5c919e7d33d30723a5c68944c0c59102.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 “In science, there is only physics; all the rest is stamp collecting. ” -Ernest Rutherford
“In science, there is only physics; all the rest is stamp collecting. ” -Ernest Rutherford
 2 Goals 1. Determine the relationships among force, mass, and motion. 2. Calculate velocity and acceleration.
2 Goals 1. Determine the relationships among force, mass, and motion. 2. Calculate velocity and acceleration.
 1: What is Physics? ?
1: What is Physics? ?
 he concepts of sics begins with t Our study of phy • study of motion. mechanics: the nematics, or ncerned with ki We will first be co • cribe motion. how we des the causes of e will move on to • From there w r dynamics. motion, o 2 • Kinematics is th e branch concern ed with the motions of object s without being c oncerned with the forces that ca use the motion. • Dynamics- is co ncerned with the forces that affect motion.
he concepts of sics begins with t Our study of phy • study of motion. mechanics: the nematics, or ncerned with ki We will first be co • cribe motion. how we des the causes of e will move on to • From there w r dynamics. motion, o 2 • Kinematics is th e branch concern ed with the motions of object s without being c oncerned with the forces that ca use the motion. • Dynamics- is co ncerned with the forces that affect motion.
 3 ing rib esc D ion ot M
3 ing rib esc D ion ot M
 • Motion 4 *Measuring & Describing motion* – occurs when something changes position *Measuring & Describing motion* • Distance – How far something has moved – San Andreas Fault 1 cm/ year – Earth travel around the Sun 940 million kilometers/ year Measured in: meters or kilometers
• Motion 4 *Measuring & Describing motion* – occurs when something changes position *Measuring & Describing motion* • Distance – How far something has moved – San Andreas Fault 1 cm/ year – Earth travel around the Sun 940 million kilometers/ year Measured in: meters or kilometers
 5 *Measuring & Describing motion* Distance vs. • Displacement Distance is how far an object has traveled • Displacement is how far from the starting point an object actually moved
5 *Measuring & Describing motion* Distance vs. • Displacement Distance is how far an object has traveled • Displacement is how far from the starting point an object actually moved
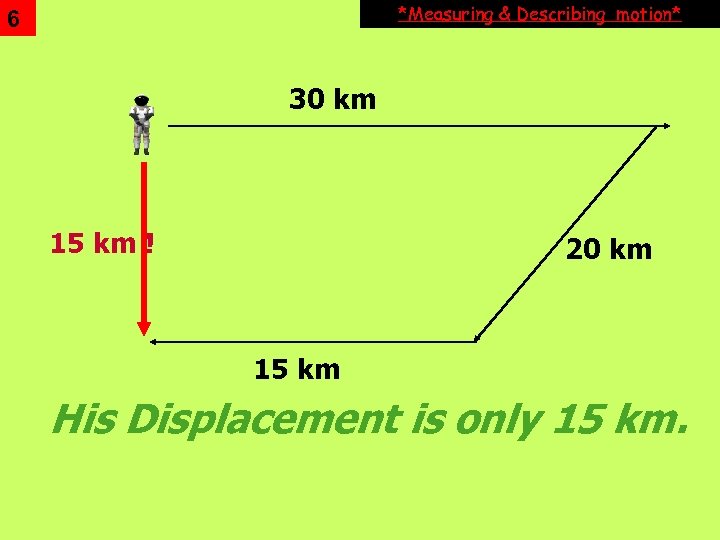 *Measuring & Describing motion* 6 30 km 15 km ! 20 km 15 km His Displacement is only 15 km.
*Measuring & Describing motion* 6 30 km 15 km ! 20 km 15 km His Displacement is only 15 km.
