374cb133e2dd3206d81222cf000d1dd1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Important – Webinar Audio Optimising network delivery of virtual desktops Jason Poole Business Development Manager, EMEA (Cloud Networking) Michael Aldridge Senior System Engineer, EMEA (Cloud Networking) 4 th October 2012 The webinar will start at 3: 00 pm (BST) The audio for this webinar is available over Vo. IP. Just select the ‘Use Mic & Speakers’ option to listen to the webinar through your computers speakers. To listen using your telephone select the ‘Use Telephone’ option. For local numbers click the ‘additional numbers’ link. You will need to use the Access Code and Audio PIN.

Industry trends and IT resources Centralisation of Resources Multiple devices Distributed workforce Work and play from any device, anywhere

Why Implement a Desktop Virtualisation Solution? • Cost reduction • Business Agility • Improved security • Improved compliance • Ease of management Change everything… but wait, consideration?

Considerations for a successful Desktop Virtualisation • Centralisation is a single point of failure • Benefits of Desktop Virtualisation are realised through centralisation • Branch office workers might experience poor experience • 80% of employees are located away from the HQ and the data centre • How to provide the access to the virtual desktop • More and more users are bringing their own devices • Requirement for remote access and maintaining security

Remote Access

HDX Smart. Access Delivers simple and seamless secure access Anywhere Access Allows users to securely access desktops and applications using any device in any location, including home computers and mobile devices.

HDX Smart. Access Delivers simple and seamless secure access Anywhere Access Network and device roaming Enables users’ sessions to transparently and securely move between networks and devices by dynamically adapting access.

HDX Smart. Access Delivers simple and seamless secure access Anywhere Access Network and device roaming Single sign-on Improves the user’s experience by reducing unnecessary authentication prompts and the number of passwords users need to remember.

HDX Smart. Access Delivers simple and seamless secure access Anywhere Access Network and device roaming Single sign-on Granular Action Control Allows the administrators to define capabilities within application to which users have access.

