ed0e98e73f1585c1c9dec1bc62291f1c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Improved isolation of the p-p Underlying Event based on minimum-bias triggerassociated hadron correlations Tom Trainor ISMD 2013

Agenda trigger-associated (TA) correlations • Measure nch dependence of p-p pt or yt SP spectra • Define a “Glauber” model for p-p collisions • Predict nch systematics for p-p angular correlations • • • Develop a two-component TA model (TCM) Extract a TA hard component jet fragments Make direct comparisons with p. QCD and dijets Test underlying-event (UE) conjectures re dijets/MPI Identify kinematic limits of dijets in p-p collisions 2
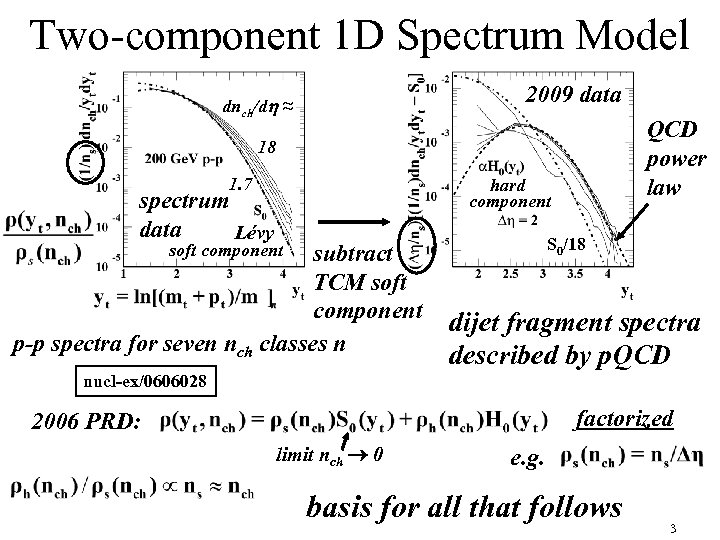
Two-component 1 D Spectrum Model 2009 data dnch/dh ≈ QCD power law 18 1. 7 hard component spectrum data Lévy subtract TCM soft component p-p spectra for seven nch classes n S 0/18 soft component dijet fragment spectra described by p. QCD nucl-ex/0606028 factorized 2006 PRD: limit nch 0 e. g. basis for all that follows 3
