917dbea8ad7efd02a31a49e1ec0f32b4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks Klaus Pulverer ICT Workshop, Brasilia November 2006 © Siemens 2006

End-user have High Expectations for Seamless Communication… Convenience Availability Same look & feel control and manage on various devices more effectively leads to higher when and how to acceptance and usage be contacted Customer Expectations any access, Demand for individual, any device, lively & colorful any location, communication services any time Personalized services Independency End-users go for the most attractive service bundle Page 2 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006

IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks Content § IMS motivation § Convergence: Mobility and new services § Migration: how to get there Page 3 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
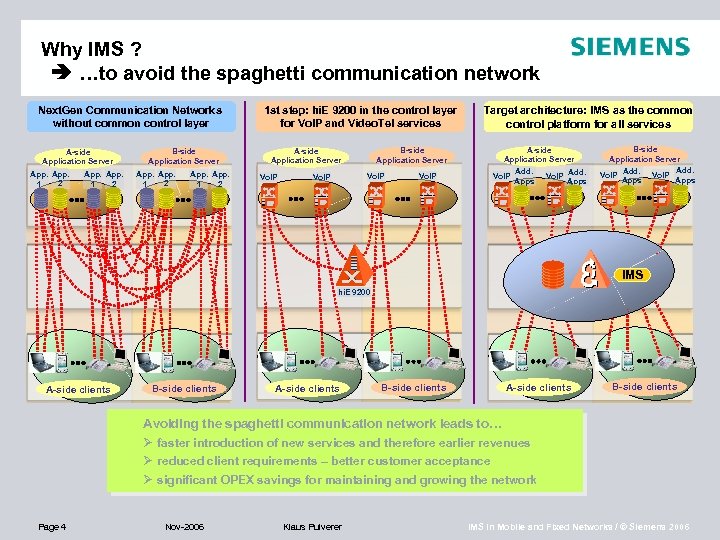
Why IMS ? …to avoid the spaghetti communication network Next. Gen Communication Networks without common control layer A-side Application Server App. 2 1 App. 1 2 B-side Application Server App. 2 1 App. 1 2 1 st step: hi. E 9200 in the control layer for Vo. IP and Video. Tel services B-side Application Server A-side Application Server Vo. IP Target architecture: IMS as the common control platform for all services A-side Application Server Add. Vo. IP Apps B-side Application Server Add. Vo. IP Apps IMS hi. E 9200 A-side clients B-side clients Avoiding the spaghetti communication network leads to… Ø faster introduction of new services and therefore earlier revenues Ø reduced client requirements – better customer acceptance Ø significant OPEX savings for maintaining and growing the network Page 4 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
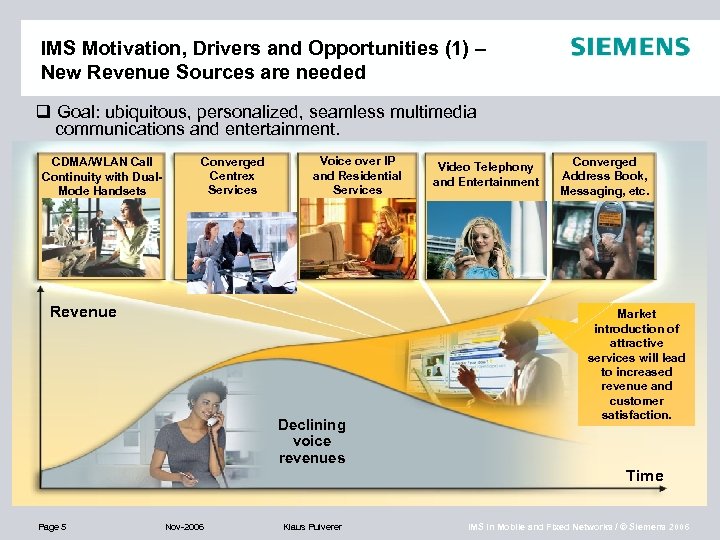
