33a1268c50aac876082c67e95240bb12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 195
 In a Nutshell – Key Questions and Concepts on Historical Eras By M. A. Rivera
In a Nutshell – Key Questions and Concepts on Historical Eras By M. A. Rivera
 Colonial Era and American Revolution – In a Nutshell Early 1600’s British settle American colonies because of adventure, fortune, and liberty Ideas of representative government, religious freedom, and freedom of the press were well-established by the time of the American Revolution After French and Indian War in 1763 – tensions between U. S. and Britain increase At end of American Revolution, Britain recognizes U. S. as independent
Colonial Era and American Revolution – In a Nutshell Early 1600’s British settle American colonies because of adventure, fortune, and liberty Ideas of representative government, religious freedom, and freedom of the press were well-established by the time of the American Revolution After French and Indian War in 1763 – tensions between U. S. and Britain increase At end of American Revolution, Britain recognizes U. S. as independent
 What major religious groups settled in the original thirteen colonies? Puritans – Massachusetts Roman Catholics – Maryland (Chesapeake Bay) Quakers – Pennsylvania Anglicans in the southern colonies Puritan intolerance led to establishment of Rhode Island
What major religious groups settled in the original thirteen colonies? Puritans – Massachusetts Roman Catholics – Maryland (Chesapeake Bay) Quakers – Pennsylvania Anglicans in the southern colonies Puritan intolerance led to establishment of Rhode Island
 What was the last of the thirteen colonies? Georgia Founded as haven for debtors Buffer between Spanish and English colonies
What was the last of the thirteen colonies? Georgia Founded as haven for debtors Buffer between Spanish and English colonies
 What was the Great Awakening? Wave of religious enthusiasm in the late 1730 s to 1760 s Characterized by emotionalism and individualism Leads to creation of new religious groups and strengthens belief in religious freedom
What was the Great Awakening? Wave of religious enthusiasm in the late 1730 s to 1760 s Characterized by emotionalism and individualism Leads to creation of new religious groups and strengthens belief in religious freedom
 Why did the English go to war against the French and Indians in 1754? A struggle for control of the Ohio Valley France lost empire in North America
Why did the English go to war against the French and Indians in 1754? A struggle for control of the Ohio Valley France lost empire in North America
 What caused the American Revolution? French and Indian War ended British government tried to regulate and tax colonies to pay for the war Policies spark protests that lead to the war in 1775
What caused the American Revolution? French and Indian War ended British government tried to regulate and tax colonies to pay for the war Policies spark protests that lead to the war in 1775
 When did Americans declare independence from Britain? One year after fighting for: “rights of Englishmen” “taxation without representation Inspired by Thomas Paine’s Common Sense Written by Thomas Jefferson
When did Americans declare independence from Britain? One year after fighting for: “rights of Englishmen” “taxation without representation Inspired by Thomas Paine’s Common Sense Written by Thomas Jefferson
 What significant battles led to the American victory over the English forces? American victory in Saratoga, New York inspired French to actively support Americans Ends in 1781 in the Battle of Yorktown, Virginia led by George Washington defeated General Cornwallis’ British army Treaty of Paris of 1783 puts an end to the American Revolution
What significant battles led to the American victory over the English forces? American victory in Saratoga, New York inspired French to actively support Americans Ends in 1781 in the Battle of Yorktown, Virginia led by George Washington defeated General Cornwallis’ British army Treaty of Paris of 1783 puts an end to the American Revolution
 The New Republic – In a Nutshell Weaknesses in national government under Articles of Confederation led to Constitutional Convention where new, more powerful central government was created 1790 s – George Washington presides over creation of new government Political parties created during Washington’s tenure Party division, territorial growth and a war in Europe shape U. S. history in the early 19 th century
The New Republic – In a Nutshell Weaknesses in national government under Articles of Confederation led to Constitutional Convention where new, more powerful central government was created 1790 s – George Washington presides over creation of new government Political parties created during Washington’s tenure Party division, territorial growth and a war in Europe shape U. S. history in the early 19 th century
 What event prompted delegates to write a new constitution? Daniel Shays led a rebellion of debtor farmers against MA government in winter of 1786 -1787 Unsuccessful but made prominent Americans aware that the Confederation Congress was powerless to protect the nation from invasion or domestic violence
What event prompted delegates to write a new constitution? Daniel Shays led a rebellion of debtor farmers against MA government in winter of 1786 -1787 Unsuccessful but made prominent Americans aware that the Confederation Congress was powerless to protect the nation from invasion or domestic violence
 Who attended the Constitutional Convention? Rhode Island boycotts 55 delegates from 12 states attended Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787 George Washington of Virginia presided Alexander Hamilton of New York spoke in favor of strong central government Ben Franklin of Pennsylvania gave prestige James Madison of Virginia considered the “Father of the Constitution” John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, and Patrick Henry did not attend
Who attended the Constitutional Convention? Rhode Island boycotts 55 delegates from 12 states attended Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787 George Washington of Virginia presided Alexander Hamilton of New York spoke in favor of strong central government Ben Franklin of Pennsylvania gave prestige James Madison of Virginia considered the “Father of the Constitution” John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, and Patrick Henry did not attend
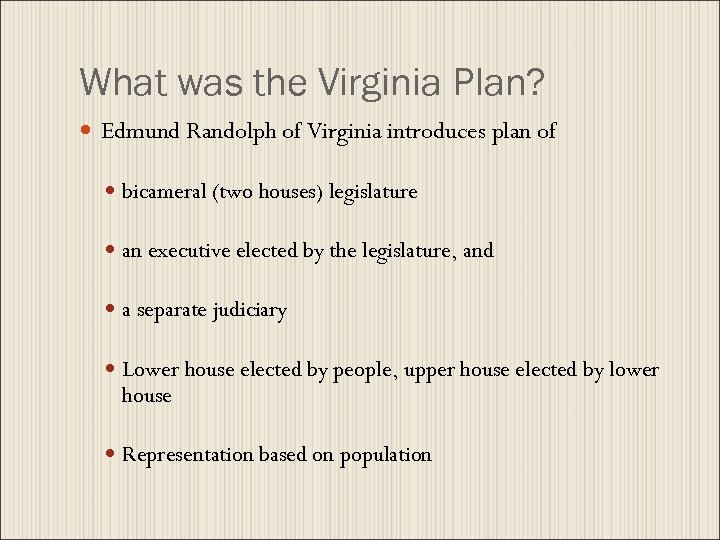 What was the Virginia Plan? Edmund Randolph of Virginia introduces plan of bicameral (two houses) legislature an executive elected by the legislature, and a separate judiciary Lower house elected by people, upper house elected by lower house Representation based on population
What was the Virginia Plan? Edmund Randolph of Virginia introduces plan of bicameral (two houses) legislature an executive elected by the legislature, and a separate judiciary Lower house elected by people, upper house elected by lower house Representation based on population
 What was the New Jersey Plan? William Paterson of New Jersey Plan presents a desire of small states to have equal representation in unicameral (one house) legislature
What was the New Jersey Plan? William Paterson of New Jersey Plan presents a desire of small states to have equal representation in unicameral (one house) legislature
 What was the Great Compromise? Delegates from Connecticut introduce compromise Federal legislature is bicameral Upper house (Senate) based on equal representation from each state Lower House (House of Representatives) based on population
What was the Great Compromise? Delegates from Connecticut introduce compromise Federal legislature is bicameral Upper house (Senate) based on equal representation from each state Lower House (House of Representatives) based on population
 What was the Three-Fifths Compromise? Delegates decided to count slaves as 3/5 of a person for both taxation and representation.
What was the Three-Fifths Compromise? Delegates decided to count slaves as 3/5 of a person for both taxation and representation.
 What form of government was created by the U. S. Constitution? Republican form of government based on separation of powers between three branches of government Executive Legislative Judicial Federal system of government that separates powers between national government and state government
What form of government was created by the U. S. Constitution? Republican form of government based on separation of powers between three branches of government Executive Legislative Judicial Federal system of government that separates powers between national government and state government
 What arguments were presented in the debate over ratification of the U. S. Constitution? Antifederalists Believed new government would destroy power of the states and not protect individual rights Federalists Believed strengthening central government would provide stability and power to prevent foreign domination and domestic rebellion Believed creating a republican government with limited power would protect the rights of the people
What arguments were presented in the debate over ratification of the U. S. Constitution? Antifederalists Believed new government would destroy power of the states and not protect individual rights Federalists Believed strengthening central government would provide stability and power to prevent foreign domination and domestic rebellion Believed creating a republican government with limited power would protect the rights of the people
 When was the Constitution ratified? 1788 after required 9 of 13 states voted for adopting the new form of government Only Rhode Island North Carolina voted against ratification New government took power in 1789
When was the Constitution ratified? 1788 after required 9 of 13 states voted for adopting the new form of government Only Rhode Island North Carolina voted against ratification New government took power in 1789
 What were the major achievements of George Washington and the First Congress? Established Executive Departments State, Treasury, and War Created a Federal Court System with a Supreme Court Passed a Revenue Tariff Adapted the first ten amendments (Bill of Rights) and ratified them in 1791
What were the major achievements of George Washington and the First Congress? Established Executive Departments State, Treasury, and War Created a Federal Court System with a Supreme Court Passed a Revenue Tariff Adapted the first ten amendments (Bill of Rights) and ratified them in 1791
 What policies did Alexander Hamilton adopt to strengthen the nation’s financial policies? To fund federal debt, Secretary of Treasury raised money through Excise taxes Tariffs Sale of western land Proposed federal bank take over states’ debts Created of strong national currency Created the Bank of the United States, a private bank where federal government deposited federal funds In showing financial responsibility, Hamilton’s policies strengthened the power of the national government
What policies did Alexander Hamilton adopt to strengthen the nation’s financial policies? To fund federal debt, Secretary of Treasury raised money through Excise taxes Tariffs Sale of western land Proposed federal bank take over states’ debts Created of strong national currency Created the Bank of the United States, a private bank where federal government deposited federal funds In showing financial responsibility, Hamilton’s policies strengthened the power of the national government
 What criticisms were leveled at Hamilton’s financial policies? Tariff created higher prices – states didn’t like paying other states’ debts Farmers in Pennsylvania protested excise tax on whiskey (Whiskey Rebellion) – a protest that ended when Washington sent in Federal troops Bank of the United States criticized for favoring the wealthy, northerners and lack of constitutionality
What criticisms were leveled at Hamilton’s financial policies? Tariff created higher prices – states didn’t like paying other states’ debts Farmers in Pennsylvania protested excise tax on whiskey (Whiskey Rebellion) – a protest that ended when Washington sent in Federal troops Bank of the United States criticized for favoring the wealthy, northerners and lack of constitutionality
 How did the French Revolution affect the United States? At first, most Americans support French Revolution in 1789 Attitudes changed when France declared war on Britain, Spain and Holland President Washington proclaimed neutrality in the European conflict
How did the French Revolution affect the United States? At first, most Americans support French Revolution in 1789 Attitudes changed when France declared war on Britain, Spain and Holland President Washington proclaimed neutrality in the European conflict
 Why were political parties created? Political and economic differences between Hamilton and Jefferson launched the two political parties Federalists supported Hamilton Strong central government Loose interpretation of the Constitution Bank of the United States Revenue tariffs England in its war against France Democratic-Republicans Supported Jefferson and opposed all of the other Federalist ideals
Why were political parties created? Political and economic differences between Hamilton and Jefferson launched the two political parties Federalists supported Hamilton Strong central government Loose interpretation of the Constitution Bank of the United States Revenue tariffs England in its war against France Democratic-Republicans Supported Jefferson and opposed all of the other Federalist ideals
 What were the most important issues during John Adams’ presidency? Served at a time of great division between political parties and a potential war with France Federalists, controlled the government, passed the Alien and Sedition Acts to silence Democratic-Republicans’ criticisms and prevent war with France
What were the most important issues during John Adams’ presidency? Served at a time of great division between political parties and a potential war with France Federalists, controlled the government, passed the Alien and Sedition Acts to silence Democratic-Republicans’ criticisms and prevent war with France
 What happened in the election of 1800? Tie in the Electoral College between John Adams and Thomas Jefferson elected by the House of Representatives to be the 3 rd President of the U. S. Established important precedent of transition between two different political parties from Federalists to Democratic. Republicans
What happened in the election of 1800? Tie in the Electoral College between John Adams and Thomas Jefferson elected by the House of Representatives to be the 3 rd President of the U. S. Established important precedent of transition between two different political parties from Federalists to Democratic. Republicans