Availability

High Availability • Goal: Network Infrastructure Fault tolerance • Roadblocks: • Virtual desktop hosting platform • Operating system delivery • Application and desktop delivery • Desktop controllers • Application controllers
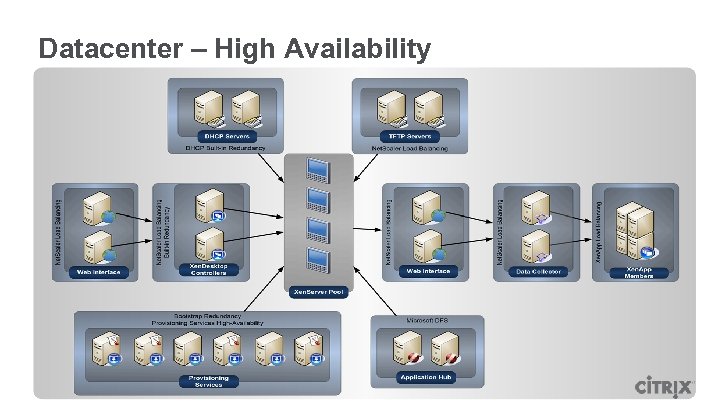
Datacenter – High Availability
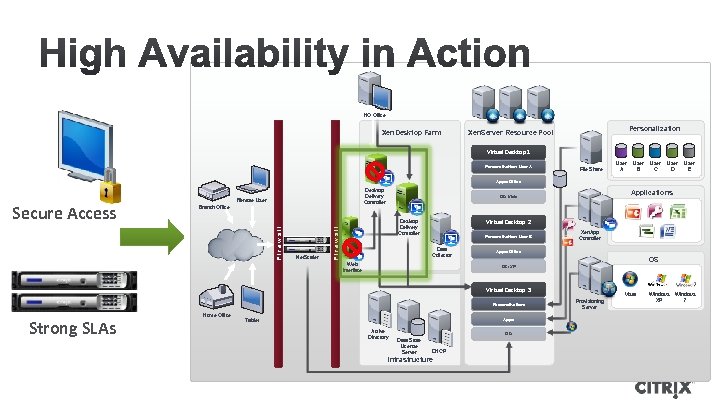
HQ Office Xen. Desktop Farm Personalization Xen. Server Resource Pool Virtual Desktop 1 Personalization: User A File Share User A User B User C User D User E Apps: Office Remote User Branch Office Net. Scaler Applications OS: Vista Virtual Desktop 2 Desktop Delivery Controller Firewall Secure Access Desktop Delivery Controller Personalization: User B Data Collector Web Interface Xen. App Controller Apps: Office OS OS: XP Virtual Desktop 3 Personalization: Strong SLAs Home Office Apps: Tablet Active Directory OS: Data Store License Server DHCP Infrastructure Vista Provisioning Server Windows XP Windows 7
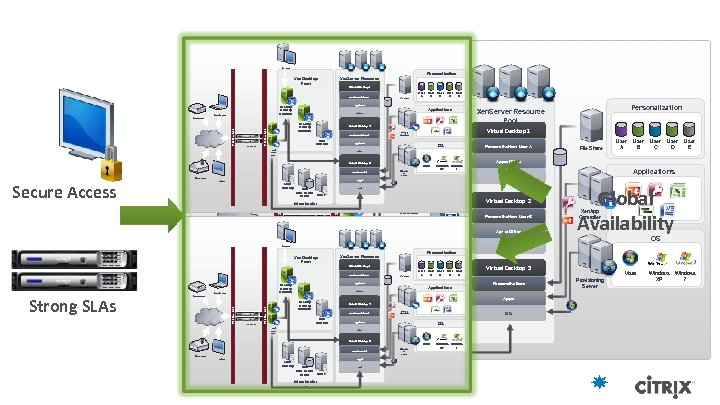
HQ Office Personalization Xen. Server Resource Pool Xen. Desktop Farm Virtual Desktop 1 HQ Office Personalization: User A Remote User File Share User A User B User C User D User E Apps: Office Desktop Delivery Controller Applications Xen. Desktop Farm OS: Vista Firewall Net. Scaler Desktop Delivery Controller Virtual Desktop 2 Virtual Desktop 1 Xen. App Controller Personalization: User B Data Collector Apps: Office Web Interf ace OS: XP Virtual Desktop 3 Remote User Vista Desktop Delivery Controlle r Apps: Active Directory Firewall Secure Access Tablet Branch Office Data Store License DHCP Server Infrastructur e Net. Scaler OS: Xen. Desktop Farm Home Office Remote User Virtual Desktop 1 File Share User A User B User C User D User E Apps: Office OS: XP Personalization: Home Office Apps: Data Store License DHCP Server Infrastructur e Applications Global Availability Xen. App Controller Virtual Desktop 3 Personalization: Apps: Active Directory Virtual Desktop 3 Active Directory User E Xen. Server Resource Pool Personalization: User B Tablet User D OS Virtual Desktop 2 Web Interf ace User C OS: XP Applications Data Collector User B Personalization OS: Vista Desktop Delivery Controller Firewall Net. Scaler Apps: Office Tablet Firewall Strong SLAs Branch Office Personalization: User B Data Collector User A Apps: Office Virtual Desktop 2 Desktop Delivery Controlle r Personalization: User A Desktop Delivery Controller File Share OS: Vista Web Interface HQ Office Windows XP 7 Provision ing Server Firewall Home Office Personalization: User A OS Personalization: Personalization Xen. Server Resource Pool Branch Office OS: Xen. App Controller OS: Data OS Store DHC License P Server Infrastructure Vista Provision ing Server Windows XP 7 Vista Provisioning Server Windows XP Windows 7
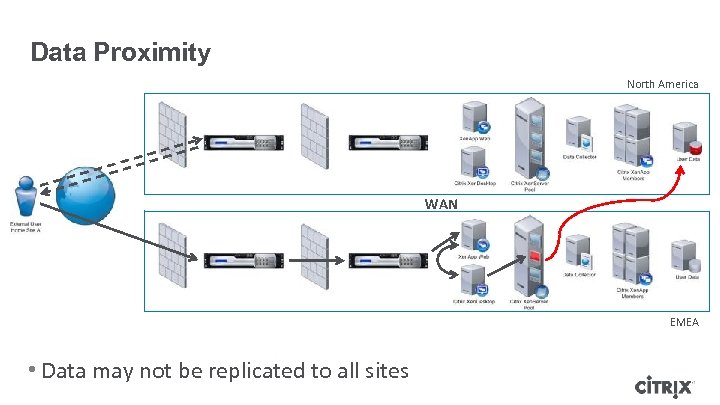
Data Proximity North America WAN EMEA • Data may not be replicated to all sites
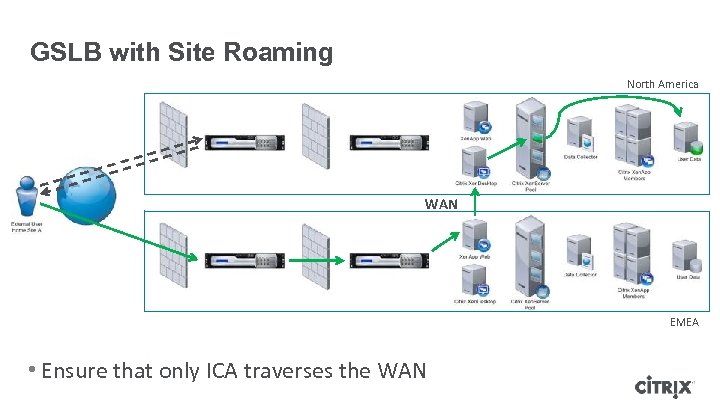
GSLB with Site Roaming North America WAN EMEA • Ensure that only ICA traverses the WAN