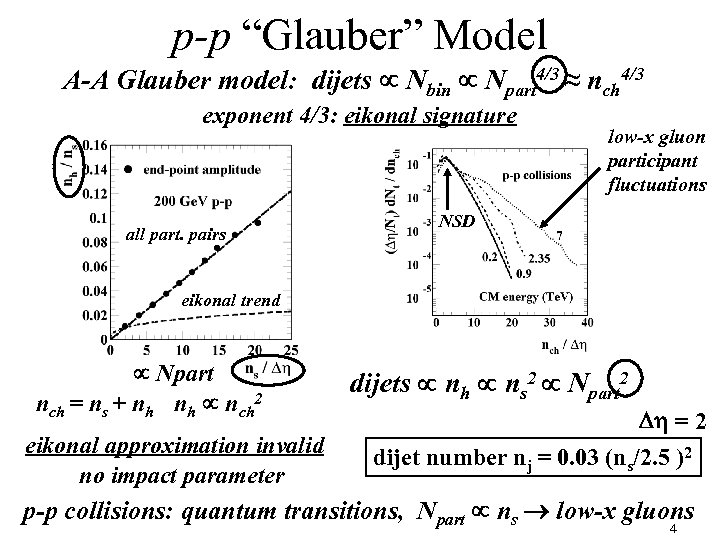
p-p “Glauber” Model A-A Glauber model: dijets Nbin Npart 4/3 ≈ nch 4/3 exponent 4/3: eikonal signature all part. pairs low-x gluon participant fluctuations NSD eikonal trend Npart nch = ns + nh nh nch 2 eikonal approximation invalid no impact parameter dijets nh ns 2 Npart 2 Dh = 2 dijet number nj = 0. 03 (ns/2. 5 )2 p-p collisions: quantum transitions, Npart ns low-x gluons 4
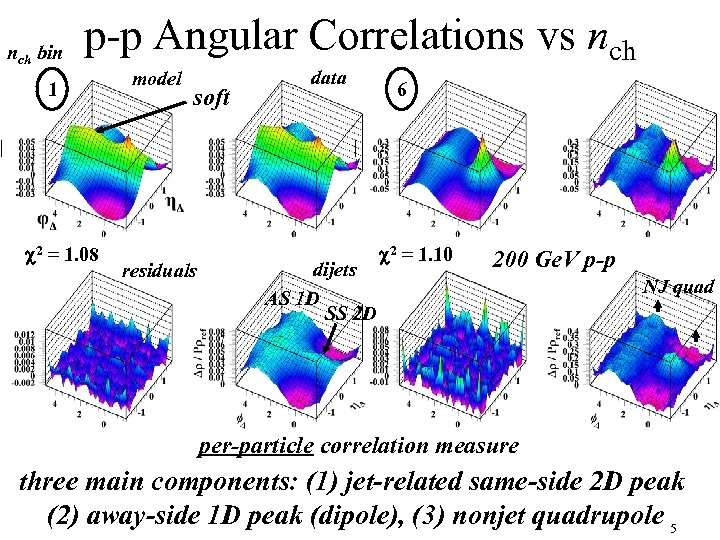
nch bin p-p Angular Correlations vs nch 1 c 2 = 1. 08 model soft residuals data dijets AS 1 D SS 2 D 6 c 2 = 1. 10 200 Ge. V p-p NJ quad per-particle correlation measure three main components: (1) jet-related same-side 2 D peak (2) away-side 1 D peak (dipole), (3) nonjet quadrupole 5
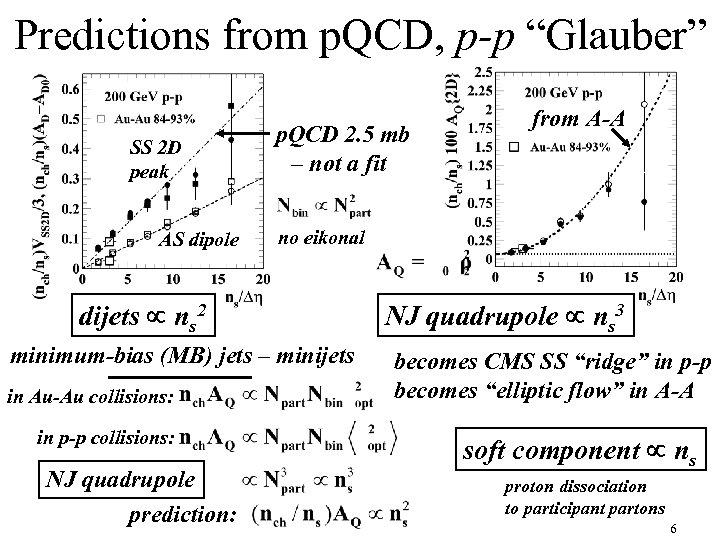