 Who was John Marshall? Chief Justice from 1801 -1835 Handed down decisions that strengthened the national government and the power of the Supreme Court Supported private property Helped establish the American free market system
Who was John Marshall? Chief Justice from 1801 -1835 Handed down decisions that strengthened the national government and the power of the Supreme Court Supported private property Helped establish the American free market system
 Westward Expansion – In a Nutshell A period of strong nationalism emerged in 1815 after the end of the second war with Great Britain The Age of Jackson (1824 -1840) was marked by new system of party politics, numerous political changes, and a variety of social reform movements The U. S. fulfilled many expansionist goals in the 1840 s Before 1860 the North and South separated by economic, political and cultural differences that became more difficult to compromise After the election of Abraham Lincoln, several southern states seceded from the Union, an action that led to the American Civil War in 1861
Westward Expansion – In a Nutshell A period of strong nationalism emerged in 1815 after the end of the second war with Great Britain The Age of Jackson (1824 -1840) was marked by new system of party politics, numerous political changes, and a variety of social reform movements The U. S. fulfilled many expansionist goals in the 1840 s Before 1860 the North and South separated by economic, political and cultural differences that became more difficult to compromise After the election of Abraham Lincoln, several southern states seceded from the Union, an action that led to the American Civil War in 1861
 How did the United States gain Louisiana? Thomas Jefferson, against his strict interpretation of the Constitution principle purchased Louisiana from France Doubles size of the U. S. Gives the U. S. full control of the Mississippi River
How did the United States gain Louisiana? Thomas Jefferson, against his strict interpretation of the Constitution principle purchased Louisiana from France Doubles size of the U. S. Gives the U. S. full control of the Mississippi River
 Why did the U. S. go into war in 1812? 1810 – New generation of political leaders known as War Hawks elected to Congress Pressure President James Madison to go to War Causes: England’s violation of Freedom of Seas Problems Americans had with Indians in the Northwest Desire to annex Canada (territorial growth) Impressments Treaty of Ghent restores conditions to how they were before
Why did the U. S. go into war in 1812? 1810 – New generation of political leaders known as War Hawks elected to Congress Pressure President James Madison to go to War Causes: England’s violation of Freedom of Seas Problems Americans had with Indians in the Northwest Desire to annex Canada (territorial growth) Impressments Treaty of Ghent restores conditions to how they were before
 What is the Era of Good Feelings? Period following the War of 1812 characterized by strong nationalism and only one major political party
What is the Era of Good Feelings? Period following the War of 1812 characterized by strong nationalism and only one major political party
 What was the American System? Henry Clay introduced the American System Proposal to make the U. S. economically self-sufficient Plan includes a Second Bank of the United States, protective tariffs and internal improvements at a federal expense
What was the American System? Henry Clay introduced the American System Proposal to make the U. S. economically self-sufficient Plan includes a Second Bank of the United States, protective tariffs and internal improvements at a federal expense
 What were the most important issues of James Monroe’s presidency? Obtained Florida from Spain Issued the Monroe Doctrine, declaring that U. S. would not allow European colonization or interference in Latin America
What were the most important issues of James Monroe’s presidency? Obtained Florida from Spain Issued the Monroe Doctrine, declaring that U. S. would not allow European colonization or interference in Latin America
 Who won the election of 1824? Andrew Jackson won the popular vote and the most electoral votes; he did not have the majority of the electoral votes John Quincy Adams elected president by the House of Representatives
Who won the election of 1824? Andrew Jackson won the popular vote and the most electoral votes; he did not have the majority of the electoral votes John Quincy Adams elected president by the House of Representatives
 How did the election of 1824 bring the Era of Good Feelings to an End? Jackson’s supporters charged that John Quincy Adams’ election was a “corrupt bargain” where Henry Clay was made secretary of state in return for his support of Adams. Brought about two political parties Supporters of Jackson – Democrats Supporters of Adams and Clay - Whigs
How did the election of 1824 bring the Era of Good Feelings to an End? Jackson’s supporters charged that John Quincy Adams’ election was a “corrupt bargain” where Henry Clay was made secretary of state in return for his support of Adams. Brought about two political parties Supporters of Jackson – Democrats Supporters of Adams and Clay - Whigs
 What was Jacksonian Democracy? Refers to the general extension of democracy between 1824 and 1828 Primary from lower classes in rebellion to aristocracy Contradicted their idea of equality as pro-slavery and anti. Indian
What was Jacksonian Democracy? Refers to the general extension of democracy between 1824 and 1828 Primary from lower classes in rebellion to aristocracy Contradicted their idea of equality as pro-slavery and anti. Indian
 How did Jackson expand the powers of the presidency? Used his veto power extensively Defied Supreme Court orders Justified his actions by claiming that the presidency was the only office representing all the people
How did Jackson expand the powers of the presidency? Used his veto power extensively Defied Supreme Court orders Justified his actions by claiming that the presidency was the only office representing all the people
 What was Jackson’s policy toward American Indians? Policy of “removal” Believed Indian land must be open to economic development Forced natives to move west of the Mississippi River
What was Jackson’s policy toward American Indians? Policy of “removal” Believed Indian land must be open to economic development Forced natives to move west of the Mississippi River
 How did Jackson destroy the Bank of the United States? Congress voted to re-charter the 2 nd Bank of the United States in 1832. Jackson vetoed the Recharter Bill. Withdrew government funds from Bank and placed them in state banks or “pet” banks Led to runaway inflation Jackson issues Specie Circular (executive order states that all land must be paid in gold/silver) which leads to the Panic of 1837
How did Jackson destroy the Bank of the United States? Congress voted to re-charter the 2 nd Bank of the United States in 1832. Jackson vetoed the Recharter Bill. Withdrew government funds from Bank and placed them in state banks or “pet” banks Led to runaway inflation Jackson issues Specie Circular (executive order states that all land must be paid in gold/silver) which leads to the Panic of 1837
 Who succeeded Andrew Jackson as president? 1836 – Martin Van Buren – hand-picked by Jackson to be president. Later blamed for Panic of 1837 and not re-elected. 1840 – William Henry Harrison elected president with John Tyler as vice president. Both parties seek votes Known as first “modern” election Harrison died after 1 month in office Tyler 1 st Vice-President elevated to President due to the death of a President
Who succeeded Andrew Jackson as president? 1836 – Martin Van Buren – hand-picked by Jackson to be president. Later blamed for Panic of 1837 and not re-elected. 1840 – William Henry Harrison elected president with John Tyler as vice president. Both parties seek votes Known as first “modern” election Harrison died after 1 month in office Tyler 1 st Vice-President elevated to President due to the death of a President
 How did the election of 1844 change the U. S. ? James K. Polk, a Democrat, elected on platform of “Re-annexation” of Texas “Re-occupation” of Oregon U. S. annexed independent Texas In treaty with Great Britain, Oregon territory is annexed Annexed land after war with Mexico Mexican-American War began after General Zachary Taylor clashed with Mexican troops near the Rio Grande U. S. gains land after Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo for $15 million
How did the election of 1844 change the U. S. ? James K. Polk, a Democrat, elected on platform of “Re-annexation” of Texas “Re-occupation” of Oregon U. S. annexed independent Texas In treaty with Great Britain, Oregon territory is annexed Annexed land after war with Mexico Mexican-American War began after General Zachary Taylor clashed with Mexican troops near the Rio Grande U. S. gains land after Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo for $15 million
 What were the differences between northern and southern states before the Civil War? North Growing manufacturing economy Several political changes Variety of dynamic reform movements South Remained primarily agricultural based on cotton and plantation system
What were the differences between northern and southern states before the Civil War? North Growing manufacturing economy Several political changes Variety of dynamic reform movements South Remained primarily agricultural based on cotton and plantation system
 What were the political differences between northern and southern states before the Civil War? Northerners generally supported The Bank of the United States A protective tariff Internal improvements at federal expense Prohibition of slavery in the new territories Southerners generally disagreed with Northerners on these issues
What were the political differences between northern and southern states before the Civil War? Northerners generally supported The Bank of the United States A protective tariff Internal improvements at federal expense Prohibition of slavery in the new territories Southerners generally disagreed with Northerners on these issues
 What did northerners think of slavery? Although abolitionist movements were growing in the North, most did not sympathize with abolitionists until the 1850 s Abolitionist supporters felt it was morally wrong Abolitionists believed Slavery led to inhumane treatment of blacks Violated principles of democracy Violated teachings of the Bible
What did northerners think of slavery? Although abolitionist movements were growing in the North, most did not sympathize with abolitionists until the 1850 s Abolitionist supporters felt it was morally wrong Abolitionists believed Slavery led to inhumane treatment of blacks Violated principles of democracy Violated teachings of the Bible
 What did southerners think of slavery? Although most southerners did not own slaves, they supported slavery Argued: It always existed Was more humane than northern capitalism Was sanctioned by the Bible
What did southerners think of slavery? Although most southerners did not own slaves, they supported slavery Argued: It always existed Was more humane than northern capitalism Was sanctioned by the Bible
 How were the differences settled before the 1850 s? End of Mexican-American War in 1848 marked a turning point in the conflict. Land obtained intensified debate over slavery in the new territories Difficult to compromise because addition of states would offset the political balance in government especially the Senate
How were the differences settled before the 1850 s? End of Mexican-American War in 1848 marked a turning point in the conflict. Land obtained intensified debate over slavery in the new territories Difficult to compromise because addition of states would offset the political balance in government especially the Senate
 What was the Compromise of 1850? California became a free state and Congress adopted a Fugitive Slave Law. Slave trade abolished in District of Columbia (D. C. ) Slavery in New Mexico and Utah based on popular sovereignty Texas boundary would be reduced Texas debt paid by the Federal government
What was the Compromise of 1850? California became a free state and Congress adopted a Fugitive Slave Law. Slave trade abolished in District of Columbia (D. C. ) Slavery in New Mexico and Utah based on popular sovereignty Texas boundary would be reduced Texas debt paid by the Federal government
 What effect did Uncle Tom’s Cabin have on sectional differences? Written by Harriet Beecher Stowe Stirred conscience of the North Increased anti-slavery sentiment
What effect did Uncle Tom’s Cabin have on sectional differences? Written by Harriet Beecher Stowe Stirred conscience of the North Increased anti-slavery sentiment
 What was the Kansas-Nebraska Act? Authored by Senator Stephen Douglas Passed as provision for creating territorial governments in Kansas and Nebraska Repealed the Missouri Compromise by ensuring that the slavery issues was not solved by the 36⁰ 30’ line but by popular sovereignty
What was the Kansas-Nebraska Act? Authored by Senator Stephen Douglas Passed as provision for creating territorial governments in Kansas and Nebraska Repealed the Missouri Compromise by ensuring that the slavery issues was not solved by the 36⁰ 30’ line but by popular sovereignty
 Why was the Republican Party created? Whig party split Northerners looking for alternative to Democratic Party’s support of popular sovereignty Kansas-Nebraska Act passing leads to creation of Republican Party – opposed to popular sovereignty and extension of slavery into new territories
Why was the Republican Party created? Whig party split Northerners looking for alternative to Democratic Party’s support of popular sovereignty Kansas-Nebraska Act passing leads to creation of Republican Party – opposed to popular sovereignty and extension of slavery into new territories
 What was the Dred Scott decision? Victory for southern slaveowners Supreme Court case in 1857 that stated that blacks were not citizens and could not sue in federal court. Court ruled that Congress could not outlaw slavery in territories because it would deprive slaveowners of their property and deny a fundamental right guaranteed by the Constitution.
What was the Dred Scott decision? Victory for southern slaveowners Supreme Court case in 1857 that stated that blacks were not citizens and could not sue in federal court. Court ruled that Congress could not outlaw slavery in territories because it would deprive slaveowners of their property and deny a fundamental right guaranteed by the Constitution.
