9bf46b9451452c3f2953dc5b1f3beded.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86

IMT-2000 Network, Operations Support Systems and Service September 25, 2002 Kouzou Sakae NTT Do. Co. Mo, Inc.

Outline • Mobile communication environment • Overview of IMT-2000 • Introduction of Do. Co. Mo Network, OSS concept & architecture • Multimedia services and necessary technologies • Mobile networks beyond IMT-2000
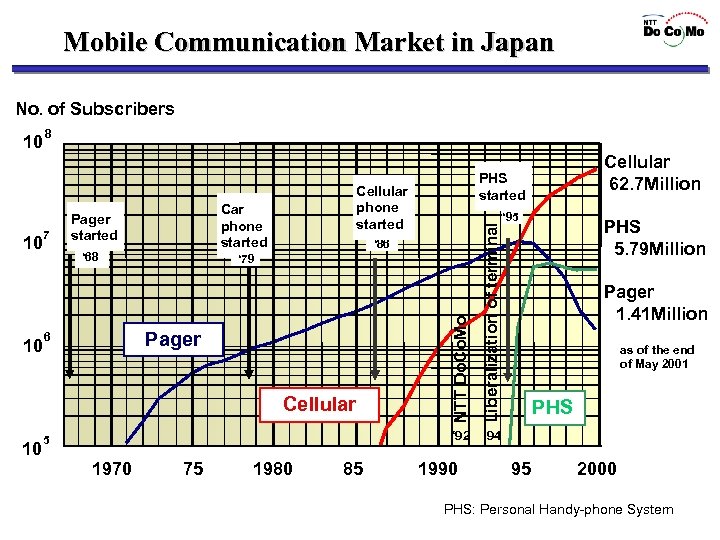
Mobile Communication Market in Japan No. of Subscribers 10 7 Cellular phone started Car phone started Pager started ‘ 92 ‘ 68 Cellular 10 5 1970 75 1980 85 ‘ 95 PHS 5. 79 Million ‘ 94 ‘ 86 ‘ 79 Pager 6 Cellular 62. 7 Million PHS started Liberalization of terminal 10 8 NTT Do. Co. Mo 10 1990 Pager 1. 41 Million as of the end of May 2001 PHS 95 2000 PHS: Personal Handy-phone System
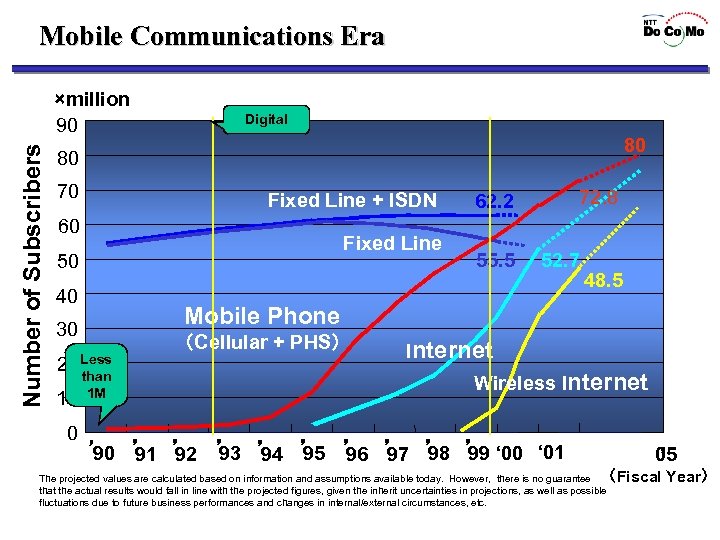
Mobile Communications Era Number of Subscribers ×million 90 Digital 80 80 70 Fixed Line + ISDN 60 Fixed Line 50 40 20 Less than 0 55. 5 52. 7 48. 5 Mobile Phone 30 10 72. 8 62. 2 1 M (Cellular + PHS) Internet Wireless Internet ’ 99 90 ’ ’ 93 ’ 95 ’ 98 ’ ‘ 00 ‘ 01 96 ’ 91 92 ’ 97 ’ 94 ’ 05 ’ (Fiscal Year) The projected values are calculated based on information and assumptions available today. However, there is no guarantee that the actual results would fall in line with the projected figures, given the inherit uncertainties in projections, as well as possible fluctuations due to future business performances and changes in internal/external circumstances, etc.
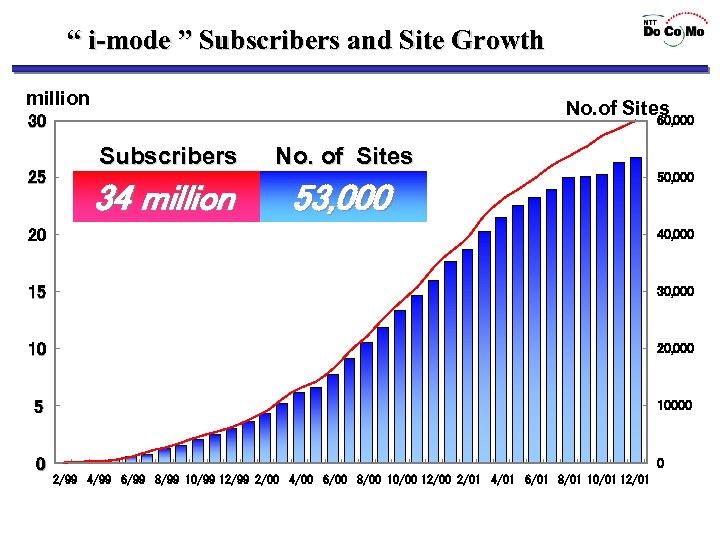
“ i-mode ” Subscribers and Site Growth million No. of Sites 30 25 60, 000 Subscribers 34 million No. of Sites 53, 000 50, 000 20 40, 000 15 30, 000 10 20, 000 5 10000 0 0 2/99 4/99 6/99 8/99 10/99 12/99 2/00 4/00 6/00 8/00 10/00 12/00 2/01 4/01 6/01 8/01 10/01 12/01
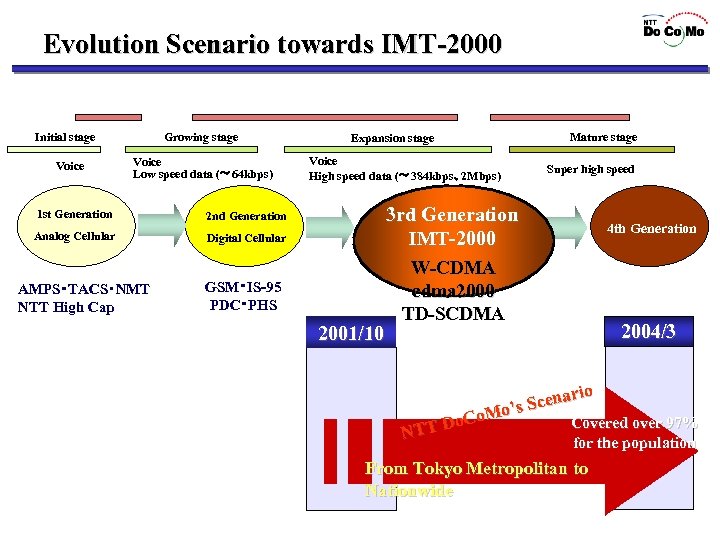
Evolution Scenario towards IMT-2000 ’ 80 S ’ 90 S Initial stage Voice Growing stage Voice Low speed data (~ 64 kbps) 1 st Generation Expansion stage Voice High speed data (~ 384 kbps、2 Mbps) Digital Cellular AMPS・TACS・NMT NTT High Cap Mature stage Super high speed 3 rd Generation IMT-2000 2 nd Generation Analog Cellular 2000 S GSM・IS-95 PDC・PHS 2001/10 4 th Generation W-CDMA cdma 2000 TD-SCDMA 2004/3 rio Scena o’s o. Co. M Covered over 97% D NTT for the population From Tokyo Metropolitan to Nationwide

An Overview of IMT-2000 • Trend, Goals, Requirements and Features • NW architecture

Why IMT-2000? • IMT-2000: International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 • The figure “ 2000” stands for • Kickoff: around year 2, 000 • Frequency: 2, 000 MHz • Transmission rate: 2, 000 Kbps (max. )

Goals of IMT-2000 Multimedia Service Capability Up to 2 Mbps High Quality Services Comparable to Fixed-Line Networks Clear Voice Multiple Operational Environment Capability (Outdoor/Indoor ) Anywhere Global Mobility Capability International