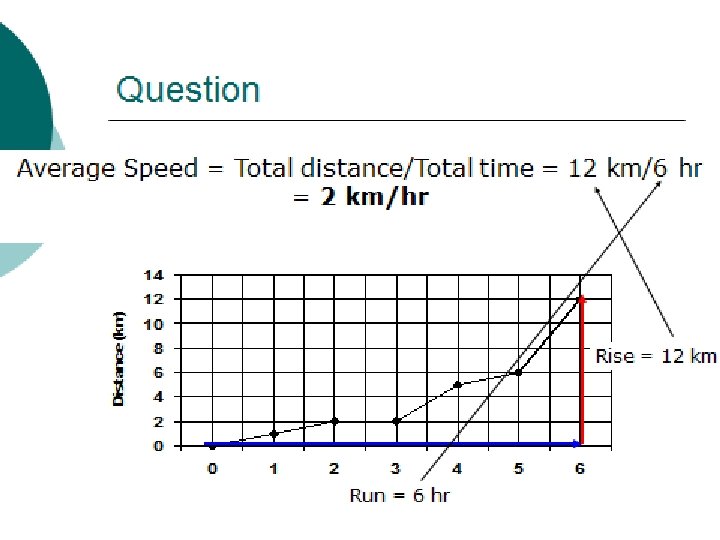
 7 *Measuring & Describing motion* How fast Something Moves is SPEED Speed is the distance an object travels in a certain period of time.
7 *Measuring & Describing motion* How fast Something Moves is SPEED Speed is the distance an object travels in a certain period of time.
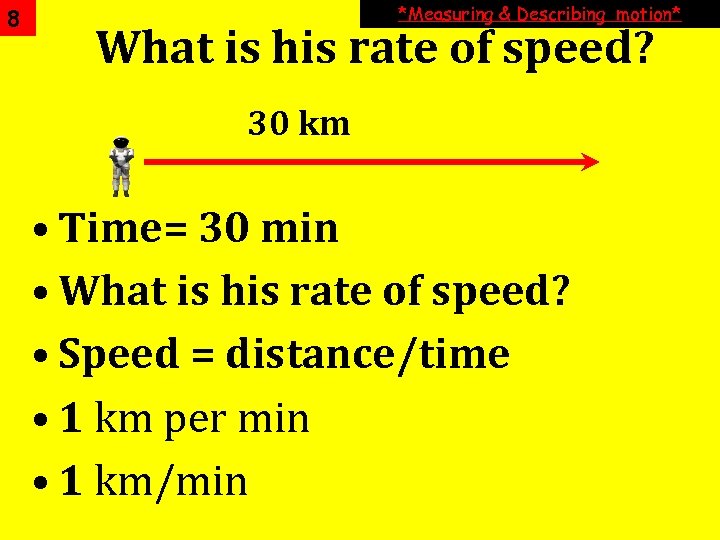 8 *Measuring & Describing motion* What is his rate of speed? 30 km • Time= 30 min • What is his rate of speed? • Speed = distance/time • 1 km per min • 1 km/min
8 *Measuring & Describing motion* What is his rate of speed? 30 km • Time= 30 min • What is his rate of speed? • Speed = distance/time • 1 km per min • 1 km/min
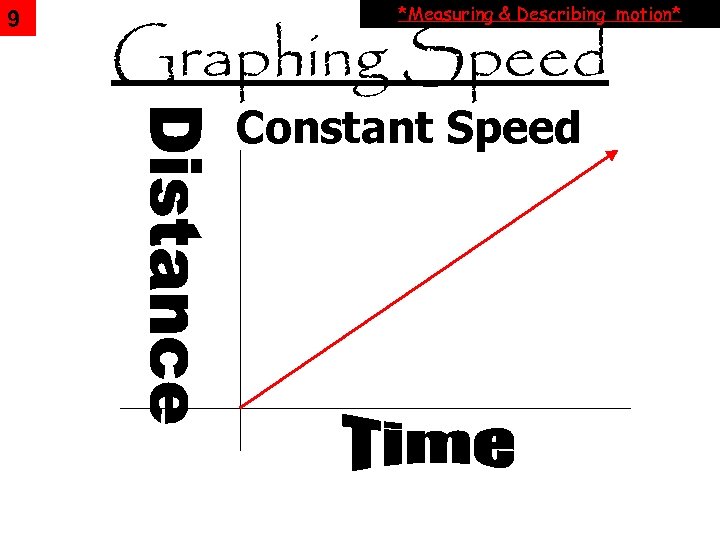 9 *Measuring & Describing motion* Graphing Speed Constant Speed
9 *Measuring & Describing motion* Graphing Speed Constant Speed
 10 CONSTANT SPEED
10 CONSTANT SPEED
 11 10 m/s
11 10 m/s
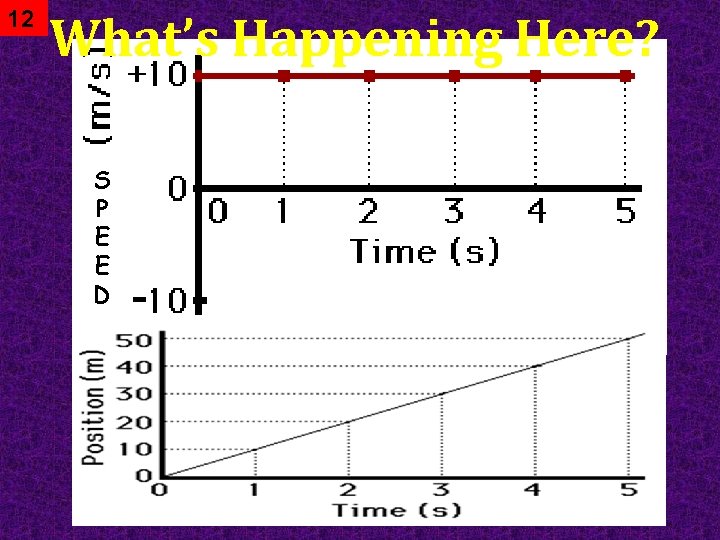 12 What’s Happening Here? S P E E D
12 What’s Happening Here? S P E E D
 13 What is the difference between Speed and Velocity? Speed is just distance/time. Velocity includes direction as well.