IMS Motivation, Drivers and Opportunities (1) – New Revenue Sources are needed q Goal: ubiquitous, personalized, seamless multimedia communications and entertainment. CDMA/WLAN Call Continuity with Dual. Mode Handsets Converged Centrex Services Voice over IP and Residential Services Revenue Declining voice revenues Video Telephony and Entertainment Converged Address Book, Messaging, etc. … Market introduction of attractive services will lead to increased revenue and customer satisfaction. Time Page 5 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
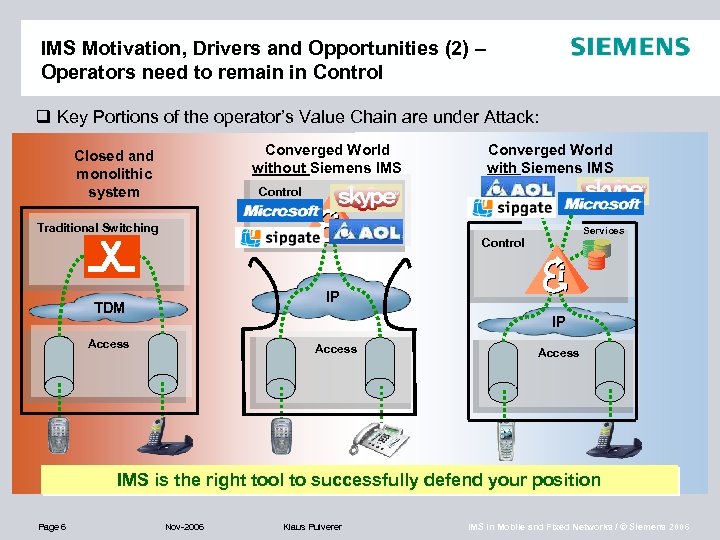
IMS Motivation, Drivers and Opportunities (2) – Operators need to remain in Control q Key Portions of the operator’s Value Chain are under Attack: Converged World without Siemens IMS Closed and monolithic system Converged World with Siemens IMS Control Traditional Switching Services Control IP TDM IP Access IMS is the right tool to successfully defend your position Page 6 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
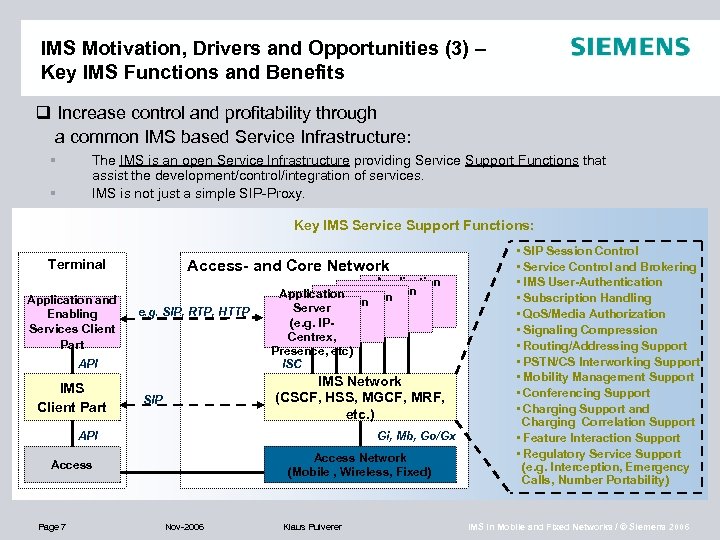
IMS Motivation, Drivers and Opportunities (3) – Key IMS Functions and Benefits q Increase control and profitability through a common IMS based Service Infrastructure: § § The IMS is an open Service Infrastructure providing Service Support Functions that assist the development/control/integration of services. IMS is not just a simple SIP-Proxy. Key IMS Service Support Functions: Terminal Application and Enabling Services Client Part Access- and Core Network e. g. SIP, RTP, HTTP API IMS Client Part Application Server Application Server (e. g. IPCentrex, Presence, etc) ISC IMS Network (CSCF, HSS, MGCF, MRF, etc. ) SIP API Gi, Mb, Go/Gx Access Network (Mobile , Wireless, Fixed) Access Page 7 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer • SIP Session Control • Service Control and Brokering • IMS User-Authentication • Subscription Handling • Qo. S/Media Authorization • Signaling Compression • Routing/Addressing Support • PSTN/CS Interworking Support • Mobility Management Support • Conferencing Support • Charging Support and Charging Correlation Support • Feature Interaction Support • Regulatory Service Support (e. g. Interception, Emergency Calls, Number Portability) IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
