b138eb938cf4a42c66db00dd1883f3c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Improving outcomes in AKI and CRRT: Does Quality matter? Timothy E. Bunchman Professor and Director Pediatric Nephrology & Transplantation Timothy. bunchman@vcuhealth. org pedscrrt@gmail. com www. pcrrt. com
Improving outcomes in AKI and CRRT: Does Quality matter? Timothy E. Bunchman Professor and Director Pediatric Nephrology & Transplantation Timothy. bunchman@vcuhealth. org pedscrrt@gmail. com www. pcrrt. com
 Overview n n What has occurred to improve the diagnosis and outcome in AKI in children What has occurred to improve the use of CRRT in children
Overview n n What has occurred to improve the diagnosis and outcome in AKI in children What has occurred to improve the use of CRRT in children
 How do you diagnosis AKI? n n Severity of illness score? Biomarkers? FO? Uremia?
How do you diagnosis AKI? n n Severity of illness score? Biomarkers? FO? Uremia?
 Historically n AKI diagnosis was synominous with the need for renal replacement therapy n n Uremia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis In 2000 ADQI occurred and began to quantitate and measure markers of AKI
Historically n AKI diagnosis was synominous with the need for renal replacement therapy n n Uremia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis In 2000 ADQI occurred and began to quantitate and measure markers of AKI
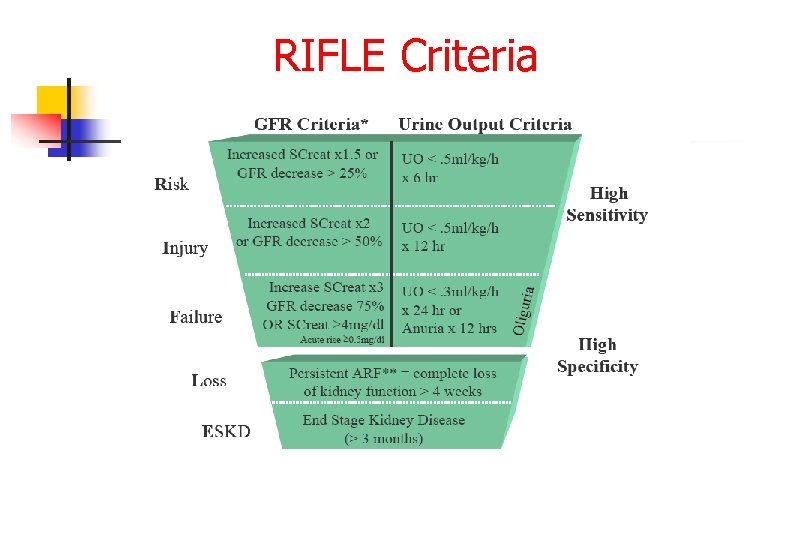 RIFLE Criteria
RIFLE Criteria
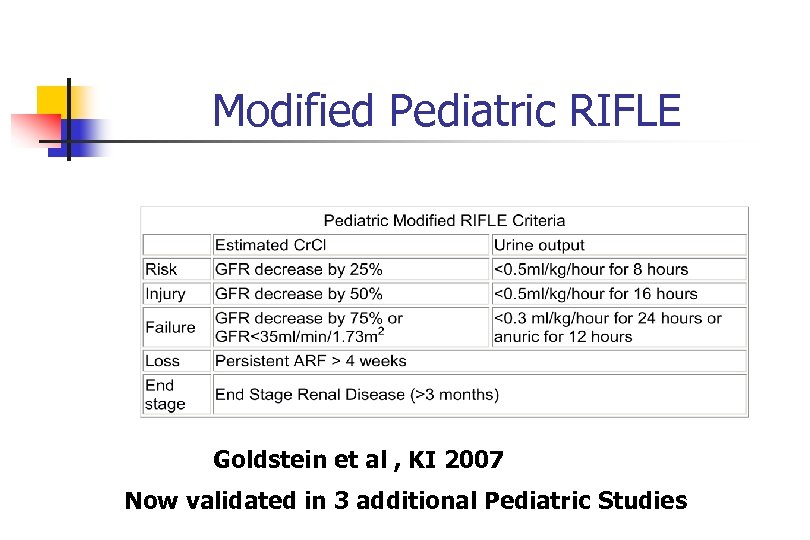 Modified Pediatric RIFLE Goldstein et al , KI 2007 Now validated in 3 additional Pediatric Studies
Modified Pediatric RIFLE Goldstein et al , KI 2007 Now validated in 3 additional Pediatric Studies