Predictions from p. QCD, p-p “Glauber” SS 2 D peak AS dipole p. QCD 2. 5 mb – not a fit no eikonal dijets ns 2 minimum-bias (MB) jets – minijets in Au-Au collisions: in p-p collisions: NJ quadrupole prediction: from A-A NJ quadrupole ns 3 becomes CMS SS “ridge” in p-p becomes “elliptic flow” in A-A soft component ns proton dissociation to participant partons 6
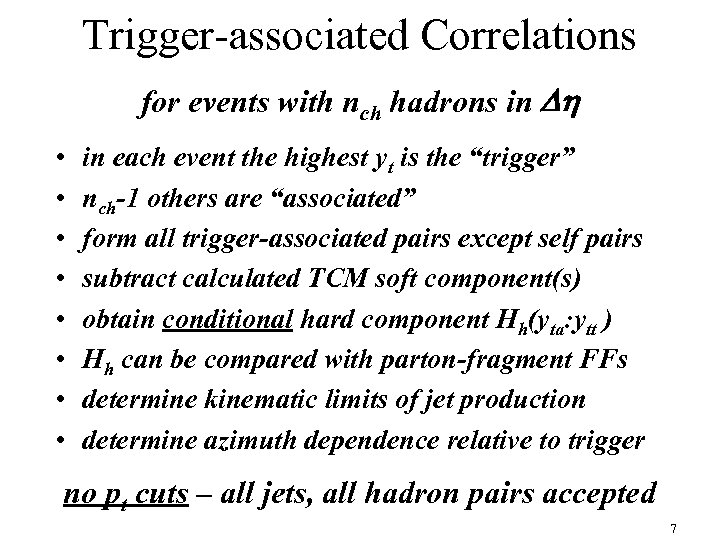
Trigger-associated Correlations for events with nch hadrons in Dh • • in each event the highest yt is the “trigger” nch-1 others are “associated” form all trigger-associated pairs except self pairs subtract calculated TCM soft component(s) obtain conditional hard component Hh(yta: ytt ) Hh can be compared with parton-fragment FFs determine kinematic limits of jet production determine azimuth dependence relative to trigger no pt cuts – all jets, all hadron pairs accepted 7
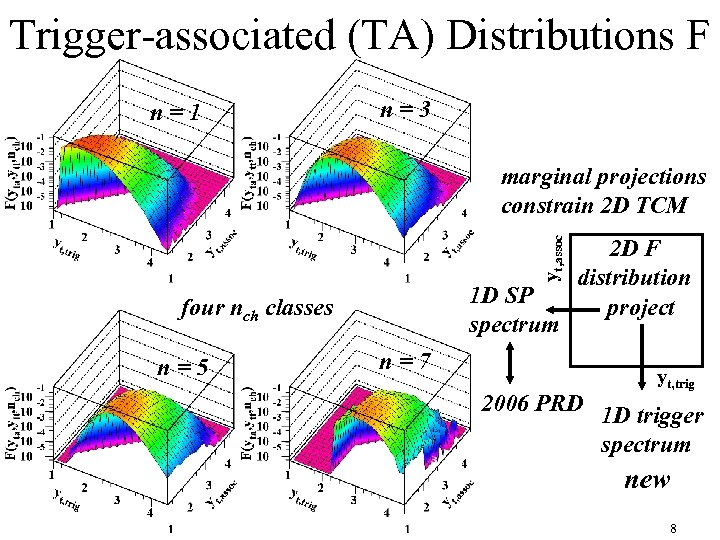
Trigger-associated (TA) Distributions F n=1 n=3 yt, assoc marginal projections constrain 2 D TCM 1 D SP spectrum four nch classes n=5 n=7 2 D F distribution project yt, trig 2006 PRD 1 D trigger spectrum new 8