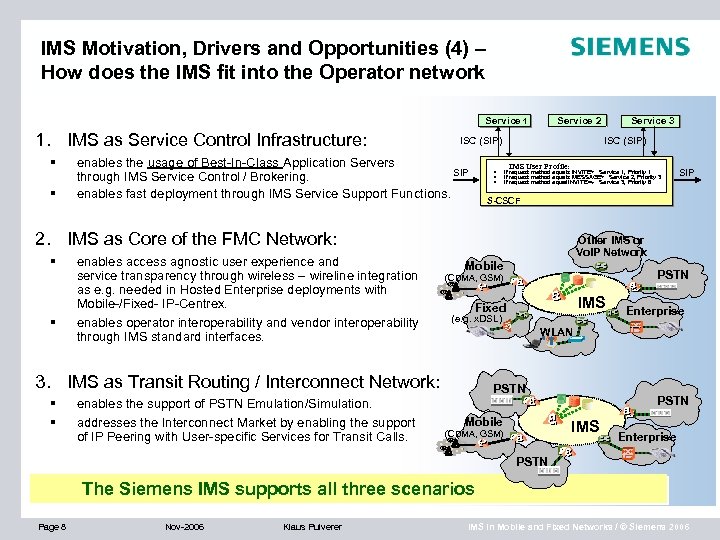
IMS Motivation, Drivers and Opportunities (4) – How does the IMS fit into the Operator network Service 1 1. IMS as Service Control Infrastructure: § § Service 2 ISC (SIP) enables the usage of Best-In-Class Application Servers SIP through IMS Service Control / Brokering. enables fast deployment through IMS Service Support Functions. § § § ISC (SIP) IMS User Profile: Þ If request method equals INVITE Service 1, Priority 1 Þ If request method equals MESSAGE Service 2, Priority 3 If request method equal INVITE Þ Service 3, Priority 6 s § enables access agnostic user experience and service transparency through wireless – wireline integration as e. g. needed in Hosted Enterprise deployments with Mobile-/Fixed- IP-Centrex. enables operator interoperability and vendor interoperability through IMS standard interfaces. Other IMS or Vo. IP Network Mobile enables the support of PSTN Emulation/Simulation. addresses the Interconnect Market by enabling the support of IP Peering with User-specific Services for Transit Calls. PSTN (CDMA, GSM) IMS Fixed (e. g. x. DSL) Enterprise WLAN 3. IMS as Transit Routing / Interconnect Network: § § SIP S-CSCF 2. IMS as Core of the FMC Network: § Service 3 PSTN Mobile PSTN IMS (CDMA, GSM) Enterprise PSTN The Siemens IMS supports all three scenarios Page 8 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
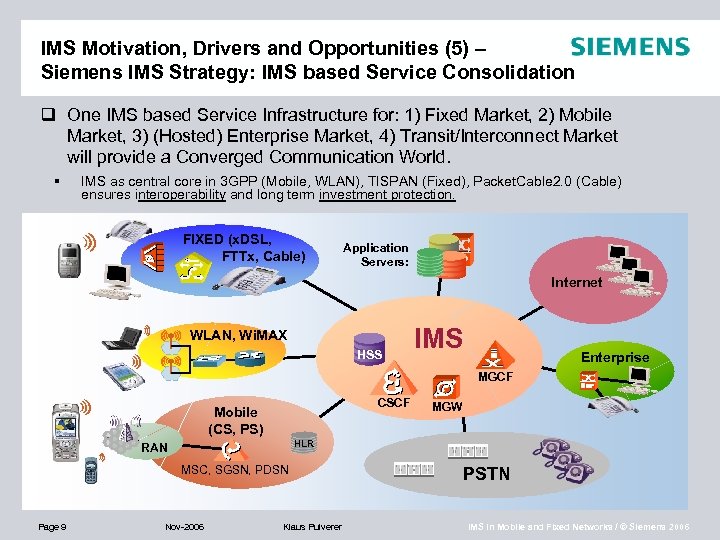
IMS Motivation, Drivers and Opportunities (5) – Siemens IMS Strategy: IMS based Service Consolidation q One IMS based Service Infrastructure for: 1) Fixed Market, 2) Mobile Market, 3) (Hosted) Enterprise Market, 4) Transit/Interconnect Market will provide a Converged Communication World. § IMS as central core in 3 GPP (Mobile, WLAN), TISPAN (Fixed), Packet. Cable 2. 