Requirements for IMT-2000 1. Supporting the transmission rate of minimum 144 kbps in any radio environment and 2 Mbps in indoor environment. 2. Supporting roaming between different IMT-2000 operating environments and international roaming. 3. Guaranteeing communications quality equivalent to that of the fixed network.
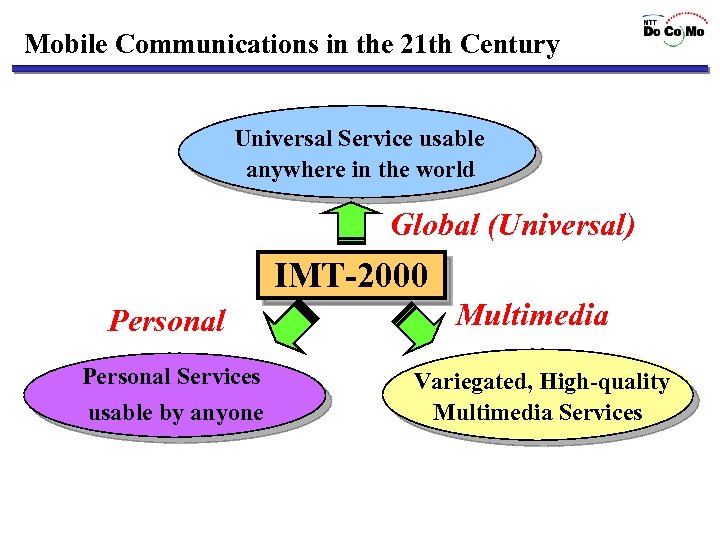
Mobile Communications in the 21 th Century Universal Service usable anywhere in the world Global (Universal) IMT-2000 Personal Services usable by anyone Multimedia Variegated, High-quality Multimedia Services
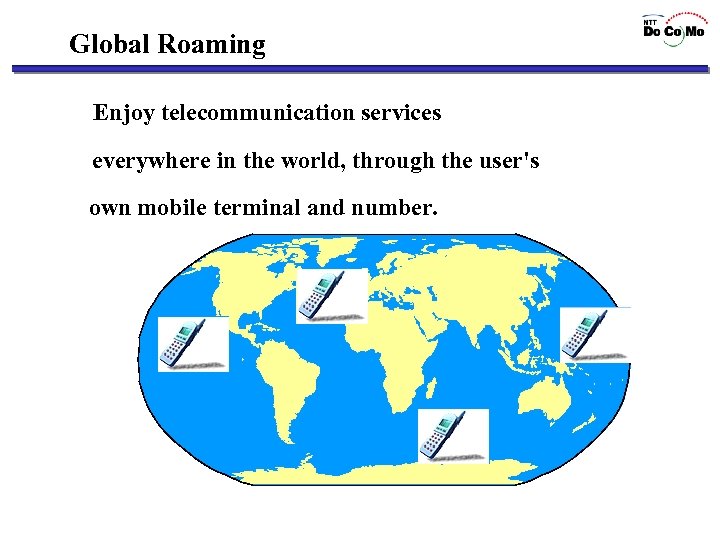
Global Roaming Enjoy telecommunication services everywhere in the world, through the user's own mobile terminal and number.
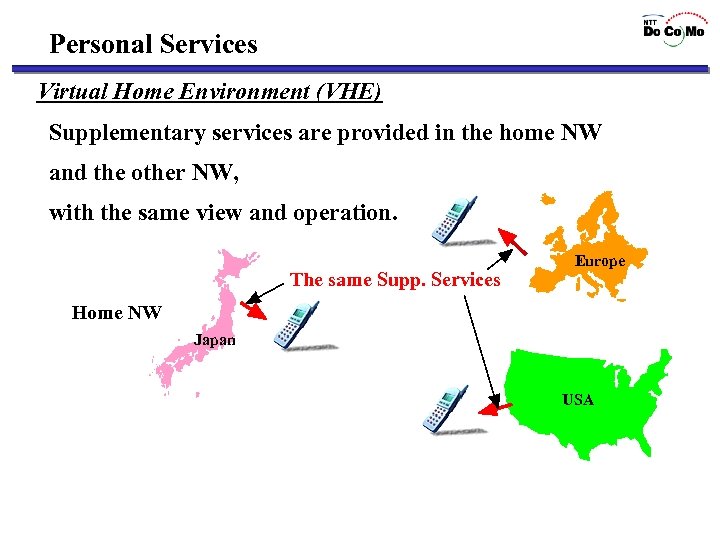
Personal Services Virtual Home Environment (VHE) Supplementary services are provided in the home NW and the other NW, with the same view and operation. The same Supp. Services Europe Home NW Japan USA
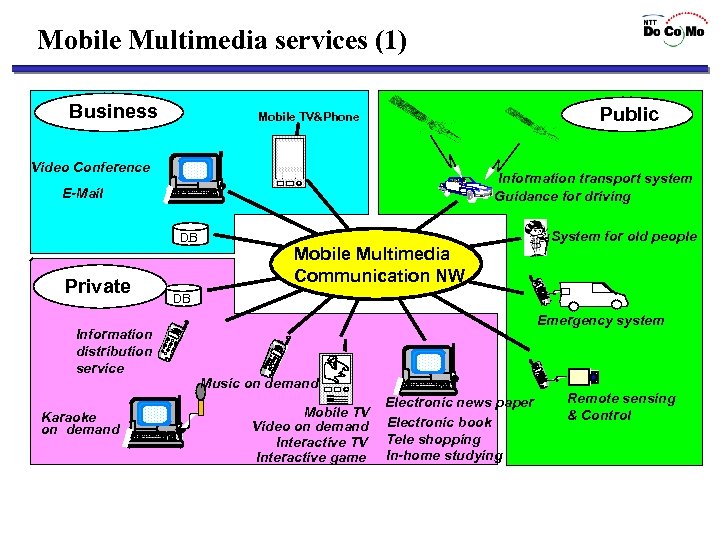
Mobile Multimedia services (1) Business Public Mobile TV&Phone Video Conference Information transport system Guidance for driving E-Mail System for old people DB Private Information distribution service Karaoke on demand Mobile Multimedia Communication NW DB Emergency system Music on demand Mobile TV Video on demand Interactive TV Interactive game Electronic news paper Electronic book Tele shopping In-home studying Remote sensing & Control
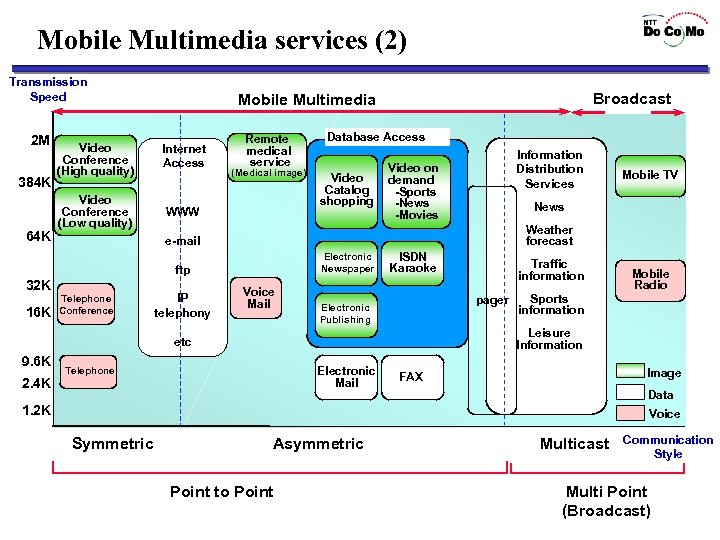
Mobile Multimedia services (2) Transmission Speed 2 M 384 K 64 K Video Conference (High quality) Internet Access Video Conference (Low quality) Remote medical service WWW 16 K Database Access Video Catalog shopping ISDN Karaoke Telephone Conference IP telephony Voice Mail 2. 4 K Traffic information pager Electronic Publishing Mobile TV News Weather forecast e-mail Sports information Mobile Radio Leisure Information etc 9. 6 K Information Distribution Services Video on demand -Sports -News -Movies Electronic Newspaper (Medical image) ftp 32 K Broadcast Mobile Multimedia Electronic Mail Telephone Image FAX Data 1. 2 K Voice Symmetric Asymmetric Point to Point Multicast Communication Style Multi Point (Broadcast)

Key Functions for IMT-2000 • Support of broad bandwidth to accommodate services from low-speed voice to high-speed graphic communications • Provision of variable-speed communications for video transmission • Provision of asymmetric communications as in video on demand • Provision of point-to-multipoint communications as in information-distribution services

IMT-2000 system requirements - High spectrum efficiency more than double of current most efficient systems - Universal mobility global, personal, terminal - Intelligent Service and its Portability flexible and quick service installation, VHE - Multimedia capability high speed and multi rate transmission ~144 kpbs(vehicular) / ~384 kbps(outdoor) / ~2 Mbps(indoor)
Features of IMT-2000 • High-speed and Wide-band • Multiple data rates – Independent transmission rate for uplink and downlink • High spectrum efficiency • Multimedia compatible • Global standard