13 What is the difference between Speed and Velocity? Speed is just distance/time. Velocity includes direction as well.
 14 Velocity • In order to completely describe the motion of an object we need to include not only the speed of the object, but also –the direction !
14 Velocity • In order to completely describe the motion of an object we need to include not only the speed of the object, but also –the direction !
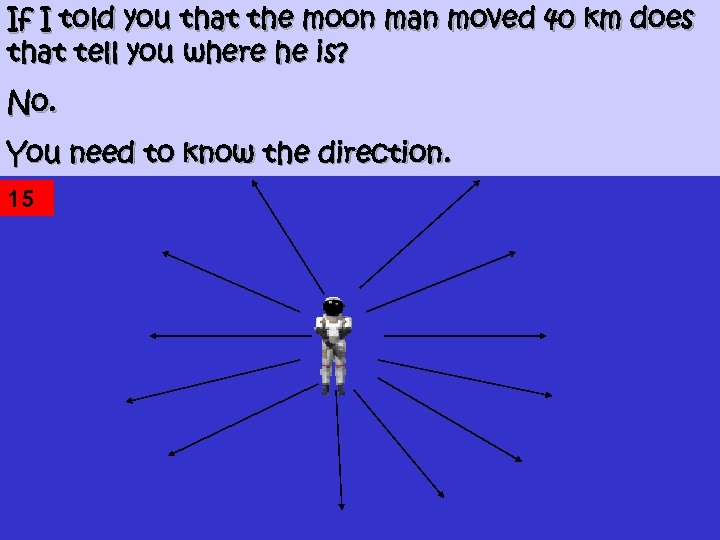 If I told you that the moon man moved 40 km does that tell you where he is? No. You need to know the direction. 15
If I told you that the moon man moved 40 km does that tell you where he is? No. You need to know the direction. 15
 16 When describing velocity, you need to state the direction. • Ex. 40 km/hr east • Why is this important?
16 When describing velocity, you need to state the direction. • Ex. 40 km/hr east • Why is this important?
 Starter… Put answers on bottom of p. 5. 1) If a car travels 400 m in 20 seconds , what is its average speed? 2) It takes Serina 0. 25 hours to drive to school. Her route is 16 km long. What is Serina’s average speed on her drive to school?