User Experience Deployment across a WAN
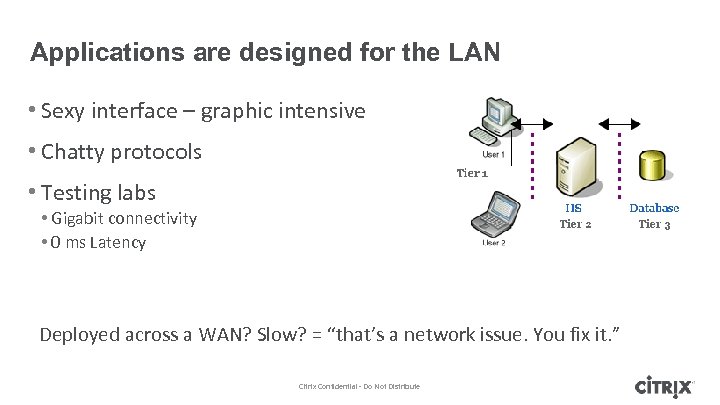
Applications are designed for the LAN • Sexy interface – graphic intensive • Chatty protocols • Testing labs • Gigabit connectivity • 0 ms Latency Deployed across a WAN? Slow? = “that’s a network issue. You fix it. ” Citrix Confidential - Do Not Distribute

HDX ICA protocol is an underlying technology for HDX (High-Definition User Experience)

Bandwidth Allocation for ICA • How much bandwidth is enough? • It depends on: • Other network traffic • Application bandwidth requirements • Number of users • User behavior • And more! vs.

Insufficient Bandwidth Causes. . . • ICA sessions to drop • Users experience choppy typing or screen paints • Session Reliability to be invoked (if enabled) • User sees application but can’t use it Dear Mr. Templeton, I love Citrix Xen. App! How can I purchase more licenses?

ICA Compression • Already highly compressed and optimized • Automatically tunes itself to further compress when less bandwidth available • Single session bandwidth testing not valid! ICA Session

