91b41484d3880b409cde14596021672e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Income poverty and material deprivation in the Czech Republic with focus on children Tomáš Sirovátka, Ondřej Hora Masaryk University and Research Institute of Labor and Social Affairs Paper for the International Workshop Impact of Poverty and Social Exclusion on Children´ s Lives and Their Well-being 8 -9 September 2008, Bratislava
Income poverty and material deprivation in the Czech Republic with focus on children Tomáš Sirovátka, Ondřej Hora Masaryk University and Research Institute of Labor and Social Affairs Paper for the International Workshop Impact of Poverty and Social Exclusion on Children´ s Lives and Their Well-being 8 -9 September 2008, Bratislava
 Why (child) poverty in focus ? • reducing poverty as a fundamental goal of social policy, and an indicator of its effectiveness, social inclusion agenda • ‚new social risks‘ (LM instability, family instability etc. ), • welfares state re-calibration, activation policies • poverty is negatively affecting one’s life chances: low education and deficient cognitive skills, lower earnings and high unemployment risks • problem for an “open society”, equality of opportunity is the prerequisite for the legitimacy of market competition • children are a country’s future - but they cannot immediately take full responsibility
Why (child) poverty in focus ? • reducing poverty as a fundamental goal of social policy, and an indicator of its effectiveness, social inclusion agenda • ‚new social risks‘ (LM instability, family instability etc. ), • welfares state re-calibration, activation policies • poverty is negatively affecting one’s life chances: low education and deficient cognitive skills, lower earnings and high unemployment risks • problem for an “open society”, equality of opportunity is the prerequisite for the legitimacy of market competition • children are a country’s future - but they cannot immediately take full responsibility
 Aim of the paper evaluation of the risk of poverty and material deprivation among children in the Czech within the general context (including the role of social protection) • risk of child poverty, households with children • indicators of material deprivation • role and effects of social transfers in the elimination of the risk of poverty • factors which influence the risk of income poverty and material deprivation • international comparisons
Aim of the paper evaluation of the risk of poverty and material deprivation among children in the Czech within the general context (including the role of social protection) • risk of child poverty, households with children • indicators of material deprivation • role and effects of social transfers in the elimination of the risk of poverty • factors which influence the risk of income poverty and material deprivation • international comparisons
 Data sources • data - European Union – Statistics on Income and Living Conditions (EU-SILC) • References to other sources (UNICEF, Czech surveys) • SILC in CZ: • In 2005 - 4351 households, then 3852 different ones in 2006, the households surveyed in 2005 were surveyed again a year later; of these households 3631 were successfully surveyed • The response rate of the newly-surveyed households in 2006 was excellent (89 %), but among households surveyed for the second time only 65. 5 %, which together made the overall response rate a satisfying 75. 8 percent.
Data sources • data - European Union – Statistics on Income and Living Conditions (EU-SILC) • References to other sources (UNICEF, Czech surveys) • SILC in CZ: • In 2005 - 4351 households, then 3852 different ones in 2006, the households surveyed in 2005 were surveyed again a year later; of these households 3631 were successfully surveyed • The response rate of the newly-surveyed households in 2006 was excellent (89 %), but among households surveyed for the second time only 65. 5 %, which together made the overall response rate a satisfying 75. 8 percent.