0 (Cable) ensures interoperability and long term investment protection. FIXED (x. DSL, FTTx, Cable) Application Servers: Internet WLAN, Wi. MAX HSS IMS Enterprise MGCF CSCF Mobile (CS, PS) HLR RAN MSC, SGSN, PDSN Page 9 MGW Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer PSTN IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006

IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks Content § IMS motivation § Convergence: Mobility and new services § Migration: how to get there Page 10 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006

Quadruple Play – Mobile Operators have one Unique Competitive Advantage: Mobility Rich Voice Mobile Data Broadband Access FNO Voice Mobility handover Access Point GERAN Page 11 Cable Prov. Vo. IP Content Mobile Infotainment MNO Mobility Office Cellular Access ISP Wi. Fi Access UTRAN Nov-2006 3 G+ BWA Klaus Pulverer MW … DSL IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
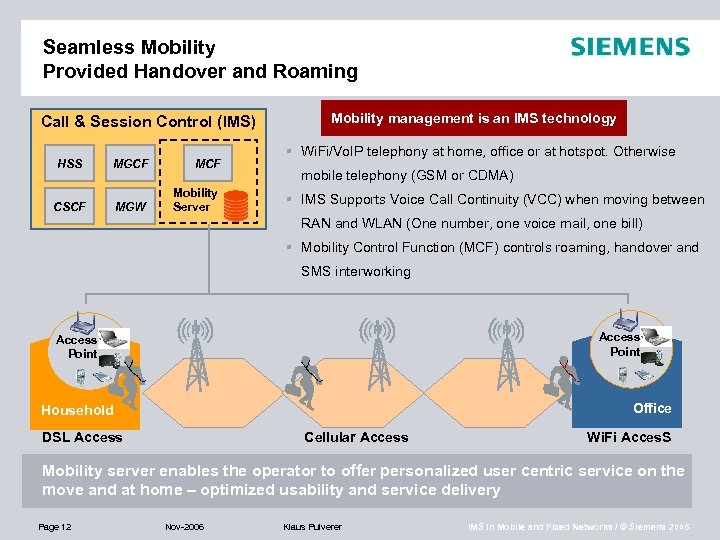
Seamless Mobility Provided Handover and Roaming Call & Session Control (IMS) HSS MGCF MCF CSCF MGW Mobility Server Mobility management is an IMS technology § Wi. Fi/Vo. IP telephony at home, office or at hotspot. Otherwise mobile telephony (GSM or CDMA) § IMS Supports Voice Call Continuity (VCC) when moving between RAN and WLAN (One number, one voice mail, one bill) § Mobility Control Function (MCF) controls roaming, handover and SMS interworking Access Point Office Household DSL Access Cellular Access Wi. Fi Acces. S Mobility server enables the operator to offer personalized user centric service on the move and at home – optimized usability and service delivery Page 12 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
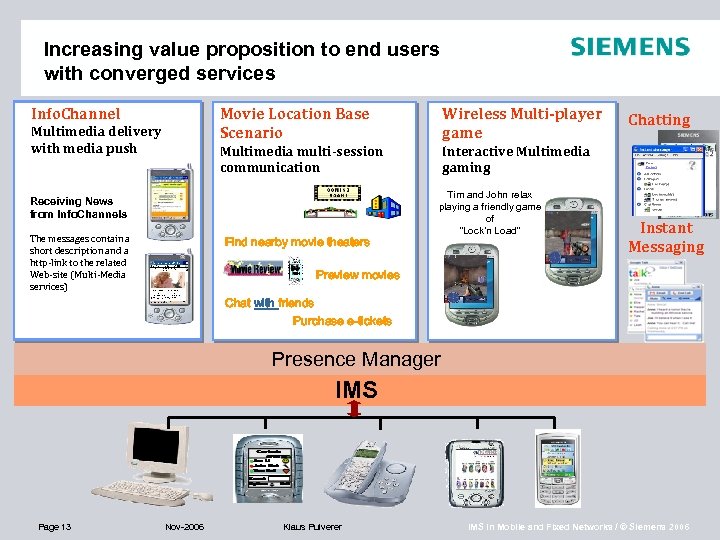
