a63c2b1b290440a2bd86f0023176a084.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 INAT and Research First Meeting of the Core Group of the Subgroup on Introducing New Tools and Approaches (INAT) 12 th November 2010 Berlin Christian Lienhardt Stop TB Partnership Geneva
INAT and Research First Meeting of the Core Group of the Subgroup on Introducing New Tools and Approaches (INAT) 12 th November 2010 Berlin Christian Lienhardt Stop TB Partnership Geneva
 Aims of this presentation Background: the TB situation today The Stop TB strategy and the Global Plan to Stop TB 2006 -2015 Why a revised Global Plan to Stop TB 20112015 ? The role of new tools in achieving the goal of TB elimination Key challenges and opportunities that can facilitate or impede the Plan’s success: the role of INAT
Aims of this presentation Background: the TB situation today The Stop TB strategy and the Global Plan to Stop TB 2006 -2015 Why a revised Global Plan to Stop TB 20112015 ? The role of new tools in achieving the goal of TB elimination Key challenges and opportunities that can facilitate or impede the Plan’s success: the role of INAT
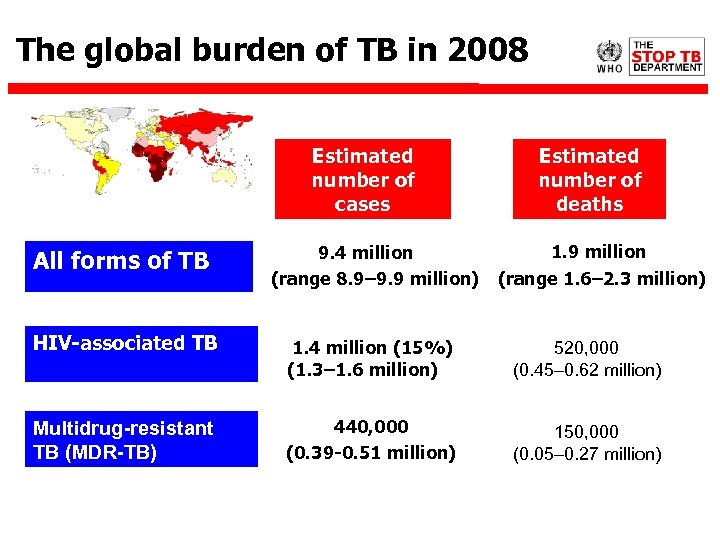 The global burden of TB in 2008 Estimated number of cases All forms of TB Estimated number of deaths 1. 9 million 9. 4 million (range 8. 9– 9. 9 million) (range 1. 6– 2. 3 million) HIV-associated TB 1. 4 million (15%) (1. 3– 1. 6 million) 520, 000 (0. 45– 0. 62 million) Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) 440, 000 (0. 39 -0. 51 million) 150, 000 (0. 05– 0. 27 million)
The global burden of TB in 2008 Estimated number of cases All forms of TB Estimated number of deaths 1. 9 million 9. 4 million (range 8. 9– 9. 9 million) (range 1. 6– 2. 3 million) HIV-associated TB 1. 4 million (15%) (1. 3– 1. 6 million) 520, 000 (0. 45– 0. 62 million) Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) 440, 000 (0. 39 -0. 51 million) 150, 000 (0. 05– 0. 27 million)
 The global response: Stop TB Strategy & Global Plan 1. Pursue high-quality DOTS expansion and enhancement 2. Address TB-HIV, MDR-TB, and needs of the poor and vulnerable 3. Contribute to health system strengthening 4. Engage all care providers 5. Empower people with TB and communities 6. Enable and promote research
The global response: Stop TB Strategy & Global Plan 1. Pursue high-quality DOTS expansion and enhancement 2. Address TB-HIV, MDR-TB, and needs of the poor and vulnerable 3. Contribute to health system strengthening 4. Engage all care providers 5. Empower people with TB and communities 6. Enable and promote research