 The risk of poverty -basic findings • in the CR (10 %) - among the lowest in Europe (the average in the EU 25 is around 16 %) • strongly concentrated within a specific categories of the population • differences in the at-risk-of poverty rate among these groups are very high • children in the CR are in much greater danger of risk of poverty than the rest of the population, basically twice as much (18 %)
The risk of poverty -basic findings • in the CR (10 %) - among the lowest in Europe (the average in the EU 25 is around 16 %) • strongly concentrated within a specific categories of the population • differences in the at-risk-of poverty rate among these groups are very high • children in the CR are in much greater danger of risk of poverty than the rest of the population, basically twice as much (18 %)
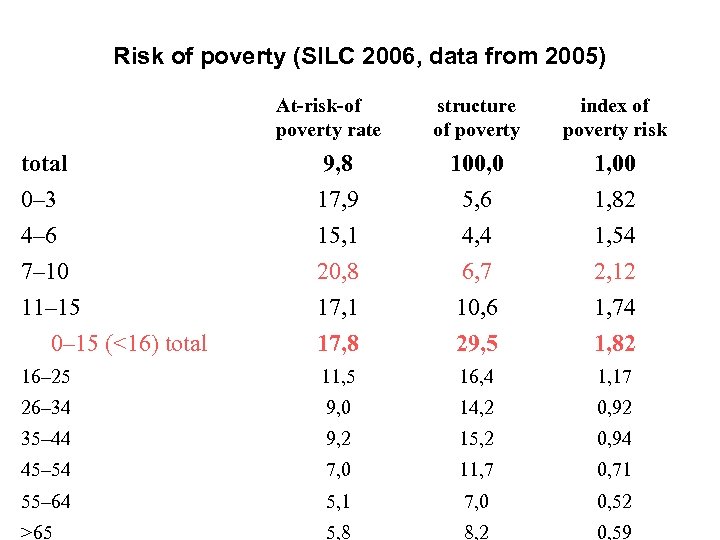 Risk of poverty (SILC 2006, data from 2005) At-risk-of poverty rate structure of poverty index of poverty risk total 9, 8 100, 0 1, 00 0– 3 4– 6 7– 10 11– 15 0– 15 (<16) total 17, 9 15, 1 20, 8 17, 1 17, 8 5, 6 4, 4 6, 7 10, 6 29, 5 1, 82 1, 54 2, 12 1, 74 1, 82 16– 25 11, 5 16, 4 1, 17 26– 34 9, 0 14, 2 0, 92 35– 44 9, 2 15, 2 0, 94 45– 54 7, 0 11, 7 0, 71 55– 64 5, 1 7, 0 0, 52 >65 5, 8 8, 2 0, 59
Risk of poverty (SILC 2006, data from 2005) At-risk-of poverty rate structure of poverty index of poverty risk total 9, 8 100, 0 1, 00 0– 3 4– 6 7– 10 11– 15 0– 15 (<16) total 17, 9 15, 1 20, 8 17, 1 17, 8 5, 6 4, 4 6, 7 10, 6 29, 5 1, 82 1, 54 2, 12 1, 74 1, 82 16– 25 11, 5 16, 4 1, 17 26– 34 9, 0 14, 2 0, 92 35– 44 9, 2 15, 2 0, 94 45– 54 7, 0 11, 7 0, 71 55– 64 5, 1 7, 0 0, 52 >65 5, 8 8, 2 0, 59
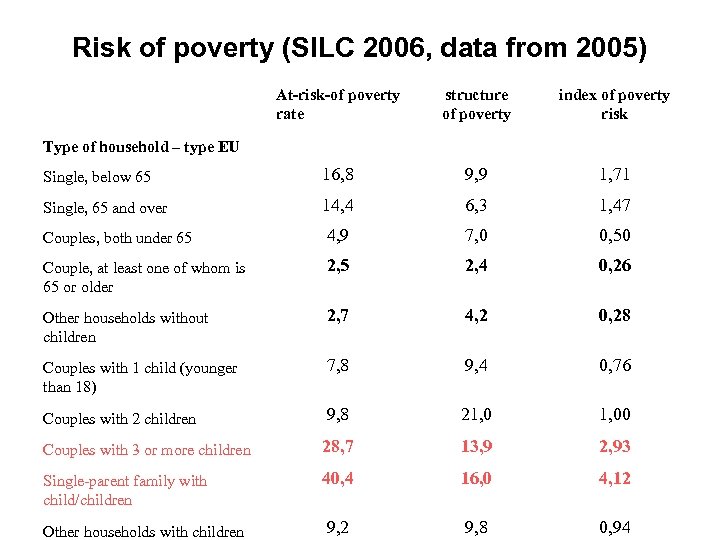 Risk of poverty (SILC 2006, data from 2005) At-risk-of poverty rate structure of poverty index of poverty risk Single, below 65 16, 8 9, 9 1, 71 Single, 65 and over 14, 4 6, 3 1, 47 Couples, both under 65 4, 9 7, 0 0, 50 Couple, at least one of whom is 65 or older 2, 5 2, 4 0, 26 Other households without children 2, 7 4, 2 0, 28 Couples with 1 child (younger than 18) 7, 8 9, 4 0, 76 Couples with 2 children 9, 8 21, 00 Couples with 3 or more children 28, 7 13, 9 2, 93 Single-parent family with child/children 40, 4 16, 0 4, 12 Other households with children 9, 2 9, 8 0, 94 Type of household – type EU
Risk of poverty (SILC 2006, data from 2005) At-risk-of poverty rate structure of poverty index of poverty risk Single, below 65 16, 8 9, 9 1, 71 Single, 65 and over 14, 4 6, 3 1, 47 Couples, both under 65 4, 9 7, 0 0, 50 Couple, at least one of whom is 65 or older 2, 5 2, 4 0, 26 Other households without children 2, 7 4, 2 0, 28 Couples with 1 child (younger than 18) 7, 8 9, 4 0, 76 Couples with 2 children 9, 8 21, 00 Couples with 3 or more children 28, 7 13, 9 2, 93 Single-parent family with child/children 40, 4 16, 0 4, 12 Other households with children 9, 2 9, 8 0, 94 Type of household – type EU
