286860aa59095cf5439573534cfcd59c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Improving direct microscopy by overnight bleach sedimentation: a simple tool for peripheral Health Centres Maryline Bonnet 1, Laramie Gagnidze 1, Willie Githui 2, Francis Varaine 3, Andrew Ramsay 4, 5, Philippe J Guerin 1 1 Epicentre, 2 Centre for Respiratory Diseases Research, Kenya Medical Research Institute, 3 Médecins Sans Frontières, 4 Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, 5 TDR/WHO

TB diagnosis in peripheral health care centres q Ziehl-Neelsen Direct Smear microscopy § Only available tool in most settings § 50% sensitivity q No new test expected in near future q Improvement of smear microscopy § Sputum collection (e. g. sputum induction) § Sputum processing (e. g. sputum concentration) § Staining and reading (e. g. fluorescence microscopy)

Rationale q Sodium hypochlorite (“household bleach”) with overnight sedimentation § Encouraging results § Could be implemented in any setting q Still no recommendations due to study limitations
Objective 1. To evaluate the diagnostic yield and feasibility of microscopy after overnight bleach sedimentation in a peripheral laboratory 1. To compare direct smear microscopy and overnight bleach sedimentation 1. Smear-positive patient detection 2. Smear-positive specimen detection 2. To evaluate practical aspects of overnight bleach sedimentation
Method q Population § Mathare, Nairobi § High HIV prevalence § > 15 years, pulmonary TB suspects (cough > 2 weeks) q Consecutive sampling q Procedure § Collection of 3 sputa in 2 days § Hot Ziehl Neelsen method
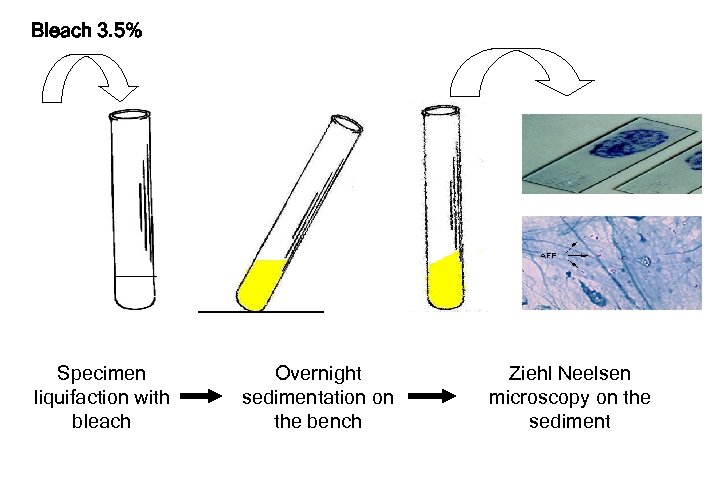
Bleach 3. 5% Specimen liquifaction with bleach Overnight sedimentation on the bench Ziehl Neelsen microscopy on the sediment
Method q Case definitions § Smear-positive result: > 9 AFB/100 fields § Smear-positive patient § > 2 smear-positive results § > 1 smear-positive result q Analysis § Mc. Nemar test for comparison of matched data § Kappa coefficient for inter-reader and test-retest reliability (K >0. 8: very good reliability)
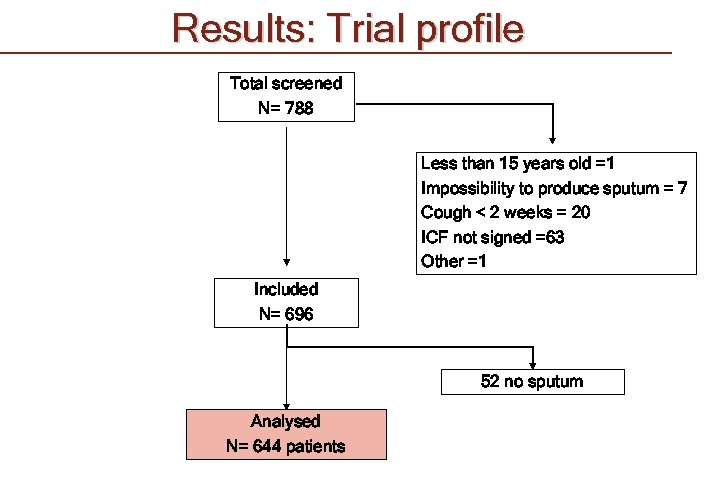
Results: Trial profile Total screened N= 788 Less than 15 years old =1 Impossibility to produce sputum = 7 Cough < 2 weeks = 20 ICF not signed =63 Other =1 Included N= 696 52 no sputum Analysed N= 644 patients

