983d5f6ae23a65bf98b61d1c20a1000c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65

In the heart of hematopoïesis
HORIBA ABX Pentra range 1. Leukopoïesis 2. Erythropoïesis 3. Thrombopoïesis

Leukopoïesis exploration

Leukopoïesis - Technologies 1. WBC counting 2. Differencial leukocytes
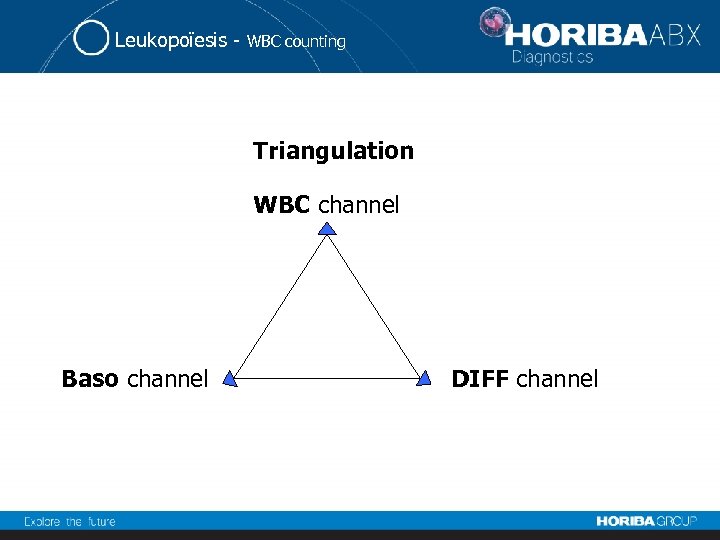
Leukopoïesis - WBC counting Triangulation WBC channel Baso channel DIFF channel
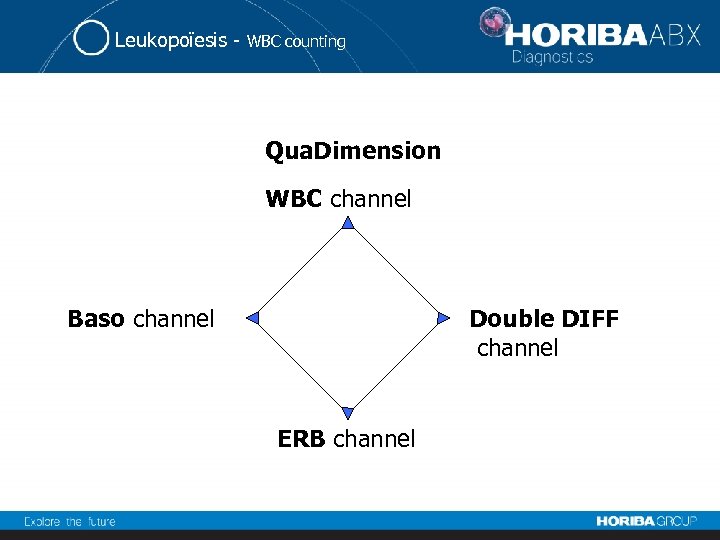
Leukopoïesis - WBC counting Qua. Dimension WBC channel Baso channel Double DIFF channel ERB channel

Leukopoïesis - DIFF 3 reference principles Cytometry - Focalization with double hydrofocusing cytometer Cytochemistry - Marking with cytochemistry (Chlorazol Black) Impedance - Cell volume measurement

Leukopoïesis - DIFF Cytochemistry The Leucodiff reagent lyses the RBC, stabilizes the WBC's in their native forms and differentially stains the leukocytes. The intensity of the stain is proportional to the nucleic acid quantity, to the maturity of this nucleic acid, to the lipids and enzyme quantity. The absorbance measurement is then proportional to the stain intensity.
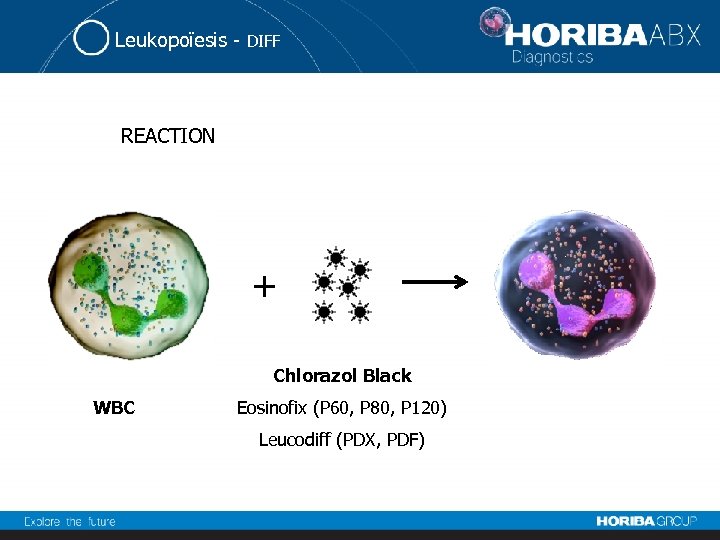
Leukopoïesis - DIFF REACTION + Chlorazol Black WBC Eosinofix (P 60, P 80, P 120) Leucodiff (PDX, PDF)
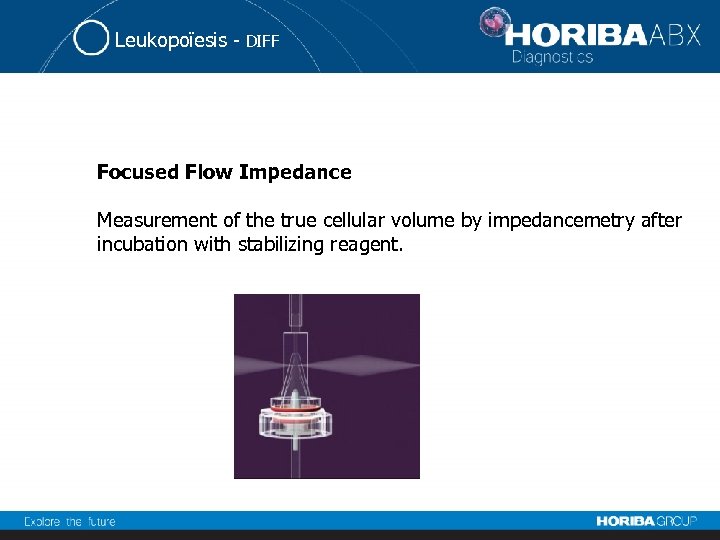
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Focused Flow Impedance Measurement of the true cellular volume by impedancemetry after incubation with stabilizing reagent.

