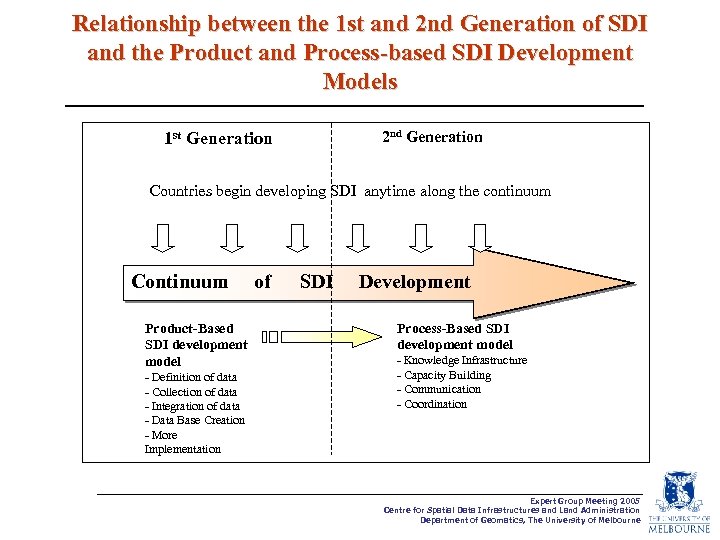
Relationship between the 1 st and 2 nd Generation of SDI and the Product and Process-based SDI Development Models 2 nd Generation 1 st Generation Countries begin developing SDI anytime along the continuum Continuum Product-Based SDI development model - Definition of data - Collection of data - Integration of data - Data Base Creation - More Implementation of SDI Development Process-Based SDI development model - Knowledge Infrastructure - Capacity Building - Communication - Coordination Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
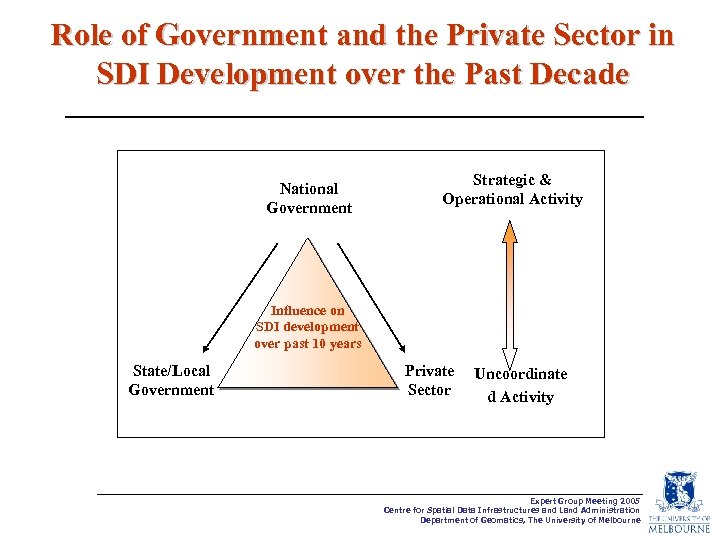
Role of Government and the Private Sector in SDI Development over the Past Decade National Government Strategic & Operational Activity Influence on SDI development over past 10 years State/Local Government Private Sector Uncoordinate d Activity Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
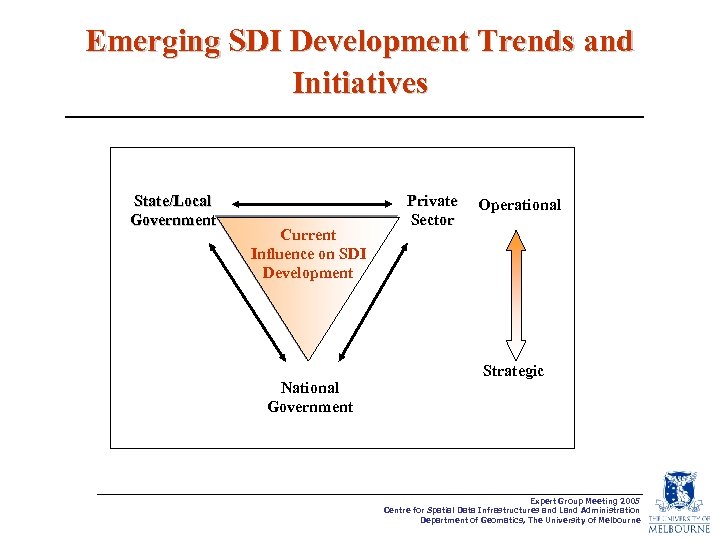
Emerging SDI Development Trends and Initiatives State/Local Government Current Influence on SDI Development National Government Private Sector Operational Strategic Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
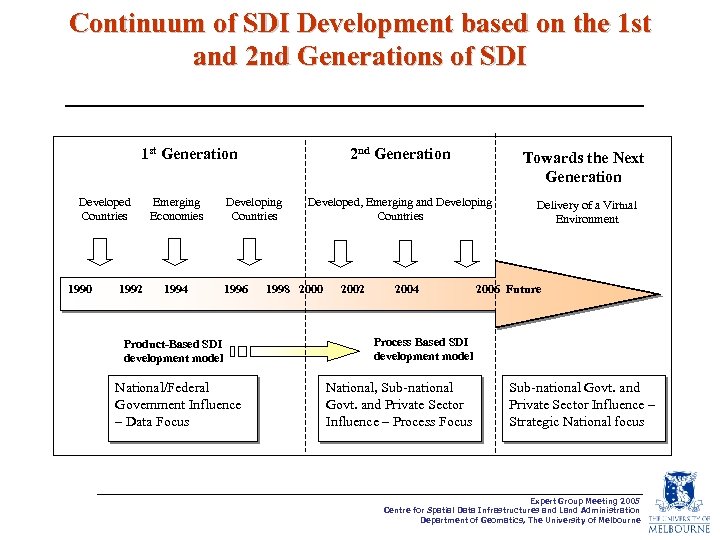
Continuum of SDI Development based on the 1 st and 2 nd Generations of SDI 1 st Generation Developed Countries 1990 1992 Emerging Economies 1994 2 nd Generation Developing Countries 1996 Product-Based SDI development model National/Federal Government Influence – Data Focus Towards the Next Generation Developed, Emerging and Developing Countries Delivery of a