Increasing value proposition to end users with converged services Info. Channel Movie Location Base Scenario Multimedia multi-session communication Multimedia delivery with media push Wireless Multi-player game Interactive Multimedia gaming Receiving News from Info. Channels The messages contain a short description and a http-link to the related Web-site (Multi-Media services) Find nearby movie theaters Tim and John relax playing a friendly game of “Lock’n Load” Chatting Instant Messaging Preview movies Chat with friends Purchase e-tickets Presence Manager IMS Page 13 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
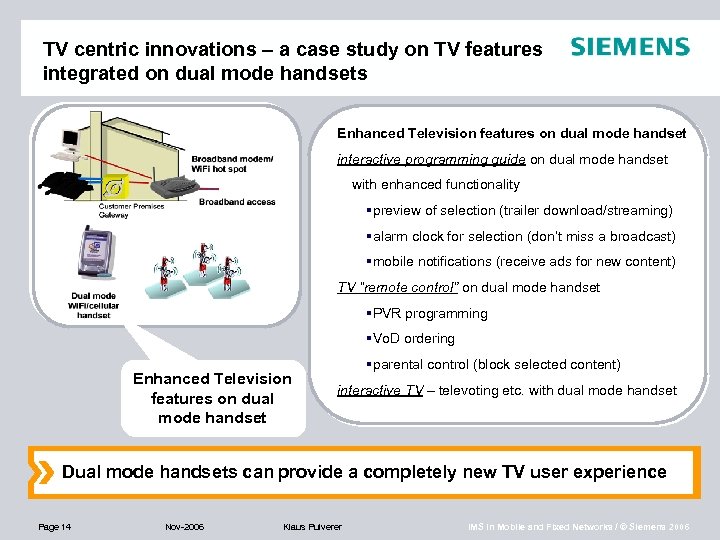
TV centric innovations – a case study on TV features integrated on dual mode handsets Enhanced Television features on dual mode handset interactive programming guide on dual mode handset with enhanced functionality §preview of selection (trailer download/streaming) §alarm clock for selection (don’t miss a broadcast) §mobile notifications (receive ads for new content) TV “remote control” on dual mode handset §PVR programming §Vo. D ordering Enhanced Television features on dual mode handset §parental control (block selected content) interactive TV – televoting etc. with dual mode handset Dual mode handsets can provide a completely new TV user experience Page 14 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
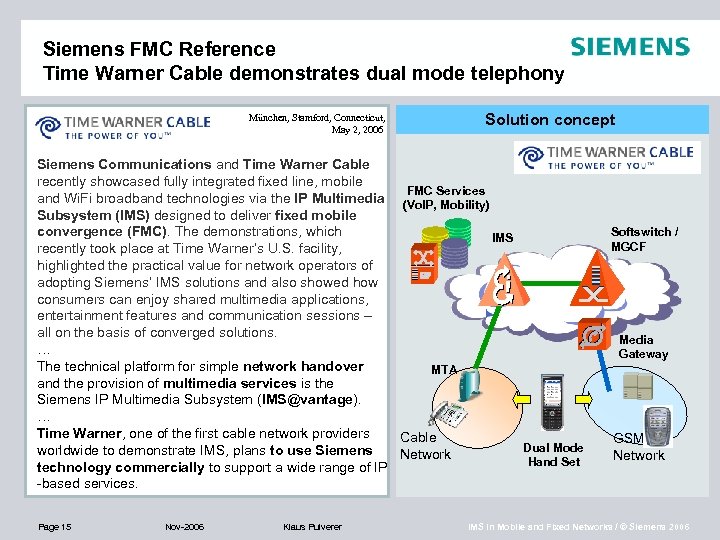
Siemens FMC Reference Time Warner Cable demonstrates dual mode telephony München, Stamford, Connecticut, May 2, 2006 Solution concept Siemens Communications and Time Warner Cable recently showcased fully integrated fixed line, mobile FMC Services and Wi. Fi broadband technologies via the IP Multimedia (Vo. IP, Mobility) Subsystem (IMS) designed to deliver fixed mobile convergence (FMC). The demonstrations, which IMS recently took place at Time Warner’s U. S. facility, highlighted the practical value for network operators of adopting Siemens’ IMS solutions and also showed how consumers can enjoy shared multimedia applications, entertainment features and communication sessions – all on the basis of converged solutions. … The technical platform for simple network handover MTA and the provision of