Leukopoïesis - DIFF Double Hydrodynamic Sequential System (DHSS) Exclusive ABX patent The analysis of the white blood cells fixed in their original state by using a specific reagent (Leucodiff TM), is carried out by flow-cytometry with a double hydrodynamic focusing system, characteristic of the DHSS* technological principle. Analysis of the internal structure by measuring the cellular absorbance of light. *DHSS Analysis of cell content (optical absorbance).
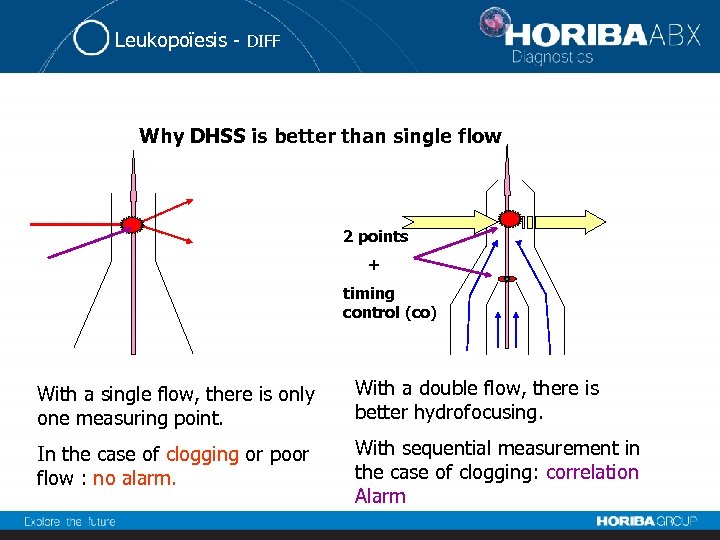
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Why DHSS is better than single flow 2 points + timing control (co) With a single flow, there is only one measuring point. With a double flow, there is better hydrofocusing. In the case of clogging or poor flow : no alarm. With sequential measurement in the case of clogging: correlation Alarm
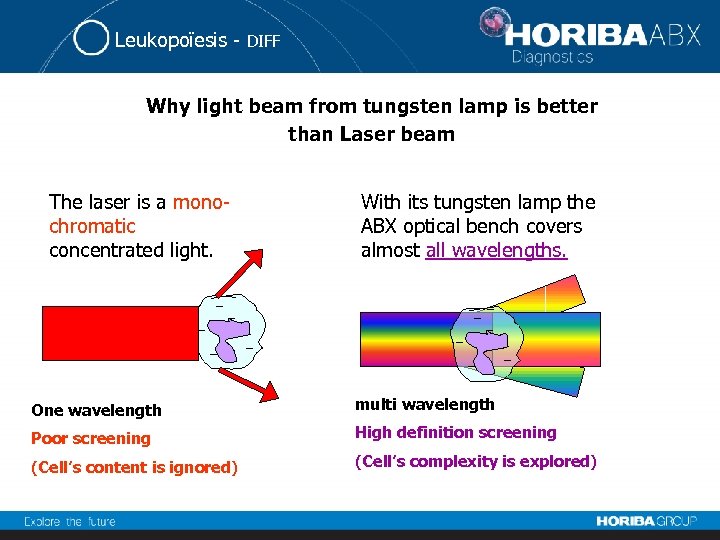
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Why light beam from tungsten lamp is better than Laser beam The laser is a monochromatic concentrated light. With its tungsten lamp the ABX optical bench covers almost all wavelengths. One wavelength multi wavelength Poor screening High definition screening (Cell’s content is ignored) (Cell’s complexity is explored)
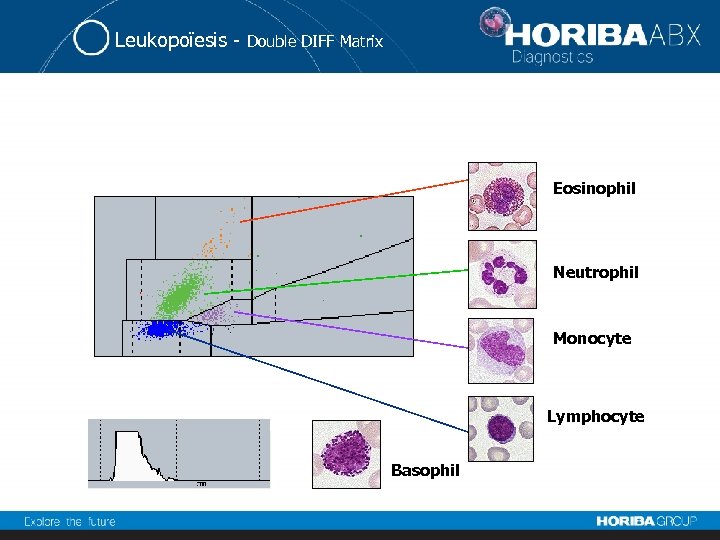
Leukopoïesis - Double DIFF Matrix Eosinophil Neutrophil Monocyte Lymphocyte Basophil
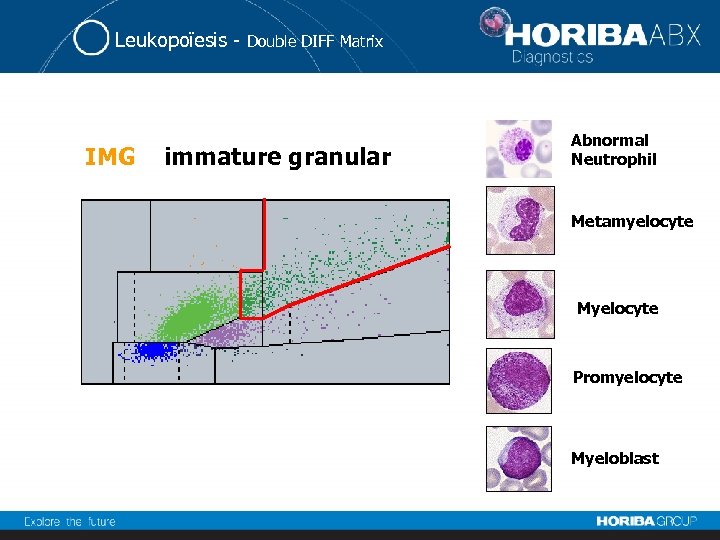
Leukopoïesis - IMG Double DIFF Matrix immature granular Abnormal Neutrophil Metamyelocyte Myelocyte Promyelocyte Myeloblast
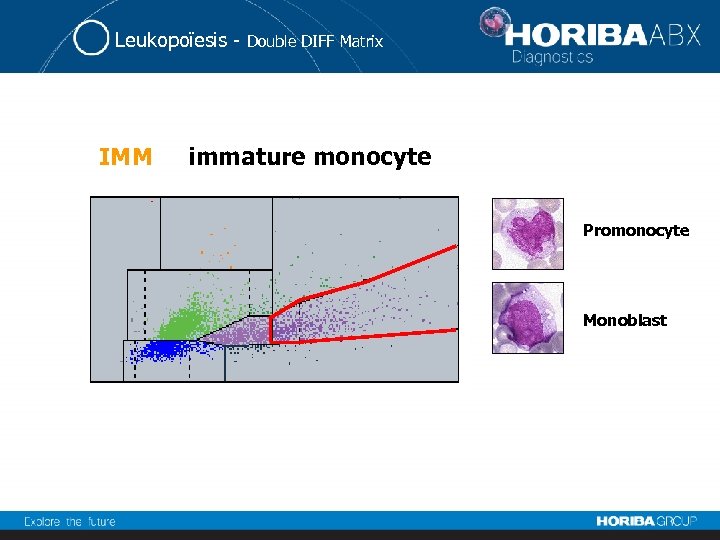
Leukopoïesis - IMM Double DIFF Matrix immature monocyte Promonocyte Monoblast
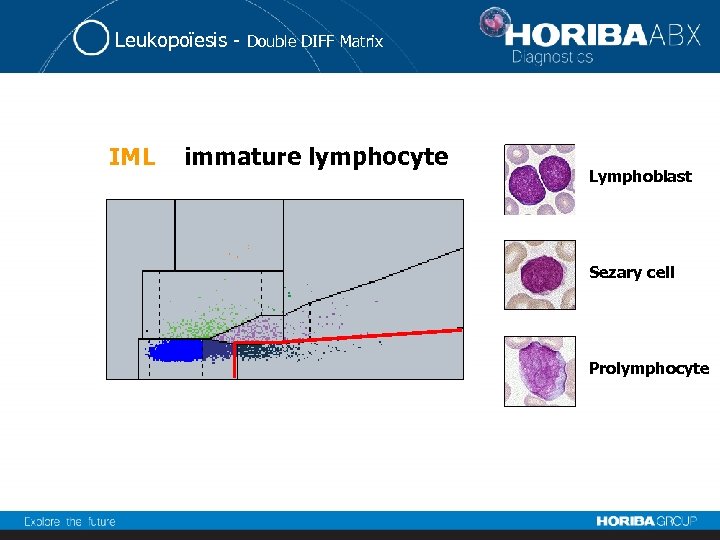
Leukopoïesis - IML Double DIFF Matrix immature lymphocyte Lymphoblast Sezary cell Prolymphocyte
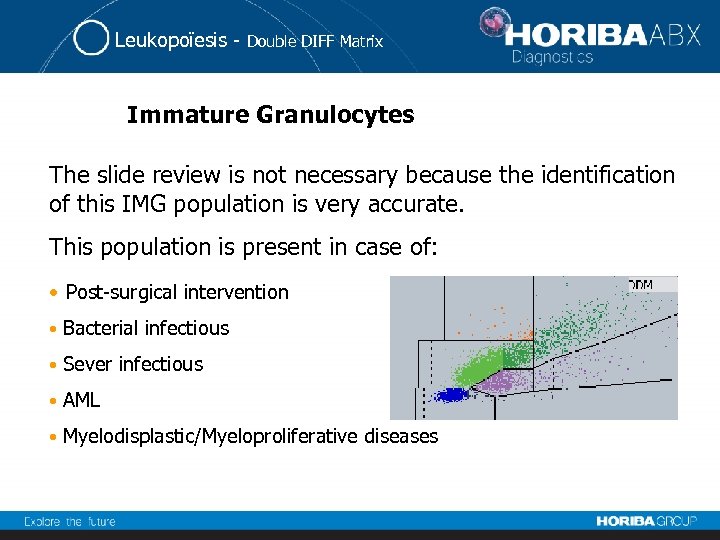