Starter… Put answers on bottom of p. 5. 1) If a car travels 400 m in 20 seconds , what is its average speed? 2) It takes Serina 0. 25 hours to drive to school. Her route is 16 km long. What is Serina’s average speed on her drive to school?
 p. 2. . #s 1 -7
p. 2. . #s 1 -7
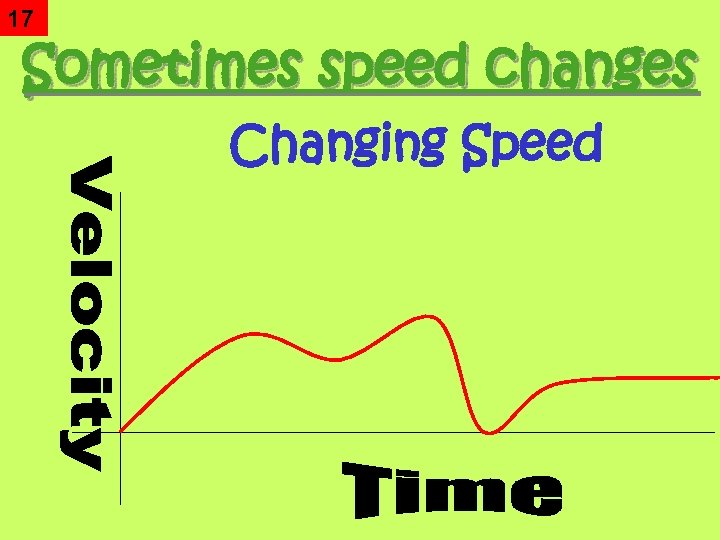 17 Sometimes speed changes Changing Speed
17 Sometimes speed changes Changing Speed
 18 Acceleration • Changing Speed – How fast the speed is changing. – the rate at which velocity changes – Can be an: • Increase in speed • Decrease in speed • Change in direction • Units: m/s 2 – Velocity per sec
18 Acceleration • Changing Speed – How fast the speed is changing. – the rate at which velocity changes – Can be an: • Increase in speed • Decrease in speed • Change in direction • Units: m/s 2 – Velocity per sec
 19 • EX: If the 2 acceleration is 10 m/s • The object is increasing its speed by 10 m/s every sec. !
19 • EX: If the 2 acceleration is 10 m/s • The object is increasing its speed by 10 m/s every sec. !
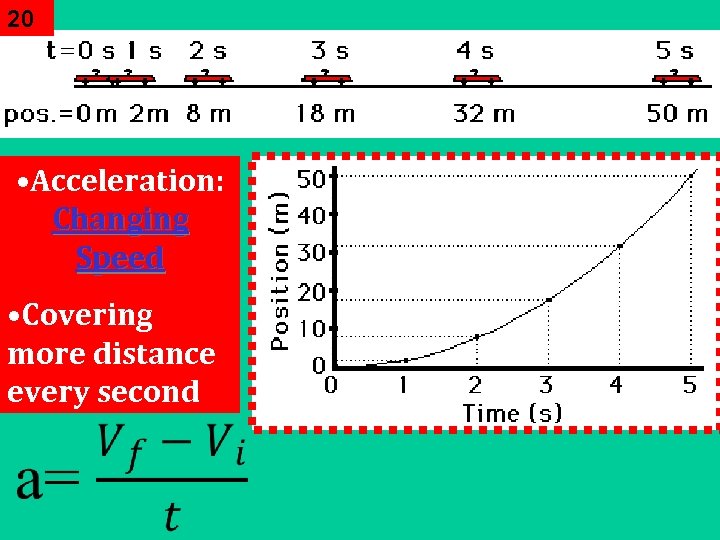 20 • Acceleration: Changing Speed • Covering more distance every second
20 • Acceleration: Changing Speed • Covering more distance every second
 Let’s Practice………… A cyclist accelerates from 0 m/s to 8 m/s in 3 seconds. What is his acceleration ?