 Risk of poverty (SILC 2006, data from 2005) rate structure index working-employed non-working – unemployed 3, 5 43, 7 45, 8 36, 1 0, 36 4, 46 non-working retired non-working – other non-active 6, 7 14, 5 12, 7 5, 4 0, 68 1, 48 26, 5 19, 2 2, 70 7, 8 76, 4 0, 80 2, 4 0, 20 low level of education - both basic education middle level (at least one) high level (at least one)
Risk of poverty (SILC 2006, data from 2005) rate structure index working-employed non-working – unemployed 3, 5 43, 7 45, 8 36, 1 0, 36 4, 46 non-working retired non-working – other non-active 6, 7 14, 5 12, 7 5, 4 0, 68 1, 48 26, 5 19, 2 2, 70 7, 8 76, 4 0, 80 2, 4 0, 20 low level of education - both basic education middle level (at least one) high level (at least one)
 The risk of (child)poverty • at-risk-of poverty rate among children up to 10 years of age in single-parent families ranges from 40 to 50 % • in families with numerous members (over 3 children) it ranges from 22 – 31 % • In unemployed families child at-risk-of poverty rate is on the level of 43 -68 % (depending on age of child) • The poverty gap is not generally greater among poor children than in overall population at-risk-of poverty (18. 9 % among poor children versus the average of 21. 1 %) • but among children up to 3 years old who are at-risk-of poverty, the poverty gap reaches 27. 6 %
The risk of (child)poverty • at-risk-of poverty rate among children up to 10 years of age in single-parent families ranges from 40 to 50 % • in families with numerous members (over 3 children) it ranges from 22 – 31 % • In unemployed families child at-risk-of poverty rate is on the level of 43 -68 % (depending on age of child) • The poverty gap is not generally greater among poor children than in overall population at-risk-of poverty (18. 9 % among poor children versus the average of 21. 1 %) • but among children up to 3 years old who are at-risk-of poverty, the poverty gap reaches 27. 6 %
 Effectiveness of social transfers • It is relatively high (before social transfers the at-risk-of poverty rate was at 39 %; the effect of social payments in reducing poverty is 75 %) • children under 16 years: only 48 % and after pensions it is 43 % • families with three or more children: 48 % and after pensions it is only 42 % • in single-parent families: 31 %
Effectiveness of social transfers • It is relatively high (before social transfers the at-risk-of poverty rate was at 39 %; the effect of social payments in reducing poverty is 75 %) • children under 16 years: only 48 % and after pensions it is 43 % • families with three or more children: 48 % and after pensions it is only 42 % • in single-parent families: 31 %
 Financial and material deprivation Importance of data: variables like consumption patterns, prices and costs, inflation, ability to use resources, additional resources, duration of income poverty risk…‘what standard of living can the poor achieve? ‘ • data on income and material deprivation confirm some findings concerning the atrisk-of poverty rate (Sp =. 392 - for income poverty risk and income deprivation)