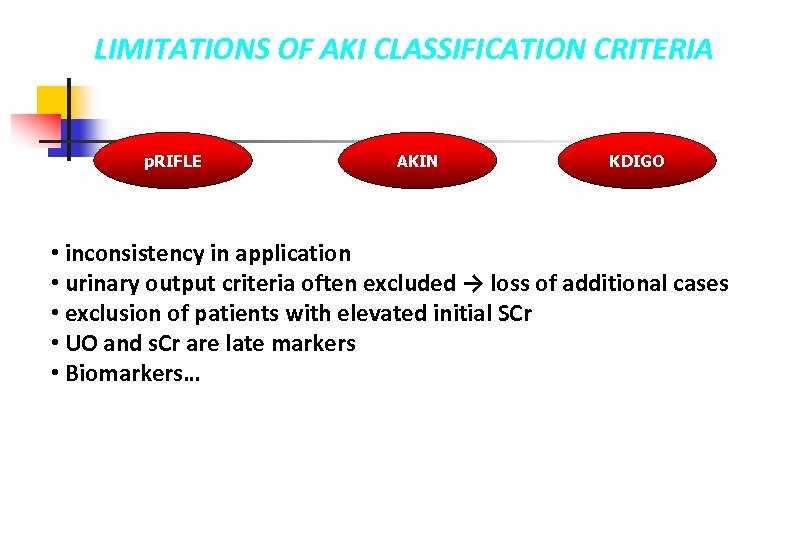 LIMITATIONS OF AKI CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA p. RIFLE AKIN KDIGO • inconsistency in application • urinary output criteria often excluded → loss of additional cases • exclusion of patients with elevated initial SCr • UO and s. Cr are late markers • Biomarkers…
LIMITATIONS OF AKI CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA p. RIFLE AKIN KDIGO • inconsistency in application • urinary output criteria often excluded → loss of additional cases • exclusion of patients with elevated initial SCr • UO and s. Cr are late markers • Biomarkers…
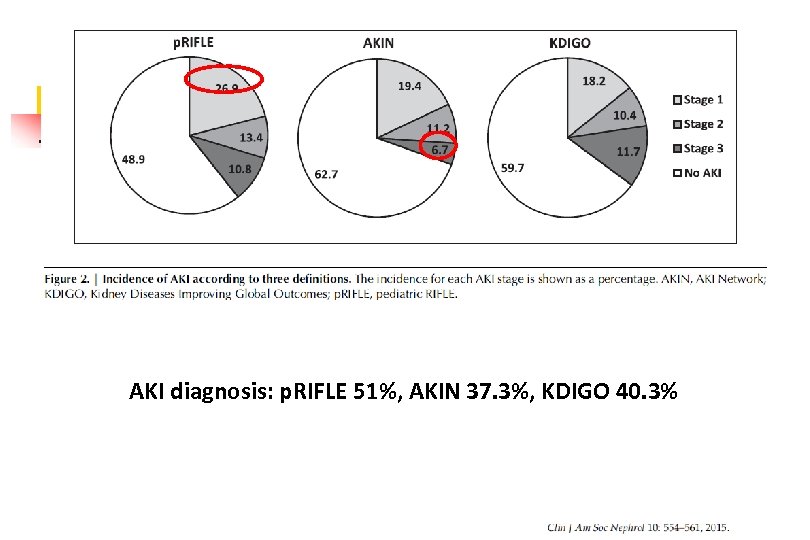 AKI diagnosis: p. RIFLE 51%, AKIN 37. 3%, KDIGO 40. 3%
AKI diagnosis: p. RIFLE 51%, AKIN 37. 3%, KDIGO 40. 3%
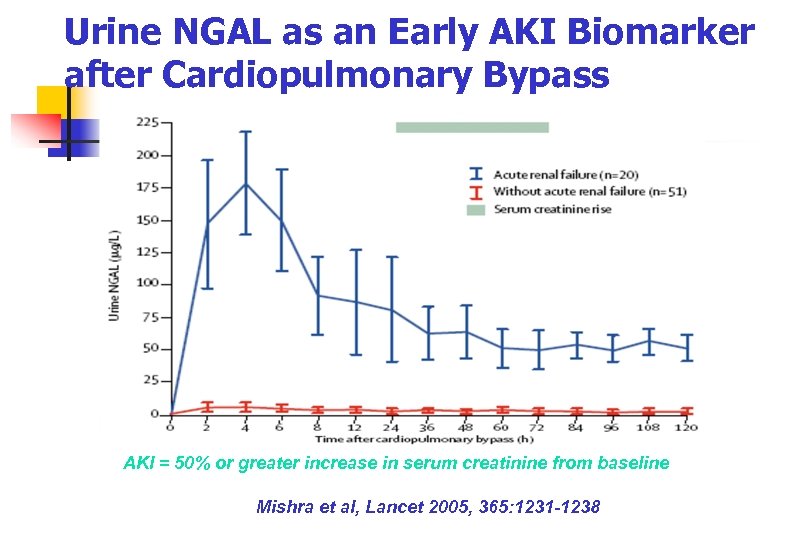 Urine NGAL as an Early AKI Biomarker after Cardiopulmonary Bypass AKI = 50% or greater increase in serum creatinine from baseline Mishra et al, Lancet 2005, 365: 1231 -1238
Urine NGAL as an Early AKI Biomarker after Cardiopulmonary Bypass AKI = 50% or greater increase in serum creatinine from baseline Mishra et al, Lancet 2005, 365: 1231 -1238
 Dialysis Dose and Outcome Ronco et al. Lancet 2000; 351: 26 -30 425 patients Endpoint = survival 15 days after D/C HF 146 UF rate 20 ml/kg/hr survival significantly lower in this group compared to the others 139 UF rate 35 ml/kg/hr p=0. 0007 140 UF rate 45 ml/kg/hr p=0. 0013 • Conclusions: – Minimum UF rates should be ~ 35 ml/kg/hr – Survivors had lower BUNs than non-survivors prior to commencement of hemofiltration
Dialysis Dose and Outcome Ronco et al. Lancet 2000; 351: 26 -30 425 patients Endpoint = survival 15 days after D/C HF 146 UF rate 20 ml/kg/hr survival significantly lower in this group compared to the others 139 UF rate 35 ml/kg/hr p=0. 0007 140 UF rate 45 ml/kg/hr p=0. 0013 • Conclusions: – Minimum UF rates should be ~ 35 ml/kg/hr – Survivors had lower BUNs than non-survivors prior to commencement of hemofiltration