Leukopoïesis - Double DIFF Matrix Immature Granulocytes The slide review is not necessary because the identification of this IMG population is very accurate. This population is present in case of: • Post-surgical intervention • Bacterial infectious • Sever infectious • AML • Myelodisplastic/Myeloproliferative diseases
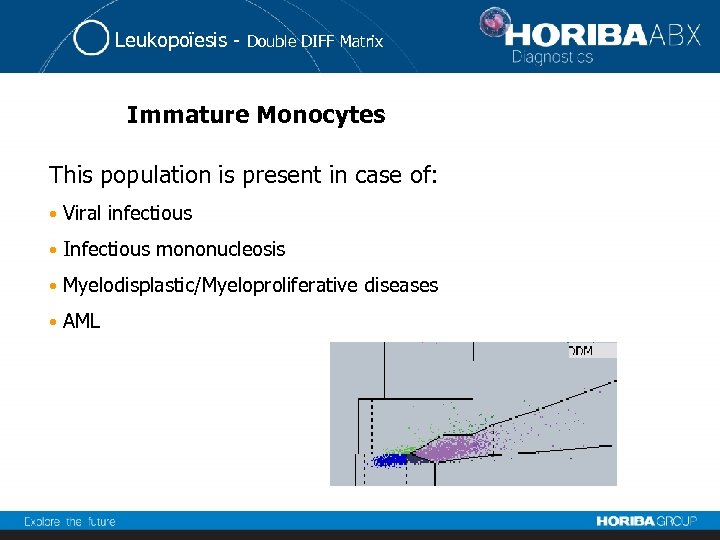
Leukopoïesis - Double DIFF Matrix Immature Monocytes This population is present in case of: • Viral infectious • Infectious mononucleosis • Myelodisplastic/Myeloproliferative diseases • AML
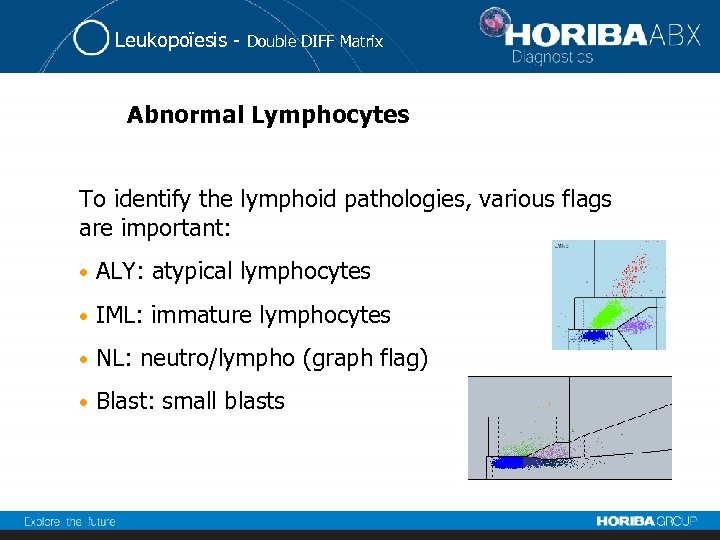
Leukopoïesis - Double DIFF Matrix Abnormal Lymphocytes To identify the lymphoid pathologies, various flags are important: • ALY: atypical lymphocytes • IML: immature lymphocytes • NL: neutro/lympho (graph flag) • Blast: small blasts
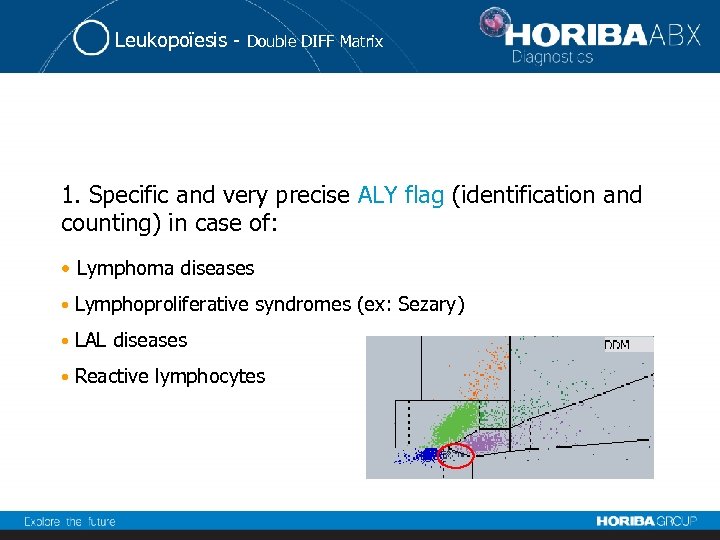
Leukopoïesis - Double DIFF Matrix 1. Specific and very precise ALY flag (identification and counting) in case of: • Lymphoma diseases • Lymphoproliferative syndromes (ex: Sezary) • LAL diseases • Reactive lymphocytes
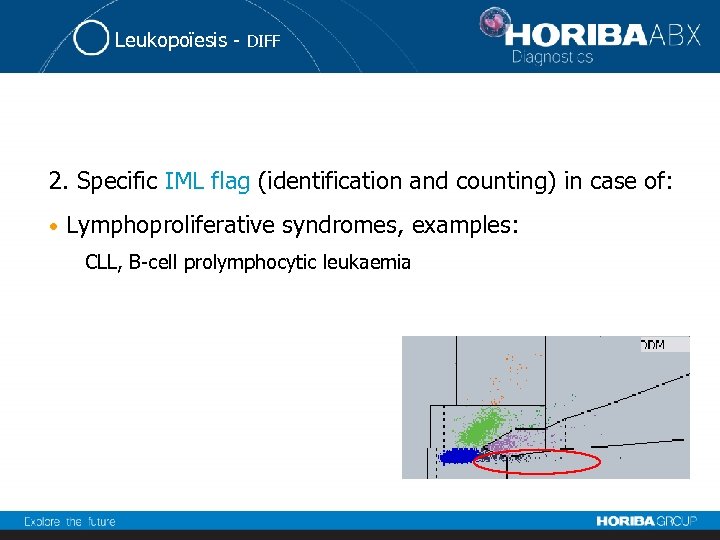
Leukopoïesis - DIFF 2. Specific IML flag (identification and counting) in case of: • Lymphoproliferative syndromes, examples: CLL, B-cell prolymphocytic leukaemia
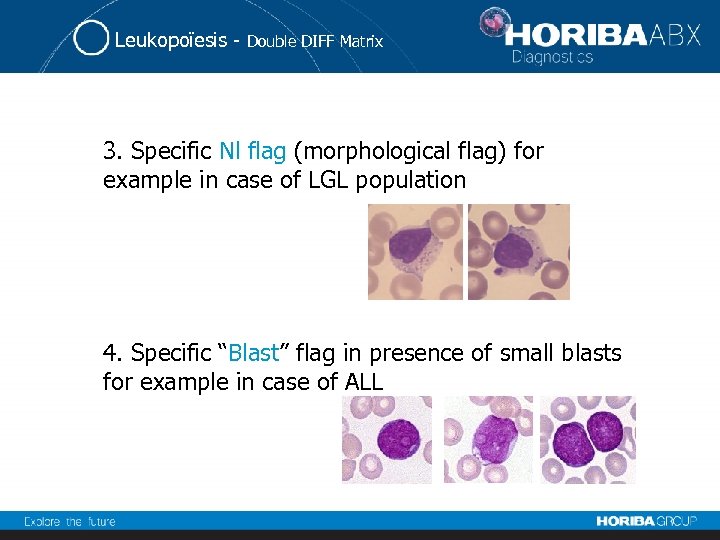
Leukopoïesis - Double DIFF Matrix 3. Specific Nl flag (morphological flag) for example in case of LGL population 4. Specific “Blast” flag in presence of small blasts for example in case of ALL
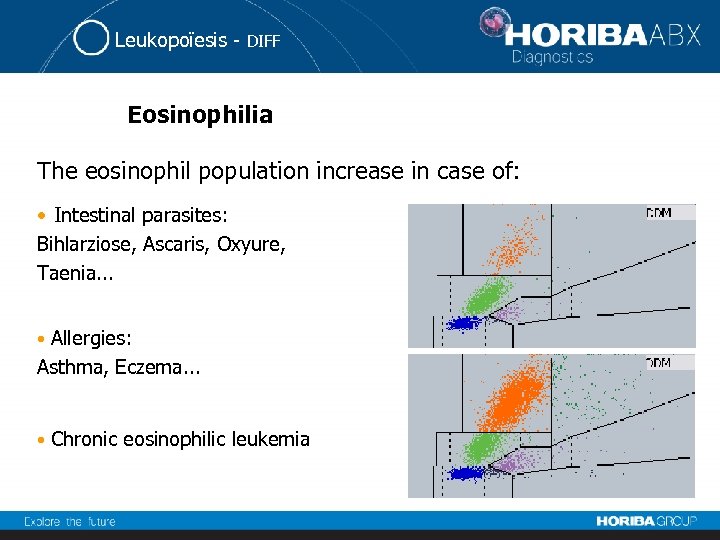
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Eosinophilia The eosinophil population increase in case of: • Intestinal parasites: Bihlarziose, Ascaris, Oxyure, Taenia. . . Allergies: Asthma, Eczema. . . • • Chronic eosinophilic leukemia
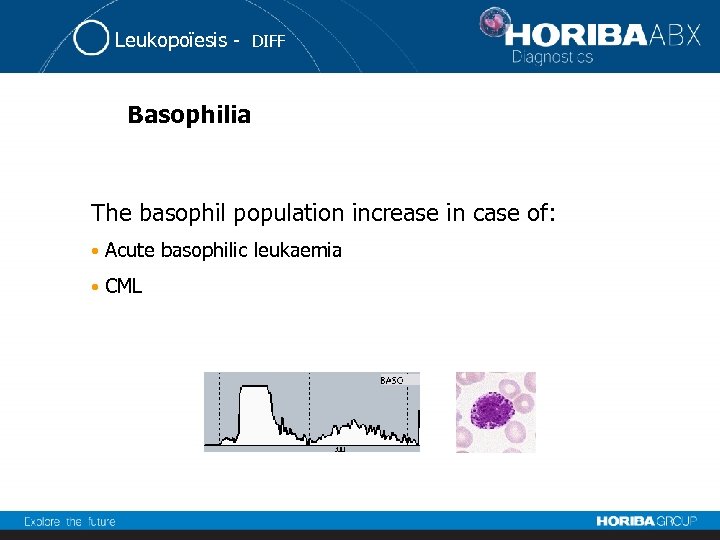
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Basophilia The basophil population increase in case of: • Acute basophilic leukaemia • CML
Leukopoïesis - DIFF More information in the DIFF Matrix: Detection of platelets aggregates Detection of Nrbc population Detection of lyse resistant cells Detection of band cells