NW Capability for IMT-2000 ● Mobile multimedia service capabilities - High Speed Data Services - Point to Multipoint Transmission - Quality of Service - Various Supplementary Services ● Support of Internet Connection Service - IP based application services (ex. E-mail, WWW, . . . ) - IP address allocation (fixed and dynamic) - IP based CUG (Closed User Groups) - Mobile Oriented Application Protocol (ex. WAP, . . )

Creation of Global Common Specifications ◆ In the future, the demand for mobile internet access and video transmission services will increase drastically, and the volume of data traffic will far exceed that of voice traffic. ◆ Along with globalization, mobile communications should be made available anywhere in the world. ★ Study of radio access scheme was initiated by ITU-R in 1985. ★ Study of signaling scheme was initiated by ITU-T in 1993. ★ Creation of global common standard specifications was initiated by 3 GPP (in 1998) and 3 GPP 2 (in 1999).

ITU and 3 GPP Activities • ITU-R – Specifications of the Radio Interfaces • ITU-T – Framework and Architecture (Family Concept) – Network Functional Model (Radio Access Network and Core Network ) – Standardization of the interfaces between family member systems for roaming • 3 GPP/3 GPP 2 – Common Technical Specifications and Technical Reports – Based on W-CDMA and GSM in 3 GPP – Based on cdma 2000 and ANSI-41 in 3 GPP 2
Network Architecture in IMT-2000 • Core Network (CN) • Radio Access Network (RAN) • Terminal
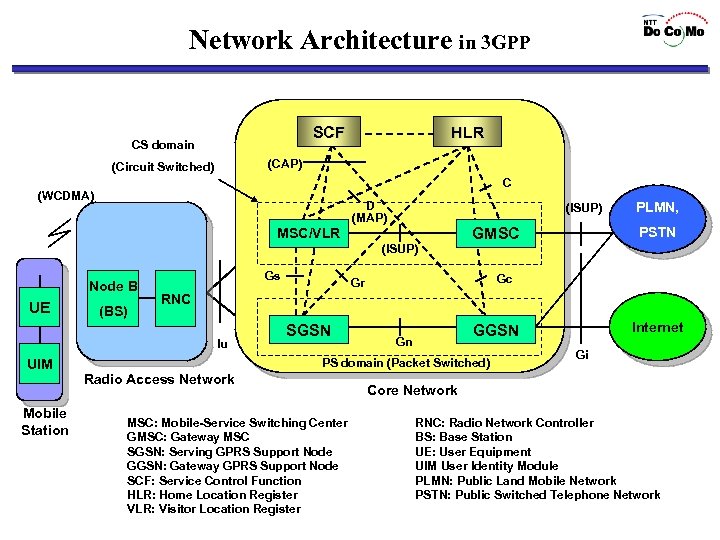
Network Architecture in 3 GPP SCF CS domain HLR (CAP) (Circuit Switched) C (WCDMA) D (MAP) (ISUP) PSTN GMSC MSC/VLR PLMN, (ISUP) Node B UE (BS) Gs RNC Iu UIM Mobile Station Gc Gr SGSN Gn PS domain (Packet Switched) Radio Access Network MSC: Mobile-Service Switching Center GMSC: Gateway MSC SGSN: Serving GPRS Support Node GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node SCF: Service Control Function HLR: Home Location Register VLR: Visitor Location Register Internet GGSN Gi Core Network RNC: Radio Network Controller BS: Base Station UE: User Equipment UIM User Identity Module PLMN: Public Land Mobile Network PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network
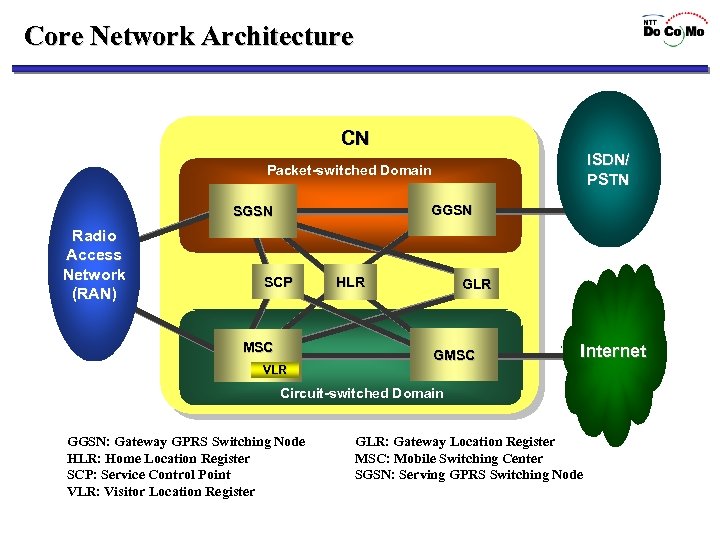
Core Network Architecture CN ISDN/ PSTN Packet-switched Domain GGSN SGSN Radio Access Network (RAN) SCP MSC VLR HLR GMSC Internet Circuit-switched Domain GGSN: Gateway GPRS Switching Node HLR: Home Location Register SCP: Service Control Point VLR: Visitor Location Register GLR: Gateway Location Register MSC: Mobile Switching Center SGSN: Serving GPRS Switching Node
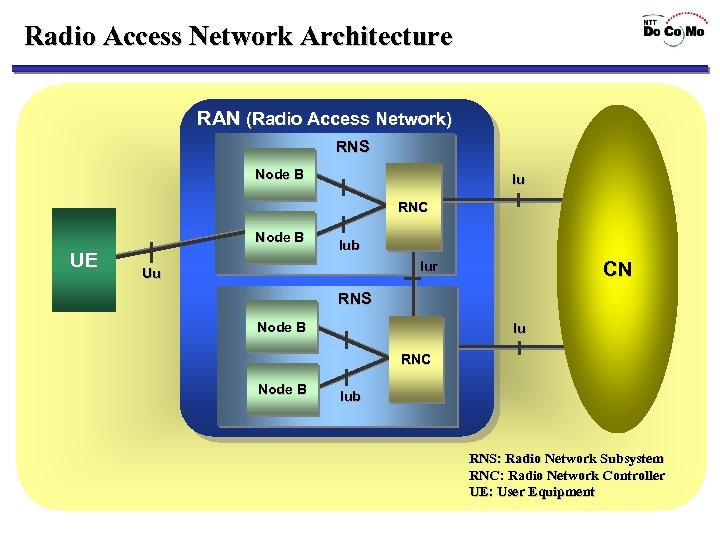
Radio Access Network Architecture RAN (Radio Access Network) RNS Node B Iu RNC Node B UE Iub Iur Uu CN RNS Node B Iu RNC Node B Iub RNS: Radio Network Subsystem RNC: Radio Network Controller UE: User Equipment
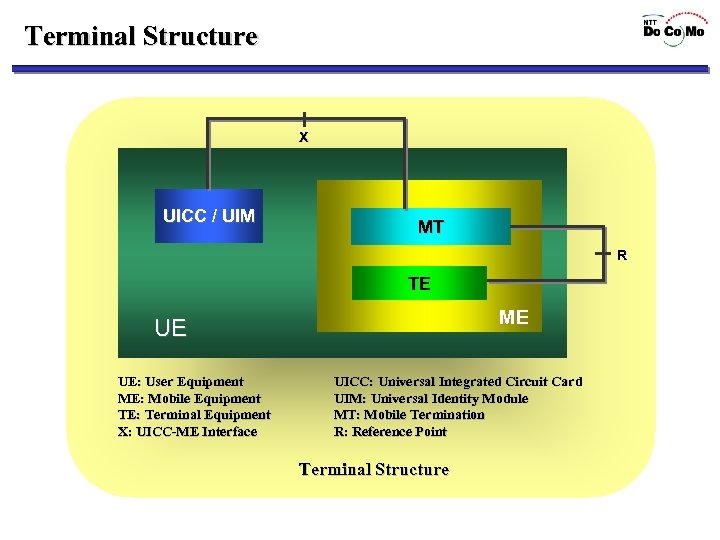
Terminal Structure X UICC / UIM MT R TE ME UE UE: User Equipment ME: Mobile Equipment TE: Terminal Equipment X: UICC-ME Interface UICC: Universal Integrated Circuit Card UIM: Universal Identity Module MT: Mobile Termination R: Reference Point Terminal Structure