Let’s Practice………… A cyclist accelerates from 0 m/s to 8 m/s in 3 seconds. What is his acceleration ?
 A car advertisement states that a certain car can accelerate from rest to 70 miles/hr in 0. 007 hours (~2. 5 s). Find the car’s average acceleration.
A car advertisement states that a certain car can accelerate from rest to 70 miles/hr in 0. 007 hours (~2. 5 s). Find the car’s average acceleration.
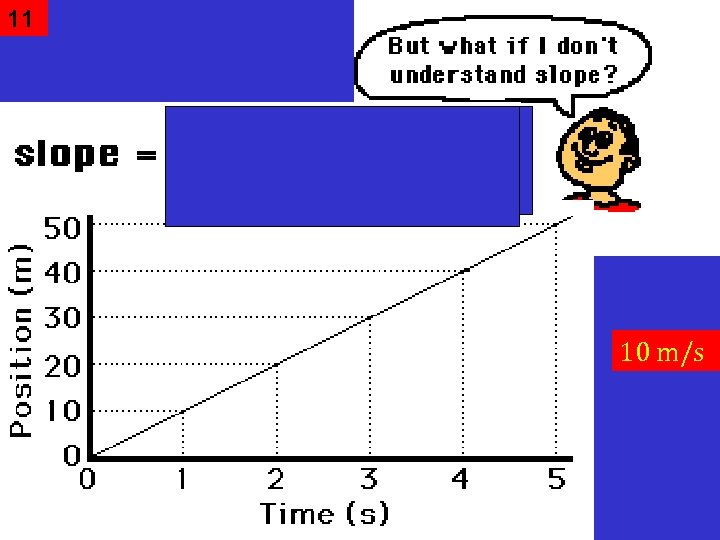
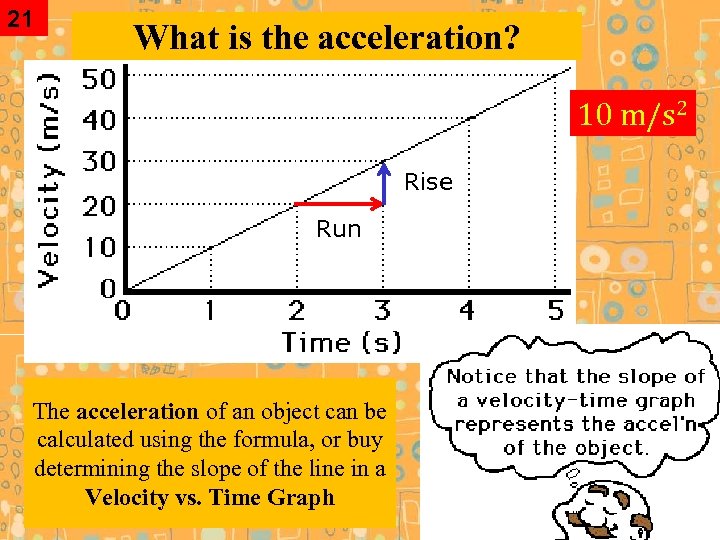 21 What is the acceleration? 10 m/s 2 Rise Run The acceleration of an object can be calculated using the formula, or buy determining the slope of the line in a Velocity vs. Time Graph
21 What is the acceleration? 10 m/s 2 Rise Run The acceleration of an object can be calculated using the formula, or buy determining the slope of the line in a Velocity vs. Time Graph
 22 Acceleration • Can be positive or negative. • Neg. Acc. Shows that the object is slowing down. • ACCELERATION IS IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION FROM THE VELOCITY!