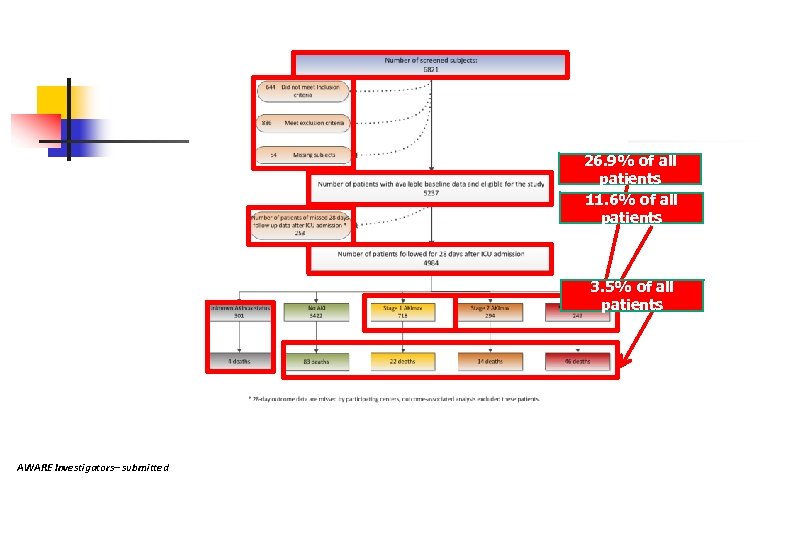 26. 9% of all patients 11. 6% of all patients 3. 5% of all patients AWARE Investigators– submitted
26. 9% of all patients 11. 6% of all patients 3. 5% of all patients AWARE Investigators– submitted
 So what! n n n The diagnosis of AKI and the need for RRT are discreptent But If AKI at risk is 25% of all PICU admissions then attention to detail of nephrotoxins and fluid over load are needed to avoid the worsening of AKI
So what! n n n The diagnosis of AKI and the need for RRT are discreptent But If AKI at risk is 25% of all PICU admissions then attention to detail of nephrotoxins and fluid over load are needed to avoid the worsening of AKI
 SPECIAL FIBERS AND FILTERS HAVE BEEN DESIGNED FOR SPECIAL CONDITIONS AND PATIENTS Minifilters Ronco C, et al Treatment of acute renal failure in newborns by Continuous Arterio-Venous Hemofiltration. Kidney International, 1984
SPECIAL FIBERS AND FILTERS HAVE BEEN DESIGNED FOR SPECIAL CONDITIONS AND PATIENTS Minifilters Ronco C, et al Treatment of acute renal failure in newborns by Continuous Arterio-Venous Hemofiltration. Kidney International, 1984
 1980 s n Following Ronco’s paper little was published except for a descriptive paper by Leone et al describing CAVH in children n n Early experience with continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in critically ill pediatric patients. Crit Care Med. 1986 Dec; 14(12): 1058 -63. Neonatal work by Zobel n Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in premature infants. Crit Care Med. 1989 Jun; 17(6): 534 -6.