Introduction of Do. Co. Mo network • Network architecture – Approach to IMT-2000 – Network configuration • OSS concept and architecture – Network monitoring and control – Network Quality Management, Planning and Design
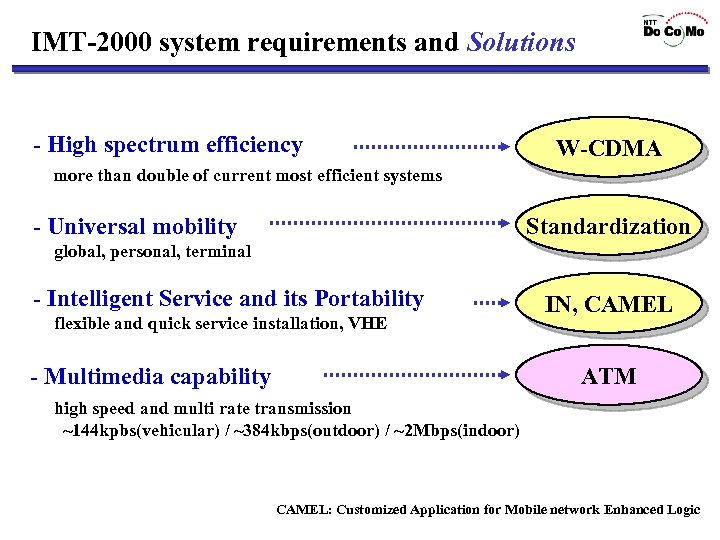
IMT-2000 system requirements and Solutions - High spectrum efficiency W-CDMA more than double of current most efficient systems Standardization - Universal mobility global, personal, terminal - Intelligent Service and its Portability flexible and quick service installation, VHE IN, CAMEL ATM - Multimedia capability high speed and multi rate transmission ~144 kpbs(vehicular) / ~384 kbps(outdoor) / ~2 Mbps(indoor) CAMEL: Customized Application for Mobile network Enhanced Logic
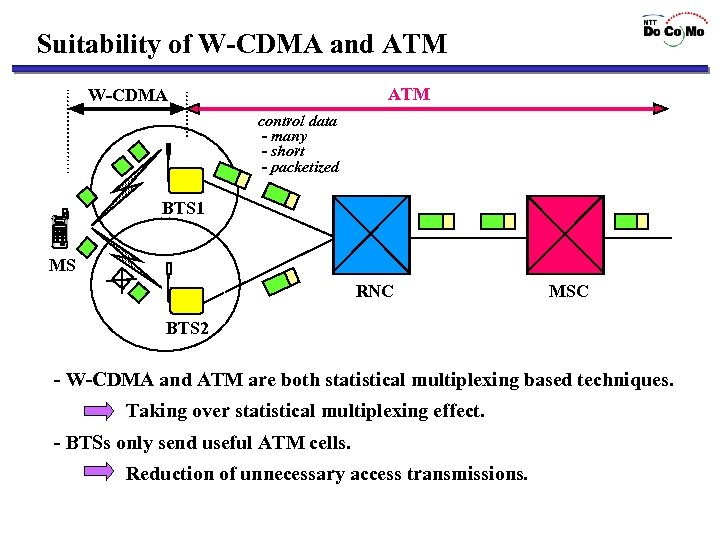
Suitability of W-CDMA and ATM W-CDMA control data - many - short - packetized BTS 1 MS RNC MSC BTS 2 - W-CDMA and ATM are both statistical multiplexing based techniques. Taking over statistical multiplexing effect. - BTSs only send useful ATM cells. Reduction of unnecessary access transmissions.
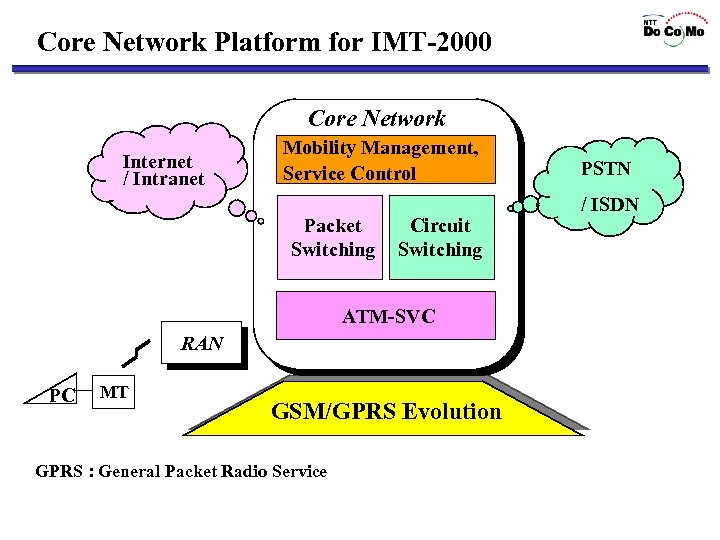
Core Network Platform for IMT-2000 Core Network Internet / Intranet Mobility Management, Service Control Packet Switching Circuit Switching ATM-SVC RAN PC MT GSM/GPRS Evolution GPRS : General Packet Radio Service PSTN / ISDN
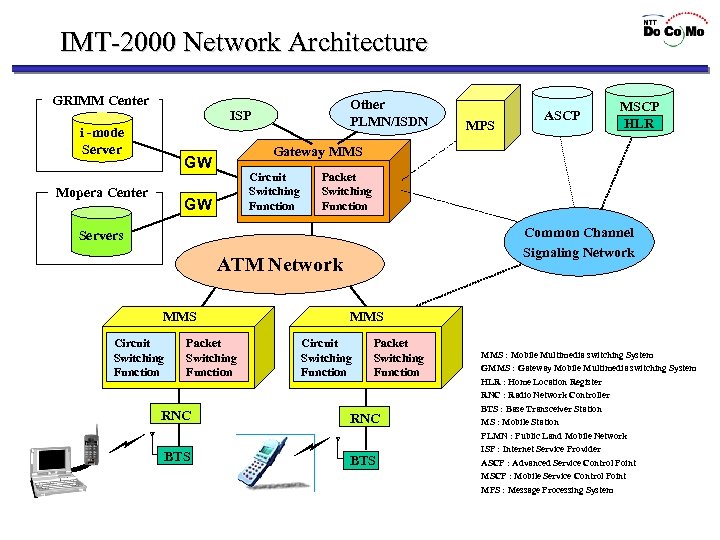
IMT-2000 Network Architecture GRIMM Center Other PLMN/ISDN ISP i -mode Server Circuit Switching Function GW Packet Switching Function Common Channel Signaling Network Servers ATM Network MMS Circuit Switching Function Packet Switching Function RNC MSCP HLR Gateway MMS GW Mopera Center MPS ASCP MMS Circuit Switching Function Packet Switching Function RNC MMS : Mobile Multimedia switching System GMMS : Gateway Mobile Multimedia switching System HLR : Home Location Register RNC : Radio Network Controller BTS : Base Transceiver Station MS : Mobile Station PLMN : Public Land Mobile Network BTS ISP : Internet Service Provider ASCP : Advanced Service Control Point MSCP : Mobile Service Control Point MPS : Message Processing System
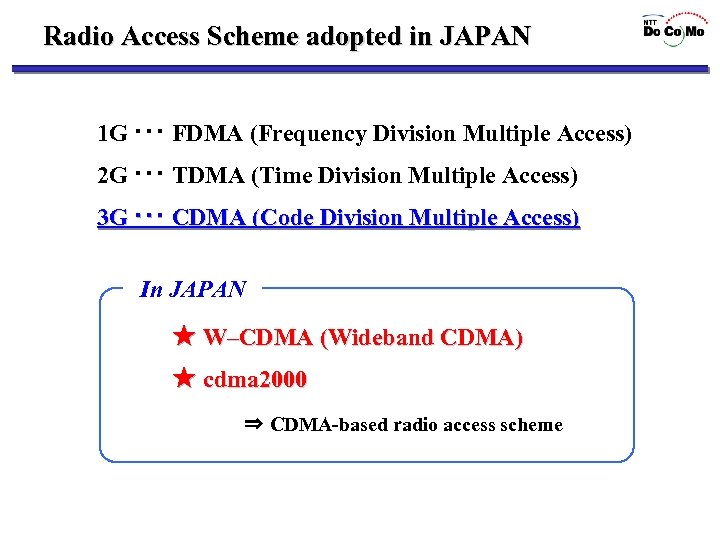
Radio Access Scheme adopted in JAPAN 1 G ・・・ FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) 2 G ・・・ TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) 3 G ・・・ CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) In JAPAN ★ W–CDMA (Wideband CDMA) ★ cdma 2000 ⇒ CDMA-based radio access scheme
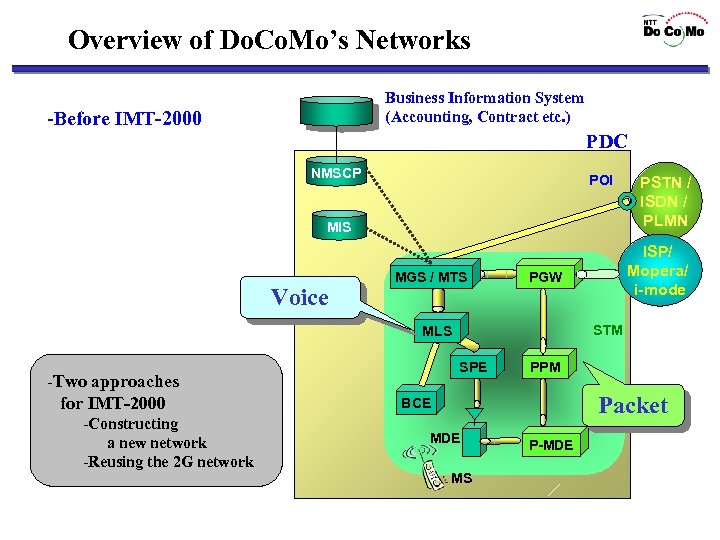
Overview of Do. Co. Mo’s Networks Business Information System (Accounting, Contract etc. ) -Before IMT-2000 PDC NMSCP POI MIS Voice MGS / MTS -Constructing a new network -Reusing the 2 G network ISP/ Mopera/ i-mode PGW STM MLS -Two approaches for IMT-2000 PSTN / ISDN / PLMN SPE PPM Packet BCE MDE MS P-MDE
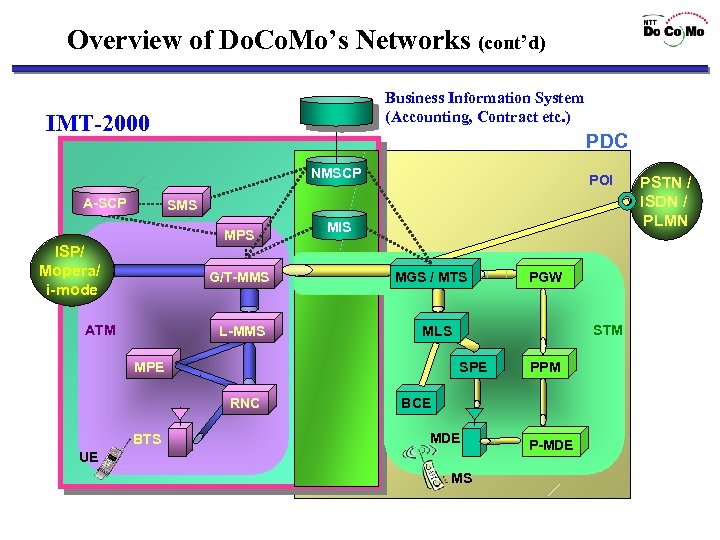
Overview of Do. Co. Mo’s Networks (cont’d) Business Information System (Accounting, Contract etc. ) IMT-2000 PDC NMSCP A-SCP POI SMS MPS ISP/ Mopera/ i-mode G/T-MMS ATM L-MMS MIS MGS / MTS BTS STM MLS MPE SPE RNC PGW PPM BCE MDE UE MS P-MDE PSTN / ISDN / PLMN
Network Construction Lifecycle Planning NW Design Service Construction
Do. Co. Mo Network Structure Operation Center OSSs Radio Access Network Core Network MS G-MMS ATM-XC SDH FTM ATM-XC MMS RNC ATM-MUX SDH FTM CLAD Leased Line (ATM ) ATM-MUX CLAD ATM-S-MUX BTS (IMT) BS MS Office d Office c Office b Office a (PDC) VC (SDH) VP VC (ATM) ATM-XC: ATM Cross Connect CLAD: Cell Assembly and Disassembly MMS: Mobile Multimedia switching System BS: Base Station PDC: Personal Digital Cellular VC (SDH) : Virtual Container VC (ATM) : Virtual Channel ATM-MUX: ATM Multiplexer FTM: Fiber Transport Module G-MMS: Gateway MMS BTS: Base Transceiver Station MS: Mobile Station VP: Virtual Path