22 Acceleration • Can be positive or negative. • Neg. Acc. Shows that the object is slowing down. • ACCELERATION IS IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION FROM THE VELOCITY!
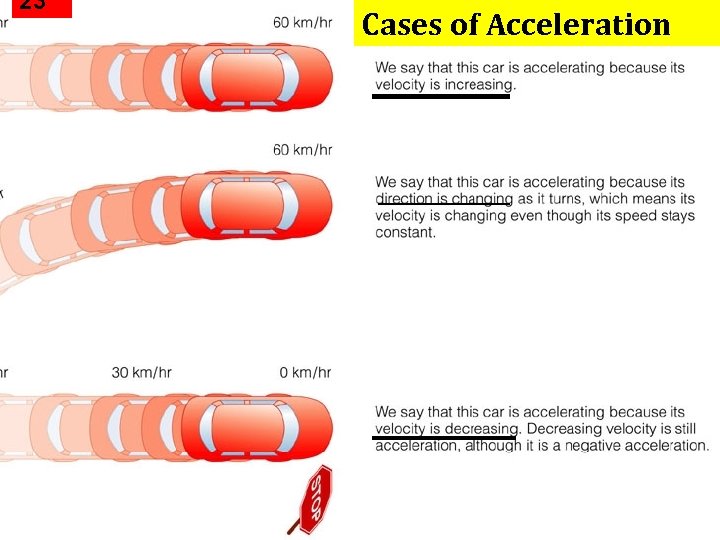 23 Cases of Acceleration
23 Cases of Acceleration
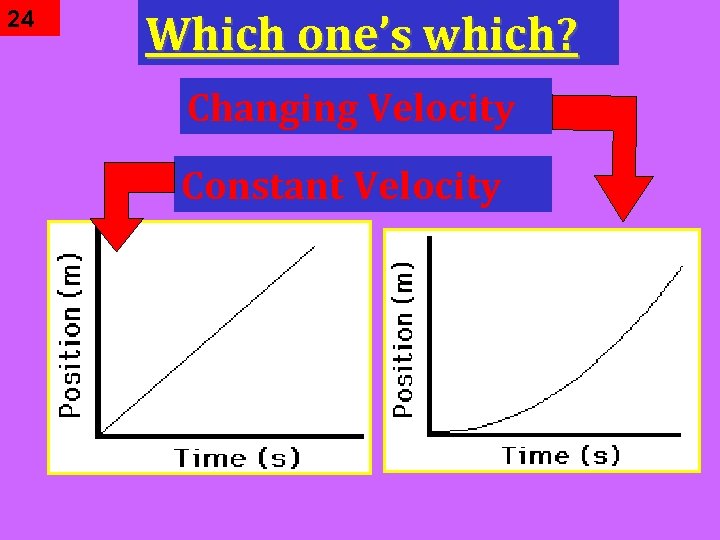 24 Which one’s which? Changing Velocity Constant Velocity
24 Which one’s which? Changing Velocity Constant Velocity
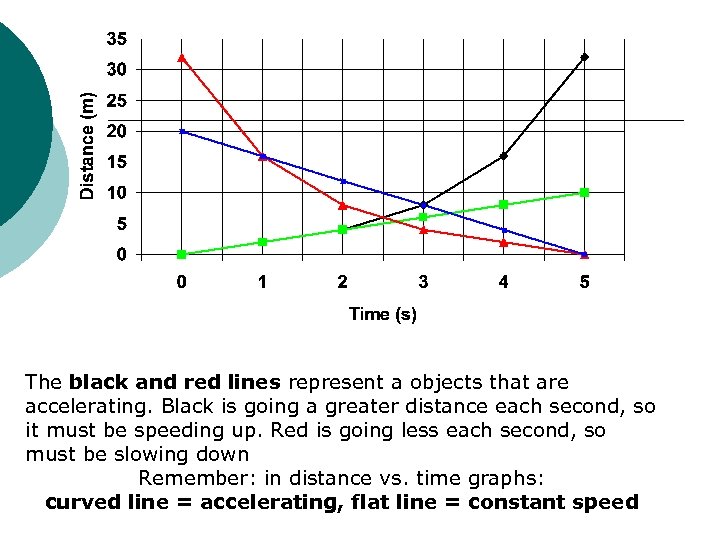 The black and red lines represent a objects that are accelerating. Black is going a greater distance each second, so it must be speeding up. Red is going less each second, so 1)Which line represents an object that is must be slowing down Remember: in distance vs. time graphs: accelerating? curved line = accelerating, flat line = constant speed
The black and red lines represent a objects that are accelerating. Black is going a greater distance each second, so it must be speeding up. Red is going less