Financial and material deprivation Importance of data: variables like consumption patterns, prices and costs, inflation, ability to use resources, additional resources, duration of income poverty risk…‘what standard of living can the poor achieve? ‘ • data on income and material deprivation confirm some findings concerning the atrisk-of poverty rate (Sp =. 392 - for income poverty risk and income deprivation)
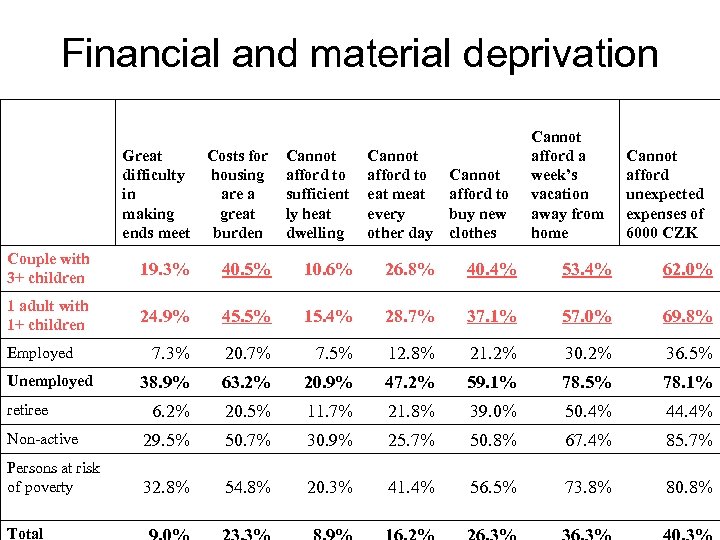 Financial and material deprivation Great difficulty in making ends meet Costs for housing are a great burden Cannot afford to sufficient ly heat dwelling Cannot afford to eat meat every other day Cannot afford to buy new clothes Cannot afford a week’s vacation away from home Couple with 3+ children 19. 3% 40. 5% 10. 6% 26. 8% 40. 4% 53. 4% 62. 0% 1 adult with 1+ children 24. 9% 45. 5% 15. 4% 28. 7% 37. 1% 57. 0% 69. 8% 7. 3% 20. 7% 7. 5% 12. 8% 21. 2% 30. 2% 36. 5% 38. 9% 63. 2% 20. 9% 47. 2% 59. 1% 78. 5% 78. 1% 6. 2% 20. 5% 11. 7% 21. 8% 39. 0% 50. 4% 44. 4% Non-active 29. 5% 50. 7% 30. 9% 25. 7% 50. 8% 67. 4% 85. 7% Persons at risk of poverty 32. 8% 54. 8% 20. 3% 41. 4% 56. 5% 73. 8% 80. 8% Employed Unemployed retiree Total Cannot afford unexpected expenses of 6000 CZK
Financial and material deprivation Great difficulty in making ends meet Costs for housing are a great burden Cannot afford to sufficient ly heat dwelling Cannot afford to eat meat every other day Cannot afford to buy new clothes Cannot afford a week’s vacation away from home Couple with 3+ children 19. 3% 40. 5% 10. 6% 26. 8% 40. 4% 53. 4% 62. 0% 1 adult with 1+ children 24. 9% 45. 5% 15. 4% 28. 7% 37. 1% 57. 0% 69. 8% 7. 3% 20. 7% 7. 5% 12. 8% 21. 2% 30. 2% 36. 5% 38. 9% 63. 2% 20. 9% 47. 2% 59. 1% 78. 5% 78. 1% 6. 2% 20. 5% 11. 7% 21. 8% 39. 0% 50. 4% 44. 4% Non-active 29. 5% 50. 7% 30. 9% 25. 7% 50. 8% 67. 4% 85. 7% Persons at risk of poverty 32. 8% 54. 8% 20. 3% 41. 4% 56. 5% 73. 8% 80. 8% Employed Unemployed retiree Total Cannot afford unexpected expenses of 6000 CZK
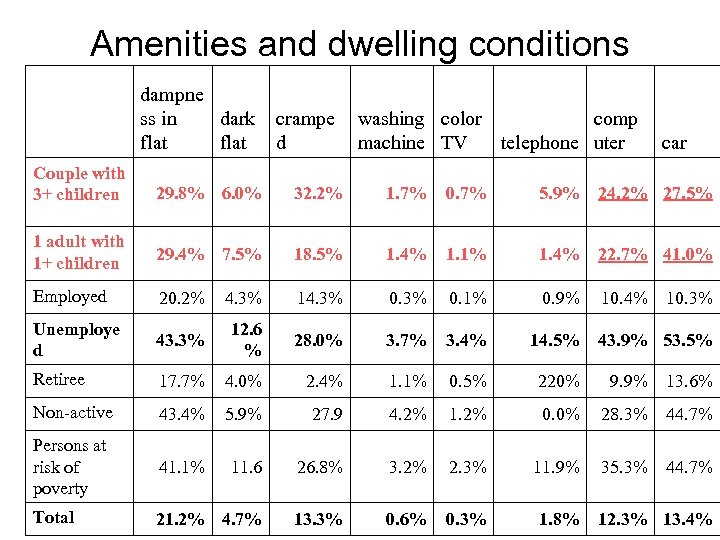 Amenities and dwelling conditions dampne dark ss in flat crampe d washing color comp machine TV telephone uter car Couple with 3+ children 29. 8% 6. 0% 32. 2% 1. 7% 0. 7% 5. 9% 24. 2% 27. 5% 1 adult with 1+ children 29. 4% 7. 5% 18. 5% 1. 4% 1. 1% 1. 4% 22. 7% 41. 0% Employed 20. 2% 4. 3% 14. 3% 0. 1% 0. 9% 10. 4% Unemploye d 43. 3% 12. 6 % 28. 0% 3. 7% 3. 4% 14. 5% Retiree 17. 7% 4. 0% 2. 4% 1. 1% 0. 5% 220% 9. 9% 13. 6% Non-active 43. 4% 5. 9% 27. 9 4. 2% 1. 2% 0. 0% 28. 3% 44. 7% Persons at risk of poverty 41. 1% 11. 6 26. 8% 3. 2% 2. 3% 11. 9% 35. 3% 44. 7% Total 21. 2% 4. 7% 13. 3% 0. 6% 0. 3% 1. 8% 10. 3% 43. 9% 53. 5% 12. 3% 13. 4%
Amenities and dwelling conditions dampne dark ss in flat crampe d washing color comp machine TV telephone uter car Couple with 3+ children 29. 8% 6. 0% 32. 2% 1. 7% 0. 7% 5. 9% 24. 2% 27. 5% 1 adult with 1+ children 29. 4% 7. 5% 18. 5% 1. 4% 1. 1% 1. 4% 22. 7% 41. 0% Employed 20. 2% 4. 3% 14. 3% 0. 1% 0. 9% 10. 4% Unemploye d 43. 3% 12. 6 % 28. 0% 3. 7% 3. 4% 14. 5% Retiree 17. 7% 4. 0% 2. 4% 1. 1% 0. 5% 220% 9. 9% 13. 6% Non-active 43. 4% 5. 9% 27. 9 4. 2% 1. 2% 0. 0% 28. 3% 44. 7% Persons at risk of poverty 41. 1% 11. 6 26. 8% 3. 2% 2. 3% 11. 9% 35. 3% 44. 7% Total 21. 2% 4. 7% 13. 3% 0. 6% 0. 3% 1. 8% 10. 3% 43. 9% 53. 5% 12. 3% 13. 4%