 TB Control Global Targets 2015: Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases Target 8: to have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the incidence… Indicator 23: incidence, prevalence and deaths associated with TB Indicator 24: proportion of TB cases detected and cured under DOTS 2015: 50% reduction in TB prevalence and deaths relative to 1990 levels 2050: elimination (<1 case per million population)
TB Control Global Targets 2015: Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases Target 8: to have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the incidence… Indicator 23: incidence, prevalence and deaths associated with TB Indicator 24: proportion of TB cases detected and cured under DOTS 2015: 50% reduction in TB prevalence and deaths relative to 1990 levels 2050: elimination (<1 case per million population)
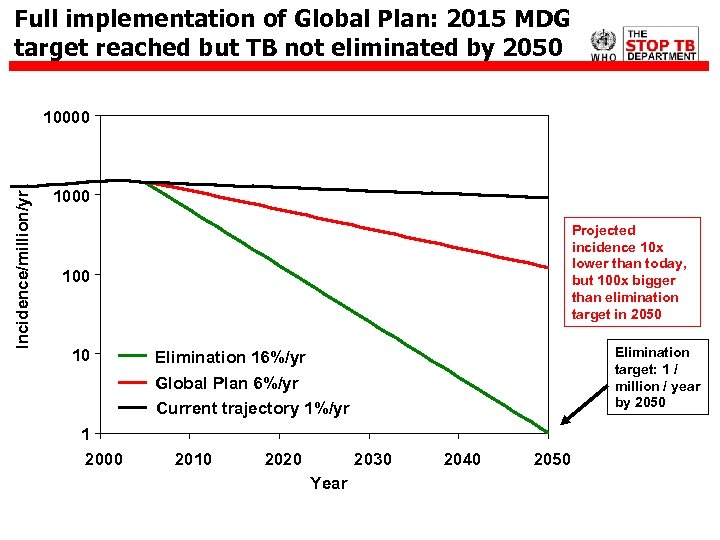 Full implementation of Global Plan: 2015 MDG target reached but TB not eliminated by 2050 Incidence/million/yr 10000 1000 Projected incidence 10 x lower than today, but 100 x bigger than elimination target in 2050 10 Elimination target: 1 / million / year by 2050 Elimination 16%/yr Global Plan 6%/yr Current trajectory 1%/yr 1 2000 2010 2020 2030 Year 2040 2050
Full implementation of Global Plan: 2015 MDG target reached but TB not eliminated by 2050 Incidence/million/yr 10000 1000 Projected incidence 10 x lower than today, but 100 x bigger than elimination target in 2050 10 Elimination target: 1 / million / year by 2050 Elimination 16%/yr Global Plan 6%/yr Current trajectory 1%/yr 1 2000 2010 2020 2030 Year 2040 2050
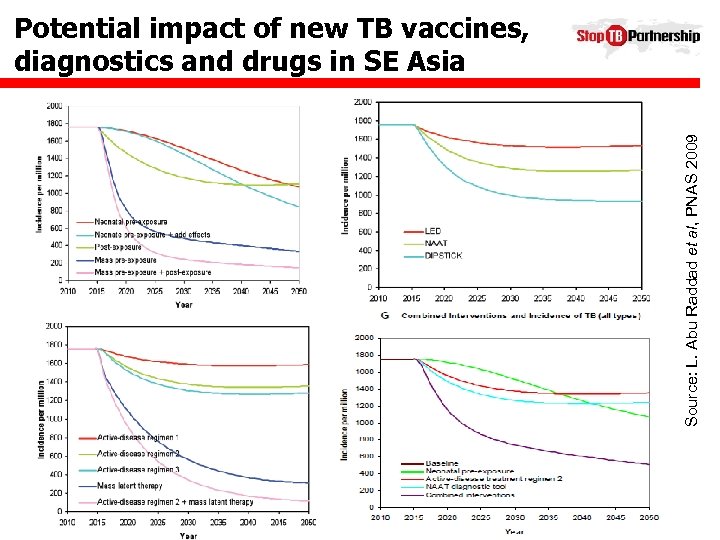 Source: L. Abu Raddad et al, PNAS 2009 Potential impact of new TB vaccines, diagnostics and drugs in SE Asia
Source: L. Abu Raddad et al, PNAS 2009 Potential impact of new TB vaccines, diagnostics and drugs in SE Asia
 "Moving beyond the TB box" Core TB control area not enough TB care and control Health systems And policies Development Research Need to expand on research
"Moving beyond the TB box" Core TB control area not enough TB care and control Health systems And policies Development Research Need to expand on research
 Strengthening the fight The Global Plan 2006 -2015 defined direction and costs The Global Plan 2011 -2015 strengthens the fight 11 billion US$ to develop new tools 9. 8 billion US$ to develop new tools