each second, so 1)Which line represents an object that is must be slowing down Remember: in distance vs. time graphs: accelerating? curved line = accelerating, flat line = constant speed
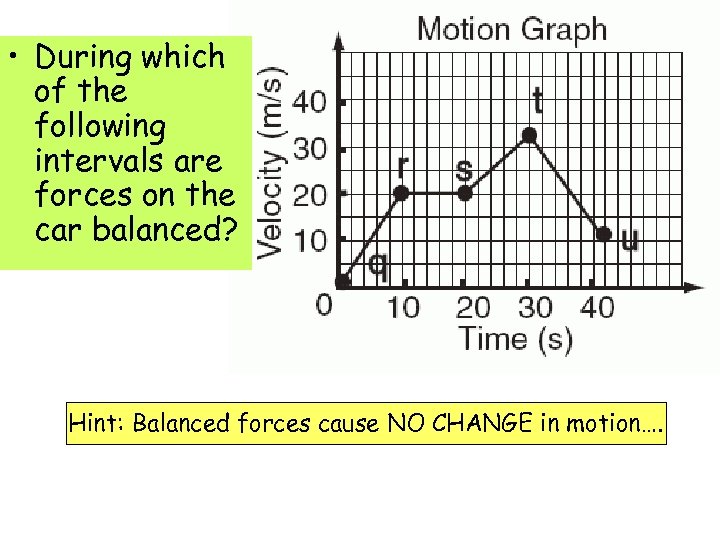 • During which of the following intervals are forces on the car balanced? Hint: Balanced forces cause NO CHANGE in motion….
• During which of the following intervals are forces on the car balanced? Hint: Balanced forces cause NO CHANGE in motion….
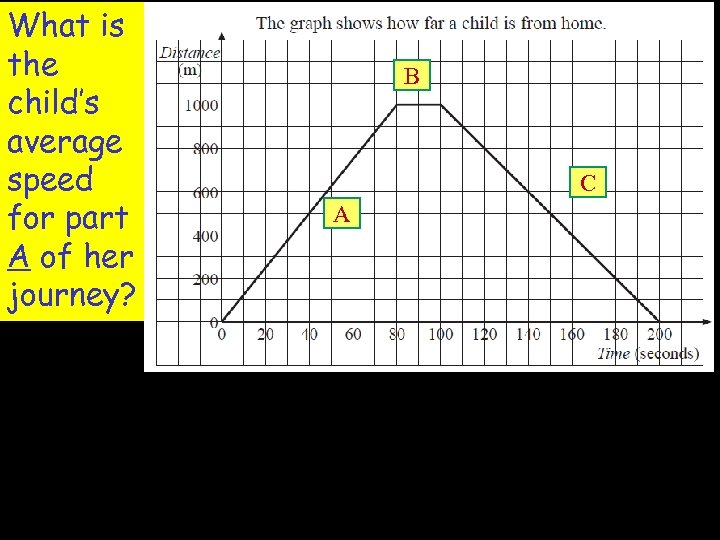 What is the child’s average speed for part A of her journey? B C A
What is the child’s average speed for part A of her journey? B C A
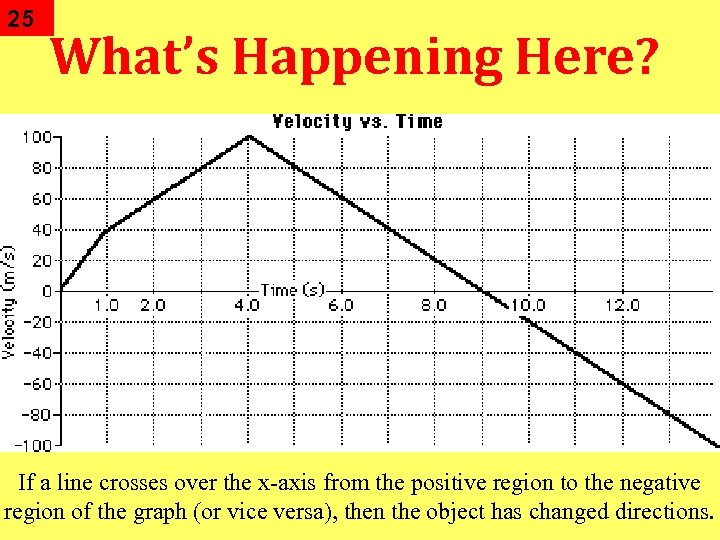 25 What’s Happening Here? If a line crosses over the x-axis from the positive region to the negative region of the graph (or vice versa), then the object has changed directions.
25 What’s Happening Here? If a line crosses over the x-axis from the positive region to the negative region of the graph (or vice versa), then the object has changed directions.