multimedia services is the Siemens IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS@vantage). … Time Warner, one of the first cable network providers Cable Dual Mode worldwide to demonstrate IMS, plans to use Siemens Network Hand Set technology commercially to support a wide range of IP -based services. Page 15 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer Softswitch / MGCF Media Gateway GSM Network IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006

TV centric innovations Deliver FMC applications to the TV set In the Set-Top-Box On a PC Kreatel i 3 Micro On a Mobile Phone Page 16 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
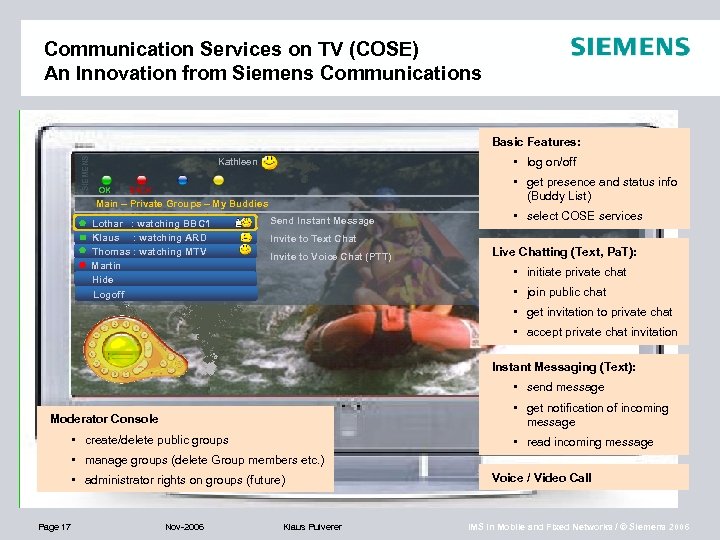
Communication Services on TV (COSE) An Innovation from Siemens Communications SIEMENS Basic Features: • log on/off Kathleen OK • get presence and status info (Buddy List) BACK Main – Private Groups – My Buddies Lothar : watching BBC 1 Klaus : watching ARD Thomas : watching MTV Martin Hide Logoff Send Instant Message • select COSE services Invite to Text Chat Invite to Voice Chat (PTT) Live Chatting (Text, Pa. T): • initiate private chat • join public chat • get invitation to private chat • accept private chat invitation Instant Messaging (Text): • send message • get notification of incoming message Moderator Console • create/delete public groups • read incoming message • manage groups (delete Group members etc. ) • administrator rights on groups (future) Page 17 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer Voice / Video Call IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006

IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks Content § IMS motivation § Convergence: Mobility and new services § Migration: how to get there Page 18 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
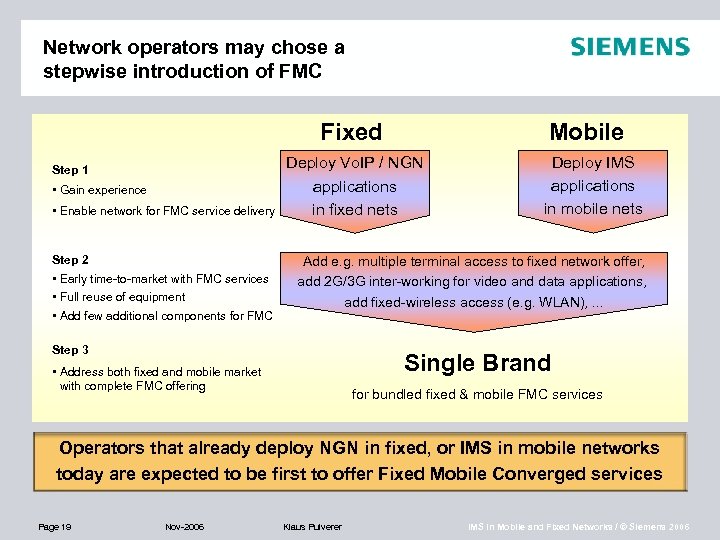