Strengthening the fight The Global Plan 2006 -2015 defined direction and costs The Global Plan 2011 -2015 strengthens the fight 11 billion US$ to develop new tools 9. 8 billion US$ to develop new tools
 Improve TB Control Basic Science Translational Studies Preclinical Studies Clinical Studies/Trials Operational Studies/Trials
Improve TB Control Basic Science Translational Studies Preclinical Studies Clinical Studies/Trials Operational Studies/Trials
 Improve TB Control Develop Point of Care Diagnostics Basic Science Develop a Safe and Effective Vaccine Transform the Field of Therapeutics Translational Studies Preclinical Studies Clinical Studies/Trials Operational Studies/Trials
Improve TB Control Develop Point of Care Diagnostics Basic Science Develop a Safe and Effective Vaccine Transform the Field of Therapeutics Translational Studies Preclinical Studies Clinical Studies/Trials Operational Studies/Trials
 • Knowledge gaps Fundamental questions in TB • Resources gaps
• Knowledge gaps Fundamental questions in TB • Resources gaps
 Fundamental Research Fundamental science is an integral part of an aggressive, transformational research response to the continuing global TB epidemic • • FR is crucial to addressing questions that underpin development of new diagnostics, drugs and vaccines and the creation of improved control strategies to meet the goal of elimination of TB by 2050
Fundamental Research Fundamental science is an integral part of an aggressive, transformational research response to the continuing global TB epidemic • • FR is crucial to addressing questions that underpin development of new diagnostics, drugs and vaccines and the creation of improved control strategies to meet the goal of elimination of TB by 2050
 Diagnostics Development To diagnose all forms of TB (PTB, EPTB, DS/DRTB, LTBI) in all populations • • To develop a Point of Care Diagnostics of TB • To develop a Point of Care Diagnostics of Latent TB Infection To ensure wide availability of and equitable access to new diagnostic tools at all health care levels in endemic countries •
Diagnostics Development To diagnose all forms of TB (PTB, EPTB, DS/DRTB, LTBI) in all populations • • To develop a Point of Care Diagnostics of TB • To develop a Point of Care Diagnostics of Latent TB Infection To ensure wide availability of and equitable access to new diagnostic tools at all health care levels in endemic countries •
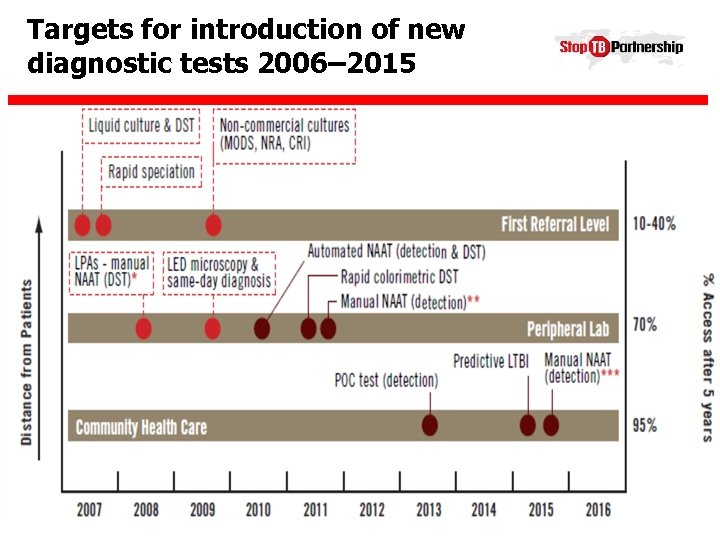 Targets for introduction of new diagnostic tests 2006– 2015
Targets for introduction of new diagnostic tests 2006– 2015