WAN Optimisation for Desktop Virtualisation
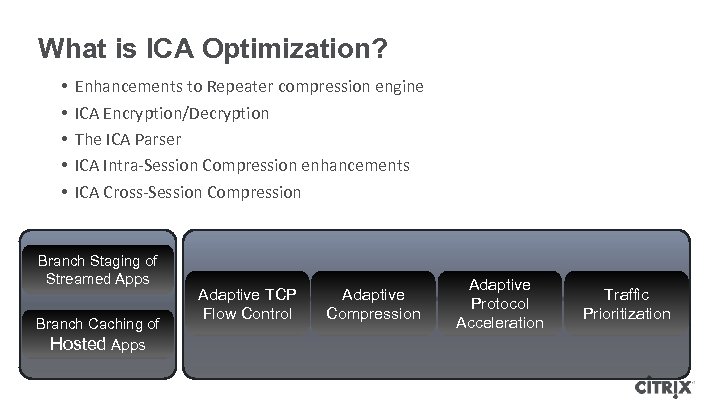
What is ICA Optimization? • • • Enhancements to Repeater compression engine ICA Encryption/Decryption The ICA Parser ICA Intra-Session Compression enhancements ICA Cross-Session Compression Branch Staging of Streamed Apps Branch Caching of Hosted Apps Adaptive TCP Flow Control Adaptive Compression Adaptive Protocol Acceleration Traffic Prioritization
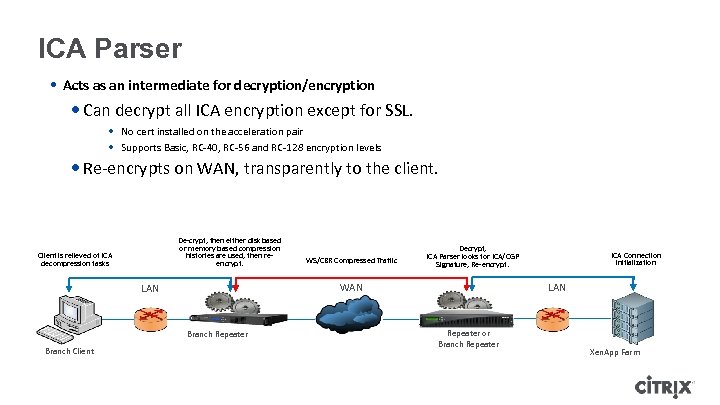
ICA Parser • Acts as an intermediate for decryption/encryption • Can decrypt all ICA encryption except for SSL. • No cert installed on the acceleration pair • Supports Basic, RC-40, RC-56 and RC-128 encryption levels • Re-encrypts on WAN, transparently to the client. De-crypt, then either disk based or memory based compression histories are used, then reencrypt. Client is relieved of ICA decompression tasks Decrypt, ICA Parser looks for ICA/CGP Signature, Re-encrypt. WAN LAN Branch Repeater Branch Client WS/CBR Compressed Traffic ICA Connection initialization LAN Repeater or Branch Repeater Xen. App Farm
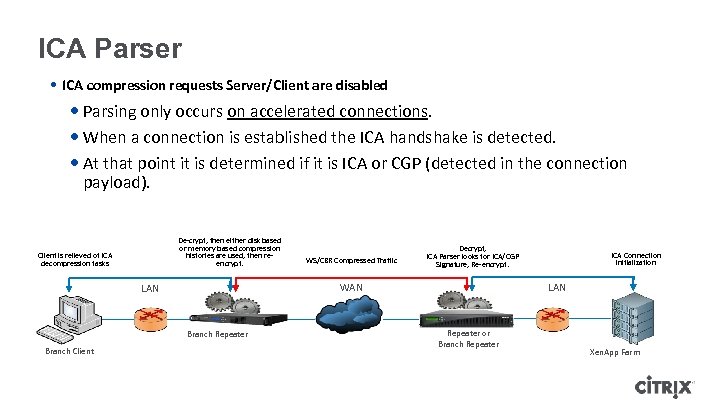
ICA Parser • ICA compression requests Server/Client are disabled • Parsing only occurs on accelerated connections. • When a connection is established the ICA handshake is detected. • At that point it is determined if it is ICA or CGP (detected in the connection payload). De-crypt, then either disk based or memory based compression histories are used, then reencrypt. Client is relieved of ICA decompression tasks Decrypt, ICA Parser looks for ICA/CGP Signature, Re-encrypt. WAN LAN Branch Repeater Branch Client WS/CBR Compressed Traffic ICA Connection initialization LAN Repeater or Branch Repeater Xen. App Farm
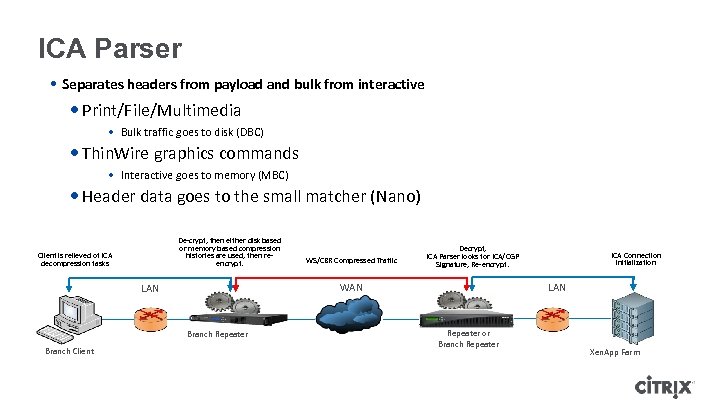