1980 s n Following Ronco’s paper little was published except for a descriptive paper by Leone et al describing CAVH in children n n Early experience with continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in critically ill pediatric patients. Crit Care Med. 1986 Dec; 14(12): 1058 -63. Neonatal work by Zobel n Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in premature infants. Crit Care Med. 1989 Jun; 17(6): 534 -6.
 1990 s n n n Equipment during this era was “adaptive” Solutions for convection or diffusion was pharmacy made or lactate based Latter part of 1990 s industry began to market machines that did not take momentum until turn of the decade
1990 s n n n Equipment during this era was “adaptive” Solutions for convection or diffusion was pharmacy made or lactate based Latter part of 1990 s industry began to market machines that did not take momentum until turn of the decade
 1990 s n n Important work on Access was presented by John Gardner RN describing the MAHURKAR™ Catheter that is now marked by Covidien “how to do it papers” n n n Out come paper by Smoyer et al on n n Continuous arterial-venous diahemofiltration and continuous veno-venous diahemofiltration in infants and children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1994 Feb; 8(1): 96 -102. Continuous venous hemodiafiltration in infants and children. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995 Jan; 25(1): 17 -21. Determinants of survival in pediatric continuous hemofiltration. J Am Soc Neph 1995 Nov; 6(5): 1401 -9. Comparison paper on CAVH vs CVVH by our group in Am J Kid Dis 1995 Maxvold and colleagues began comparison of modalities n Management of acute renal failure in the pediatric patient: hemofiltration versus hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997 Nov; 30(5 Suppl 4): S 84 -8.
1990 s n n Important work on Access was presented by John Gardner RN describing the MAHURKAR™ Catheter that is now marked by Covidien “how to do it papers” n n n Out come paper by Smoyer et al on n n Continuous arterial-venous diahemofiltration and continuous veno-venous diahemofiltration in infants and children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1994 Feb; 8(1): 96 -102. Continuous venous hemodiafiltration in infants and children. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995 Jan; 25(1): 17 -21. Determinants of survival in pediatric continuous hemofiltration. J Am Soc Neph 1995 Nov; 6(5): 1401 -9. Comparison paper on CAVH vs CVVH by our group in Am J Kid Dis 1995 Maxvold and colleagues began comparison of modalities n Management of acute renal failure in the pediatric patient: hemofiltration versus hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997 Nov; 30(5 Suppl 4): S 84 -8.