Operations Support Systems • Features of Do. Co. Mo’s OSS • Overview of OSS Architecture

Video Program • Operations Support Systems for IMT-2000
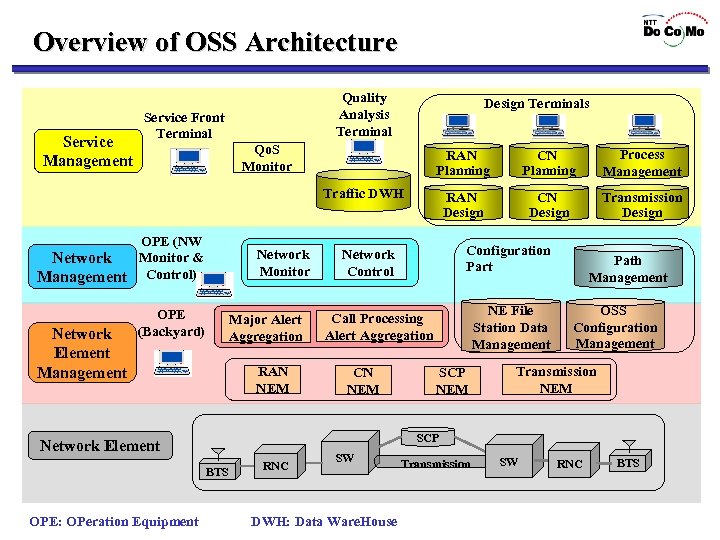
Overview of OSS Architecture Service Management Quality Analysis Terminal Service Front Terminal Design Terminals Qo. S Monitor RAN Planning CN Planning Process Management RAN Design CN Design Transmission Design Traffic DWH OPE (NW Monitor & Network Management Control) Network Element Management Network Monitor OPE (Backyard) Major Alert Aggregation RAN NEM NE File Station Data Management Call Processing Alert Aggregation CN NEM SCP NEM Path Management OSS Configuration Management Transmission NEM SCP Network Element BTS OPE: OPeration Equipment Configuration Part Network Control RNC SW DWH: Data Ware. House Transmission SW RNC BTS
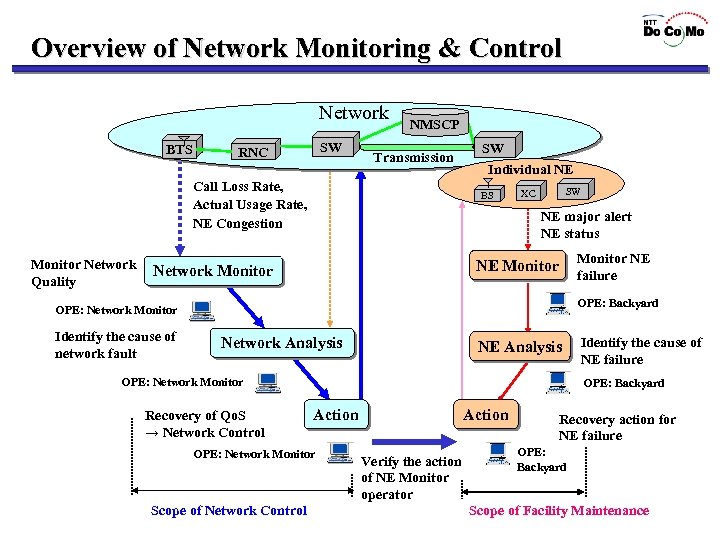
Overview of Network Monitoring & Control Network BTS SW RNC NMSCP Transmission Call Loss Rate, Actual Usage Rate, NE Congestion Monitor Network Quality SW Individual NE BS SW XC NE major alert NE status Monitor NE failure NE Monitor Network Monitor OPE: Backyard OPE: Network Monitor Identify the cause of network fault Network Analysis NE Analysis OPE: Network Monitor Recovery of Qo. S → Network Control OPE: Backyard Action OPE: Network Monitor Scope of Network Control Identify the cause of NE failure Action Verify the action of NE Monitor operator Recovery action for NE failure OPE: Backyard Scope of Facility Maintenance
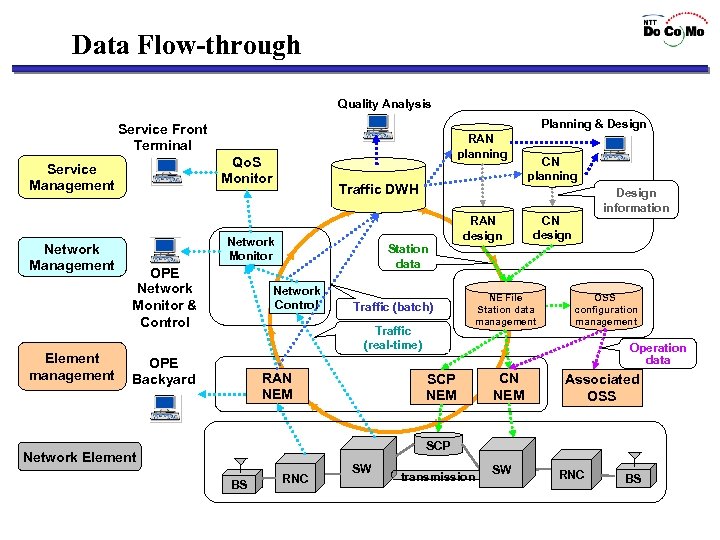
Data Flow-through Quality Analysis Planning & Design Service Front Terminal Qo. S Monitor Service Management Network Management Element management RAN planning Traffic DWH RAN design Network Monitor OPE Network Monitor & Control Design information CN design Station data Network Control Traffic (batch) Traffic (real-time) OPE Backyard CN planning RAN NEM NE File Station data management OSS configuration management Operation data SCP NEM CN NEM Associated OSS SCP Network Element BS RNC SW transmission SW RNC BS
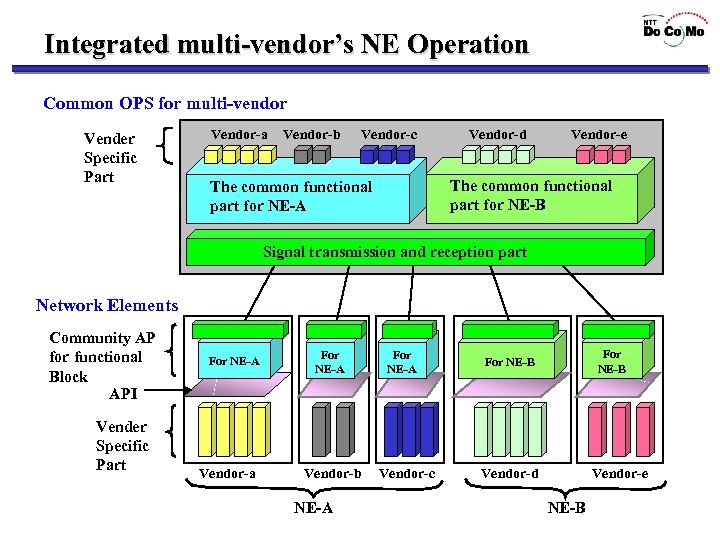
Integrated multi-vendor’s NE Operation Common OPS for multi-vendor Vender Specific Part Vendor-a Vendor-b Vendor-c Vendor-d Vendor-e The common functional part for NE-B The common functional part for NE-A Signal transmission and reception part Network Elements Community AP for functional Block API Vender Specific Part For NE-A Vendor-a For NE-A Vendor-b NE-A For NE-A Vendor-c For NE-B Vendor-d Vendor-e NE-B
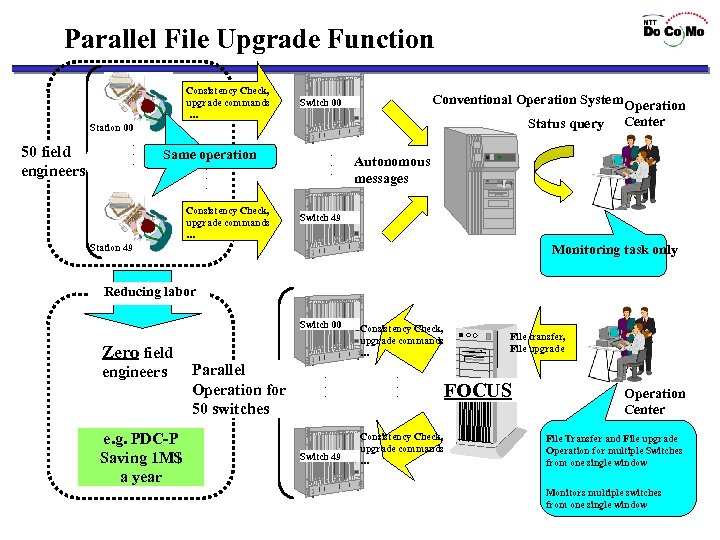
Parallel File Upgrade Function Consistency Check, upgrade commands … Conventional Operation System Operation Switch 00 Status query Station 00 50 field engineers ・ ・ ・ Same operation ・ ・ ・ Consistency Check, upgrade commands … Center Autonomous messages Switch 49 Monitoring task only Station 49 Reducing labor Switch 00 Zero field engineers e. g. PDC-P Saving 1 M$ a year Parallel Operation for 50 switches ・ ・ ・ Switch 49 Consistency Check, upgrade commands … ・ ・ ・ File transfer, File upgrade FOCUS Consistency Check, upgrade commands … Operation Center File Transfer and File upgrade Operation for multiple Switches from one single window Monitors multiple switches from one single window
Element Management GUI: Sample
Network Monitor & Control GUI: Sample
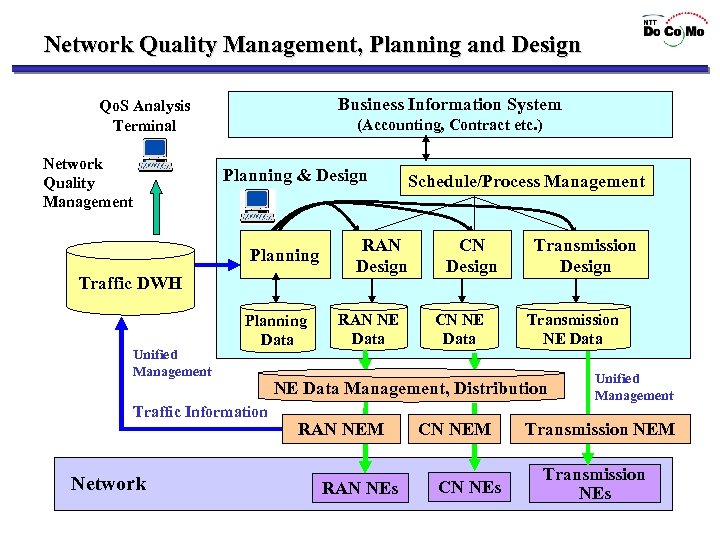
Network Quality Management, Planning and Design Business Information System Qo. S Analysis Terminal Network Quality Management (Accounting, Contract etc. ) Planning & Design Planning Traffic DWH Unified Management Planning Data Traffic Information Network RAN Design RAN NE Data Schedule/Process Management CN Design CN NE Data Transmission Design Transmission NE Data Management, Distribution RAN NEM RAN NEs CN NEM CN NEs Unified Management Transmission NEM Transmission NEs
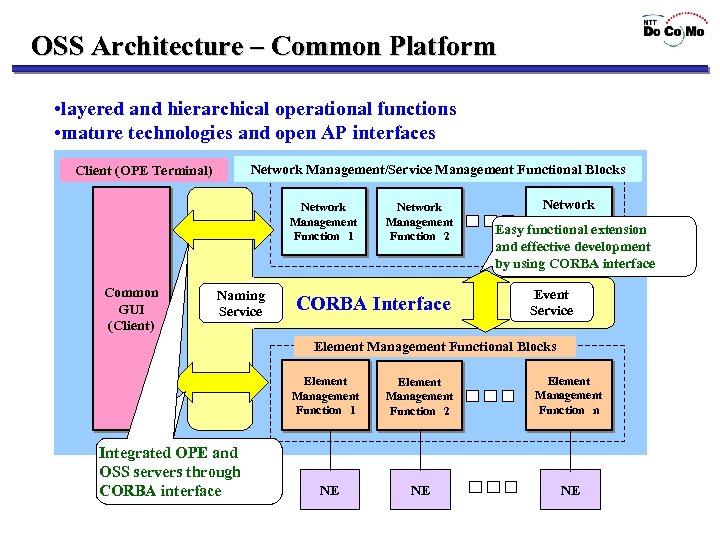
OSS Architecture – Common Platform • layered and hierarchical operational functions • mature technologies and open AP interfaces Client (OPE Terminal) Network Management/Service Management Functional Blocks Network Management Function 1 Common GUI (Client) Naming Service Network Management Function 2 CORBA Interface Network Management Easy functional extension Function n and effective development by using CORBA interface Event Service Element Management Functional Blocks Element Management Function 1 CORBAインタフェースにより Integrated OPE and OPE servers through OSS ~サーバ間の連携が CORBA interface 容易に実現 NE Element Management Function 2 Element Management Function n NE NE
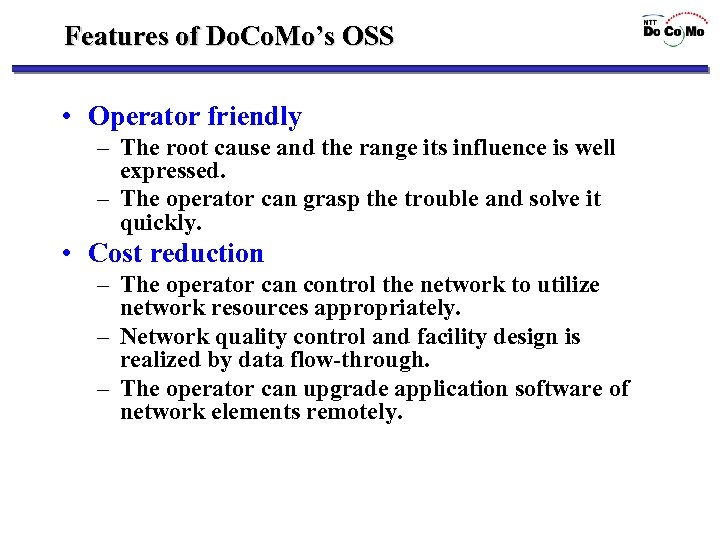
Features of Do. Co. Mo’s OSS • Operator friendly – The root cause and the range its influence is well expressed. – The operator can grasp the trouble and solve it quickly. • Cost reduction – The operator can control the network to utilize network resources appropriately. – Network quality control and facility design is realized by data flow-through. – The operator can upgrade application software of network elements remotely.