ICA Parser • Separates headers from payload and bulk from interactive • Print/File/Multimedia • Bulk traffic goes to disk (DBC) • Thin. Wire graphics commands • Interactive goes to memory (MBC) • Header data goes to the small matcher (Nano) De-crypt, then either disk based or memory based compression histories are used, then reencrypt. Client is relieved of ICA decompression tasks Decrypt, ICA Parser looks for ICA/CGP Signature, Re-encrypt. WAN LAN Branch Repeater Branch Client WS/CBR Compressed Traffic ICA Connection initialization LAN Repeater or Branch Repeater Xen. App Farm
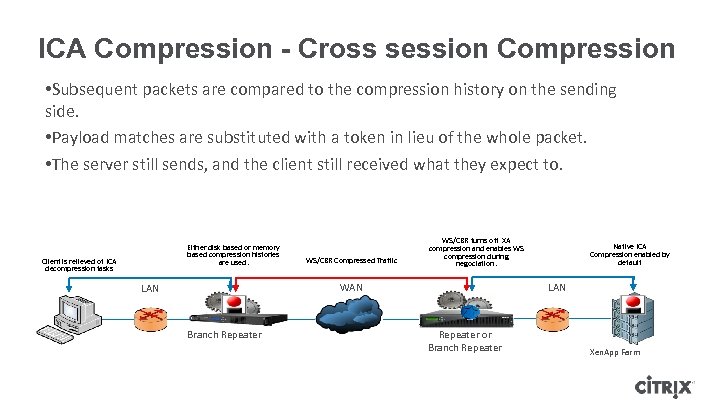
ICA Compression - Cross session Compression • Subsequent packets are compared to the compression history on the sending side. • Payload matches are substituted with a token in lieu of the whole packet. • The server still sends, and the client still received what they expect to. Either disk based or memory based compression histories are used. Client is relieved of ICA decompression tasks WS/CBR Compressed Traffic WS/CBR turns off XA compression and enables WS compression during negociation. WAN LAN Branch Repeater Native ICA Compression enabled by default LAN Repeater or Branch Repeater Xen. App Farm
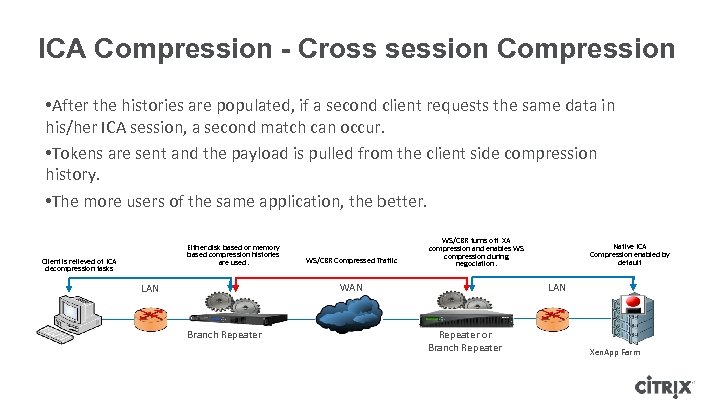
ICA Compression - Cross session Compression • After the histories are populated, if a second client requests the same data in his/her ICA session, a second match can occur. • Tokens are sent and the payload is pulled from the client side compression history. • The more users of the same application, the better. Either disk based or memory based compression histories are used. Client is relieved of ICA decompression tasks WS/CBR Compressed Traffic WS/CBR turns off XA compression and enables WS compression during negociation. WAN LAN Branch Repeater Native ICA Compression enabled by default LAN Repeater or Branch Repeater Xen. App Farm
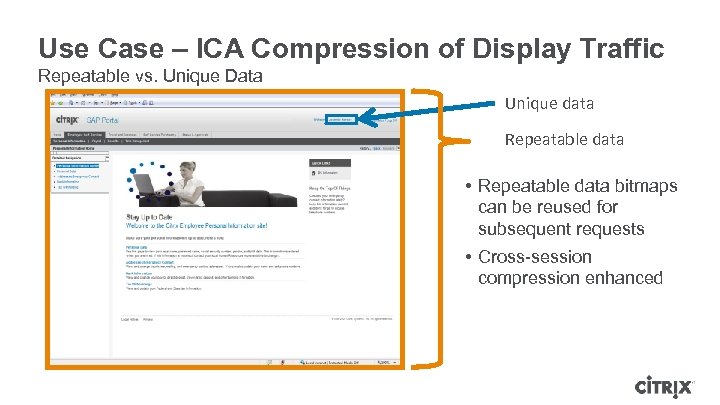
Use Case – ICA Compression of Display Traffic Repeatable vs. Unique Data Unique data Repeatable data • Repeatable data bitmaps can be reused for subsequent requests • Cross-session compression enhanced