 1990 s n n Evaluation of PICU needs and RRT beyond AKI began Parekh RS et al n n Dialysis support in the pediatric intensive care unit. Adv Renal Replac Therapy 1996 Oct; 3(4): 326 -36. Quigley and associates on use of HD and hemofiltration in TLS n Hyperphosphatemia in tumor lysis syndrome: the role of hemodialysis and continuous veno-venous hemofiltration. Peds Nephrol 1994, 8: 351 -3
1990 s n n Evaluation of PICU needs and RRT beyond AKI began Parekh RS et al n n Dialysis support in the pediatric intensive care unit. Adv Renal Replac Therapy 1996 Oct; 3(4): 326 -36. Quigley and associates on use of HD and hemofiltration in TLS n Hyperphosphatemia in tumor lysis syndrome: the role of hemodialysis and continuous veno-venous hemofiltration. Peds Nephrol 1994, 8: 351 -3
 2000 s n This era exploded with advancements in n n Equipment FDA approval of bicarbonate based Solutions Nutrition in AKI/CRRT Avoidance of complications Anticoagulation protocols
2000 s n This era exploded with advancements in n n Equipment FDA approval of bicarbonate based Solutions Nutrition in AKI/CRRT Avoidance of complications Anticoagulation protocols
 2000 s n Gambro and B Braun (and soon to follow Baxter) came out with machines with commonality of warmer, accurate fluid control as well as blood flow and solutions controllers
2000 s n Gambro and B Braun (and soon to follow Baxter) came out with machines with commonality of warmer, accurate fluid control as well as blood flow and solutions controllers
 2000 s n FDA approval of bicarbonate based Solutions by Dialysis Solution Inc and Walter O’Rourke n n Pediatric hemofiltration: Normocarb dialysate solution with citrate anticoagulation. Pediatr Nephrol 2002 17: 150 -4 Maxvold et al described Nutrition needs and losses in AKI/CRRT n Amino acid loss and nitrogen balance in critically ill children with acute renal failure: a prospective comparison between classic hemofiltration and hemofiltration with dialysis. Crit Care Med 2000 28: 1161 -5
2000 s n FDA approval of bicarbonate based Solutions by Dialysis Solution Inc and Walter O’Rourke n n Pediatric hemofiltration: Normocarb dialysate solution with citrate anticoagulation. Pediatr Nephrol 2002 17: 150 -4 Maxvold et al described Nutrition needs and losses in AKI/CRRT n Amino acid loss and nitrogen balance in critically ill children with acute renal failure: a prospective comparison between classic hemofiltration and hemofiltration with dialysis. Crit Care Med 2000 28: 1161 -5
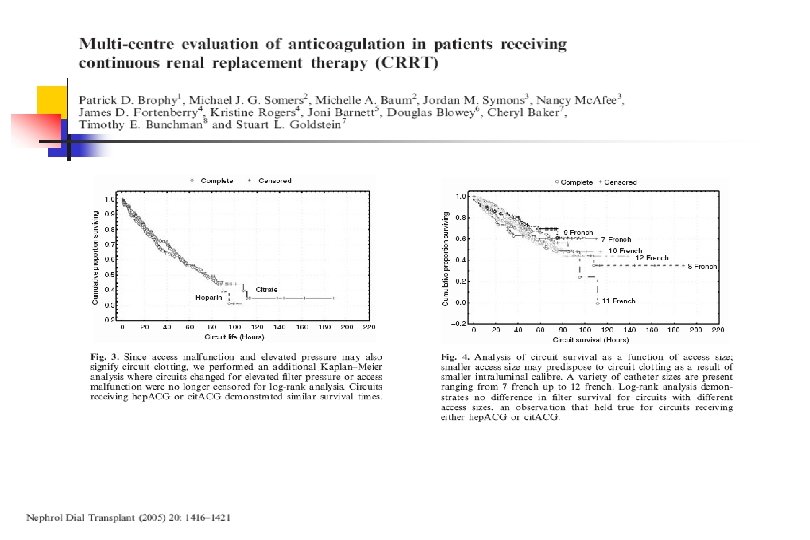