Evaluation references ABX PENTRA DX 120: EVALUATION OF THE NEW PARAMETERS A side-by-side comparison with manual slide review (Double Matrix / Erythroblasts) and immunophenotyping (Erythroblasts) Dr. Jose Maria JOU Servei d’Hemostàsia i Hemoteràpia Hospital Clínico Universitario de Barcelona, C/ Villarroel nº 170, 08036 Barcelona, SPAIN. Myeloid Immaturity and Instrumental Findings AM. Cenci°, B. Casolari°, M. Maconi* °Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, AUSL Agency S. Agostino Hospital, Modena; *Laboratory of Chemical Analysis Clinics, Santa Maria Nuova General Hospital, Reggio Emilia.

Evaluation references Evaluation of the ABX Pentra DX 120 Dr. Francis Lacombe Laboratoire d’Hématologie, Hôpital Haut-Lévêque, France New technologies and study of blood cells: the performance of HORIBA ABX PENTRA DX 120 B. Casolaria, M. Maconib, A. M. Cencia a. Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, AUSL Agency S. Agostino Hospital, Modena; b. Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, O. I. R. M. Hospital Agency - S. Anna, Turin. Detection of atypical lymphocyte populations and lymphoid pathology diagnosis in adults and children (ALY alarm) P. Lemaire, Laboratoire de Longpont-Sur-Orge (91310) Georges Pompidou European Hospital (75015 Paris), France

Erythropoïesis exploration
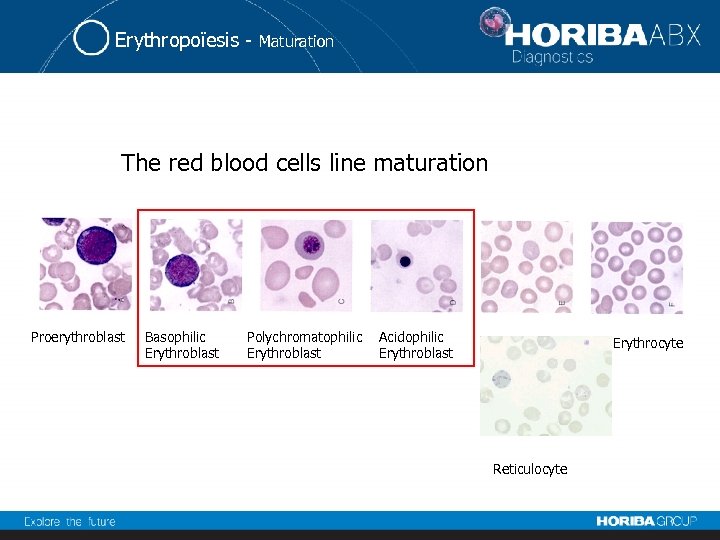
Erythropoïesis - Maturation The red blood cells line maturation Proerythroblast Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast Acidophilic Erythroblast Erythrocyte Reticulocyte
Erythropoïesis - Erythroblasts • Lyse of RBC • Thiazole orange is a fluorochrome specific to nucleic acids (reference method) • The measurement is performed with a flow cytometer (light source: argon-ion laser) • Automatic WBC correction
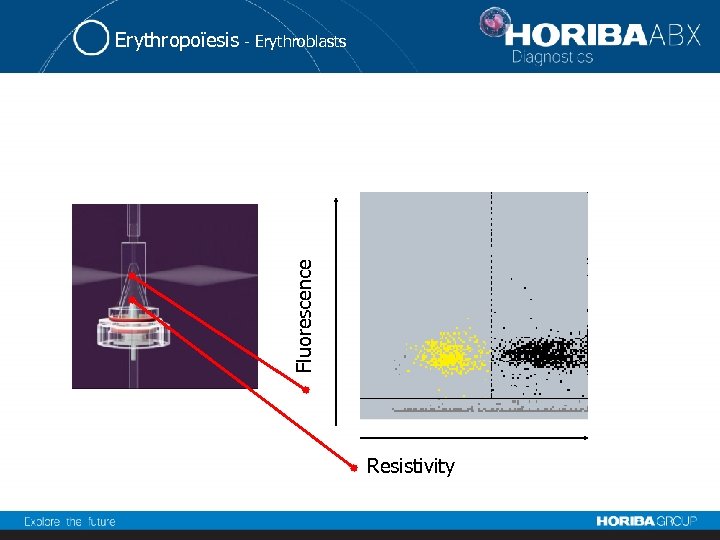
Fluorescence Erythropoïesis - Erythroblasts Resistivity
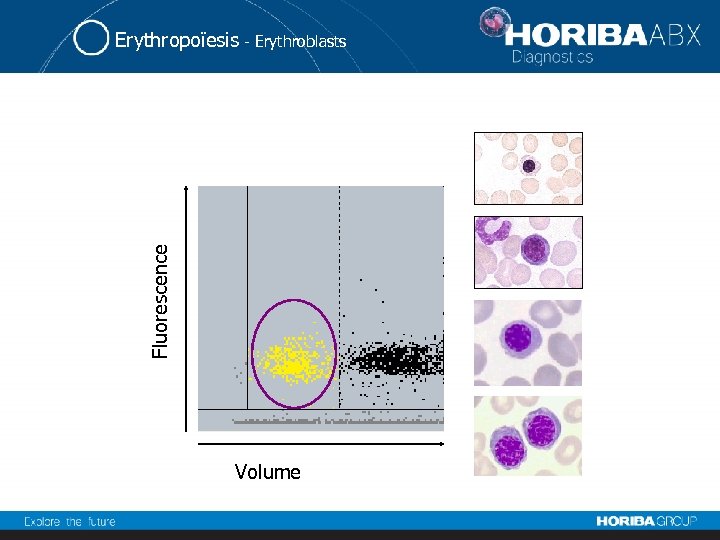
Fluorescence Erythropoïesis - Erythroblasts Volume