Multimedia Services of IMT-2000 • IMT-2000 service features • Mobile multimedia services • Relevant technologies – Transport technologies – Application technologies • Multimedia service platform
Evolutions of Mobile Communications Further Evolution by three components Voice to Non-voice To Multimedia Existing Industry To Ubiquitous All mobilers To Global Future Industry Province Nation to International
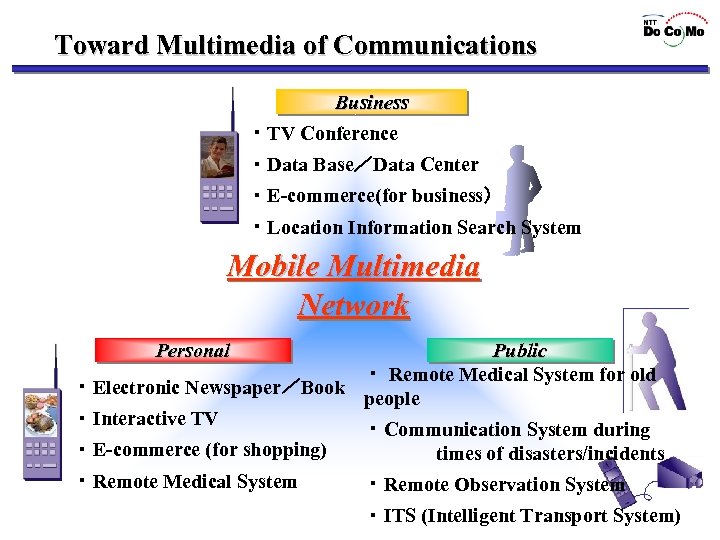
Toward Multimedia of Communications Business ・TV Conference ・Data Base/Data Center ・E-commerce(for business) ・Location Information Search System Mobile Multimedia Network Personal Public ・ Remote Medical System for old ・Electronic Newspaper/Book people ・Interactive TV ・Communication System during ・E-commerce (for shopping) times of disasters/incidents ・Remote Medical System ・Remote Observation System ・ITS (Intelligent Transport System)
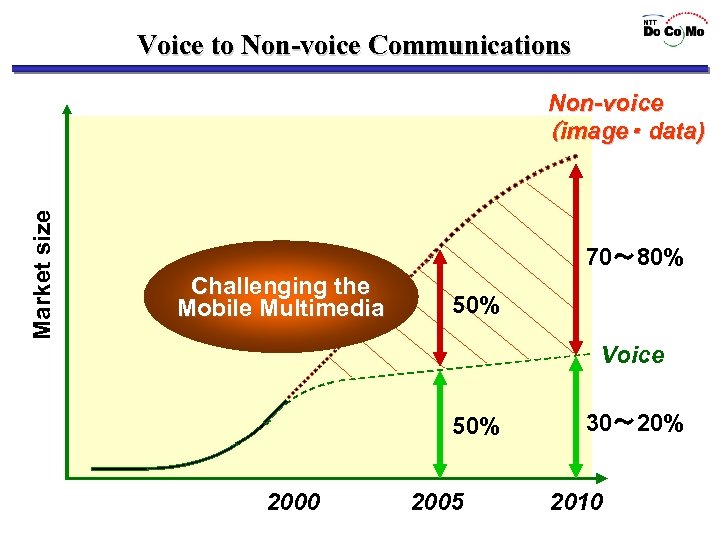
Voice to Non-voice Communications Market size Non-voice (image・ data) 70~ 80% Challenging the Mobile Multimedia 50% Voice 50% 2000 2005 30~ 20% 2010
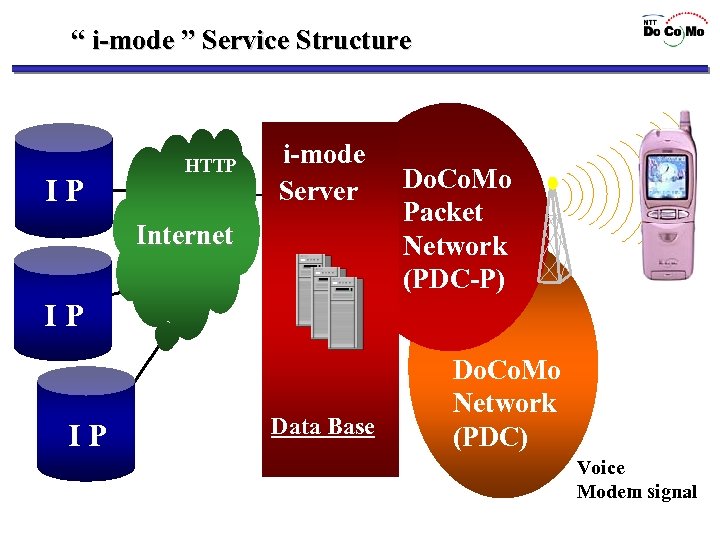
“ i-mode ” Service Structure IP HTTP i-mode Server Internet Do. Co. Mo Packet Network (PDC-P) IP IP Data Base Do. Co. Mo Network (PDC) Voice Modem signal
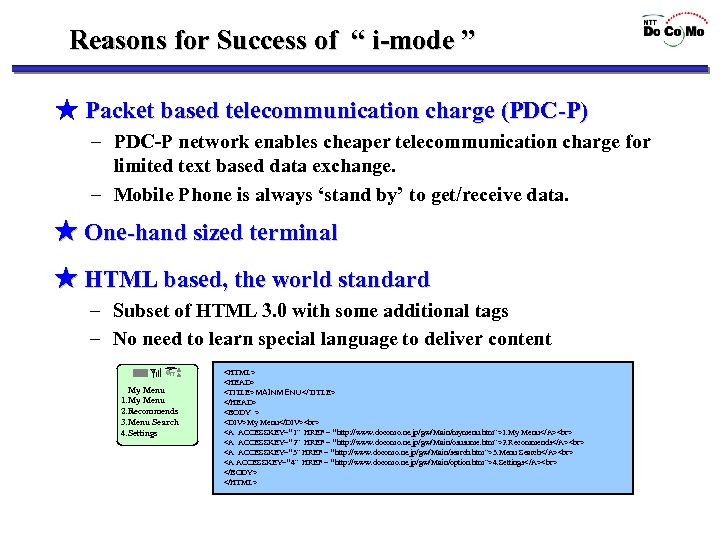
Reasons for Success of “ i-mode ” ★ Packet based telecommunication charge (PDC-P) – PDC-P network enables cheaper telecommunication charge for limited text based data exchange. – Mobile Phone is always ‘stand by’ to get/receive data. ★ One-hand sized terminal ★ HTML based, the world standard – Subset of HTML 3. 0 with some additional tags – No need to learn special language to deliver content My Menu 1. My Menu 2. Recommends 3. Menu Search 4. Settings <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>MAINMENU</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY > <DIV>My Menu</DIV> <A ACCESSKEY=“ 1” HREF = “http: //www. docomo. ne. jp/gw/Main/mymenu. htm”>1. My Menu</A> <A ACCESSKEY=“ 2” HREF = “http: //www. docomo. ne. jp/gw/Main/osusume. htm”>2. Recommends</A> <A ACCESSKEY=“ 3” HREF = “http: //www. docomo. ne. jp/gw/Main/search. htm”>3. Menu Search</A> <A ACCESSKEY=“ 4” HREF = “http: //www. docomo. ne. jp/gw/Main/option. htm”>4. Settings</A> </BODY> </HTML>
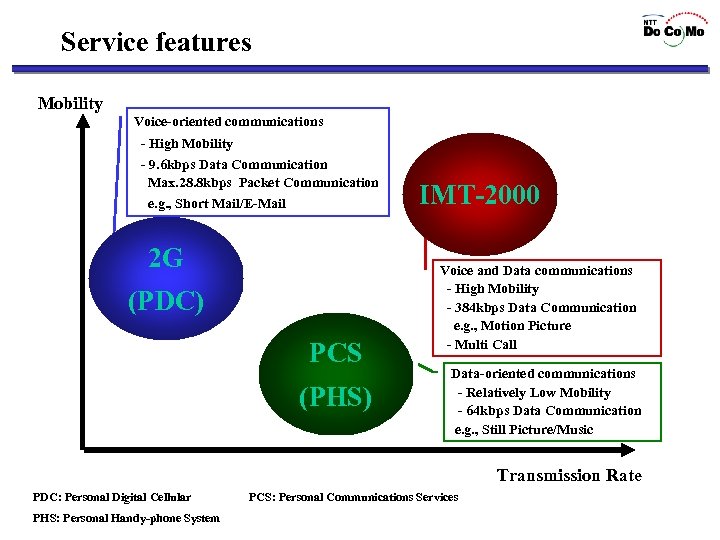
Service features Mobility Voice-oriented communications - High Mobility - 9. 6 kbps Data Communication Max. 28. 8 kbps Packet Communication e. g. , Short Mail/E-Mail 2 G (PDC) PCS (PHS) IMT-2000 Voice and Data communications - High Mobility - 384 kbps Data Communication e. g. , Motion Picture - Multi Call Data-oriented communications - Relatively Low Mobility - 64 kbps Data Communication e. g. , Still Picture/Music Transmission Rate PDC: Personal Digital Cellular PHS: Personal Handy-phone System PCS: Personal Communications Services
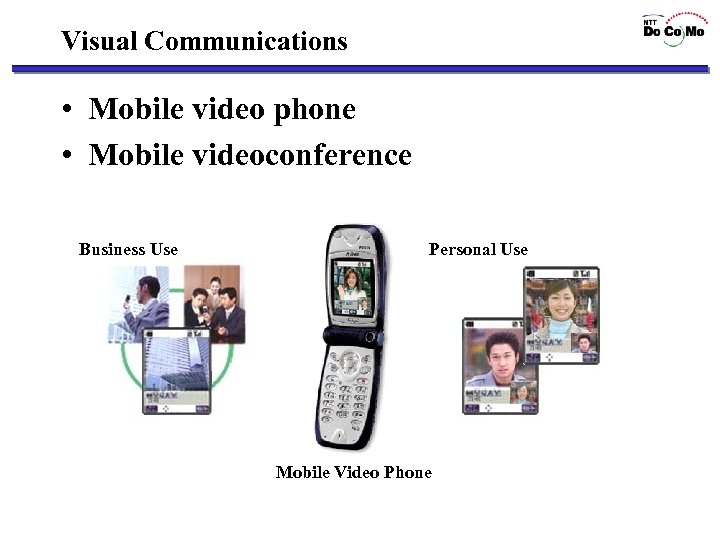
Visual Communications • Mobile video phone • Mobile videoconference Business Use Personal Use Mobile Video Phone
Mobile Internet Services • IP oriented services with high data rate – High speed web access, Multimedia email & messaging, Music or video file downloading, etc. ♪♪ ♪Peekaboo♪ i-mode server Example of Email Service BOOM!!!
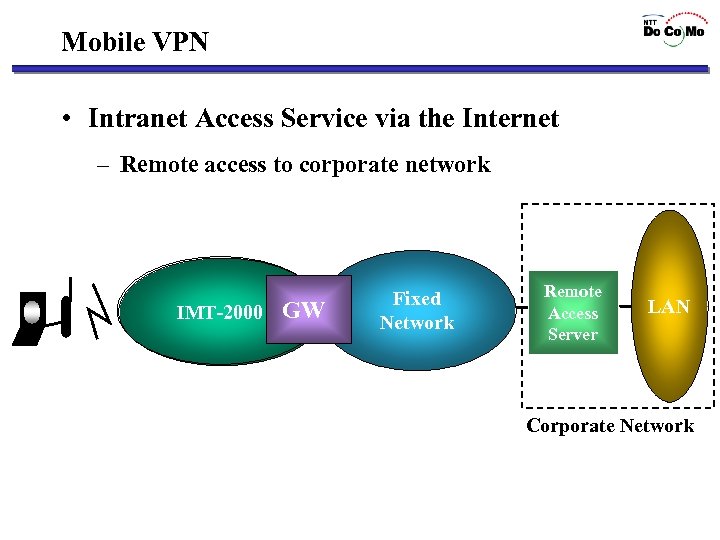
Mobile VPN • Intranet Access Service via the Internet – Remote access to corporate network IMT-2000 GW Fixed Network Remote Access Server LAN Corporate Network