Patients’ characteristics q Mean age: 32. 5 years (SD 10. 3) q Sex ratio, M/F: 0. 8 q Past TB history: 121 (18. 8%) q Intake of antibiotics in the last 2 weeks: 37 (5. 7%) q Production of 3 sputa: 614 (95. 3%)
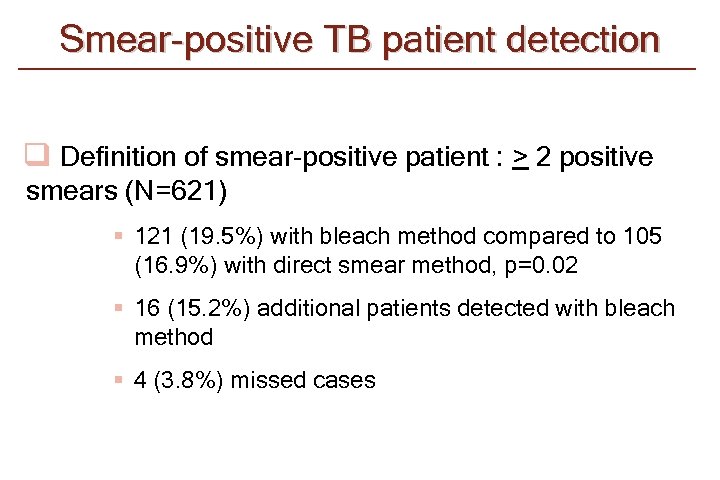
Smear-positive TB patient detection q Definition of smear-positive patient : > 2 positive smears (N=621) § 121 (19. 5%) with bleach method compared to 105 (16. 9%) with direct smear method, p=0. 02 § 16 (15. 2%) additional patients detected with bleach method § 4 (3. 8%) missed cases
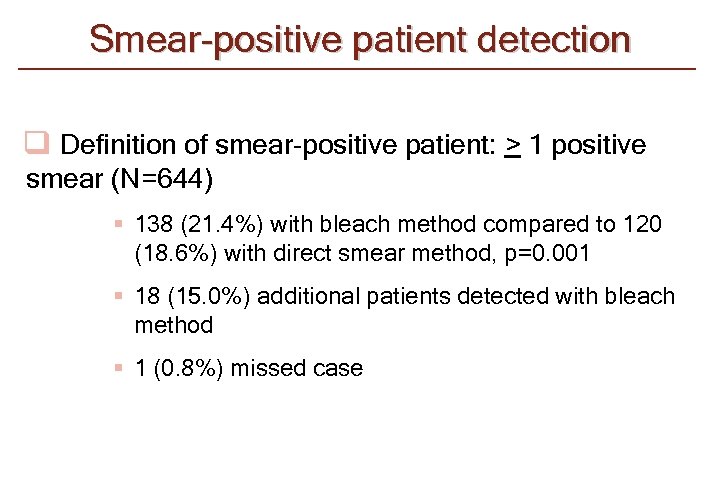
Smear-positive patient detection q Definition of smear-positive patient: > 1 positive smear (N=644) § 138 (21. 4%) with bleach method compared to 120 (18. 6%) with direct smear method, p=0. 001 § 18 (15. 0%) additional patients detected with bleach method § 1 (0. 8%) missed case
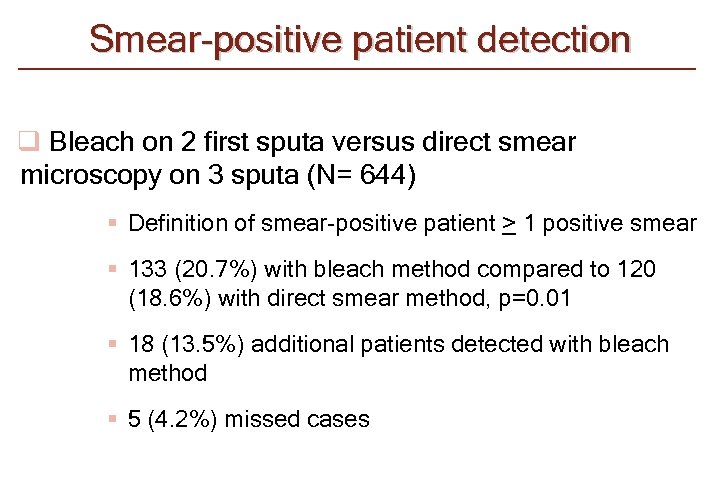
Smear-positive patient detection q Bleach on 2 first sputa versus direct smear microscopy on 3 sputa (N= 644) § Definition of smear-positive patient > 1 positive smear § 133 (20. 7%) with bleach method compared to 120 (18. 6%) with direct smear method, p=0. 01 § 18 (13. 5%) additional patients detected with bleach method § 5 (4. 2%) missed cases
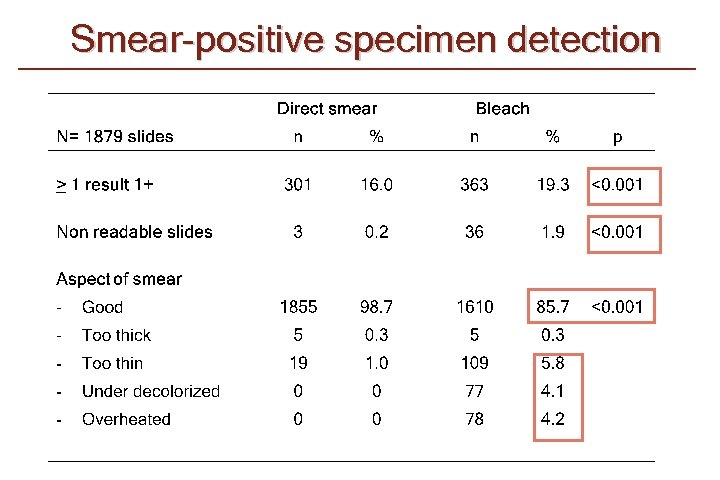
Smear-positive specimen detection
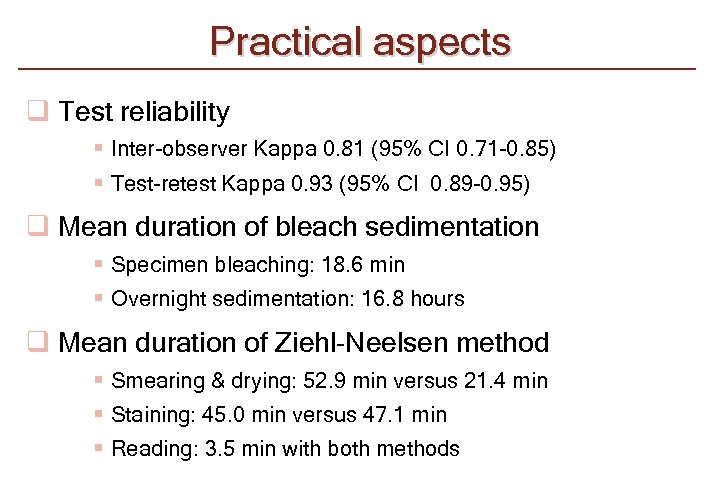
Practical aspects q Test reliability § Inter-observer Kappa 0. 81 (95% CI 0. 71 -0. 85) § Test-retest Kappa 0. 93 (95% CI 0. 89 -0. 95) q Mean duration of bleach sedimentation § Specimen bleaching: 18. 6 min § Overnight sedimentation: 16. 8 hours q Mean duration of Ziehl-Neelsen method § Smearing & drying: 52. 9 min versus 21. 4 min § Staining: 45. 0 min versus 47. 1 min § Reading: 3. 5 min with both methods