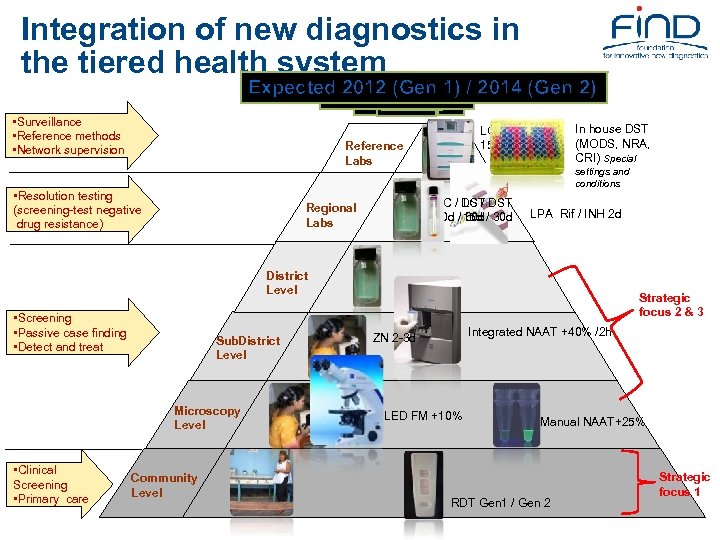 Integration of new diagnostics in the tiered health system Expected 2012 2009 1) / 2014 (Gen 2) (Gen Expected 2011 2010 2007 Until 2007 2008 • Surveillance • Reference methods • Network supervision Reference Labs • Resolution testing (screening-test negative drug resistance) settings and conditions SC / DST LC / 30 d / 15 d / 30 d 60 d Regional Labs In house DST (MODS, NRA, CRI) Special LC / DST 15 d/ 30 d LPA Rif / INH 2 d District Level • Screening • Passive case finding • Detect and treat Sub. District Level Microscopy Level • Clinical Screening • Primary care Community Level Strategic focus 2 & 3 Integrated NAAT +40% /2 h ZN 2 -3 d LED FM +10% Manual NAAT+25% RDT Gen 1 / Gen 2 Strategic focus 1
Integration of new diagnostics in the tiered health system Expected 2012 2009 1) / 2014 (Gen 2) (Gen Expected 2011 2010 2007 Until 2007 2008 • Surveillance • Reference methods • Network supervision Reference Labs • Resolution testing (screening-test negative drug resistance) settings and conditions SC / DST LC / 30 d / 15 d / 30 d 60 d Regional Labs In house DST (MODS, NRA, CRI) Special LC / DST 15 d/ 30 d LPA Rif / INH 2 d District Level • Screening • Passive case finding • Detect and treat Sub. District Level Microscopy Level • Clinical Screening • Primary care Community Level Strategic focus 2 & 3 Integrated NAAT +40% /2 h ZN 2 -3 d LED FM +10% Manual NAAT+25% RDT Gen 1 / Gen 2 Strategic focus 1
 Drug Development • To develop safe, short and high-efficacy drug regimens for treatment of DS-TB, DR-TB and LTBI, that can be used in children and in combination with HIV treatment; • To build and maintain trial site capacity necessary to support trials for drug-sensitive and -resistant TB, as well as latent TB infection; • To ensure clear and efficient regulatory guidelines for approval of new TB drugs and regimens, from development to registration, and ensure adoption of new TB drugs and regimens at the country level.
Drug Development • To develop safe, short and high-efficacy drug regimens for treatment of DS-TB, DR-TB and LTBI, that can be used in children and in combination with HIV treatment; • To build and maintain trial site capacity necessary to support trials for drug-sensitive and -resistant TB, as well as latent TB infection; • To ensure clear and efficient regulatory guidelines for approval of new TB drugs and regimens, from development to registration, and ensure adoption of new TB drugs and regimens at the country level.