 What were the Lincoln-Douglas debates? Election for U. S. Senate in 1858 Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas debated in Illinois Douglas won the election Lincoln becomes nationally known Douglas argued that Congress might not keep slavery out of the territories but people could
What were the Lincoln-Douglas debates? Election for U. S. Senate in 1858 Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas debated in Illinois Douglas won the election Lincoln becomes nationally known Douglas argued that Congress might not keep slavery out of the territories but people could
 What happened at Harper’s Ferry, Virginia in 1859? John Brown, a radical abolitionist, led a raid on a Federal arsenal at Harper’s Ferry Hoped to seize weapons and start a slave revolt in the South Captured and charged with treason Executed and martyred by many Northerners. Southerners saw Brown as part of a conspiracy and increased their own rhetoric
What happened at Harper’s Ferry, Virginia in 1859? John Brown, a radical abolitionist, led a raid on a Federal arsenal at Harper’s Ferry Hoped to seize weapons and start a slave revolt in the South Captured and charged with treason Executed and martyred by many Northerners. Southerners saw Brown as part of a conspiracy and increased their own rhetoric
 What happened in the election of 1860? Abraham Lincoln won a minority of popular votes running against three (3) other candidates Won a majority of electoral votes Chosen sixteenth (16 th) president of the U. S. Seven (7) southern states responded by seceding and forming the Confederate States of America
What happened in the election of 1860? Abraham Lincoln won a minority of popular votes running against three (3) other candidates Won a majority of electoral votes Chosen sixteenth (16 th) president of the U. S. Seven (7) southern states responded by seceding and forming the Confederate States of America
 In a Nutshell – The Civil War Union forces seemed to have numerous advantages but Confederate forces win some key battles at the beginning of the war After victories at Vicksburg and Gettysburg, Union begins to win the war Reconstruction begins after the war President Johnson and Congress clash over policies, specifically with regard to former slaves Reconstruction ends in 1877 when northern troops pulled out of the South
In a Nutshell – The Civil War Union forces seemed to have numerous advantages but Confederate forces win some key battles at the beginning of the war After victories at Vicksburg and Gettysburg, Union begins to win the war Reconstruction begins after the war President Johnson and Congress clash over policies, specifically with regard to former slaves Reconstruction ends in 1877 when northern troops pulled out of the South
 When did the Civil War begin? April 12, 1861 when Confederate troops attacked Union forces at Ft. Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. President Lincoln calls on group of volunteers to put down rebellion 4 southern states secede and join 7 states already in Confederacy (total of 11)
When did the Civil War begin? April 12, 1861 when Confederate troops attacked Union forces at Ft. Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. President Lincoln calls on group of volunteers to put down rebellion 4 southern states secede and join 7 states already in Confederacy (total of 11)
 What was the Emancipation Proclamation? Issued after important northern victory in Antietam, Maryland Freed all slaves living in rebelling states Inspired northern population to win support of European nations
What was the Emancipation Proclamation? Issued after important northern victory in Antietam, Maryland Freed all slaves living in rebelling states Inspired northern population to win support of European nations
 What were the northern advantages in the Civil War? South had better military leadership and fighting a defensive war on their soil Northern advantages included: Population Industrial resources Agricultural resources Naval resources Financial resources Were over-confident and expected a short resolution to the war
What were the northern advantages in the Civil War? South had better military leadership and fighting a defensive war on their soil Northern advantages included: Population Industrial resources Agricultural resources Naval resources Financial resources Were over-confident and expected a short resolution to the war
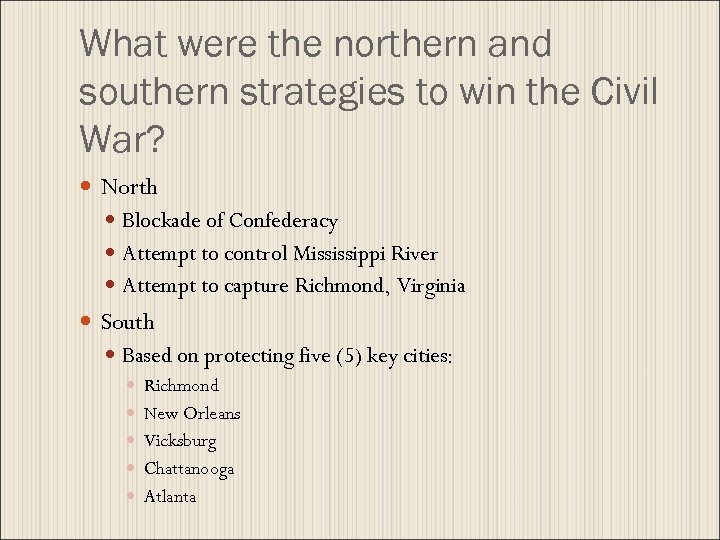 What were the northern and southern strategies to win the Civil War? North Blockade of Confederacy Attempt to control Mississippi River Attempt to capture Richmond, Virginia South Based on protecting five (5) key cities: Richmond New Orleans Vicksburg Chattanooga Atlanta
What were the northern and southern strategies to win the Civil War? North Blockade of Confederacy Attempt to control Mississippi River Attempt to capture Richmond, Virginia South Based on protecting five (5) key cities: Richmond New Orleans Vicksburg Chattanooga Atlanta
 Why did southerners believe “King Cotton” would win the war? Hoped that England’s need for cotton would lead to their support Cotton surpluses in Egypt and India and British need for northern wheat forced England not to support South fully
Why did southerners believe “King Cotton” would win the war? Hoped that England’s need for cotton would lead to their support Cotton surpluses in Egypt and India and British need for northern wheat forced England not to support South fully
 Why was the Battle of the Bull Run important? South won the first major battle of the war Southerners became overconfident Northerners begin preparing for long, difficult war
Why was the Battle of the Bull Run important? South won the first major battle of the war Southerners became overconfident Northerners begin preparing for long, difficult war
 Why was the year 1863 considered the turning point of the Civil War? Confederacy won many great victories prior to 1863 Battle of Vicksburg (1863) North takes over Mississippi Rivera Battle of Gettysburg (1863) North demonstrates that South will never be able to successfully invade the North
Why was the year 1863 considered the turning point of the Civil War? Confederacy won many great victories prior to 1863 Battle of Vicksburg (1863) North takes over Mississippi Rivera Battle of Gettysburg (1863) North demonstrates that South will never be able to successfully invade the North
 When did the Civil War end? Robert E. Lee and his Confederate forces surrender Forces led by General Ulysses S. Grant Appomattox Court House April 9, 1865
When did the Civil War end? Robert E. Lee and his Confederate forces surrender Forces led by General Ulysses S. Grant Appomattox Court House April 9, 1865
 What were some of the long-term results of the Civil War? Slavery abolished Supremacy of federal government established Northern industry begins dominating the economy
What were some of the long-term results of the Civil War? Slavery abolished Supremacy of federal government established Northern industry begins dominating the economy
 What political questions needed to be answered with the U. S. government’s Reconstruction policy? U. S. government decided what conditions southern states should meet to re-join the Union Whether the president or Congress most responsible for making Reconstruction policy What rights should be granted to former slaves
What political questions needed to be answered with the U. S. government’s Reconstruction policy? U. S. government decided what conditions southern states should meet to re-join the Union Whether the president or Congress most responsible for making Reconstruction policy What rights should be granted to former slaves
 What were the Reconstruction policies of the Lincoln-Johnson administrations? Lincoln’s policies Based on his belief that southern states had not seceded (southern states had been in state of rebellion) Believed president was most responsible for Reconstruction policies because he had the power of pardon Believed policies should be lenient to southerners in order to gain loyalty Assassination in April 14, 1865 put southerner, Andrew Johnson in office Generally tried to follow Lincoln policies Let southern states determine legal status of freed slaves
What were the Reconstruction policies of the Lincoln-Johnson administrations? Lincoln’s policies Based on his belief that southern states had not seceded (southern states had been in state of rebellion) Believed president was most responsible for Reconstruction policies because he had the power of pardon Believed policies should be lenient to southerners in order to gain loyalty Assassination in April 14, 1865 put southerner, Andrew Johnson in office Generally tried to follow Lincoln policies Let southern states determine legal status of freed slaves
 What were the Black Codes? Implemented by Southern states immediately after Civil War Restricted the rights of African Americans by denying them the right to Bear arms Serve on juries Sue whites Testify against whites
What were the Black Codes? Implemented by Southern states immediately after Civil War Restricted the rights of African Americans by denying them the right to Bear arms Serve on juries Sue whites Testify against whites
 What were the Reconstruction policies of the Radical Republicans in the U. S. Congress? Treated the South as if it was a conquered territory Wanted to punish the South Wanted to protect legal rights of freed slaves Congressional power to admit new states led them to believe they had a right to determine Reconstruction policies
What were the Reconstruction policies of the Radical Republicans in the U. S. Congress? Treated the South as if it was a conquered territory Wanted to punish the South Wanted to protect legal rights of freed slaves Congressional power to admit new states led them to believe they had a right to determine Reconstruction policies
 Why was President Johnson impeached? He faced a political stalemate with Congress Impeached on the grounds that he violated the Tenure of Office Act Senate failed by one vote to convict him and remove him from office
Why was President Johnson impeached? He faced a political stalemate with Congress Impeached on the grounds that he violated the Tenure of Office Act Senate failed by one vote to convict him and remove him from office
 What effect did the election of Ulysses S. Grant have on Reconstruction policies? Election of Grant in 1868 gave Radical Republicans a president willing to carry out their policies
What effect did the election of Ulysses S. Grant have on Reconstruction policies? Election of Grant in 1868 gave Radical Republicans a president willing to carry out their policies
 What were the results of the Reconstruction policies of the Radical Republicans? Return of all southern states to the Union by 1870 Were under “carpetbag” governments and enforced Radical policies Increased sectional bitterness Southern vigilante groups tried to “redeem” the South Tried to deny the power of carpetbaggers (northerners), scalawags (southern Republicans), and African-Americans.
What were the results of the Reconstruction policies of the Radical Republicans? Return of all southern states to the Union by 1870 Were under “carpetbag” governments and enforced Radical policies Increased sectional bitterness Southern vigilante groups tried to “redeem” the South Tried to deny the power of carpetbaggers (northerners), scalawags (southern Republicans), and African-Americans.
 What effect did the election of 1876 have on Reconstruction policies? Rutherford Hayes was sworn in as President after he agreed to pull northern troops out of the south. Reconstruction comes to an end after President Hayes pulls the troops from the South
What effect did the election of 1876 have on Reconstruction policies? Rutherford Hayes was sworn in as President after he agreed to pull northern troops out of the south. Reconstruction comes to an end after President Hayes pulls the troops from the South
 What happened to African. Americans after U. S. troops pulled out of the South? Found themselves at the mercy of southern state governments after U. S. troops pulled out Race relations remain moderate because of leadership of Booker T. Washington and southern Bourbons 1890 s – southern states began to deny African-Americans the right to vote (Jim Crow laws) and a rigid segregation established
What happened to African. Americans after U. S. troops pulled out of the South? Found themselves at the mercy of southern state governments after U. S. troops pulled out Race relations remain moderate because of leadership of Booker T. Washington and southern Bourbons 1890 s – southern states began to deny African-Americans the right to vote (Jim Crow laws) and a rigid segregation established
 In a Nutshell - The Gilded Age (and 2 nd Industrial Revolution) U. S. experienced industrial takeoff in the late 1800 s Industrialization increased power and the standard of living Industrialization also creates many problems for farmers, workers and consumers Problems lead to the desire for government intervention in the economy
In a Nutshell - The Gilded Age (and 2 nd Industrial Revolution) U. S. experienced industrial takeoff in the late 1800 s Industrialization increased power and the standard of living Industrialization also creates many problems for farmers, workers and consumers Problems lead to the desire for government intervention in the economy
 How did the U. S. economy change after the Civil War? Corporations formed the basis for economic wealth U. S. entered industrial takeoff in the late 1800 s Industrial revolution leads to Urbanization Improved standard of living Greater concentration of wealth and power in fewer people Growth of labor unions By 1890 s – U. S. leading industrial nation in the world By 1917 – U. S. a creditor nation for the first time
How did the U. S. economy change after the Civil War? Corporations formed the basis for economic wealth U. S. entered industrial takeoff in the late 1800 s Industrial revolution leads to Urbanization Improved standard of living Greater concentration of wealth and power in fewer people Growth of labor unions By 1890 s – U. S. leading industrial nation in the world By 1917 – U. S. a creditor nation for the first time
 How did the U. S. government react to the Industrial Revolution in the late 19 th century? Laissez Faire Allowed a few individuals to accumulate wealth and eliminate competition
How did the U. S. government react to the Industrial Revolution in the late 19 th century? Laissez Faire Allowed a few individuals to accumulate wealth and eliminate competition
 What effect did the industrial revolution have on the union movement? Low pay, long hours, and bad working conditions more workers join unions Workers felt big business ignored the welfare of workers and demanded collective bargaining agreements with unions Labor unions faced many obstacles including: General anti-union government policies Division amongst the labor groups Violent confrontations with business owners and government
What effect did the industrial revolution have on the union movement? Low pay, long hours, and bad working conditions more workers join unions Workers felt big business ignored the welfare of workers and demanded collective bargaining agreements with unions Labor unions faced many obstacles including: General anti-union government policies Division amongst the labor groups Violent confrontations with business owners and government
 What effect did the industrial revolution have on farmers? Farmers faced serious problems in late 1800 s Railroad monopolies increase the price of shipping Deflation of the currency and agricultural overproduction drive prices down Farmers were debtors so deflation made it difficult for them to repay loans Farmers had to pay high prices for manufactured goods because of protective tariffs and monopolistic pricing Organizations protested by demanding government regulation of business and inflation of the currency
What effect did the industrial revolution have on farmers? Farmers faced serious problems in late 1800 s Railroad monopolies increase the price of shipping Deflation of the currency and agricultural overproduction drive prices down Farmers were debtors so deflation made it difficult for them to repay loans Farmers had to pay high prices for manufactured goods because of protective tariffs and monopolistic pricing Organizations protested by demanding government regulation of business and inflation of the currency
 Why was the Populist party created? Democrats and Republicans were unresponsive to needs of farmers Populist Party created in 1889 in demand of: Free silver Nationalization of railroads A progressive income tax Women’s suffrage Direct election of senators Secret ballots
Why was the Populist party created? Democrats and Republicans were unresponsive to needs of farmers Populist Party created in 1889 in demand of: Free silver Nationalization of railroads A progressive income tax Women’s suffrage Direct election of senators Secret ballots