 Factors influencing (child) poverty and deprivation • two main “social risks”, often in combination: these are unemployment, and instability/incompleteness of the family • overlap is most often seen among families with many children, and single-parent families with children • Important problem - necessity of covering from one’s income certain vital expenses such as rent, energy, and services, or partially necessary expenses such as example medicine, telephone, children’s needs, basic food and clothing
Factors influencing (child) poverty and deprivation • two main “social risks”, often in combination: these are unemployment, and instability/incompleteness of the family • overlap is most often seen among families with many children, and single-parent families with children • Important problem - necessity of covering from one’s income certain vital expenses such as rent, energy, and services, or partially necessary expenses such as example medicine, telephone, children’s needs, basic food and clothing
 Factors influencing (child) poverty and deprivation • 70 % of people in risk of income poverty in the CR live in families with children • children mean in many cases non-activity on the labor market, and/or diffusion of income – whether wages or social benefits – among a larger number of family members • about 8 % of children in the Czech Republic are living in jobless households • parental leave is provided for a longer period – up to 4 years of a child (but at relative low rate), after parental leave when women enter the labor market, they face two -four times higher risk of unemployment than men or women without children
Factors influencing (child) poverty and deprivation • 70 % of people in risk of income poverty in the CR live in families with children • children mean in many cases non-activity on the labor market, and/or diffusion of income – whether wages or social benefits – among a larger number of family members • about 8 % of children in the Czech Republic are living in jobless households • parental leave is provided for a longer period – up to 4 years of a child (but at relative low rate), after parental leave when women enter the labor market, they face two -four times higher risk of unemployment than men or women without children
 Factors influencing (child) poverty and deprivation • Regression analysis (logistic regression) shows that (other factors controled): • people in unemployed households are exposed about 37 times as high risk of poverty than people in the employed households and people in non-active households to about 21 times as high • the households with three and more children, incomplete families with children about 16 times as high risk than households of the partners without children • Summed up, the most important is the impact of labor market status of the household, and then (in a lesser degree) family situation - the number of children and completeness of the family