Network operators may chose a stepwise introduction of FMC Fixed Step 1 • Gain experience • Enable network for FMC service delivery Step 2 • Early time-to-market with FMC services • Full reuse of equipment • Add few additional components for FMC Mobile Deploy Vo. IP / NGN applications in fixed nets Deploy IMS applications in mobile nets Add e. g. multiple terminal access to fixed network offer, add 2 G/3 G inter-working for video and data applications, add fixed-wireless access (e. g. WLAN), . . . Step 3 Single Brand • Address both fixed and mobile market with complete FMC offering for bundled fixed & mobile FMC services Operators that already deploy NGN in fixed, or IMS in mobile networks today are expected to be first to offer Fixed Mobile Converged services Page 19 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
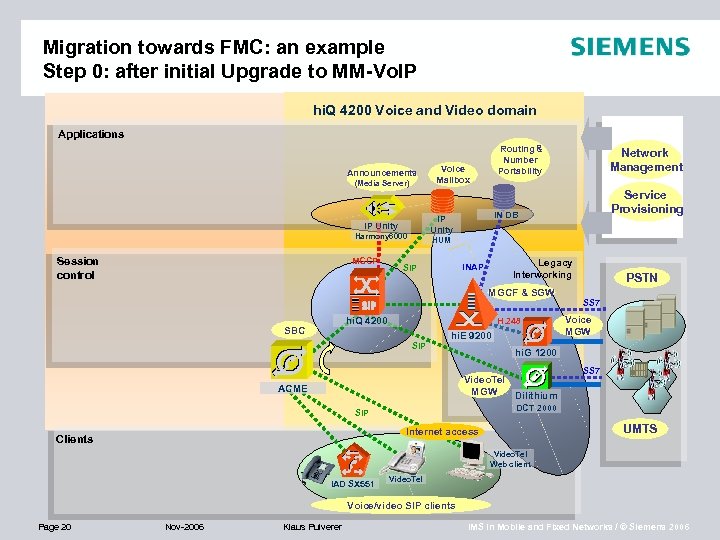
Migration towards FMC: an example Step 0: after initial Upgrade to MM-Vo. IP hi. Q 4200 Voice and Video domain Applications Announcements (Media Server) Harmony 6000 MGCP Voice Mailbox Legacy Interworking INAP SIP hi. Q 4200 H. 248 SIP hi. E 9200 ACME PSTN SS 7 Voice MGW hi. G 1200 Video. Tel MGW Dilithium SS 7 DCT 2000 SIP UMTS Internet access Clients Service Provisioning HUM MGCF & SGW SBC Network Management IN DB IP Unity Session control Routing & Number Portability Video. Tel Web client IAD SX 551 Video. Tel Voice/video SIP clients Page 20 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
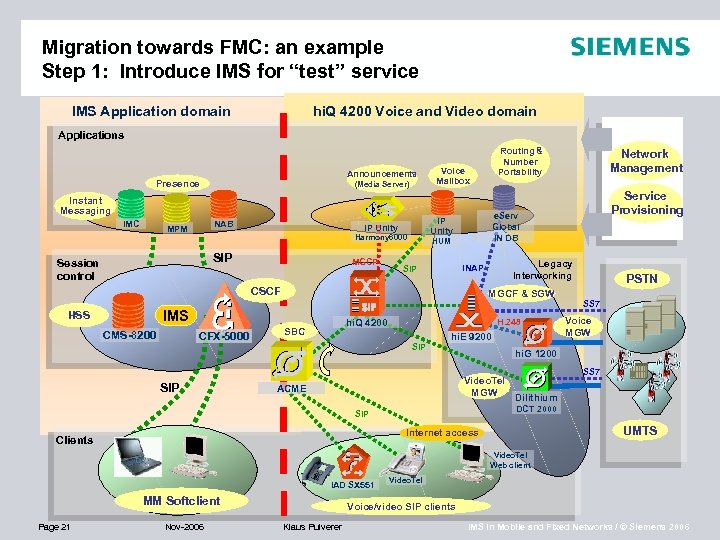
Migration towards FMC: an example Step 1: Introduce IMS for “test” service IMS Application domain hi. Q 4200 Voice and Video domain Applications Announcements Presence (Media Server) Instant Messaging IMC NAB MPM SIP MGCP Voice Mailbox HUM CSCF MGCF & SGW IMS HSS CMS-8200 CFX-5000 SIP hi. Q 4200 SBC H. 248 SIP hi. E 9200 SS 7 Voice MGW SS 7 DCT 2000 SIP UMTS Internet access Clients PSTN hi. G 1200 Video. Tel MGW Dilithium ACME Service Provisioning Legacy Interworking INAP SIP Network Management e. Serv Global IN DB IP Unity Harmony 6000 Session control Routing & Number Portability Video. Tel Web client IAD SX 551 MM Softclient Page 21 Nov-2006 Video. Tel Voice/video SIP clients Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