Requirements for Mobile Multimedia Services • Rapid supply of various multimedia services to customers • Broadband data communication • Internet interactive solutions to x. SP • Open and unified interface between carrier and x. SP networks • Security management
Technical Requirements • Wireless Transport Technologies • Application Technologies
Wireless Transport Technologies ü ü Wireless TCP HTTP optimization
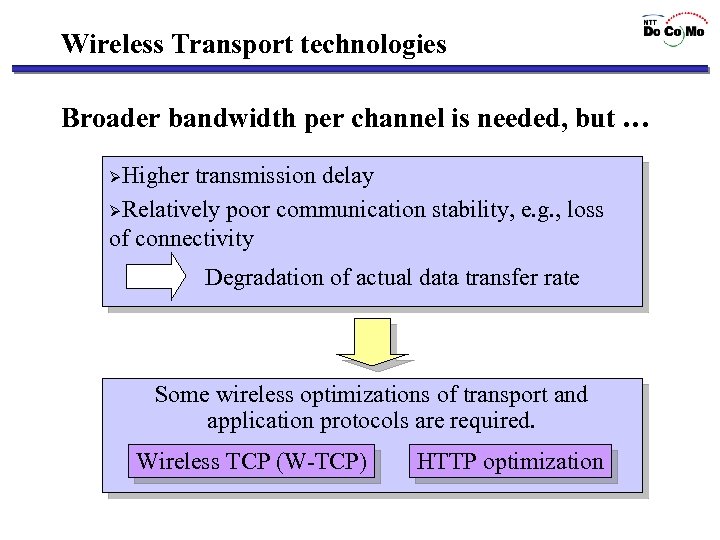
Wireless Transport technologies Broader bandwidth per channel is needed, but … ØHigher transmission delay ØRelatively poor communication stability, e. g. , loss of connectivity Degradation of actual data transfer rate Some wireless optimizations of transport and application protocols are required. Wireless TCP (W-TCP) HTTP optimization
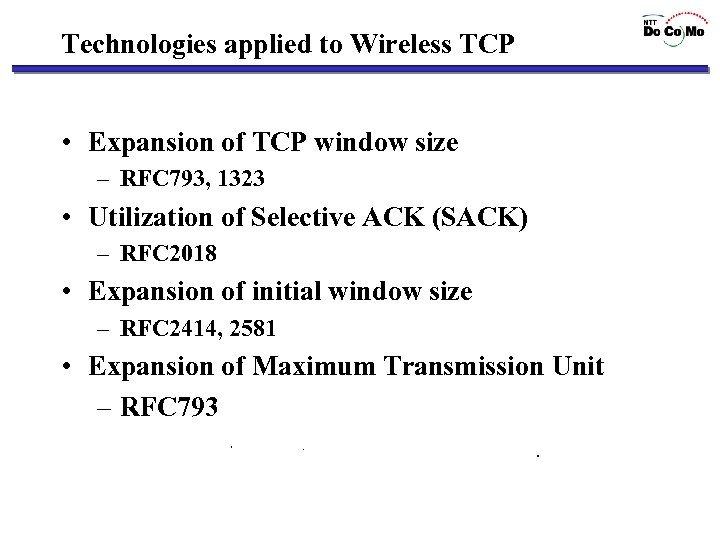
Technologies applied to Wireless TCP • Expansion of TCP window size – RFC 793, 1323 • Utilization of Selective ACK (SACK) – RFC 2018 • Expansion of initial window size – RFC 2414, 2581 • Expansion of Maximum Transmission Unit – RFC 793
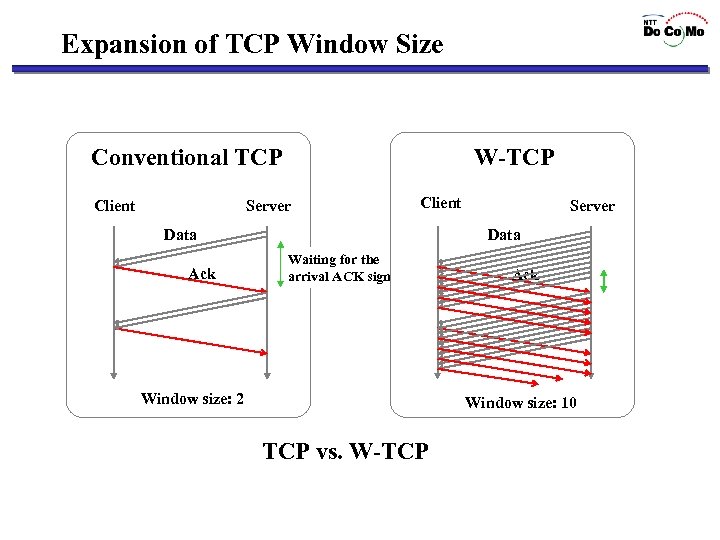
Expansion of TCP Window Size Conventional TCP Client W-TCP Server Client Data Ack Server Waiting for the arrival ACK signal Window size: 2 Ack Window size: 10 TCP vs. W-TCP
HTTP Optimization • Performance of HTTP access over IMT-2000 network may degrade when : – Establishing many TCP connections, e. g. , a content with too many gif pictures – Inefficient usage of bandwidth caused by higher transmission delay Request pipelining improves web access performance.
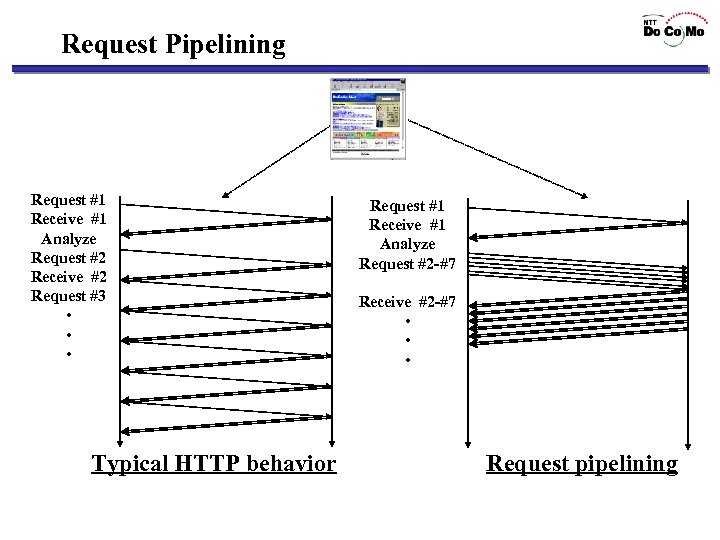
Request Pipelining Request #1 Receive #1 Analyze Request #2 Receive #2 Request #3 • • • Typical HTTP behavior Request #1 Receive #1 Analyze Request #2 -#7 Receive #2 -#7 • • • Request pipelining

Application Technologies ü Markup Languages for Micro browser ü ü Visual communications ü ü Compact HTML (CHTML), Extensible HTML (XHTML), Wireless Markup Language (WML) … 3 G-324 M Application Environment ü Mobile Execution Environment (MEx. E: Java based)
Enhanced Terminal Capability Progress of Mobile Terminals (MTs) : • Stronger processing power with lower electricity consumption • Larger size of memory and storage • High-definition and larger color display The capability of MTs is not equal to general terminals used in the Internet, such as PCs. Difference between MTs & PCs • MTs run on batteries with small capacity. • MTs have relatively poor processing power, memory, storage, and a display.

Micro Browser • Mobile terminals need special browsers, i. e. , micro browsers in order to meet mobile-specific requirements. – Light-weight markup languages • Compact HTML (CHTML) • Extensible HTML (XHTML) • Wireless Markup Language (WML)

Micro Browser (Cont’d) • What is the trend of micro browser and markup language? – XML (e. Xtensible Markup Language) related technologies – Following the evolution of PC’s web browsers – Expanding features to satisfy common needs in compact devices, such as PDA
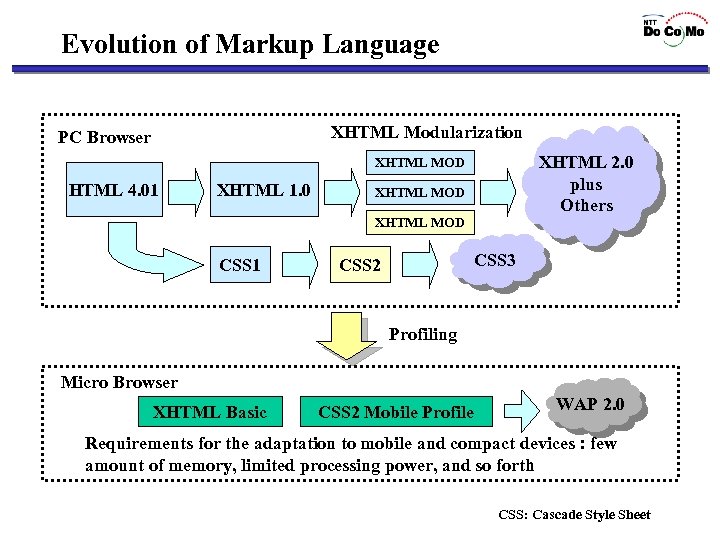
Evolution of Markup Language XHTML Modularization PC Browser XHTML 2. 0 plus Others XHTML MOD HTML 4. 01 XHTML 1. 0 XHTML MOD CSS 1 CSS 3 CSS 2 Profiling Micro Browser XHTML Basic CSS 2 Mobile Profile WAP 2. 0 Requirements for the adaptation to mobile and compact devices : few amount of memory, limited processing power, and so forth CSS: Cascade Style Sheet

Streaming over wireless • 3 G-324 M is a streaming technology optimized for visual communications over wireless networks. • Compared with commercialized IP based streaming technologies, such as WMT, 3 G-324 M has the following benefits : – Stable transfer of stream data – Better visual quality – Quick start up of visual communications – Cost-effectiveness – Prevention of copying visual contents WMT: Windows Media Technology
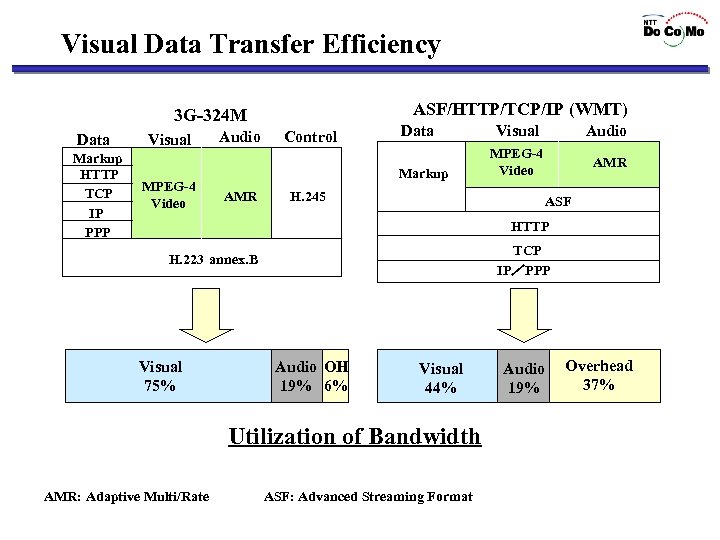
Visual Data Transfer Efficiency ASF/HTTP/TCP/IP (WMT) 3 G-324 M Data Markup HTTP TCP IP PPP Visual MPEG-4 Video Audio Control Data Markup AMR H. 245 Visual Audio MPEG-4 Video AMR ASF HTTP TCP IP/PPP H. 223 annex. B Visual 75% Audio OH 19% 6% Visual 44% Utilization of Bandwidth AMR: Adaptive Multi/Rate ASF: Advanced Streaming Format Audio 19% Overhead 37%