Factors influencing (child) poverty and deprivation • Regression analysis (logistic regression) shows that (other factors controled): • people in unemployed households are exposed about 37 times as high risk of poverty than people in the employed households and people in non-active households to about 21 times as high • the households with three and more children, incomplete families with children about 16 times as high risk than households of the partners without children • Summed up, the most important is the impact of labor market status of the household, and then (in a lesser degree) family situation - the number of children and completeness of the family
 Social Protection and Child Poverty • as soon as a household becomes dependent predominantly on social benefits (besides pensions), it falls below the poverty line • in public political debate there is a predominant conviction that social payments are generous • the subsistence level has been indexed, unlike pensions, pegged to the rise of employment income • when we compare the average replacement rates of social assistance benefits to average wages for four types of families (a single person, a couple, a lone parent + two children, a couple + two children), in 22 OECD countries in the income group of 67 % of APW, then the replacement rate in the Czech Republic is 52. 1 %, while the average in 22 OECD countries it is 54. 8 % (based on 2004 data) • It is lower only in Poland, Spain, Slovakia, Hungary, Greece and Italy
Social Protection and Child Poverty • as soon as a household becomes dependent predominantly on social benefits (besides pensions), it falls below the poverty line • in public political debate there is a predominant conviction that social payments are generous • the subsistence level has been indexed, unlike pensions, pegged to the rise of employment income • when we compare the average replacement rates of social assistance benefits to average wages for four types of families (a single person, a couple, a lone parent + two children, a couple + two children), in 22 OECD countries in the income group of 67 % of APW, then the replacement rate in the Czech Republic is 52. 1 %, while the average in 22 OECD countries it is 54. 8 % (based on 2004 data) • It is lower only in Poland, Spain, Slovakia, Hungary, Greece and Italy
 Social Protection and Child Poverty • Social/family related benefits aimed at families have declined relatively as a result of the link between eligibility and their amount to the subsistence level (it is declining compared to earnings) • there has been an increase in the cost of living, especially the cost of housing (evident in data on financial deprivation) • Since 2008 (though it is not yet apparent in the data) there has been a freeze in the subsistence level due to the discontinuing of regular indexing • while prices including the price of food have risen faster than in previous years • in addition, household expenses are rising in other areas such as health care, including care for children (cofinancing).