Virtual Environment 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 Future Process Based SDI development model National, Sub-national Govt. and Private Sector Influence – Process Focus Sub-national Govt. and Private Sector Influence – Strategic National focus Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
UN-FIG Bogor Declaration on Cadastral Reform (1996) The spatial cadastral framework (usually a cadastral map) should be a fundamental layer within a Nation SDI so that topographic and cadastral maps are homogenous. Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne

Integration of Built and Natural Environmental Datasets within a National SDI Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
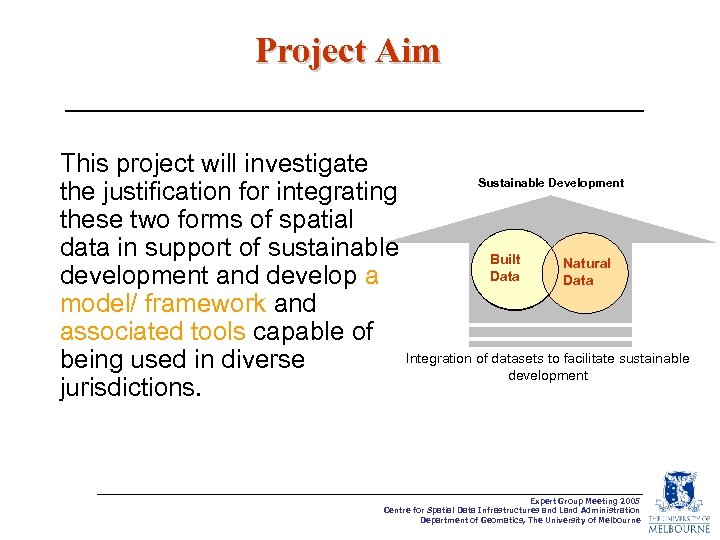
Project Aim This project will investigate Sustainable Development the justification for integrating these two forms of spatial data in support of sustainable Built Natural Data development and develop a Data model/ framework and associated tools capable of Integration of datasets to facilitate sustainable being used in diverse development jurisdictions. Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
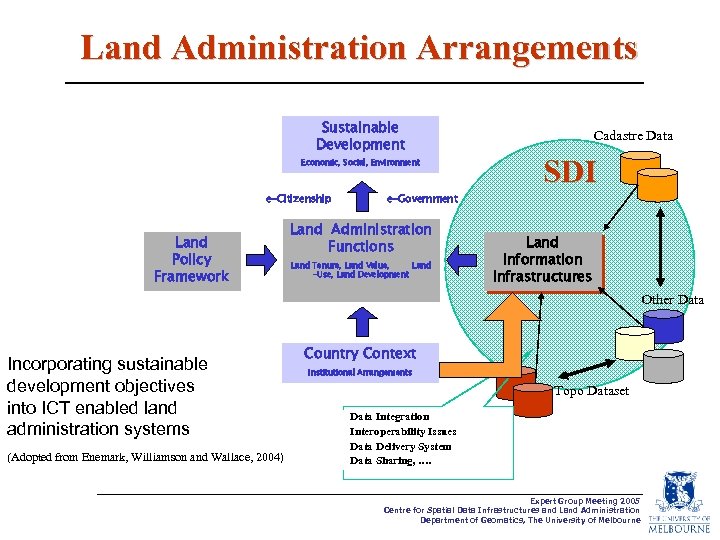
Land Administration Arrangements Sustainable Development Economic, Social, Environment e-Citizenship Land Policy Framework Cadastre Data SDI e-Government Land Administration Functions Land Tenure, Land Value, Land -Use, Land Development Land Information Infrastructures Other Data Incorporating sustainable development objectives into ICT enabled land administration systems (Adopted from Enemark, Williamson and Wallace, 2004) Country Context Institutional Arrangements Topo Dataset Data Integration Interoperability Issues Data Delivery System Data Sharing, …. Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
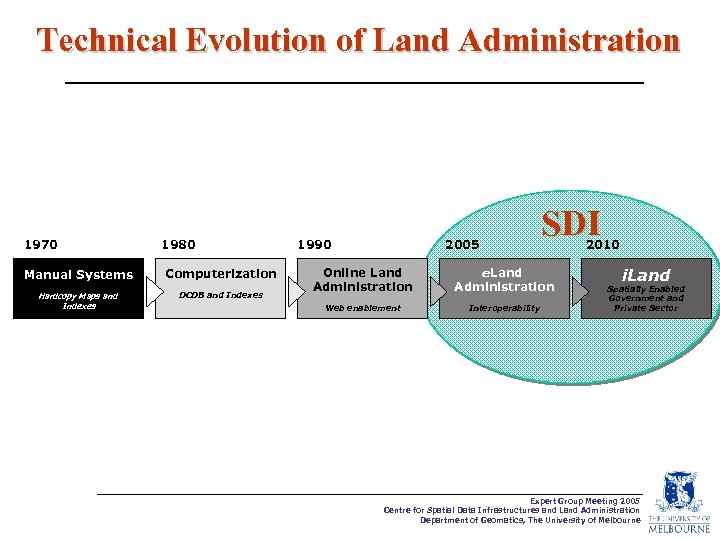
Technical Evolution of Land Administration 1970 Manual Systems Hardcopy Maps and Indexes 1980 Computerization DCDB and Indexes 1990 2005 SDI Online Land Administration e. Land Administration Web enablement Interoperability 2010 i. Land Spatially Enabled Government and Private Sector Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
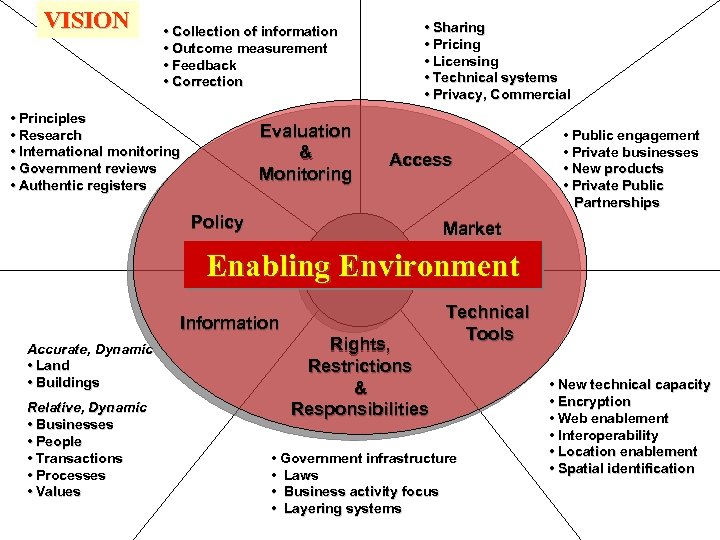
VISION • Collection of information • Outcome measurement • Feedback • Correction • Principles • Research • International monitoring • Government reviews • Authentic registers Evaluation & Monitoring • Sharing • Pricing • Licensing • Technical systems • Privacy, Commercial Access Policy • Public engagement • Private businesses • New products • Private Public Partnerships Market Services Enabling Environment i. Land Information Accurate, Dynamic • Land • Buildings Relative, Dynamic • Businesses • People • Transactions • Processes • Values Rights, Restrictions & Responsibilities Technical Tools • Government infrastructure • Laws • Business activity focus • Layering systems • New technical capacity • Encryption • Web enablement • Interoperability • Location enablement • Spatial identification

Thank you Expert Group Meeting 2005 Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
d3ce7a04d87471bfd9400ae354eaf24d.ppt