 2000 s n Anticoagulation Protocols n n n Pediatric acute renal failure: outcome by modality and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 2001, 16: 1067 -71 Pediatric convective hemofiltration: Normocarb replacement fluid and citrate anticoagulation. Am J Kid Dis 2003 42: 1248 -52 Brophy et al n Multi-centre evaluation of anticoagulation in patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). NDT 2005 20: 1416 -21
2000 s n Anticoagulation Protocols n n n Pediatric acute renal failure: outcome by modality and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 2001, 16: 1067 -71 Pediatric convective hemofiltration: Normocarb replacement fluid and citrate anticoagulation. Am J Kid Dis 2003 42: 1248 -52 Brophy et al n Multi-centre evaluation of anticoagulation in patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). NDT 2005 20: 1416 -21
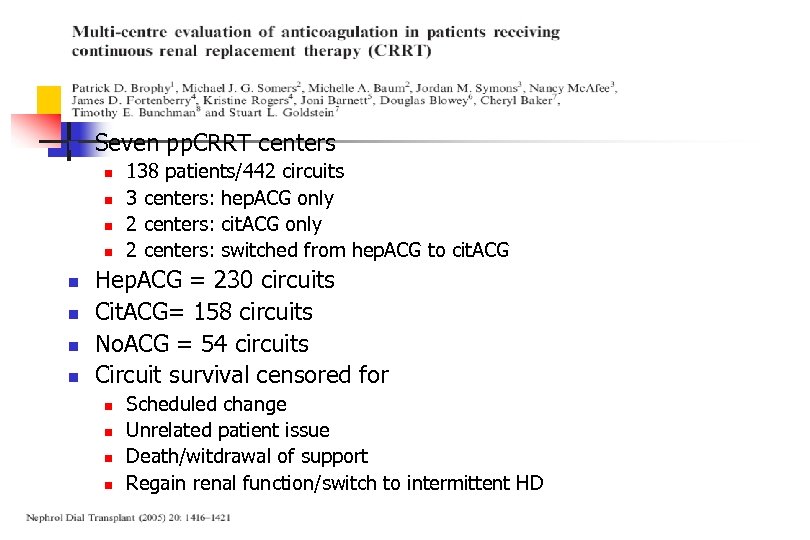 n Seven pp. CRRT centers n n n n 138 patients/442 circuits 3 centers: hep. ACG only 2 centers: cit. ACG only 2 centers: switched from hep. ACG to cit. ACG Hep. ACG = 230 circuits Cit. ACG= 158 circuits No. ACG = 54 circuits Circuit survival censored for n n Scheduled change Unrelated patient issue Death/witdrawal of support Regain renal function/switch to intermittent HD
n Seven pp. CRRT centers n n n n 138 patients/442 circuits 3 centers: hep. ACG only 2 centers: cit. ACG only 2 centers: switched from hep. ACG to cit. ACG Hep. ACG = 230 circuits Cit. ACG= 158 circuits No. ACG = 54 circuits Circuit survival censored for n n Scheduled change Unrelated patient issue Death/witdrawal of support Regain renal function/switch to intermittent HD
 Heparin vs citrate prospective study Zaoral et al, Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 17(9): e 399–e 405, SEP 2016 n “ We showed in our study that citrate provided significantly longer circuit lifetimes than heparin for continuous venous hemodialysis in children. Citrate was superior to heparin for the transfusion requirements. Citrate was feasible and safe in children and infants”.
Heparin vs citrate prospective study Zaoral et al, Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 17(9): e 399–e 405, SEP 2016 n “ We showed in our study that citrate provided significantly longer circuit lifetimes than heparin for continuous venous hemodialysis in children. Citrate was superior to heparin for the transfusion requirements. Citrate was feasible and safe in children and infants”.
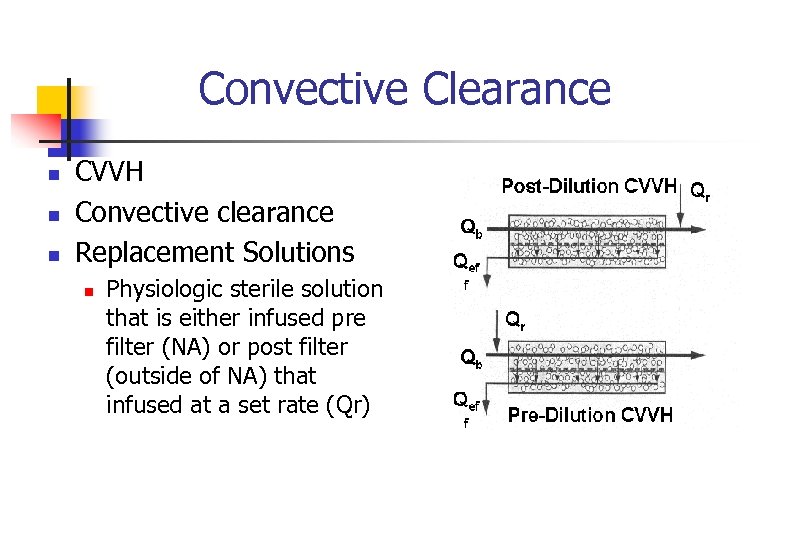 Convective Clearance n n n CVVH Convective clearance Replacement Solutions n Physiologic sterile solution that is either infused pre filter (NA) or post filter (outside of NA) that infused at a set rate (Qr)
Convective Clearance n n n CVVH Convective clearance Replacement Solutions n Physiologic sterile solution that is either infused pre filter (NA) or post filter (outside of NA) that infused at a set rate (Qr)