 Drug Development Pipeline
Drug Development Pipeline
 Vaccine Development • To develop safe, short and high-efficacy drug regimens for treatment of DS-TB, DR-TB and LTBI, that can be used in children and in combination with HIV treatment; • To build and maintain trial site capacity necessary to support trials for drug-sensitive and -resistant TB, as well as latent TB infection; • To ensure clear and efficient regulatory guidelines for approval of new TB drugs and regimens, from development to registration, and ensure adoption of new TB drugs and regimens at the country level.
Vaccine Development • To develop safe, short and high-efficacy drug regimens for treatment of DS-TB, DR-TB and LTBI, that can be used in children and in combination with HIV treatment; • To build and maintain trial site capacity necessary to support trials for drug-sensitive and -resistant TB, as well as latent TB infection; • To ensure clear and efficient regulatory guidelines for approval of new TB drugs and regimens, from development to registration, and ensure adoption of new TB drugs and regimens at the country level.
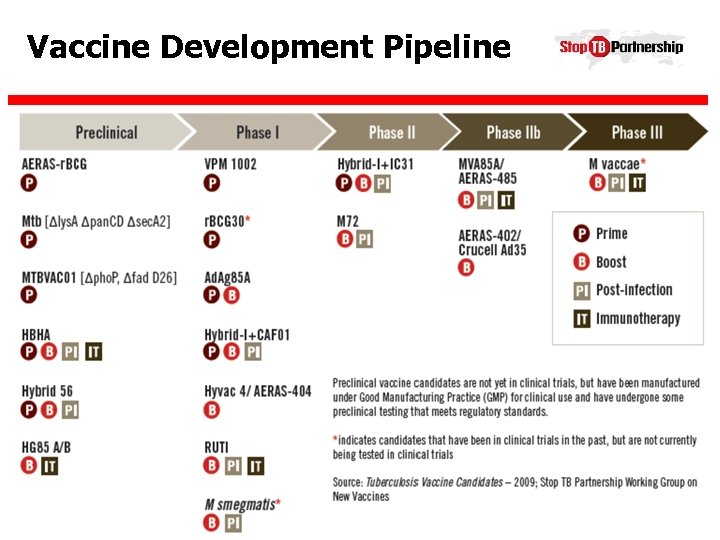 Vaccine Development Pipeline
Vaccine Development Pipeline
 Operational Research • • • The "missing link" between development of new tools and effective uptake in programmatic practice include several aspects: improving programme performance and outcomes; assessing the feasibility, effectiveness and impact of on-going or new strategies or interventions on TB control; collecting data to guide policy recommendations on specific interventions.
Operational Research • • • The "missing link" between development of new tools and effective uptake in programmatic practice include several aspects: improving programme performance and outcomes; assessing the feasibility, effectiveness and impact of on-going or new strategies or interventions on TB control; collecting data to guide policy recommendations on specific interventions.
 Funding required - Global Plan to Stop TB 2011 -2015
Funding required - Global Plan to Stop TB 2011 -2015
 What are the research challenges for full implementation of the Global Plan ? 1. Massive scale-up of research necessary to accelerate progress in TB control 2. Profound need of Fundamental research "upstream" to feed the development of new tools for TB control 3. Better understanding of the whole spectrum of infection for development of appropriate diagnostic and prevention tools 4. Need to field test new drugs, diagnostics and vaccines in GCLP compliant sites→ capacity building and technology transfer
What are the research challenges for full implementation of the Global Plan ? 1. Massive scale-up of research necessary to accelerate progress in TB control 2. Profound need of Fundamental research "upstream" to feed the development of new tools for TB control 3. Better understanding of the whole spectrum of infection for development of appropriate diagnostic and prevention tools 4. Need to field test new drugs, diagnostics and vaccines in GCLP compliant sites→ capacity building and technology transfer
 What are the research challenges for full implementation of the Global Plan ? 5. Need of combined and synergistic implementation of several novel strategies: - diagnosing TB much earlier - treating cases in a much shorter time (≤ 2 months), - scaling-up treatment of LTBI (especially in high-risk populations) - mass vaccinations using a more effective vaccine 6. Research needed downstream to fight obstacles to optimal TB control: - early diagnosis and case detection (DS and DR-TB), - prevent development of TB in high-risk groups, - ensure uptake of innovations within existing health systems 7. Weak health systems and services compromising TB care; lack of bold policies on free access to care, drug quality and restriction, labs, human resources, infection control, etc.