 What happened after the election of 1896? Democratic Party and Populist Party nominate William Jennings Bryan for president Republicans nominate William Mc. Kinley, a pro-business conservative Mc. Kinley wins and a return to prosperity ends farmers’ protests movement Populist party died out but most reforms were passed in Progressive Era (19011914). Election of 1896 established Bryan as a leader of the Democratic Party Nominated for president in two more elections Election of 1896 solidifies a shift in American politics Liberalism, traditionally in favor of limited government and laissez-faire economics, enters new century in favor of big government and regulation of economy
What happened after the election of 1896? Democratic Party and Populist Party nominate William Jennings Bryan for president Republicans nominate William Mc. Kinley, a pro-business conservative Mc. Kinley wins and a return to prosperity ends farmers’ protests movement Populist party died out but most reforms were passed in Progressive Era (19011914). Election of 1896 established Bryan as a leader of the Democratic Party Nominated for president in two more elections Election of 1896 solidifies a shift in American politics Liberalism, traditionally in favor of limited government and laissez-faire economics, enters new century in favor of big government and regulation of economy
 In a Nutshell - The Progressive Era (and Imperialism) Demands for reform of politics and economics was widespread in the early 1900 s Government regulation of economic system began at the state level but because of national monopolies, help was needed of federal government in order to get meaningful reform Theodore Roosevelt becomes president and U. S. entered a period of reform under Roosevelt, William H. Taft, and Woodrow Wilson. The reforms passed under these three presidents would institutionalize a regulated capitalism
In a Nutshell - The Progressive Era (and Imperialism) Demands for reform of politics and economics was widespread in the early 1900 s Government regulation of economic system began at the state level but because of national monopolies, help was needed of federal government in order to get meaningful reform Theodore Roosevelt becomes president and U. S. entered a period of reform under Roosevelt, William H. Taft, and Woodrow Wilson. The reforms passed under these three presidents would institutionalize a regulated capitalism
 In a Nutshell - The Progressive Era (and Imperialism) Late 1800 s marked the rise of imperialism in the U. S. After war with Spain in 1898, U. S. gained territory in the Pacific and Caribbean Theodore Roosevelt expanded the original meaning of the Monroe Doctrine in Latin America
In a Nutshell - The Progressive Era (and Imperialism) Late 1800 s marked the rise of imperialism in the U. S. After war with Spain in 1898, U. S. gained territory in the Pacific and Caribbean Theodore Roosevelt expanded the original meaning of the Monroe Doctrine in Latin America
 What was the progressive movement? Response to problems created from a shift in the U. S. society moved from a rural society to an urban and industrial society People who wanted government to solve society’s problems In the early 1900 s, it focused on government regulation of big business in order to protect interests of American public
What was the progressive movement? Response to problems created from a shift in the U. S. society moved from a rural society to an urban and industrial society People who wanted government to solve society’s problems In the early 1900 s, it focused on government regulation of big business in order to protect interests of American public
 How effective was government regulation of big business before 1901? Regulation starts at state level with several farm states regulating railroad monopolies Supreme Court ends state regulation in Wabash v. Illinois, and shift turns to federal regulation First attempt comes with Interstate Commerce Commission Also attempts the Sherman Anti-Trust Act Generally ineffective because they were not enforced and limited by the Supreme Court Sherman Anti-Trust Act was used mostly to break up unions rather than trusts
How effective was government regulation of big business before 1901? Regulation starts at state level with several farm states regulating railroad monopolies Supreme Court ends state regulation in Wabash v. Illinois, and shift turns to federal regulation First attempt comes with Interstate Commerce Commission Also attempts the Sherman Anti-Trust Act Generally ineffective because they were not enforced and limited by the Supreme Court Sherman Anti-Trust Act was used mostly to break up unions rather than trusts
 When did effective regulation of big business begin at the federal level? In 1901 after Theodore Roosevelt became president After assassination of William Mc. Kinley, Roosevelt, vice- president and former governor of the state of New York took over Roosevelt selected because big business bosses wanted him out of New York and wanted him to be “useless” as VP Roosevelt begins progressive reform and regulates Big business Trust busting Conservation of natural resources
When did effective regulation of big business begin at the federal level? In 1901 after Theodore Roosevelt became president After assassination of William Mc. Kinley, Roosevelt, vice- president and former governor of the state of New York took over Roosevelt selected because big business bosses wanted him out of New York and wanted him to be “useless” as VP Roosevelt begins progressive reform and regulates Big business Trust busting Conservation of natural resources
 Did the public support the Progressive Reforms under Roosevelt? Muckraking journalists graphically exposed social, political, and economic problems Public was beginning to demand government action and generally supported progressive reforms Social Gospel movement had many Americans wanting government action and apply Jesus’ teachings to social and industrial problems created by rapid growth of big business
Did the public support the Progressive Reforms under Roosevelt? Muckraking journalists graphically exposed social, political, and economic problems Public was beginning to demand government action and generally supported progressive reforms Social Gospel movement had many Americans wanting government action and apply Jesus’ teachings to social and industrial problems created by rapid growth of big business
 Who became president after Theodore Roosevelt? William Howard Taft was Roosevelt’s hand-picked successor because of Roosevelt’s popularity Continued Roosevelt’s Square Deal by continuing to regulate business break up trusts Conserve natural resources
Who became president after Theodore Roosevelt? William Howard Taft was Roosevelt’s hand-picked successor because of Roosevelt’s popularity Continued Roosevelt’s Square Deal by continuing to regulate business break up trusts Conserve natural resources
 What happened in 1912? In election of 1912, Roosevelt challenged Taft for Republican nomination Because Taft controlled the party machinery, he beat Roosevelt for the nomination Roosevelt ran as a third-party candidate for the Progressive or “Bull Moose” Party Split in Republican party allows Woodrow Wilson, a Democrat to win the election
What happened in 1912? In election of 1912, Roosevelt challenged Taft for Republican nomination Because Taft controlled the party machinery, he beat Roosevelt for the nomination Roosevelt ran as a third-party candidate for the Progressive or “Bull Moose” Party Split in Republican party allows Woodrow Wilson, a Democrat to win the election
 What ideas were proposed by Roosevelt and Wilson in the 1912 election? Roosevelt’s New Nationalism Big government regulates big business Monopolies not harmful if regulated by federal government Wilson’s New Freedom Monopolies would be broken up Breakup would re-establish business competition and allow for small government
What ideas were proposed by Roosevelt and Wilson in the 1912 election? Roosevelt’s New Nationalism Big government regulates big business Monopolies not harmful if regulated by federal government Wilson’s New Freedom Monopolies would be broken up Breakup would re-establish business competition and allow for small government
 How did the reforms of the progressive era change the U. S. ? After pieces of reform passed under Woodrow Wilson, laissez-faire was replaced by regulated capitalism. Reform did not provide government relief to the poor and needy until Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal of the 1930 s
How did the reforms of the progressive era change the U. S. ? After pieces of reform passed under Woodrow Wilson, laissez-faire was replaced by regulated capitalism. Reform did not provide government relief to the poor and needy until Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal of the 1930 s
 How did U. S. foreign policy change in the late 1800 s? Adopted an imperialist foreign policy Imperialism was a result of the desire to: Protect overseas investments Fulfill the “white man’s burden” To obtain overseas naval bases Imperialism was an extension of the belief of Manifest Destiny
How did U. S. foreign policy change in the late 1800 s? Adopted an imperialist foreign policy Imperialism was a result of the desire to: Protect overseas investments Fulfill the “white man’s burden” To obtain overseas naval bases Imperialism was an extension of the belief of Manifest Destiny
 Why did the United States go to war against Spain in 1898? An attempt to help Cubans gain their independence from Spain Spanish violation of human rights in Cuba and American jingoism promoted by yellow journalism played a large role in desire to go to war Immediate cause: sinking of U. S. S. Maine in Havana harbor
Why did the United States go to war against Spain in 1898? An attempt to help Cubans gain their independence from Spain Spanish violation of human rights in Cuba and American jingoism promoted by yellow journalism played a large role in desire to go to war Immediate cause: sinking of U. S. S. Maine in Havana harbor
 What were the results of the Spanish-American War? U. S. army not fully prepared U. S. financially strong, industrially strong, and had a powerful navy Able to defeat Spain after just sixteen (16) weeks of fighting Land: Cuba became a protectorate Hawaii and the Samoas are annexed Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines given to the U. S. as territories
What were the results of the Spanish-American War? U. S. army not fully prepared U. S. financially strong, industrially strong, and had a powerful navy Able to defeat Spain after just sixteen (16) weeks of fighting Land: Cuba became a protectorate Hawaii and the Samoas are annexed Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines given to the U. S. as territories
 How did the U. S. obtain the rights to build a canal through Panama? Panama’s independence from Columbia in 1903 allowed U. S. to build canal through Central America Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty Panama became U. S. protectorate 10 -mile strip of land through Panama given to the U. S. so that a canal could be built
How did the U. S. obtain the rights to build a canal through Panama? Panama’s independence from Columbia in 1903 allowed U. S. to build canal through Central America Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty Panama became U. S. protectorate 10 -mile strip of land through Panama given to the U. S. so that a canal could be built
 What was the Roosevelt Corollary? Expanded the meaning of the Monroe Doctrine Established the U. S. as the policeman of the Western Hemisphere Used to justify “gunboat” diplomacy. “Dollar Diplomacy” Roosevelt left office President Taft encouraged investment in Latin America
What was the Roosevelt Corollary? Expanded the meaning of the Monroe Doctrine Established the U. S. as the policeman of the Western Hemisphere Used to justify “gunboat” diplomacy. “Dollar Diplomacy” Roosevelt left office President Taft encouraged investment in Latin America
 In a Nutshell - World War I began in Europe in 1914 Woodrow Wilson declares neutrality initially Enters the War in 1917 After WWI, President Wilson worked for an idealistic post- war plan that was rejected by European nations and the U. S. Senate
In a Nutshell - World War I began in Europe in 1914 Woodrow Wilson declares neutrality initially Enters the War in 1917 After WWI, President Wilson worked for an idealistic post- war plan that was rejected by European nations and the U. S. Senate
 What caused World War I? European imperialism Competition for overseas markets Nationalism Militarism (military build up and alliances) Lack of self-determination Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in 1914 set off a series of crises that led to the war
What caused World War I? European imperialism Competition for overseas markets Nationalism Militarism (military build up and alliances) Lack of self-determination Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in 1914 set off a series of crises that led to the war
 How did President Wilson respond to European nations goingt o war in 1914? Many Americans supported Allied Powers (Britain, France, and Russia), many supported the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy) President Wilson declared American neutrality initially Wilson asked Americans to be “neutral in thoughts as well as action”
How did President Wilson respond to European nations goingt o war in 1914? Many Americans supported Allied Powers (Britain, France, and Russia), many supported the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy) President Wilson declared American neutrality initially Wilson asked Americans to be “neutral in thoughts as well as action”
 When did American sentiment begin turning against Germany? After sinking of Lusitania in 1915, Americans increasingly supported the Allied powers
When did American sentiment begin turning against Germany? After sinking of Lusitania in 1915, Americans increasingly supported the Allied powers
 When did the U. S. declare war on Germany? Zimmerman Telegram and Germany continuance of unrestricted warfare led U. S. to declare war in April 1917
When did the U. S. declare war on Germany? Zimmerman Telegram and Germany continuance of unrestricted warfare led U. S. to declare war in April 1917
 What effect did the entry of U. S. forces have on World War I? American Expeditionary Force led by John J. Pershing arrived on western front and provided balance for Allied victory Armistice signed in November 1918
What effect did the entry of U. S. forces have on World War I? American Expeditionary Force led by John J. Pershing arrived on western front and provided balance for Allied victory Armistice signed in November 1918
 What were Wilson’s goals during World War I? Fighting a “war to end war” Winning “peace without victory” Making “the world safe for democracy” All ideas above outlined in Fourteen Points included: Removing the causes of war through open diplomacy Freedom of the seas Removal of tariff barriers Reduction in the size of armies Colonial independence Provisions for self-determination in Europe League of Nations
What were Wilson’s goals during World War I? Fighting a “war to end war” Winning “peace without victory” Making “the world safe for democracy” All ideas above outlined in Fourteen Points included: Removing the causes of war through open diplomacy Freedom of the seas Removal of tariff barriers Reduction in the size of armies Colonial independence Provisions for self-determination in Europe League of Nations
 What provisions of Wilson’s Fourteen Points adopted after World War I? Allied had already made several secret agreements prior to Wilson’s arrival in France to divide the spoils of the war Wilson found Allies wanted revenge against Germany Britain did not want to allow freedom of the seas Most 14 Points were rejected Contrary to Wilson’s desires, Treaty of Versailles punished Germany in military, territory, and finances Agreed to the League of Nations
What provisions of Wilson’s Fourteen Points adopted after World War I? Allied had already made several secret agreements prior to Wilson’s arrival in France to divide the spoils of the war Wilson found Allies wanted revenge against Germany Britain did not want to allow freedom of the seas Most 14 Points were rejected Contrary to Wilson’s desires, Treaty of Versailles punished Germany in military, territory, and finances Agreed to the League of Nations
 Was the Treaty of Versailles ratified by the U. S. Senate? Wilson worked hard to get Senate ratification Senate controlled by Republicans and divided over joining the League of Nations Democrats, known as internationalists, supported the treaty while Republicans opposed the treaty Republican reservationist senators would support treaty if U. S. troops not used in League actions Wilson suffered stroke and not able to push for treaty U. S. signed separate treaty with Germany and never joined League of Nations