Discussion q Study strengths § Prospective and controlled § Outpatient suspected TB cases in peripheral clinic § Standardised concentration method § Practical aspects § Reliability data q Study limitations Absence of comparison to the culture Gold Standard
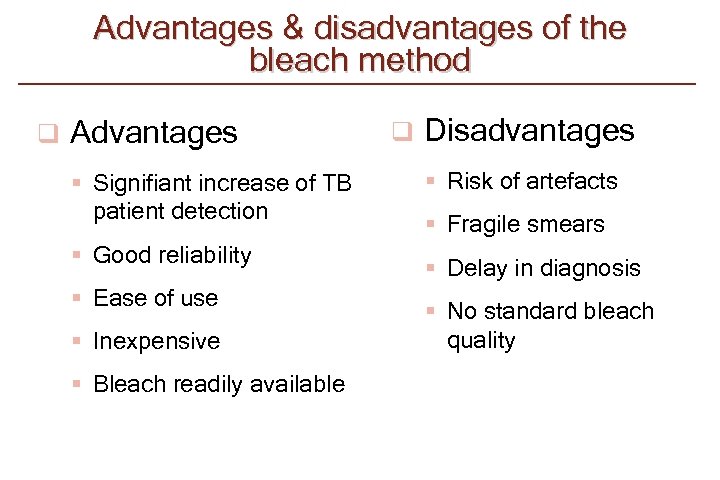
Advantages & disadvantages of the bleach method q Advantages § Signifiant increase of TB patient detection § Good reliability § Ease of use § Inexpensive § Bleach readily available q Disadvantages § Risk of artefacts § Fragile smears § Delay in diagnosis § No standard bleach quality