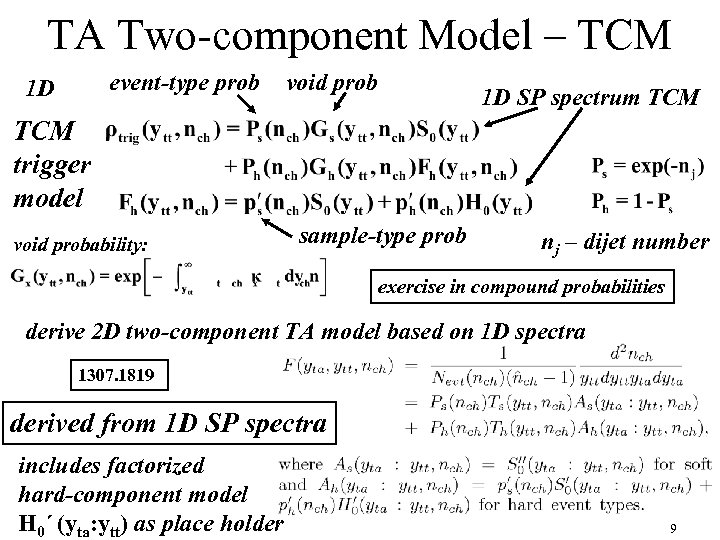
TA Two-component Model – TCM event-type prob 1 D void prob 1 D SP spectrum TCM trigger model void probability: sample-type prob nj – dijet number exercise in compound probabilities derive 2 D two-component TA model based on 1 D spectra 1307. 1819 derived from 1 D SP spectra includes factorized hard-component model H 0´ (yta: ytt) as place holder 9
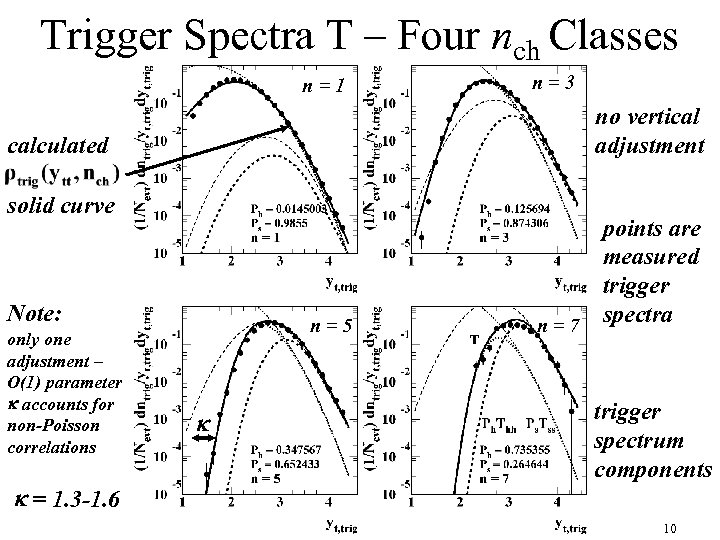
Trigger Spectra T – Four nch Classes n=1 no vertical adjustment calculated solid curve Note: only one adjustment – O(1) parameter k accounts for non-Poisson correlations k = 1. 3 -1. 6 n=3 n=5 k points are measured trigger spectra n=7 trigger spectrum components 10
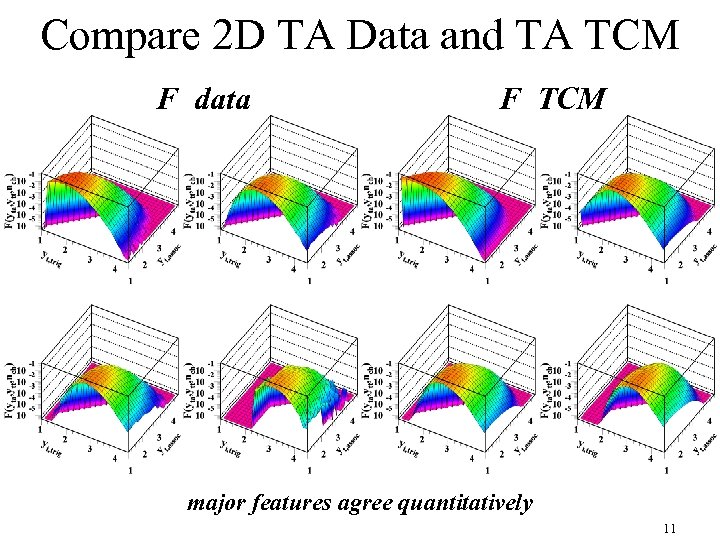
Compare 2 D TA Data and TA TCM F data F TCM major features agree quantitatively 11
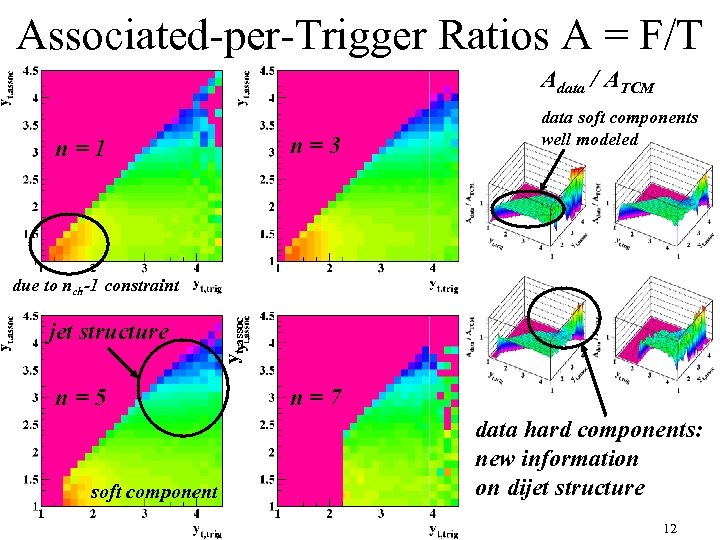