Was the Treaty of Versailles ratified by the U. S. Senate? Wilson worked hard to get Senate ratification Senate controlled by Republicans and divided over joining the League of Nations Democrats, known as internationalists, supported the treaty while Republicans opposed the treaty Republican reservationist senators would support treaty if U. S. troops not used in League actions Wilson suffered stroke and not able to push for treaty U. S. signed separate treaty with Germany and never joined League of Nations
 In a Nutshell – The Roaring and Not-so-Roaring 20 s Prosperous time where government is generally conservative and pro-business U. S. divided over “city” values and “country” values
In a Nutshell – The Roaring and Not-so-Roaring 20 s Prosperous time where government is generally conservative and pro-business U. S. divided over “city” values and “country” values
 What happened during the Red Scare after World War I? Widespread fear of communism and radicalism as a result of the Russian Revolution of 1917 Americans feared that post-war strikes and bombing sweeping the nation were product of radical influences Government began jailing radicals and deporting immigrants (nativism) Actions led by Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer were known as the Palmer Raids. U. S. Intelligence Bureau begins spying on Americans Although it continued, panic generally ended by 1920 when it became clear that there was no serious threat and Palmer was a demagogue
What happened during the Red Scare after World War I? Widespread fear of communism and radicalism as a result of the Russian Revolution of 1917 Americans feared that post-war strikes and bombing sweeping the nation were product of radical influences Government began jailing radicals and deporting immigrants (nativism) Actions led by Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer were known as the Palmer Raids. U. S. Intelligence Bureau begins spying on Americans Although it continued, panic generally ended by 1920 when it became clear that there was no serious threat and Palmer was a demagogue
 In what ways were Americans divided in the 1920 s? “City” versus “Country” values Examples of this division were found in the: Scopes Trial Strength of the Ku Klux Klan Prohibition of alcohol
In what ways were Americans divided in the 1920 s? “City” versus “Country” values Examples of this division were found in the: Scopes Trial Strength of the Ku Klux Klan Prohibition of alcohol
 What was the Scopes Trial? Product of debate between Religious Fundamentalists and Modernists Issue: teaching of evolution in schools John Scopes, a biology teacher, was arrested for teaching evolution in Dayton, Tennessee
What was the Scopes Trial? Product of debate between Religious Fundamentalists and Modernists Issue: teaching of evolution in schools John Scopes, a biology teacher, was arrested for teaching evolution in Dayton, Tennessee
 How did the Ku Klux Klan shape U. S. history in the 1920 s? Contained over 5 million members Worked to “purify” America taking action to restrict the rights of: African Americans Jews Catholics Worked to “protect” America from radicals, immigrants, and nonconformists Late 1920 s – KKK declines in power because of corruption in Klan leadership
How did the Ku Klux Klan shape U. S. history in the 1920 s? Contained over 5 million members Worked to “purify” America taking action to restrict the rights of: African Americans Jews Catholics Worked to “protect” America from radicals, immigrants, and nonconformists Late 1920 s – KKK declines in power because of corruption in Klan leadership
 What effect did prohibition of alcohol have on the U. S. ? Adopted under Volstead Act with good intentions Impossible to enforce Was openly violated Led to disrespect of the law Increased organized crime Was repealed in 1933
What effect did prohibition of alcohol have on the U. S. ? Adopted under Volstead Act with good intentions Impossible to enforce Was openly violated Led to disrespect of the law Increased organized crime Was repealed in 1933
 What characterized American politics in the 1920 s? Most progressive reforms had been passed in Progressive Era and U. S. generally prosperous leads to politically conservative decade Warren Harding, nominated by Old Guard Republicans was elected on basis of: Lower taxes Cuts in government regulations Increase in tariffs “Normalcy” Harding died and Coolidge became president Coolidge supported: Business interests served untouched by scandals and corruption that characterized Harding administration
What characterized American politics in the 1920 s? Most progressive reforms had been passed in Progressive Era and U. S. generally prosperous leads to politically conservative decade Warren Harding, nominated by Old Guard Republicans was elected on basis of: Lower taxes Cuts in government regulations Increase in tariffs “Normalcy” Harding died and Coolidge became president Coolidge supported: Business interests served untouched by scandals and corruption that characterized Harding administration
 What happened in the election of 1928? Democrats nominated Al Smith, first Catholic to be chosen to run for President Smith lost to Herbert Hoover, first Republican since Reconstruction to win the Solid South
What happened in the election of 1928? Democrats nominated Al Smith, first Catholic to be chosen to run for President Smith lost to Herbert Hoover, first Republican since Reconstruction to win the Solid South
 The Great Depression – In a Nutshell Stock Market crash on October 29, 1929 signaled the beginning of the Great Depression – worst financial crisis in U. S. History Depression got worse – President Hoover followed policy o f denying government relief to unemployed – not re-elected in 1932 President Franklin Roosevelt pushed several legislative programs through Congress in attempt to end Great Depression ends after Americans found employment building war materials for WWII
The Great Depression – In a Nutshell Stock Market crash on October 29, 1929 signaled the beginning of the Great Depression – worst financial crisis in U. S. History Depression got worse – President Hoover followed policy o f denying government relief to unemployed – not re-elected in 1932 President Franklin Roosevelt pushed several legislative programs through Congress in attempt to end Great Depression ends after Americans found employment building war materials for WWII
 What caused the Great Depression? Caused by an economic system out of balance – too much supply, too little demand Created by: Monopolistic pricing Unsound banking practices Overproduction High tariffs Tightening of money supply by the Federal Reserve Board
What caused the Great Depression? Caused by an economic system out of balance – too much supply, too little demand Created by: Monopolistic pricing Unsound banking practices Overproduction High tariffs Tightening of money supply by the Federal Reserve Board
 What caused the stock market crash? Stock Market Crash of October 1929 caused by: A slump in economic activity Overspeculation in stocks Buying stocks “on margin” Stock Market Crash marked the beginning of the Great Depression
What caused the stock market crash? Stock Market Crash of October 1929 caused by: A slump in economic activity Overspeculation in stocks Buying stocks “on margin” Stock Market Crash marked the beginning of the Great Depression
 What were the characteristics of the Great Depression? Characteristics include: High unemployment Loss of farms and businesses Closing of Banks Driving up of credit Low purchasing power Hunger among plenty Not everyone suffered but many felt capitalism failed and democracy could not solve the problems
What were the characteristics of the Great Depression? Characteristics include: High unemployment Loss of farms and businesses Closing of Banks Driving up of credit Low purchasing power Hunger among plenty Not everyone suffered but many felt capitalism failed and democracy could not solve the problems
 How did President Herbert Hoover react to the problem? Hoover believed in and acted on ideas of: “Rugged individualism” Minimal government interference Supplying optimism Expanding public works Loaning money to struggling banks
How did President Herbert Hoover react to the problem? Hoover believed in and acted on ideas of: “Rugged individualism” Minimal government interference Supplying optimism Expanding public works Loaning money to struggling banks
 What was the Bonus March? Summer of 1932 20, 000 impoverished veterans from World War I marched to Washington, D. C Wanted early pay of financial bonus due in 1945 Bonus bill failed in Congress President Hoover ordered troops to evacuate veterans in D. C. Douglas Mac. Arthur and his army forcefully drove veterans out of city Event ended Hoover’s chance at re-election and fostered growing fear of revolution in America
What was the Bonus March? Summer of 1932 20, 000 impoverished veterans from World War I marched to Washington, D. C Wanted early pay of financial bonus due in 1945 Bonus bill failed in Congress President Hoover ordered troops to evacuate veterans in D. C. Douglas Mac. Arthur and his army forcefully drove veterans out of city Event ended Hoover’s chance at re-election and fostered growing fear of revolution in America
 What happened in the presidential election of 1932? Economy in rock bottom; Hoover and Republican Party blamed for Depression Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) elected promising to Save capitalism Help the common man Provide work rather than the handout FDR remained vague about his plan, but promised to try something
What happened in the presidential election of 1932? Economy in rock bottom; Hoover and Republican Party blamed for Depression Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) elected promising to Save capitalism Help the common man Provide work rather than the handout FDR remained vague about his plan, but promised to try something
 What was the New Deal? FDR’s plan to pull the nation out of the Depression was known as the New Deal Devised by FDRs “brain trust” it instituted policies of: Relief for the poor Recovery from the Depression Reform of the economic system First New Deal passed in first 100 days of FDRs presidency Growing pressures of left wing of American politics and leveling of economy in 1935, FDR pushed for a Second New Deal Cut government spending in 1937 to decrease budget deficit – economy fell back into a recession
What was the New Deal? FDR’s plan to pull the nation out of the Depression was known as the New Deal Devised by FDRs “brain trust” it instituted policies of: Relief for the poor Recovery from the Depression Reform of the economic system First New Deal passed in first 100 days of FDRs presidency Growing pressures of left wing of American politics and leveling of economy in 1935, FDR pushed for a Second New Deal Cut government spending in 1937 to decrease budget deficit – economy fell back into a recession
 Did FDR and the New Deal win the support of the American public? 1936 – FDR elected by electoral landslide (523 -8). Also re-elected in 1940 and 1944 Became the only president in U. S. history to be elected four (4) times.
Did FDR and the New Deal win the support of the American public? 1936 – FDR elected by electoral landslide (523 -8). Also re-elected in 1940 and 1944 Became the only president in U. S. history to be elected four (4) times.
 Who were the critics of the New Deal? Criticized by The Republican party believed: Increase in federal debt was too high Government was becoming too big and presidency too powerful New Deal was destroying private initiative, would lead to ruinous inflation, considered “creeping socialism” Far left-wing of American politics Believed FDR was not doing enough to help poor people Called for greater and more equitable distribution of wealth Far right-wing of American politics Attacked bankers and Jews
Who were the critics of the New Deal? Criticized by The Republican party believed: Increase in federal debt was too high Government was becoming too big and presidency too powerful New Deal was destroying private initiative, would lead to ruinous inflation, considered “creeping socialism” Far left-wing of American politics Believed FDR was not doing enough to help poor people Called for greater and more equitable distribution of wealth Far right-wing of American politics Attacked bankers and Jews
 Why did FDR try to “pack” the Supreme Court? FDR was angered because Supreme Court declared several New Deal programs unconstitutional Introduced legislation to increase size of Court Hoped to place justices favorable to New Deal on the Supreme Court Plan failed and weakened FDR politically
Why did FDR try to “pack” the Supreme Court? FDR was angered because Supreme Court declared several New Deal programs unconstitutional Introduced legislation to increase size of Court Hoped to place justices favorable to New Deal on the Supreme Court Plan failed and weakened FDR politically
 How did the Depression end? Depression ended after Americans found employment producing war materials for World War II
How did the Depression end? Depression ended after Americans found employment producing war materials for World War II
 World War II – In an Nutshell World War II began in 1939 when Germany invaded Poland U. S. entered World War II when Japan attacked Pearl Harbor in 1941 Leaders of Allied Nations held several wartime conferences to discuss military strategies and decide character of postwar world WWII ended after Germany surrendered in May 1945 and Japan surrendered in August 1945
World War II – In an Nutshell World War II began in 1939 when Germany invaded Poland U. S. entered World War II when Japan attacked Pearl Harbor in 1941 Leaders of Allied Nations held several wartime conferences to discuss military strategies and decide character of postwar world WWII ended after Germany surrendered in May 1945 and Japan surrendered in August 1945
 What were the characteristics of fascism in the 1920 s and 1930 s? Fascism characterized by extreme nationalism – accompanied by anti-Marxist, anti-democratic, and social Darwinist beliefs Germany – fascist dictator Adolph Hitler promised to make Germany a world power Blamed communists and Jews for Germany’s problems Italy and Japan governed by fascist dictators
What were the characteristics of fascism in the 1920 s and 1930 s? Fascism characterized by extreme nationalism – accompanied by anti-Marxist, anti-democratic, and social Darwinist beliefs Germany – fascist dictator Adolph Hitler promised to make Germany a world power Blamed communists and Jews for Germany’s problems Italy and Japan governed by fascist dictators
 How did German aggression lead to World War II? Germany occupied the Rhineland Austria Announced desire to occupy a section of Czechoslovakia Britain and France adopted a policy of appeasement toward Germany Policy is ineffective Germany invades Czechoslovakia European alliance formed to resist German aggression August 1939, Germany signed Non-Aggression Pact with Soviet Union Cleared the way for invasion of Poland Germany invaded poland September 1939 and began WWII
How did German aggression lead to World War II? Germany occupied the Rhineland Austria Announced desire to occupy a section of Czechoslovakia Britain and France adopted a policy of appeasement toward Germany Policy is ineffective Germany invades Czechoslovakia European alliance formed to resist German aggression August 1939, Germany signed Non-Aggression Pact with Soviet Union Cleared the way for invasion of Poland Germany invaded poland September 1939 and began WWII
 What happened in Europe after Germany invaded Poland? France fell in 1940 Great Britain fought alone against Germany June 1941 – Germany attacked Soviet Union
What happened in Europe after Germany invaded Poland? France fell in 1940 Great Britain fought alone against Germany June 1941 – Germany attacked Soviet Union
 What characterized U. S. foreign policy in the 1920 s and 1930 s? U. S. generally adhered to isolationist foreign policy 1930 s – U. S. desire to stay isolated from global conflicts leads to Neutrality Acts Restricted American involvement with nations at war After invasion of Poland fall of France the U. S. became and “arsenal of democracy” Started supplying Allied nations with war materials
What characterized U. S. foreign policy in the 1920 s and 1930 s? U. S. generally adhered to isolationist foreign policy 1930 s – U. S. desire to stay isolated from global conflicts leads to Neutrality Acts Restricted American involvement with nations at war After invasion of Poland fall of France the U. S. became and “arsenal of democracy” Started supplying Allied nations with war materials
 How did the U. S. get involved in World War II? December 1941 – After several years of protest against Japanese invasion of China – Japan attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii U. S. declared war on Japan Germany and Italy, Japanese allies, declare war on U. S.
How did the U. S. get involved in World War II? December 1941 – After several years of protest against Japanese invasion of China – Japan attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii U. S. declared war on Japan Germany and Italy, Japanese allies, declare war on U. S.