Conclusions q Effective, simple and affordable q Further research needed § Best strategy based on cost-effectiveness analysis § Feasibility in routine program conditions § Overnight BS and fluorescence microscopy § Shorter sedimentation time

Acknowledgements q Médecins Sans Frontières, study promotor q Stéphanie Charrondière q Tom, Purity, Ali, Andrew and Lucy q The team in Blue House q The team in the Mycobacteriological Laboratory, KEMRI q The Kenyan National TB Control Program

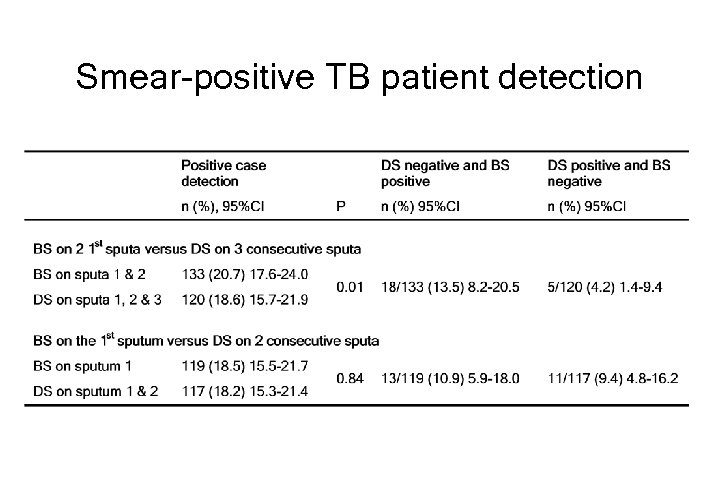
Smear-positive TB patient detection
286860aa59095cf5439573534cfcd59c.ppt