Associated-per-Trigger Ratios A = F/T Adata / ATCM n=3 n=1 data soft components well modeled jet structure n=5 soft component yt, assoc due to nch-1 constraint n=7 data hard components: new information on dijet structure 12
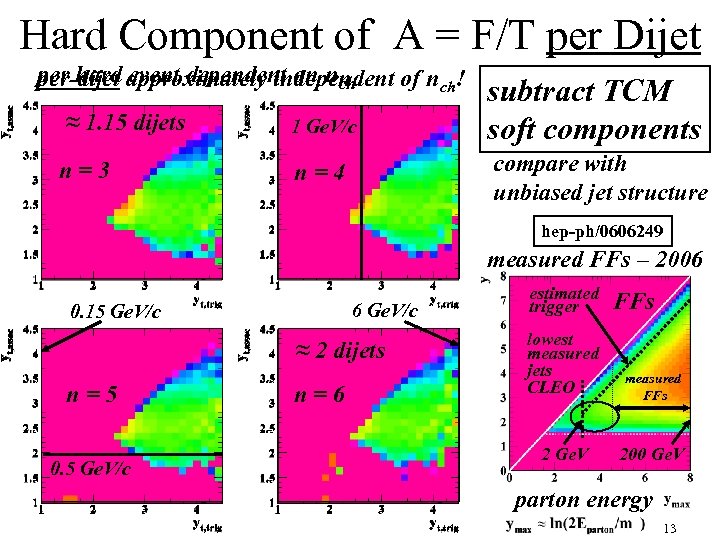
Hard Component of A = F/T per Dijet per hard event dependent on nch per-dijet approximately independent of nch! ≈ 1. 15 dijets n=3 1 Ge. V/c subtract TCM soft components compare with unbiased jet structure n=4 hep-ph/0606249 measured FFs – 2006 6 Ge. V/c 0. 15 Ge. V/c ≈ 2 dijets n=5 0. 5 Ge. V/c n=6 estimated trigger FFs lowest measured jets CLEO measured FFs 2 Ge. V 200 Ge. V parton energy 13
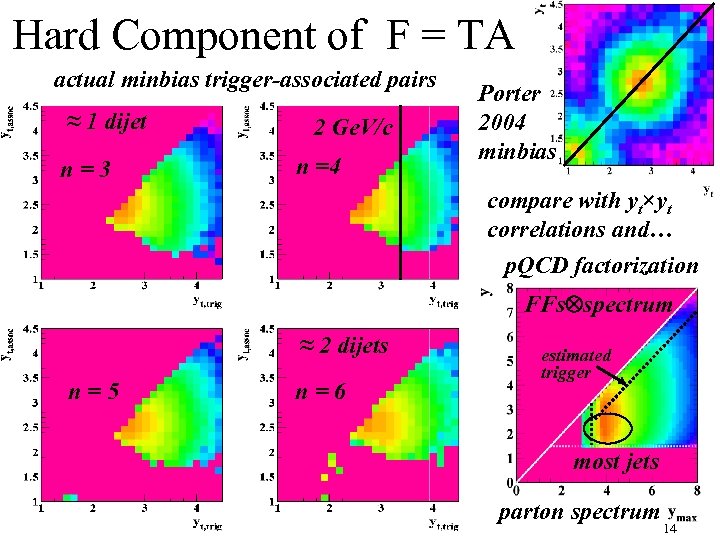
Hard Component of F = TA actual minbias trigger-associated pairs ≈ 1 dijet n=3 2 Ge. V/c n =4 Porter 2004 minbias compare with yt×yt correlations and… p. QCD factorization FFs spectrum ≈ 2 dijets n=5 n=6 estimated trigger most jets parton spectrum 14
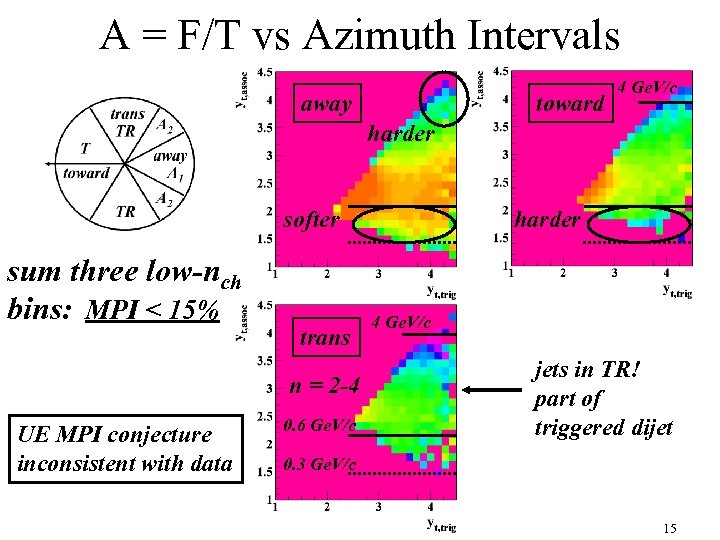