Erythropoïesis - Erythroblasts pathologies The abnormal presence of erythroblasts in blood could indicate: • micro or macrocytic anemia • pregnancy patient monitoring: erythroblast high value in maternal blood could indicate a pathological situation • myelodisplasia

Erythropoïesis - Erythroblasts on ABX Pentra DX 120 • Reflex testing • One fluorochrome ERB + RET • 3 control levels • Good precision (separated channels)

Evaluation references ABX PENTRA DX 120 : EVALUATION OF THE NEW PARAMETERS A side-by-side comparison with manual slide review (Double Matrix / Erythroblasts) and immunophenotyping (Erythroblasts) Dr. Jose Maria JOU Servei d’Hemostàsia i Hemoteràpia Hospital Clínico Universitario de Barcelona, C/ Villarroel nº 170, 08036 Barcelona, SPAIN. Automated Nucleated RBC Counting: Comparison to Flow Cytometry. Bruce H. Davis*, Kathleen T. Davis*, Esther Tournier+, Karen Becker* *Trillium Diagnostics, LLC and Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine 04074 USA +Horiba. ABX Diagnostics, Montpellier, France
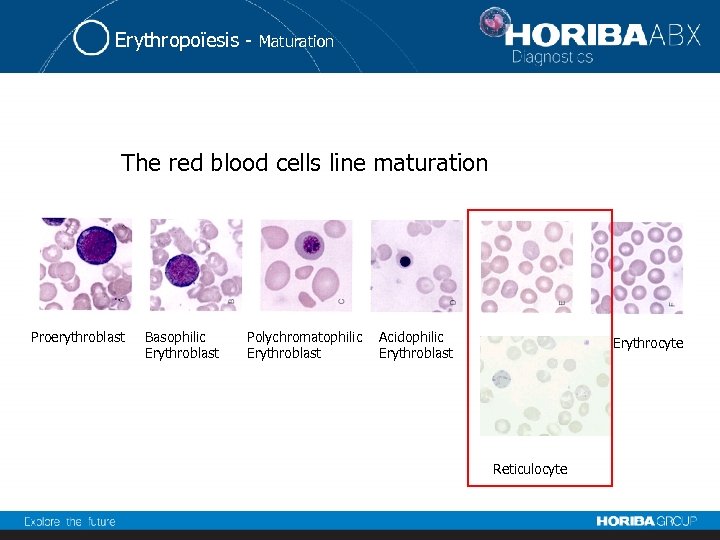
Erythropoïesis - Maturation The red blood cells line maturation Proerythroblast Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast Acidophilic Erythroblast Erythrocyte Reticulocyte
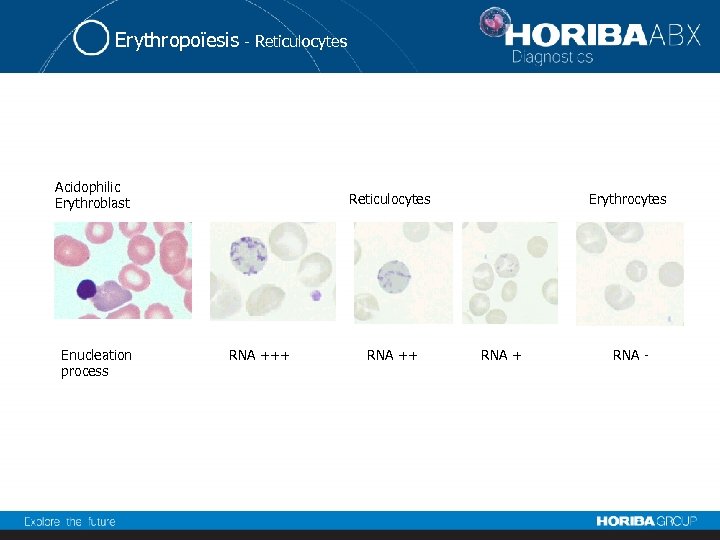
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes Acidophilic Erythroblast Enucleation process Reticulocytes RNA +++ RNA ++ Erythrocytes RNA + RNA -

Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes • Thiazole orange: specific RNA fluorochrome. • Flow cytometer: light source: argon-ion laser.
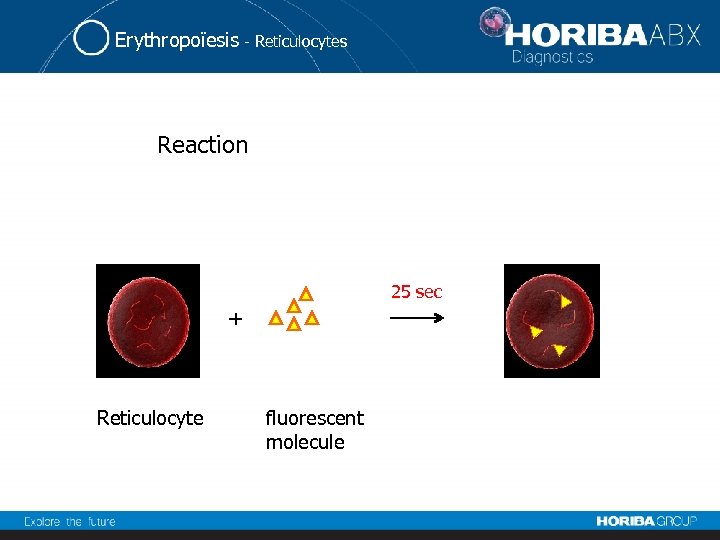
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes Reaction 25 sec + Reticulocyte fluorescent molecule
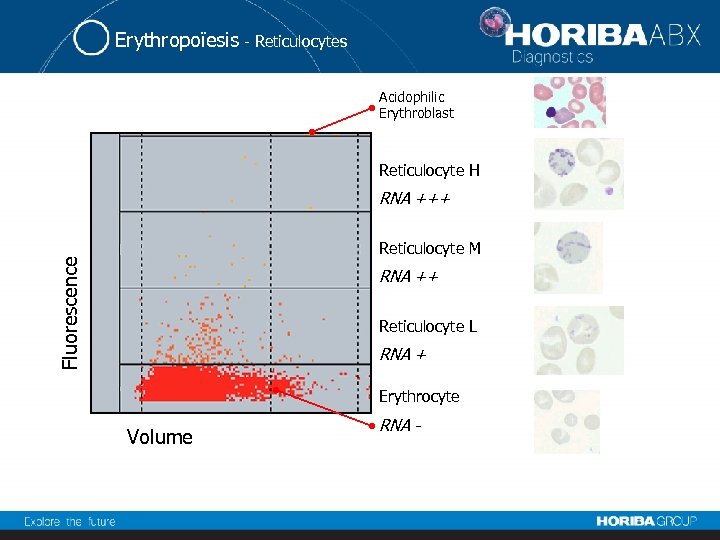
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes Acidophilic Erythroblast Reticulocyte H RNA +++ Fluorescence Reticulocyte M RNA ++ Reticulocyte L RNA + Erythrocyte Volume RNA -
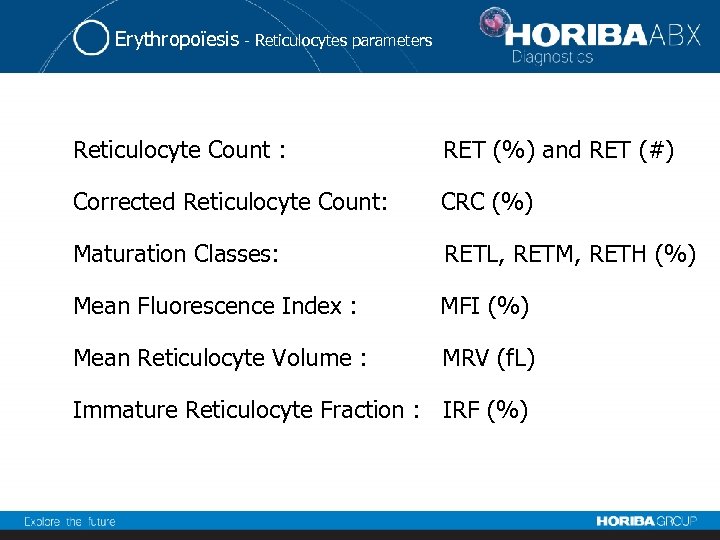
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes parameters Reticulocyte Count : RET (%) and RET (#) Corrected Reticulocyte Count: CRC (%) Maturation Classes: RETL, RETM, RETH (%) Mean Fluorescence Index : MFI (%) Mean Reticulocyte Volume : MRV (f. L) Immature Reticulocyte Fraction : IRF (%)
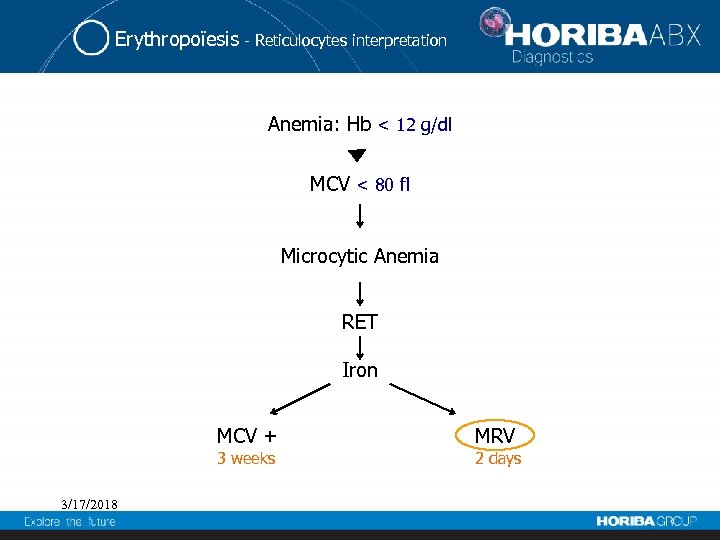
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes interpretation Anemia: Hb < 12 g/dl MCV < 80 fl Microcytic Anemia RET Iron MCV + 3 weeks 3/17/2018 MRV 2 days
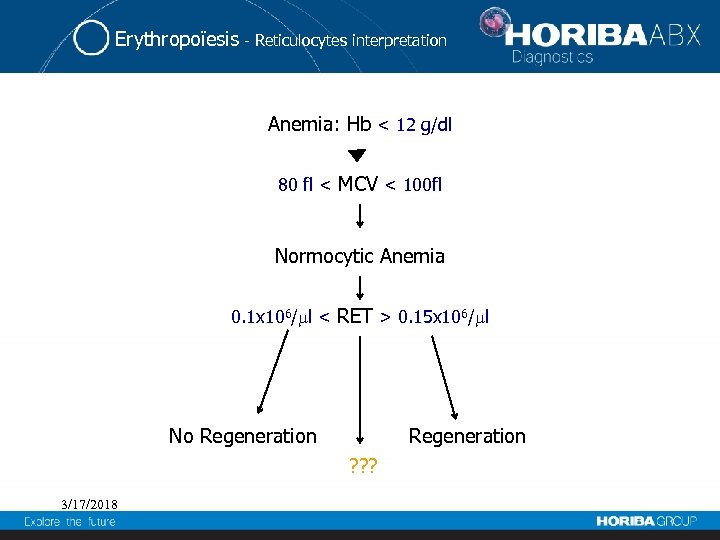
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes interpretation Anemia: Hb < 12 g/dl 80 fl < MCV < 100 fl Normocytic Anemia 0. 1 x 106/ l < RET > 0. 15 x 106/ l No Regeneration ? ? ? 3/17/2018
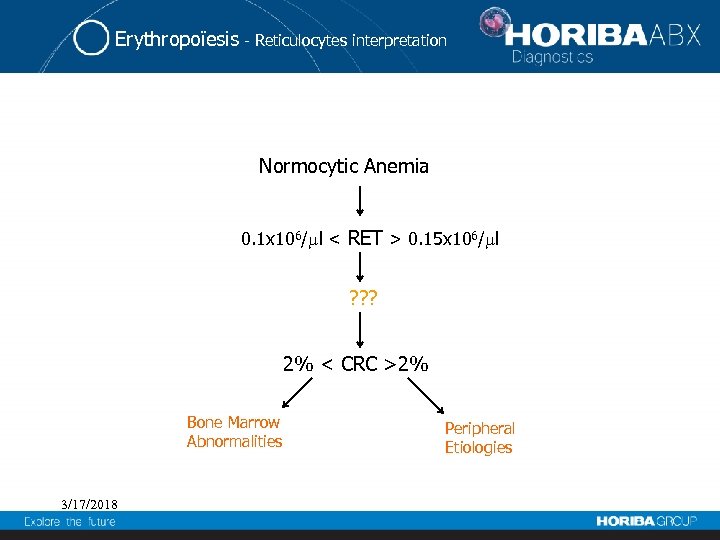
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes interpretation Normocytic Anemia 0. 1 x 106/ l < RET > 0. 15 x 106/ l ? ? ? 2% < CRC >2% Bone Marrow Abnormalities 3/17/2018 Peripheral Etiologies
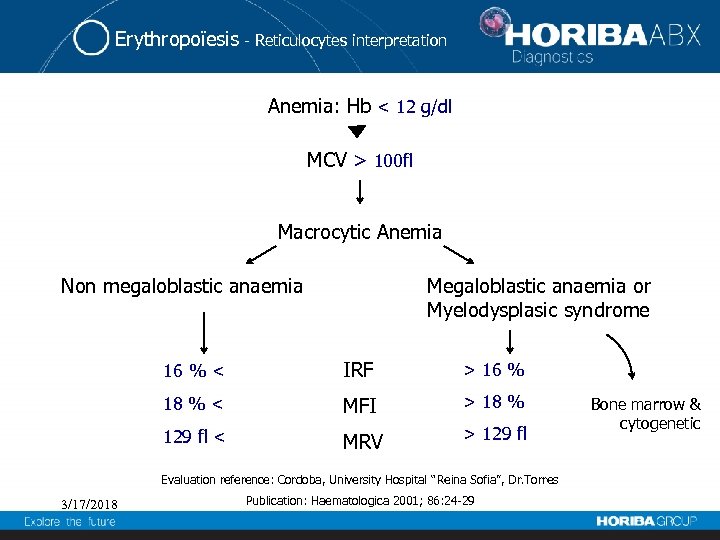
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes interpretation Anemia: Hb < 12 g/dl MCV > 100 fl Macrocytic Anemia Non megaloblastic anaemia Megaloblastic anaemia or Myelodysplasic syndrome 16 % < IRF > 16 % 18 % < MFI > 18 % 129 fl < MRV > 129 fl Evaluation reference: Cordoba, University Hospital “Reina Sofia”, Dr. Torres 3/17/2018 Publication: Haematologica 2001; 86: 24 -29 Bone marrow & cytogenetic
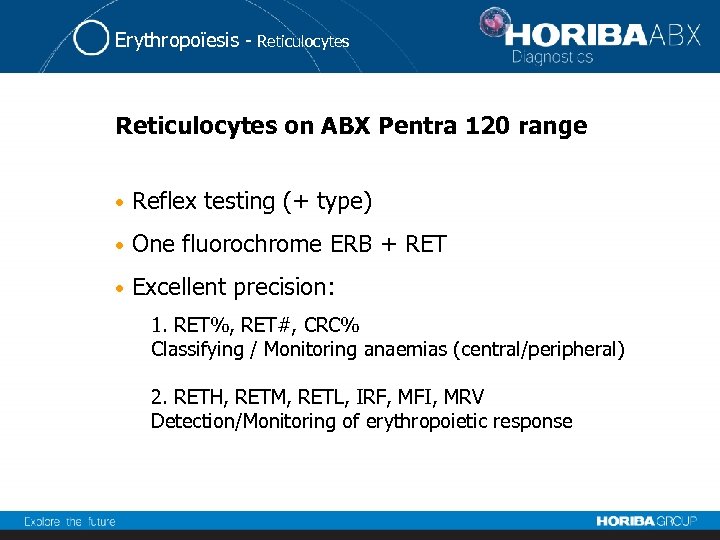
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes on ABX Pentra 120 range • Reflex testing (+ type) • One fluorochrome ERB + RET • Excellent precision: 1. RET%, RET#, CRC% Classifying / Monitoring anaemias (central/peripheral) 2. RETH, RETM, RETL, IRF, MFI, MRV Detection/Monitoring of erythropoietic response