 26 Instantaneous Speed Instantaneous speed is the motion rate of an object at a particular time period or moment.
26 Instantaneous Speed Instantaneous speed is the motion rate of an object at a particular time period or moment.
 27 EOCT QUESTIONS What is the average speed of a car that travels 350 kilometers in 5 hours? A. B. C. D. 7 km/hr 70 km/hr 300 km/hr 1750 km/hr
27 EOCT QUESTIONS What is the average speed of a car that travels 350 kilometers in 5 hours? A. B. C. D. 7 km/hr 70 km/hr 300 km/hr 1750 km/hr
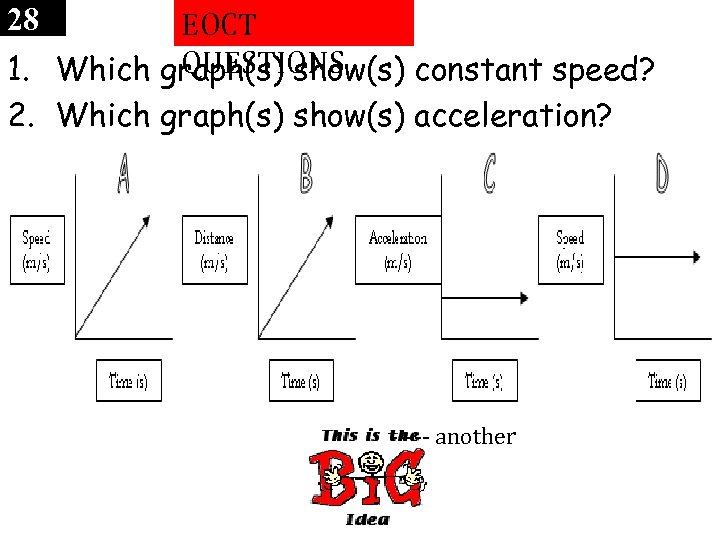 28 EOCT QUESTIONS 1. Which graph(s) show(s) constant speed? 2. Which graph(s) show(s) acceleration? ----- another
28 EOCT QUESTIONS 1. Which graph(s) show(s) constant speed? 2. Which graph(s) show(s) acceleration? ----- another
 …with a partner…. p. 2. . #s 9 -11 and p. 3. . #s 12 -16
…with a partner…. p. 2. . #s 9 -11 and p. 3. . #s 12 -16
 29 THE END
29 THE END