Use Case - ICA Optimization of Print Traffic • Repeater compresses using disk (disk-based compression) ᵒ Minus the headers ᵒ Second pass of the same print job • ~70: 1 compression ᵒ Small modifications followed by a print-job resend • Compresses well (35 -40: 1)
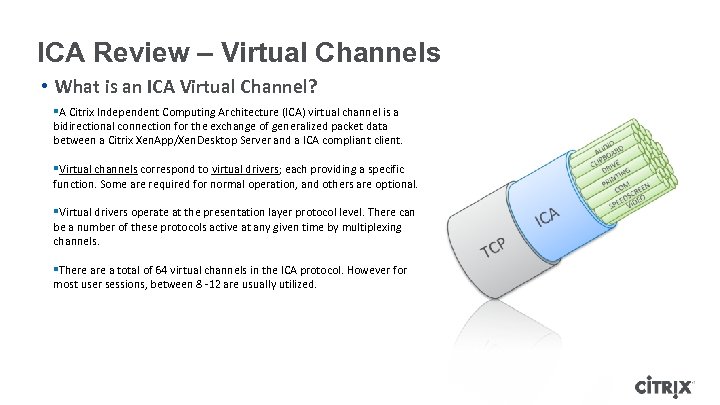
ICA Review – Virtual Channels • What is an ICA Virtual Channel? §A Citrix Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) virtual channel is a bidirectional connection for the exchange of generalized packet data between a Citrix Xen. App/Xen. Desktop Server and a ICA compliant client. §Virtual channels correspond to virtual drivers; each providing a specific function. Some are required for normal operation, and others are optional. §Virtual drivers operate at the presentation layer protocol level. There can be a number of these protocols active at any given time by multiplexing channels. §There a total of 64 virtual channels in the ICA protocol. However for most user sessions, between 8 -12 are usually utilized.
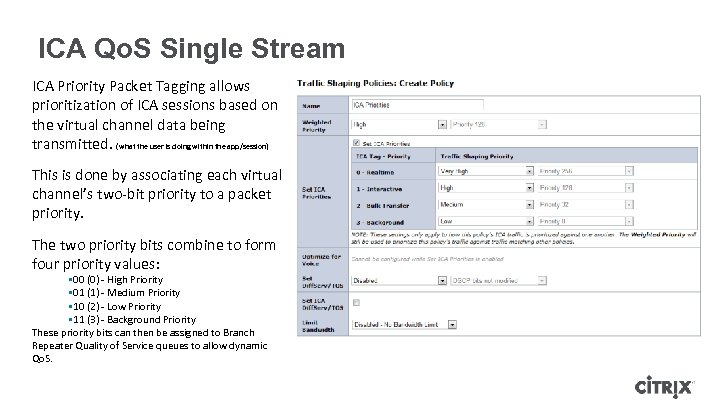
ICA Qo. S Single Stream ICA Priority Packet Tagging allows prioritization of ICA sessions based on the virtual channel data being transmitted. (what the user is doing within the app/session) This is done by associating each virtual channel’s two-bit priority to a packet priority. The two priority bits combine to form four priority values: § 00 (0) - High Priority § 01 (1) - Medium Priority § 10 (2) - Low Priority § 11 (3) - Background Priority These priority bits can then be assigned to Branch Repeater Quality of Service queues to allow dynamic Qo. S.
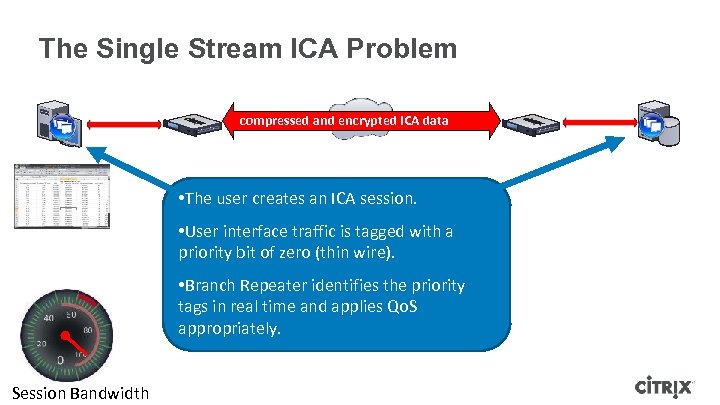
The Single Stream ICA Problem compressed and encrypted ICA data • The user creates an ICA session. • User interface traffic is tagged with a priority bit of zero (thin wire). • Branch Repeater identifies the priority tags in real time and applies Qo. S appropriately. Session Bandwidth
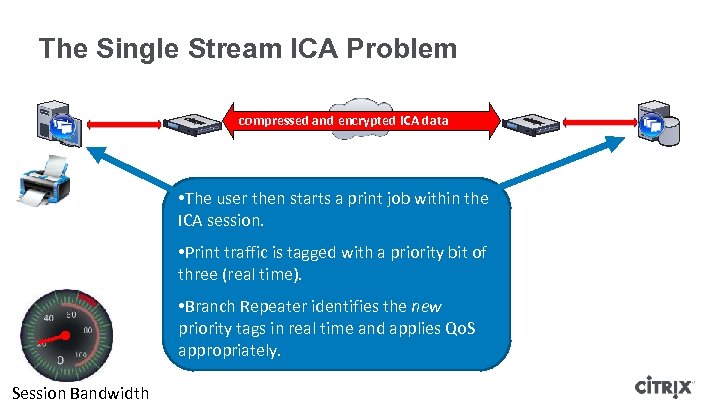
The Single Stream ICA Problem compressed and encrypted ICA data • The user then starts a print job within the ICA session. • Print traffic is tagged with a priority bit of three (real time). • Branch Repeater identifies the new priority tags in real time and applies Qo. S appropriately. Session Bandwidth