MEx. E (Mobile Execution Environment) • MEx. E classmark 1 – Based on WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) – Limited input and output • MEx. E classmark 2 – Based on Personal Java (subset of Java SE) – Optimized for consumer electric devices – Java. Phone API • MEx. E classmark 3 – Based on Java 2 ME, CLDC and MIDP – Optimized for embedded devices SE: Standard Edition ME: Micro Edition MIDP: Mobile Information Device Profile CLDC: Connected, Limited Device Configuration
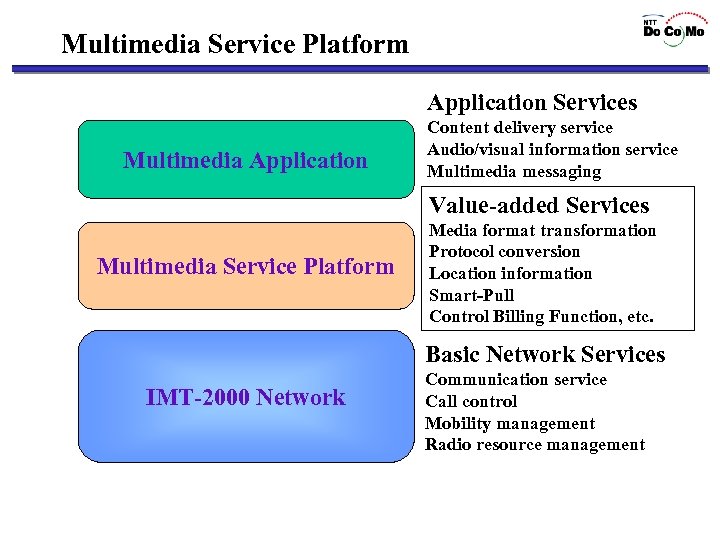
Multimedia Service Platform Application Services Multimedia Application Content delivery service Audio/visual information service Multimedia messaging Value-added Services Multimedia Service Platform Media format transformation Protocol conversion Location information Smart-Pull Control Billing Function, etc. Basic Network Services IMT-2000 Network Communication service Call control Mobility management Radio resource management
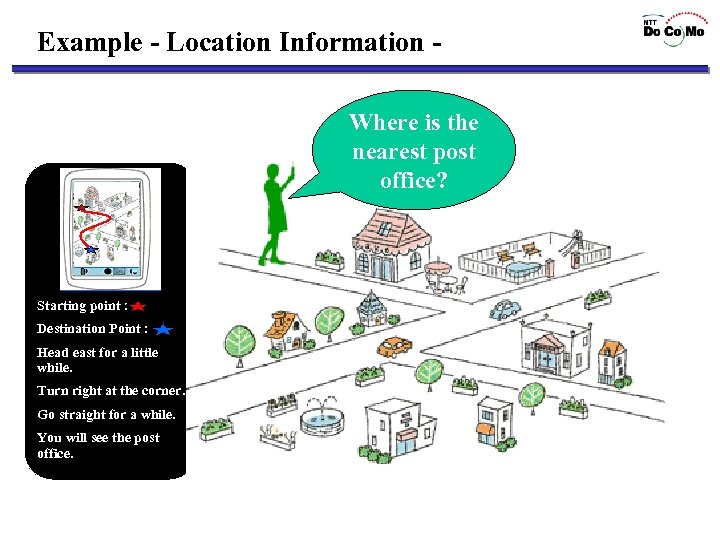
Example - Location Information Where is the nearest post office? Starting point : Current Location Destination Point : Head east for a little while. Turn right at the corner. Go straight for a while. You will see the post office. Post Office
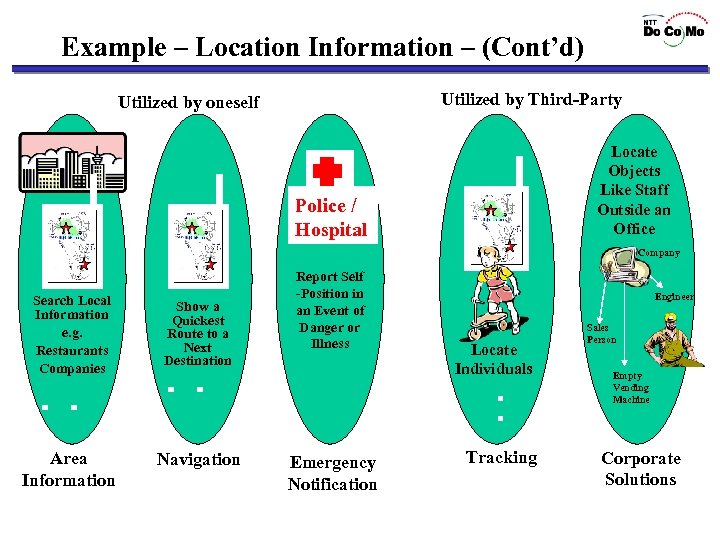
Example – Location Information – (Cont’d) Utilized by Third-Party Utilized by oneself Locate Objects Like Staff Outside an Office Police / Hospital Company Search Local Information e. g. Restaurants Companies ・ ・ Area Information Show a Quickest Route to a Next Destination Report Self -Position in an Event of Danger or Illness ・ ・ Navigation Engineer Locate Individuals ・ ・ Emergency Notification Tracking Sales Person Empty Vending Machine Corporate Solutions

Brand Name for NTT Do. Co. Mo’s IMT-2000 Services Freedom Of Mobile multimedia Access

FOMA Services ★ Internet Access “ i-mode ” for example, Web browsing and E-mail, etc. ★ Video Conferencing ★ Data Communications (circuit-switch and packet-switch) CS : 64 kbps for uplink and downlink PS : Max 384 kbps for uplink and downlink on the best effort basis ★ Voice Communications AMR (Adoptive Multi Rate) is adopted as cording scheme. ★ Multi Call This allows users to use packet-switched services(ex. E-mail) during a voice call.

FOMA Terminals P 2002 N 2002 Standard Type P 2101 V D 2101 V Visual Type P 2401 Data-Card Type With detachable UIM (User Identify Module) loaded with information to identify users Depending on a specific usage, users can select terminals.

FOMA Terminals (Cont’d) F 2601 SH 2101 V All from one terminal

Other Services ★ i-motion - Video clipping(downloading) service by i-mode - Introduced in December, 2001 ★ M-Stage Music and Visual - Music and Video distribution service for specialized terminals - Visual: Introduced in July, 2002 ★ Dual Network Service with the PDC - Subscriber can use one phone number for both FOMA (3 G) and PDC (2 G) - Introduced in July, 2002 ★ International Roaming - One mobile terminal can be used anywhere in the world
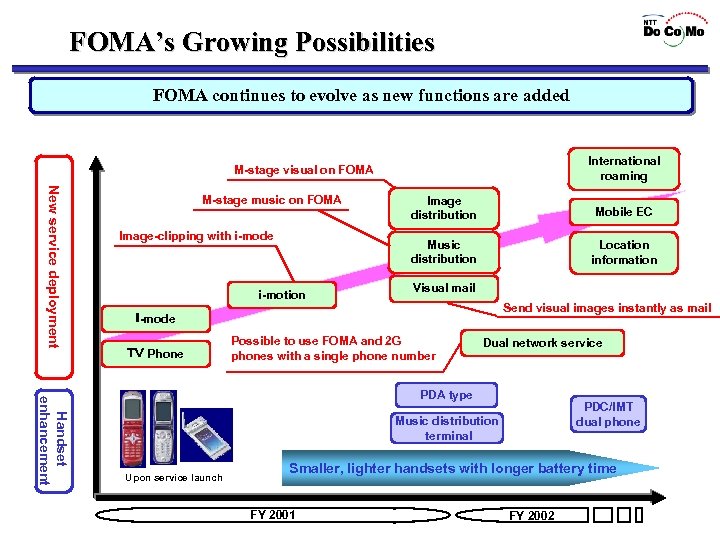
FOMA’s Growing Possibilities FOMA continues to evolve as new functions are added International roaming M-stage visual on FOMA New service deployment M-stage music on FOMA i-motion Mobile EC Music distribution Image-clipping with i-mode Image distribution Location information Visual mail Send visual images instantly as mail i-mode TV Phone Possible to use FOMA and 2 G phones with a single phone number Dual network service Handset enhancement PDA type PDC/IMT dual phone Music distribution terminal Upon service launch Smaller, lighter handsets with longer battery time FY 2001 FY 2002
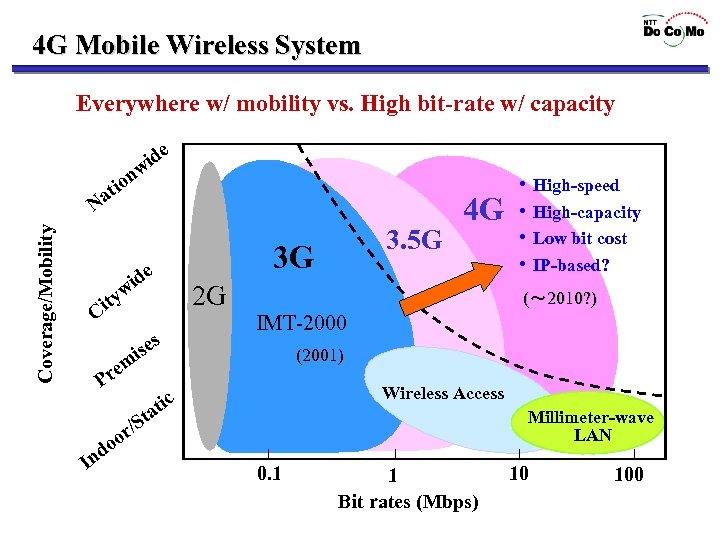
4 G Mobile Wireless System Everywhere w/ mobility vs. High bit-rate w/ capacity e id w ion t Coverage/Mobility Na w ity C e id s se i 3 G 2 G (~ 2010? ) IMT-2000 (2001) m re P 3. 5 G 4 G Wireless Access ic at St Millimeter-wave LAN r/ I o do n • High-speed • High-capacity • Low bit cost • IP-based? 0. 1 1 Bit rates (Mbps) 10 100
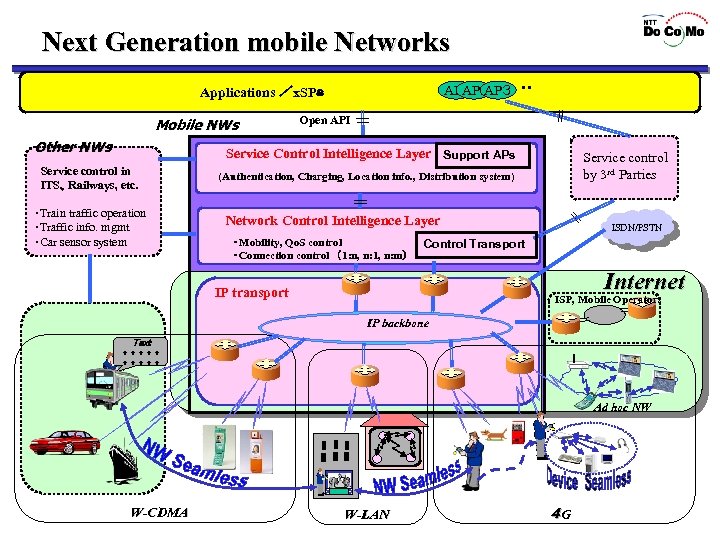
Next Generation mobile Networks AP 1 P 1 AP3 A Applications /x. SPs Mobile NWs Other NWs Open API Service Control Intelligence Layer Support APs Service control in ITS、Railways, etc. ・Train traffic operation ・Traffic info. mgmt ・Car sensor system Service control by 3 rd Parties (Authentication, Charging, Location info. , Distribution system) Network Control Intelligence Layer ・Mobility, Qo. S control ・Connection control (1: n, n: 1, n: m) ISDN/PSTN Control Transport Internet IP transport ISP, Mobile Operators IP backbone Text ***** Ad hoc NW W-CDMA W-LAN 4 G

http: //www. nttdocomo. co. jp/english/index. shtml
9bf46b9451452c3f2953dc5b1f3beded.ppt