What are the research challenges for full implementation of the Global Plan ? 5. Need of combined and synergistic implementation of several novel strategies: - diagnosing TB much earlier - treating cases in a much shorter time (≤ 2 months), - scaling-up treatment of LTBI (especially in high-risk populations) - mass vaccinations using a more effective vaccine 6. Research needed downstream to fight obstacles to optimal TB control: - early diagnosis and case detection (DS and DR-TB), - prevent development of TB in high-risk groups, - ensure uptake of innovations within existing health systems 7. Weak health systems and services compromising TB care; lack of bold policies on free access to care, drug quality and restriction, labs, human resources, infection control, etc.
 INAT Objectives • To address the challenges of introducing and implementing new tools or new approaches in TB control programmes as an integral part of accelerating progress toward the MDGs • To set priorities for operational and evaluation research that will facilitate the wide-scale implementation of new tools or new approaches • To advocate for the appropriate uptake of new tools and approaches at the country level • To track progress in the uptake and expansion of new policies and approaches.
INAT Objectives • To address the challenges of introducing and implementing new tools or new approaches in TB control programmes as an integral part of accelerating progress toward the MDGs • To set priorities for operational and evaluation research that will facilitate the wide-scale implementation of new tools or new approaches • To advocate for the appropriate uptake of new tools and approaches at the country level • To track progress in the uptake and expansion of new policies and approaches.
 Removing Barriers: A role for INAT In close collaboration with the Stop TB Partnership WGs, the TB Research Movement and WHO/STB, the role of INAT would be: • to engage in early dialogue with partners (i. e. pharmaceutical companies, regulatory authorities, research groups, technical partners, PDPs and donors) to alert them on the need to take into account programmatic questions; • to promote collaboration and action by partners for optimal use of new tools to improve TB control in all populations, including HIV infected persons and M/XDR-TB; • To assist in collecting evidence on the impact of new tools/approaches on case detection, case management and equitable access to care to inform policy development;
Removing Barriers: A role for INAT In close collaboration with the Stop TB Partnership WGs, the TB Research Movement and WHO/STB, the role of INAT would be: • to engage in early dialogue with partners (i. e. pharmaceutical companies, regulatory authorities, research groups, technical partners, PDPs and donors) to alert them on the need to take into account programmatic questions; • to promote collaboration and action by partners for optimal use of new tools to improve TB control in all populations, including HIV infected persons and M/XDR-TB; • To assist in collecting evidence on the impact of new tools/approaches on case detection, case management and equitable access to care to inform policy development;
 Removing Barriers: A role for INAT • to help guide/promote the conduct of feasibility studies and costeffectiveness studies at an early stage in collaboration with partners, in order to inform policy-making; • to increase awareness and engagement of national authorities in the implementation of policies and guidelines for proper use of new tools and approaches at all levels of health care • to contribute to the harmonization of regulatory requirements for TB diagnostics, drugs and vaccines
Removing Barriers: A role for INAT • to help guide/promote the conduct of feasibility studies and costeffectiveness studies at an early stage in collaboration with partners, in order to inform policy-making; • to increase awareness and engagement of national authorities in the implementation of policies and guidelines for proper use of new tools and approaches at all levels of health care • to contribute to the harmonization of regulatory requirements for TB diagnostics, drugs and vaccines
 Thank you for your attention !
Thank you for your attention !