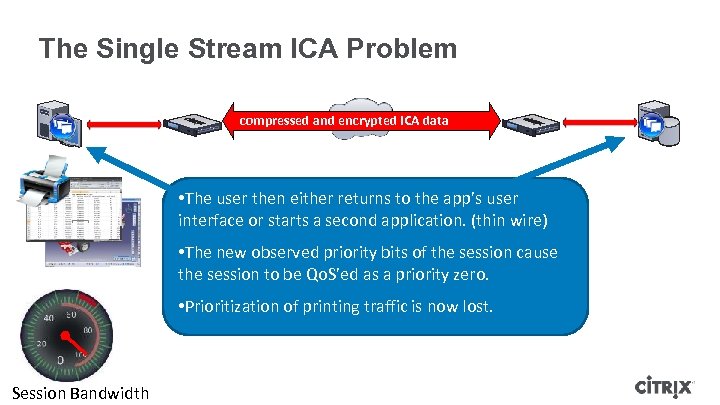
The Single Stream ICA Problem compressed and encrypted ICA data • The user then either returns to the app’s user interface or starts a second application. (thin wire) • The new observed priority bits of the session cause the session to be Qo. S’ed as a priority zero. • Prioritization of printing traffic is now lost. Session Bandwidth
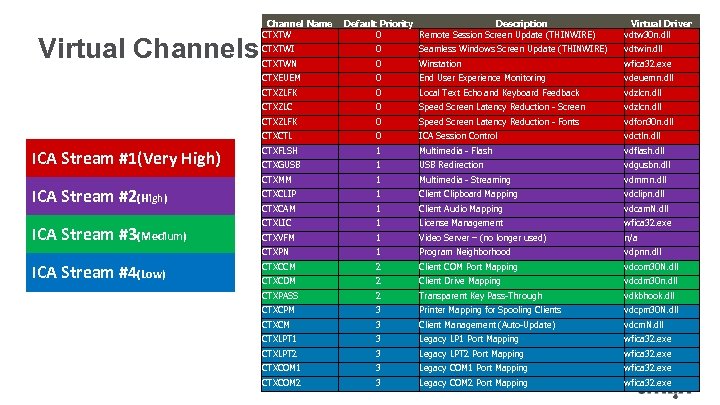
Virtual Channels Channel Name CTXTW Default Priority Description 0 Remote Session Screen Update (THINWIRE) Virtual Driver vdtw 30 n. dll wfica 32. exe 0 End User Experience Monitoring vdeuemn. dll 0 Local Text Echo and Keyboard Feedback vdzlcn. dll 0 Speed Screen Latency Reduction - Screen vdzlcn. dll CTXZLFK 0 Speed Screen Latency Reduction - Fonts vdfon 30 n. dll CTXCTL 0 ICA Session Control vdctln. dll CTXFLSH 1 Multimedia - Flash vdflash. dll CTXGUSB 1 USB Redirection vdgusbn. dll CTXMM 1 Multimedia - Streaming vdmmn. dll CTXCLIP 1 Client Clipboard Mapping vdclipn. dll CTXCAM 1 Client Audio Mapping vdcam. N. dll CTXLIC 1 License Management wfica 32. exe CTXVFM 1 Video Server – (no longer used) n/a CTXPN ICA Stream #4(Low) vdtwin. dll Winstation CTXZLC ICA Stream #3(Medium) Seamless Windows Screen Update (THINWIRE) 0 CTXZLFK ICA Stream #2(High) 0 CTXTWN CTXEUEM ICA Stream #1(Very High) CTXTWI 1 Program Neighborhood vdpnn. dll CTXCCM 2 Client COM Port Mapping vdcom 30 N. dll CTXCDM 2 Client Drive Mapping vdcdm 30 n. dll CTXPASS 2 Transparent Key Pass-Through vdkbhook. dll CTXCPM 3 Printer Mapping for Spooling Clients vdcpm 30 N. dll CTXCM 3 Client Management (Auto-Update) vdcm. N. dll CTXLPT 1 3 Legacy LP 1 Port Mapping wfica 32. exe CTXLPT 2 3 Legacy LPT 2 Port Mapping wfica 32. exe CTXCOM 1 3 Legacy COM 1 Port Mapping wfica 32. exe CTXCOM 2 3 Legacy COM 2 Port Mapping wfica 32. exe