Social Protection and Child Poverty • Social/family related benefits aimed at families have declined relatively as a result of the link between eligibility and their amount to the subsistence level (it is declining compared to earnings) • there has been an increase in the cost of living, especially the cost of housing (evident in data on financial deprivation) • Since 2008 (though it is not yet apparent in the data) there has been a freeze in the subsistence level due to the discontinuing of regular indexing • while prices including the price of food have risen faster than in previous years • in addition, household expenses are rising in other areas such as health care, including care for children (cofinancing).
 International comparison • Czech Republic is the only country in the EU to exhibit a large difference between the overall risk of income poverty and higher level of risk of poverty among children • findings by UNICEF (2007) on child well-being rank Czech Republic in the lowest third (on 18 th position) out of 25 OECD countries • about 40 % of Czech children reported low family affluence (lacking car, own bedroom, holidays last year, a computer) • 28 % of Czech children reported less than six educational possessions (lacking a study desk, quiet place for study, a computer, calculator, dictionary, text books) • negative impacts on educational disadvantage and transmission of poverty have been indicated: people in income disadvantage only in 50% reported that they have the choice for sending children to college/middle school (Sirovátka and Mareš 2008).
International comparison • Czech Republic is the only country in the EU to exhibit a large difference between the overall risk of income poverty and higher level of risk of poverty among children • findings by UNICEF (2007) on child well-being rank Czech Republic in the lowest third (on 18 th position) out of 25 OECD countries • about 40 % of Czech children reported low family affluence (lacking car, own bedroom, holidays last year, a computer) • 28 % of Czech children reported less than six educational possessions (lacking a study desk, quiet place for study, a computer, calculator, dictionary, text books) • negative impacts on educational disadvantage and transmission of poverty have been indicated: people in income disadvantage only in 50% reported that they have the choice for sending children to college/middle school (Sirovátka and Mareš 2008).
 Conclusions • the risk of income poverty among children is almost twice as high compared to the population • highly concentrated (children) from several reasons • the effectiveness of social transfers in eliminating poverty risk is lower in the case of children • the problem of child poverty has not yet been seriously reflected upon or discussed by the public and political sphere or the relevant actors in that area • material deprivation is also an important problem for children - in many areas exceeding the level of the risk of income poverty
Conclusions • the risk of income poverty among children is almost twice as high compared to the population • highly concentrated (children) from several reasons • the effectiveness of social transfers in eliminating poverty risk is lower in the case of children • the problem of child poverty has not yet been seriously reflected upon or discussed by the public and political sphere or the relevant actors in that area • material deprivation is also an important problem for children - in many areas exceeding the level of the risk of income poverty
 Conclusions • key factors - the status of the household on the labor market, and family situation • burdensome for many households is the cost of housing • lagging of the subsistence level relative to the development of other incomes • this weakens also the extent and level of eligibility for family benefits which are tied to a multiple of the subsistence level What is needed the most ? • improved access to the labor market for the vulnerable groups (among other women during and after parental leave) • when employment is not accessible due to caring obligations, adequacy of the benefits plays more and more important role
Conclusions • key factors - the status of the household on the labor market, and family situation • burdensome for many households is the cost of housing • lagging of the subsistence level relative to the development of other incomes • this weakens also the extent and level of eligibility for family benefits which are tied to a multiple of the subsistence level What is needed the most ? • improved access to the labor market for the vulnerable groups (among other women during and after parental leave) • when employment is not accessible due to caring obligations, adequacy of the benefits plays more and more important role