 What military problems confronted the U. S. in WWII? U. S. faced greater military problems than WWI U. S. fought war on opposite ends of the world at the same time By 1942, Axis powers controlled Europe, North Africa, and South Pacific To many Americans, Axis powers seemed unbeatable U. S. entered war with much less idealism than WWI Power of American industry eventually provides Allies resources to win the war
What military problems confronted the U. S. in WWII? U. S. faced greater military problems than WWI U. S. fought war on opposite ends of the world at the same time By 1942, Axis powers controlled Europe, North Africa, and South Pacific To many Americans, Axis powers seemed unbeatable U. S. entered war with much less idealism than WWI Power of American industry eventually provides Allies resources to win the war
 How did the U. S. forces help defeat Germany? Decided to concentrate on beating Germany first, then Japan U. S. pushed German forces out of North Africa, Sicily and Italy June 1944 – U. S. opened a second front against Germany Soviet Union invaded Germany from the east Other Allied nations invade from the west Germany surrendered in May 1945
How did the U. S. forces help defeat Germany? Decided to concentrate on beating Germany first, then Japan U. S. pushed German forces out of North Africa, Sicily and Italy June 1944 – U. S. opened a second front against Germany Soviet Union invaded Germany from the east Other Allied nations invade from the west Germany surrendered in May 1945
 How was Japan defeated? Japanese forces occupied southeast Asia and South Pacific U. S. began “island hopping” In order to avoid invasion and save lives Truman ordered atomic bombs dropped on Japan Hiroshima (Little Boy) and Nagasaki (Fat Man) bombed Ended WWII in August 1945 Historians believed Truman dropped bomb as show of force against Soviet Union
How was Japan defeated? Japanese forces occupied southeast Asia and South Pacific U. S. began “island hopping” In order to avoid invasion and save lives Truman ordered atomic bombs dropped on Japan Hiroshima (Little Boy) and Nagasaki (Fat Man) bombed Ended WWII in August 1945 Historians believed Truman dropped bomb as show of force against Soviet Union
 What happened at the Yalta Conference? FDR, Winston Churchill and Joseph Stalin met at the Yalta Conference in 1945 Discussed final defeat of Axis powers Soviet Union consented to enter war against Japan after Germany Soviet Union would allow occupation of eastern Europe after the war Stalin would allow “free and unfettered elections” After war, Soviet Union violated Yalta agreement Established pro-Soviet, communist dictatorships Some Americans believed FDR “sold out” to the Soviet Union Supporters said FDR was trying to get Soviet Union to help with Japanese invasion and felt the Soviets would expand its sphere of influence
What happened at the Yalta Conference? FDR, Winston Churchill and Joseph Stalin met at the Yalta Conference in 1945 Discussed final defeat of Axis powers Soviet Union consented to enter war against Japan after Germany Soviet Union would allow occupation of eastern Europe after the war Stalin would allow “free and unfettered elections” After war, Soviet Union violated Yalta agreement Established pro-Soviet, communist dictatorships Some Americans believed FDR “sold out” to the Soviet Union Supporters said FDR was trying to get Soviet Union to help with Japanese invasion and felt the Soviets would expand its sphere of influence
 What happened at the Potsdam Conference? Final wartime conference held in Potsdam, Germany – July 1945 Stalin represented Soviet Union, Clement Atlee represented Great Britain, Harry Truman represented the U. S. Decided to put Nazis on trial for crimes against humanity Allies called for Japan’s unconditional surrender before total destruction
What happened at the Potsdam Conference? Final wartime conference held in Potsdam, Germany – July 1945 Stalin represented Soviet Union, Clement Atlee represented Great Britain, Harry Truman represented the U. S. Decided to put Nazis on trial for crimes against humanity Allies called for Japan’s unconditional surrender before total destruction
 The Cold War – Truman. Eisenhower Era – In a Nutshell Cold War began after WWII with disagreement between U. S. and Soviet Union over self-determination in Eastern Europe American struggle against communism spread to Asia after Communist forces took over China and after North Korea and South Korea Struggle against communism overseas led some Americans to believe communists were in U. S. President Truman and Eisenhower’s “containment” policy led to Eisenhower’s expansion of the arms race, beginning of covert operations by the CIA, and beginning of space race Heavy consumer spending and increased productivity lead to highest standard of living the world had every known; some groups don’t hare in prosperity; social critics attacked American materialism and conformity
The Cold War – Truman. Eisenhower Era – In a Nutshell Cold War began after WWII with disagreement between U. S. and Soviet Union over self-determination in Eastern Europe American struggle against communism spread to Asia after Communist forces took over China and after North Korea and South Korea Struggle against communism overseas led some Americans to believe communists were in U. S. President Truman and Eisenhower’s “containment” policy led to Eisenhower’s expansion of the arms race, beginning of covert operations by the CIA, and beginning of space race Heavy consumer spending and increased productivity lead to highest standard of living the world had every known; some groups don’t hare in prosperity; social critics attacked American materialism and conformity
 How did U. S. foreign policy change after World War II? Adopted internationalist foreign policy Joined permanent alliances during peacetime Truman’s policy also focused on containment
How did U. S. foreign policy change after World War II? Adopted internationalist foreign policy Joined permanent alliances during peacetime Truman’s policy also focused on containment
 How was the United Nations (UN) created? UN created after WWII to maintain international peace Consists of General Assembly – every member nation meets Security Council – enforces UN resolutions Five permanent members include U. S. , Russia (originally Soviet Union, Great Britain, France, and China Each of five members of Security Council was given veto power over actions
How was the United Nations (UN) created? UN created after WWII to maintain international peace Consists of General Assembly – every member nation meets Security Council – enforces UN resolutions Five permanent members include U. S. , Russia (originally Soviet Union, Great Britain, France, and China Each of five members of Security Council was given veto power over actions
 How did the Cold War begin? U. S. objected to the Soviet Union’s establishment of satellite states in Eastern Europe
How did the Cold War begin? U. S. objected to the Soviet Union’s establishment of satellite states in Eastern Europe
 What happened to Germany after World War II? Germany and the capital city of Berlin divided into four zones Berlin was in East Germany, the Soviet zone of occupation Division of Berlin led to great conflict during Cold War
What happened to Germany after World War II? Germany and the capital city of Berlin divided into four zones Berlin was in East Germany, the Soviet zone of occupation Division of Berlin led to great conflict during Cold War
 What was the Truman Doctrine? U. S. declared it would come to the aid of any country threatened by communism Received bipartisan support Announced initially to provide aid to Greece and Turkey Cornerstone of U. S. foreign policy for several decades
What was the Truman Doctrine? U. S. declared it would come to the aid of any country threatened by communism Received bipartisan support Announced initially to provide aid to Greece and Turkey Cornerstone of U. S. foreign policy for several decades
 What was the Marshall Plan? 1947 – Marshall Plan offered financial aid to spark economic recovery of Western European nations suffering from WWII Provided counterforce to U. S. S. R. No nation that received aid because of Marshall Plan ever turned to communism
What was the Marshall Plan? 1947 – Marshall Plan offered financial aid to spark economic recovery of Western European nations suffering from WWII Provided counterforce to U. S. S. R. No nation that received aid because of Marshall Plan ever turned to communism
 Why was NATO created? A military alliance of North Atlantic nations Established in 1949 to combat Soviet aggression in Europe U. S. broke the precedent set by George Washington of not entering peacetime alliances
Why was NATO created? A military alliance of North Atlantic nations Established in 1949 to combat Soviet aggression in Europe U. S. broke the precedent set by George Washington of not entering peacetime alliances
 When did China turn to communism? Communists took control of China in 1949 Mao Zedong defeated Chiang Kai-shek, a Nationalist leader of China Before civil war, China presented a policy dilemma for President Truman Civil war between Communists and Nationalists led to conflicting advice by the State Department and the Defense Department State Department – Communists would win; Chiang Kai-shek was corrupt; relationship between Chinese and Soviet communism was nonexistent Defense Department – loss of China to communists presented insurmountable strategic loss Unable to communist takeover of China, Truman administration was attacked by some people for “losing” China After Communists took over China, Nationalist Chinese relocated to island of Taiwan U. S. did not formally recognize Communist China until 1979
When did China turn to communism? Communists took control of China in 1949 Mao Zedong defeated Chiang Kai-shek, a Nationalist leader of China Before civil war, China presented a policy dilemma for President Truman Civil war between Communists and Nationalists led to conflicting advice by the State Department and the Defense Department State Department – Communists would win; Chiang Kai-shek was corrupt; relationship between Chinese and Soviet communism was nonexistent Defense Department – loss of China to communists presented insurmountable strategic loss Unable to communist takeover of China, Truman administration was attacked by some people for “losing” China After Communists took over China, Nationalist Chinese relocated to island of Taiwan U. S. did not formally recognize Communist China until 1979
 Who was Joseph Mc. Carthy? 1950 – Joseph Mc. Carthy, senator from Wisconsin Announced he had a list of communists working for the State Department Began a five-year crusade against communists in America Never uncovered a single communist Eventually censured by U. S. Senate for misconduct Mc. Carthyism refers to false accusations that an individual is not loyal to the U. S.
Who was Joseph Mc. Carthy? 1950 – Joseph Mc. Carthy, senator from Wisconsin Announced he had a list of communists working for the State Department Began a five-year crusade against communists in America Never uncovered a single communist Eventually censured by U. S. Senate for misconduct Mc. Carthyism refers to false accusations that an individual is not loyal to the U. S.
 What happened in the Korean War? June 1950 – North Korea invade South Korea United Nations sent forces to stop aggression Stated goal of U. N. ’s “police action” was status quo ante – achieved by September 1950 U. N. troops entered North Korea in October 1950 Chinese troops entered the war Chinese push U. N. forces out of North Korea General Douglas Mac. Arthur proposed bombing China and “unleashing Chiang” Truman rejects Mac. Arthur’s idea and talking war began until truce in 1953 President Truman relieved Mac. Arthur of his command after Mac. Arthur publicly criticized Truman’s policies
What happened in the Korean War? June 1950 – North Korea invade South Korea United Nations sent forces to stop aggression Stated goal of U. N. ’s “police action” was status quo ante – achieved by September 1950 U. N. troops entered North Korea in October 1950 Chinese troops entered the war Chinese push U. N. forces out of North Korea General Douglas Mac. Arthur proposed bombing China and “unleashing Chiang” Truman rejects Mac. Arthur’s idea and talking war began until truce in 1953 President Truman relieved Mac. Arthur of his command after Mac. Arthur publicly criticized Truman’s policies
 In what ways did Dwight Eisenhower’s foreign policy differ from Harry Truman’s foreign policy? Dwight Eisenhower continued policy of containment begun by Harry Truman Under Eisenhower, however, summit meetings were held with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev in an attempt to promote “peaceful coexistence” “Peaceful coexistence” ended in 1960 when U. S. U-2 spy plane was shot down over the Soviet Union
In what ways did Dwight Eisenhower’s foreign policy differ from Harry Truman’s foreign policy? Dwight Eisenhower continued policy of containment begun by Harry Truman Under Eisenhower, however, summit meetings were held with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev in an attempt to promote “peaceful coexistence” “Peaceful coexistence” ended in 1960 when U. S. U-2 spy plane was shot down over the Soviet Union
 What happened politically during the Truman-Eisenhower era? Republicans took control of both houses of Congress after the 1946 and 1952 elections for the only times between 1932 and 1994. 1948 - Harry Truman unexpectedly won the presidential election defeating Thomas Dewey. Dwight D. Eisenhower easily defeated Adlai Stevenson in both the 1952 and 1956 elections
What happened politically during the Truman-Eisenhower era? Republicans took control of both houses of Congress after the 1946 and 1952 elections for the only times between 1932 and 1994. 1948 - Harry Truman unexpectedly won the presidential election defeating Thomas Dewey. Dwight D. Eisenhower easily defeated Adlai Stevenson in both the 1952 and 1956 elections
 The Civil Rights Movement – In a Nutshell 1950 s – Supreme Court ruled against racial segregation and put weight of constitutional laws behind demand for civil rights Mid-50 s to mid-60 s – the fight for civil rights led primarily by leaders advocating nonviolence and civil disobedience Mid-60 s – Congress passed laws promoting civil rights and voting rights Laws strengthened federal government’s power to regulate state government’s denial of civil rights Late 60 s – violent protests and race riots 1970 s – debates over civil rights focus on busing and affirmative action
The Civil Rights Movement – In a Nutshell 1950 s – Supreme Court ruled against racial segregation and put weight of constitutional laws behind demand for civil rights Mid-50 s to mid-60 s – the fight for civil rights led primarily by leaders advocating nonviolence and civil disobedience Mid-60 s – Congress passed laws promoting civil rights and voting rights Laws strengthened federal government’s power to regulate state government’s denial of civil rights Late 60 s – violent protests and race riots 1970 s – debates over civil rights focus on busing and affirmative action
 What was the legal status of African-Americans before 1954? Late 1800 s – states pass Jim Crow laws to segregate races and restrict rights of African-Americans Southern states pass laws to keep African-Americans from voting Laws combined with social and economic discrimination made African-Americans second-class citizens 1896 Supreme Court case – Plessy v. Ferguson – segregation was constitutional Southern states segregated by law and on purpose Northern states segregated based on racism (not law) and by default (people didn’t know how to do anything else)
What was the legal status of African-Americans before 1954? Late 1800 s – states pass Jim Crow laws to segregate races and restrict rights of African-Americans Southern states pass laws to keep African-Americans from voting Laws combined with social and economic discrimination made African-Americans second-class citizens 1896 Supreme Court case – Plessy v. Ferguson – segregation was constitutional Southern states segregated by law and on purpose Northern states segregated based on racism (not law) and by default (people didn’t know how to do anything else)
 When did protests against segregation and discrimination begin to make a difference? Federal government responded to African-Americans’ protest when FDR banned discrimination in the war industries After WWII, Harry Truman integrated the armed forces
When did protests against segregation and discrimination begin to make a difference? Federal government responded to African-Americans’ protest when FDR banned discrimination in the war industries After WWII, Harry Truman integrated the armed forces
 How did Brown v. the Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas change to legal status of African. Americans? 1954 – Supreme Court ruled in Brown that segregated schools were inherently unequal. Considered a landmark case that reversed Plessy v. Ferguson.
How did Brown v. the Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas change to legal status of African. Americans? 1954 – Supreme Court ruled in Brown that segregated schools were inherently unequal. Considered a landmark case that reversed Plessy v. Ferguson.
 What happened in Little Rock, Arkansas in 1957? 9 African-American students admitted to Central High School Mob of angry whites and Arkansas National Guard tried to prevent nine students from entering school To enforce federal court’s ruling, President Eisenhower sent federal troops to little Rock to protect nine students
What happened in Little Rock, Arkansas in 1957? 9 African-American students admitted to Central High School Mob of angry whites and Arkansas National Guard tried to prevent nine students from entering school To enforce federal court’s ruling, President Eisenhower sent federal troops to little Rock to protect nine students
 When did the Civil Rights movement begin moving toward direct action and civil disobedience? Arrest of Rosa Parks in 1955 led African-Americans to boycott bus system in Montgomery, Alabama Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. played a key role in leading the boycott and helped establish civil disobedience as a tactic for ending segregation and discrimination.
When did the Civil Rights movement begin moving toward direct action and civil disobedience? Arrest of Rosa Parks in 1955 led African-Americans to boycott bus system in Montgomery, Alabama Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. played a key role in leading the boycott and helped establish civil disobedience as a tactic for ending segregation and discrimination.