Multi-Stream ICA Terminology • Single-port, Multi-stream ICA (MSI Default) ᵒ 4 random ports at client, 1 primary port on server ᵒ Automatically enabled on ICA server by Branch Repeater 6. 0. • Multi-port, Multi-stream ICA ᵒ 4 random ports at client, 1 primary and up to 3 secondary ports on server ᵒ Most common deployment if used without Branch Repeater • Single-port, Single-stream ICA ᵒ 1 random port at client, 1 primary port on server ᵒ The pre-MSI default connection type ᵒ If any Branch Repeater on the link vetos MSI, or old versions used
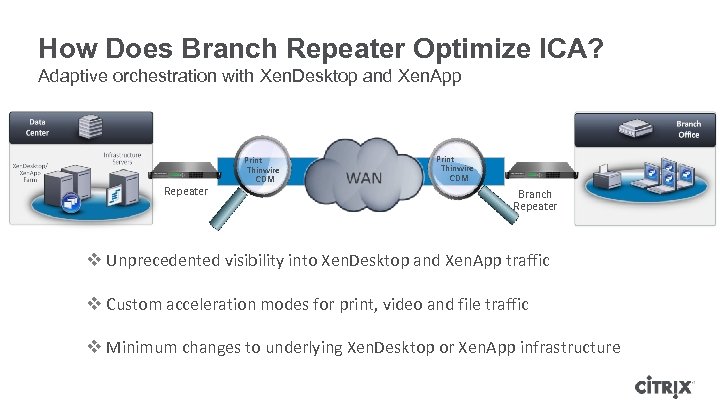
How Does Branch Repeater Optimize ICA? Adaptive orchestration with Xen. Desktop and Xen. App Repeater Print Thinwire CDM Branch Repeater v Unprecedented visibility into Xen. Desktop and Xen. App traffic v Custom acceleration modes for print, video and file traffic v Minimum changes to underlying Xen. Desktop or Xen. App infrastructure
Branch Repeater with ICA
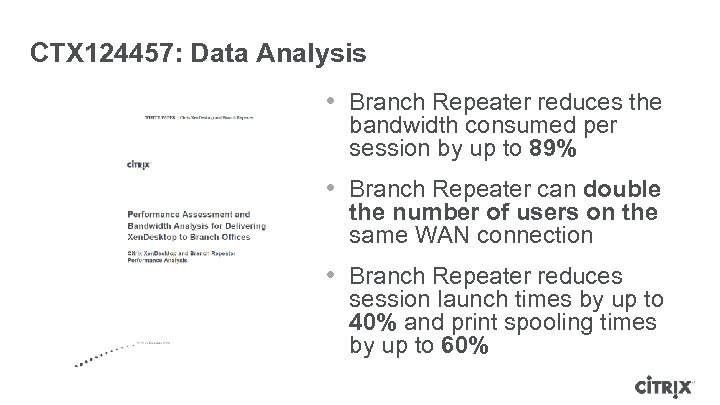
CTX 124457: Data Analysis • Branch Repeater reduces the bandwidth consumed per session by up to 89% • Branch Repeater can double the number of users on the same WAN connection • Branch Repeater reduces session launch times by up to 40% and print spooling times by up to 60%
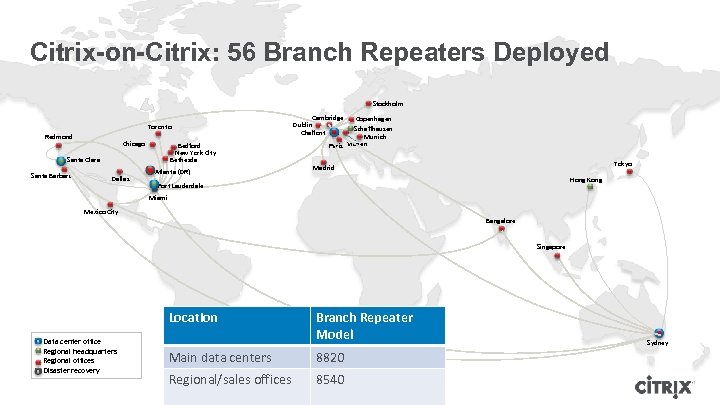
Citrix-on-Citrix: 56 Branch Repeaters Deployed Stockholm Toronto Redmond Chicago Bedford New York City Bethesda Santa Clara Santa Barbara Dallas Atlanta (DR) Cambridge Dublin Chalfont Copenhagen Schaffhausen Munich Paris Vianen Tokyo Madrid Hong Kong Fort Lauderdale Miami Mexico City Bangalore Singapore Location Data center office Regional headquarters Regional offices Disaster recovery Branch Repeater Model Main data centers 8820 Regional/sales offices 8540 Sydney

Summary • • Industry trends are driving desktop virtualisation as a solution The same trends mean there are considerations for successful deployments Networks must be optimised to ensure Availability and User experience Citrix has the components to ensure Enterprises can realise the benefits of Centralisation, Consumerisation and Geographical dispersion Desktop virtualisation is a solution not a product 43

Follow us… • Citrix blog • Desktop Virtualisation community http: //blogs. citrix. com/author/patricki/ • @patrick_irwin • Citrix Web Community


Work better. Live better.
374cb133e2dd3206d81222cf000d1dd1.ppt