A = F/T vs Azimuth Intervals away toward 4 Ge. V/c harder softer sum three low-nch bins: MPI < 15% trans n = 2 -4 UE MPI conjecture inconsistent with data 0. 6 Ge. V/c harder 4 Ge. V/c jets in TR! part of triggered dijet 0. 3 Ge. V/c 15
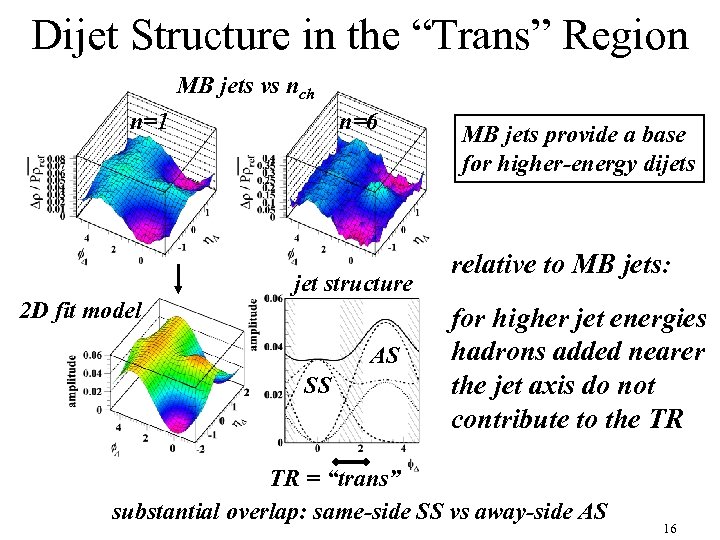
Dijet Structure in the “Trans” Region MB jets vs nch n=1 n=6 jet structure 2 D fit model AS SS MB jets provide a base for higher-energy dijets relative to MB jets: for higher jet energies hadrons added nearer the jet axis do not contribute to the TR TR = “trans” substantial overlap: same-side SS vs away-side AS 16
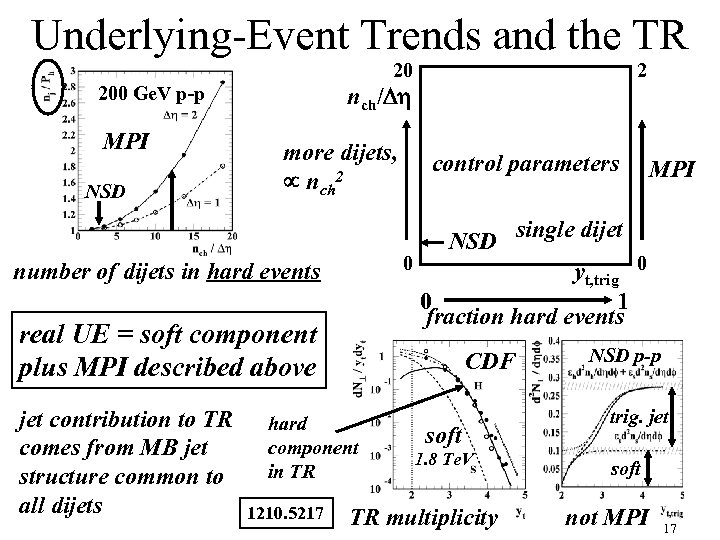
Underlying-Event Trends and the TR 20 200 Ge. V p-p MPI NSD nch/Dh more dijets, nch 2 real UE = soft component plus MPI described above CDF hard component in TR 1210. 5217 control parameters MPI NSD single dijet 0 yt, trig 0 0 1 fraction hard events number of dijets in hard events jet contribution to TR comes from MB jet structure common to all dijets 2 soft 1. 8 Te. V TR multiplicity NSD p-p trig. jet soft not MPI 17