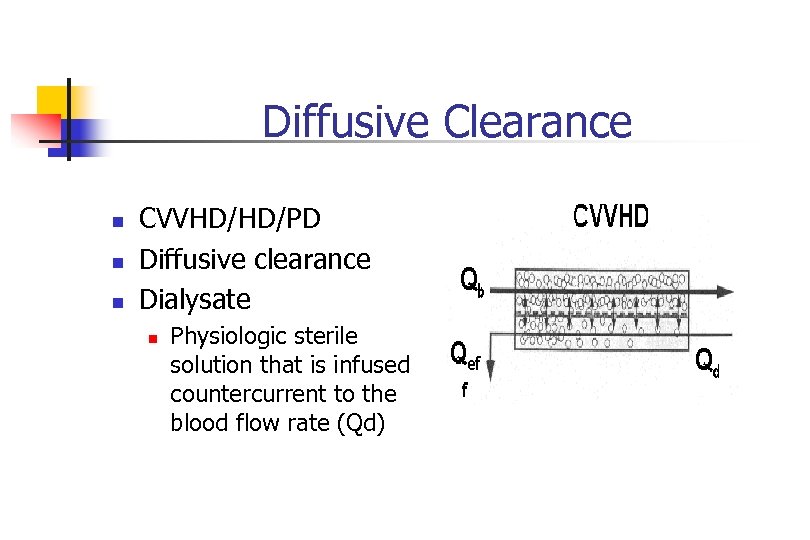 Diffusive Clearance n n n CVVHD/HD/PD Diffusive clearance Dialysate n Physiologic sterile solution that is infused countercurrent to the blood flow rate (Qd)
Diffusive Clearance n n n CVVHD/HD/PD Diffusive clearance Dialysate n Physiologic sterile solution that is infused countercurrent to the blood flow rate (Qd)
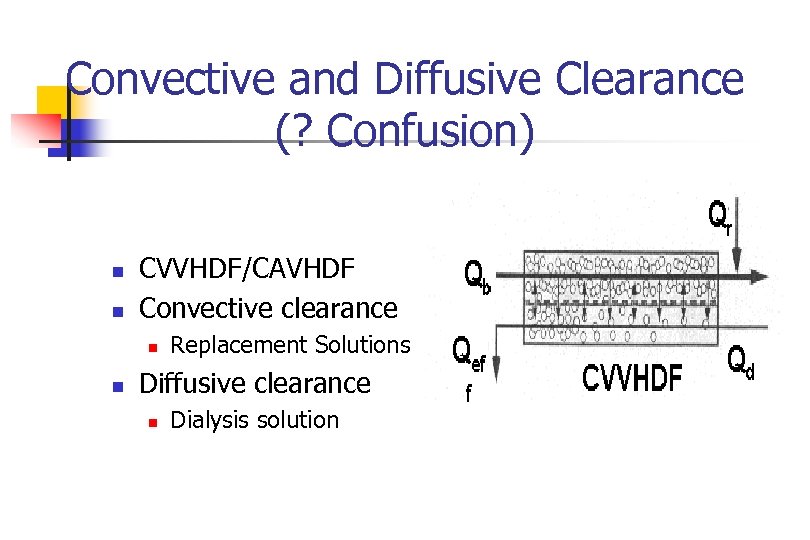 Convective and Diffusive Clearance (? Confusion) n n CVVHDF/CAVHDF Convective clearance n n Replacement Solutions Diffusive clearance n Dialysis solution
Convective and Diffusive Clearance (? Confusion) n n CVVHDF/CAVHDF Convective clearance n n Replacement Solutions Diffusive clearance n Dialysis solution
 Stem Cell Transplant: pp. CRRT n n n 51 patients in pp. CRRT with SCT Mean %FO = 12. 41 + 3. 7%. 45% survival n n n Convection: 17/29 survived (59%) Diffusion: 6/22 (27%), p<0. 05 Survival lower in MODS and ventilated patients Flores FX et al: Pediatr Nephrol. 2008 Apr; 23(4): 625 -30
Stem Cell Transplant: pp. CRRT n n n 51 patients in pp. CRRT with SCT Mean %FO = 12. 41 + 3. 7%. 45% survival n n n Convection: 17/29 survived (59%) Diffusion: 6/22 (27%), p<0. 05 Survival lower in MODS and ventilated patients Flores FX et al: Pediatr Nephrol. 2008 Apr; 23(4): 625 -30
 Prospective Pediatric Study n n 40 patients with Sepsis/ARF at 4 pp. CRRT centers Randomized crossover design n n 2500 ml/hr/1. 73 m 2 clearance Dialysis/Replacement fluid with [HC 03]=35 mmol/l Citrate ACG Serum collection at 0, 1, 24, 25 and 48 hours n n 24 hours of CVVH or CVVHD, then crossover TNF-alpha IL-1 beta IL-6, IL- 8, IL-10, IL-18 Six hours of effluent for CK’s for clearance estimation
Prospective Pediatric Study n n 40 patients with Sepsis/ARF at 4 pp. CRRT centers Randomized crossover design n n 2500 ml/hr/1. 73 m 2 clearance Dialysis/Replacement fluid with [HC 03]=35 mmol/l Citrate ACG Serum collection at 0, 1, 24, 25 and 48 hours n n 24 hours of CVVH or CVVHD, then crossover TNF-alpha IL-1 beta IL-6, IL- 8, IL-10, IL-18 Six hours of effluent for CK’s for clearance estimation
 pp. CRRT Sepsis Study n 10 patients enrolled to date n n 6 male, 4 female Mean age 12 + 4. 8 years Mean weight 44 + 21 kg PELOD n n Mean = 27 + 10 Median = 22 (range 11 -42)
pp. CRRT Sepsis Study n 10 patients enrolled to date n n 6 male, 4 female Mean age 12 + 4. 8 years Mean weight 44 + 21 kg PELOD n n Mean = 27 + 10 Median = 22 (range 11 -42)