Evaluation references The Mean Reticulocyte Volume (MRV) on the HORIBA ABX Pentra 120/DX as an alternative measurement to the Reticulocyte Haemoglobin Content (CHr™ ) A. H. Roderick – Department of Haematology, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff. UK J. M. Jou – Servei d’Hemoterapia, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona. Spain W. G. B. Rees, E. Thomas – Haematology Department, West Wales General Hospital, Carmarthen. UK Early diagnosis of iron deficiency anaemia by Mean Reticulocyte Volume (MRV) screening Dr. Ruud Muusze, clinical chemist, Ziekenhuis Zeeuws Viaanderen, Terneuzen, Holland.
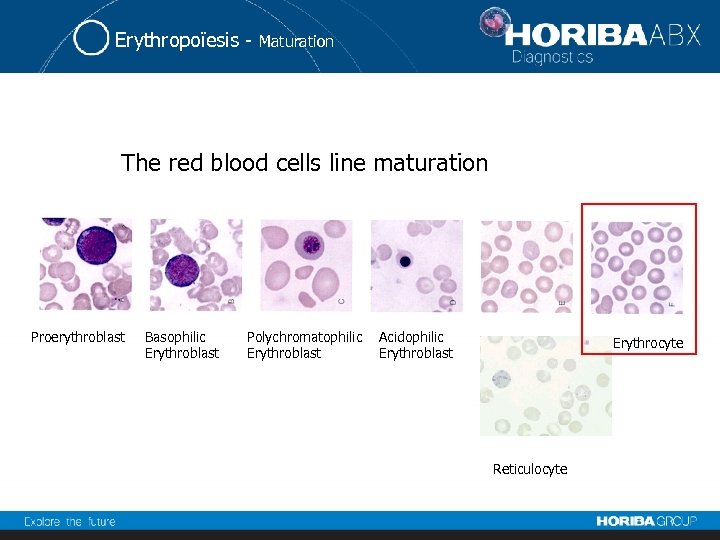
Erythropoïesis - Maturation The red blood cells line maturation Proerythroblast Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast Acidophilic Erythroblast Erythrocyte Reticulocyte

Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells To identify the RBC pathologies, various quantitative or morphology flags are important.

Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Quantitative & morphologic flags: • Anemia • MIC • Polyglobulia • MAC • Cold agglutinins • Anisocytosis • Micro/macrocytosis • No (noise)

Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Specific quantitative flags: • Anemia: Hgb • Polyglobulia: RBC • Cold agglutinin: MCHC • Micro/macrocytosis: MCV
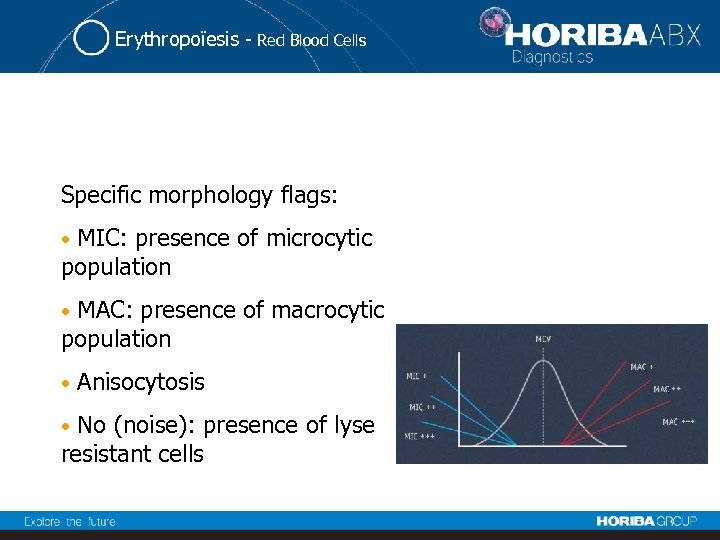
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Specific morphology flags: MIC: presence of microcytic population • MAC: presence of macrocytic population • • Anisocytosis No (noise): presence of lyse resistant cells •
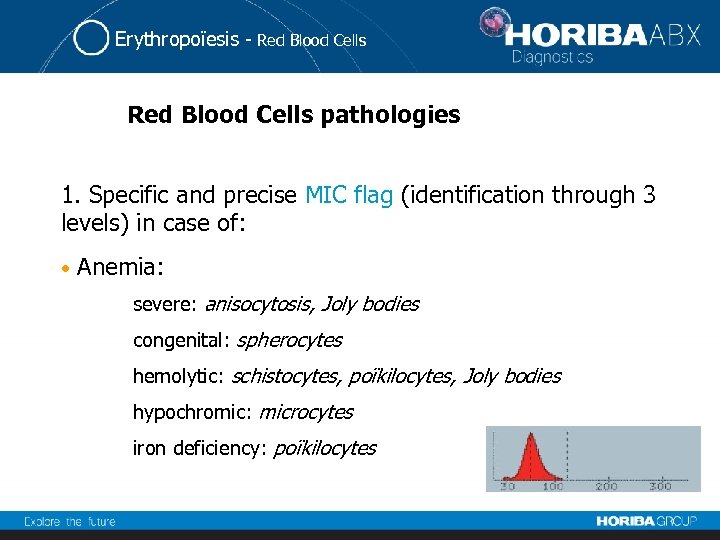
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells pathologies 1. Specific and precise MIC flag (identification through 3 levels) in case of: • Anemia: severe: anisocytosis, Joly bodies congenital: spherocytes hemolytic: schistocytes, poïkilocytes, Joly bodies hypochromic: microcytes iron deficiency: poïkilocytes

Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells pathologies • Myelofibrosis: tear drops • Thalassemia: poïkilocytes, sickle cells, target cells • Hemoglobinopathies: Hb. C: spherocytes, target cells Hb. SS: sickle cells • Microangiopathic hemolysis: poïkilocytes, schistocytes
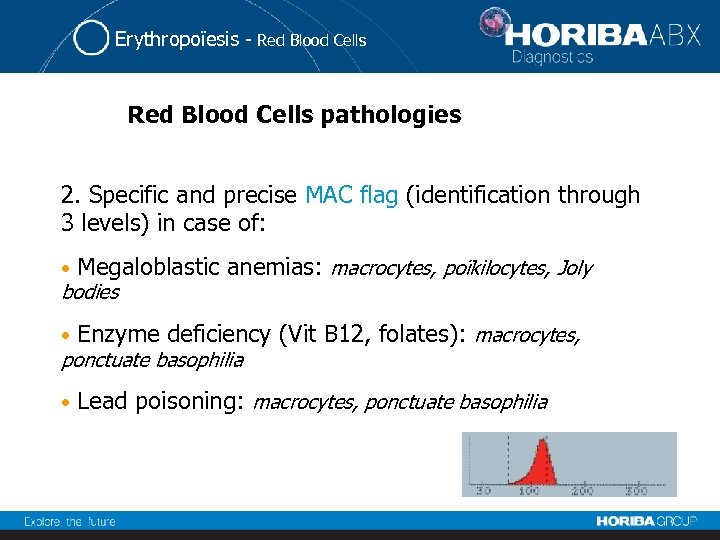
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells pathologies 2. Specific and precise MAC flag (identification through 3 levels) in case of: • Megaloblastic anemias: macrocytes, poïkilocytes, Joly • Enzyme deficiency (Vit B 12, folates): macrocytes, • Lead poisoning: macrocytes, ponctuate basophilia bodies ponctuate basophilia
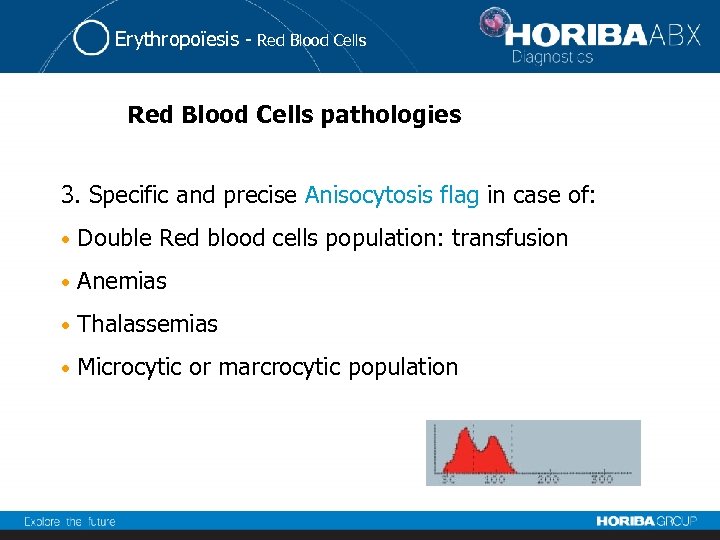
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells pathologies 3. Specific and precise Anisocytosis flag in case of: • Double Red blood cells population: transfusion • Anemias • Thalassemias • Microcytic or marcrocytic population
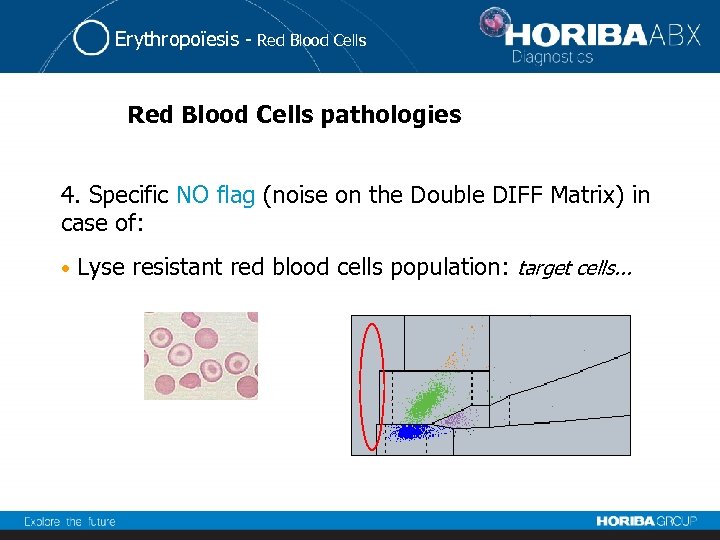
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells pathologies 4. Specific NO flag (noise on the Double DIFF Matrix) in case of: • Lyse resistant red blood cells population: target cells. . .
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Erythrocytes on ABX Pentra range • Flags: customized configuration • Abnormal population detection (MIC/MAC MCV) • Reference principle • Choice: two lyses (with or without cyanide)

Thrombopoïesis exploration
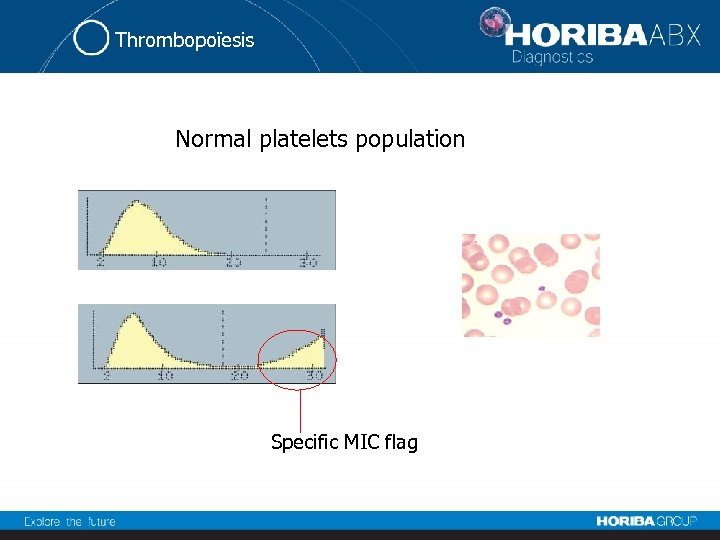
Thrombopoïesis Normal platelets population Specific MIC flag
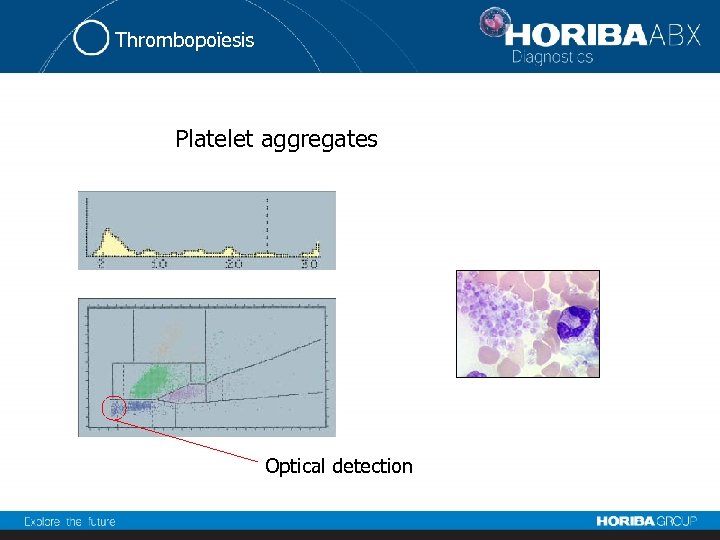
Thrombopoïesis Platelet aggregates Optical detection
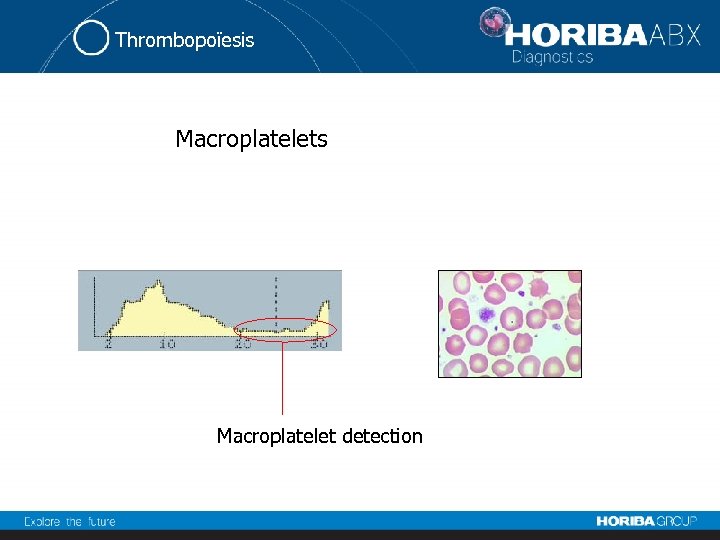
Thrombopoïesis Macroplatelet detection
Thrombopoïesis Thrombocytes on ABX Pentra range • Flags: customized configuration • PLT aggregates & macroplatelets detection • Reference principle

Thank you
983d5f6ae23a65bf98b61d1c20a1000c.ppt