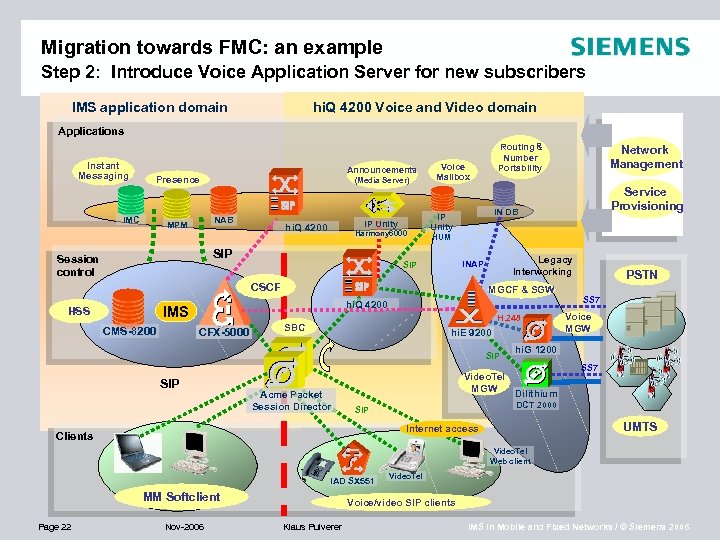
Migration towards FMC: an example Step 2: Introduce Voice Application Server for new subscribers IMS application domain hi. Q 4200 Voice and Video domain Applications Instant Messaging Announcements Presence IMC (Media Server) NAB MPM IP Unity hi. Q 4200 Harmony 6000 SIP Session control MGCP Voice Mailbox CMS-8200 CFX-5000 Legacy Interworking INAP SIP MGCF & SGW H. 248 SBC hi. E 9200 SIP Acme Packet Session Director PSTN SS 7 Voice MGW hi. G 1200 Video. Tel MGW Dilithium SS 7 DCT 2000 SIP UMTS Internet access Clients Service Provisioning HUM hi. Q 4200 IMS Network Management IN DB IP Unity CSCF HSS Routing & Number Portability Video. Tel Web client IAD SX 551 MM Softclient Page 22 Nov-2006 Video. Tel Voice/video SIP clients Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
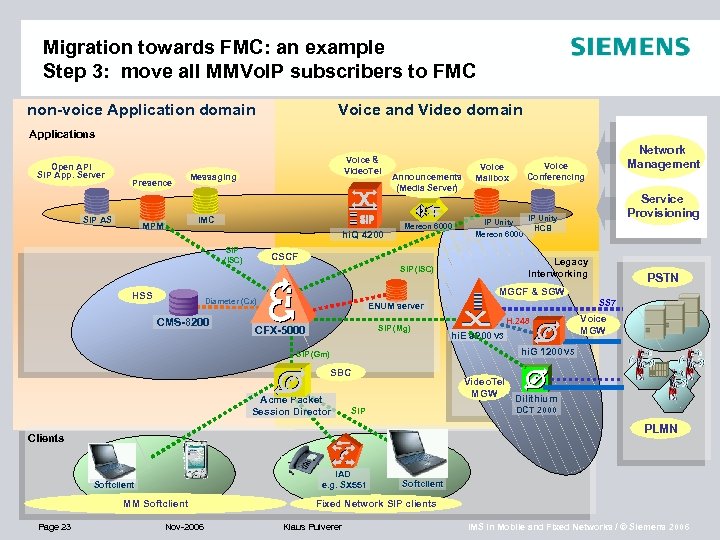
Migration towards FMC: an example Step 3: move all MMVo. IP subscribers to FMC non-voice Application domain Voice and Video domain Applications Open API SIP App. Server Presence SIP AS Voice & Video. Tel Messaging IMC MPM hi. Q 4200 SIP (ISC) Announcements (Media Server) Mereon 6000 Voice Mailbox CSCF ENUM server SIP (Mg) CFX-5000 H. 248 hi. E 9200 V 3 PSTN SS 7 Voice MGW hi. G 1200 V 5 SIP (Gm) SBC Acme Packet Session Director Video. Tel MGW Dilithium DCT 2000 SIP PLMN Clients IAD e. g. SX 551 Softclient MM Softclient Page 23 Service Provisioning Legacy Interworking MGCF & SGW Diameter (Cx) CMS-8200 Voice Conferencing IP Unity HCB Mereon 6000 SIP (ISC) HSS Network Management Nov-2006 Softclient Fixed Network SIP clients Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006

Can there be any future without Vo. IP? Probably not Page 24 Nov-2006 Klaus Pulverer IMS in Mobile and Fixed Networks / © Siemens 2006
917dbea8ad7efd02a31a49e1ec0f32b4.ppt