![pp. CRRT [Cytokine] % Change: Convection vs. Diffusion Cytokine TNF-alpha IL-1 beta IL-6 IL-8 pp. CRRT [Cytokine] % Change: Convection vs. Diffusion Cytokine TNF-alpha IL-1 beta IL-6 IL-8](https://present5.com/presentation/b138eb938cf4a42c66db00dd1883f3c7/image-31.jpg) pp. CRRT [Cytokine] % Change: Convection vs. Diffusion Cytokine TNF-alpha IL-1 beta IL-6 IL-8 IL-10 IL-18 PELOD Convection -3. 7 + 9. 6 Diffusion 3. 9 + 9. 1 p 0. 08 -2. 8 + 14. 8 1. 4 + 12. 9 0. 46 32. 7 + 102. 8 -2. 6 + 18. 4 0. 21 -29. 1 + 26. 0 - 8. 3 + 17. 2 0. 018 -44. 6 + 29. 0 3. 1 + 45. 0 0. 007 -13. 6 + 17. 9 16. 9 + 24. 7 0. 002 -22 + 34 -6 + 30 0. 26
pp. CRRT [Cytokine] % Change: Convection vs. Diffusion Cytokine TNF-alpha IL-1 beta IL-6 IL-8 IL-10 IL-18 PELOD Convection -3. 7 + 9. 6 Diffusion 3. 9 + 9. 1 p 0. 08 -2. 8 + 14. 8 1. 4 + 12. 9 0. 46 32. 7 + 102. 8 -2. 6 + 18. 4 0. 21 -29. 1 + 26. 0 - 8. 3 + 17. 2 0. 018 -44. 6 + 29. 0 3. 1 + 45. 0 0. 007 -13. 6 + 17. 9 16. 9 + 24. 7 0. 002 -22 + 34 -6 + 30 0. 26
 Leaders in the Field n Stu Goldstein began the pp. CRRT and now the pp. AKI study groups that have balanced research, QI with advancements
Leaders in the Field n Stu Goldstein began the pp. CRRT and now the pp. AKI study groups that have balanced research, QI with advancements
 Has RRT improved out come? n n All modalities of RRT have changed from adaptive to newer products for children of all ages In the 90’s reports of 45 % survival rates have been replaced by current 65% survival rates in sepsis AKI
Has RRT improved out come? n n All modalities of RRT have changed from adaptive to newer products for children of all ages In the 90’s reports of 45 % survival rates have been replaced by current 65% survival rates in sepsis AKI
 Has RRT improved out come? n In the 90’s reports of 17 % survival rates have been replaced by current 53% survival rates in liver AKI as reported by Deep and Colleagues
Has RRT improved out come? n In the 90’s reports of 17 % survival rates have been replaced by current 53% survival rates in liver AKI as reported by Deep and Colleagues
 Conclusion n n QI and Research have improved the diagnosis of AKI and the use of RRT Since the beginning of this time, patients have more co-morbidities and are more complicated
Conclusion n n QI and Research have improved the diagnosis of AKI and the use of RRT Since the beginning of this time, patients have more co-morbidities and are more complicated
 Future n Areas primed for prospective and future research/QI include n n Optimal med dosing Optimal nutrition delivery Non dialytic options of treatment of AKI Science around starting and stopping RRT
Future n Areas primed for prospective and future research/QI include n n Optimal med dosing Optimal nutrition delivery Non dialytic options of treatment of AKI Science around starting and stopping RRT