 What is civil disobedience? Combines nonviolent teachings of Jesus with ideas of disobeying unjust laws that came from Henry David Thoreau and Mohandes Ghandi. Designed to win the support of general public to bring out change Early phase of Civil Rights Movement characterized by civil disobedience and included Sit-ins in North Carolina Freedom rides in Alabama and Mississippi Protests in Birmingham, Alabama
What is civil disobedience? Combines nonviolent teachings of Jesus with ideas of disobeying unjust laws that came from Henry David Thoreau and Mohandes Ghandi. Designed to win the support of general public to bring out change Early phase of Civil Rights Movement characterized by civil disobedience and included Sit-ins in North Carolina Freedom rides in Alabama and Mississippi Protests in Birmingham, Alabama
 What was the March on Washington? August 1963 – over 250, 000 people gathered at Lincoln Memorial to ask Congress for Civil rights legislation Highlight is Dr. King’s “I Have a Dream” speech
What was the March on Washington? August 1963 – over 250, 000 people gathered at Lincoln Memorial to ask Congress for Civil rights legislation Highlight is Dr. King’s “I Have a Dream” speech
 When did Congress pass civil rights legislation? President Lyndon Johnson used public support, tribute to JFK and political expertise to pass Civil Rights Act of 1964 through Congress Outlawed discrimination in employment, hotels, restaurants and other public places Empowered attorney general to bring violators of the law to court 1965 – Voting Rights Act – protected every citizen’s right to vote and authorized federal government to oversee voter registration and elections Civil Rights Act of 1968 – outlawed discrimination in the sale and rental of housing
When did Congress pass civil rights legislation? President Lyndon Johnson used public support, tribute to JFK and political expertise to pass Civil Rights Act of 1964 through Congress Outlawed discrimination in employment, hotels, restaurants and other public places Empowered attorney general to bring violators of the law to court 1965 – Voting Rights Act – protected every citizen’s right to vote and authorized federal government to oversee voter registration and elections Civil Rights Act of 1968 – outlawed discrimination in the sale and rental of housing
 What happened to the Civil Rights movement in the late 1960 s? Civil rights leaders like Martin Luther King, Jr. found themselves isolated from the increased militancy of the African- American community Watts, California riot in 1965 and many others followed throughout the U. S.
What happened to the Civil Rights movement in the late 1960 s? Civil rights leaders like Martin Luther King, Jr. found themselves isolated from the increased militancy of the African- American community Watts, California riot in 1965 and many others followed throughout the U. S.
 What was the Nation of Islam? African-American organization led by Elijah Muhammad Sometimes referred to as Black Muslims Members of Nation of Islam called for African-Americans to gain self-respect by staying sober and morally pure Preached racial separation Believed in maintaining separation and seizing freedom by any means necessary, including violence Malcolm X was a spokesperson but left in 1964, and was assassinated in 1965
What was the Nation of Islam? African-American organization led by Elijah Muhammad Sometimes referred to as Black Muslims Members of Nation of Islam called for African-Americans to gain self-respect by staying sober and morally pure Preached racial separation Believed in maintaining separation and seizing freedom by any means necessary, including violence Malcolm X was a spokesperson but left in 1964, and was assassinated in 1965
 Who were the Black Panthers? 1966 – organized to control the streets and ghettos Late 60 s – became an organization of revolutionaries who advocated using violence to draw attention to conditions in the ghettos
Who were the Black Panthers? 1966 – organized to control the streets and ghettos Late 60 s – became an organization of revolutionaries who advocated using violence to draw attention to conditions in the ghettos
 When was Martin Luther King, Jr. assassinated? Was planning a Poor People’s March on Washington Assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee on April 4, 1968 His assassination touched off rioting in over 150 cities Rioting in D. C. reached such intensity that U. S. troops were called in to protect the U. S. Capitol Building for the first time since the Civil War
When was Martin Luther King, Jr. assassinated? Was planning a Poor People’s March on Washington Assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee on April 4, 1968 His assassination touched off rioting in over 150 cities Rioting in D. C. reached such intensity that U. S. troops were called in to protect the U. S. Capitol Building for the first time since the Civil War
 What happened to the Civil Rights Movement after King’s assassination? By 1970 s more than 15 years had passed since Supreme Court had ruled for desegregation Few schools were actually desegregated Court-ordered busing was used to achieve racial integration Busing became a controversial issue Legal barriers were lifted but several generations of racial segregation barred many Americans from enjoying the opportunities 1978 – Bakke Supreme Court decision states schools cannot give preference to members of any group on the basis of ethnic or racial identity alone Also ruled that racial factors could be taken into account in school’s overall admissions policy
What happened to the Civil Rights Movement after King’s assassination? By 1970 s more than 15 years had passed since Supreme Court had ruled for desegregation Few schools were actually desegregated Court-ordered busing was used to achieve racial integration Busing became a controversial issue Legal barriers were lifted but several generations of racial segregation barred many Americans from enjoying the opportunities 1978 – Bakke Supreme Court decision states schools cannot give preference to members of any group on the basis of ethnic or racial identity alone Also ruled that racial factors could be taken into account in school’s overall admissions policy
 What is Indochina? Part of southeast Asia and includes Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Indochina people fought Chinese domination for over 1, 000 yrs Colonized by the French in the late nineteenth century In 1919, Vietnamese leader, Ho Chi Minh, tried to appeal personally to Woodrow Wilson in Paris to support selfdetermination for the Vietnamese people
What is Indochina? Part of southeast Asia and includes Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Indochina people fought Chinese domination for over 1, 000 yrs Colonized by the French in the late nineteenth century In 1919, Vietnamese leader, Ho Chi Minh, tried to appeal personally to Woodrow Wilson in Paris to support selfdetermination for the Vietnamese people
 What happened in the French. Indochina War? During WWII, Vietnam under Japanese control After Japan’s defeat by Allies, French tried to re- colonize Indochina Met with heavy resistance from Vietnamese Nationalist movement led by now communist, Ho Chi Minh French crumbled under Vietminh guerilla tactics Despite massive aid from U. S. , French forces eventually surrendered to the Vietnamese in 1954 at Dienbienphu
What happened in the French. Indochina War? During WWII, Vietnam under Japanese control After Japan’s defeat by Allies, French tried to re- colonize Indochina Met with heavy resistance from Vietnamese Nationalist movement led by now communist, Ho Chi Minh French crumbled under Vietminh guerilla tactics Despite massive aid from U. S. , French forces eventually surrendered to the Vietnamese in 1954 at Dienbienphu
 What was the Geneva Conference 1954, U. S. , France, Britain, Red China, the Soviet Union, and nine other nations met to discuss Indochina’s future Agreed to divide Vietnam at the 17 th parallel with communists in control of North Vietnam and Vietnamese supporters of the French in control of South Vietnam U. S. didn’t sign agreement Ho Chi Minh consented to agreement with promise to hold election in 1956 to unify Vietnam
What was the Geneva Conference 1954, U. S. , France, Britain, Red China, the Soviet Union, and nine other nations met to discuss Indochina’s future Agreed to divide Vietnam at the 17 th parallel with communists in control of North Vietnam and Vietnamese supporters of the French in control of South Vietnam U. S. didn’t sign agreement Ho Chi Minh consented to agreement with promise to hold election in 1956 to unify Vietnam
 What happened in South Vietnam after the Geneva Conference? With help from U. S. , pro- Western government under Ngo Dinh Diem was put in power in South Vietnam The 1956 election to unify Vietnam canceled primarily b/c the communists under Ho Chi Minh seemed certain to win After the canceled election, loyalist to Ho Chi Minh in South Vietnam organized the National Liberation Front (NLF) launching a civil war in South Vietnam These forces were known as the Vietcong and fought against Diem’s forces known as ARVN
What happened in South Vietnam after the Geneva Conference? With help from U. S. , pro- Western government under Ngo Dinh Diem was put in power in South Vietnam The 1956 election to unify Vietnam canceled primarily b/c the communists under Ho Chi Minh seemed certain to win After the canceled election, loyalist to Ho Chi Minh in South Vietnam organized the National Liberation Front (NLF) launching a civil war in South Vietnam These forces were known as the Vietcong and fought against Diem’s forces known as ARVN
 What was Dwight Eisenhower’s policy toward Vietnam? Eisenhower, believing in the domino theory, concerned if communists took control of Indochina rest of Asia would fall under communist control Therefore, Eisenhower decided to support Diem with American military hardware, military advisers, and covert operations
What was Dwight Eisenhower’s policy toward Vietnam? Eisenhower, believing in the domino theory, concerned if communists took control of Indochina rest of Asia would fall under communist control Therefore, Eisenhower decided to support Diem with American military hardware, military advisers, and covert operations
 What was John Kennedy’s policy toward South Vietnam? Despite American help, South Vietnamese government under Diem ruled with little support from South Vietnamese people To protect Diem’s government, Kennedy increased aid to South Vietnam From 1961 to 1963, the number of American advisers in Vietnam increased from 600 to 17, 000
What was John Kennedy’s policy toward South Vietnam? Despite American help, South Vietnamese government under Diem ruled with little support from South Vietnamese people To protect Diem’s government, Kennedy increased aid to South Vietnam From 1961 to 1963, the number of American advisers in Vietnam increased from 600 to 17, 000
 What happened to Ngo Dinh Diem? 1963, uprising by Buddhist monks against Diem’s repressive government convinced Kennedy administration to drop support for Diem November 1963, Diem was assassinated in a military coup encouraged by U. S. government Diem’s assassination led to great political instability in South Vietnam and ARVN forces looked like they would lose to communist forces
What happened to Ngo Dinh Diem? 1963, uprising by Buddhist monks against Diem’s repressive government convinced Kennedy administration to drop support for Diem November 1963, Diem was assassinated in a military coup encouraged by U. S. government Diem’s assassination led to great political instability in South Vietnam and ARVN forces looked like they would lose to communist forces
 What was Lyndon Johnson’s policy toward South Vietnam? August 1964, President Johnson announced an American destroyer on patrol in the Gulf of Tonkin was attacked by North Vietnamese torpedo boats Congress then passed resolutions giving him a “blank check” to stop communist aggression in Vietnam Early 1965, potential defeat of South Vietnamese forces led Johnson’s decision to have U. S forces assume responsibility of fighting the war He began an escalation of U. S. troops reaching over 550, 000 by 1967
What was Lyndon Johnson’s policy toward South Vietnam? August 1964, President Johnson announced an American destroyer on patrol in the Gulf of Tonkin was attacked by North Vietnamese torpedo boats Congress then passed resolutions giving him a “blank check” to stop communist aggression in Vietnam Early 1965, potential defeat of South Vietnamese forces led Johnson’s decision to have U. S forces assume responsibility of fighting the war He began an escalation of U. S. troops reaching over 550, 000 by 1967
 What happened after Johnson began escalating the war? U. S. faced a stalemate in South Vietnam for a variety of reasons including Vietnam’s geography aided Vietcong guerrillas The stalemate, combined with much of American public believing U. S. troops should not be in Vietnam, caused great division in U. S. “Hawks” believed in massive force to win the war “ Doves” believed Johnson should end the war by pulling U. S. troops out
What happened after Johnson began escalating the war? U. S. faced a stalemate in South Vietnam for a variety of reasons including Vietnam’s geography aided Vietcong guerrillas The stalemate, combined with much of American public believing U. S. troops should not be in Vietnam, caused great division in U. S. “Hawks” believed in massive force to win the war “ Doves” believed Johnson should end the war by pulling U. S. troops out
 What was the Tet Offensive? Vietcong in Jan. 1968 launched attack on U. S. forces in South Vietnam During offensive, Vietcong forces occupied 5 major cities, 36 provincial capitals, 64 district capitals, and U. S. embassy U. S. forces eventually stopped attack, but perception that conflict was far from over caused major news organizations, and general public, to turn against Johnson’s policies in Vietnam
What was the Tet Offensive? Vietcong in Jan. 1968 launched attack on U. S. forces in South Vietnam During offensive, Vietcong forces occupied 5 major cities, 36 provincial capitals, 64 district capitals, and U. S. embassy U. S. forces eventually stopped attack, but perception that conflict was far from over caused major news organizations, and general public, to turn against Johnson’s policies in Vietnam
 What happened in the election of 1968? Facing antiwar challenge from Eugene Mc. Carthy and Robert Kennedy, Johnson withdrew from presidential race After Kennedy’s assassination, Johnson’s vice president Hubert Humphrey was nominated by Democrats to run against Republican candidate Richard Nixon Humphrey, hurt by Johnson’s unpopular handling of the war, lost to Nixon who had secret peace plan
What happened in the election of 1968? Facing antiwar challenge from Eugene Mc. Carthy and Robert Kennedy, Johnson withdrew from presidential race After Kennedy’s assassination, Johnson’s vice president Hubert Humphrey was nominated by Democrats to run against Republican candidate Richard Nixon Humphrey, hurt by Johnson’s unpopular handling of the war, lost to Nixon who had secret peace plan
 What was Richard Nixon’s policy toward South Vietnam? 1969, Nixon begins Vietnamization ( gradual withdrawal of U. S. troops while South Vietnamese forces prepared to fight for themselves) After invasions in Cambodia (1970), Laos (1971), and massive bombing failed to force communist surrender, Nixon pulls all U. S. troops out of Vietnam in 1973
What was Richard Nixon’s policy toward South Vietnam? 1969, Nixon begins Vietnamization ( gradual withdrawal of U. S. troops while South Vietnamese forces prepared to fight for themselves) After invasions in Cambodia (1970), Laos (1971), and massive bombing failed to force communist surrender, Nixon pulls all U. S. troops out of Vietnam in 1973
 What happened after U. S. forces were pulled out of Vietnam? 1975, communist forces took control of South Vietnam
What happened after U. S. forces were pulled out of Vietnam? 1975, communist forces took control of South Vietnam