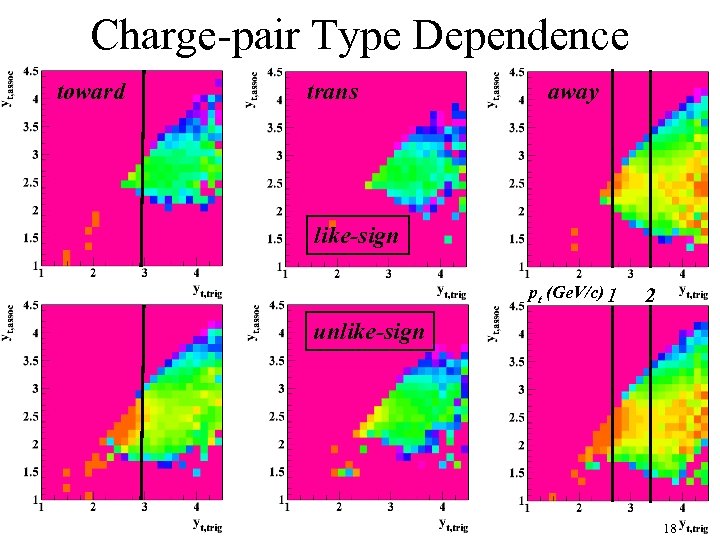
Charge-pair Type Dependence toward trans away like-sign pt (Ge. V/c) 1 2 unlike-sign 18

Kinematic Space for Jets & Fragments effective boundaries for jet formation • Trigger hadrons extend down to 1 Ge. V/c • Associated hadrons extend down to 0. 4 Ge. V/c (AS) or 0. 8 Ge. V/c (SS) • TA results consistent with measured FFs from LEP, HERA and CDF and with a p. QCD parton spectrum that predicts measured dijet production • Conventional trigger-associated pt cuts accept a tiny fraction of the actual jet number and jet fragments, produce a deceptive picture of jets in HE collisions 19
Summary • • “Glauber” model for p-p collisions, no eikonal “Soft” component represents participant partons Predict trends for dijet, nonjet-quadrupole correlations MPI trend with nch, jet contributions to “trans” region • • Develop TCM for trigger-associated TA correlations 1 D T spectrum, 2 D F = TA two-component models Hard components of F, A by subtraction MB jets Direct link to measured fragmentation functions and underlying p. QCD parton spectrum • TA results confirm trigger contribution to “trans” region 20
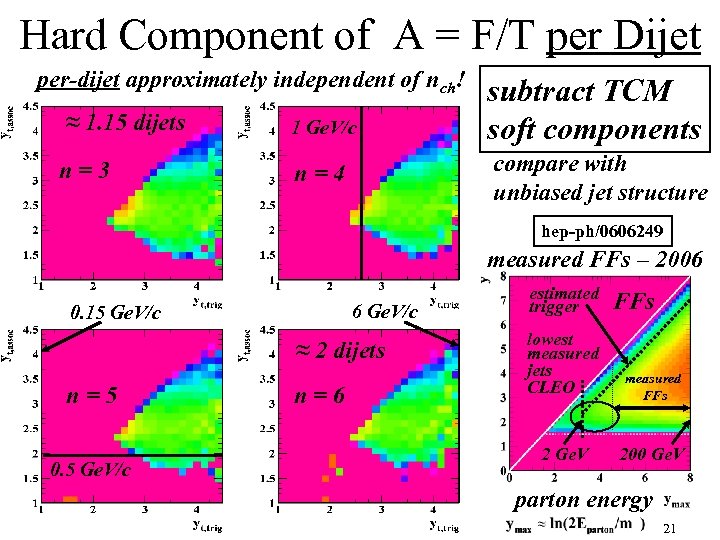
Hard Component of A = F/T per Dijet per-dijet approximately independent of nch! ≈ 1. 15 dijets n=3 1 Ge. V/c subtract TCM soft components compare with unbiased jet structure n=4 hep-ph/0606249 measured FFs – 2006 6 Ge. V/c 0. 15 Ge. V/c ≈ 2 dijets n=5 0. 5 Ge. V/c n=6 estimated trigger FFs lowest measured jets CLEO measured FFs 2 Ge. V 200 Ge. V parton energy 21
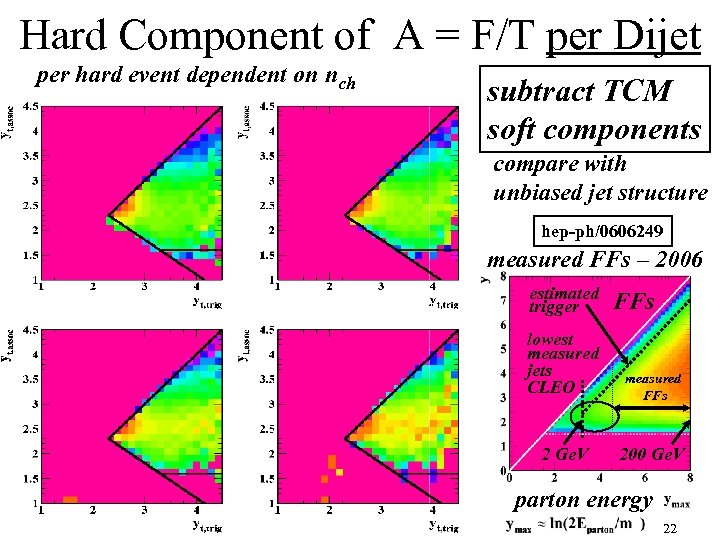
Hard Component of A = F/T per Dijet per hard event dependent on nch subtract TCM soft components compare with unbiased jet structure hep-ph/0606249 measured FFs – 2006 estimated trigger FFs lowest measured jets CLEO measured FFs 2 Ge. V 200 Ge. V parton energy 22
ed0e98e73f1585c1c9dec1bc62291f1c.ppt