 What are the lessons of Vietnam? 1995, Robert Mc. Namara, Secretary of Defense under Kennedy and Johnson, wrote U. S. government made many mistakes in Vietnam Government officials didn’t understand Vietnamese people, underestimated the power of nationalism to motivate Vietnamese forces Admitted he exaggerated of the importance of the struggle in Vietnam, misled Congress and public, failed to recognize ineffectiveness of high-tech equipment to defeat committed guerillas Wrote U. S. should never commit troops anywhere unless there are clear attainable goals, and troops fighting with public and congressional support
What are the lessons of Vietnam? 1995, Robert Mc. Namara, Secretary of Defense under Kennedy and Johnson, wrote U. S. government made many mistakes in Vietnam Government officials didn’t understand Vietnamese people, underestimated the power of nationalism to motivate Vietnamese forces Admitted he exaggerated of the importance of the struggle in Vietnam, misled Congress and public, failed to recognize ineffectiveness of high-tech equipment to defeat committed guerillas Wrote U. S. should never commit troops anywhere unless there are clear attainable goals, and troops fighting with public and congressional support
 What did John Kennedy bring to the presidency? 1 st Catholic elected president Youngest person elected president His election brought a sense of youthful idealism and optimistic program to pursue national opportunities in civil rights, economics, international relations, and space exploration Called his program New Frontier
What did John Kennedy bring to the presidency? 1 st Catholic elected president Youngest person elected president His election brought a sense of youthful idealism and optimistic program to pursue national opportunities in civil rights, economics, international relations, and space exploration Called his program New Frontier
 What happened in the Bay of Pigs? April 1961, 3 months into Kennedy presidency, U. S. sponsored Cuban invasion by anti-communists Cuban refugees to overthrow pro- Soviet leader Fidel Castro U. S. believed it would prompt Cuban people to rise up and overthrow Castro Was a disaster Cubans didn’t rise up and invasion was crushed Although Kennedy publicly accepted responsibility, he privately blamed intelligence agencies and military for providing him with unreliable info
What happened in the Bay of Pigs? April 1961, 3 months into Kennedy presidency, U. S. sponsored Cuban invasion by anti-communists Cuban refugees to overthrow pro- Soviet leader Fidel Castro U. S. believed it would prompt Cuban people to rise up and overthrow Castro Was a disaster Cubans didn’t rise up and invasion was crushed Although Kennedy publicly accepted responsibility, he privately blamed intelligence agencies and military for providing him with unreliable info
 What was the Cuban missile crisis? October 1962, U. S. spy planes discovered missiles in Cuba Although several of Kennedy’s advisers suggested invasion, he decided to blockade Cuba and keep Russian ships from delivering warheads Soviet Union agreed to withdraw missiles after Kennedy agreed not to invade Cuba and to remove missiles from Turkey
What was the Cuban missile crisis? October 1962, U. S. spy planes discovered missiles in Cuba Although several of Kennedy’s advisers suggested invasion, he decided to blockade Cuba and keep Russian ships from delivering warheads Soviet Union agreed to withdraw missiles after Kennedy agreed not to invade Cuba and to remove missiles from Turkey
 When was the Berlin Wall built? After Soviet Union threatened to cut off Western access to Berlin, Kennedy mobilized U. S. troops and gathered National Guard to federal service This show of force caused Soviets to build wall separating communist sector of Berlin from free sector
When was the Berlin Wall built? After Soviet Union threatened to cut off Western access to Berlin, Kennedy mobilized U. S. troops and gathered National Guard to federal service This show of force caused Soviets to build wall separating communist sector of Berlin from free sector
 How did Kennedy’s assassination affect the United States? Traumatized and shocked by the assassination, Americans also had to deal with unanswered questions behind the assassination As tribute to Kennedy, Johnson was able to push some of Kennedy’s programs through Congress
How did Kennedy’s assassination affect the United States? Traumatized and shocked by the assassination, Americans also had to deal with unanswered questions behind the assassination As tribute to Kennedy, Johnson was able to push some of Kennedy’s programs through Congress
 What was the Great Society? Was Johnson’s program to bring “ abundance and liberty” to all Americans Used his political expertise to push massive amounts of legislation to Congress Landmark legislation under Johnson: civil rights, health care, education, environment, housing, immigration, and funding for cultural endeavors Great Society characterized primarily by “War on Poverty”
What was the Great Society? Was Johnson’s program to bring “ abundance and liberty” to all Americans Used his political expertise to push massive amounts of legislation to Congress Landmark legislation under Johnson: civil rights, health care, education, environment, housing, immigration, and funding for cultural endeavors Great Society characterized primarily by “War on Poverty”
 Why was the Warren Court important? Chief Justice Earl Warren, served 1954 -69, presided over Supreme Court provided nation fundamental changes in constitutional law Warren Court in several landmark cases made Bill of Rights to apply to actions of state and local governments Shifting emphasis of constitutional law from property rights to personal rights, Warren court responsible for revolution in individual rights characterized 60’s
Why was the Warren Court important? Chief Justice Earl Warren, served 1954 -69, presided over Supreme Court provided nation fundamental changes in constitutional law Warren Court in several landmark cases made Bill of Rights to apply to actions of state and local governments Shifting emphasis of constitutional law from property rights to personal rights, Warren court responsible for revolution in individual rights characterized 60’s
 What caused the protests and rebellions of the 1960 s? Seeds of protest of 60’s planted in the 50’s, included rebellious activities by youth groups, feminists, racial minorities, and ethnic minorities Numerous groups demanded equal rights and fair treatment long denied to women and minorities Youth protests characterized by New Left which wanted a more democratic society and counterculture rebelled against materialism, racism, and violence in modern world
What caused the protests and rebellions of the 1960 s? Seeds of protest of 60’s planted in the 50’s, included rebellious activities by youth groups, feminists, racial minorities, and ethnic minorities Numerous groups demanded equal rights and fair treatment long denied to women and minorities Youth protests characterized by New Left which wanted a more democratic society and counterculture rebelled against materialism, racism, and violence in modern world
 What characterized Richard Nixon’s domestic policies? Significant expansion of liberal programs usually denounced by conservative Republicans Extended government benefits for health and welfare, transformed affirmative action that set specific goals and timetables for hiring minorities, created Environmental Protection Agency, and program of revenue sharing with state governments Faced economic problems- high inflation, beginning of large trade deficit, ordered a wage and price freeze
What characterized Richard Nixon’s domestic policies? Significant expansion of liberal programs usually denounced by conservative Republicans Extended government benefits for health and welfare, transformed affirmative action that set specific goals and timetables for hiring minorities, created Environmental Protection Agency, and program of revenue sharing with state governments Faced economic problems- high inflation, beginning of large trade deficit, ordered a wage and price freeze
 How did U. S. foreign policy change under Richard Nixon? Henry Kissinger, Nixon’s top foreign policy advisor, viewed world as multipolar, rather than bipolar Nixon then adopted foreign policy based on trilateralism, recognition non- communist world had 3 major powers: U. S. , Western Europe, and Japan Wanting better relations with China, Nixon visited in 1972 and began process of formally recognizing communist government completed in 1979 Hoped to create better relations with Soviet Union, began policy of relaxing tension with Soviets known as détente Under Nixon, U. S. signed treaty with Soviets limiting size of nuclear arsenals
How did U. S. foreign policy change under Richard Nixon? Henry Kissinger, Nixon’s top foreign policy advisor, viewed world as multipolar, rather than bipolar Nixon then adopted foreign policy based on trilateralism, recognition non- communist world had 3 major powers: U. S. , Western Europe, and Japan Wanting better relations with China, Nixon visited in 1972 and began process of formally recognizing communist government completed in 1979 Hoped to create better relations with Soviet Union, began policy of relaxing tension with Soviets known as détente Under Nixon, U. S. signed treaty with Soviets limiting size of nuclear arsenals
 What was the Watergate break-in? After several yrs of wire-tapping and other illegal activities, Nixon administration member caught breaking in Democratic Party headquarters in Watergate office building in Washington, D. C. Cover- up launched to protect Nixon’s presidency knowing a full investigation of the break-in would uncover several members of Nixon administration and Nixon reelection organization involved in illegal activities
What was the Watergate break-in? After several yrs of wire-tapping and other illegal activities, Nixon administration member caught breaking in Democratic Party headquarters in Watergate office building in Washington, D. C. Cover- up launched to protect Nixon’s presidency knowing a full investigation of the break-in would uncover several members of Nixon administration and Nixon reelection organization involved in illegal activities
 How were the illegal activities associated with the Watergate break –in uncovered? After newspaper reporters uncovered damaging info, U. S. Senate and special prosecutor appointed by Nixon’s attorney general began investigating break-in Led to court orders for Nixon to turn over tape recordings of conversations he made about break-ins Nixon’s decision not to comply led to a constitutional crisis
How were the illegal activities associated with the Watergate break –in uncovered? After newspaper reporters uncovered damaging info, U. S. Senate and special prosecutor appointed by Nixon’s attorney general began investigating break-in Led to court orders for Nixon to turn over tape recordings of conversations he made about break-ins Nixon’s decision not to comply led to a constitutional crisis
 Why did Nixon resign the presidency? Nixon fired the special prosecutor after he refused to drop his demand to hear Watergate tapes Prompted impeachment proceedings against Nixon, House Judiciary Committee voted for three articles of impeachment Charges against him included obstruction of justice, defying court orders, and abuse of power Supreme Court ordered tape recordings be turned over, they revealed Nixon part of the cover-up Nixon tried to use CIA to stop FBI investigation of Watergate break-in Fearing he lost support in Congress, Nixon resigned presidency and later pardoned by President Ford
Why did Nixon resign the presidency? Nixon fired the special prosecutor after he refused to drop his demand to hear Watergate tapes Prompted impeachment proceedings against Nixon, House Judiciary Committee voted for three articles of impeachment Charges against him included obstruction of justice, defying court orders, and abuse of power Supreme Court ordered tape recordings be turned over, they revealed Nixon part of the cover-up Nixon tried to use CIA to stop FBI investigation of Watergate break-in Fearing he lost support in Congress, Nixon resigned presidency and later pardoned by President Ford
 Why did Arabs boycott the sale of oil to the United States? After U. S. supported Israel in Arab- Israeli conflicts, Arab nations boycotted sale of oil b/c of Yom Kippur War of 1973 Boycott led to long lines at gas stations and high prices for gas in the U. S.
Why did Arabs boycott the sale of oil to the United States? After U. S. supported Israel in Arab- Israeli conflicts, Arab nations boycotted sale of oil b/c of Yom Kippur War of 1973 Boycott led to long lines at gas stations and high prices for gas in the U. S.
 What economic problems plagued the United States in the 1970 s? Due to Arab oil boycott and end of Vietnam war, U. S. hit with new economic problem- high inflation with sluggish economic growth known as stagflation U. S. faced growing budget deficits, trade deficit, decline in real wages
What economic problems plagued the United States in the 1970 s? Due to Arab oil boycott and end of Vietnam war, U. S. hit with new economic problem- high inflation with sluggish economic growth known as stagflation U. S. faced growing budget deficits, trade deficit, decline in real wages
 Why was Jimmy Carter elected in 1976? Running as Washington outsider, Carter elected president promising honesty in government Beat incumbent president Gerald Ford who was hurt by pardoning Nixon, rising gas prices, deficits, and stagflation
Why was Jimmy Carter elected in 1976? Running as Washington outsider, Carter elected president promising honesty in government Beat incumbent president Gerald Ford who was hurt by pardoning Nixon, rising gas prices, deficits, and stagflation
 What characterized Jimmy Carter’s domestic policies? Carter declared need for national energy policy the moral equivalent of war, only able to pass water-down energy legislation through Congress Wasn’t able to deal with stagflation, high interests rates, and growing deficits Popularity began to wane in his final presidency year
What characterized Jimmy Carter’s domestic policies? Carter declared need for national energy policy the moral equivalent of war, only able to pass water-down energy legislation through Congress Wasn’t able to deal with stagflation, high interests rates, and growing deficits Popularity began to wane in his final presidency year
 What characterized Jimmy Carter’s foreign policies? At beginning Carter tried to make human rights instead of anti-communism the center of foreign policy Invasion of Afghanistan by Soviets led to end to détente and resumption to Cold War tensions Carter’s foreign policy achievements included Panama Canal Treaty, U. S. agreed to relinquish control of Panama Canal to Panama, Camp David Accords, Carter negotiated peace agreement between Egypt and Israel
What characterized Jimmy Carter’s foreign policies? At beginning Carter tried to make human rights instead of anti-communism the center of foreign policy Invasion of Afghanistan by Soviets led to end to détente and resumption to Cold War tensions Carter’s foreign policy achievements included Panama Canal Treaty, U. S. agreed to relinquish control of Panama Canal to Panama, Camp David Accords, Carter negotiated peace agreement between Egypt and Israel
 What happened in the Iranian hostage crisis? After decades of U. S. support, shah of Iran overthrown in Islamic fundamentalist revolution 1979, Iranian students took American hostages in U. S. embassy in Iran and demanded U. S. return the shah to Iran Hostage crisis continued throughout 1980, along with nation’s economic problems, hurt Carter’s chance of reelection After 444 days in captivity, hostages released day of Reagan’s inauguration
What happened in the Iranian hostage crisis? After decades of U. S. support, shah of Iran overthrown in Islamic fundamentalist revolution 1979, Iranian students took American hostages in U. S. embassy in Iran and demanded U. S. return the shah to Iran Hostage crisis continued throughout 1980, along with nation’s economic problems, hurt Carter’s chance of reelection After 444 days in captivity, hostages released day of Reagan’s inauguration


